Investigating Drought Propagation Time, Relationship, and Drivers in Perennial River Basins of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
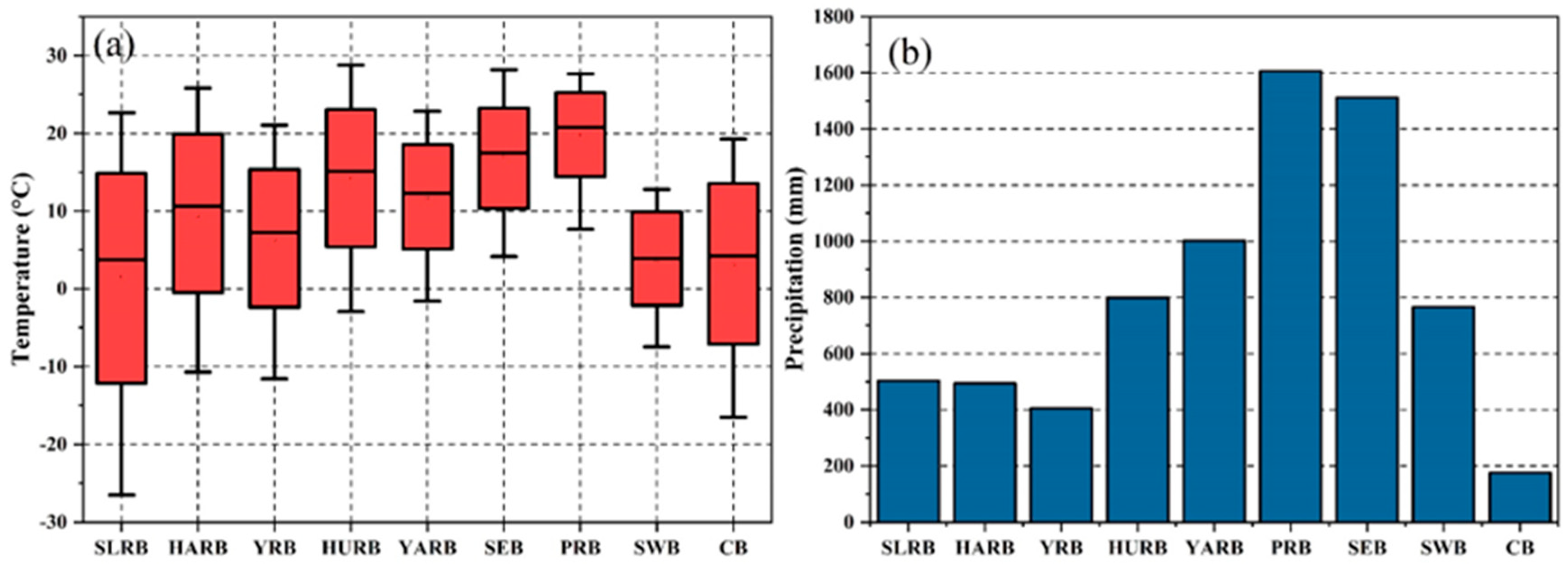
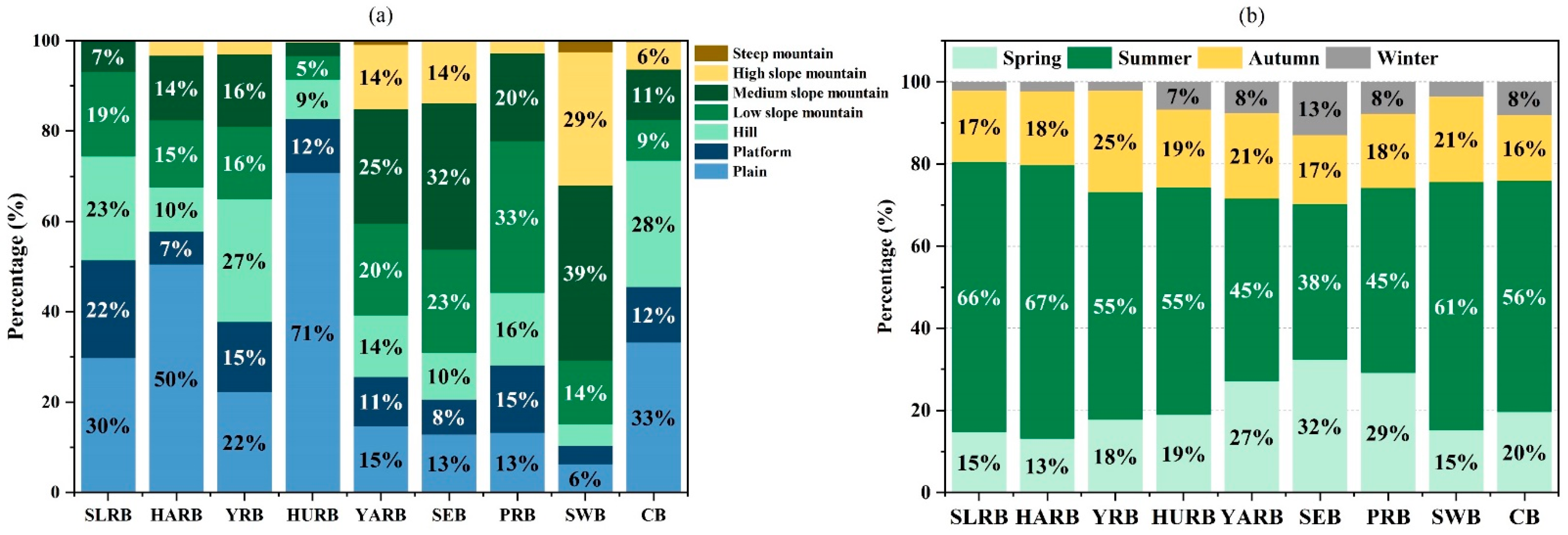
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Meteorological Drought Index: Standardized Precipitation Index
2.3.2. Hydrological Drought Index: Standardized Runoff Index
2.3.3. Drought Propagation Relationship
2.3.4. Drivers of Drought Propagation
3. Results
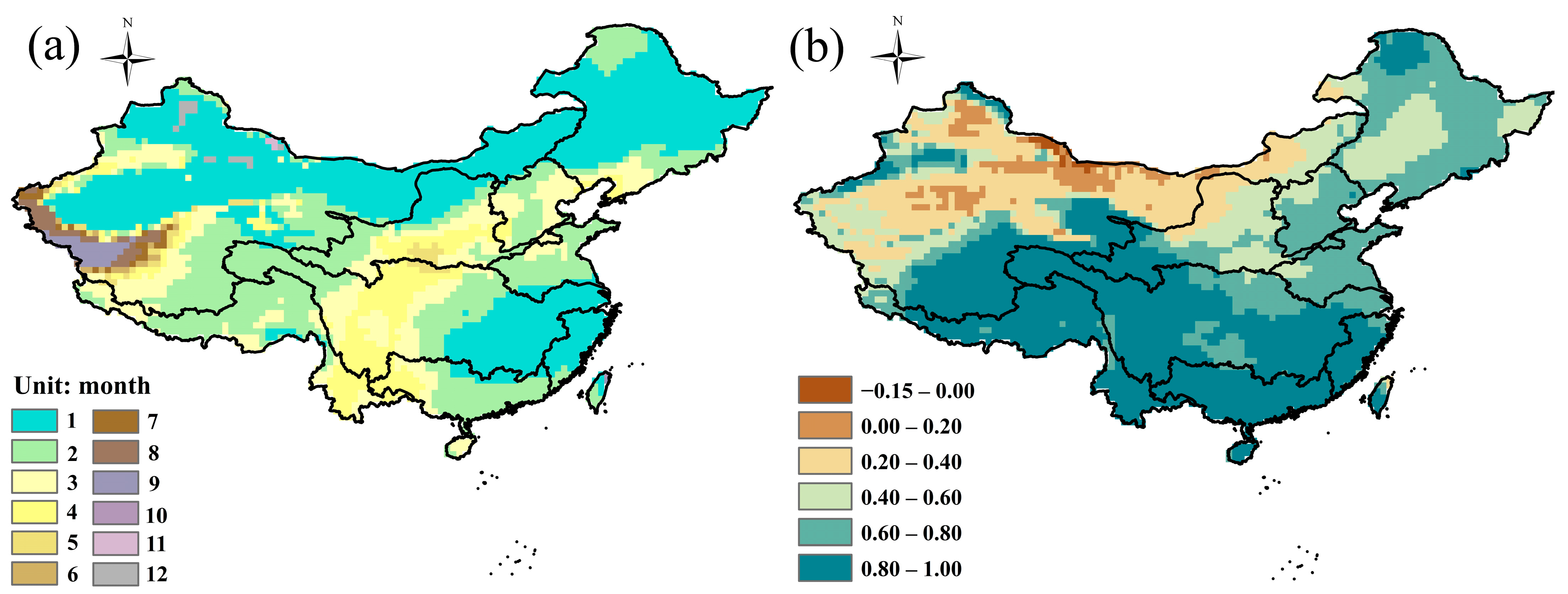
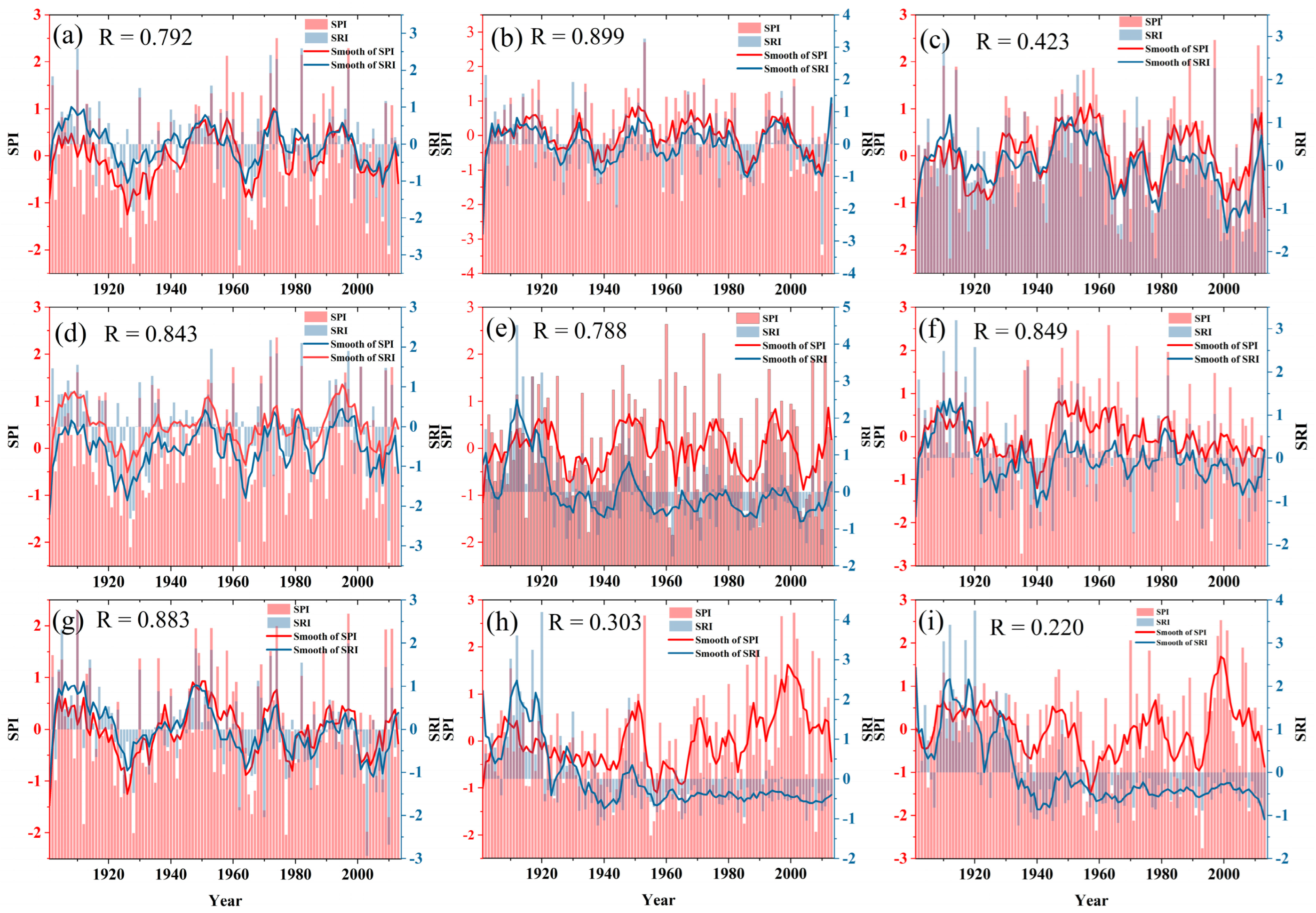
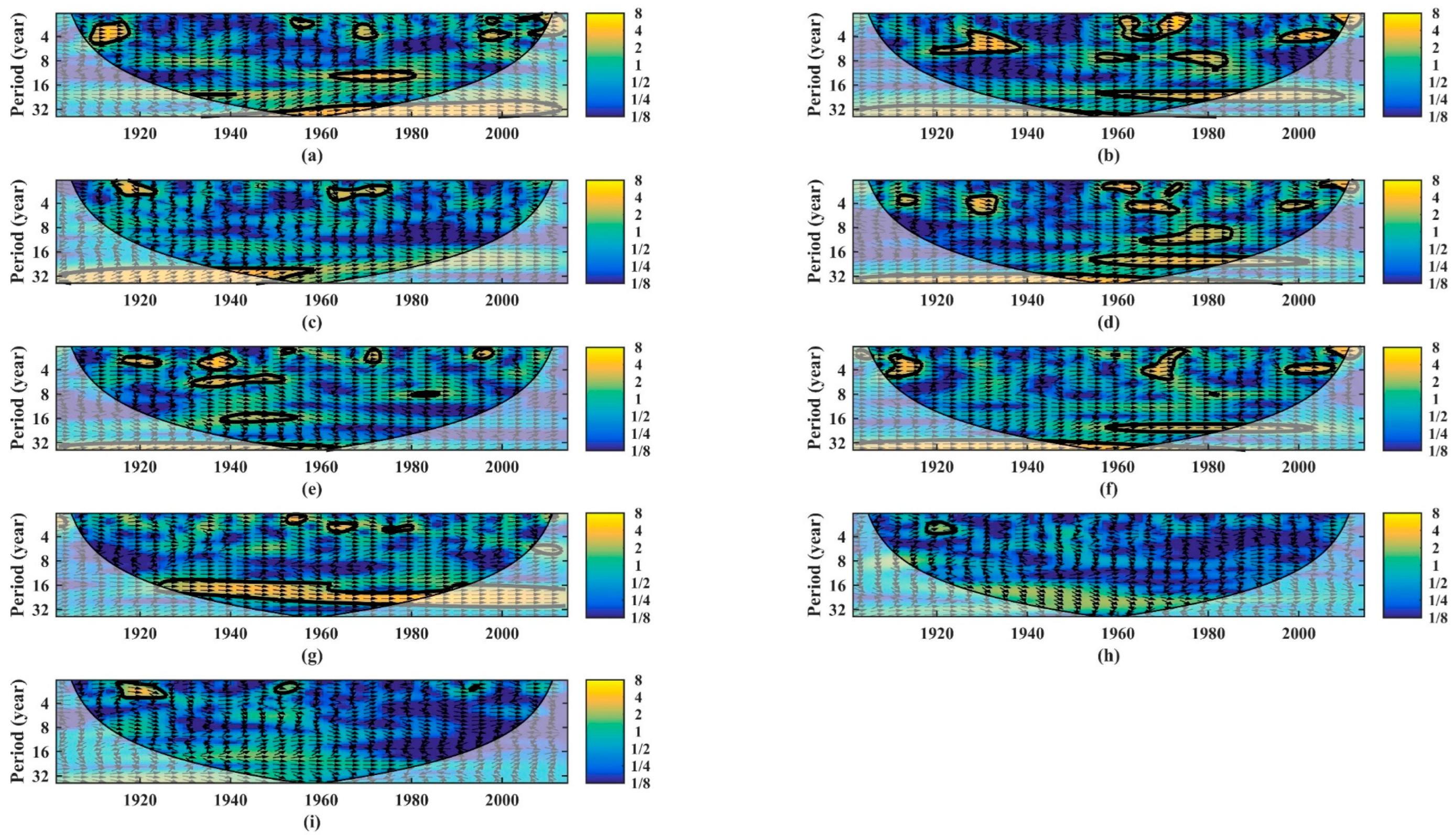
3.1. Long Time Series Drought Propagation
3.2. Annual Scale Drought Propagation
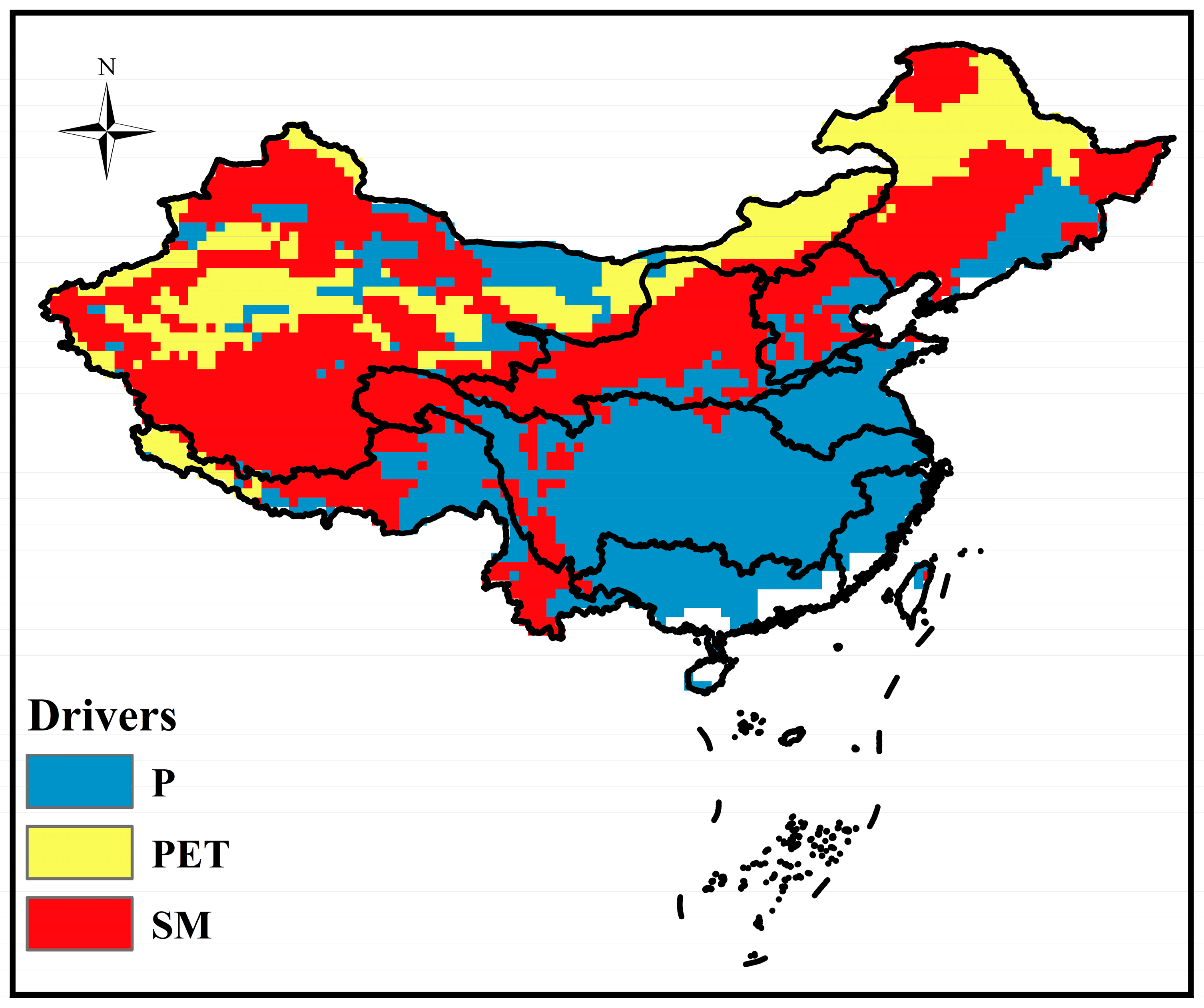
3.3. Attribution Analysis of Drought Propagation
4. Discussion
4.1. Difference Analysis of Drought Propagation in Different River Basins
4.2. Comparisons and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, R.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, L.; Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Li, D.; Niyogi, D. Quantitative analysis of agricultural drought propagation process in the Yangtze River Basin by using cross wavelet analysis and spatial autocorrelation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 280, 107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, H.; Fu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, S. Investigating the Propagation from Meteorological to Hydrological Drought by Introducing the Nonlinear Dependence with Directed Information Transfer Index. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR030028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Shah, D.; Aadhar, S.; Mishra, V. Propagation of Meteorological to Hydrological Droughts in India. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; AghaKouchak, A.; Yang, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, G. A water-energy balance approach for multi-category drought -assessment across globally diverse hydrological basins. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 264, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, H.; Fu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. Characteristics of propagation from meteorological drought to hydrological drought in the Pearl River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, H.; Fu, Q.; Li, T.; Gan, T.Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, K. Is the cold region in Northeast China still getting warmer under climate change impact? Atmos. Res. 2020, 237, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Ding, Y.B.; Shi, H.Y.; Cai, H.J.; Fu, Q.; Liu, S.N.; Li, T.X. Analysis and prediction of vegetation dynamic changes in China: Past, present and future. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cai, H.; Shi, H. Assessing the responses of vegetation to meteorological drought and its influencing factors with partial wavelet coherence analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, C.; Sun, S. How is the risk of hydrological drought in the Tarim River Basin, Northwest China? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Angulo, M.; El Kenawy, A. A New Global 0.5° Gridded Dataset (1901–2006) of a Multiscalar Drought Index: Comparison with Current Drought Index Datasets Based on the Palmer Drought Severity Index. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, P.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Hou, B.; Ma, L. The propagation from meteorological to hydrological drought and its potential influence factors. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Wu, C.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Dai, H.; Hu, B.X. Global precipitation-related extremes at 1.5 °C and 2 °C of global warming targets: Projection and uncertainty assessment based on the CESM-LWR experiment. Atmos. Res. 2021, 264, 105868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-j.; Wang, X.-p.; Zhao, C.-y.; Yang, X.-m. Diverse responses of vegetation growth to meteorological drought across climate zones and land biomes in northern China from 1981 to 2014. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 262, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Di, D.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Q.; Hussain, Z. Comprehensive evaluation of hydrological drought and its relationships with meteorological drought in the Yellow River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Gong, X.; Xing, Z.; Cai, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, D.; Sun, P.; Shi, H. Attribution of meteorological, hydrological and agricultural drought propagation in different climatic regions of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Wang, H.; Bai, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, L.; Du, M. Propagation dynamics from meteorological to groundwater drought and their possible influence factors. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, J.; Gu, L.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L. Impacts and socioeconomic exposures of global extreme precipitation events in 1.5 and 2.0 degrees C warmer climates. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Cai, H.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shi, H. Propagation of meteorological to hydrological drought for different climate regions in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 283, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Wood, A.W. Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L02405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forootan, E.; Khaki, M.; Schumacher, M.; Wulfmeyer, V.; Mehrnegar, N.; van Dijk, A.; Brocca, L.; Farzaneh, S.; Akinluyi, F.; Ramillien, G.; et al. Understanding the global hydrological droughts of 2003–2016 and their relationships with teleconnections. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650 Pt 2, 2587–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Camarero, J.J.; Azorin-Molina, C. Diverse responses of forest growth to drought time-scales in the Northern Hemisphere. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi Zarch, M.A.; Sivakumar, B.; Sharma, A. Droughts in a warming climate: A global assessment of Standardized precipitation index (SPI) and Reconnaissance drought index (RDI). J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Miao, C.; Tang, X.; Duan, Q.; He, X. A nonparametric standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrological drought on the Loess Plateau, China. Glob. Planet. Change 2018, 161, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, T.; Wei, J. Evaluation of the gridded CRU TS precipitation dataset with the point raingauge records over the Three-River Headwaters Region. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Koppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Ge, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Niu, H. sc_PDSI is more sensitive to precipitation than to reference evapotranspiration in China during the time period 1951–2015. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Osborn, T.J.; Jones, P.; Lister, D. Version 4 of the CRU TS monthly high-resolution gridded multivariate climate dataset. Sci. Data. 2020, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Pandey, A. A detailed assessment of meteorological drought characteristics using simplified rainfall index over Narmada River Basin, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Pandey, A.; Kalura, P. Inclusion of groundwater and socio-economic factors for assessing comprehensive drought vulnerability over Narmada River Basin, India: A geospatial approach. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Pandey, A.; Dayal, D. Identification of Meteorological Extreme Years over Central Division of Odisha Using an Index-Based Approach. Hydrol. Extrem. 2021, 97, 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Pandey, A. Assessment of meteorological droughts over Hoshangabad district, India. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 491, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Fang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Propagation thresholds of meteorological drought for triggering hydrological drought at various levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Li, Y.; Lei, T.; Peng, L. Drought evolution, severity and trends in mainland China over 1961–2013. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Li, L.; Feng, P.; Feng, H.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Hu, X.; Li, Y. Projections of drought characteristics in China based on a standardized precipitation and evapotranspiration index and multiple GCMs. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, R.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y. A drought index: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration runoff index. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Q.; Xia, Y.L.; Huning, L.S.; Wei, J.H.; Wang, G.Q.; AghaKouchak, A. A Framework for Global Multicategory and Multiscalar Drought Characterization Accounting for Snow Processes. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 9258–9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Cai, H. Spatial and temporal effects of drought on Chinese vegetation under different coverage levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, D.; Peng, H.; Xiao, S. Evaluation of precipitation in CMIP6 over the Yangtze River Basin. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hou, X.; Zhao, Y. Changes in consecutive dry/wet days and their relationships with local and remote climate drivers in the coastal area of China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, R.; Lai, C.; Zeng, Z.; Lian, Y.; Bai, X. Climate change enhances the severity and variability of drought in the Pearl River Basin in South China in the 21st century. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiggi, G.; Humphrey, V.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Gudmundsson, L. GRUN: An observation-based global gridded runoff dataset from 1902 to 2014. Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2019, 11, 1655–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.Y.; Jiang, S.H.; Ren, L.L. Evaluation and comparison of three long-term gauge-based precipitation products for drought monitoring over mainland China from 1961 to 2016. Nat. Hazards 2020, 104, 1371–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Q.; Chen, Y.N.; Yu, X.J.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, X.F.; Yang, L.M. Evaluation of multiple gridded precipitation datasets for the arid region of northwestern China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 236, 104818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Jones, P.D.; Osborn, T.J.; Lister, D.H. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations—The CRU TS3.10 Dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigaignon, L.; Fieuzal, R.; Delon, C.; Tallec, T. Combination of two methodologies, artificial neural network and linear interpolation, to gap-fill daily nitrous oxide flux measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 291, 108037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Huang, S.Z.; Huang, Q.; Huang, G.H.; Wang, H.; Leng, G.Y.; Wang, L. Identifying drought propagation by simultaneously considering linear and nonlinear dependence in the Wei River basin of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Kundu, A.; Patel, N.R.; Saha, S.K.; Siddiqui, A.R. Assessment of agricultural drought in Rajasthan (India) using remote sensing derived Vegetation Condition Index (VCI) and Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI). Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Yang, D.; Ayantobo, O.O. Bias correction of precipitation data and its effects on aridity and drought assessment in China over 1961-2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.-H.; Kho, Y.W.; Shin, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, T. Regression equations of probability plot correlation coefficient test statistics from several probability distributions. J. Hydrol. 2008, 355, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Zhou, S.; Chai, R.; Hua, W.; Deng, P.; Wang, J.; Lou, W. Revisiting the evolution of the 2009–2011 meteorological drought over Southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Song, Z. Historical global land surface air apparent temperature and its future changes based on CMIP6 projections. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 816, 151656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Tang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Y. Predicting wheat productivity: Integrating time series of vegetation indices into crop modeling via sequential assimilation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 272–273, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, A.; Barcza, Z.; Marjanović, H.; Árendás, T.; Fodor, N.; Bónis, P.; Bognár, P.; Lichtenberger, J. Statistical modelling of crop yield in Central Europe using climate data and remote sensing vegetation indices. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 260, 300–320. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Xiao, J. Regional contributions to interannual variability of net primary production and climatic attributions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 303, 108384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.; Jin, Y.; Li, G.; Zheng, C.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Luo, J. Groundwater depletion and contamination: Spatial distribution of groundwater resources sustainability in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosh Bin Ghomash, S.; Caviedes-Voullieme, D.; Hinz, C. Effects of erosion-induced changes to topography on runoff dynamics. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, P.; Krishnakumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Anoop Krishnan, K. Isotopic study on the effect of reservoirs and drought on water cycle dynamics in the tropical Periyar basin draining the slopes of Western Ghats. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selten, F.M.; Bintanja, R.; Vautard, R.; van den Hurk, B. Future continental summer warming constrained by the present-day seasonal cycle of surface hydrology. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Xie, Y.; Jia, X.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Xue, X. Land use/land cover change and it’s impacts on diurnal temperature range over the agricultural pastoral ecotone of Northern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3009–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, Z.; Yang, B.; Wang, L. Snowmelt water drives higher soil erosion than rainfall water in a mid-high latitude upland watershed. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, J.; Gao, S.; Jin, H. Unraveling of permafrost hydrological variabilities on Central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau using stable isotopic technique. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Kang, A. The use of combined soil moisture data to characterize agricultural drought conditions and the relationship among different drought types in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Sheffield, J. Soil Moisture Drought in China, 1950–2006. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3257–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Xu, D.; Wang, S. Decreasing potential evaporation trends in China from 1956 to 2005: Accelerated in regions with significant agricultural influence? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 154, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Kiem, A.S.; Willgoose, G. Mechanisms influencing non-stationarity in rainfall-runoff relationships in southeast Australia. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Jiang, D.; Fan, G. Seasonality of Precipitation over China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 40, 1191–1203. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.; Singh, V.P. Drought characterization from a multivariate perspective: A review. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Hao, Z.; Singh, V.P.; Hao, F. Propagation from meteorological drought to hydrological drought under the impact of human activities: A case study in northern China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Yang, X.Q.; Gong, F.X.; Su, Y.X.; Huang, G.Q.; Chen, X.Z. The Novel Microwave Temperature Vegetation Drought Index (MTVDI) Captures Canopy Seasonality across Amazonian Tropical Evergreen Forests. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ding, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Cai, H.; Liu, S.; Shi, H. Comprehensive evaluation of vegetation responses to meteorological drought from both linear and nonlinear perspectives. Front. Earth Sci.-Switz. 2022, 10, 953805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Ge, J.; Yang, P.; Wu, F. Investigating Drought Propagation Time, Relationship, and Drivers in Perennial River Basins of China. Water 2022, 14, 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182812
Li L, Zhao L, Ge J, Yang P, Wu F. Investigating Drought Propagation Time, Relationship, and Drivers in Perennial River Basins of China. Water. 2022; 14(18):2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182812
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lusheng, Lili Zhao, Jiankun Ge, Peiwen Yang, and Feng Wu. 2022. "Investigating Drought Propagation Time, Relationship, and Drivers in Perennial River Basins of China" Water 14, no. 18: 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182812
APA StyleLi, L., Zhao, L., Ge, J., Yang, P., & Wu, F. (2022). Investigating Drought Propagation Time, Relationship, and Drivers in Perennial River Basins of China. Water, 14(18), 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182812




