Application of Stable Isotopic Compositions of Rainfall Runoff for Evaporation Estimation in Thailand Mekong River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
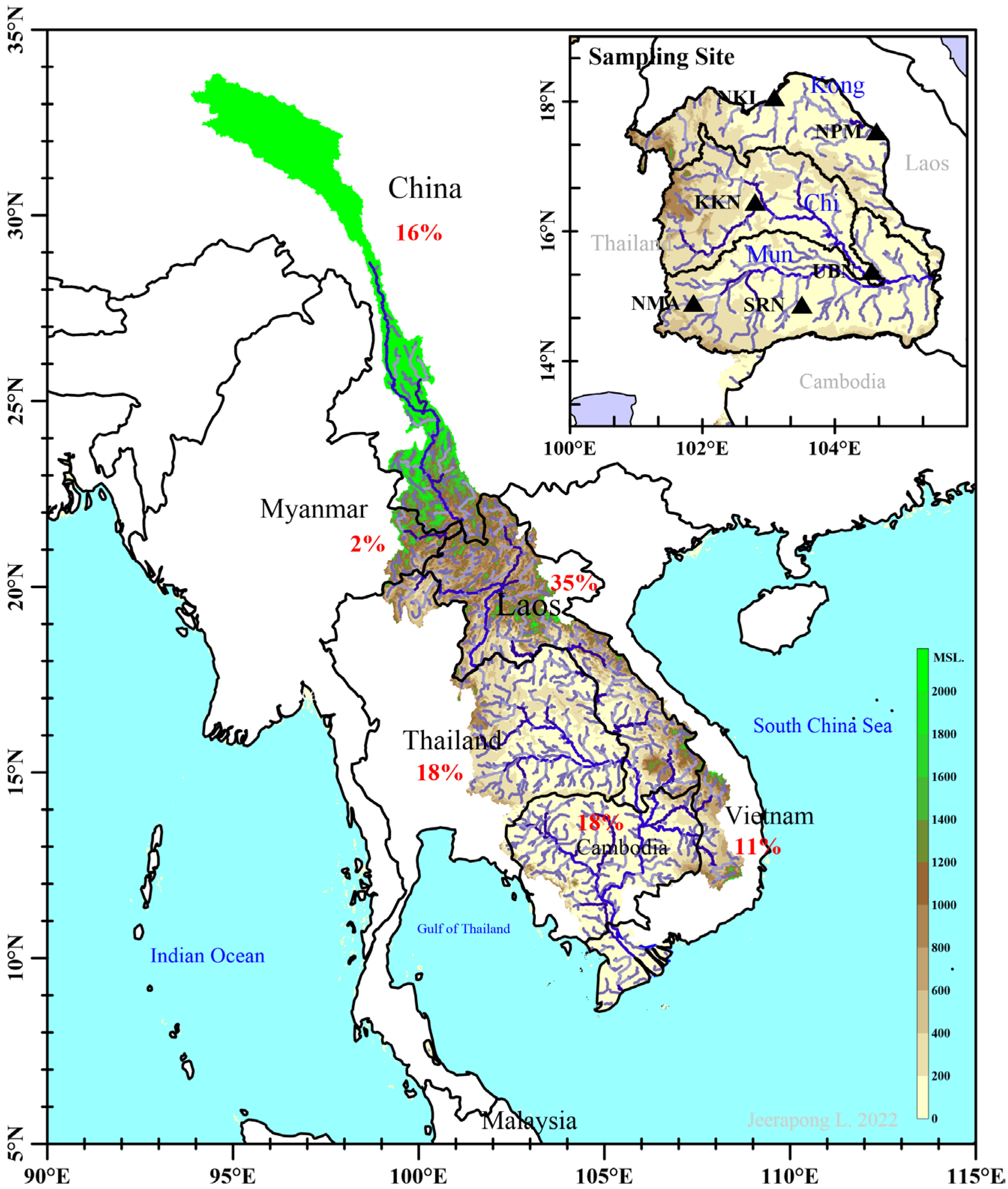
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Laboratory Analysis
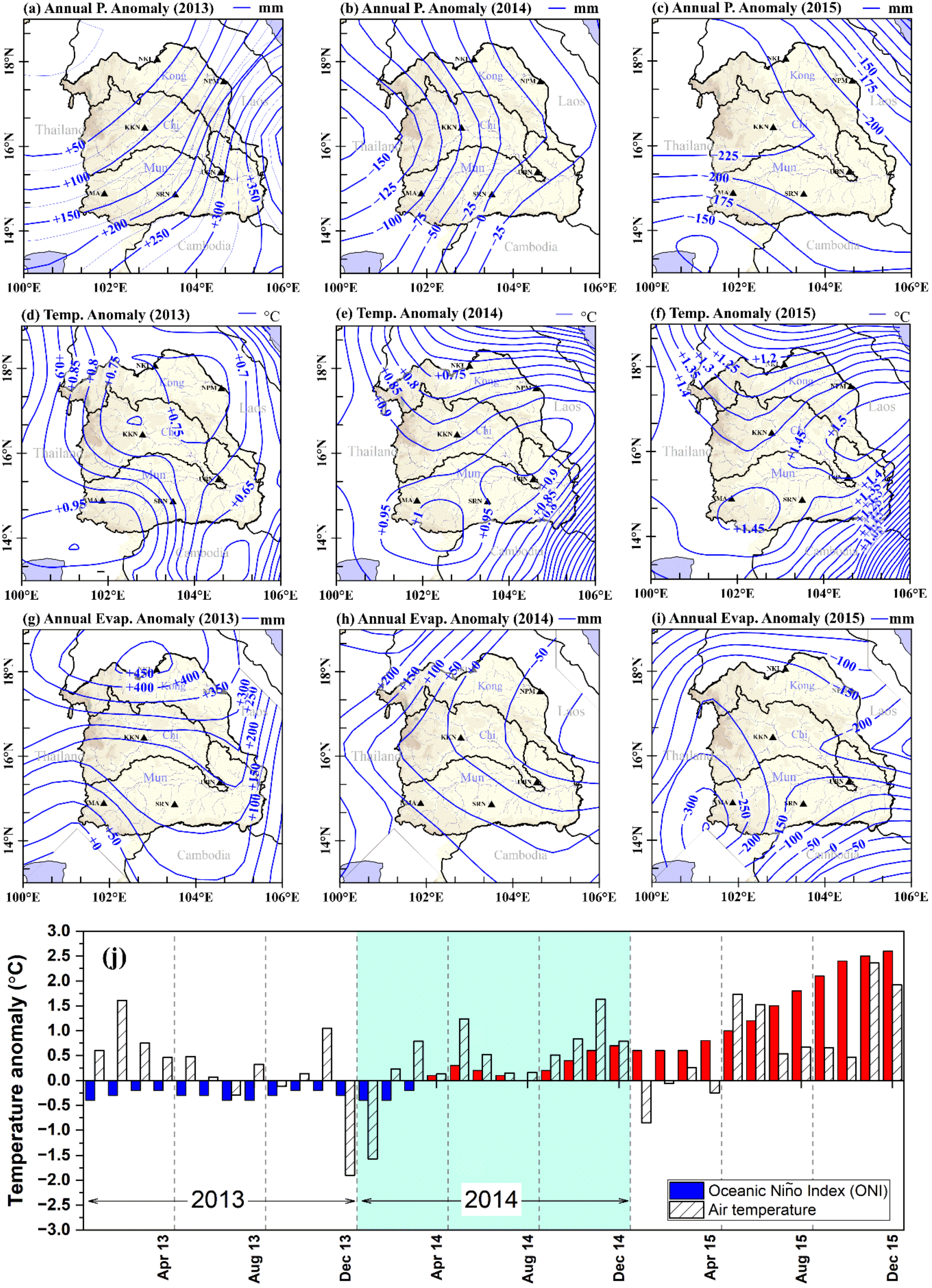
2.3. Climate Anomalies
2.4. Evaporative Loss Estimation
3. Results and Discussions
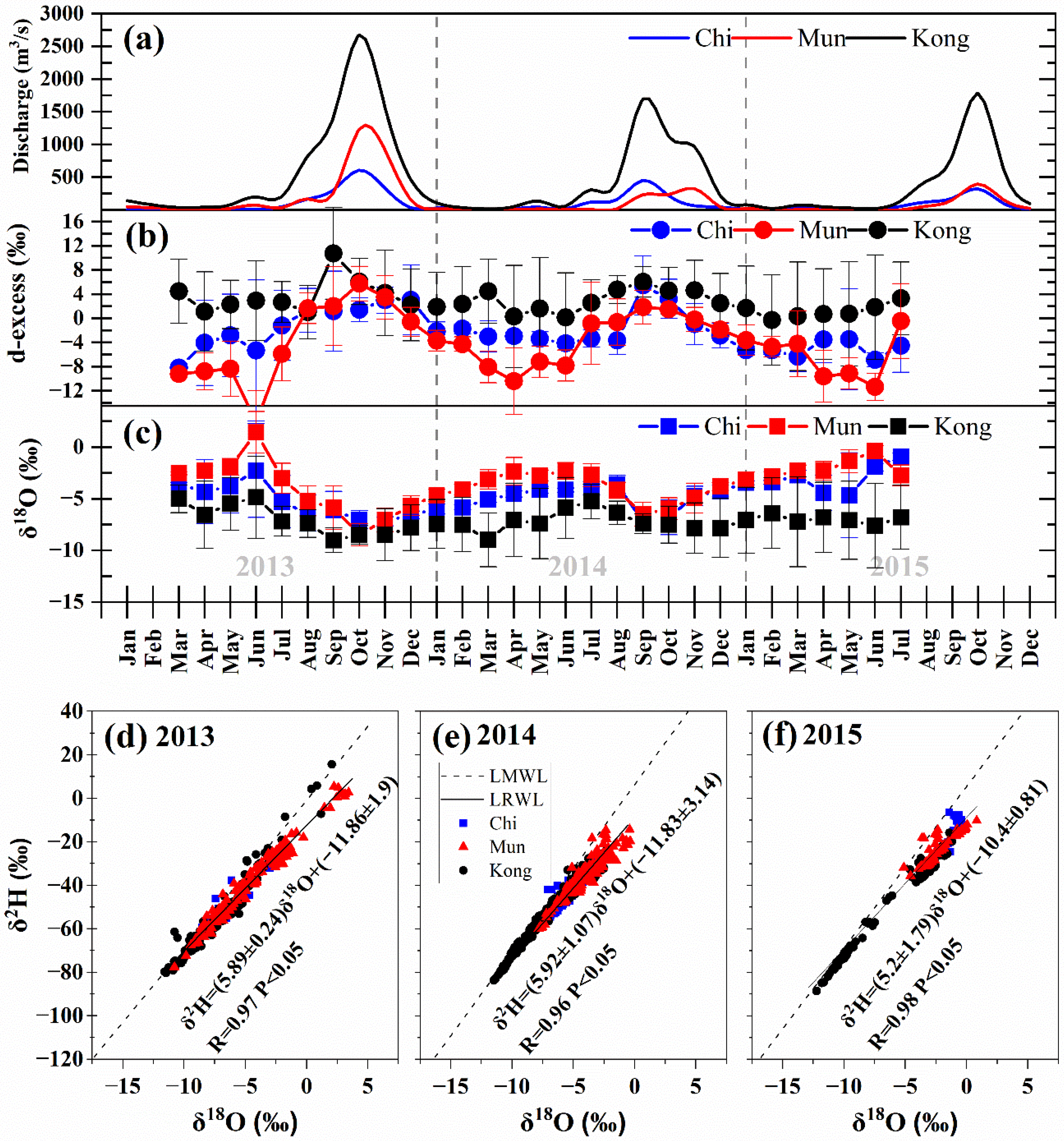
3.1. Isotopic Composition in Precipitation
3.2. LMWL
3.3. Isotopic Composition in River Water
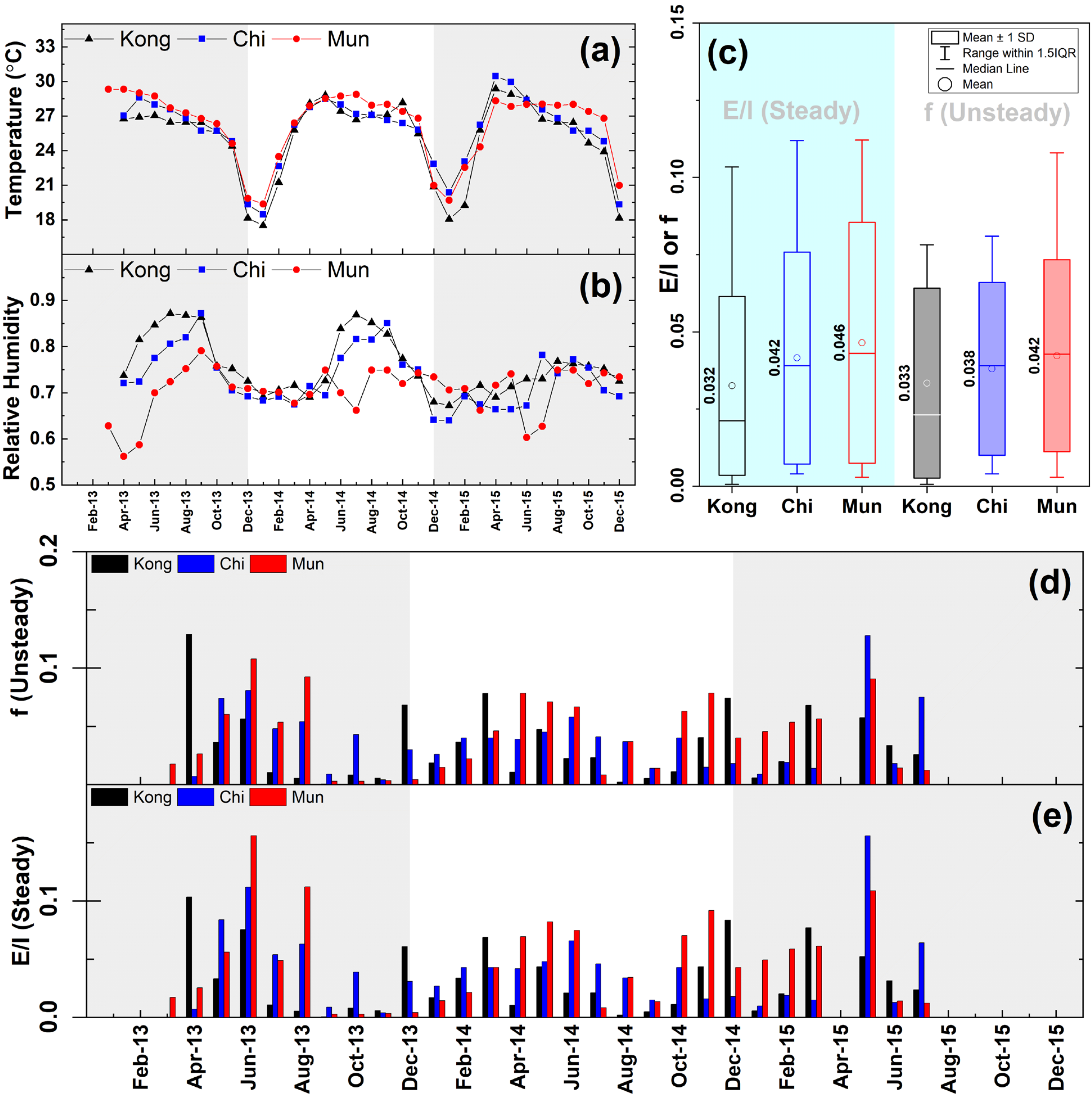
3.4. Evaporative Enrichment in Isotopic Water
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, G.; Mei, J.; Meng, Y.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y. Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes in precipitation and the environmental controls in tropical monsoon climatic zone. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 5417–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Edwards, T.W.D.; Birks, S.J.; St Amour, N.A.; Buhay, W.M.; McEachern, P.; Wolfe, B.B.; Peters, D.L. Progress in isotope tracer hydrology in Canada. Hydrol. Processes 2005, 19, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.K. Stable isotope fractionation due to evaporation and isotopic exchange of falling waterdrops: Applications to atmospheric processes and evaporation of lakes. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laonamsai, J.; Ichiyanagi, K.; Kamdee, K.; Putthividhya, A.; Tanoue, M. Spatial and temporal distributions of stable isotopes in precipitation over Thailand. Hydrol. Processes 2021, 35, e13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Goodkin, N.F.; Jackisch, D.; Ong, M.R.; Samanta, D. Continuous real-time analysis of the isotopic composition of precipitation during tropical rain events: Insights into tropical convection. Hydrol. Processes Int. J. 2018, 32, 1531–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laonamsai, J.; Ichiyanagi, K.; Patsinghasanee, S. Isotopic temporal and spatial variations of tropical rivers in Thailand reflect monsoon precipitation signals. Hydrol. Processes 2021, 35, e14068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Edwards, T.W.D.; Bursey, G.G.; Prowse, T.D. Estimating Evaporation Using Stable Isotopes: Quantitative Results and Sensitivity Analysis for Two Catchments in Northern Canada: Paper presented at the 9th Northern Res. Basin Symposium/Workshop (Whitehorse/Dawson/Inuvik, Canada-August 1992). Hydrol. Res. 1993, 24, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Reid, R. Stable isotope fingerprint of open-water evaporation losses and effective drainage area fluctuations in a subarctic shield watershed. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, J.; Rozanski, K.; Cohen, S. Isotope effects in the evaporation of water: A status report of the Craig–Gordon model. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2008, 44, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamalikis, V.; Argiriou, A.A.; Dotsika, E. Isotopic modeling of the sub-cloud evaporation effect in precipitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, M.; Yabusaki, S. Influence of Evaporation on River Water in Arid and Semi-arid Australia: Relationships between Stable Isotope Ratios and Climatic Factors. Inst. Nat. Sci. Fac. Arts Sci. Nihon Univ. 2017, 52, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. IAEA/GNIP Precipitation Sampling Guide V2; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J. A new precipitation weighted method for determining the meteoric water line for hydrological applications demonstrated using Australian and global GNIP data. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H.; Gordon, L.I. Deuterium and Oxygen 18 Variations in the Ocean and the Marine Atmosphere; Laboratorio di Geologia Nucleare: Pisa, Italy, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Skrzypek, G.; Mydłowski, A.; Dogramaci, S.; Hedley, P.; Gibson, J.J.; Grierson, P.F. Estimation of evaporative loss based on the stable isotope composition of water using Hydrocalculator. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Araguas-Araguas, L.; Aggarwal, P.K. A unified Craig-Gordon isotope model of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation during fresh or saltwater evaporation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 235, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.K.; Alduchov, O.A.; Froehlich, K.O.; Araguas-Araguas, L.J.; Sturchio, N.C.; Kurita, N. Stable isotopes in global precipitation: A unified interpretation based on atmospheric moisture residence time. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J. Spatial and temporal variation in precipitation isotopes in the Sydney Basin, Australia. J. Hydrol. 2013, 489, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiyanagi, K. Studies and applications of stable isotopes in precipitation. J. Jpn. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2007, 37, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegenthaler, U.; Oeschger, H. Correlation of 18O in precipitation with temperature and altitude. Nature 1980, 285, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Mu, H.; Guo, J.; Bao, X.; Martín, J.D. Temperature and rainfall amount effects on hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope in precipitation. Quat. Int. 2019, 519, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, N.; Ichiyanagi, K.; Matsumoto, J.; Yamanaka, M.D.; Ohata, T. The relationship between the isotopic content of precipitation and the precipitation amount in tropical regions. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtsever, Y.; Gat, J.R. Stable isotope hydrology: Deuterium and oxygen-18 in the water cycle. Atmos. Waters 1981, 210, 103–142. [Google Scholar]
- Araguás-Araguás, L.; Froehlich, K.; Rozanski, K. Stable isotope composition of precipitation over southeast Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 28721–28742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, A.; Shimada, J. The origin of precipitation in eastern Asia by deuterium excess. J. Jpn. Soc. Hydrol. Water Resour. 1997, 10, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, A.L.; Fiorella, R.P.; Bowen, G.J.; Cai, Z. A global perspective on local meteoric water lines: Meta-analytic insight into fundamental controls and practical constraints. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6896–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noone, D. Pairing measurements of the water vapor isotope ratio with humidity to deduce atmospheric moistening and dehydration in the tropical midtroposphere. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 4476–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Fung, I. “Amount effect” of water isotopes and quantitative analysis of post-condensation processes. Hydrol. Processes Int. J. 2008, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noone, D.; Galewsky, J.; Sharp, Z.D.; Worden, J.; Barnes, J.; Baer, D.; Bailey, A.; Brown, D.P.; Christensen, L.; Crosson, E. Properties of air mass mixing and humidity in the subtropics from measurements of the D/H isotope ratio of water vapor at the Mauna Loa Observatory. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risi, C.; Noone, D.; Frankenberg, C.; Worden, J. Role of continental recycling in intraseasonal variations of continental moisture as deduced from model simulations and water vapor isotopic measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4136–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Tian, F.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S. Stable isotope composition of river waters across the world. Water 2019, 11, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Cumulative effects of cascade dams on river water cycle: Evidence from hydrogen and oxygen isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, G.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Impact of human activities on urban river system and its implication for water-environment risks: An isotope-based investigation in Chengdu, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 27, 1416–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Liu, G.; Meng, Y.; Jiang, F. Reveal the threat of water quality risks in Yellow River Delta based on evidences from isotopic and hydrochemical analyses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 177, 113532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellman, J.B.; Dogramaci, S.; Skrzypek, G.; Dodson, W.; Grierson, P.F. Hydrologic control of dissolved organic matter biogeochemistry in pools of a subtropical dryland river. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeniger, P.; Leibundgut, C.; Stichler, W. Spatial and temporal characterization of stable isotopes in river water as indicators of groundwater contribution and confirmation of modelling results; a study of the Weser river, Germany. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2009, 45, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.H.; Koh, D.-C.; Kwon, H.-I.; Jung, Y.-Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Yoon, Y.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Moon, H.S.; Ha, K. Identifying and quantifying groundwater inflow to a stream using 220Rn and 222Rn as natural tracers. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 33, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porntepkasemsan, B.; Kulsawat, W.; Nochit, P. Estimation of Evaporative Loss of Surface Water Using Stable Isotopes in a Lowland Rice Field, Suphanburi, Thailand. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bäch, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; Athanasopoulos, P.; Hendry, M.J. Isotope hydrology of precipitation, surface and ground waters in the Okanagan Valley, British Columbia, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laonamsai, J.; Ichiyanagi, K.; Patsinghasanee, S.; Kamdee, K.; Tomun, N. Application of Stable Isotopic Compositions of Rainfall Runoff for Evaporation Estimation in Thailand Mekong River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 2803. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182803
Laonamsai J, Ichiyanagi K, Patsinghasanee S, Kamdee K, Tomun N. Application of Stable Isotopic Compositions of Rainfall Runoff for Evaporation Estimation in Thailand Mekong River Basin. Water. 2022; 14(18):2803. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182803
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaonamsai, Jeerapong, Kimpei Ichiyanagi, Supapap Patsinghasanee, Kiattipong Kamdee, and Nattapong Tomun. 2022. "Application of Stable Isotopic Compositions of Rainfall Runoff for Evaporation Estimation in Thailand Mekong River Basin" Water 14, no. 18: 2803. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182803
APA StyleLaonamsai, J., Ichiyanagi, K., Patsinghasanee, S., Kamdee, K., & Tomun, N. (2022). Application of Stable Isotopic Compositions of Rainfall Runoff for Evaporation Estimation in Thailand Mekong River Basin. Water, 14(18), 2803. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14182803





