Membrane Fouling Mechanism of HTR-PVDF and HMR-PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes in MBR System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Characteristic
2.3. Feed Water Characteristic
2.4. Filtration Models
2.5. Membrane Adsorption
2.6. Fouling Mechanism
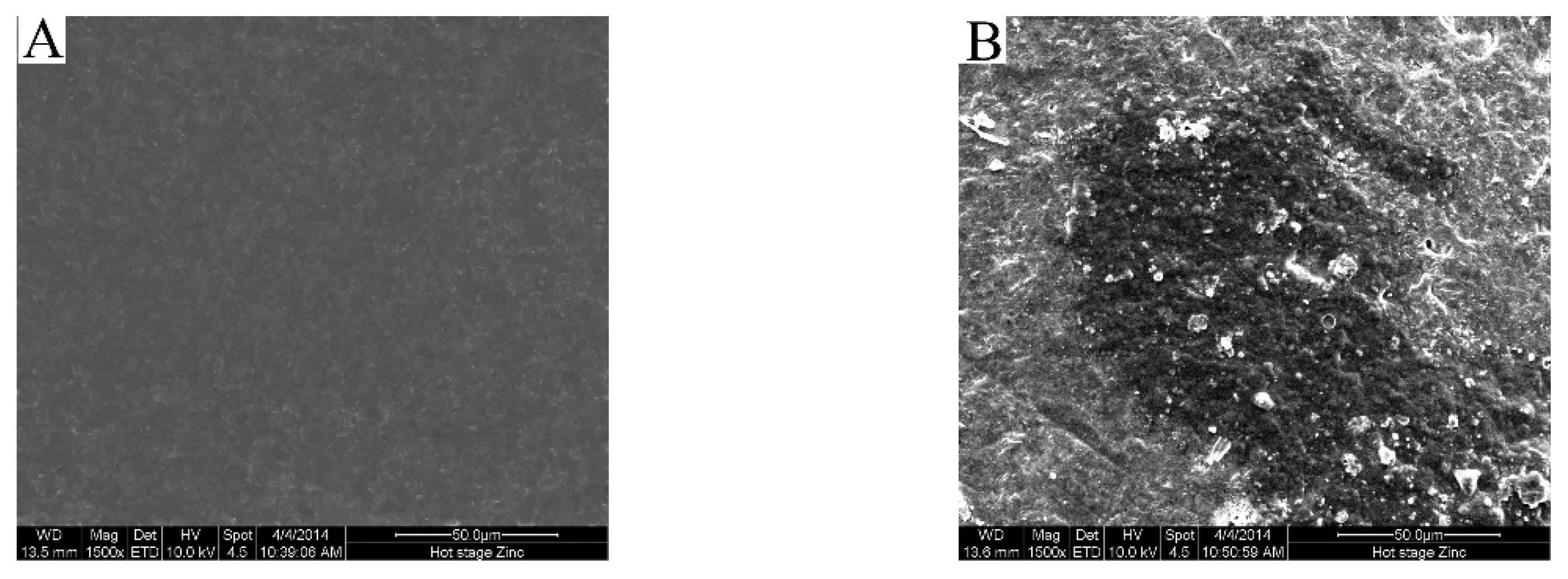
2.7. Morphology Observation
3. Results and Discussions
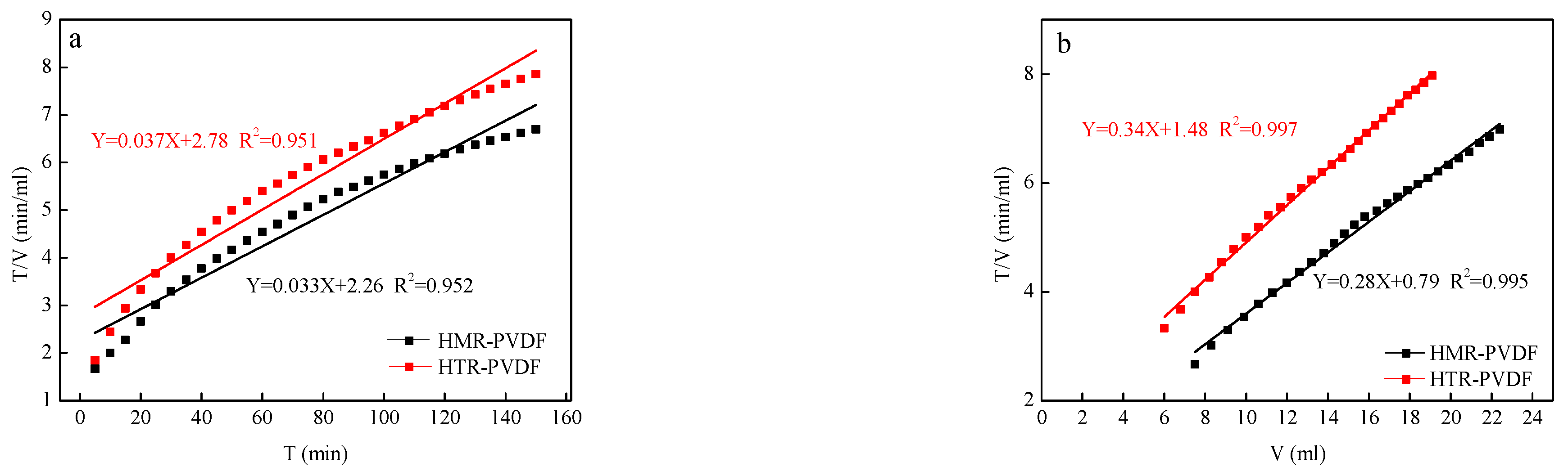
3.1. Filtration Models
3.2. Membrane Adsorption
3.3. Fouling Mechanism
3.3.1. The Membrane Resistance Distribution after Short-Time Operation
3.3.2. The Membrane Resistance Distribution after Long-Time Operation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sengar, A.; Vijayanandan, A. Effects of pharmaceuticals on membrane bioreactor: Review on membrane fouling mechanisms and fouling control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Energy-Efficient AnMBRs Technology for Treatment of Wastewaters: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoyunlu, B.; Daly, S.; Casey, E. Membrane bioreactors for the production of value-added products: Recent developments, challenges and perspectives. Biores. Technol. 2021, 341, 125793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moattari, R.M.; Mohammadi, T.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Dabiryan, H.; Matsuyama, H. Reinforced hollow fiber membranes: A comprehensive review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 122, 284–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, X. A review on microporous polyvinylidene fluoride membranes fabricated via thermally induced phase separation for MF/UF application. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 639, 119759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Huang, Q.; Li, H. Progress on polymeric hollow fiber membrane preparation technique from the perspective of green and sustainable development. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiao, C.; Huang, Q.; Hu, X. Preparation and interface structure study on dual-layer polyvinyl chloride matrix reinforced hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 472, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xiao, C.; Liu, H.; Ling, H. Design of robust twisted fiber bundle-reinforced cellulose triacetate hollow fiber reverse osmosis membrane with thin separation layer for seawater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 578, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Chen, K.; Xiao, C.; Ji, D. Improving pressure durability and fractionation property via reinforced PES loose nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for textile wastewater treatment. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 108, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikita, S.; Shintani, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Matsuyama, H. Structure control of hydrophilized PVDF hollow-fiber membranes using amphiphilic copolymers: PMMA-co-P (HEMA-co-MEA). J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S. Comparing the antifouling effects of activated carbon and TiO2 in ultrafiltration membrane development. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 515, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.; Ismail, N.; Essalhi, M.; Tysklind, M. Assessment of the environmental impact of polymeric membrane production. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 622, 118987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, T.; Mehrnia, M.R.; Ghezelgheshlaghi, S. Influence of alumina nanoparticles on the performance of polyacrylonitrile membranes in MBR. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Comparison of polypropylene and ceramic microfiltration membranes applied for separation of 1, 3-PD fermentation broths and Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast suspensions. Membranes 2021, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Cross-flow microfiltration of glycerol fermentation broths with Citrobacter freundii. Membranes 2020, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarvis, P.; Carra, I.; Jafari, M.; Judd, S.J. Ceramic vs polymeric membrane implementation for potable water treatment. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, C.; Hu, X.; Jin, X. Study on the interfacial bonding state and fouling phenomena of polyvinylidene fluoride matrix-reinforced hollow fiber membranes during microfiltration. Desalination 2013, 330, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Xiao, C.F.; Liu, H.L.; Zhao, W.; Hu, X.Y.; Huan, G.L. Preparation and Properties of Two-Dimensional Braid Heterogeneous-Reinforced Polyvinylidene Fluoride Hollow Fiber Membrane. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Materials Science and Engineering Technology(MSET 2014), Shanghai, China, 28–29 June 2014; pp. 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Harouna, B.M.; Benkortbi, O.; Hanini, S.; Amrane, A. Modeling of transitional pore blockage to cake filtration and modified fouling index–Dynamical surface phenomena in membrane filtration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 193, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zang, H.; Wang, S.; Du, X. Filtration behaviour of cement-based grout in porous media. Trans. Porous Media 2018, 125, 435–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Y. Unrevealing the role of in-situ Fe (II)/S2O82-oxidation in sludge solid-liquid separation and membrane fouling behaviors of membrane bioreactor (MBR). Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Li, X.; Hua, Z.; Ren, Y. The growth process of the cake layer and membrane fouling alleviation mechanism in a MBR assisted with the self-generated electric field. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, S.; Wang, S.; Liang, S.; Xiao, K. Effect of the relative degree of foulant “hydrophobicity” on membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Q. Fouling potentials and properties of foulants in an innovative algal-sludge membrane bioreactor. Environ. Int. 2021, 151, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bao, Q.; Wu, H.; Shao, M. Impact of polysaccharide and protein interactions on membrane fouling: Particle deposition and layer formation. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoodi, M.; Jacquin, C.; Teychené, B.; Heran, M.; Tarabara, V.V. Emerging investigator series: Photocatalysis for MBR effluent post-treatment: Assessing the effects of effluent organic matter characteristics. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, S.; Etemadi, H.; Yegani, R. A comprehensive analysis of membrane fouling in microfiltration of complex linear macromolecules based on theoretical modeling and FESEM images. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hube, S.; Wang, J.; Sim, L.N.; Ólafsdóttir, D.; Chong, T.H. Fouling and mitigation mechanisms during direct microfiltration and ultrafiltration of primary wastewater. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2021, 44, 102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laksono, S.; ElSherbiny, I.M.A.; Huber, S.A.; Panglisch, S. Fouling scenarios in hollow fiber membranes during mini-plant filtration tests and correlation to microalgae-loaded feed characteristics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Wu, Q.; Tian, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, W. Fouling mechanism of forward osmosis membrane in domestic wastewater concentration: Role of substrate structures. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Mehejabin, F.; Momtahin, A.; Tasannum, N. Strategies to improve membrane performance in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 135527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Components | Concentration (mg/L) | Components | Concentration (mg/L) | Components | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 300.00 | Carbamide | 30.00 | Ferric Chloride | 0.25 |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | 30.00 | Magnesium Sulfate | 12.00 | Calcium Chloride | 6.00 |
| Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate | 12.75 | Manganese Sulfate | 6.00 | Sodium Chloride | 150.00 |
| Items | HTR-PVDF | HMR-PVDF |
|---|---|---|
| Average Pore Size (μm) | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.02 |
| Porosity (%) | 45.67 ± 0.2 | 50.19 ± 0.35 |
| Contact Angle (°) | 74.50 ± 0.5 | 72.00 ± 0.6 |
| Protein Rejection Rate (%) | 96.03 ± 1.1 | 97.88 ± 0.9 |
| Pure Water Flux (L·m−2·h−1) | 269.34 ± 2.2 | 293.82 ± 2.5 |
| Items | HTR-PVDF | HMR-PVDF |
|---|---|---|
| J0 (L·m−2·h−1) | 218.38 | 251.59 |
| J1 (L·m−2·h−1) | 213.65 | 221.66 |
| J2 (L·m−2·h−1) | 177.00 | 181.50 |
| J3 (L·m−2·h−1) | 155.25 | 171.56 |
| Items | HTR-PVDF a | HTR-PVDF b | HMR-PVDF a | HMR-PVDF b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J0 (L·m−2·h−1) | 218.38 | 218.38 | 246.67 | 251.59 |
| J1 (L·m−2·h−1) | 16.68 | 19.43 | 12.85 | 10.83 |
| J2 (L·m−2·h−1) | 40.72 | 42.08 | 20.50 | 17.21 |
| J3 (L·m−2·h−1) | 90.99 | 91.04 | 31.34 | 23.89 |
| J4 (L·m−2·h−1) | 210.42 | 195.63 | 243.20 | 168.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Q. Membrane Fouling Mechanism of HTR-PVDF and HMR-PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes in MBR System. Water 2022, 14, 2576. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162576
Chen K, Zhao W, Xiao C, Zhu H, Wang Q. Membrane Fouling Mechanism of HTR-PVDF and HMR-PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes in MBR System. Water. 2022; 14(16):2576. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162576
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Kaikai, Wei Zhao, Changfa Xiao, Hui Zhu, and Qiming Wang. 2022. "Membrane Fouling Mechanism of HTR-PVDF and HMR-PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes in MBR System" Water 14, no. 16: 2576. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162576
APA StyleChen, K., Zhao, W., Xiao, C., Zhu, H., & Wang, Q. (2022). Membrane Fouling Mechanism of HTR-PVDF and HMR-PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes in MBR System. Water, 14(16), 2576. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162576






