Defining a Precipitation Stable Isotope Framework in the Wider Carpathian Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- To determine the local meteoric water line, to compare it with the lines derived from previous local studies, and to analyze the dependence of the regional atmospheric moisture sources.
- -
- To describe the temporal variability of δ18O, δ2H, and d-excess and their relationship with temperature, altitude, and topography.
- -
- To provide spatial and seasonal distribution of water isotopes and d-excess at the country level.
- -
- To construct the seasonal maps of the spatial distribution of the δ18O values in precipitation in Romania and the Republic of Moldova.
- -
- To investigate the influence of the large-scale atmospheric circulation on seasonal δ18O variability.
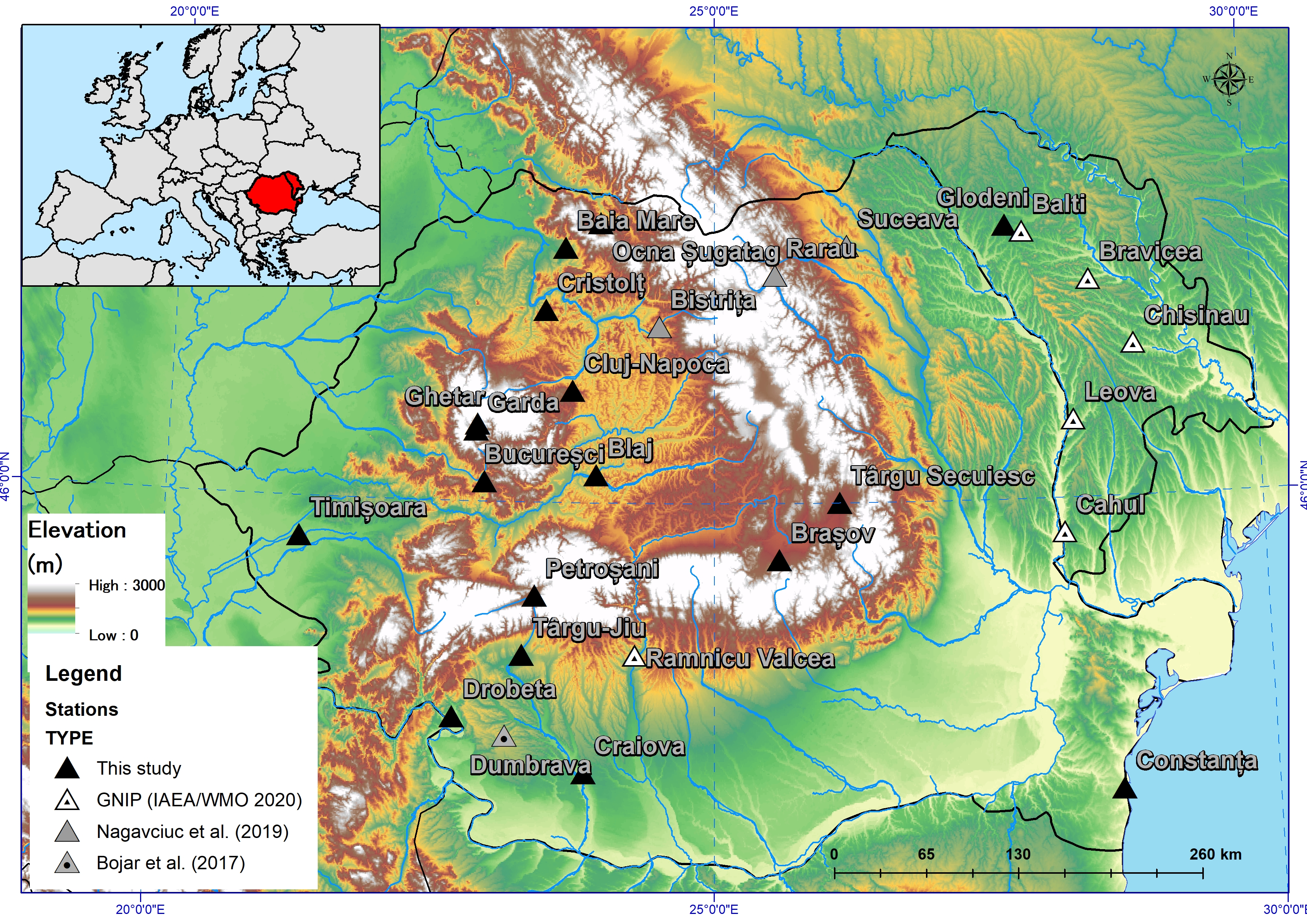
2. Materials and Methods
| NR | Station Name | Abbreviation | Country | Latitude | Longitude | Altitude (m. a.s.l.) | Analyzed Period | Study/Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baia Mare | BM | Romania | 47°37′8.86″ N | 23°36′21.42″ E | 284 | March 2012–December 2014 | This study |
| 2 | Blaj | BJ | Romania | 46°10′42.67″ N | 23°55′11.99″ E | 257 | March 2012–December 2014 | This study |
| 3 | Brașov | BV | Romania | 45°39′27.56″ N | 25°34′51.59″ E | 555 | April 2012–July 2014 | This study |
| 4 | Bucureșci | BU | Romania | 46°7′37.56″ N | 22°53′53.64″ E | 320 | April 2012–June 2013 | This study |
| 5 | Cluj Napoca | CJ | Romania | 46°42′41.67″ N | 23°41′33.58″ E | 362 | March 2012–July 2013 | This study |
| 6 | Constanța | CT | Romania | 44°8′33.00″ N | 28°37′17.00″ E | 35 | June 2013–November 2014 | This study |
| 7 | Craiova | CR | Romania | 44°17′5.40″ N | 23°50′19.45″ E | 112 | March 2012–December 2014 | This study |
| 8 | Cristolț | CT | Romania | 47°13′20.94″ N | 23°26′2.82″ E | 296 | March 2012–March 2013 | This study |
| 9 | Drobeta Turnu Severin | DTS | Romania | 44°37′42.87″ N | 22°39′38.01″ E | 62 | March 2012–December 2014 | This study |
| 10 | Gârda | GD | Romania | 46°27′47.67″ N | 22°49′28.48″ E | 747 | March 2012–June 2013 | This study |
| 11 | Ghețar | CH | Romania | 46°29′28.45″ N | 22°49′26.02″ E | 1101 | March 2012–December 2013 | Bădăluță et al. (2020) [27] |
| 12 | Glodeni | GL | Rep. Moldova | 47°44′30.37″ N | 27°43′27.03″ E | 150 | May 2013–December 2014 | This study |
| 13 | Ocna Șugatag | OS | Romania | 47°46′53.41″ N | 23°56′22.18″ E | 495 | March 2012–December 2013 | This study |
| 14 | Petroșani | PT | Romania | 45°24′49.21″ N | 23°22′0.10″ E | 603 | May 2012–July 2013 | This study |
| 15 | Târgu Secuiesc | TgS | Romania | 46°0′10.46″ N | 26°8′31.29″ E | 567 | April 2012–April 2013 | This study |
| 16 | Târgu-Jiu | TgJ | Romania | 45°2′1.70″ N | 23°16′32.91″ E | 204 | March 2012–December 2012 | This study |
| 17 | Timișoara | TM | Romania | 45°44′48.90″ N | 21°13′50.37″ E | 90 | March 2012–December 2014 | This study |
| 18 | Bistrița | BN | Romania | 47°7′20.59″ N | 24°29′25.23″ E | 400 | March 2012–January 2014 | Nagavciuc et al. (2019) [22] |
| 19 | Suceava | SV | Romania | 47°37′00.00″ N | 26°13′59.99″ E | 350 | March 2012–December 2014 | Nagavciuc et al. (2019) [22] |
| 20 | Rarau | RA | Romania | 47°27′00.0″ N | 25°33′59.99″ E | 1600 | March 2012–December 2014 | Nagavciuc et al. (2019) [22] |
| 21 | Ramnicu Valcea | RV | Romania | 45°02′07.00″ N | 24°17′3.00″ E | 237 | January 2012–December 2014 | GNIP [3] |
| 22 | Balti | BL | Rep. Moldova | 47°42′00.00″ N | 27°52′59.99″ E | 231 | January 2012–December 2014 | GNIP [3] |
| 23 | Bravicea | BR | Rep. Moldova | 47°24′00.00″ N | 28°29′29.97″ E | 78 | January 2012–December 2014 | GNIP [3] |
| 24 | Cahul | CA | Rep. Moldova | 45°47′59.99″ N | 28°11′59.99″ E | 113 | January 2012–December 2014 | GNIP [3] |
| 25 | Chișinău | CH | Rep. Moldova | 46°57′59.99″ N | 28°54′00.00″ E | 125 | January 2012–December 2014 | GNIP [3] |
| 26 | Leova | LE | Rep. Moldova | 46°29′49.99″ N | 28°18′00.00″ E | 156 | January 2012–December 2014 | GNIP [3] |
| 27 | Dumbrava | DU | Romania | 44°31′0.00″ N | 23°7′59.99″ E | 335 | April 2012–November 2014 | Bojar et al. (2017) [21] |
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Local Meteoric Water Lines
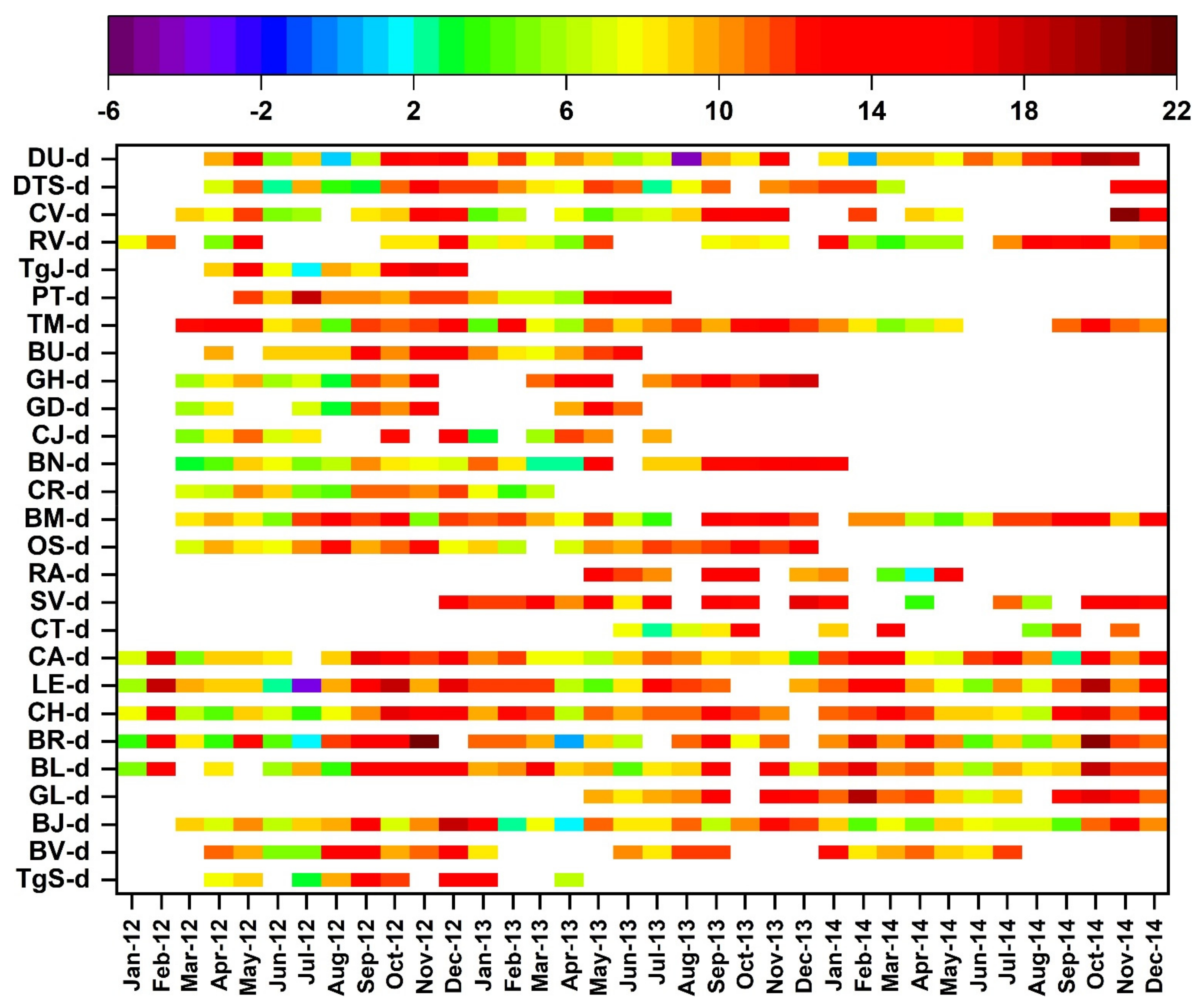
3.2. Temporal Variability of δ18O, δ2H, and D-Excess
3.3. Temperature, Altitude, and Topographic Relationships
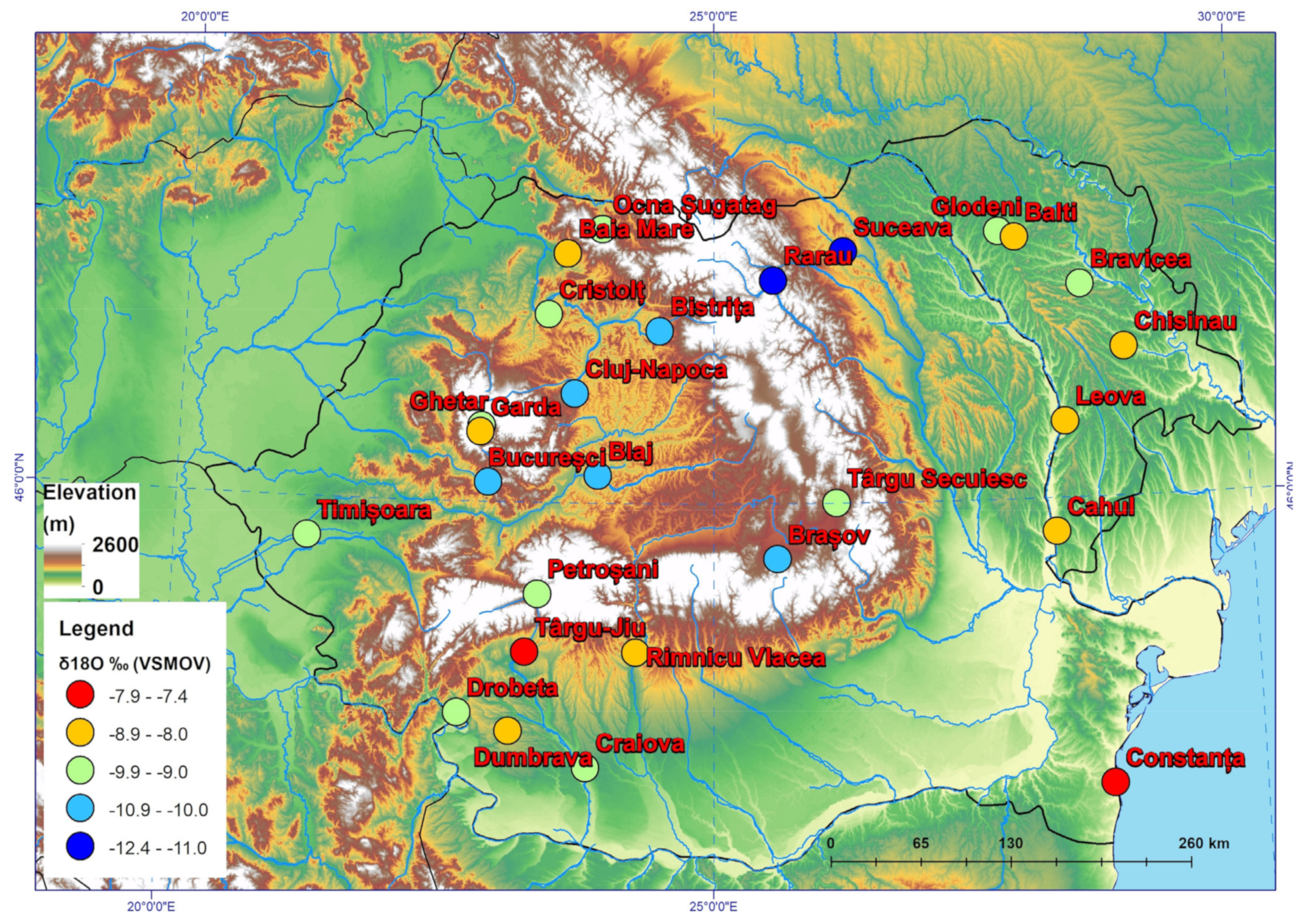
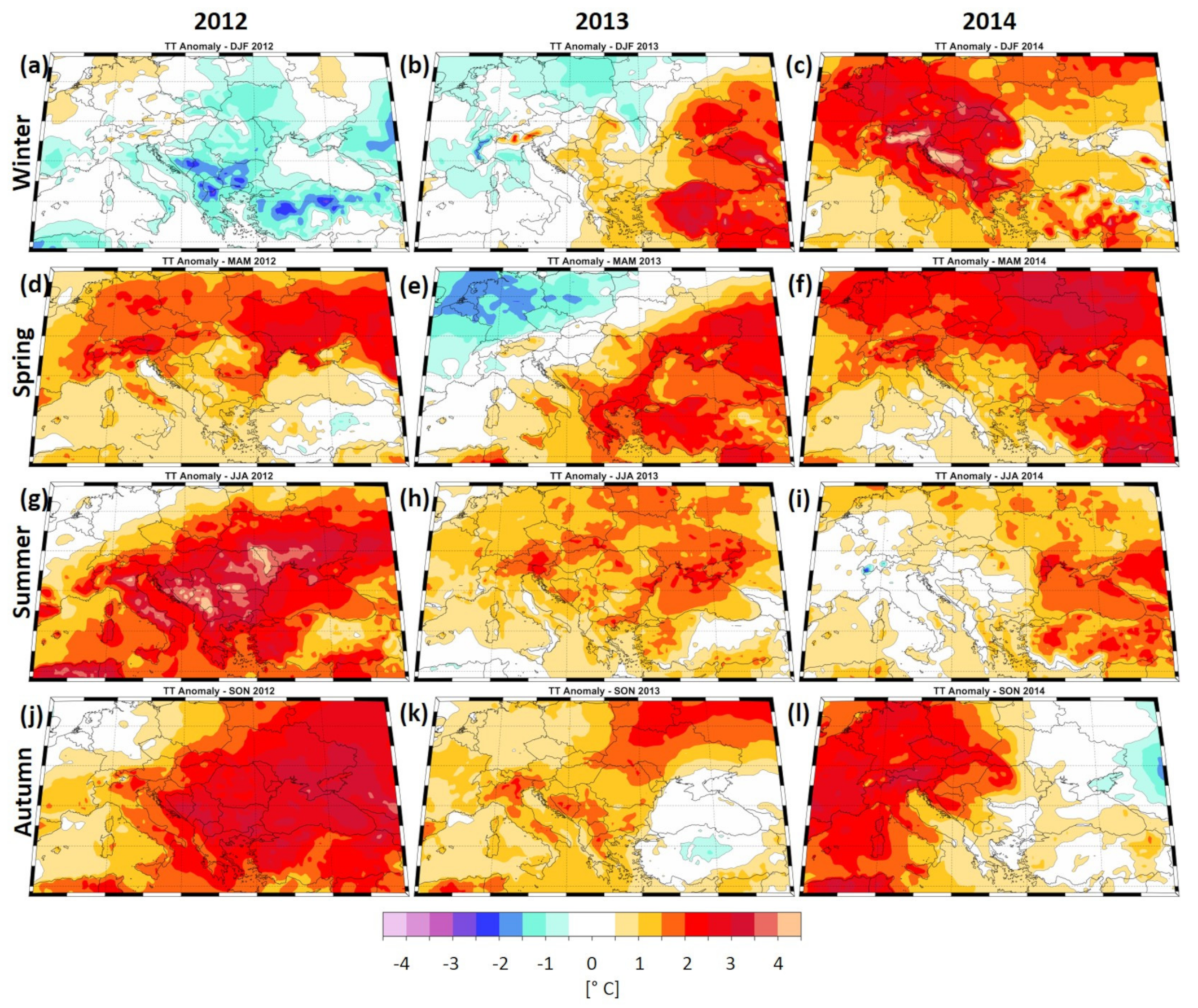
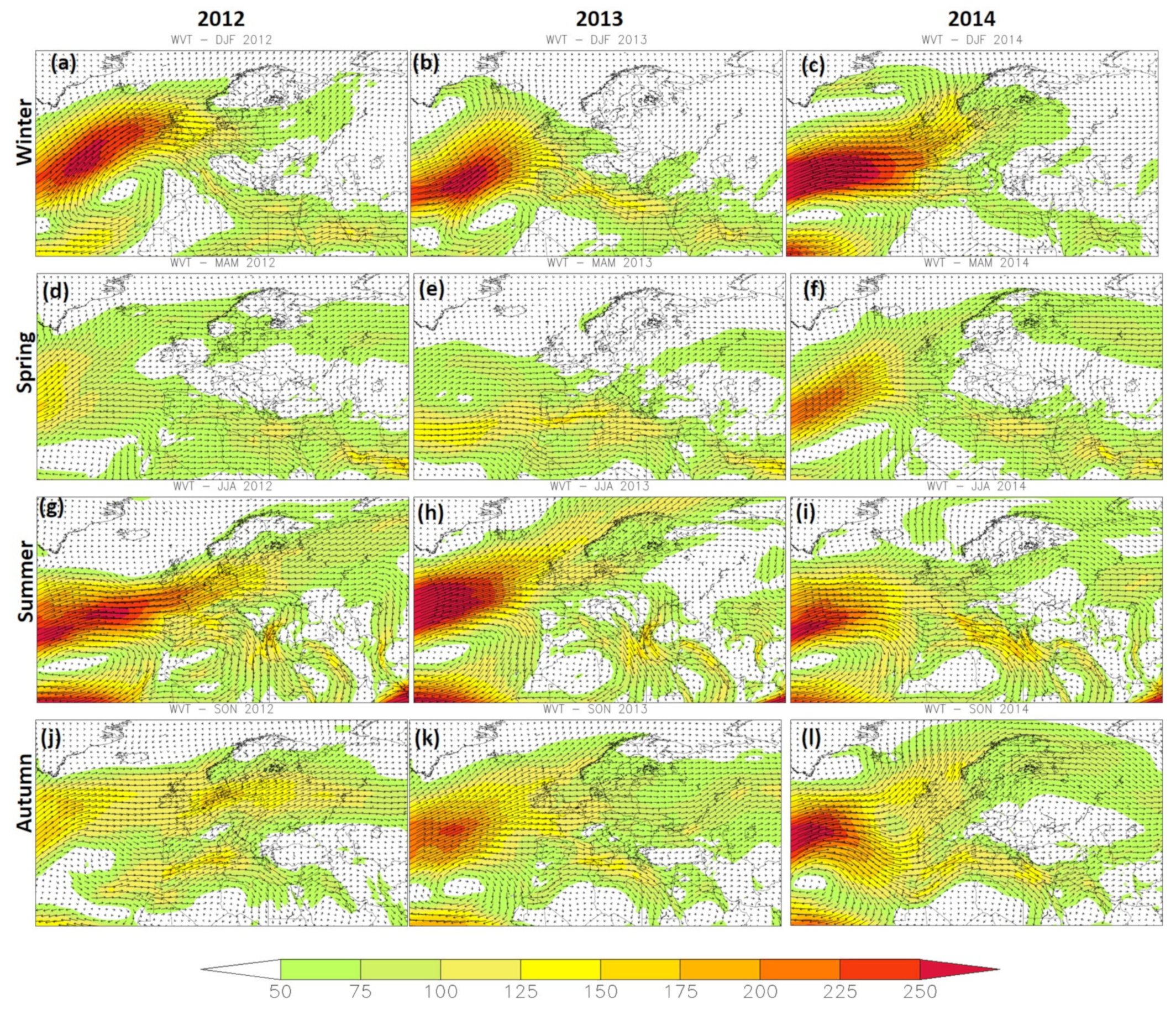
3.4. Spatial Variability of δ18O, δ2H, and D-Excess and Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopes in the Hydrologic Cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IAEA/WMO. Global Network of Isotopes in Precipitation. The GNIP Database. Available online: https://nucleus.iaea.org/wiser/index.aspx (accessed on 5 January 2020).
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 4, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanski, K.; Araguás-Araguás, L.; Gonfiantini, R. Isotopic Patterns in Modern Global Precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 78, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araguas, L.; Danesi, P.; Froehlich, K.; Rozanski, K. Global Monitoring of the isotopic composition of precipitation. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1996, 205, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langebroek, P.M.; Werner, M.; Lohmann, G. Climate information imprinted in oxygen-isotopic composition of precipitation in Europe. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 311, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Crawford, J.; Hughes, C.E.; Du, M.; Liu, X. The effect of moisture source and synoptic conditions on precipitation isotopes in arid central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 2667–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krklec, K.; Domínguez-Villar, D.; Lojen, S. The impact of moisture sources on the oxygen isotope composition of precipitation at a continental site in central Europe. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojar, A.V.; Ottner, F.; Bojar, H.P.; Grigorescu, D.; Perşoiu, A. Stable isotope and mineralogical investigations on clays from the Late Cretaceous sequences, Haţeg Basin, Romania. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 45, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verča, P.; Bronić, I.K.; Horvatinčić, N.; Barešić, J. Isotopic characteristics of precipitation in Slovenia and Croatia: Comparison of continental and maritime stations. J. Hydrol. 2006, 330, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Fekete, B.M.; Bowen, G.J. Stable Isotopes in Large Scale Hydrological Applications. In Isoscapes: Understanding Movement Pattern and Process on Earth through Isotope Mapping; West, J.B., Bowen, G.J., Dawson, T.E., Tu, K.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 389–405. ISBN 978-90-481-3354-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, G.J.; Cerling, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R.B.T.-T.E. Stable Isotopes and Human Water Resources: Signals of Change. In Stable Isotopes as Indicators of Ecological Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 283–300. ISBN 1936-7961. [Google Scholar]
- Coplen, T.B.; Herczeg, A.L.; Barnes, C. Isotope Engineering—Using Stable Isotopes of the Water Molecule to Solve Practical Problems. In Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology; Cook, P.G., Herczeg, A.L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 79–110. ISBN 978-1-4615-4557-6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, F.; Hu, T.; Zhao, K.; Gao, T.; Zhao, H.; Ning, T. Using stable isotopes to quantify water uptake from different soil layers and water use efficiency of wheat under long-term tillage and straw return practices. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 229, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Revenaugh, J. Interpolating the isotopic composition of modern meteoric precipitation. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.; Langebroek, P.M.; Carlsen, T.; Herold, M.; Lohmann, G. Stable water isotopes in the ECHAM5 general circulation model: Toward high-resolution isotope modeling on a global scale. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risi, C.; Noone, D.; Worden, J.; Frankenberg, C.; Stiller, G.; Kiefer, M.; Funke, B.; Walker, K.; Bernath, P.; Schneider, M.; et al. Process-evaluation of tropospheric humidity simulated by general circulation models using water vapor isotopologues: 1. Comparison between models and observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.B.; Basler, D.; Kahmen, A. Precipitation isotope time series predictions from machine learning applied in Europe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holko, L.; Dóša, M.; Michalko, J.; Kostka, Z.; Šanda, M. Isotopes of oxygen-18 and deuterium in precipitation in Slovakia. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2012, 60, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojar, A.V.; Halas, S.; Bojar, H.P.; Chmiel, S. Stable isotope hydrology of precipitation and groundwater of a region with high continentality, South Carpathians, Romania. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 12, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagavciuc, V.; Bădăluţă, C.-A.; Ionita, M. Tracing the Relationship between Precipitation and River Water in the Northern Carpathians Base on the Evaluation of Water Isotope Data. Geosciences 2019, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bădăluță, C.-A.; Perșoiu, A.; Ionita, M.; Nagavciuc, V.; Bistricean, P.-I. Stable H and O isotope-based investigation of moisture sources and their role in river and groundwater recharge in the NE Carpathian Mountains, East-Central Europe. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2019, 55, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drăgușin, V.; Balan, S.; Blamart, D.; Forray, F.L.; Marin, C.; Mirea, I.; Nagavciuc, V.; Perșoiu, A.; Tîrlă, L.; Tudorache, A.; et al. Transfer of environmental signals from surface to the underground at Ascunsă Cave, Romania. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5357–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagavciuc, V.; Bădăluţă, C.-A.; Ionita, M. The influence of the Carpathian Mountains on the variability of stable isotopes in precipitation and the relationship with large-scale atmospheric circulation. In Stable Isotope Studies of the Water Cycle and Terrestrial Environments; Special Publications; Bojar, A.-V., Pelc, A., Lecuyer, C., Eds.; Geological Society: London, UK, 2021; Volume 507, pp. 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- Butzin, M.; Werner, M.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Risi, C.; Frankenberg, C.; Gribanov, K.; Jouzel, J.; Zakharov, V.I. Variations of oxygen-18 in West Siberian precipitation during the last 50 years. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5853–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bădăluță, C.-A.; Perșoiu, A.; Ionita, M.; Piotrowska, N. Stable isotopes in cave ice suggest summer temperatures in east-central Europe are linked to Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation variability. Clim. Past 2020, 16, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. Technical Procedures for GNIP Stations. Available online: http://www.nawb.iaea.org/napc/ih/documents/other/GNIPstationoperationmanual_Feb13_EN.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Ersek, V.; Onac, B.P.; Perșoiu, A. Kinetic processes and stable isotopes in cave dripwaters as indicators of winter severity. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2856–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdevich, O.; Duca, G.; Sidoroff, M.E.; Stanica, A.; Perșoiu, A.; Ashok, V. Groundwater Resource Investigation Using Isotope Technology on River-Sea Systems. In Handbook of Research on Water Sciences and Society; Ashok, V., Duca, G., Travin, S., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 87–100. ISBN 0000000256490. [Google Scholar]
- Roeckner, E.; Bäuml, G.; Bonaventura, L.; Brokopf, R.; Kornblueh, M.; Giorgetta, M.; Hagemann, S.; Kirchner, I.; Tompkins, L.; Manzini, E.; et al. The atmpspheric general circulation model ECHAM5. Part I: Model description. MPI Rep. 2003, 349, 1–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.P.; Oort, A.H. Physics of Climate; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Cornes, R.C.; van der Schrier, G.; van den Besselaar, E.J.M.; Jones, P.D. An Ensemble Version of the E-OBS Temperature and Precipitation Data Sets. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 9391–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. Statistical Treatment of Data on Environmental Isotopes in Precipitation; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J. A new precipitation weighted method for determining the meteoric water line for hydrological applications demonstrated using Australian and global GNIP data. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464–465, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiao, R.; Zhang, M.; Crawford, J.; Hughes, C.E.; Chen, F. Changes in Below-Cloud Evaporation Affect Precipitation Isotopes During Five Decades of Warming Across China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, M.; Caldarescu, D.E.; Nagavciuc, V. Compound Hot and Dry Events in Europe: Variability and Large-Scale Drivers. Front. Clim. 2021, 3, 688991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagavciuc, V.; Scholz, P.; Ionita, M. Hotspots for warm and dry summers in Romania. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 1347–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, A.L.; Fiorella, R.P.; Bowen, G.J.; Cai, Z. A Global Perspective on Local Meteoric Water Lines: Meta-analytic Insight Into Fundamental Controls and Practical Constraints. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6896–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, Z. Principles of Stable Isotope Geochemistry; Rapp, C., Ed.; Pearson: London, UK; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 13:978-0-13-009139-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dar, S.S.; Ghosh, P.; Hillaire-Marcel, C. Convection, Terrestrial Recycling and Oceanic Moisture Regulate the Isotopic Composition of Precipitation at Srinagar, Kashmir Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD032853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagavciuc, V.; Perșoiu, A.; Bădăluță, C.-A.; Bogdevich, O.; Bănică, S.; Bîrsan, M.-V.; Boengiu, S.; Onaca, A.; Ionita, M. Defining a Precipitation Stable Isotope Framework in the Wider Carpathian Region. Water 2022, 14, 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162547
Nagavciuc V, Perșoiu A, Bădăluță C-A, Bogdevich O, Bănică S, Bîrsan M-V, Boengiu S, Onaca A, Ionita M. Defining a Precipitation Stable Isotope Framework in the Wider Carpathian Region. Water. 2022; 14(16):2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162547
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagavciuc, Viorica, Aurel Perșoiu, Carmen-Andreea Bădăluță, Oleg Bogdevich, Sorin Bănică, Marius-Victor Bîrsan, Sandu Boengiu, Alexandru Onaca, and Monica Ionita. 2022. "Defining a Precipitation Stable Isotope Framework in the Wider Carpathian Region" Water 14, no. 16: 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162547
APA StyleNagavciuc, V., Perșoiu, A., Bădăluță, C.-A., Bogdevich, O., Bănică, S., Bîrsan, M.-V., Boengiu, S., Onaca, A., & Ionita, M. (2022). Defining a Precipitation Stable Isotope Framework in the Wider Carpathian Region. Water, 14(16), 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162547






