Analyzing Relationships of Conductivity and Alkalinity Using Historical Datasets from Streams in Northern Alberta, Canada
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
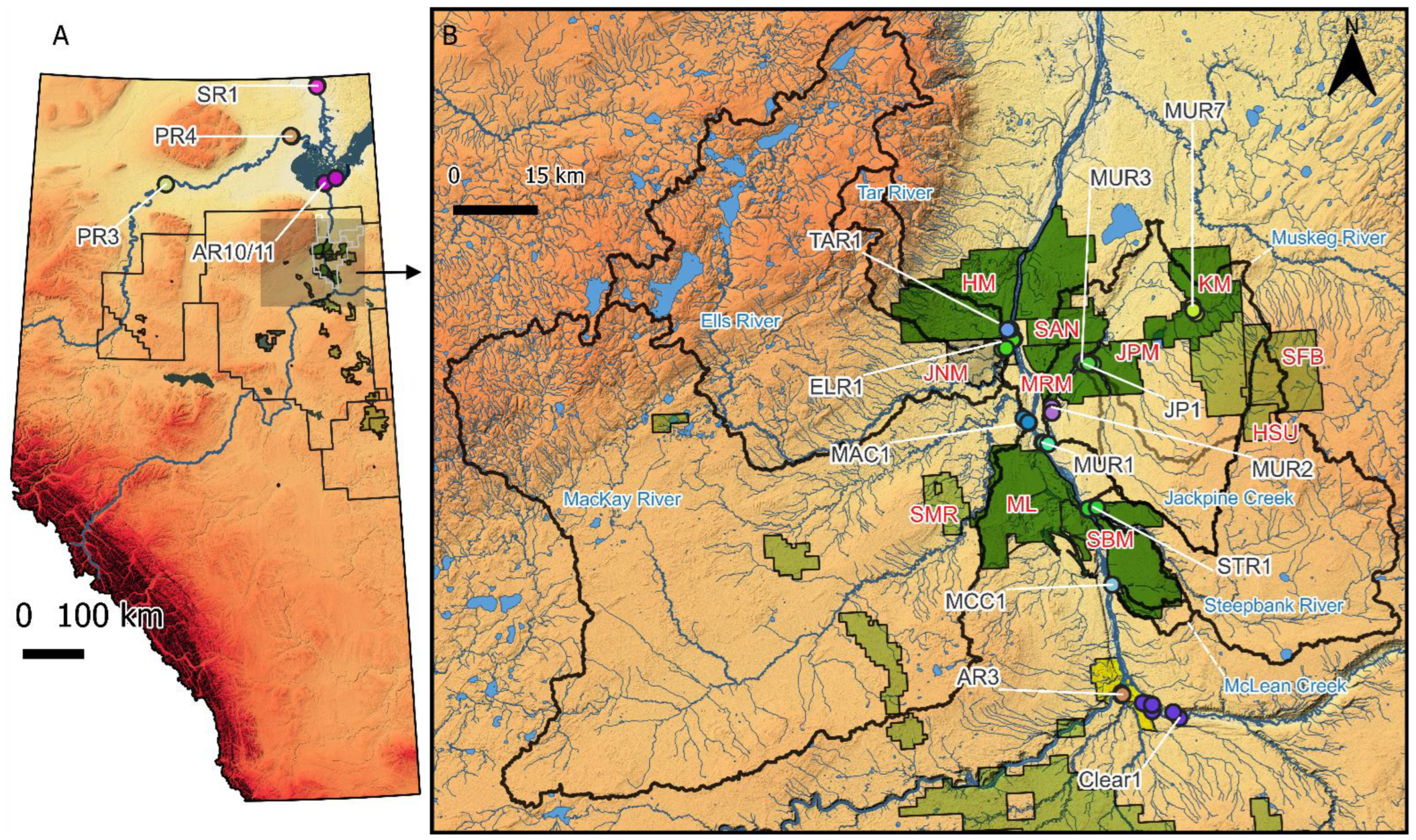
2.1. Data Compilation and Preparation
2.2. Data Analyses
2.3. Generalized Estimating Equations
2.4. Data Interpretation
3. Results and Discussion
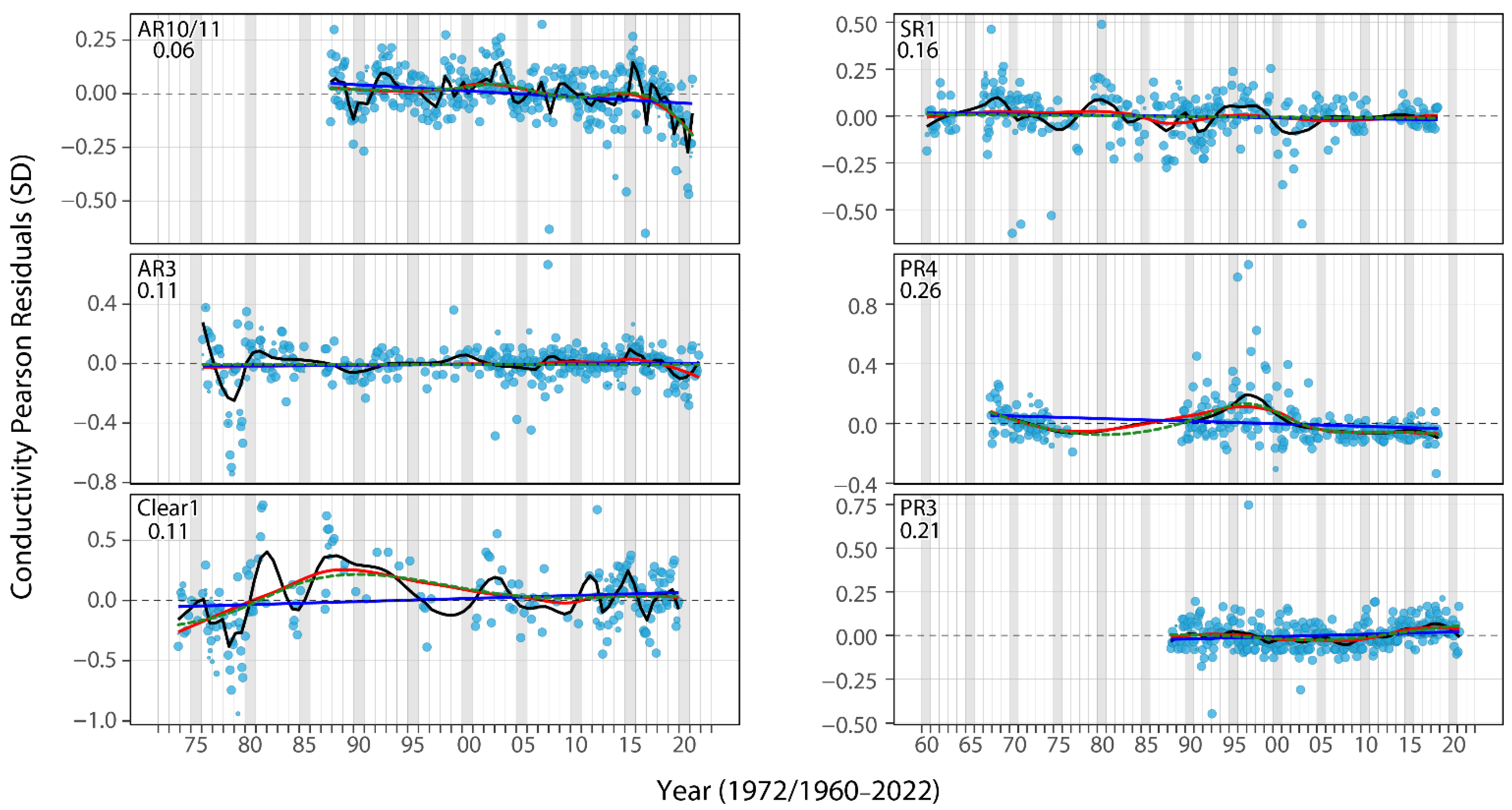
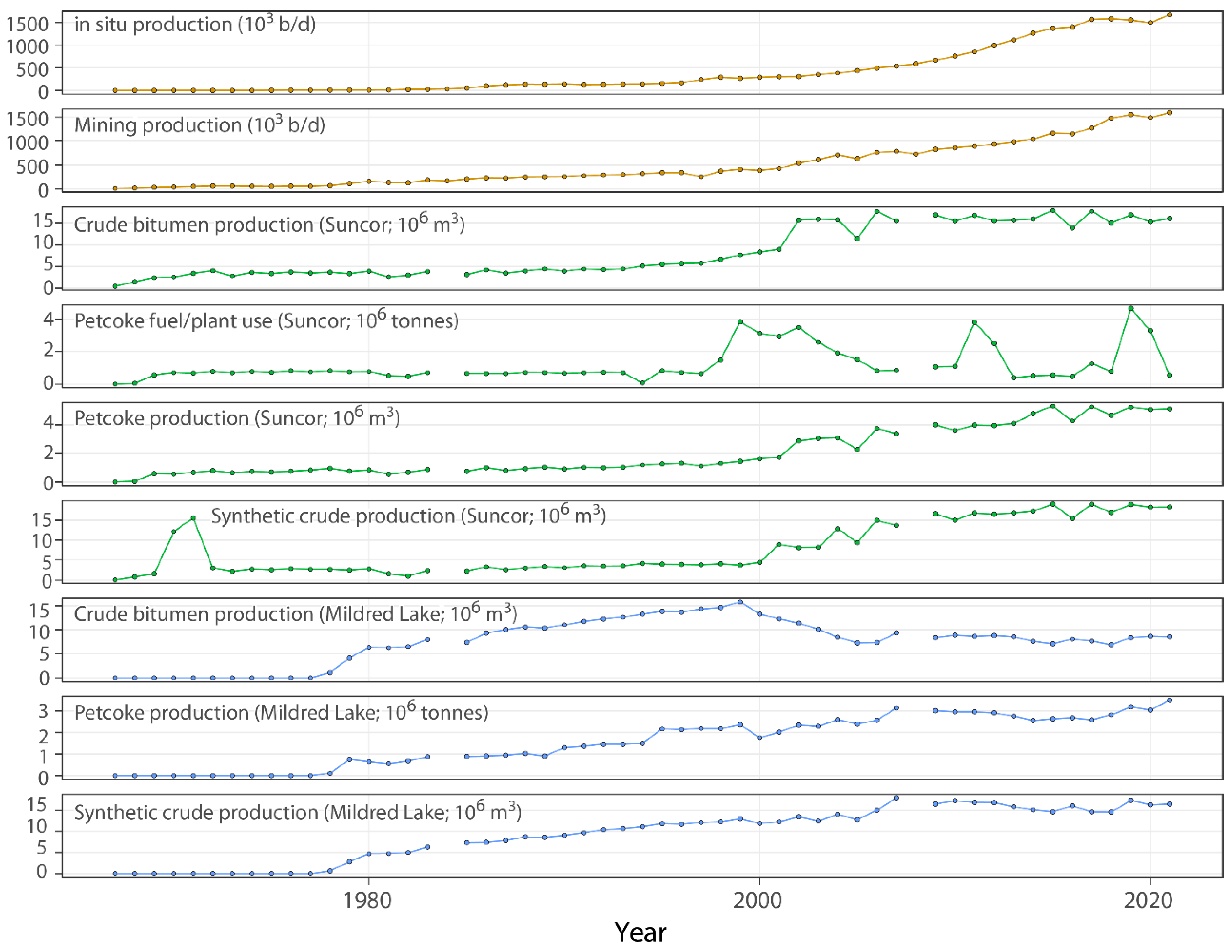
3.1. Potential Influence of Industrial Development in the Late 1970s and Early 1980s
3.2. Additional Evidence of Petroleum Coke Fly Ash: Late 1990s and Early 2000s
3.3. Local Development and Temporal Changes in Residual Conductivity
3.4. Potential Influence of OSPW Seepage
3.5. Potential Responses to Non-Oil Sands Stressors
3.6. Challenges with Residual Conductivity and Further Work
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Cooke, C.A.; Kirk, J.L.; Muir, D.C.G.; Wiklund, J.A.; Wang, X.; Gleason, A.; Evans, M.S. Spatial and Temporal Patterns in Trace Element Deposition to Lakes in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region (Alberta, Canada). Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 124001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalapillai, Y.; Kirk, J.L.; Landis, M.S.; Muir, D.C.G.; Cooke, C.A.; Gleason, A.; Ho, A.; Kelly, E.; Schindler, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Source Analysis of Pollutant Elements in Winter Air Deposition in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region: A Temporal and Spatial Study. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 1656–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.C.; Chambers, P.A. Assessment of Seven Canadian Rivers in Relation to Stages in Oil Sands Industrial Development, 1972–2010. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciszewski, T.J.; Hazewinkel, R.R.O.; Dubé, M.G. A Critical Review of the Ecological Status of Lakes and Rivers from Canada’s Oil Sands Region. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2022, 18, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shotyk, W.; Bicalho, B.; Cuss, C.; Donner, M.; Grant-Weaver, I.; Javed, M.B.; Noernberg, T. Trace Elements in the Athabasca Bituminous Sands: A Geochemical Explanation for the Paucity of Environmental Contamination by Chalcophile Elements. Chem. Geol. 2021, 581, 120392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prowse, T.D.; Beltaos, S.; Gardner, J.T.; Gibson, J.J.; Granger, R.J.; Leconte, R.; Peters, D.L.; Pietroniro, A.; Romolo, L.A.; Toth, B. Climate Change, Flow Regulation and Land-Use Effects on the Hydrology of the Peace-Athabasca-Slave System; Findings from the Northern Rivers Ecosystem Initiative. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 113, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubé, M.G.; Wilson, J.E. Accumulated State Assessment of the Peace-Athabasca-Slave River System. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2013, 9, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsel, D.R. Statistics for Censored Environmental Data Using Minitab® and R: Second Edition; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 77, ISBN 9780470479889. [Google Scholar]
- Donner, M.W.; Siddique, T. A Rapid and Sensitive IC-ICP-MS Method for Determining Selenium Speciation in Natural Waters. Can. J. Chem. 2018, 96, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotyk, W.; Bicalho, B.; Cuss, C.W.; Donner, M.W.; Grant-Weaver, I.; Haas-Neill, S.; Javed, M.B.; Krachler, M.; Noernberg, T.; Pelletier, R.; et al. Trace Metals in the Dissolved Fraction (<0.45 mm) of the Lower Athabasca River: Analytical Challenges and Environmental Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debels, P.; Figueroa, R.; Urrutia, R.; Barra, R.; Niell, X. Evaluation of Water Quality in the Chillán River (Central Chile) Using Physicochemical Parameters and a Modified Water Quality Index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 110, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Hussian, A. Water Quality Index Development for Groundwater Quality Assessment of Greater Noida Sub-Basin, Uttar Pradesh, India. Cogent. Eng. 2016, 3, 1177155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, T.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Bier, R.; Helton, A.M.; Brittany Merola, R.; Vengosh, A.; di Giulio, R.T. Cumulative Impacts of Mountaintop Mining on an Appalachian Watershed. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20929–20934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, E.S.; Lutz, B.D.; King, R.S.; Fay, J.P.; Carter, C.E.; Helton, A.M.; Campagna, D.; Amos, J. How Many Mountains Can We Mine? Assessing the Regional Degradation of Central Appalachian Rivers by Surface Coal Mining. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8115–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stets, E.G.; Kelly, V.J.; Crawford, C.G. Long-Term Trends in Alkalinity in Large Rivers of the Conterminous US in Relation to Acidification, Agriculture, and Hydrologic Modification. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, E.; Haase, P.; Kuemmerlen, M.; Leps, M.; Schäfer, R.B.; Sundermann, A. Water Quality Variables and Pollution Sources Shaping Stream Macroinvertebrate Communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormier, S.M.; Zheng, L.; Hill, R.A.; Novak, R.M.; Flaherty, C.M. A Flow-Chart for Developing Water Quality Criteria from Two Field-Based Methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hounslow, A. Water Quality Data: Analysis and Interpretation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 1351404903. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, R.J.; Nichols, J.W.; Cook, P.M.; Ankley, G.T. Bioavailability of Chemical Contaminants in Aquatic Systems. In The Toxicology of Fishes; CRC Press: London, UK, 2008; Volume 9, pp. 9–54. ISBN 9780203647295. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinow, K.M.; Nichols, J.W.; Hayton, W.L.; McKim, J.M.; Barron, M.G. Toxicokinetics in Fishes. In The Toxicology of Fishes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 55–152. [Google Scholar]
- Clements, W.H.; Kotalik, C. Effects of Major Ions on Natural Benthic Communities: An Experimental Assessment of the US Environmental Protection Agency Aquatic Life Benchmark for Conductivity. Freshw. Sci. 2016, 35, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M.B.; Norton, S.B.; Alexander, L.C.; Pollard, A.I.; LeDuc, S.D. The Effects of Mountaintop Mines and Valley Fills on the Physicochemical Quality of Stream Ecosystems in the Central Appalachians: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 417–418, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstead, M.Y.; Bitzer-Creathers, L.; Wilson, M. The Effects of Elevated Specific Conductivity on the Chronic Toxicity of Mining Influenced Streams Using Ceriodaphnia Dubia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.R.; Haas, A.; Fritz, K.M. Use of Spatially Explicit Physicochemical Data to Measure Downstream Impacts of Headwater Stream Disturbance. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W09526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Geoscience of Climate and Energy 12. Water Quality Issues in the Oil Sands Region of the Lower Athabasca River, Alberta. Geosci. Can. 2013, 40, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.C.; Chambers, P.A.; Jeffries, D.S. Episodic Acidification of 5 Rivers in Canada’s Oil Sands during Snowmelt: A 25-Year Record. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, J.V.; Crosley, B.; Conly, F.M.; Quagraine, E.K. The Characterization and Distribution of Inorganic Chemicals in Tributary Waters of the Lower Athabasca River, Oilsands Region, Canada. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2005, 40, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodo, B.A. Statistical Analyses of Regional Surface Water Quality in Southeastern Ontario. Env. Monit Assess 1992, 23, 165–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akena, A.M. An Intensive Surface Water Quality Study of the Muskeg River Watershed, Volume I; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1979.
- Proulx, C.L.; Kilgour, B.W.; Francis, A.P.; Bouwhuis, R.F.; Hill, J.R. Using a Conductivity–Alkalinity Relationship as a Tool to Identify Surface Waters in Reference Condition across Canada. Water Qual. Res. J. 2018, 53, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechriest, R. Relationship Between Total Alkalinity, Conductivity, Original PH, and Buffer Action of Natural Water. Ohio J. Sci. 1960, 60, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Akena, A.M.; Christian, L. Water Quality of the Athabasca Oil Sands Area: Volume IV-an Interim Compilation of Non-AOSERP Water Quality Data; Alberta Oil Sands Environmental Research Program; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1981.
- Environment and Climate Change Canada Canada-Alberta Oil Sands Environmental Monitoring. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/oil-sands-monitoring.html (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Kisters OSM Environmental Data Viewer. 2021. Available online: Https://Www.Canada.ca/En/Environment-Climate-Change/Services/Oil-Sands-Monitoring.Html (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Liang, K.Y.; Zeger, S.L. Longitudinal Data Analysis Using Generalized Linear Models. Biometrika 1986, 73, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, P.; Gurrin, L.; Sly, P. Extending the Simple Linear Regression Model to Account for Correlated Responses: An Introduction to Generalized Estimating Equations and Multi-level Mixed Modelling. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 1261–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballinger, G.A. Using Generalized Estimating Equations for Longitudinal Data Analysis. Organ. Res. Methods 2004, 7, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, R.; Henderson, B.L. Estimation of Nonlinear Trends in Water Quality: An Improved Approach Using Generalized Additive Models. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halekoh, U.; Højsgaard, S.; Yan, J. The R Package Geepack for Generalized Estimating Equations. J. Stat. Softw. 2006, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, J.W.; Hilbe, J.M. Generalized Estimating Equations; CRC Press: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Qian, G. Selection of Working Correlation Structure and Best Model in GEE Analyses of Longitudinal Data. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2007, 36, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, F.E. Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications to Linear Models, Logistic and Ordinal Regression, and Survival Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 3319194259. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Wickham, M.H. Package ‘Ggplot2.’ Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics; CRAN: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Hufkens, K.; Basler, D.; Milliman, T.; Melaas, E.K.; Richardson, A.D. An Integrated Phenology Modelling Framework in R. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsands, P.G. Application to the Alberta Energy Resources Conservation Board for an Oil Sands Mining Project; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1978.
- Murray, W.A. The 1981 Snowpack Survey in the AOSERP Study Area; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1981.
- Rogers, W.; Lake, W. Acute Lethality of Mine Depressurization Water to Trout-Perch (Percopsis Omiscomaycus) and Rainbow Trout (Salmo Gairdneri) Volume II.; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1979.
- Lake, W.; Rogers, W. Acute Lethality of Mine Depressurization Water to Trout-Perch (Percopsis Omiscomaycus) and Rainbow Trout (Salmo Gairdneri) Volume I.; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, USA, 1979.
- AER ST39|Alberta Energy Regulator. Statistical Report 39. Available online: https://www.aer.ca/providing-information/data-and-reports/statistical-reports/st39 (accessed on 29 May 2021).
- Shelfentook, W. An Inventory System for Atmospheric Emissions in the AOSERP Study Area; SNC Tottrup Services Ltd.: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Wasiuta, V.; Kirk, J.L.; Chambers, P.A.; Alexander, A.C.; Wyatt, F.R.; Rooney, R.C.; Cooke, C.A. Accumulating Mercury and Methylmercury Burdens in Watersheds Impacted by Oil Sands Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12856–12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciszewski, T.J. A Re-Analysis and Review of Elemental and Polycyclic Aromatic Compound Deposition in Snow and Lake Sediments from Canada’s Oil Sands Region Integrating Industrial Performance and Climatic Variables. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrie, L.A.; Kovalick, J. A Wintertime Investigation of the Deposition of Pollutants around an Isolated Power Plant in Northern Alberta; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1980.
- Arciszewski, T.J. Exploring the Influence of Industrial and Climatic Variables on Communities of Benthic Macroinvertebrates Collected in Streams and Lakes in Canada’s Oil Sands Region. Environments 2021, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciszewski, T.J.; Ussery, E.J.; McMaster, M.E. Incorporating Industrial and Climatic Covariates into Analyses of Fish Health Indicators Measured in a Stream in Canada’s Oil Sands Region. Environments 2022, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullan-Boudreau, G.; Davies, L.; Devito, K.; Froese, D.; Noernberg, T.; Pelletier, R.; Shotyk, W. Reconstructing Past Rates of Atmospheric Dust Deposition in the Athabasca Bituminous Sands Region Using Peat Cores from Bogs. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 2468–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullan-Boudreau, G.; Belland, R.; Devito, K.; Noernberg, T.; Pelletier, R.; Shotyk, W. Sphagnum Moss as an Indicator of Contemporary Rates of Atmospheric Dust Deposition in the Athabasca Bituminous Sands Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7422–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.; Jackson, T. Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of the Mainstem Athabasca River System in the AOSERP Study Area; Alberta Oil Sands Environmental Research Program; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1978. [CrossRef]
- Corkum, L. Water Quality of the Athabasca Oil Sands Area: A Regional Study; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1985. [CrossRef]
- Syncrude Canada. Environmental Impact Assessment for the Syncrude Aurora Mine; Syncrude Canada Ltd.: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.; Davies, M.; Janzen, K.; Muir, D.; Hazewinkel, R.; Kirk, J.; de Boer, D. PAH Distributions in Sediments in the Oil Sands Monitoring Area and Western Lake Athabasca: Concentration, Composition and Diagnostic Ratios. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RAMP Regional Aquatics Monitoring in Support of the Joint Oil Sands Monitoring Plan Final 2015 Program Report; AMERA: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2016.
- Timoney, K.P.; Lee, P. Does the Alberta Tar Sands Industry Pollute? The Scientific Evidence. Open Conserv. Biol. J. 2009, 3, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.B.; Cuss, C.W.; Shotyk, W. Dissolved versus Particulate Forms of Trace Elements in the Athabasca River, Upstream and Downstream of Bitumen Mines and Upgraders. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 122, 104706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, C.E.; Kirk, J.L.; St Louis, V.L.; Lehnherr, I.; Ariya, P.A.; Rangel-Alvarado, R.B. Sources of Methylmercury to Snowpacks of the Alberta Oil Sands Region: A Study of in Situ Methylation and Particulates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shotyk, W.; Appleby, P.G.; Bicalho, B.; Davies, L.J.; Froese, D.; Grant-Weaver, I.; Magnan, G.; Mullan-Boudreau, G.; Noernberg, T.; Pelletier, R.; et al. Peat Bogs Document Decades of Declining Atmospheric Contamination by Trace Metals in the Athabasca Bituminous Sands Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6237–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volik, O.; Elmes, M.; Petrone, R.; Kessel, E.; Green, A.; Cobbaert, D.; Price, J. Wetlands in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region: The Nexus between Wetland Hydrological Function and Resource Extraction. Environ. Rev. 2020, 28, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemt, W.H.; Kay, M.L.; Wiklund, J.A.; Wolfe, B.B.; Hall, R.I. Assessment of Vanadium and Nickel Enrichment in Lower Athabasca River Floodplain Lake Sediment within the Athabasca Oil Sands Region (Canada). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, S.J.; Cho, S.; Taylor, E.; Yi, Y.; Gibson, J.J. Characterizing the PAHs in Surface Waters and Snow in the Athabasca Region: Implications for Identifying Hydrological Pathways of Atmospheric Deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzanne, C.L. Effects of Natural and Anthropogenic Non-Point Source Disturbances on the Structure and Function of Tributary Ecosystems in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region. Master’s Thesis, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, J.W.; Bickerton, G.; Frank, R.A.; Grapentine, L.; Hewitt, L.M. Assessing Risks of Shallow Riparian Groundwater Quality near an Oil Sands Tailings Pond. Groundwater 2016, 54, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, P.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Bird, G.; Macklin, M.G.; Brewer, P.A.; Williams, R.D.; Jamieson, H.E. Water Quality Impacts and River System Recovery Following the 2014 Mount Polley Mine Tailings Dam Spill, British Columbia, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 91, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, C.A.; Schwindt, C.; Davies, M.; Donahue, W.F.; Azim, E. Initial Environmental Impacts of the Obed Mountain Coal Mine Process Water Spill into the Athabasca River (Alberta, Canada). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korosi, J.B.; Irvine, G.; Skierszkan, E.K.; Doyle, J.R.; Kimpe, L.E.; Janvier, J.; Blais, J.M. Localized Enrichment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil, Spruce Needles, and Lake Sediments Linked to in-Situ Bitumen Extraction near Cold Lake, Alberta. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skierszkan, E.K.; Irvine, G.; Doyle, J.R.; Kimpe, L.E.; Blais, J.M. Is There Widespread Metal Contamination from In-Situ Bitumen Extraction at Cold Lake, Alberta Heavy Oil Field? Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munkittrick, K.R.; Arciszewski, T.J. Using Normal Ranges for Interpreting Results of Monitoring and Tiering to Guide Future Work: A Case Study of Increasing Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds in Lake Sediments from the Cold Lake Oil Sands (Alberta, Canada) Described in Korosi et al. (2016). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselin, P.; Hrudey, S.E.; Naeth, M.A.; Plourde, A.; Therrien, R.; van der Kraak, G.; Xu, Z. Environmental and Health Impacts of Canada’s Oil Sands Industry; Royal Society of Canada: Ottawa, OT, USA, 2010; p. 438. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Shotyk, W.; Cuss, C.W.; Donner, M.W.; Fennell, J.; Javed, M.; Noernberg, T.; Poesch, M.; Pelletier, R.; Sinnatamby, N.; et al. Characterization of Naphthenic Acids and Other Dissolved Organics in Natural Water from the Athabasca Oil Sands Region, Canada. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9524–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.S.; Pereira, A.D.S.; Fennell, J.; Davies, M.; Johnson, J.; Sliva, L.; Martin, J.W. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Naphthenic Acids in Natural Waters Surrounding the Canadian Oil Sands Industry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12796–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, J.; Arciszewski, T.J. Current Knowledge of Seepage from Oil Sands Tailings Ponds and Its Environmental Influence in Northeastern Alberta. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.W. Process Water Treatment in Canada’s Oil Sands Industry: II. A Review of Emerging Technologies. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 7, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, A.D.; Kinley, C.M.; Hendrikse, M.; Gaspari, D.P.; Calomeni, A.J.; Iwinski, K.J.; Castle, J.W.; Haakensen, M.C.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; et al. A Risk-Based Approach for Identifying Constituents of Concern in Oil Sands Process-Affected Water from the Athabasca Oil Sands Region. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.A.; Bauer, A.E.; Roy, J.W.; Bickerton, G.; Rudy, M.D.; Vanderveen, R.; Batchelor, S.; Barrett, S.E.; Milestone, C.B.; Peru, K.M.; et al. Preparative Isolation, Fractionation and Chemical Characterization of Dissolved Organics from Natural and Industrially Derived Bitumen-Influenced Groundwaters from the Athabasca River Watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, G.P.; Rudolph, D.L.; Barker, J.F. Hydrodynamics of a Large Oil Sand Tailings Impoundment and Related Environmental Implications. Can. Geotech. J. 2009, 46, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.M.; Bouthillier, P.H.; Gallup, D.N.; Greenhill, S.; MacKay, W.E.; Morgenstern, N.R. Great Canadian Oil Sands Dyke Discharge Water. Summary Report of the Scientific Enquiry Committee; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 1976.
- Gibson, J.J.; Yi, Y.; Birks, S.J. Isotope-Based Partitioning of Streamflow in the Oil Sands Region, Northern Alberta: Towards a Monitoring Strategy for Assessing Flow Sources and Water Quality Controls. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 5, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumulative Environmental Management Association (CEMA). Review of Potential Cumulative Impacts to Surface Water and Groundwater from Current and Proposed In-Situ Oil Sands Operations; CEMA: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Prowse, T.D.; Conly, F.M. A Review of Hydroecological Results of the Northern River Basins Study, Canada. Part 2. Peace-Athabasca Delta. River Res. Appl. 2002, 18, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster, M.E.; Evans, M.S.; Alaee, M.; Muir, D.C.G.; Hewitt, L.M. Northern Rivers Ecosystem Initiative: Distribution and Effects of Contaminants. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 113, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.B. Alberta Oil Sands Environmental Research Program 1975-1980: Summary Report; Alberta Oil Sands Environmental Research Program; Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development: Calgary, AB, Canada, 1981.
- Arciszewski, T.J.; McMaster, M.E. Potential Influence of Sewage Phosphorus and Wet and Dry Deposition Detected in Fish Collected in the Athabasca River North of Fort Mcmurray. Environement 2021, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, A.J.; Dubé, M.G. Development of an Effects-Based Approach for Watershed Scale Aquatic Cumulative Effects Assessment. Integr Env. Assess Manag 2013, 9, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrimgeour, G.J.; Chambers, P.A. Cumulative Effects of Pulp Mill and Municipal Effluents on Epilithic Biomass and Nutrient Limitation in a Large Northern River Ecosystem. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 1342–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciszewski, T.J.; Hazewinkel, R.R.; Munkittrick, K.R.; Kilgour, B.W. Developing and Applying Control Charts to Detect Changes in Water Chemistry Parameters Measured in the Athabasca River near the Oil Sands: A Tool for Surveillance Monitoring. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2296–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.M.; Zipper, C.E.; Donovan, P.F.; Daniels, W.L. Long-Term Trends of Specific Conductance in Waters Discharged by Coal-Mine Valley Fills in Central Appalachia, USA. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, G.J.; Passmore, M.E.; Pointon, N.D.; Felbinger, J.K.; Walker, C.A.; Krock, K.J.G.; Fulton, J.B.; Nash, W.L. Long-Term Impacts on Macroinvertebrates Downstream of Reclaimed Mountaintop Mining Valley Fills in Central Appalachia. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerton, C.A.; Cooke, C.A.; Hustins, S.; Silins, U.; Emelko, M.B.; Lewis, T.; Kruk, M.K.; Taube, N.; Zhu, D.; Jackson, B.; et al. Severe Western Canadian Wildfire Affects Water Quality Even at Large Basin Scales. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, M.; Johnson, B.; Dunn, G.; Culp, J.; Cash, K.; Munkittrick, K.; Wong, I.; Hedley, K.; Booty, W.; Lam, D.; et al. Development of a New Approach to Cumulative Effects Assessment: A Northern River Ecosystem Example. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 113, 87–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciszewski, T.J.; Roberts, D.R.; Munkittrick, K.R.; Scrimgeour, G.J. Challenges and Benefits of Approaches Used to Integrate Regional Monitoring Programs. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, K.; Scrimgeour, G. A Study Design for Enhanced Environmental Monitoring of the Lower Athabasca River; Office of the Chief Scientist, Ministry of Environment and Parks: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2019; ISBN 1460145364.
- Wellen, C.; Shatilla, N.J.; Carey, S.K. The Influence of Mining on Hydrology and Solute Transport in the Elk Valley, British Columbia, Canada. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 074012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, S.J.; Moncur, M.C.; Gibson, J.J.; Yi, Y.; Fennell, J.W.; Taylor, E.B. Origin and Hydrogeological Setting of Saline Groundwater Discharges to the Athabasca River: Geochemical and Isotopic Characterization of the Hyporheic Zone. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 172–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, J.L.; Marentette, J.R.; Hewitt, L.M.; McMaster, M.E.; Gillis, P.L.; Norwood, W.P.; Kirk, J.L.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Wang, Z.; et al. Meltwater from Snow Contaminated by Oil Sands Emissions Is Toxic to Larval Fish, but Not Spring River Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, W.L.; Zipper, C.E.; Orndorff, Z.W.; Skousen, J.; Barton, C.D.; McDonald, L.M.; Beck, M.A. Predicting Total Dissolved Solids Release from Central Appalachian Coal Mine Spoils. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, J.R. Strong Inference: Certain Systematic Methods of Scientific Thinking May Produce Much More Rapid Progress than Others. Science 1964, 146, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurek, J.; Kirk, J.L.; Muir, D.C.G.G.; Wang, X.; Evans, M.S.; Smol, J.P. Legacy of a Half Century of Athabasca Oil Sands Development Recorded by Lake Ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atekwana, E.A.; Atekwana, E.A.; Rowe, R.S.; Werkema, D.D.; Legall, F.D. The Relationship of Total Dissolved Solids Measurements to Bulk Electrical Conductivity in an Aquifer Contaminated with Hydrocarbon. J. Appl. Geophys. 2004, 56, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, J.M.; Glozier, N.E.; Baird, D.J.; Wrona, F.J.; Brua, R.B.; Ritcey, A.L.; Peters, D.L.; Choung, C.B.; Curry, C.J. Assessing Ecosystem Health in Benthic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages of the Athabasca River Main Stem, Tributaries and Peace-Athabasca Delta; Government of Alberta: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2018.
- Arciszewski, T.J.; Munkittrick, K.R.; Scrimgeour, G.J.; Dubé, M.G.; Wrona, F.J.; Hazewinkel, R.R. Using Adaptive Processes and Adverse Outcome Pathways to Develop Meaningful, Robust, and Actionable Environmental Monitoring Programs. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glozier, N.E.; Pippy, K.; Levesque, L.; Ritcey, A.; Armstrong, B.; Tobin, O.; Cooke, C.A.; Conly, M.; Dirk, L.; Epp, C.; et al. Surface Water Quality of the Athabasca, Peace and Slave Rivers and Riverine Waterbodies within the Peace-Athabasca Delta; Oil Sands Monitoring Program Technical Report Series No. 1.4; Alberta Environment and Parks: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2018; ISBN 9781460140284. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arciszewski, T.J.; Roberts, D.R. Analyzing Relationships of Conductivity and Alkalinity Using Historical Datasets from Streams in Northern Alberta, Canada. Water 2022, 14, 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162503
Arciszewski TJ, Roberts DR. Analyzing Relationships of Conductivity and Alkalinity Using Historical Datasets from Streams in Northern Alberta, Canada. Water. 2022; 14(16):2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162503
Chicago/Turabian StyleArciszewski, Tim J., and David R. Roberts. 2022. "Analyzing Relationships of Conductivity and Alkalinity Using Historical Datasets from Streams in Northern Alberta, Canada" Water 14, no. 16: 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162503
APA StyleArciszewski, T. J., & Roberts, D. R. (2022). Analyzing Relationships of Conductivity and Alkalinity Using Historical Datasets from Streams in Northern Alberta, Canada. Water, 14(16), 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162503





