Analysis on the Return Period of “7.20” Rainstorm in the Xiaohua Section of the Yellow River in 2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
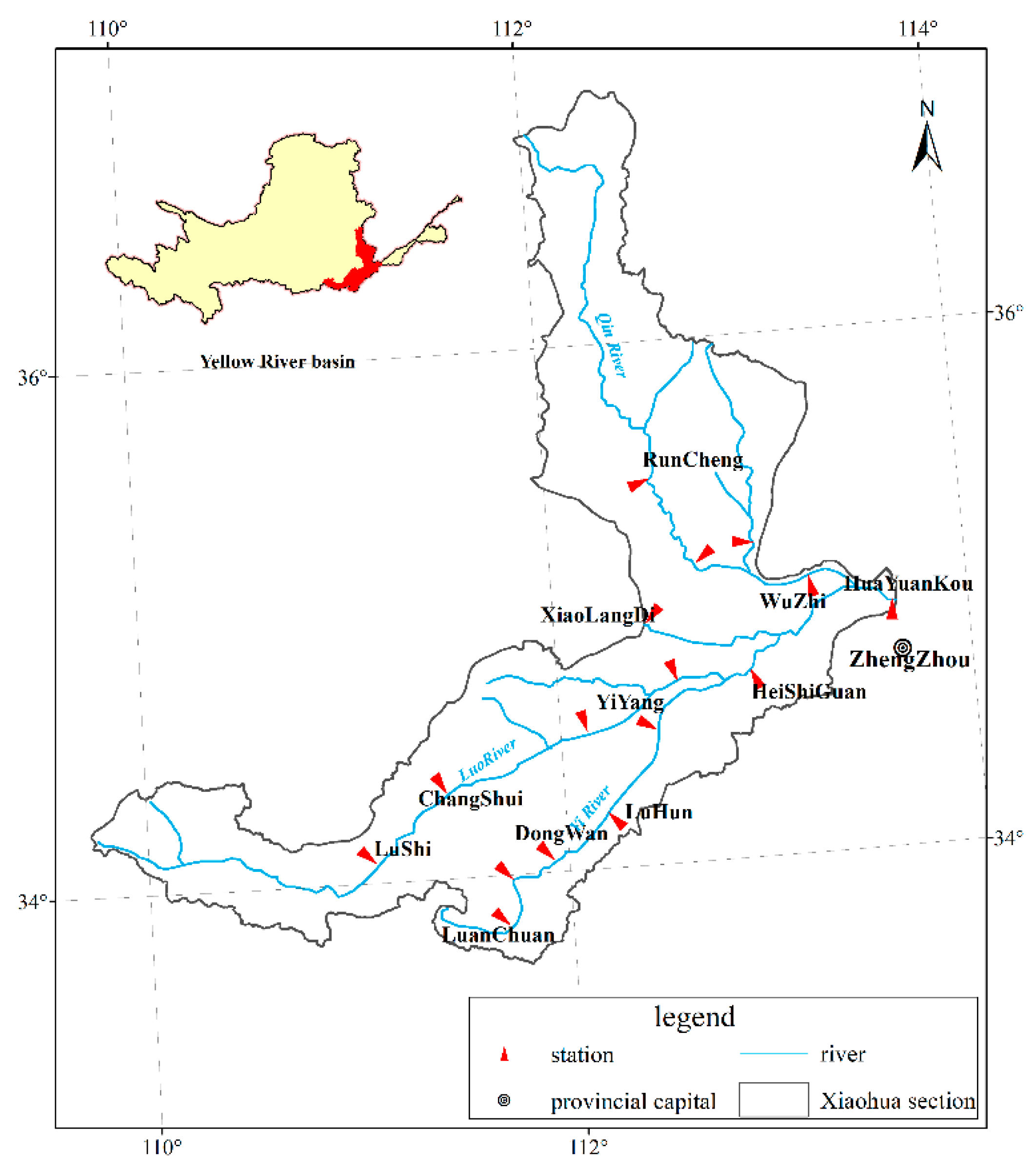
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Basic Data
2.3. Method
3. Results and Discussion
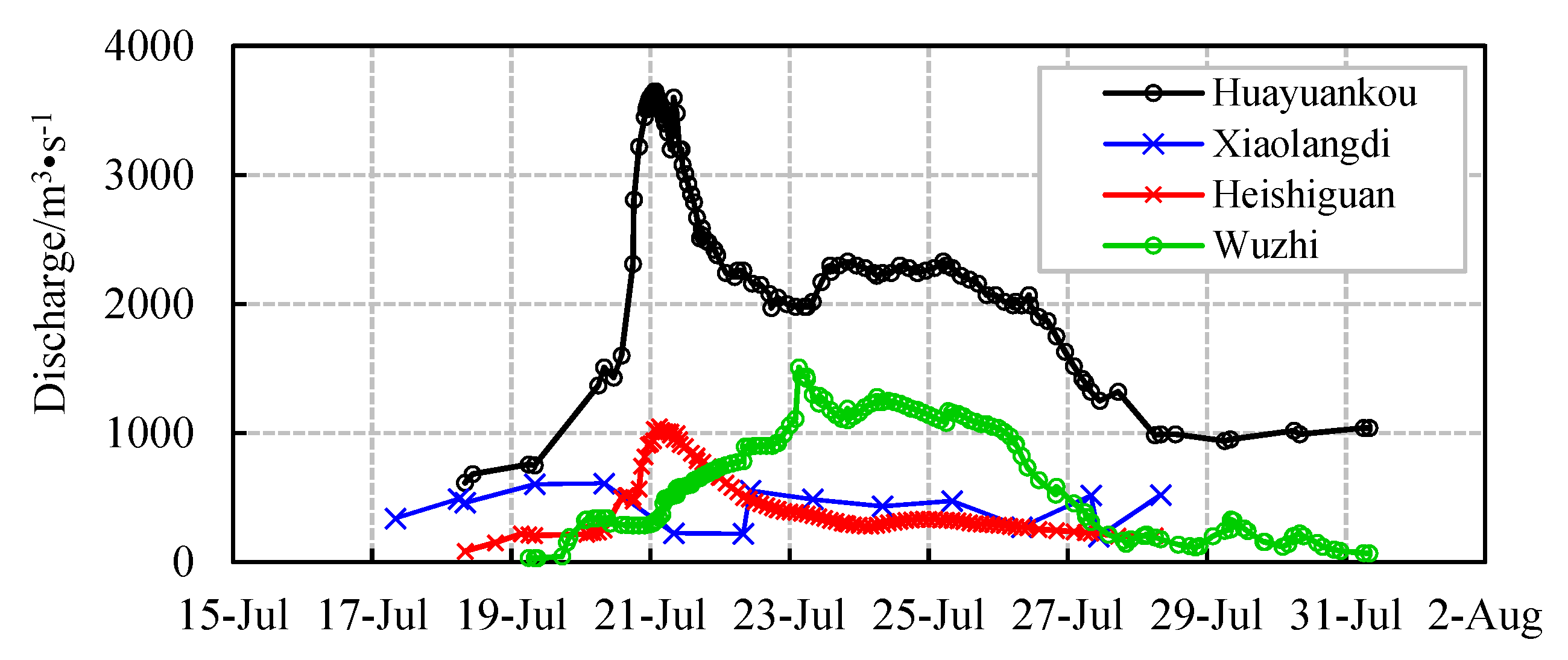
3.1. “7.20” Rainstorm and Flood
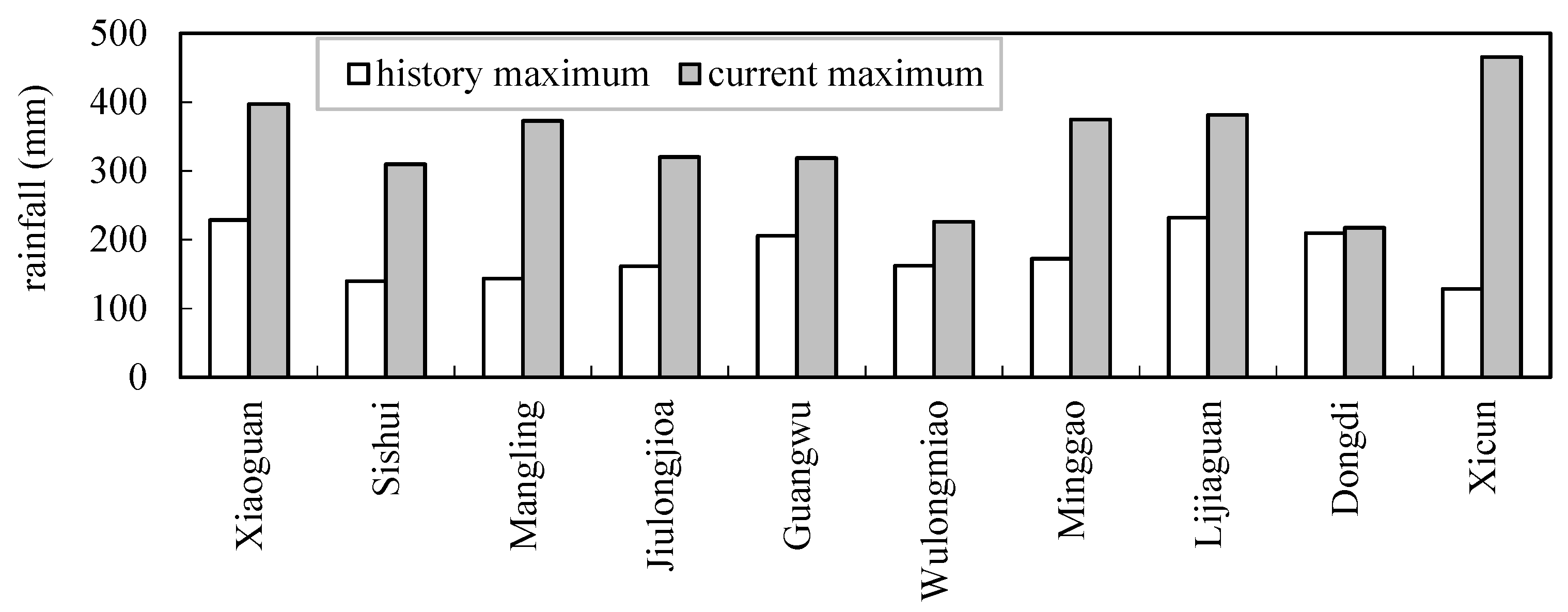
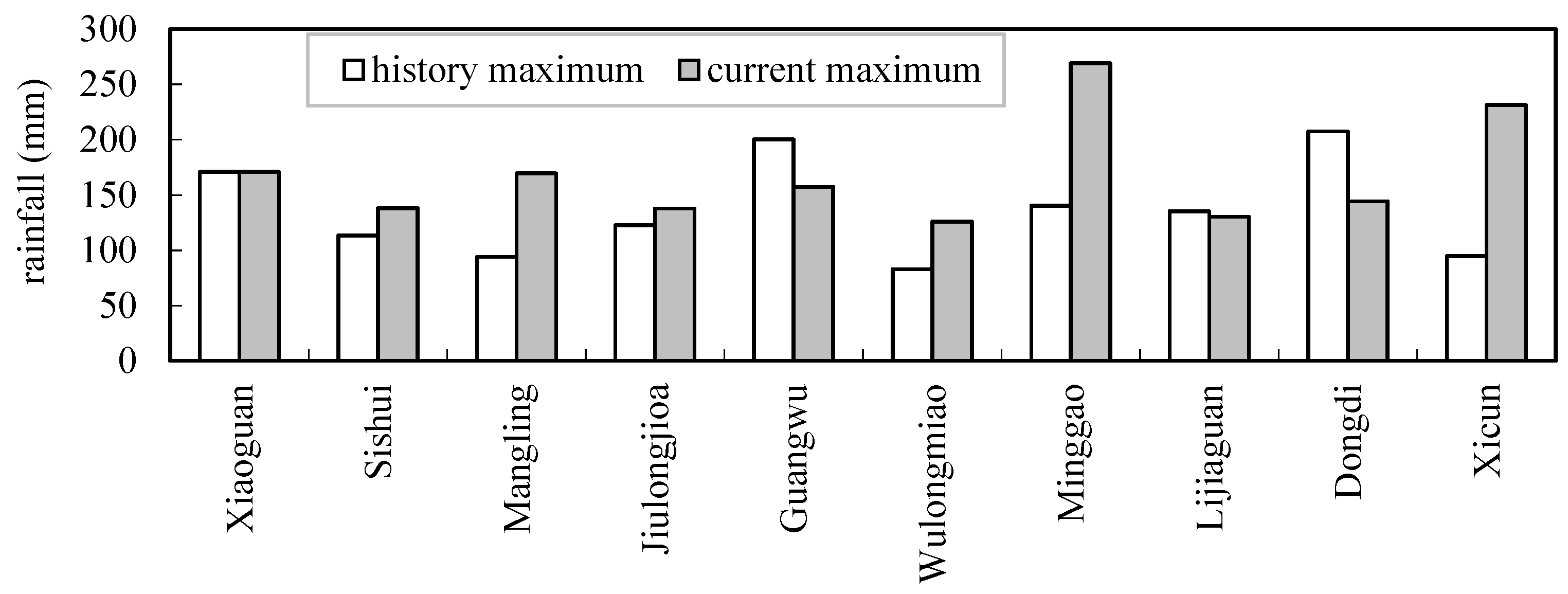
3.2. The Comparison of Historical and Current Maximum 24 h Rainfall
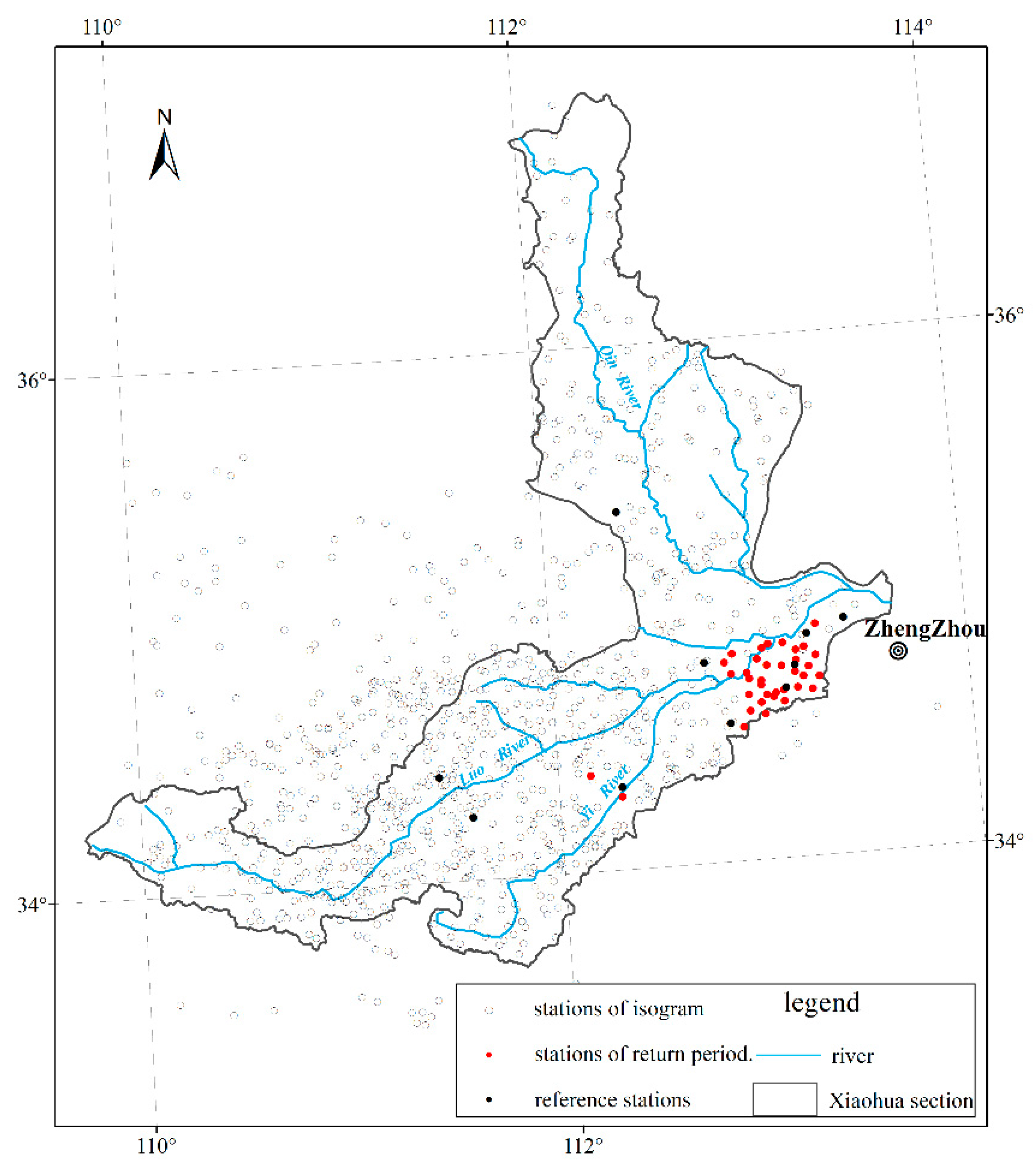
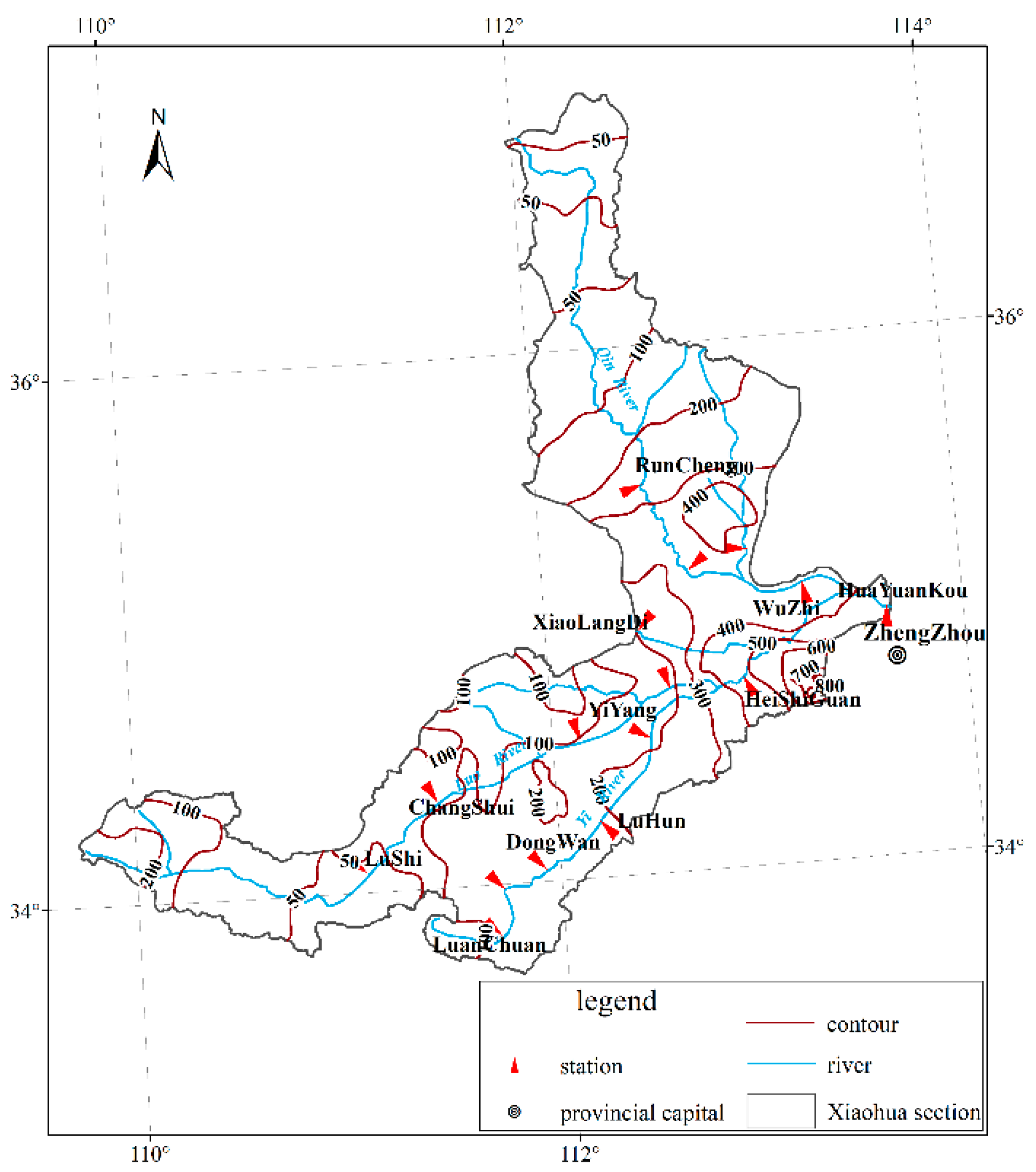
3.3. The Analysis of Rainfall Isogram
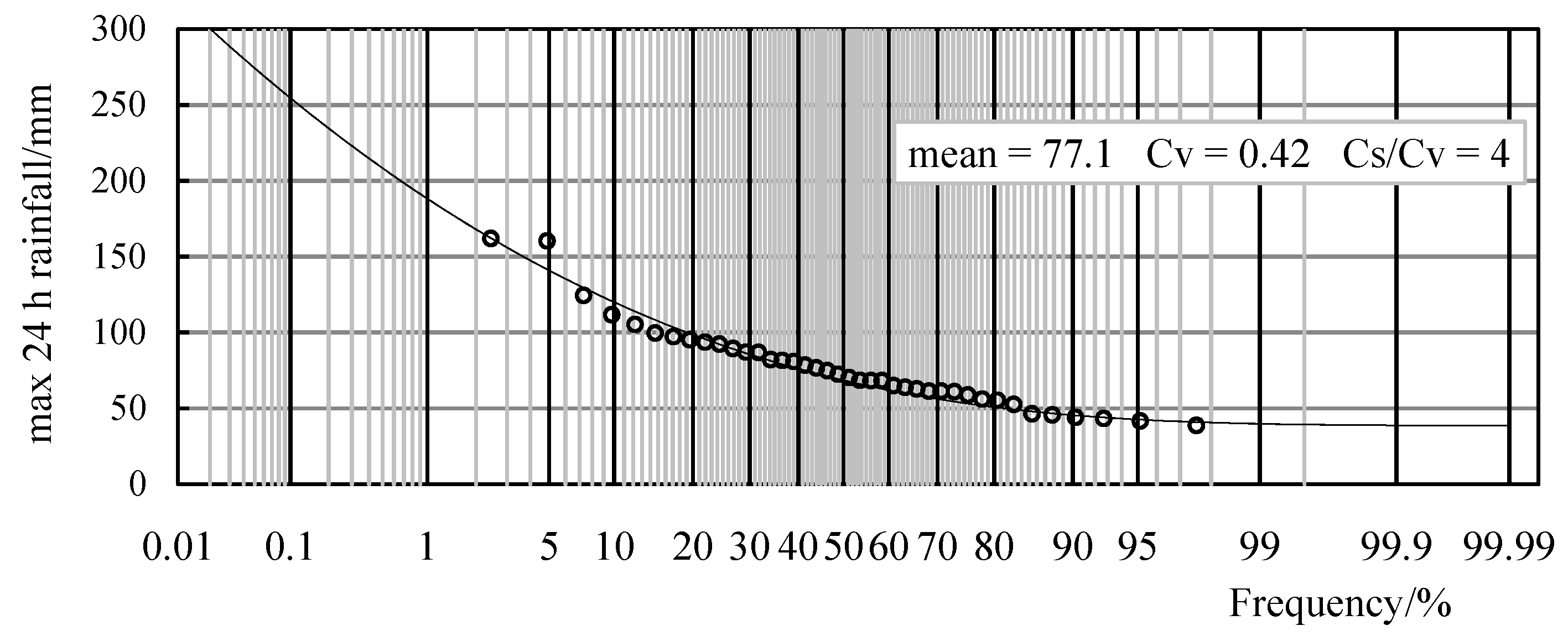
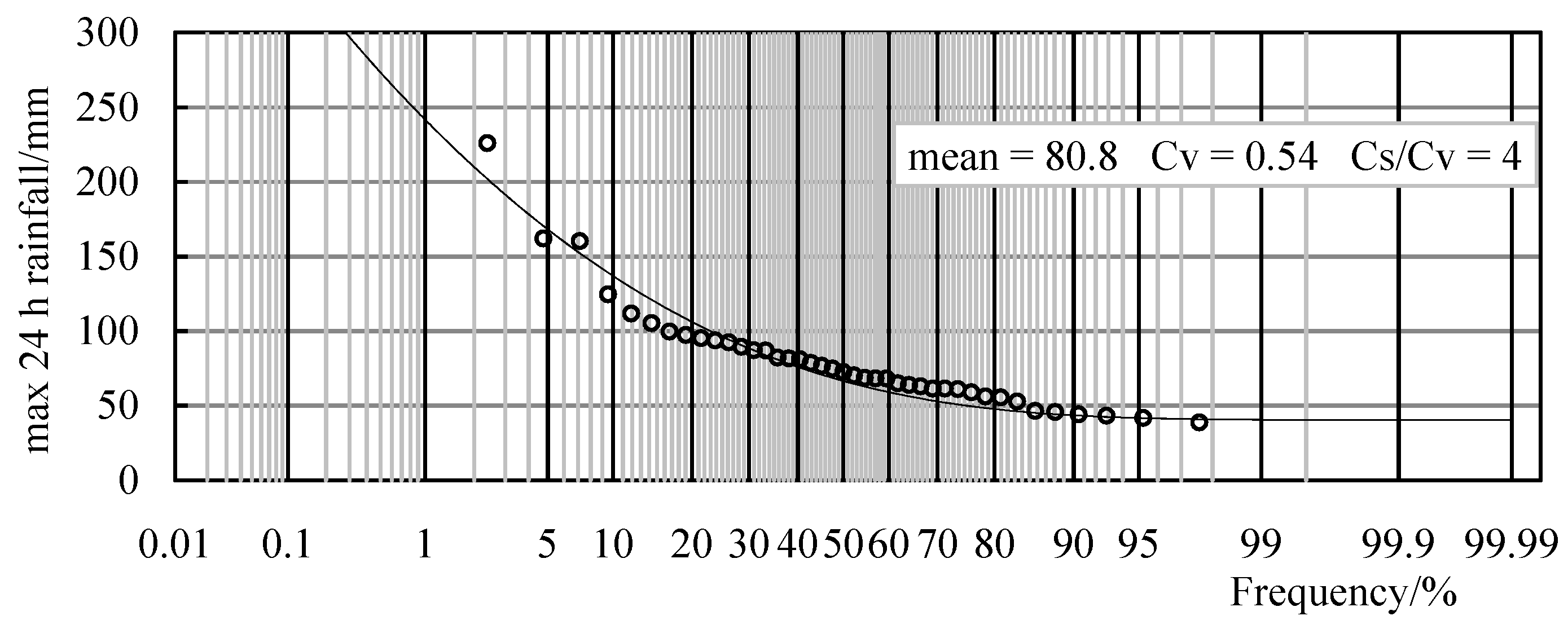
3.4. The Frequency Curve and Return Period
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfahl, S.; O’Gorman, P.A.; Fischer, E.M. Understanding the regional pattern of projected future changes in extreme precipitation. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.V.; Zhang, X.; Peterson, T.C.; Caesar, J.; Gleason, B.; Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Haylock, M.; Collins, D.; Trewin, B.; Rahimzadeh, F.; et al. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D05109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; He, R.M.; HU, Q.; Song, X. Discussion on the urban flood and waterlogging and causes analysis in China. Adv. Water Sci. 2016, 27, 485–491. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Climate Change Center of China Meteorological Administration. Blue Book on Climate Change in China in 2019; Climate Change Center of China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 21–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Disaster Investigation Team of the State Council. Investigation Report on “July 20” Heavy Rain Disaster in Zhengzhou, Henan Province, Jan.2022; Disaster Investigation Team of the State Council: Beijing, China, 2022. Available online: http://gxt.guizhou.gov.cn/ztzl/aqscyhdzl/jsjy/202202/t20220215_72553334.html (accessed on 23 June 2022). (In Chinese)
- Li, H.; Wang, X.M.; Zhu, F. Comprehensive Evaluations of Multi-Model Forecast Performance of “21·7” Henan Extreme Rainstorm. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences. Available online: https://doi.org/10.13878/j.cnki.dqkxxb.20211019002 (accessed on 1 January 2022). (In Chinese).
- Sun, J.S.; He, N.; Wang, G.; Chen, M.; Liao, X.; Wang, H. Preliminary analysis on synoptic configuration evolvement and mechanism of a torrential rain occurring in Beijing on 21 July 2012. Torr. Rain Disaster 2012, 31, 218–225. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.D. Investigation of Beijing extreme flooding event on 21 July 2012. J. Meteorol. 2012, 38, 1313–1329. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.Q.; Yu, P.L.; Huang, Q.T. Estimating 24-hour Rainfall Frequency for “2012.8” Flood in North-west Hubei Province. Flood Manag. Emerg. Response 2015, 25, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.X.; Chen, H.; Ren, M.F.; Cheng, T. Progress on disaster mechanism and risk assessment of urban flood/waterlogging disasters in China. Adv. Water Sci. 2020, 31, 713–724. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.X.; Ren, X.F.; Yang, X.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y. Rainstorm intensity formula and design rainstorm pattern for Jilin City. J. Arid. Metrol. 2021, 39, 151–158. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Guo, S.H.; Gong, J. Research on frequency curves and parameters of extreme storm. Water Power 2021, 47, 24–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, X. Analysis on Extremity and Characteristics of the 19 July 2016 Severe Torrential Rain in the North of Henan Province. Meteorol. Mon. 2018, 44, 1136–1147. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Manton, M.J.; Della-Marta, P.M.; Haylock, M.R.; Hennessy, K.J.; Nicholls, N.; Chambers, L.E.; Collins, D.A.; Daw, G.; Finet, A.; Gunawan, D. Trends in extreme daily rainfall and temperature in Southeast Asia and the South Pacific: 1961–1998. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellou, B.; Rahali, H. Assessment of the joint impact of extreme rainfall and storm surge on the risk of flooding in a coastal area. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Sang, Y.F. Precipitation complexity and its spatial difference in the Taihu Lake Basin, China. Entropy 2019, 21, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, Y.W.; Wang, Y.W.; Wang, Y.K.; Wang, D. Analysis of spatio-temporal distribution of rainstorms in the western region of Taihu Lake Basin. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 2020, 3, 43–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.Q.; Xu, Y.P.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, J.; Hu, Z.L. Change in return period of storm flood in plain river network area under urbanization-taking Wuchengxiyu region of Taihu Lake basin as a case study. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 27–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.L. Yellow River Conservancy Commission, MWR. Yellow River Flood-Prevention Dictionary; Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 1995. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Yang, X.L. Land use /cover change effects on floods with different return periods: A case study of Beijing, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.Y.; Gao, Y.J.; Xu, J.H. The impact of series length and maximum processing on the estimation of the rainfall return period. J. China Hydrol. 2019, 39, 26–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shiau, J.T. Return period of bivariate distributed extreme hydrological events. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk Assess. 2003, 17, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, E.; Fiori, A. Hydraulic structures subject to bivariate hydrological loads: Return period, design, and risk assessment. Water. Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglione, A.; Merz, R.; Josee, L.S.; Giinter, B. Flood frequency hydrology: 3. A Bayesian analysis. Water. Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 675–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.Y. The Principle and Method of Hydrology Statistics; China Industrial Press: Beijing, China, 1964. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.P.; Chen, Y.F. Hydrologic Statistics; China Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vyver, H. Spatial regression models for extreme rainfall in Belgium. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Tan, S.L.; Guan, S.; Wu, R.; Chen, J.C.; Liu, Z.F. Calculation of Multivariate Storm Frequency Based on Copula Functions. Pearl River 2016, 37, 20–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Salvadoril, G.; Michele, C. On the use of Copulas in hydrology: Theory and practice. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.G.; Zhu, C.F.; Jiang, Y.T.; Li, Z.J. Encounter analysis of flood and tide of Yongjiang River basin based on Copula function. Water Resour. Power 2018, 36, 24–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.L.; Guo, J.L.; Guo, J.; Dong, X.H.; Hu, R.; Peng, T.; Liu, J. Design rainstorm estimation of Ganjiang River Basin based on ensemble of multi- GCM. Yangtze River 2016, 37, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Li, C.F.; Liu, Z.L. Risk probability analysis of design storm combination of urban pipe drainage and river drainage. Eng. J. Wuhan Univ. 2012, 45, 171–176. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, J. Revision of Extreme Precipitation Frequency Estimation Based on Annual Maximum Series. J. China Hydrol. 2019, 39, 7–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wright, D.B.; Smith, J.A.; Villarini, G.; Baeck, M.L. Long-term high-resolution radar rainfall fields for urban hydrology. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 713–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tian, F.; Smith, J.A.; Hu, H. Urban signatures in the spatial clustering of summer heavy rainfall events over the Beijing metropolitan region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Smith, J.A.; Wright, D.B.; Baeck, M.L.; Yang, L.; Liu, S. Storm catalog-based analysis of rainfall heterogeneity and frequency in a complex terrain. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 1871–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Z.; Liu, S.G.; Wright, D.B. Analysis of urban de-sign storm based on stochastic storm transposition. Adv. Water Sci. 2020, 31, 583–591. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.H.; Xu, W.Z.; Li, Q.F.; Zhou, Z. Study on long duration comprehensive rainstorm formula based on rainstorm attenuation characteristics in Shanghai. Adv. Water Sci. 2021, 32, 211–217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lima, C.H.R.; Kwon, H.H.; Kim, J.Y. A Bayesian beta distribution model for estimating rainfall IDF curves in a changing climate. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabul, A.M.; Elshorbagy, A. Quantification of the climate change induced variations in intensity- duration-frequency curves in the Canadian Prairies. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 990–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.Y.; Aghakouchak, A. Nonstationary precipitation intensity-duration-frequency curves for infrastructure design in a changing climate. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.J.; Hu, Y.M.; Kong, J.H.; Lv, L.Y.; Xi, L. Reviewing the predictability of extraordinary rainstorm in Henan in July 2021 and the metrological services for decision making. Metrol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 45, 38–51. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.M.; Xu, J.; Xu, G.Q.; Wang, Y.D.; Dai, K.; Gong, X. Thinking of extreme rainstorms from the August 1975 event to the July 2021 event. Metrol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 45, 1–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.J.; Jin, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, G.F. Analysis of impact characteristics and suggestions on disaster reduction for “7.20” extreme rainstorm disasters in Henan Province, 2021. China Flood Drought Manag. 2022, 32, 31–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.X.; Ren, M.F.; Cheng, T.; Chen, H. Managing urban floods: The urban water cycle is the foundation, the unified man-agement of river basins is the fundamental. China Flood Drought Manag. 2020, 30, 20–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Li, Z.; Yao, C.; Li, Q.; Yan, M. Spatial combination modeling framework of saturation-excess and infiltration-excess runoff for semi-humid watersheds. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 5173984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrology Bureau of Water Resources Ministry. Hydrology Year Book of Yellow River Basin, 1960–2020; Hydrology Bureau of Water Resources Ministry: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese)
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.C.; Guo, H.J.; Zhang, M.B.; Guo, Y.B.; Xu, G.H.; Wang, Z.X.; Jiang, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, D.L.; et al. Regulation for Calculating Design Flood of Water Resources and Hydropower Projects; China Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, D.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, Y.F. Engineering Hydrology; China Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.L.; Ye, S.Z. The empirical frequency formula in hydrologic calculation. J. Wuhan Inst. Water Conserv. Electr. Power 1992, 25, 38–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| No. | Station | Date | Rainfall | No. | Station | Date | Rainfall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fenggou | 20 July | 454.5 | 11 | Heluozhen | 20 July | 326 |
| 2 | Liuhe | 20 July | 429 | 12 | Xinzhong | 19 July | 322 |
| 3 | Duanhecun | 20 July | 424.5 | 13 | Shidonggou | 20 July | 316 |
| 4 | Huancuiyu | 20 July | 396.5 | 14 | Honghe | 19 July | 312.5 |
| 5 | Huancuiyu | 19 July | 390.5 | 15 | Zhulin | 20 July | 309 |
| 6 | Hegou | 20 July | 386 | 16 | Gongchuan | 19 July | 309 |
| 7 | Xiaoguan | 19 July | 366 | 17 | Gaoshan | 20 July | 308 |
| 8 | Xinzhong | 20 July | 362.5 | 18 | Zhulin | 19 July | 304.5 |
| 9 | Llijiaguan | 19 July | 360.4 | 19 | Shennan | 20 July | 298 |
| 10 | Xiayu | 19 July | 341.5 | 20 | Liangshuiquan | 19 July | 295 |
| Section | Covered Area under Different Rainfall | Area/km2 | Mean Rainfall/mm | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~100 | 100~200 | 200~300 | 300~400 | 400~500 | 500~600 | 600~700 | 700~800 | 800~860 | |||
| Upper Baimasi | 7276 | 3964 | 629 | 21.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11,891 | 102.6 |
| Upper Longmenzhen | 796 | 3264 | 1100 | 149 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5318 | 165.3 |
| B, L~Heishiguan | 0 | 221 | 436 | 372 | 315 | 33.0 | 5.2 | 1.7 | 0 | 1384 | 315.7 |
| Upper Runcheng | 5272 | 1580 | 406 | 13.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7273 | 88.4 |
| R~Wulongkou | 14 | 499 | 706 | 659 | 94.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1972 | 266.4 |
| Upper Shanluping | 10 | 631 | 1619 | 439 | 350 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3049 | 266.1 |
| W, S~Wuzhi | 0 | 0 | 48.1 | 412 | 119 | 7.83 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 586 | 364.7 |
| Xiaohua main stream | 0 | 157 | 778.3 | 1603 | 1065 | 391 | 205 | 119 | 23 | 4342 | 395.1 |
| Xiaohua Section | 13,368 | 10,317 | 5724 | 3669 | 1950 | 434 | 211 | 121 | 23 | 35,815 | 180.9 |
| No. | Station | Series/a | Parameters | Max/mm | Frequency/% | Return Period/a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean/mm | Cv | Cs/Cv | ||||||
| 1 | Xiaoguan | 34 | 96.2 | 0.51 | 3.5 | 228.5 | 0.057 | 1754 |
| 35 | 104.8 | 0.65 | 3.5 | 397.4 | 0.602 | 166 | ||
| 2 | Sishui | 38 | 84.0 | 0.41 | 3 | 139.8 | 0.009 | 11,123 |
| 39 | 89.8 | 0.52 | 3 | 309.8 | 0.2056 | 486 | ||
| 3 | Mangling | 32 | 67.8 | 0.42 | 5 | 143.7 | 0.00113 | 88,730 |
| 33 | 77.1 | 0.85 | 5 | 372.8 | 0.951 | 105 | ||
| 4 | Jiulongjioa | 40 | 72.4 | 0.45 | 4 | 161.4 | 0.01174 | 8515 |
| 41 | 78.4 | 0.62 | 4 | 320.4 | 0.03733 | 268 | ||
| 5 | Guangwu | 30 | 76.5 | 0.53 | 4 | 205.5 | 0.1097 | 911 |
| 31 | 84.3 | 0.78 | 4 | 318.6 | 1.4908 | 67 | ||
| 6 | Wulongmiao | 40 | 77.1 | 0.42 | 4 | 162 | 0.2738 | 365 |
| 41 | 80.8 | 0.54 | 4 | 225.8 | 1.409 | 71 | ||
| 7 | Minggao | 47 | 77.3 | 0.47 | 4 | 172.4 | 0.0077 | 13,004 |
| 48 | 83.5 | 0.66 | 4 | 374.8 | 0.320 | 313 | ||
| 8 | Lijiaguan | 40 | 98.6 | 0.55 | 3 | 232 | 0.1285 | 778 |
| 41 | 105.5 | 0.64 | 3 | 381.6 | 0.582 | 172 | ||
| 9 | Dongdi | 38 | 84.9 | 0.56 | 3.5 | 209.3 | 2.246 | 45 |
| 39 | 88.3 | 0.59 | 3.5 | 217.4 | 3.127 | 32 | ||
| 10 | Xicun | 38 | 70.2 | 0.42 | 4 | 128.5 | - | - |
| 39 | 80.3 | 0.85 | 4 | 465.6 | 0.37 | 270 | ||
| No. | Station | Series/a | Parameters | max/mm | Frequency/% | Return Period/a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean/mm | Cv | Cs/Cv | ||||||
| 1 | Xiaoguan | 34 | 64.2 | 0.52 | 4 | 171 | 6.17 | 16 |
| 35 | 65.9 | 0.55 | 4 | 171 | 7.41 | 13 | ||
| 2 | Sishui | 38 | 63.5 | 0.45 | 3 | 113.6 | 2.19 | 46 |
| 39 | 65.5 | 0.44 | 3 | 138.2 | 2.41 | 41 | ||
| 3 | Mangling | 32 | 47.1 | 0.45 | 5 | 94.2 | 0.151 | 662 |
| 33 | 50.8 | 0.56 | 5 | 169.6 | 0.85 | 118 | ||
| 4 | Jiulongjioa | 40 | 54.1 | 0.51 | 4 | 122.8 | 1.79 | 56 |
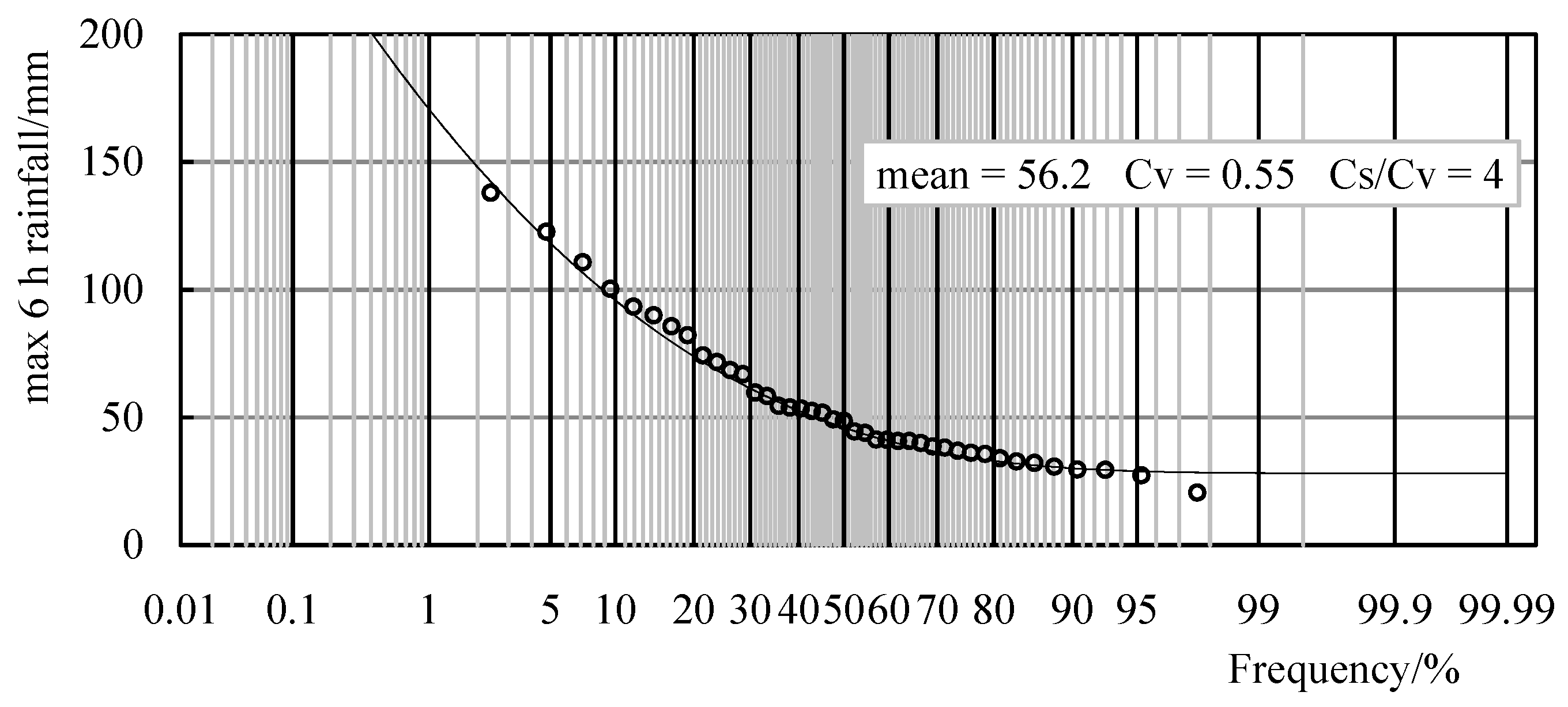
| 41 | 56.2 | 0.55 | 4 | 138 | 2.71 | 37 | ||
| 5 | Guangwu | 30 | 60.6 | 0.67 | 4 | 200.2 | 3.63 | 28 |
| 31 | 63.7 | 0.78 | 4 | 157.4 | 5.47 | 18 | ||
| 6 | Wulongmioa | 40 | 49.8 | 0.32 | 4 | 83.1 | 0.122 | 820 |
| 41 | 51.7 | 0.42 | 4 | 126 | 1.01 | 99 | ||
| 7 | Minggao | 47 | 52.6 | 0.56 | 4 | 140.5 | 0.0353 | 2937 |
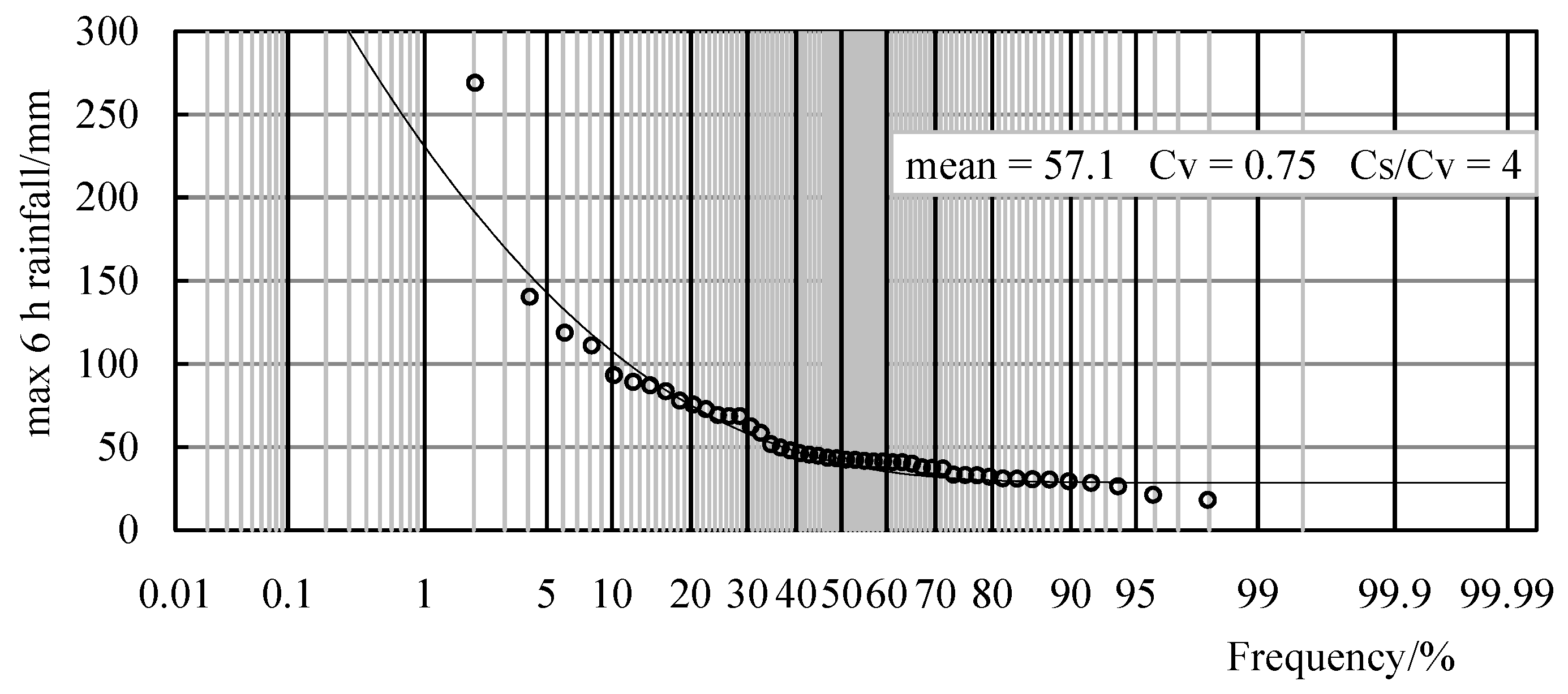
| 48 | 57.1 | 0.75 | 4 | 269.2 | 0.506 | 198 | ||
| 8 | Lijiaguan | 40 | 65.2 | 0.49 | 3 | 135.4 | 4.49 | 22 |
| 41 | 66.8 | 0.5 | 3 | 130.4 | 5.27 | 19 | ||
| 9 | Dongdi | 38 | 57.1 | 0.66 | 3.5 | 207.5 | 3.77 | 27 |
| 39 | 59.4 | 0.76 | 3.5 | 144.4 | 5.59 | 18 | ||
| 10 | Xicun | 38 | 52.1 | 0.45 | 4 | 94.8 | 0.0113 | 8850 |
| 39 | 56.7 | 0.62 | 4 | 231.4 | 0.375 | 267 | ||
| No. | River | Station | Max 24 h (>300 mm) | Max 6 h (>100 mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall/mm | Return Period/a | Rainfall/mm | Return Period/a | |||
| 1 | Yiluo River | Huancuiyu | 643.5 | 4424 | 257.5 | 440 |
| 2 | Yiluo River | Liuhe | 572.5 | 1725 | 247.5 | 340 |
| 3 | Yiluo River | Duanhecun | 539 | 1105 | 232.5 | 231 |
| 4 | Yiluo River | Xinzhong | 536 | 1062 | 216.5 | 153 |
| 5 | Yiluo River | Fenggou | 533 | 1020 | 246 | 327 |
| 6 | Yiluo River | Hegou | 476.5 | 480 | 233.5 | 237 |
| 7 | Yiluo River | Zhulin | 476 | 4051 | 181 | 137 |
| 8 | Yiluo River | Xicun | 465.6 | 270 | 231.4 | 267 |
| 9 | Yiluo River | Heluozhen | 440 | 295 | 234.5 | 243 |
| 10 | Yiluo River | Gongchuan | 433 | 1922 | 173.5 | 109 |
| 11 | Yiluo River | Tiejianglu | 428.5 | 253 | 166.5 | 42 |
| 12 | Yiluo River | Zhangyao | 417.5 | 157 | 195 | 239 |
| 13 | Yiluo River | Shanhua | 413 | 151 | 196.5 | 249 |
| 14 | Yiluo River | Xiayu | 412.5 | 204 | 134.5 | 18 |
| 15 | Yiluo River | Liangshuiquan | 408.5 | 194 | 162 | 37 |
| 16 | Yiluo River | Changzhuang | 408.5 | 194 | 168.5 | 44 |
| 17 | Yellow River | Xiaoguan | 397.4 | 166 | 123.8 | 13 |
| 18 | Yiluo River | Shennan | 396 | 164 | 227 | 201 |
| 19 | Yiluo River | Honghe | 394.5 | 160 | 132 | 17 |
| 20 | Yiluo River | Nanhedu | 383.5 | 138 | 215.5 | 149 |
| 21 | Yiluo River | Lijiaguan | 381.6 | 172 | 130.4 | 19 |
| 22 | Yiluo River | Shidonggou | 377.5 | 128 | 173.5 | 50 |
| 23 | Yiluo River | Minggao | 374.8 | 313 | 269.2 | 198 |
| 24 | Yiluo River | Heishiguan | 374.4 | 107 | 172.6 | 128 |
| 25 | Yellow River | Mangling | 372.8 | 105 | 169.6 | 118 |
| 26 | Yiluo River | Jiuhouxiang | 362.5 | 260 | 257 | 160 |
| 27 | Yiluo River | Shanchuan | 360 | 101 | 149 | 27 |
| 28 | Yiluo River | Zhaogou | 357.5 | 92 | 171.5 | 125 |
| 29 | Yiluo River | Hetaoyuan | 353.5 | 92 | 119 | 12 |
| 30 | Yellow River | Gaoshan | 353.5 | 92 | 154.5 | 31 |
| 31 | Yiluo River | Zhanjie | 352.5 | 91 | 181 | 61 |
| 32 | Yiluo River | Didong | 335.5 | 350 | 159 | 70 |
| 33 | Yiluo River | Wuluo | 333.5 | 71 | 159 | 35 |
| 34 | Yiluo River | Mihezhen | 333.5 | 71 | 134.5 | 18 |
| 35 | Yiluo River | Wanggou | 332 | 73 | 145 | 59 |
| 36 | Yiluo River | Guandimiao | 331 | 323 | 146.5 | 48 |
| 37 | Yiluo River | Jiulongjiao | 320.4 | 268 | 138 | 37 |
| 38 | Yellow River | Guangwu | 318.6 | 67 | 157.4 | 18 |
| 39 | Yiluo River | Fangluo | 316 | 66 | 127.5 | 12 |
| 40 | Yiluo River | Jiajinkou | 315.5 | 55 | 140.5 | 22 |
| 41 | Yiluo River | Shecun | 315 | 55 | 112.5 | 11 |
| 42 | Yiluo River | Sishui | 309.8 | 486 | 138.2 | 41 |
| 43 | Yiluo River | Lifeng | - | - | 199 | 57 |
| 44 | Yiluo River | Baiyu | - | - | 186.5 | 162 |
| 45 | Qin River | Dongdi | - | - | 144.4 | 18 |
| 46 | Yiluo River | Wulongmiao | - | - | 126 | 99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, S.; Guo, S.; Huo, W. Analysis on the Return Period of “7.20” Rainstorm in the Xiaohua Section of the Yellow River in 2021. Water 2022, 14, 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152444
Jin S, Guo S, Huo W. Analysis on the Return Period of “7.20” Rainstorm in the Xiaohua Section of the Yellow River in 2021. Water. 2022; 14(15):2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152444
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Shuangyan, Shaomeng Guo, and Wenbo Huo. 2022. "Analysis on the Return Period of “7.20” Rainstorm in the Xiaohua Section of the Yellow River in 2021" Water 14, no. 15: 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152444
APA StyleJin, S., Guo, S., & Huo, W. (2022). Analysis on the Return Period of “7.20” Rainstorm in the Xiaohua Section of the Yellow River in 2021. Water, 14(15), 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152444





