Evaluation of TIGGE Precipitation Forecast and Its Applicability in Streamflow Predictions over a Mountain River Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
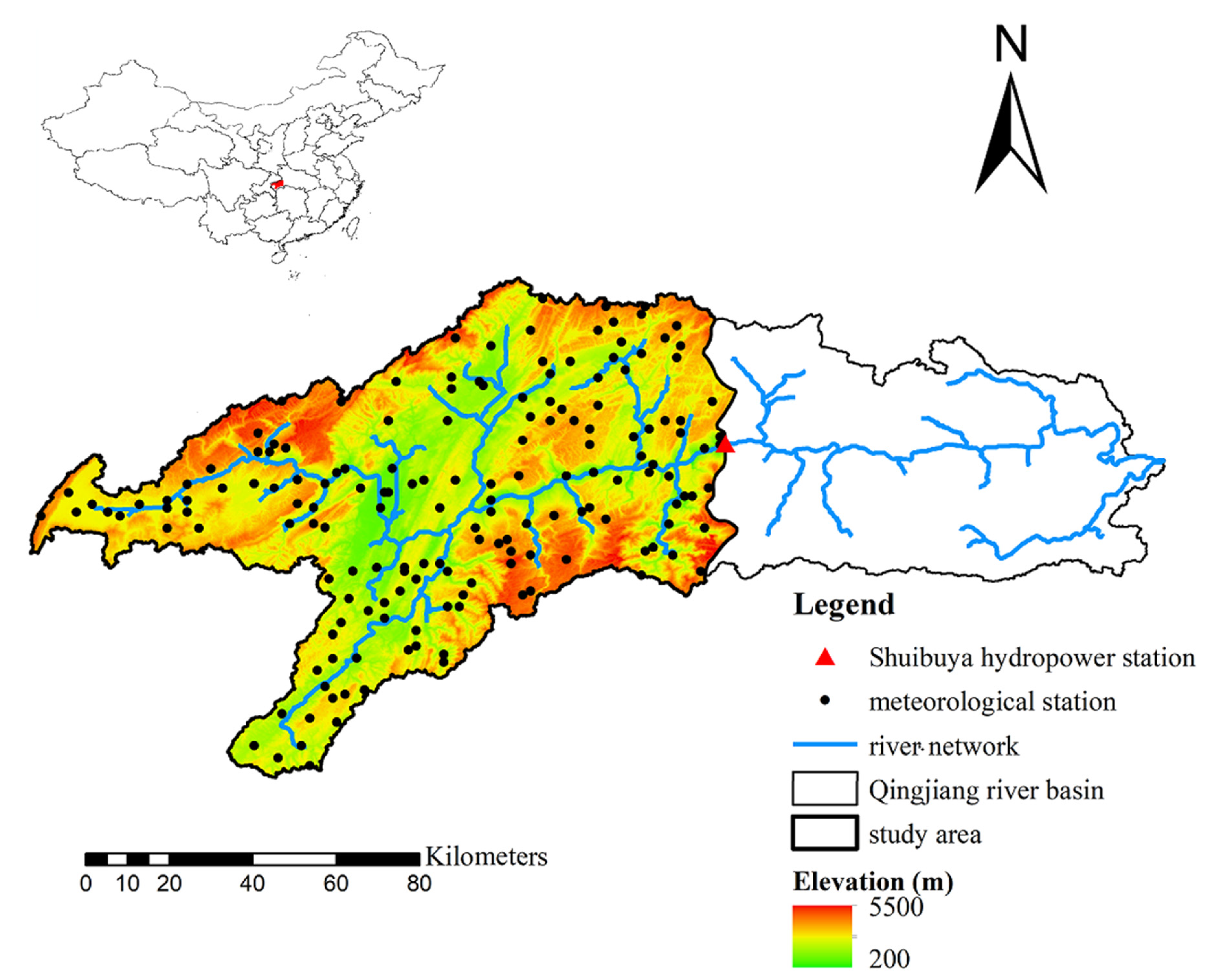
2. Study Area and Datasets
3. Methodology
3.1. Postprocessing Methods
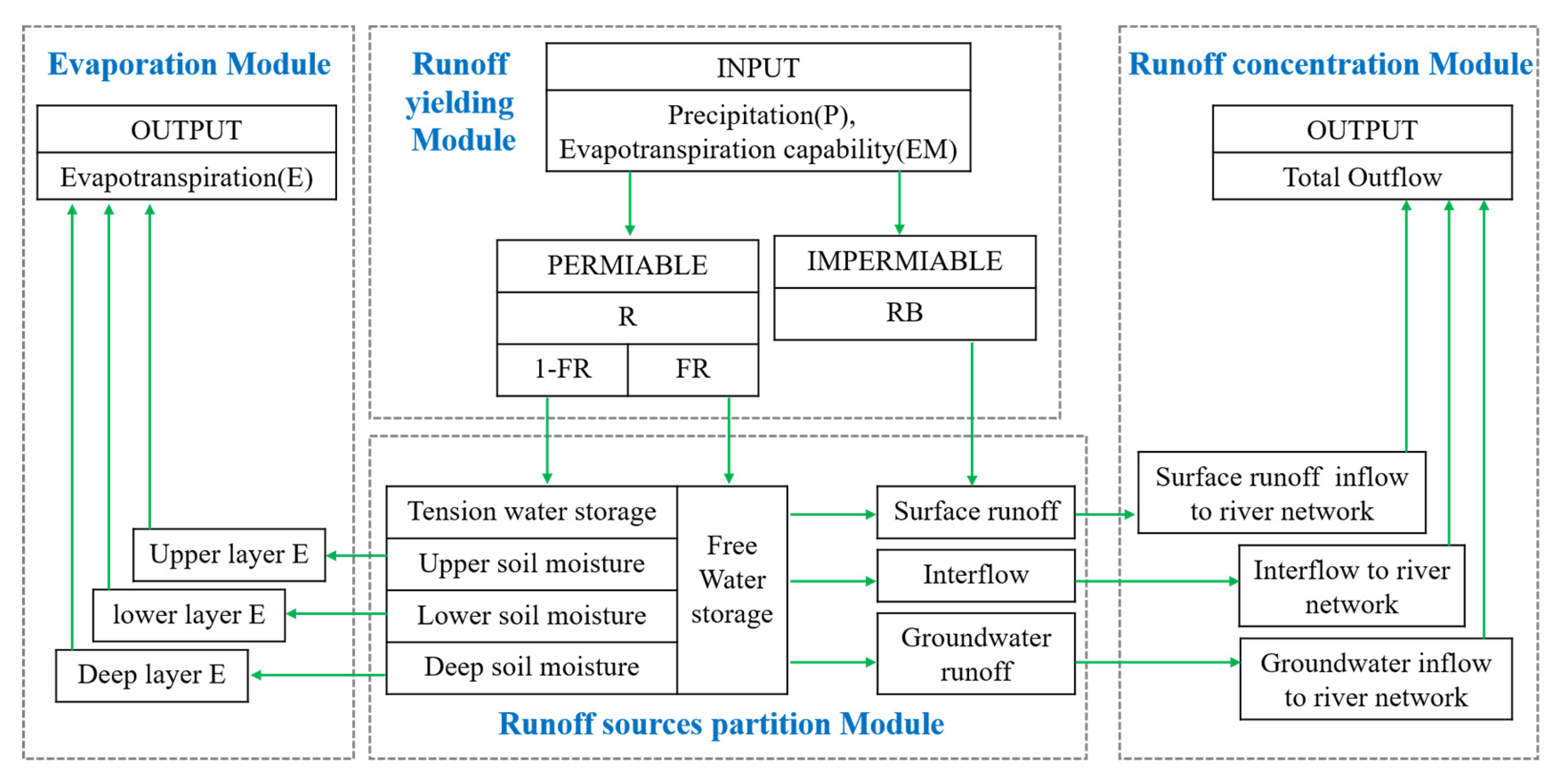
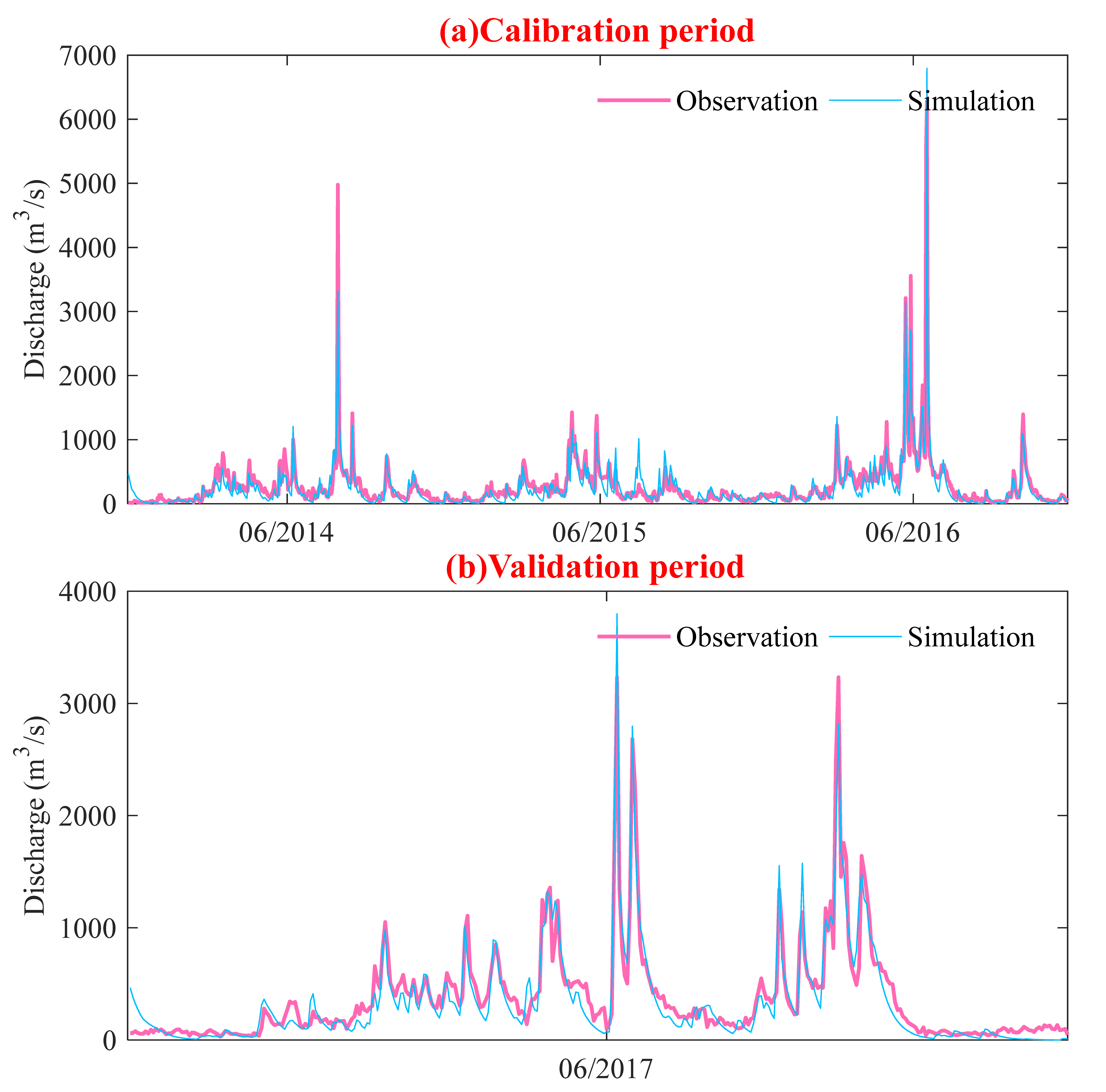
3.2. Hydrological Model
3.3. Verification Metrics
4. Results and Discussion
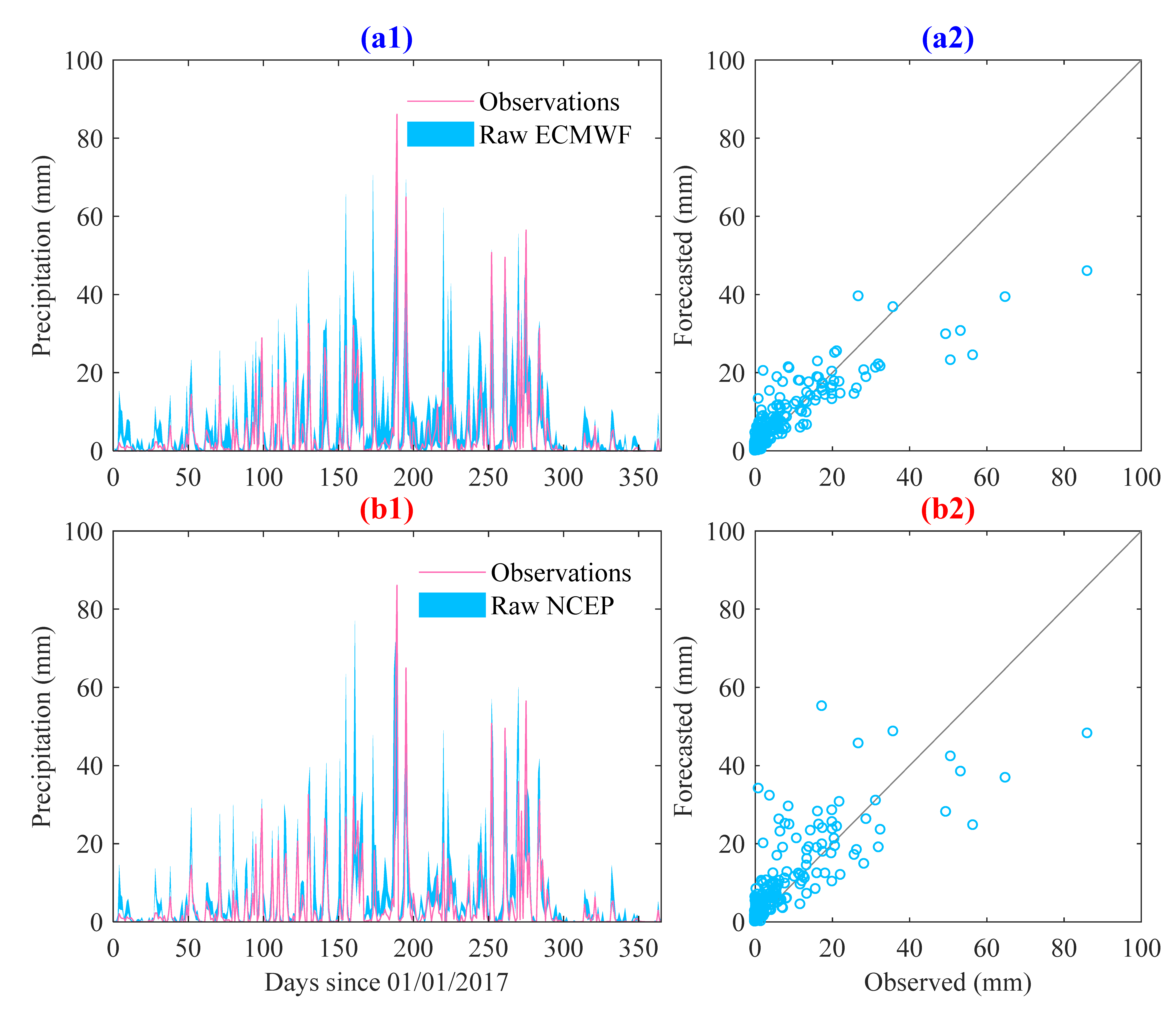
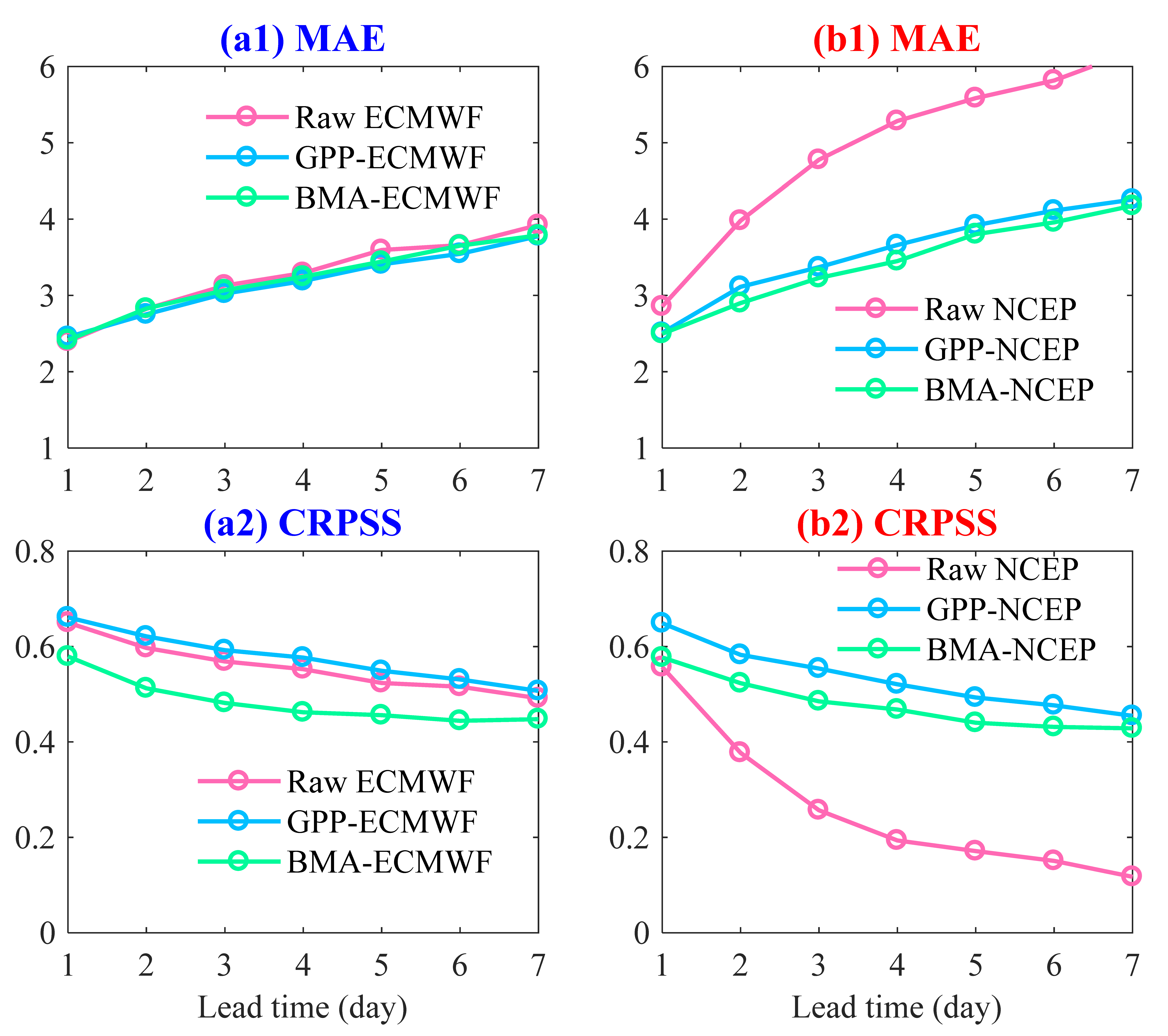
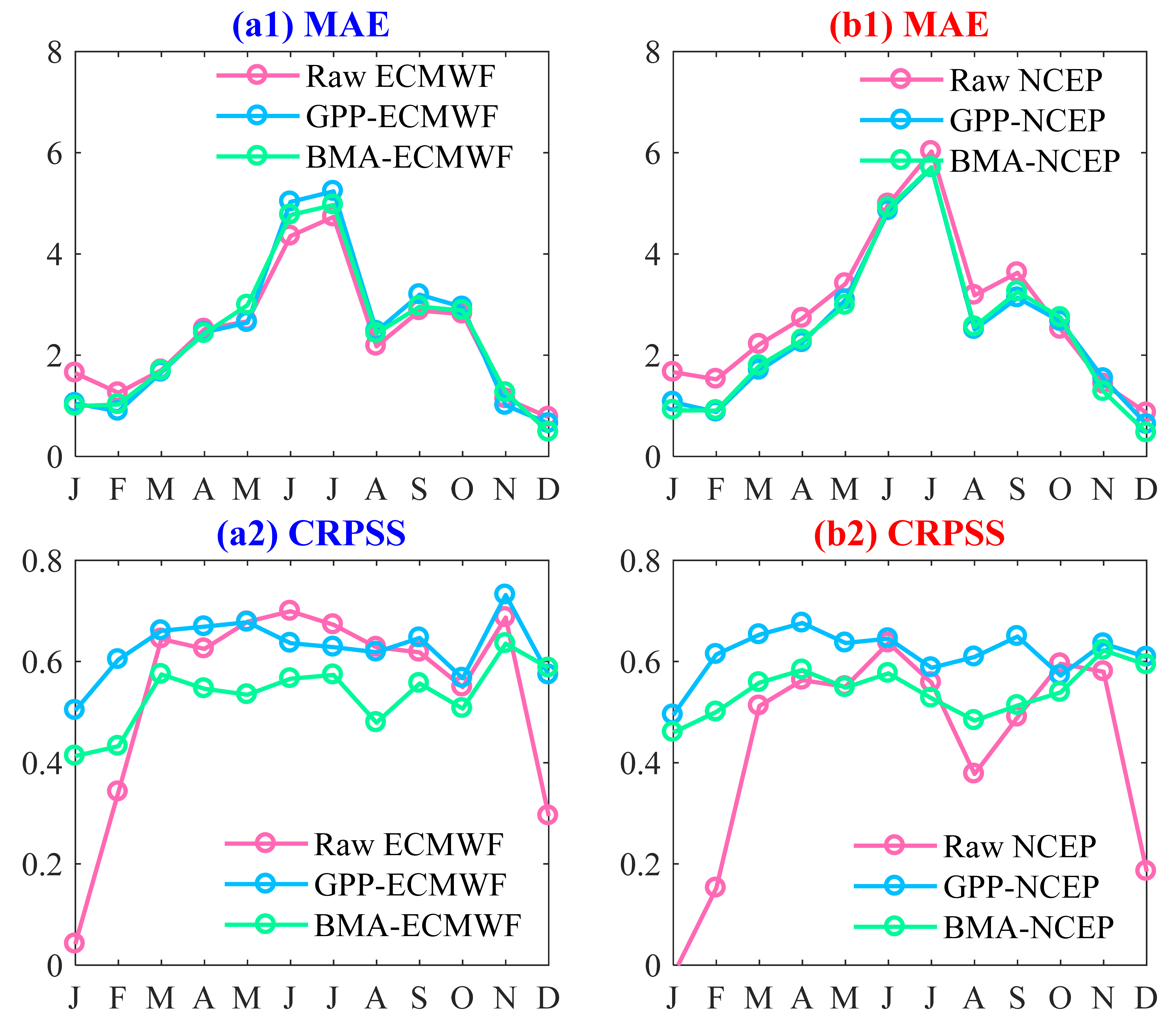
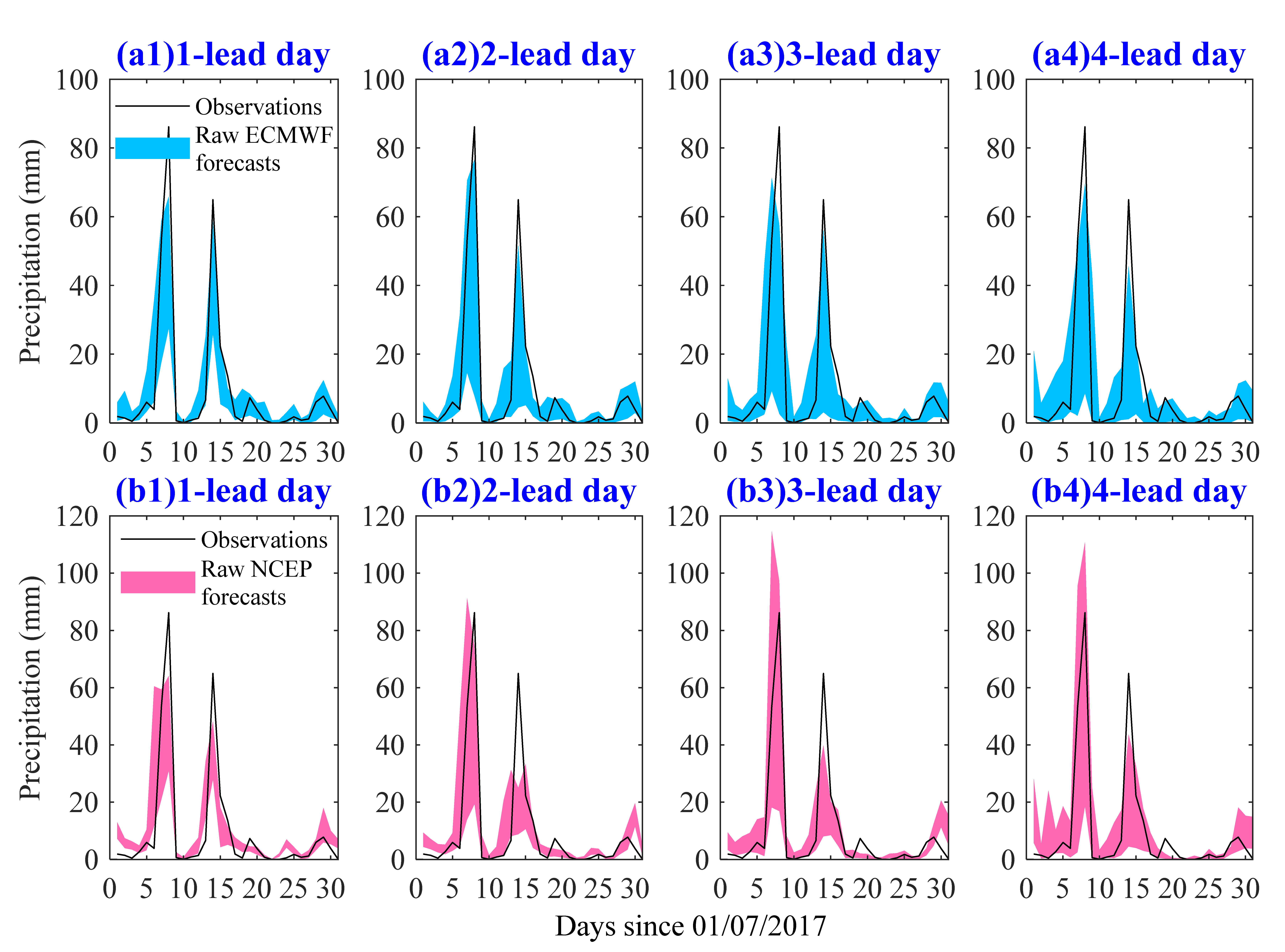
4.1. Performance of the Ensemble Precipitation Forecasts
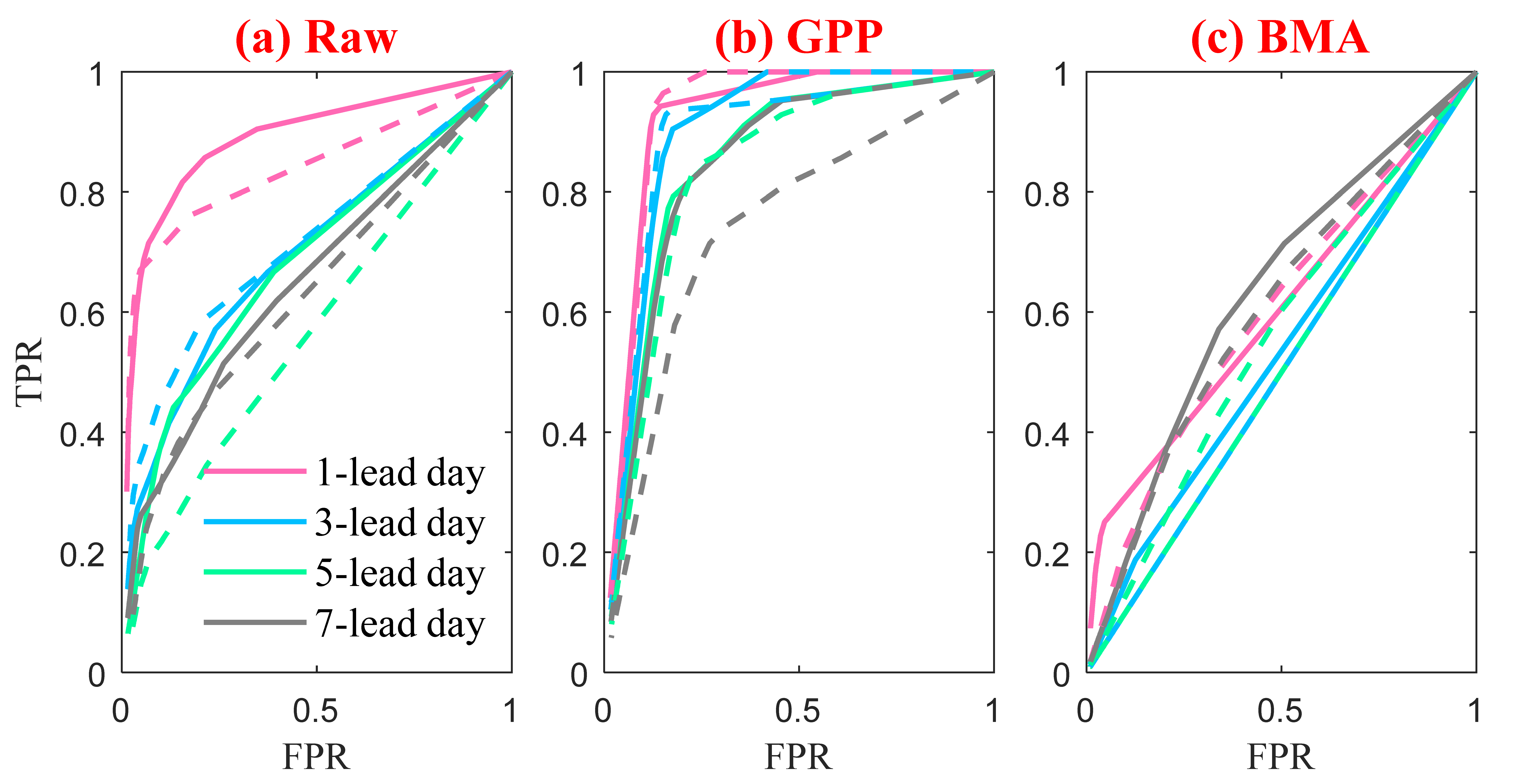
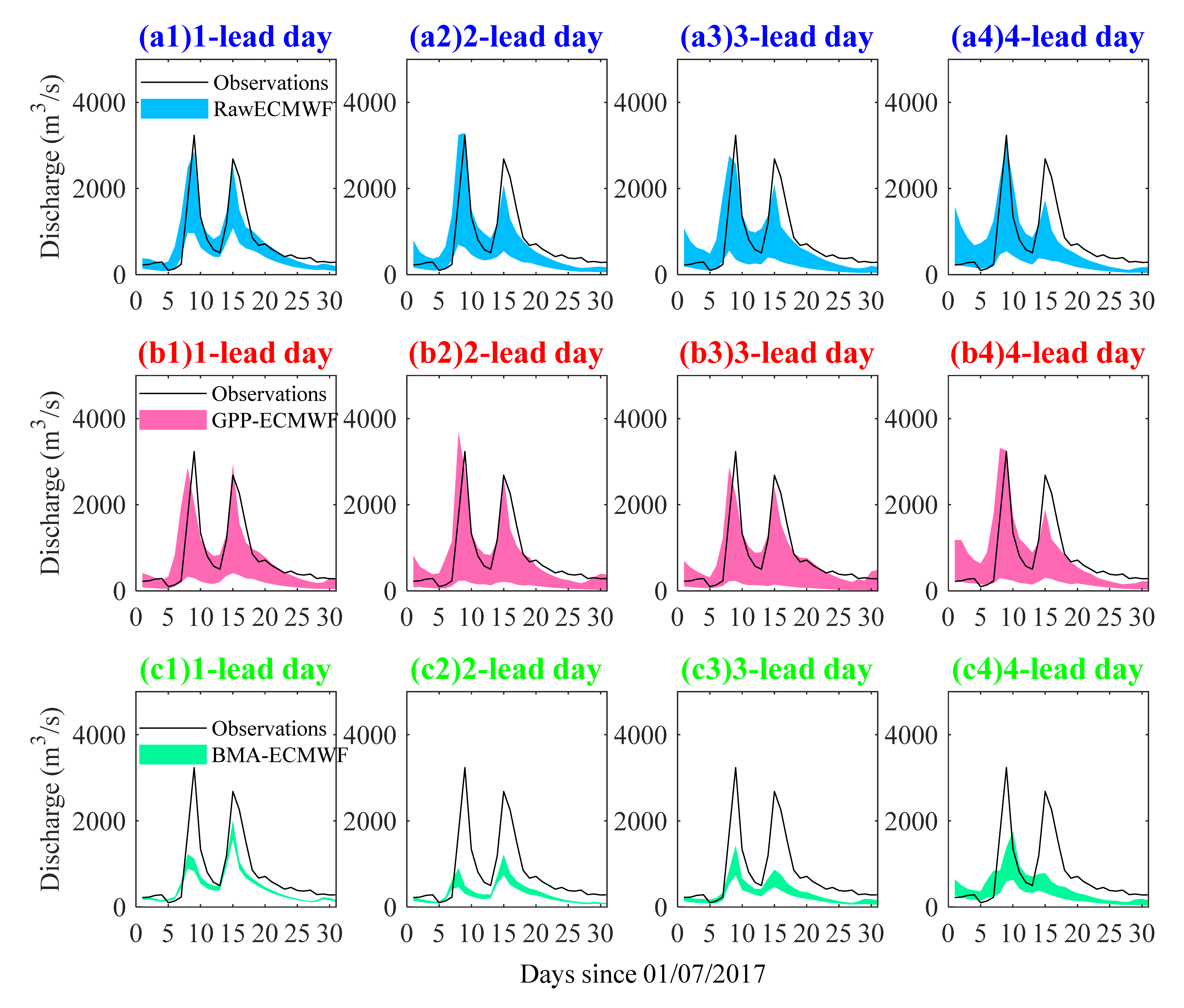
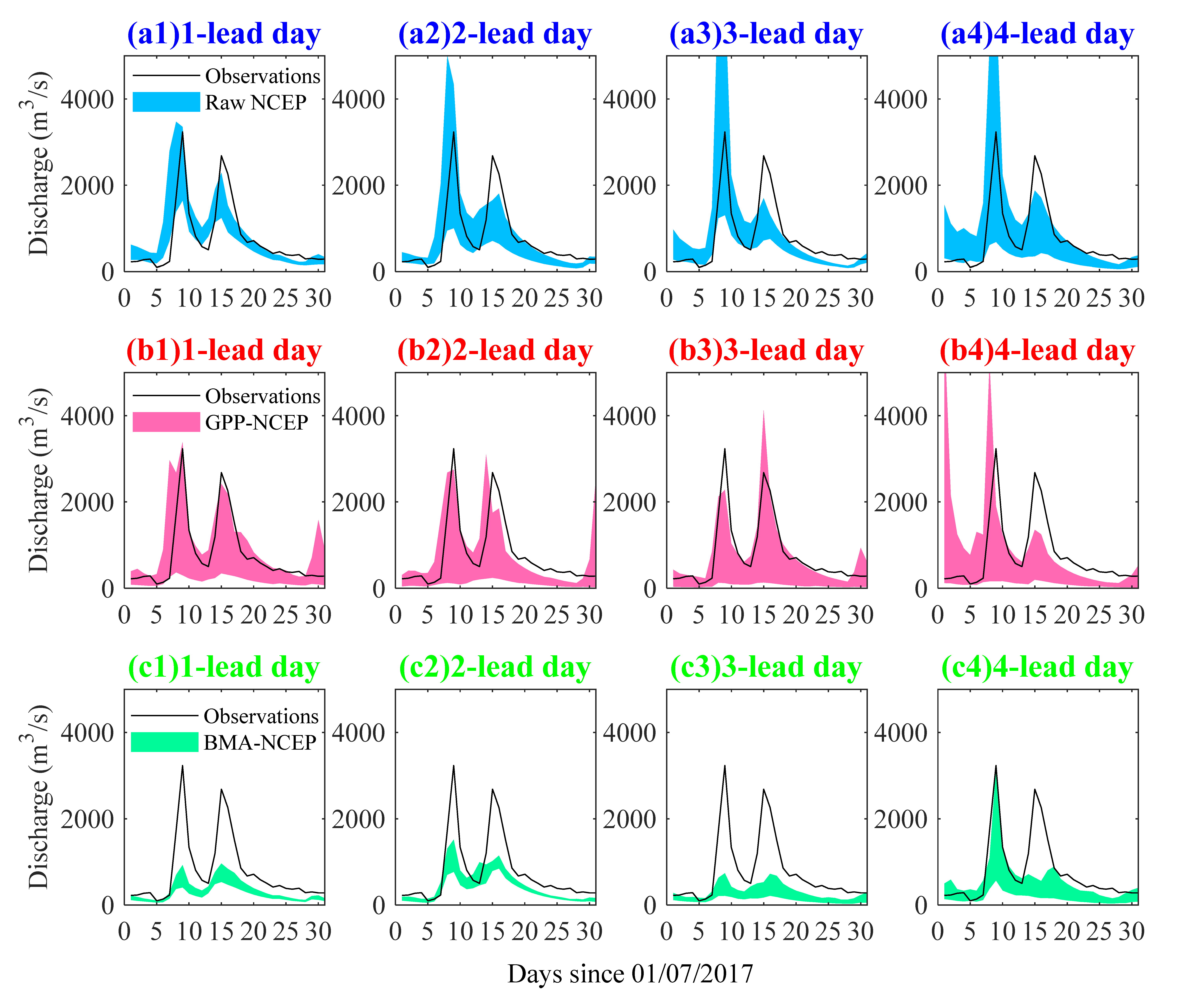
4.2. Performance of the Ensemble Streamflow Forecasts
5. Conclusions
- Raw ECMWF shows a better performance in EPF than raw NCEP in terms of lower MAE and higher CRPSS at all 7 lead days. Raw ECMWF also shows a better performance in ESP with high skill for 1~3 lead days, and both magnitudes and peak occurrence time of peak events were captured better.
- The GPP method performs better than BMA in improving both EPF and ESP performances, and the improvements are more significant for the NCEP with worse raw performances.
- Both ECMWF and NCEP have good potential for both EPF and ESP. By using the GPP method, MAE values are lower than 4.2 and CRPSS values are higher than 0.43 for both ECMWF and NCEP EPFs at all 7 lead days. The GPP-ECMWF ESP is highly skillful for 1~5 lead days and the GPP-NCEP ESP is, on average, moderately skillful for 1~7 lead days. In addition, the skillful forecast lead time can be 3 days/2 days for GPP-ECMWF/GPP-NCEP flood predications, with absolute differences in magnitude of less than 15% for peak events.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roulin, E. Skill and Relative Economic Value of Medium-Range Hydrological Ensemble Predictions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukla, S.; Voisin, N.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Value of Medium Range Weather Forecasts in the Improvement of Seasonal Hydrologic Prediction Skill. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2825–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.-P.; Tung, Y.-K. Decision-Making In Water Management Under Uncertainty. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Wetterhall, F.; Haiden, T.; Richardson, D.; Salamon, P. Evaluation of Ensemble Streamflow Predictions in Europe. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, Y.; Duan, Q.; Ye, A.; Gong, W.; Di, Z.; Xiao, M.; Hsu, K. An Evaluation Of Post-Processed TIGGE Multimodel Ensemble Precipitation Forecast in the Huai River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2890–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swinbank, R.; Kyouda, M.; Buchanan, P.; Froude, L.; Hamill, T.M.; Hewson, T.D.; Keller, J.H.; Matsueda, M.; Methven, J.; Yamaguchi, M.; et al. The TIGGE Project and Its Achievements. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidle, F.; Wang, Y.; Smet, G. On the Impact of the Choice of Global Ensemble in Forcing a Regional Ensemble System. Weather. Forecast. 2016, 31, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titley, H.A.; Bowyer, R.L.; Cloke, H.L. A Global Evaluation Of Multi-Model Ensemble Tropical Cyclone Track Probability Forecasts. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Zhang, X.; Pappenberger, F.; Zhang, T.; Fang, Y. Multi-Model Grand Ensemble Hydrologic Forecasting in the Fu River Basin Using Bayesian Model Averaging. Water 2017, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, H.L.; Pappenberger, F. Ensemble Flood Forecasting: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wetterhall, F.; Cloke, H.L.; Pappenberger, F.; Wilson, M.; Freer, J.; McGregor, G. Tracking the Uncertainty in Flood Alerts Driven by Grand Ensemble Weather Predictions. Meteorol. Appl. A J. Forecast. Pract. Appl. Train. Tech. Model. 2009, 16, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertotti, L.; Bidlot, J.R.; Buizza, R.; Cavaleri, L.; Janousek, M. Deterministic and Ensemble-Based Prediction of Adriatic Sea Sirocco Storms Leading to ‘Acqua Alta’in Venice. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 1446–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagedorn, R.; Hamill, T.M.; Whitaker, J.S. Probabilistic Forecast Calibration Using ECMWF and GFS Ensemble Reforecasts. Part I: Two-Meter Temperatures. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2008, 136, 2608–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuerer, M.; Hamill, T.M. Statistical Postprocessing of Ensemble Precipitation Forecasts by Fitting Censored, Shifted Gamma Distributions. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2015, 143, 4578–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, T.; Reinhardt, J.; Flörke, M.; Van Griensven, A.; Hattermann, F.; Huang, S.; Koch, H.; Pechlivanidis, I.G.; Plötner, S.; Seidou, O.; et al. Evaluation of Sources of Uncertainty in Projected Hydrological Changes Under Climate Change in 12 Large-Scale River Basins. Clim. Chang. 2017, 141, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Comparison of Ensemble-MOS Methods in the Lorenz’96 Aetting. Meteorol. Appl. 2006, 13, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Balabdaoui, F.; Polakowski, M. Using Bayesian Model Averaging to Calibrate Forecast Ensembles. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2005, 133, 1155–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roulin, E.; Vannitsem, S. Postprocessing of Ensemble Precipitation Predictions with Extended Logistic Regression Based on Hindcasts. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2012, 140, 874–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Li, Z. Postprocessing of Ensemble Weather Forecasts Using a Stochastic Weather Generator. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2014, 142, 1106–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönquist, P.; Yao, C.; Ben-Nun, T.; Dryden, N.; Dueben, P.; Li, S.; Hoefler, T. Deep Learning For Post-Processing Ensemble Weather Forecasts. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20200092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, Q.J.; Wu, W.; Yang, Q. Extending a Joint Probability Modelling Approach for Post-Processing Ensemble Precipitation Forecasts from Numerical Weather Prediction Models. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, M.A.; Perreault, L.; Anctil, F.; Favre, A.C. Exploratory Analysis of Statistical Post-Processing Methods for Hydrological Ensemble Forecasts. Hydrol. Processes 2015, 29, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeits, M.J.; Kok, K.J. A Comparison Between Raw Ensemble Output, (Modified) Bayesian Model Averaging, and Extended Logistic Regression Using ECMWF Ensemble Precipitation Reforecasts. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2020, 138, 4199–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lei, X.; Tian, F.; Duan, H.; Lu, H. Comparison of Precipitation And Streamflow Correcting For Ensemble Streamflow Forecasts. Water 2018, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, P.; Li, W. Combining Postprocessed Ensemble Weather Forecasts And Multiple Hydrological Models For Ensemble Streamflow Predictions. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 04019060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of TIGGE Ensemble Predictions of Northern Hemisphere Summer Precipitation During 2008–2012. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 7292–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Zhi, X.; Peng, T.; Bai, Y.; Lin, C. Comparative Study on Probabilistic Forecasts of Heavy Rainfall in Mountainous Areas of the Wujiang River Basin in China Based On TIGGE Data. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jin, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; et al. Evaluation and Application of Quantitative Precipitation Forecast Products for Mainland China Based on TIGGE Multimodel Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 1199–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; She, D.; Chen, J.; Xia, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, T. Postprocessing of Hydrometeorological Ensemble Forecasts Based On Multisource Precipitation In Ganjiang River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gao, C.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, Y.P. Evaluation of TIGGE Daily Accumulated Precipitation Forecasts Over the Qu River Basin, China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Qi, H.; Wang, J. Case Study on Extreme Flood Forecasting Based on Ensemble Precipitation Forecast in Qingjiang Basin of the Yangtze River. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 104, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.Y.; Li, L.; Chen, H. Performance of post-processed methods in hydrological predictions evaluated by deterministic and probabilistic criteria. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 3289–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloughter, J.M.L.; Raftery, A.E.; Gneiting, T.; Fraley, C. Probabilistic Quantitative Precipitation Forecasting Using Bayesian Model Averaging. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2007, 135, 3209–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren-Jun, Z. The Xinanjiang model applied in China. J. Hydrol. 1992, 135, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Peng, T.; Yin, Z. Evaluation of Eight Global Precipitation Datasets in Hydrological Modeling. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.Y.; Gupta, V.K.; Sorooshian, S. Shuffled Complex Evolution Approach for Effective and Efficient Global Minimization. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1993, 76, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River Flow Forecasting Through Conceptual Models Part I—A Discussion of Principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.D.; Demargne, J.; Seo, D.J.; Liu, Y. The Ensemble Verification System (EVS): A Software Tool For Verifying Ensemble Forecasts of Hydrometeorological and Hydrologic Variables at Discrete Locations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 854–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Ye, A.; Deng, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Duan, Q.; Xu, J.; Miao, C.; Di, Z.; Gong, W. Evaluating the Skill of NMME Seasonal Precipitation Ensemble Predictions for 17 Hydroclimatic Regions in Continental China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J.A. The Relative Operating Characteristic in Psychology: A Technique for Isolating Effects of Response Bias Finds Wide Use in the Study of Perception and Cognition. Science 1973, 182, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.J.; Graham, N.E. Conditional Probabilities, Relative Operating Characteristics, and Relative Operating Levels. Weather. Forecast. 1999, 14, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Yang, X.; Jin, S.; Fu, S. Evaluation of ECMWF Precipitation Predictions in China during 2015–18. Weather. Forecast. 2021, 36, 1043–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Luo, Y. Evaluation of Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts By TIGGE Ensembles for South China During The Presummer Rainy Season. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 8494–8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Shrestha, D.L.; Stadnyk, T.A.; Coulibaly, P. Evaluation of Ensemble Precipitation Forecasts Generated Through Post-Processing in a Canadian Catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1957–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the Mean Squared Error and NSE Performance Criteria: Implications for Improving Hydrological Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Booij, M.J.; Xu, Y.P. Uncertainty in High and Low Flows Due to Model Structure and Parameter Errors. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan, S.; Prudhomme, C.; Parry, S.; Smith, K.; Tanguy, M. Benchmarking Ensemble Streamflow Prediction Skill in the UK. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2023–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, J.C.; Wang, Q.J.; Robertson, D.E.; Schepen, A.; Li, M.; Michael, K. Assessment of an Ensemble Seasonal Streamflow Forecasting System for Australia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6007–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Center | Country/Region | Ensemble Members (Perturbed) | Base Time | Spatial Resolution | Forecast Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECMWF | Europe | 50 | 00 UTC | 0.5° × 0.5° | 360 h at 6 h |
| NCEP | America | 20 | 00 UTC | 0.5° × 0.5° | 384 h at 6 h |
| Lead Days | ECMWF | NCEP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | GPP | BMA | Raw | GPP | BMA | |
| 1lead day | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.54 | 0.28 |
| 2lead day | 0.47 | 0.54 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.48 | 0.19 |
| 3lead day | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.39 | 0.10 |
| 4lead day | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.36 | 0.12 |
| 5lead day | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.38 | 0.15 |
| 6lead day | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.39 | 0.19 |
| 7lead day | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.37 | 0.20 |
| Mean value | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.41 | 0.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, Y.; Peng, T.; Gao, Q.; Shen, T.; Qi, H. Evaluation of TIGGE Precipitation Forecast and Its Applicability in Streamflow Predictions over a Mountain River Basin, China. Water 2022, 14, 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152432
Xiang Y, Peng T, Gao Q, Shen T, Qi H. Evaluation of TIGGE Precipitation Forecast and Its Applicability in Streamflow Predictions over a Mountain River Basin, China. Water. 2022; 14(15):2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152432
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Yiheng, Tao Peng, Qi Gao, Tieyuan Shen, and Haixia Qi. 2022. "Evaluation of TIGGE Precipitation Forecast and Its Applicability in Streamflow Predictions over a Mountain River Basin, China" Water 14, no. 15: 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152432
APA StyleXiang, Y., Peng, T., Gao, Q., Shen, T., & Qi, H. (2022). Evaluation of TIGGE Precipitation Forecast and Its Applicability in Streamflow Predictions over a Mountain River Basin, China. Water, 14(15), 2432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14152432






