Abstract
With the wide application of selenium (Se) in industrial production, different Se-based compounds (selenate and selenite) are produced and released into aquatic environments. The potential impacts of such Se compounds on the biofilms (a complex microbial aggregate in aquatic systems) need to be substantially explored. Herein, we investigated the responses of bacterial community diversity, composition and structure, and function of biofilms after 21 days of exposure to low concentrations (100 µg/L) and high concentrations (1 mg/L) of sodium selenate and sodium selenite, respectively. Distinct effects of selenium in different valences on the community structure and microbial functions of biofilms were observed. Compared with the controls, the addition of selenate and selenite solutions altered the richness of biofilms but not the diversity, which is dependent on the concentration and valences, with sodium selenite (1 mg/L) exhibiting a strong inhibition effect on community richness. Significant changes of community composition and structure were observed, with a significant increase in Proteobacteria (31.08–58.00%) and a significant decrease in Bacteroidetes (32.15–11.45%) after exposure to sodium selenite with high concentration. Also, different responses of gamma-Proteobacteria and alpha-Proteobacteria were observed between the sodium selenite and sodium selenate treatments. Moreover, results showed that sodium selenite could strengthen the function of the metabolism of biofilms, and the higher the concentration is, the more apparent the enhancement effect is. All these results suggested that the effects of different valence states of selenium were obvious, and sodium selenite with high concentration strongly changed the diversity, structure and function of biofilms.
1. Introduction
Selenium (Se) is a micronutrient element necessary for organisms, mainly entering cells in the form of selenocysteine [1,2,3]. Se containing compounds, especially the water-soluble oxyanion selenate and selenite (such as sodium selenate and sodium selenite) have been released into aquatic environments, due to the wide application of Se in industrial productions, including agriculture, mining, chemical industries, textiles, photography, and electronics [4,5]. Previous studies have demonstrated that Se is one of the most harmful trace elements to the waterfowl, fish and egg-laying aquatic vertebrates [6,7,8,9]. Se exists in different oxidation states, including Se (IV), Se (VI), Se (0), and Se (−II), and most soluble forms of selenium are biologically available, and absorbed into the cells [10]. It has been reported that the growth of algae will be inhibited when Se concentration is higher than 7.49 mg/L [11]. Thus, the potential impacts of Se in freshwaters should receive more attention, due to their potential hazardous properties on aquatic organisms.
During their transport in freshwater, selenium would come into contact with aquatic life, such as periphytic biofilms [12,13]. Ubiquitous in freshwater environments, periphytic biofilms are complex microbial communities that are present on submerged surfaces, and they might represent a first environmental medium that interact with potential stressors [13,14,15]. The multi-species community composition and structure allow biofilms to be ecologically important in multiple activities, such as primary production and organic matter decomposition, which enables biofilms to become an ecological hotspot and substantially contribute to the biogeochemical cycle in the aquatic environment [16,17]. Furthermore, biofilms are sensitive to pollutants and widely used as important indicators of aquatic ecosystems [14,15], as biofilms could change their microbial composition and function to resist the toxicity of pollutants [16]. Therefore, there is a need to evaluate the responses of microbial communities and functions of biofilms exposed to selenium in aquatic ecosystems.
Previous studies have reported that selenium accumulates in large quantities in biofilms as they enter the aquatic environment, and then can be transformed in valence with different microbial activities [18,19,20]. For example, bacteria using SeO42− as the respiratory electron acceptor were able to reduce it to SeO32− by nitrate reductase (Nar and Nap) and the action of hydrogen. SeO32− can then be reduced to Se0 enzymes by periplasmic nitrite reductase (Nir) or hydrogenase [21,22,23,24], and then further reduced to the biological element selenium had an inhibitory effect on the single bacterial strain [25,26]. Also, studies have shown that Se nanoparticles have antibacterial against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus [26,27]. Recently, the toxic effects of selenium in aquatic environments have drawn more attention. The large doses of selenate or selenite led to reduction of both functional enzymes and microbial activities [28,29]. Moreover, Espinosa-Ortiz et al. have demonstrated the toxic effect that selenite has on the morphology and respiratory activity of the biofilm of Phanerochaete chrysosporium [30]. Also, significant differences in bacterial community structure within biofilms formed from an anaerobic sludge inoculum were observed during the selenate removal in biofilm systems under the effects of nitrate and sulfate [31]. Most research focuses on the effect of Se on single-specie biofilms in lab, leaving significant knowledge gaps about the potential impacts on the multi-species biofilms in freshwater, in terms of the responses of the community structure and microbial functions.
To solve this knowledge gap, biofilms were cultivated in a lab, and exposure experiments were conducted to investigate the toxic effects of selenium in different valences on freshwater biofilms. After 21 days of an exposure, high-throughput sequencing was performed to study the responses of microbial composition and structure, and the microbial functions of biofilms to selenium. This study will be helpful to understand the ecological risk of selenium pollution in the aquatic environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biofilms Cultivation
The cultivation of biofilms followed the process we used in our previous study [32]. Briefly, the microbial sources were obtained from benthic rocks in Xuanwu Lake, Nanjing, China. Large granular particles and micro animals attached to pebbles were removed, and then the biofilm was stored in a sterile tank and brought back to the laboratory and added to ice within 1 h. Fifty liters of freshwater collected from the lake was also obtained to determine water quality parameters, which were finally determined as: pH = 7.7; total nitrogen (TN) = 2.3 mg/L; total phosphorus (TP) = 0.13 mg/L; NH4+−N = 0.62 mg/L; and NO3−−N = 0.85 mg/L.
The biofilms and water samples were further transported to a greenhouse (air temperature: 20 ± 1 °C) where they were mixed in a dynamic water tank (size: 4 m × 0.3 m × 0.3 m, flow velocity: 0.12 m/s) to simulate natural environments. Cobblestones (diameter: 2–3 cm) were laid in the water tank as substrates for biofilms development. Nutrient solution was added every five days to support biofilms growth [32]. Halogen lamps (light to dark ratio = 12:12 h) were provided as light sources. After six weeks, matured biofilm communities were observed through dry weight measuring (Figure S1) and transferred to microcosms (cylindrical plexiglass tanks) for further experiment.
2.2. Sodium Selenate and Sodium Selenite Exposure
Fifteen microcosms (diameter: approximately 30 cm) were filled with 2.5 L (about 10 cm deep) of the experimental solution used for biofilm cultivation, and contained 30 random cobbles as substrates for the biofilms. All microcosms were placed in an indoor laboratory with an average temperature of 20 ± 1 °C. Artificial light was maintained by Halogen lamps to ensure that the light and darkness were 12 h each day. Two hours of stabilization of biofilms in lab were performed, and then the selenium exposure experiments were conducted. To investigate the dose effects of selenium on freshwater biofilms, sodium selenate and sodium selenite were dissolved in distilled water first to prepare the stock suspension. Then, the stock were added into the microcosms to obtain the concentration of 100 μg/L and 1 mg/L, respectively. Control tests (cont) were also set without Se addition. The five experimental groups were named as NAH (1 mg/L sodium selenate), NAL (100 μg/L sodium selenate), NIH (1 mg/L sodium selenite), NIL (100 μg/L sodium selenite), and control. Both the control and selenium treatments included three replicates, and the exposure experiments lasted for 21 days. An agitator was installed on each microcosm and the speed was set at 150 r/min to simulate flow conditions.
After the exposure experiment, the biofilms attached to the cobbles were carefully peeled off by a disinfected brush and transferred to flasks. All samples were stored at −80 °C for subsequent DNA extraction.
2.3. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
After the exposure, approximately 1 g of each biofilm sample was collected and stored at −80 °C. DNA extraction was carried out using E.Z.N.A. ®Tissue DNA kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol [32]. The concentration and purity of extracted DNA were measured using NanoDrop One (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA). Then, the V4 region of the bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA of the extracted DNA was amplified by PCR. The investigation of the bacterial community was conducted using the Illumina MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) by MAGIGENE Biotech Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). The detailed information was provided in the Supporting Information.
For processing the sequencing data, quality filtering of paired-end raw reads was performed using Trimmomatic (V0.33, http://www.usadellab.org/cms/?page%C2%BCtrimmomatic, accessed on 21 July 2020) to obtain high-quality, clean reads. Then, paired-end clean reads were merged using FLASH (V1.2.11) to obtain spliced sequences called Raw Tags. The Mothur software (V1.35.1, https://www.mothur.org/, accessed on 21 July 2020) was used to further filter and dislodge chimeric sequences and obtain effective Clean Tags. Clean Tags were then classified into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) using the usearch software (V8.0.1517, http://www.drive5.com/usearch/, accessed on 21 July 2020), according to the sequence similarity. The most frequently occurring sequence was selected as the representative sequence for each OTU. Each representative sequence was annotated with taxonomic information using the assign_taxonomy.py script in Qiime 2 (http://qiime.org/scripts/assign_taxonomy.html, accessed on 21 July 2020), concerning the Silva database (confidence threshold ≥ 0.5). OTU abundance information were normalized at 31,774 (the least sequences) corresponding to all samples. Subsequent analysis of alpha diversity and beta diversity were all performed basing on this output normalized data.
2.4. Analysis Method of Functional Prediction
Bacterial metagenome content was predicted from the OTU (taxonomic) data, and functional inferences were made from the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genomes (KEGG) catalog using the PICRUSt software [32]. The KEGG and COG family information corresponding to OTU can be obtained through the greengenes database, and then OTU abundance from the information in the KEGG database is used to calculate the abundance of each functional category. The analysis of the bacterial functional prediction was conducted by MAGIGENE Biotech Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China).
2.5. Statistical Methods
All assays were conducted in three replicates, and data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Significant differences between treatments were analyzed in Origin 2022 using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test followed by a post hoc Tukey test; significance level was set as 0.05.
Microbial alpha diversity indices, including the Chao1 estimator and Shannon diversity, were calculated in Mothur (v1.30.1). As for the community composition, significant differences between all the treatments were determined by the Kruskal–Wallis (KW) sum-rank test, and then corrected for multiple tests according to the Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) procedure, with q values lower than 0.05. Microbial beta diversity was determined by principal co-ordinates analysis (PCoA) based on the Bray–Curtis distance using R package vegan. Analysis of similarities (Anosim) and Permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA, n = 999) were conducted to test the significance of differences between treatments using R package vegan. Linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) analysis with a non-parametric factorial Kruskal–Wallis (KW) sum-rank test under an all-against-all (a more strict) strategy was calculated and drawn using Galaxy.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Taxonomic Annotation and Alpha Diversity
After quality filtering, 549,078 sequences were detected, and then 31,774 sequences (the least value) were subsampled to compare community composition and structure within biofilms. The plateaued rarefaction plots of the Chao1 and Shannon indices, and the high species coverage (>94%) for biofilms indicated the obtained OTUs met the analysis requirements (Figure S2).
In this study, alpha diversity was characterized by community richness and community diversity. Chao1 index was used to represent the community richness, and the Shannon index was used to represent the community diversity. As shown in Figure 1, compared with the control group, the addition of selenate and selenite solutions altered the richness of biofilms but not the diversity. Specifically, neither the high nor the low concentrations of sodium selenate affected the bacterial community richness, suggesting that sodium selenate within 1 mg/L did not change the bacterial richness during the experimental period in this study. When compared to the control tests, the sodium selenite exposure with 1 mg/L significantly inhibited the bacterial community richness, and this was not observed in the 100 μg/L treatments. This results suggested that high concentrations of sodium selenite can decrease the bacterial richness after 21 days of exposure. Furthermore, significantly lower bacterial community richness was observed in 1 mg/L sodium selenite treatments compared to the 1 mg/L sodium selenate treatments (p < 0.05), suggesting that selenite showed a greater inhibiting effect on community richness than selenate. This result is consistent with previous studies [28,29].
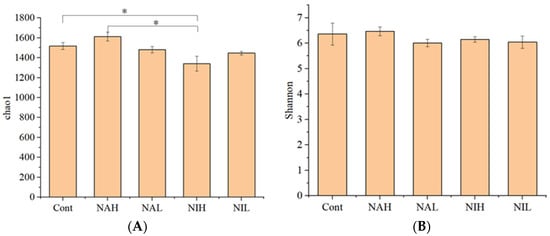
Figure 1.
Alpha diversity of biofilms from the different treatments. (A) Richness, indicated by the Chao1 index. (B) Diversity, indicated by the Shannon index. Cont: control; NAH: 1 mg/L sodium selenate; NAL: 100 μg/L sodium selenate; NIH: 1 mg/L sodium selenite; NIL: 100 μg/L sodium selenite. * represents that there is a significant difference between these two groups.
As for the Shannon index, there was no significant change in the Shannon index within biofilms after the sodium selenite and sodium selenate treatments. High alpha diversity within microbial community is helpful to maintain their ecosystem functions when faced to environmental disturbances [33]. The exposure to selenium in this study changed the alpha diversity of biofilms, which might influence the capacity of microbial communities to keep their ecological functions [34]. From the results of this study, the exposure to selenium had various toxic effects on the bacterial communities of biofilm, dependent on the concentration and valences, and sodium selenite (1 mg/L) had a strong inhibition effect on community richness.
3.2. Bacterial Community Composition and Structure in Biofilms
High-throughput sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene was used to analyze the sequence information at the phylum and class taxonomic levels. Meanwhile, taxa with a relative abundance of more than 1% were selected to draw the relative abundance distribution map. Stacked columns are taxa with relative abundance greater than 1% at each taxonomic level, and others with relative abundance less than 1% are classified as others.
As shown in Figure 2, Proteobacteria have the highest relative abundance (31.08–58.0%) in all biofilm samples, followed by Cyanobacteria (16.61–34.56%), Bacteroidetes (11.45–32.15%), and Planctomycetes (2.21–6.42%) at the phylum level.
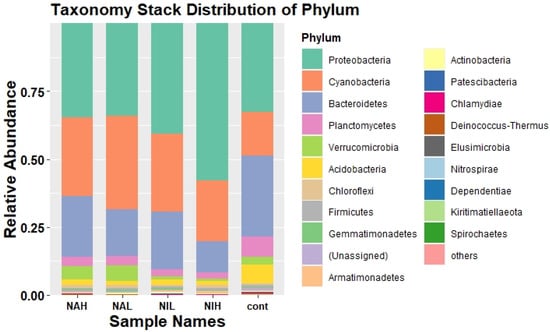
Figure 2.
Community composition at the phylum level of the different treatments, selected species with relative abundance greater than 1%. Cont: control; NAH: 1 mg/L sodium selenate); NAL: 100 μg/L sodium selenate; NIH: 1 mg/L sodium selenite; NIL: 100 μg/L sodium selenite.
The greatest change in community composition was seen in the NIH groups compared to the control group. Specifically, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria increased significantly, while Bacteroidetes decreased significantly. The abundance of Bacteroidetes decreases significantly in high concentrations of sodium selenite. Bacteroidetes can degrade cellulose, chitin and other water-soluble polymer organic matter [35], and therefore, high concentrations of sodium selenite may destroy the carbon cycle in the aquatic environment.
At the class level, there were significant differences in community composition among the treatment groups (Figure 3 and Figure S3) as determined by Kruskal–Wallis (KW) sum-rank test. Specifically, the Oxyphotobacteria, a photosynthetic bacterium, increased significantly in all treated biofilm samples after exposure (p < 0.05). Oxyphotobacteria can produce oxygen using water as an electron source and carbon dioxide as a carbon source, and the increase of Oxyphotobacteria indicated that the exposure to sodium selenate and sodium selenite could affect the process of oxygen yields in biofilms. Significant decreases of Bacteroidia were observed in all treated biofilm samples after exposure (p < 0.05), especially in the high concentrations of sodium selenite (NIH) treatments. As some members of Bacteroidia mainly contribute to the degradation of biopolymers, such as cellulose and chitinase, the decreased abundance of this class may lead to decreased heterotrophic respiration and carbon metabolism [36,37].
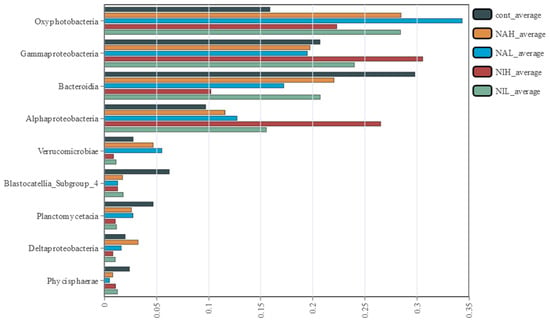
Figure 3.
Changes in the relative abundance of the dominant species at class level from different treatments (n = 3). Significant differences between all the treatments were determined by Kruskal–Wallis (KW) sum-rank test and then corrected for multiple test according to the Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) procedure, with p < 0.05. Cont: control; NAH: 1 mg/L sodium selenate); NAL: 100 μg/L sodium selenate; NIH: 1 mg/L sodium selenite; NIL: 100 μg/L sodium selenite.
Interestingly, different responses of gamma-Proteobacteria and alpha-Proteobacteria were observed between the sodium selenite and sodium selenate treatments. As for gamma-Proteobacteria, slight decreases in abundance were observed in the sodium selenate treatments (NAH and NAL), compared to the control tests (p > 0.05). Meanwhile, significantly increases of gamma-Proteobacteria were observed in the sodium selenite treatments (NIH and NIL), compared to the control tests (p < 0.05). These results suggested different effects of selenium on the community composition of biofilms, and that low valences of selenium exhibit higher impacts. Moreover, the abundance of gamma-Proteobacteria increased from 19.28 to 23.76% (in low concentrations of sodium selenite) and 30.50% (in high concentrations of sodium selenite), indicating that a high concentrations of sodium selenite had a great influence on the community composition of biofilms. Previous studies have demonstrated that distinct toxic effects of sodium selenate and sodium selenite on aquatic organisms were observed, and the strong inhibition of functional enzymes and microbial activities were obtained from the selenite treatments [28,29]. As for alpha-Proteobacteria, slight increases in abundance were observed in the sodium selenate treatments (NAH and NAL), compared to the control tests (p > 0.05). Meanwhile, significantly increases of alpha-Proteobacteria were observed in the sodium selenite treatments (NIH and NIL), compared to the control tests (p < 0.05), especially in high concentrations of sodium selenite. Studies have shown that alpha-Proteobacteria tend to form filamentous and grazing-resistant morphologies, and the strong increase of this class to sodium selenite exposure might favor biofilms maintaining their physical structure [17].
The similarities between different microbial communities were evaluated by the principal co-ordinates analysis (PCoA) ordination, and the first two principal components, PCoA1 and PCoA2, are selected for plotting (Figure 4). Results showed that the exposure to selenium led to significant changes in the community structure of biofilms, as all the selenium treated biofilms were far away from the control tests. Moreover, the high concentrations of selenite (NIH) were further away from other treatment groups, suggesting that the high concentrations of selenite had a deeper influence on bacterial communities within the experimental period of this study. These results indicated that the community structure of biofilms could be significantly altered by exposure to the contaminant selenium, and sodium selenite appears to exhibit strong impacts.
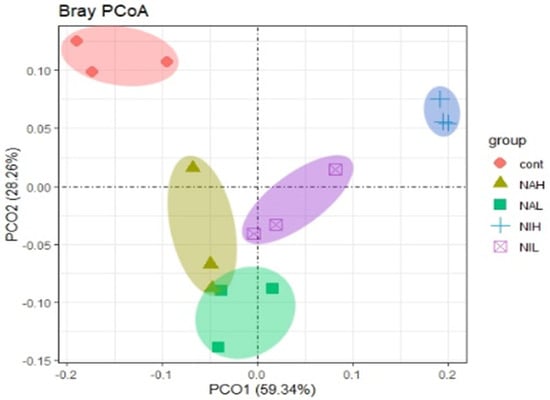
Figure 4.
Principle coordinate analysis (PCoA) of community structure based on the Bray–Curtis distance from the different treatments. Cont: control; NAH: 1 mg/L sodium selenate); NAL: 100 μg/L sodium selenate; NIH: 1 mg/L sodium selenite; NIL: 100 μg/L sodium selenite.
Furthermore, the differences of species abundance between the different groups were detected using LEfSe analysis. The phylogenetic clades of the different species detected are shown in Figure 5.
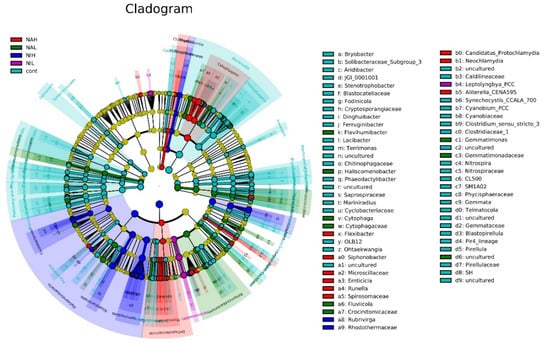
Figure 5.
Diagram of species evolution from phylum to genus in the five treatments. The circles radiating from the inside to the outside represent the taxonomic levels from phylum to genus. Each node at a different taxonomic level represents a taxon of a species at that level, and the higher the species abundance, the larger the node is. Cont: control; NAH: 1 mg/L sodium selenate); NAL: 100 μg/L sodium selenate; NIH: 1 mg/L sodium selenite; NIL: 100 μg/L sodium selenite.
The results showed that Spirosomaceae had a high relative abundance in the NAH group, and Gemmatimonas had a higher relative abundance in the NAL group, producing significant differences between the groups. The genus Rubrivirga had a significant effect on the differences between NIH groups. Leptolyngbya had high relative abundance in the in the NIL groups, which significantly affected the differences between the groups. These results indicated that the bacterial communities exposed to selenium at different concentration and valences could exhibit distinct responses. Previous studies have demonstrated that the accumulation of trace contaminants, such as heavy metals (Zn, Cu and Pb) in biofilms, might significantly change the bacterial communities [38], and then lead to influences on their trophic transfer in aquatic ecosystems [39].
3.3. Functions of Microbial on Biofilm
PICRUSt (version 1) software was used to explore the possible effects of selenate and selenite on the function of biofilms. By comparing the COG database, four kinds of functional analysis of biological metabolic pathways (metabolism, cellular processes and signaling, poorly characterized, and information storage and processing) were obtained at level 1 and are shown in Figure 6a. Results showed that metabolism was highly expressed in the high concentrations of selenite, suggesting that sodium selenite could strengthen the function of the metabolism of biofilms, and the higher the concentration is, the more apparent the enhancement effect is.
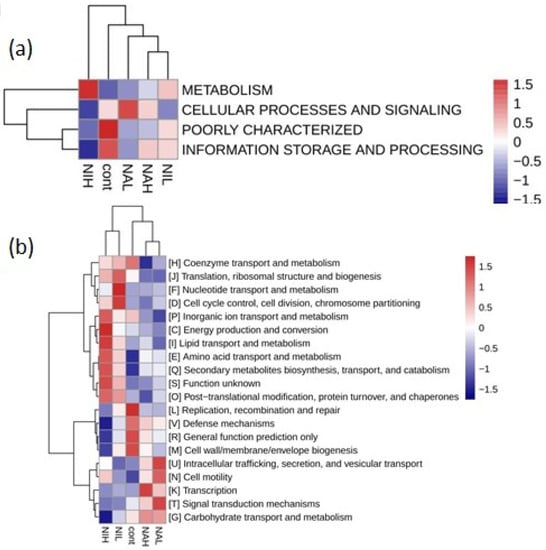
Figure 6.
COG abundance clustering heat map at the level 1 (a) and level 2 (b) in the five treatments. Cont: control; NAH: 1 mg/L sodium selenate); NAL: 100 μg/L sodium selenate; NIH: 1 mg/L sodium selenite; NIL: 100 μg/L sodium selenite.
At level 2, a total of 20 functional analyses of metabolic pathways, such as nucleotide transport and metabolism, amino acid transport and metabolism, and cell motility, were obtained. Results showed that sodium selenite (NIH) could enhance the nucleotide transport and metabolism, cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning, secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism function of biofilms, and reduce replication, recombination, and repair defense mechanisms (Figure 6b). Meanwhile, sodium selenate enhanced the intracellular trafficking, secretion, vesicular transport, and cell motility function of biofilms, but inhibited other functions of biofilm. The supporting data and statistical analysis are available in Tables S1 and S2.
Due to the complex nature and multi-species communities within biofilms, they always exhibit strong contaminant capture and degradation capacity [19]. In the face of toxic chemicals, biofilms often show the plasticity of defensive toxicity due to the stress resistance of the community [17]. In this study, the distinct effects of selenium in different valences on the community structure and microbial functions of biofilms were observed. The microbial communities might exhibit functional redundancy to maintain the same ecosystem processes despite changes in the composition of the community when facing external disturbances [32]. The alpha diversity, community structure and microbial functions of biofilms were altered by the exposure to selenium, especially in the sodium selenite treatments. These results suggested that the presence of selenium might limit the sustainability of biofilms for purification of polluted water, which should be considered for the nutrients managements of biofilm system [39,40].
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the effects of exposure to sodium selenite and sodium selenate at different concentrations on biofilms of aquatic ecosystems. The exposure to sodium selenite significantly decreased the alpha diversity (richness) of biofilms. There were significant changes in the composition of the microbial community after the Se exposure. The microbial functions, for example amino acid transport and metabolism, were strengthened, while the replication, recombination and repair were weakened after exposure to sodium selenite. In all treatment groups, distinct effects of selenium in different valences on the community structure and microbial functions of biofilms were observed. The effects of different valence states of selenium were obvious, and sodium selenite with high concentration strongly changed the diversity, structure and function of biofilms. The long-term effects of exposure to selenium in the aquatic environment on biofilms in freshwater still require further study.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w14152394/s1, Text S1: High-throughput sequencing; Figure S1: Dry weight of biofilms (g/m2) after colonization (Day 0). The dry weight became stable since Day 36. Mature and stabilized biofilms were obtained on Day 42 to conduct exposure experiments; Figure S2: Dilution curve, the sequence number is in a stable stage of the curve, and the species coverage can meet the analysis requirements; Figure S3: Community composition at class level, select species with relative abundance greater than 1%; Table S1: COG database at level 1; Table S2: COG database at level 2.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and L.M.; methodology, W.H.; data curation, W.H. and C.T.; writing—original draft preparation, W.H.; writing—review and editing, T.M.A. and Y.Z.; supervision, Y.Z. and J.H.; funding acquisition, J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51979075, and No. 52039003), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. B210202053) and Jiangsu Province “333” project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available when requested.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Arnér, E.S.J.; Holmgren, A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 20, 6102–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, S.V.; Gladyshev, V.N. Non-animal origin of animal thioredoxin reductases: Implications for selenocysteine evolution and evolution of protein function through carboxy-terminal extensions. Protein Sci. 2003, 2, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Wang, S.; Tang, C.; Duan, P.; Yao, L.; Tang, J.; Wong, P.K.; An, T.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wu, Y. Protection Mechanisms of Periphytic Biofilm to Photocatalytic Nanoparticle Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, M.; Lens, P.N. The essential toxin: The changing perception of selenium in environmental sciences. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3620–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasteen, T.G.; Bentley, R. Biomethylation of Selenium and Tellurium: Microorganisms and Plants. Chem. Rev. 2002, 103, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, J.W.; Hodson, P.V.; Slinger, S.J. The requirement and toxicity of selenium in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Nutr. 1980, 110, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, P.V.; Hilton, J.W. The Nutritional Requirements and Toxicity to Fish of Dietary and Waterborne Selenium. Eco-Log. Bull. 1983, 35, 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Cutter, G.A.; Bruland, K.W. The marine biogeochemistry of selenium: A re-evaluation1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1984, 29, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk Kurt, B.; Konukoglu, D.; Kalayci, R.; Ozdemir, S. Investigation of the Protective Role of Selenium in the Changes Caused by Chlorpyrifos in Trace Elements, Biochemical and Hematological Parameters in Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, P.R. Making sense of nonsense: The evolution of selenocysteine usage in proteins. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Y. Selenium Accumulation in Unicellular Green Alga Chlorella vulgaris and Its Effects on Antioxidant Enzymes and Content of Photosynthetic Pigments. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Yin, H.; An, T. Bacterial response mechanism during biofilm growth on different metal material substrates: EPS characteristics, oxidative stress and molecular regulatory network analysis. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Kerr, P.; Wu, Y. Distinguishing the roles of different extracellular polymeric substance fractions of a periphytic biofilm in defending against Fe2O3 nanoparticle toxicity. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, S.; Faheem, M.; Ali, N.; Kerr, P.G.; Wang, L.-F.; Kuppusamy, S.; Li, Y. Periphytic biofilm: An innovative approach for biodegradation of microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Wu, Y.; Esquivel-Elizondo, S.; Sørensen, S.J.; Rittmann, B.E. How Microbial Aggregates Protect against Nanoparticle Toxicity. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Kerr, P.G.; Yang, L. A multi-level bioreactor to remove organic matter and metals, together with its associated bacterial diversity. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battin, T.J.; Besemer, K.; Bengtsson, M.M.; Romaní, A.M.; Packmann, A.I. The ecology and biogeochemistry of stream biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larned, S.T. A prospectus for periphyton: Recent and future ecological research. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 182–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Rene, E.R. Periphytic biofilms: A promising nutrient utilization regulator in wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz, D.M.; Liber, K.; Pickering, I.J.; Wiramanaden, C.I.; Weech, S.A.; Gallego-Gallegos, M.; Driessnack, M.K.; Franz, E.D.; Goertzen, J.P.; Tse, J.J.; et al. Integrative assessment of selenium speciation, biogeochemistry, and distribution in a northern coldwater ecosystem. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2014, 10, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhnag, X.; Fan, W.-Y.; Yao, M.-C.; Yang, C.-W.; Sheng, G.-P. Redox state of microbial extracellular polymeric substances regulates reduction of selenite to elemental sele-nium accompanying with enhancing microbial detoxification in aquatic environments. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.; Lima, A.T.; Van Cappellen, P. Philippe, Selenium in buoyant marine debris biofilm. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendenedzai, J.T.; Chirwa, E.M.N.; Brink, H.G. Performance Evaluation of Selenite (SeO32−) Reduction by Enterococcus spp. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinharoy, A.; Lens, P.N.L. Biological removal of selenate and selenite from wastewater: Options for selenium recovery as nanoparticles. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 3, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, H.; Yao, J.; He, Q.; Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Huangfu, X.; Liu, H. A critical review on sulfur reduction of aqueous selenite: Mechanisms and applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 422, 126852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonaro, E.; Lampis, S.; Turner, R.J.; Qazi, S.; Vallini, G. Biogenic selenium and tellurium nanoparticles synthesized by environmental microbial isolates effica-ciously inhibit bacterial planktonic cultures and biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwani, S.A.; Shedbalkar, U.U.; Singh, R.; Chopade, B.A. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles: Current status and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2555–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Feudis, M.; Massaccesi, L.; D’Amato, R.; Bussinelli, D.; Casucci, C.; Agnelli, A. Impact of Na-selenite fertilization on the microbial biomass and enzymes of a soil under corn (Zea mays L.) cultivation. Geoderma 2020, 373, 114425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, J.; Kaklewski, K.; Klódka, D. Influence of various concentrations of selenic acid (IV) on the activity of soil enzymes. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 291, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Ortiz, E.J.; Pechaud, Y.; Lauchnor, E.; Rene, E.R.; Gerlach, R.; Peyton, B.M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Piet, N.L.L. Effect of selenite on the morphology and respiratory activity of Phanerochaete chrysosporium bio-films. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.C.; Espinosa-Ortiz, E.J.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Gerlach, R.; Lens, P.N.L. Selenate removal in biofilm systems: Effect of nitrate and sulfate on selenium removal efficiency, biofilm structure and microbial community. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2380–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Wang, P.; Hou, J.; Ning, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, T. Chronic exposure to CuO nanoparticles induced community structure shift and a delay inhibition of microbial functions in multi-species biofilms. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.D.; Stegemeier, J.P.; Bibby, K.; Marinakos, S.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Gregory, K.B. Impacts of Pristine and Transformed Ag and Cu Engineered Nanomaterials on Surficial Sediment Microbial Communities Appear Short-Lived. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2641–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Spor, A.; Hénault, C.; Bru, D.; Bizouard, F.; Jones, C.; Sarr, A.; Maron, P.-A. Loss in microbial diversity affects nitrogen cycling in soil. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; Mcmahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenk, S.; Arnds, J.; Zerjatke, K.; Musat, N.; Amann, R.; Mußmann, M. Novel groups of Gamma-Proteobacteria catalyse sulfur oxidation and carbon fixation in a coastal, intertidal sediment. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 758–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.L.; Smith, D.L.; Connolly, J.; McDonald, J.E.; Cox, M.J.; Joint, I.; Edwards, C.; McCarthy, A.J. Identification of Carbohydrate Metabolism Genes in the Metagenome of a Marine Biofilm Community Shown to Be Dominated by Gamma-Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes. Genes 2010, 1, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancion, P.-Y.; Lear, G.; Lewis, G.D. Three common metal contaminants of urban runoff (Zn, Cu & Pb) accumulate in freshwater biofilm and modify embedded bacterial communities. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2738–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnineau, C.; Artigas, J.; Chaumet, B.; Dabrin, A.; Faburé, J.; Ferrari, B.J.D.; Lebrun, J.D.; Margoum, C.; Mazzella, N.; Miège, C.; et al. Role of Biofilms in Contaminant Bioaccumulation and Trophic Transfer in Aquatic Ecosystems: Current State of Knowledge and Future Challenges. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 253, 115–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Hašková, S.; Zeman, R.; Váchal, J.; Vaníčková, R. Nutrient Management in Processing of Steam-Exploded Lignocellulose Phytomass. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 1945–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).