Depth-Dependent Concentrations of E. coli in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Data Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FSMA Final Rule on Produce Safety: Standards for the Growing, Harvesting, Packing, and Holding of Produce for Human Consumption. 2016. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceRegulation/FSMA/ucm334114.htm (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). Sampling and Consideration of Variability (Temporal and Spatial) for Monitoring of Recreational Waters. EPA-823-R-10-005; U.S. EPA Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- McEgan, R.; Mootian, G.; Goodridge, L.D.; Schaffner, D.W.; Danyluk, M.D. Predicting Salmonella populations from biological, chemical, and physical indicators in Florida surface waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4094–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Topalcengiz, Z.; Strawn, L.K.; Danyluk, M.D. Microbial quality of agricultural water in Central Florida. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaiman, S.; Allard, S.M.; Callahan, M.T.; Jiang, C.; Handy, E.; East, C.; Haymaker, J.; Bui, A.; Craddock, H.; Murray, R.; et al. Longitudinal assessment of the dynamics of Escherichia coli, total coliforms, Enterococcus spp., and Aeromonas spp. in alternative irrigation water sources: A CONSERVE Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00342-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Gu, G.; Ginn, A.; Giurcanu, M.C.; Adams, P.; Vellidis, G.; van Bruggen, A.H.; Danyluk, M.D.; Wright, A.C. Distribution and characterization of Salmonella enterica isolates from irrigation ponds in the Southeastern United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4376–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.; Tertuliano, M.; Vellidis, G.; Harris, C.; Grossman, M.K.; Rajeev, S.; Levy, K. Evaluation of grower-friendly, science-based sampling approaches for the detection of Salmonella in ponds used for irrigation of fresh produce. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antaki, E.M.; Vellidis, G.; Harris, C.; Aminabadi, P.; Levy, K.; Jay-Russell, M.T. Low concentration of Salmonella enterica and generic Escherichia coli in farm ponds and irrigation distribution systems used for mixed produce production in Southern Georgia. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRCS. Ponds—Planning, Design, Construction. Natural Resource Conservation Service. United States Department of Agriculture. 1997. Available online: https://nrcspad.sc.egov.usda.gov/distributioncenter/product.aspx?ProductID=115 (accessed on 23 January 2022).
- Dias, D.F.C.; Passos, R.G.; Von Sperling, M. A review of bacterial indicator disinfection mechanisms in waste stabilisation ponds. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2017, 16, 517–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Anderson, M.; Yates, M.V. Distribution of indicator bacteria in Canyon Lake, California. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partyka, M.L.; Bond, R.F.; Chase, J.A.; Atwill, E.R. Spatiotemporal variability in microbial quality of western U.S. agricultural water supplies: A multistate study. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.D.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Smith, J.E.; Morgan, B.J.; Hill, R.L.; Kim, M. Persistent patterns of E. coli concentrations in two irrigation ponds from 3 years of monitoring. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). Method 1603: Escherichia coli (E. coli) in Water by Membrane Filtration Using Modified Membrane-Thermotolerant Escherichia coli Agar (Modified mTEC. EPA-821-R-04-025); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 23 January 2022).
- Pachepsky, Y.; Kierzewski, R.; Stocker, M.; Sellner, K.; Mulbry, W.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. Temporal stability of Escherichia coli concentrations in waters of two irrigation ponds in Maryland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 1876–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stocker, M.D.; Smith, J.E.; Hernandez, C.; Macarisin, D.; Pachepsky, Y. Seasonality of E. coli and enterococci concentrations in creek water, sediment, and periphyton. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truitt, L.N.; Vazquez, K.M.; Pfuntner, R.C.; Rideout, S.L.; Havelaar, A.H.; Strawn, L.K. Microbial quality of agricultural water used in produce preharvest production on the Eastern Shore of Virginia. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.; Mahdi, A.; Odumeru, J. Microbial assessment of irrigation water used for production of fruit and vegetables in Ontario, Canada. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, D.M.; Telias, A.; Newell, M.; Ottesen, A.R.; Walsh, C.S. Comparing source of agricultural contact water and the presence of fecal indicator organisms on the surface of ‘Juliet’ grape tomatoes. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swallow, M.; Huffman, J.; Van Why, K.; D’Angelo, G. The effect of goose management on water quality. In Proceedings of the Vertebrate Pest Conference, Sacramento, CA, USA, 22–25 February 2010; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, G.; Luo, Z.; Cevallos-Cevallos, J.M.; Adams, P.; Vellidis, G.; Wright, A.; van Bruggen, A.H. Factors affecting the occurrence of Escherichia coli O157 contamination in irrigation ponds on produce farms in the Suwannee River Watershed. Can. J. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinheinz, G.T.; McDermott, C.M.; Hughes, S.; Brown, A. Effects of rainfall on E. coli concentrations at Door County, Wisconsin beaches. Int. J. Microbiol. 2009, 2009, 876050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, C.; da Silva, A.L.B.R.; Dunn, L.L. Factors impacting the prevalence of foodborne pathogens in agricultural water sources in the southeastern United States. Water 2019, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitman, R.L.; Nevers, M.B.; Korinek, G.C.; Byappanahalli, M.N. Solar and temporal effects on Escherichia coli concentration at a Lake Michigan swimming beach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4276–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Z.; Whitman, R.L.; Nevers, M.B.; Phanikumar, M.S.; Byappanahalli, M.N. Nearshore hydrodynamics as loading and forcing factors for Escherichia coli contamination at an embayed beach. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traister, E.; Anisfeld, S.C. Variability of indicator bacteria at different time scales in the upper Hoosic River watershed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4990–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenart-Boroń, A.; Wolanin, A.; Jelonkiewicz, Ł.; Chmielewska-Błotnicka, D.; Żelazny, M. Spatiotemporal variability in microbiological water quality of the Białka river and its relation to the selected physicochemical parameters of water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.D.; Rodriguez-Valentin, J.G.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Shelton, D.R. Spatial and temporal variation of fecal indicator organisms in two creeks in Beltsville, Maryland. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2016, 51, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.C.; Weber, L.; Suca, J.J.; Llopiz, J.K.; Mooney, T.A.; Apprill, A. Microbial and nutrient dynamics in mangrove, reef, and seagrass waters over tidal and diurnal time scales. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 85, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, A.B.; Grant, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Mowbray, S.L.; McGee, C.D.; Clark, C.D.; Wellman, D.E. Decadal and shorter period variability of surf zone water quality at Huntington Beach, California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, A.B.; Weisberg, S.B. Tidal forcing of enterococci at marine recreational beaches at fortnightly and semidiurnal frequencies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5575–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothrop, N.; Bright, K.R.; Sexton, J.; Pearce-Walker, J.; Reynolds, K.A.; Verhougstraete, M.P. Optimal strategies for monitoring irrigation water quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 199, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maraccini, P.A.; Mattioli, M.C.M.; Sassoubre, L.M.; Cao, Y.; Griffith, J.F.; Ervin, J.S.; Van De Werfhorst, L.C.; Boehm, A.B. Solar inactivation of enterococci and Escherichia coli in natural waters: Effects of water absorbance and depth. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5068–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, M.B.; Fisher, D.S.; Endale, D.M.; Adams, P. Comparative die-off of Escherichia coli 0157: H7 and fecal indicator bacteria in pond water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maïga, Y.; Wethe, J.; Denyigba, K.; Ouattara, A.S. The impact of pond depth and environmental conditions on sunlight inactivation of Escherichia coli and enterococci in wastewater in a warm climate. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, A.W.; Noike, T. Response of mixed cultures of Chlorella vulgaris and heterotrophic bacteria to variation of pH. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 30, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, R.C.; Joy, D.M.; Lee, H.; Kostaschuk, R.; Gordon, R.J. Resuspension of sediment-associated Escherichia coli in a natural stream. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.H.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Kim, J.H.; Guber, A.K.; Shelton, D.R.; Rowland, R. Release of Escherichia coli from the bottom sediment in a first-order creek: Experiment and reach-specific modeling. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.B.; Litton Mueller, R.M.; Ahn, J.H. Measuring and modeling the flux of fecal bacteria across the sediment water interface in a turbulent stream. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W05517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Stocker, M.; Saldaña, M.O.; Shelton, D. Enrichment of stream water with fecal indicator organisms during baseflow periods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Vale, C.; Chu, A. Variation in Water Quality of a Stormwater Pond from Diurnal Thermal Stratification. J. Water Resour. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 4, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouali, A.; Jupsin, H.; Ghrabi, A.; Vasel, J.L. Removal kinetic of Escherichia coli and enterococci in a laboratory pilot scale wastewater maturation pond. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hall, G.; Champagne, P. The role of algae in the removal and inactivation of pathogenic indicator organisms in wastewater stabilization pond systems. Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Weaver, L.; Davies-Colley, R.; Stott, R.; Williamson, W.; Mackenzie, M.; McGill, E.; Lin, S.; Webber, J.; Craggs, R.J. Comparison of faecal indicator and viral pathogen light and dark disinfection mechanisms in wastewater treatment pond mesocosms. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, M.; Jeon, D.; Sokolova, E.; Lee, H.; Kim, M.; Pachepsky, Y. Accounting for the Three-Dimensional Distribution of Escherichia coli Concentrations in Pond Water in Simulations of the Microbial Quality of Water Withdrawn for Irrigation. Water 2020, 12, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enns, A.A.; Vogel, L.J.; Abdelzaher, A.M.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M.; Plano, L.R.; Gidley, M.L.; Phillips, M.C.; Klaus, J.S.; Piggot, A.M.; Feng, Z.; et al. Spatial and temporal variation in indicator microbe sampling is influential in beach management decisions. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2237–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

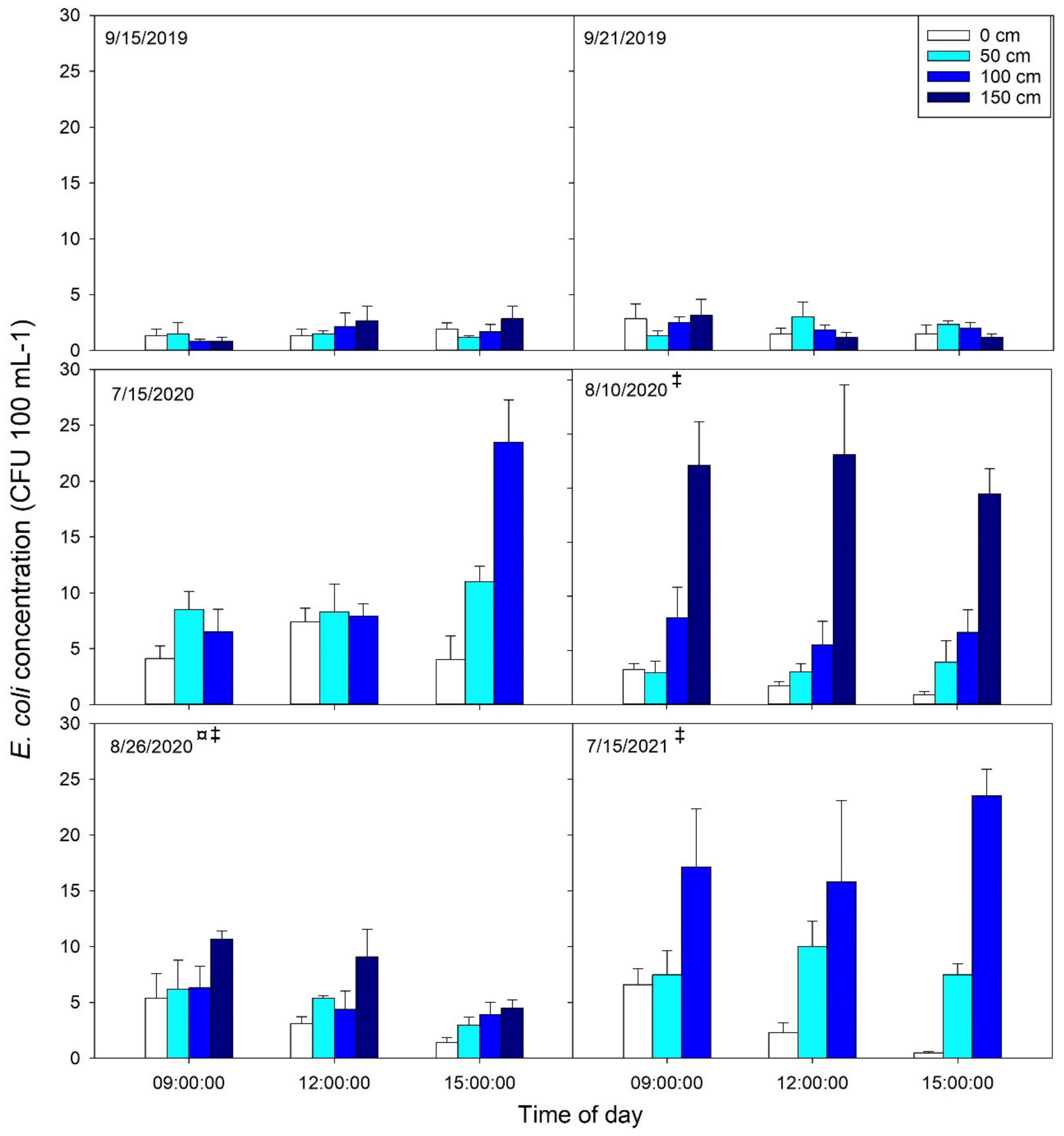
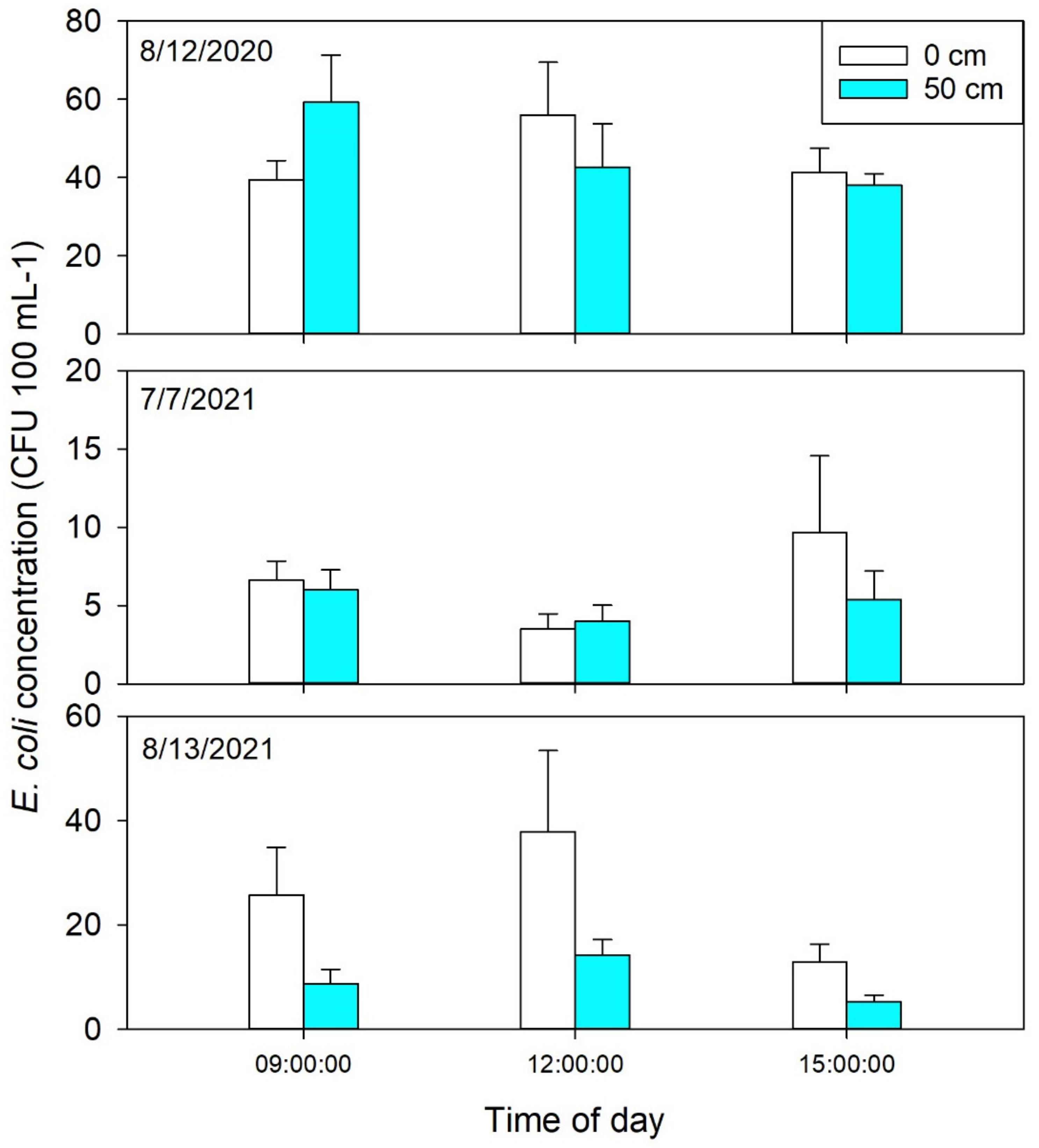
| Site | Date | Time | Depth | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pond 1 | 9/6/2019 | 0.321 | 0.368 | 0.861 |
| Pond 1 | 7/23/2020 | 0.000 | 0.183 | 0.859 |
| Pond 2 | 9/15/2019 | 0.087 | 0.274 | 0.128 |
| Pond 2 | 9/21/2019 | 0.433 | 0.822 | 0.374 |
| Pond 2 | 7/15/2020 | 0.494 | 0.336 | 0.987 |
| Pond 2 | 8/10/2020 | 0.579 | 0.000 | 0.748 |
| Pond 2 | 8/26/2020 | 0.002 | 0.028 | 0.788 |
| Pond 2 | 7/15/2021 | 0.529 | 0.001 | 0.393 |
| Pond 3 | 8/12/2020 | 0.632 | 0.621 | 0.271 |
| Pond 3 | 7/7/2021 | 0.270 | 0.554 | 0.840 |
| Pond 3 | 8/13/2021 | 0.182 | 0.098 | 0.733 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stocker, M.D.; Smith, J.E.; Pachepsky, Y.A. Depth-Dependent Concentrations of E. coli in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds. Water 2022, 14, 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142276
Stocker MD, Smith JE, Pachepsky YA. Depth-Dependent Concentrations of E. coli in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds. Water. 2022; 14(14):2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142276
Chicago/Turabian StyleStocker, Matthew D., Jaclyn E. Smith, and Yakov A. Pachepsky. 2022. "Depth-Dependent Concentrations of E. coli in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds" Water 14, no. 14: 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142276
APA StyleStocker, M. D., Smith, J. E., & Pachepsky, Y. A. (2022). Depth-Dependent Concentrations of E. coli in Agricultural Irrigation Ponds. Water, 14(14), 2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142276






