An Analysis of Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions Based on Isotopic Data from the Kaidu River Basin, South Tianshan Mountain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
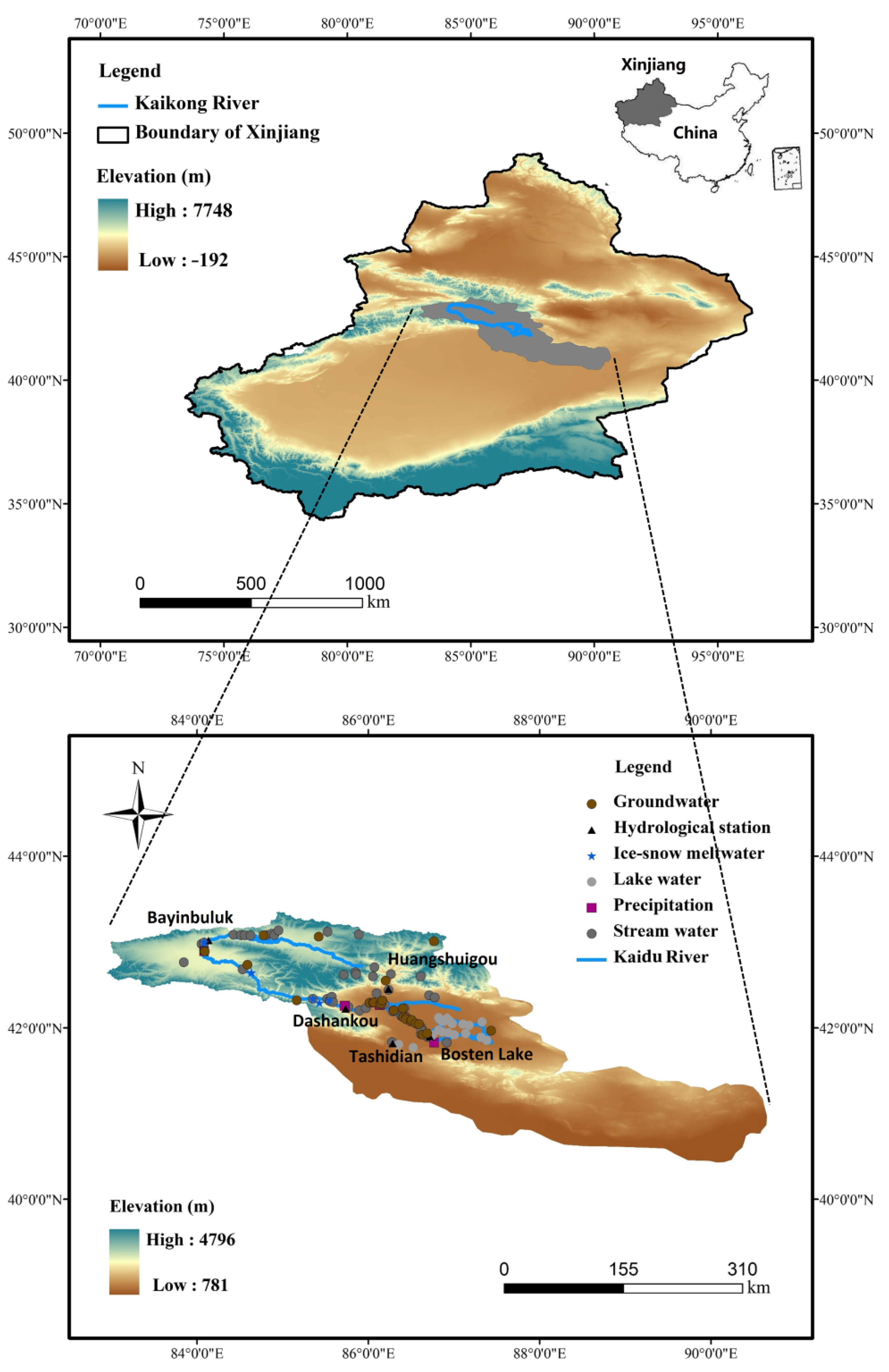
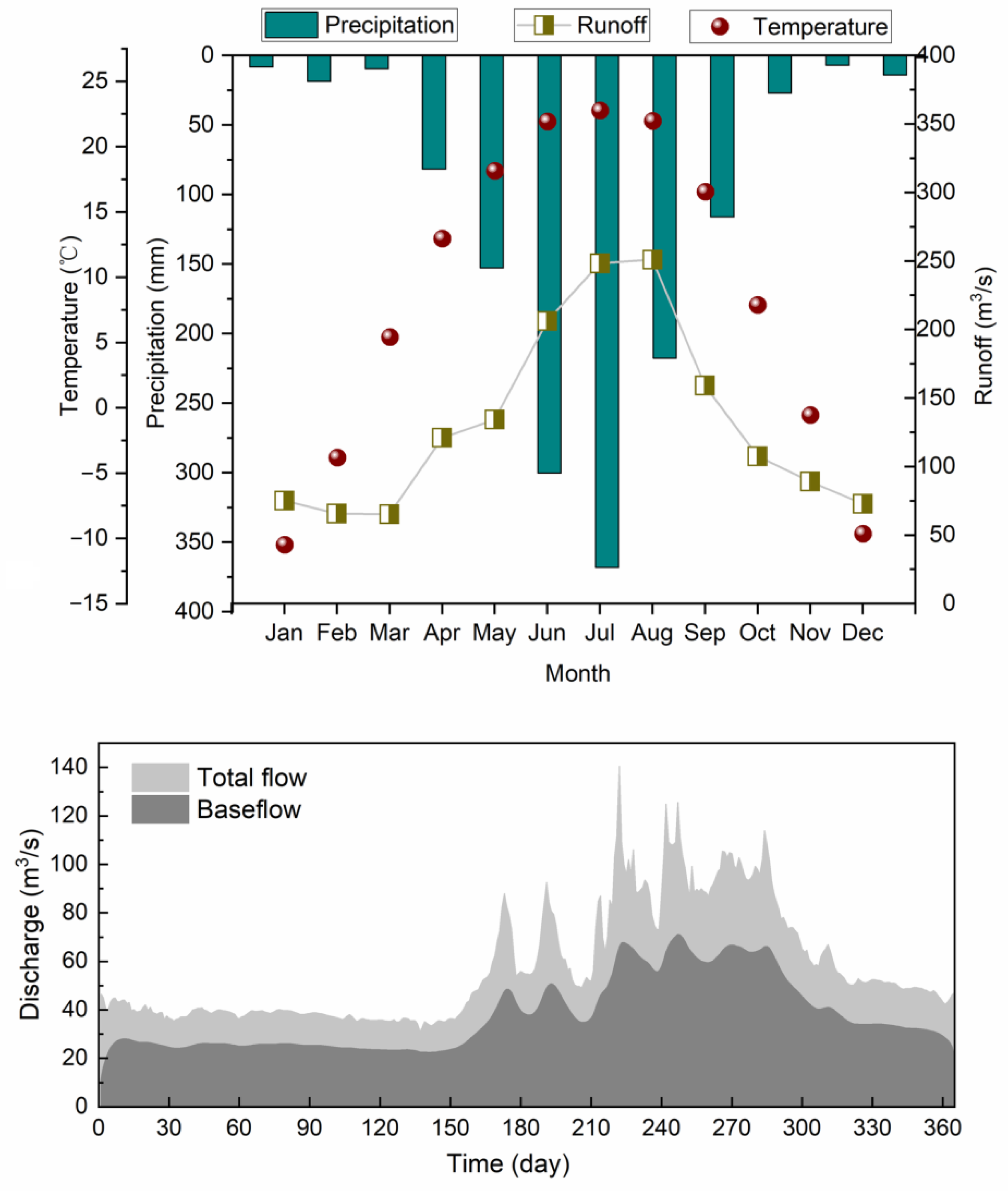
2.1. Meteorological and Hydrological Conditions of the Studied Area
2.2. Sampling and Data Analysis
2.3. Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopic Measurement
2.4. Hydrograph Separation and Data Analysis
2.4.1. Baseflow Digital Filter
2.4.2. End-Member Mixing Analysis (EMMA)
2.4.3. Bayesian Mixing Model (MixSIAR)
2.4.4. Meteorological Data Collection and Analysis
3. Results
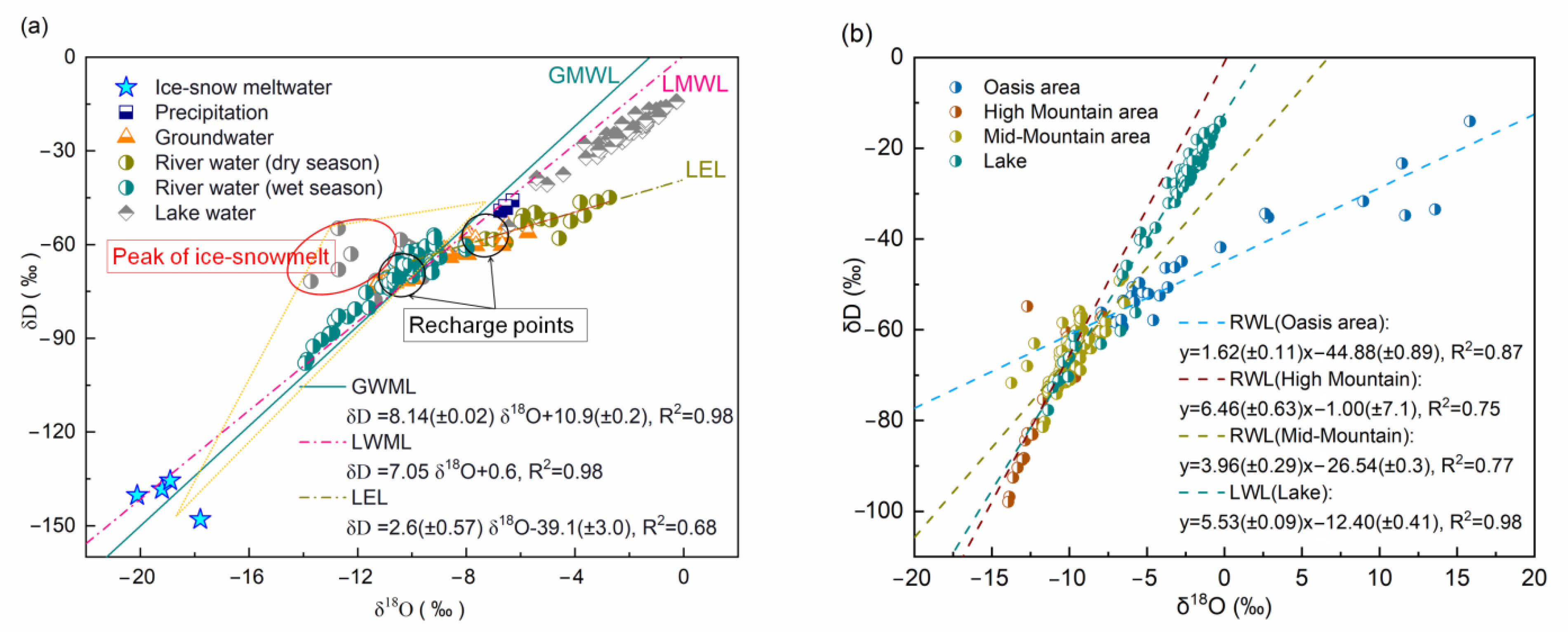
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Water Isotopes
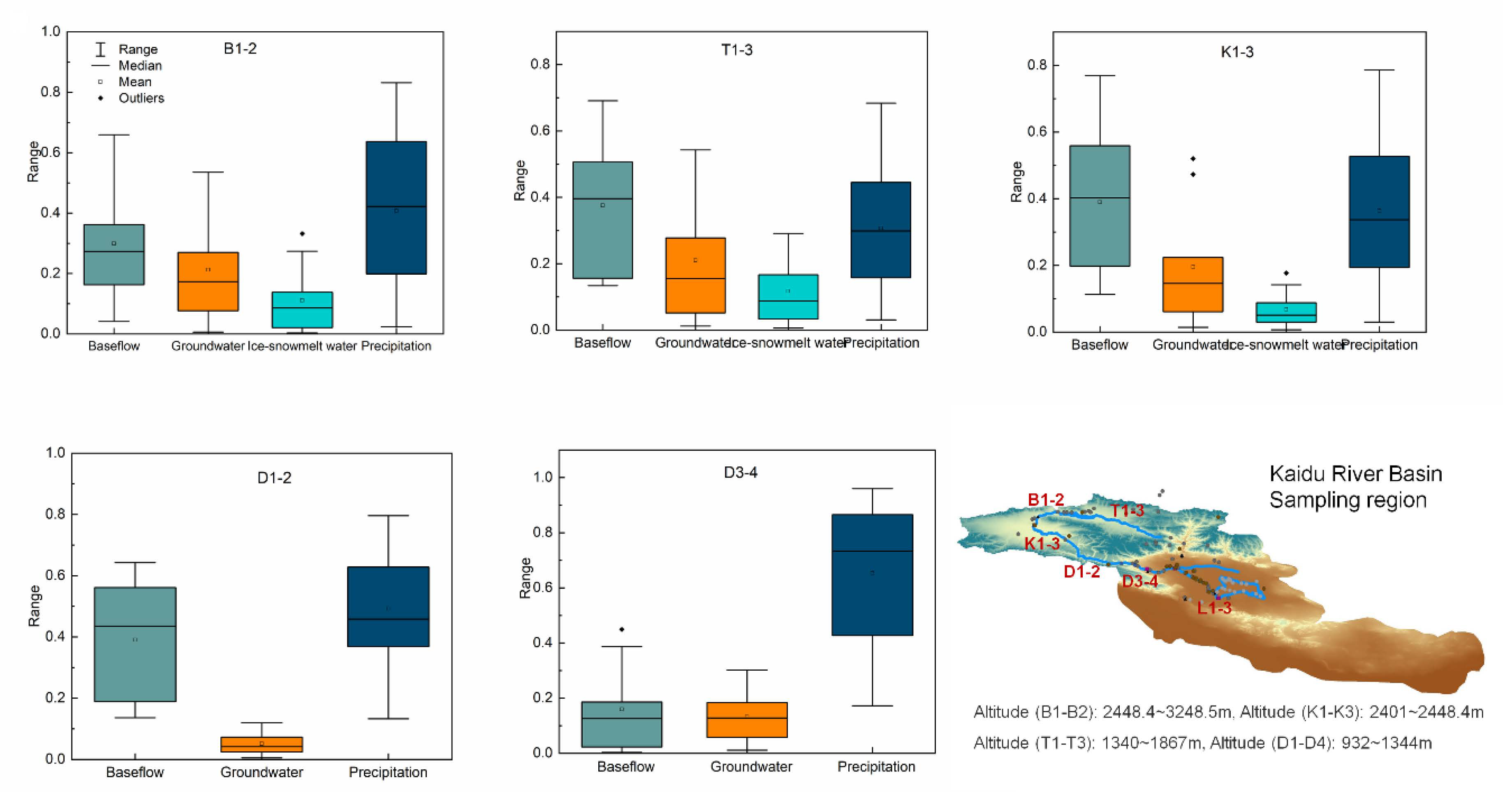
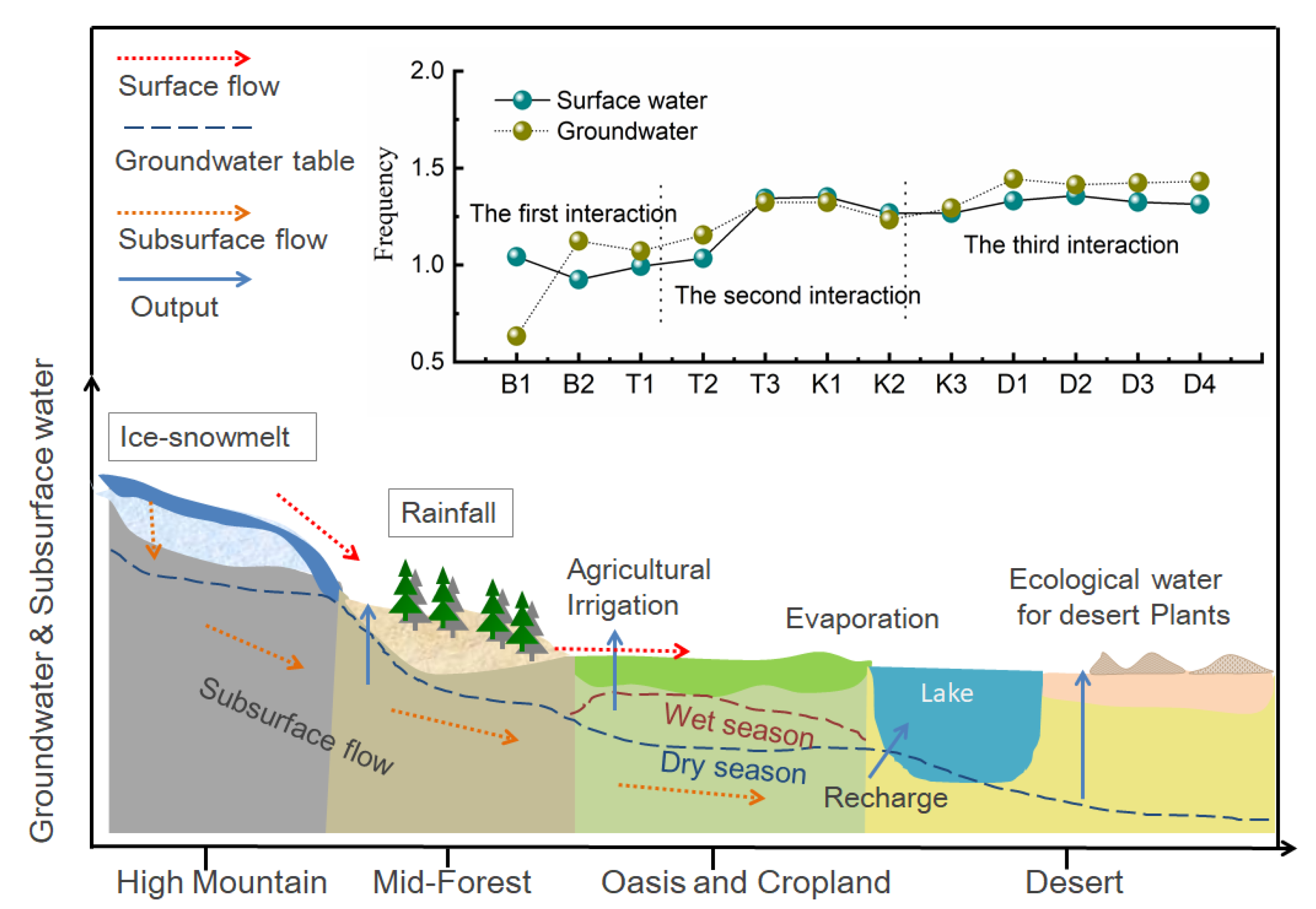
3.2. Surface Water–Groundwater Interaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, R.G.; Scanlon, B.; Döll, P.; Rodell, M.; Van Beek, R.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Leblanc, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Edmunds, M.; et al. Ground water and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Pang, Z.H.; Chen, Y.N.; Kong, Y.L.; Tianming, H.; Zhonghe, P.; Yaning, C.; Yanlong, K.; Huang, T.M.; Pang, Z.H.; et al. Groundwater circulation relative to water quality and vegetation in an arid transitional zone linking oasis, desert and river. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 3088–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, S.; Hu, H.; Yang, D.; Liu, Q. Irrigation impact on annual water balance of the oases in Tarim Basin, Northwest China. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.G.; Scott, R.L.; Huxman, T.E.; Goodrich, D.C.; Lin, G. Sensitivity of riparian ecosystems in arid and semiarid environments to moisture pulses. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 3191–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Pang, Z. The role of deuterium excess in determining the water salinisation mechanism: A case study of the arid Tarim River Basin, NW China. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Edwards, T.W.D.; Birks, S.J.; St Amour, N.A.; Buhay, W.M.; McEachern, P.; Wolfe, B.B.; Peters, D.L. Progress in isotope tracer hydrology in Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriano, M.; Howard, K.W.; Eyles, N. The role of midsummer urban aquifer recharge in stormflow generation using isotopic and chemical hydrograph separation techniques. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, T.; He, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, N.; Du, J.; Wang, C. Characteristics of water stable isotopes and hydrograph separation in Baishui catchment during the wet season in Mt.Yulong region, south western China. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3641–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenschmidt, C.; Ingwersen, J.; Sangchan, W.; Sukvanachaikul, Y.; Duffner, A.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Streck, T. A three-component hydrograph separation based on geochemical tracers in a tropical mountainous headwater catchment in northern Thailand. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Li, Q. Characteristics of water isotopes and ice-snowmelt quantification in the Tizinafu River, north Kunlun Mountains, Central Asia. Quat. Int. 2015, 380–381, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litt, G.F.; Gardner, C.B.; Ogden, F.L.; Lyons, W.B. Hydrologic tracers and thresholds: A comparison of geochemical techniques for event-based stream hydrograph separation and flowpath interpretation across multiple land covers in the Panama Canal Watershed. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 63, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behrens, D.; Langman, J.B.; Brooks, E.S.; Boll, J.; Waynant, K.; Moberly, J.G.; Dodd, J.K.; Dodd, J.W. Tracing δ18O and δ2H in Source Waters and Recharge Pathways of a Fractured-Basalt and Interbedded-Sediment Aquifer, Columbia River Flood Basalt Province. Geosciences 2021, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, G.; Engdahl, N.B.; Langman, J.B. A Basin-Scale Groundwater Flow Model of the Columbia Plateau Regional Aquifer System in the Palouse (USA): Insights for Aquifer Vulnerability Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 15, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, I.; van Beek, L.; Wada, Y.; Bierkens, M.F. Dynamic attribution of global water demand to surface water and groundwater resources: Effects of abstractions and return flows on river discharges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 64, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Hou, G.; Su, X.; Wang, D.; Dong, J.; Hao, Y.; Wang, X. Isotopes (δD and δ18O) in precipitation, groundwater and surface water in the Ordos Plateau, China: Implications with respect to groundwater recharge and circulation. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, K.; Hollins, S.; Hughes, C.; Cendón, D.; Stone, D. The influence of groundwater/surface water exchange on stable water isotopic signatures along the darling river, NSW, Australia. In Groundwater and Ecosystems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kanduč, T.; Grassa, F.; McIntosh, J.; Stibilj, V.; Ulrich-Supovec, M.; Supovec, I.; Jamnikar, S. A geochemical and stable isotope investigation of groundwater/surface-water interactions in the Velenje Basin, Slovenia. Appl. Hydrogeol. 2014, 22, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wenninger, J.; Uhlenbrook, S. A multi-method approach to quantify groundwater/surface water-interactions in the semi-arid Hailiutu River basin, northwest China. Appl. Hydrogeol. 2014, 22, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, M. Tracing the Sources and Processes of Groundwater in an Alpine Glacierized Region in Southwest China: Evidence from Environmental Isotopes. Water 2015, 7, 2673–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Wu, J.; Song, F.; Abuduwaili, J.; Saparov, A.; Chen, X.; Shen, B. Spatial distribution and controlling factors of surface water stable isotope values (δ18O and δ2H) across Kazakhstan, Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poca, M.; Nosetto, M.D.; Ballesteros, S.; Castellanos, G.; Jobbágy, E.G. Isotopic insights on continental water sources and transport in the mountains and plains of Southern South America. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2020, 56, 586–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA. IAEA/GNIP precipitation sampling guide V2.02. Glob. Netw. Isot. Precip. 2014. Available online: http://www-naweb.iaea.org/napc/ih/documents/other/gnip_manual_v2.02_en_hq.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourcy, L.; Groening, M.; Aggarwal, P. Stable Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopes in Precipitation. In Isotopes in the Water Cycle: Past, Present and Future of a Developing Science; IEA: Paris, Franch, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Froehlich, K.; Huang, T.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, F. Processes affecting isotopes in precipitation of an arid region. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyne, V.D.; Hollick, M. Stochastic time-variable rainfall-runoff modelling. In Institute of Engineers Australia National Conference; Institute of Engineers Australia: Barton, Australia, 1979; Volume 79, pp. 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, R.J.; McMahon, T.A. Evaluation of automated techniques for base flow and recession analyses. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, R.P. Diagnostic tools for mixing models of stream water chemistry. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, B.C.; Jackson, A.L.; Ward, E.J.; Parnell, A.C.; Phillips, D.L.; Semmens, B.X. Analyzing mixing systems using a new generation of Bayesian tracer mixing models. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.-Y.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, X. Contrasting water use pattern of introduced and native plants in an alpine desert ecosystem, Northeast Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.; Shah, M.; Deshpande, R.D.; Bhardwaj, R.M.; Prasad, A.; Gupta, S.K. Hydrograph separation and precipitation source identification using stable water isotopes and conductivity: River Ganga at Himalayan foothills. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z. Diminished groundwater recharge and circulation relative to degrading riparian vegetation in the middle Tarim River, Xinjiang Uygur, Western China. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 2274, 2267–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Variation of baseflows in the headstreams of the Tarim River Basin during 1960–2007. J. Hydrol. 2013, 487, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Fu, C. Spatial variations of hydrochemistry and stable isotopes in mountainous river water from the Central Asian headwaters of the Tajikistan Pamirs. CATENA 2020, 193, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, N.; An, S.; Bai, X.; Liu, F.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S. Characteristics of water isotopes and hydrograph separation during the wet season in the Heishui River, China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 353, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwey, J.L. Isotopes in Groundwater Hydrology; IAHS-AISH Publication: Wallingford, UK, 1984; Volume 144, pp. 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, A.; Fu, B.; Kano, K.-I.; Maruyama, T.; Guo, J. Late Quaternary right-lateral displacement along active faults in the Yanqi Basin, southeastern Tian Shan, northwest China. Tectonophysics 2002, 354, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wen, X.; Rao, W.; Bradd, J.; Huang, J. Temporal variation of stable isotopes in a precipitation-groundwater system: Implications for determining the mechanism of groundwater recharge in high mountain-hills of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Sampling Region | Water Type | No. | δ18O(‰ V-SMOW) | δ18O Std. Dev | δD(‰ V-SMOW) | δD Std. Dev | D-Excess | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | Mean (‰) | |||||
| Mountain area | Ice-snowmelt | 70 | −17.80 | −20.12 | −18.96 | 0.02 | −140.25 | −147.91 | −144.08 | 0.10 | 7.60 |
| Precipitation | −3.63 | −4.98 | −4.73 | 0.04 | −46.89 | −52.22 | −49.05 | 0.75 | −13.82 | ||
| River water | 15.82 | −13.73 | −8.22 | 0.07 | −14.07 | −81.43 | −62.26 | 0.69 | 4.05 | ||
| Groundwater | 8.96 | −11.37 | −7.25 | 0.04 | −31.65 | −72.72 | −60.05 | 0.68 | −2.23 | ||
| Oasis area | Precipitation | 120 | −3.87 | −6.61 | −5.24 | 0.06 | −53.12 | −54.65 | −53.88 | 1.28 | −11.96 |
| River water | −5.73 | −13.94 | −10.45 | 0.07 | −45.88 | −97.96 | −69.84 | 0.93 | 13.79 | ||
| Groundwater | −7.97 | −10.62 | −9.37 | 0.10 | −60.27 | −70.07 | −64.90 | 0.72 | 10.05 | ||
| Lake | Lake water | 89 | −0.25 | −9.99 | −2.79 | 0.06 | −14.12 | −66.03 | −27.77 | 0.64 | −5.43 |
| Groundwater | −9.93 | −10.90 | −10.51 | 0.07 | −61.66 | −72.49 | −69.00 | 0.94 | 15.08 | ||
| Along Kaidu River | Region | Water Type | Per (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr (‰) | Cu (‰) | Cu2 (‰) | Cg (‰) | |||
| A. High mountain | B1 | −4.89 | −3.66 | / | −8.96 | 23 |
| B2 | −3.19 | −0.25 | −13.59 | −7.94 | 28 | |
| K1 | −5.48 | −4.58 | / | −6.52 | 46 | |
| K2 | −5.27 | −4.19 | / | −6.64 | 44 | |
| B. Mid-mountain | K3 | −10.26 | −10.29 | / | −10.15 | 21 |
| T1 | −10.32 | −10.37 | −10.29 | −10.15 | 23 | |
| C. Oasis area | T2 | −10.05 | −10.00 | / | −10.12 | 42 |
| T3 | −8.99 | −10.26 | −9.93 | 12 | ||
| D1 | −10.07 | −10.14 | −10.01 | −10.90 | −9 | |
| D2 | −9.95 | −10.03 | −10.26 | −10.72 | −12 | |
| D3 | −8.42 | −9.03 | / | −10.98 | −31 | |
| D4 | −9.92 | −10.20 | / | −10.63 | −65 | |
| D. Lake | L1 | −10.08 | −2.27 | / | −10.12 | 99 |
| L2 | −10.03 | −1.45 | / | −10.72 | 93 | |
| L3 | −10.03 | −1.45 | / | −10.72 | 93 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yu, S.; Shang, H. An Analysis of Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions Based on Isotopic Data from the Kaidu River Basin, South Tianshan Mountain. Water 2022, 14, 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142259
Fan Y, Wu Y, Wang Y, Jiang S, Yu S, Shang H. An Analysis of Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions Based on Isotopic Data from the Kaidu River Basin, South Tianshan Mountain. Water. 2022; 14(14):2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142259
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yuting, Ye Wu, Yun Wang, Shengxia Jiang, Shulong Yu, and Huaming Shang. 2022. "An Analysis of Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions Based on Isotopic Data from the Kaidu River Basin, South Tianshan Mountain" Water 14, no. 14: 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142259






