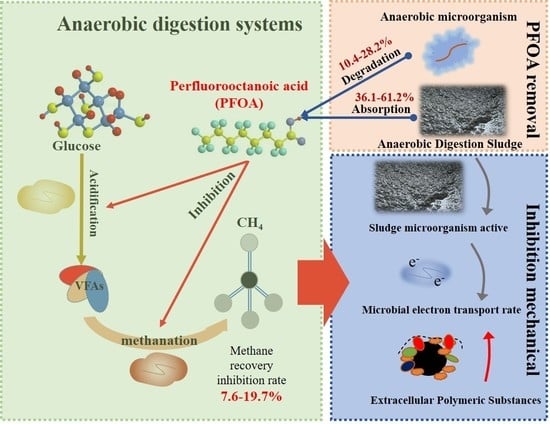
Insight into the Impacts and Removal Pathways of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Anaerobic Digestion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate and Inoculum
2.2. The Batch Test Design and Operation
2.3. Determination Indexes and Analysis Methods
2.4. Data Analysis Method
3. Results and Discussion
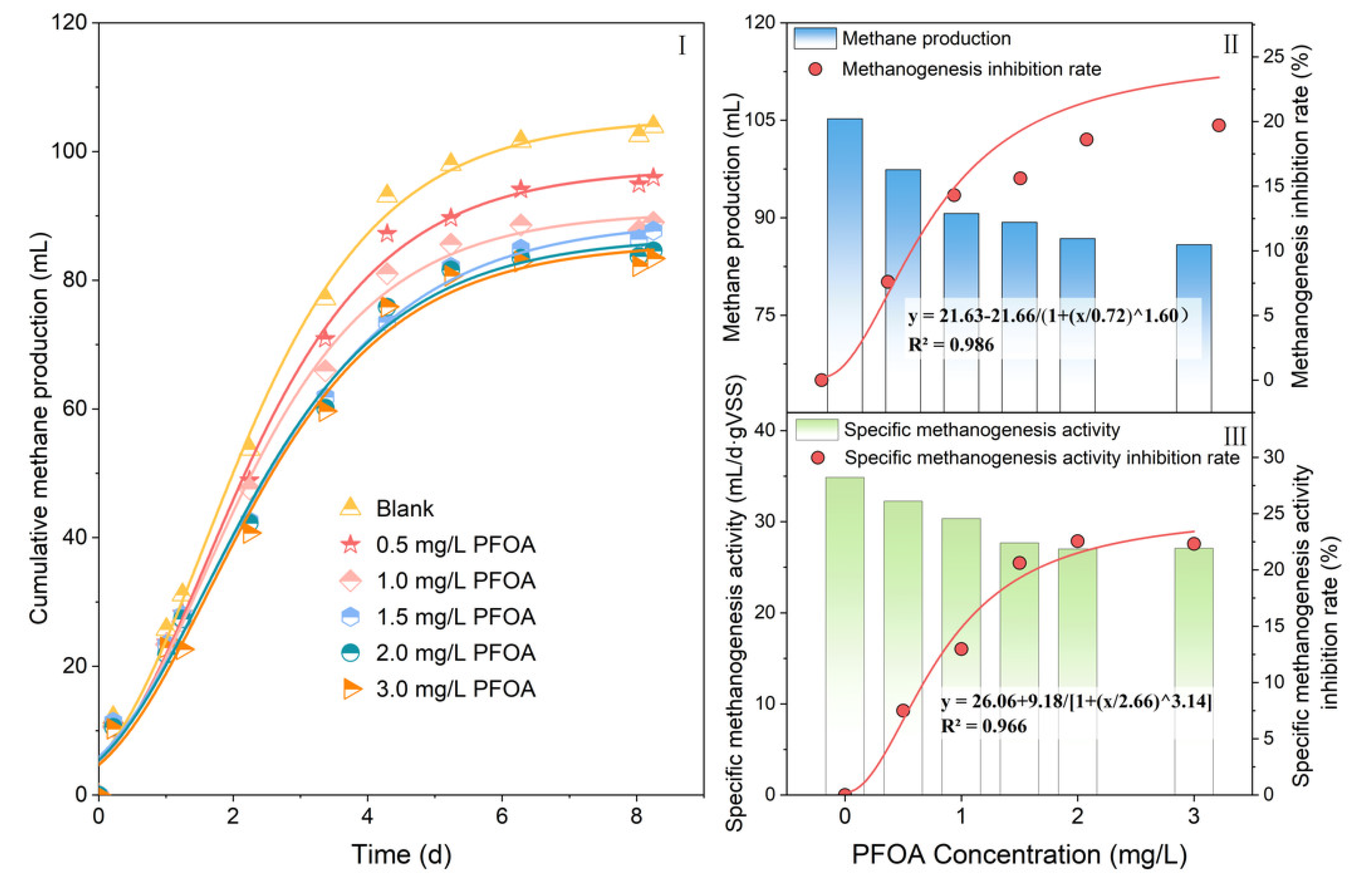
3.1. Effects of PFOA on Energy Recovery
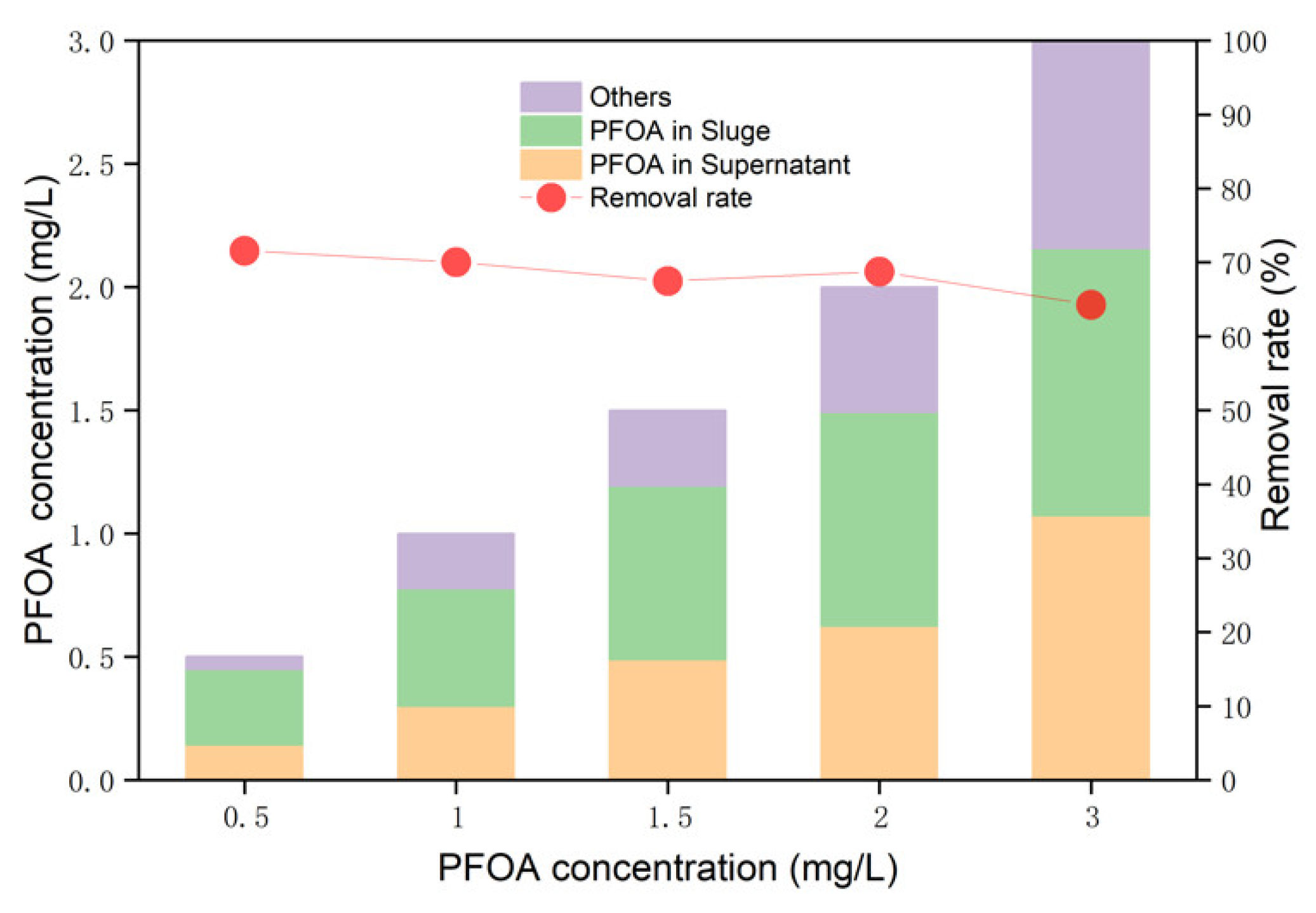
3.2. Process and Performance of PFOA Removal in AD
3.3. Inhibition Mechanism of Anaerobic Digestion under PFOA Exposure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, D.N.; Li, X.R.; Quinete, N. Occurrence, fate, sources and toxicity of PFAS: What we know so far in Florida and major gaps. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauchy, X.; Boiteux, V.; Bach, C.; Colin, A.; Hemard, J.; Rosin, C.; Munoz, J.F. Mass flows and fate of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the wastewater treat ment Plant of a fluorochemical manufacturing facility. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmler, H.-J. Synthesis of environmentally relevant fluorinated surfactants—A review. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1471–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, T.; Liu, S.; Johnson, A.C.; Sweetman, A.J.; Baninla, Y. Pollution pathways and release estimation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in central and eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, J.; Nguyen, H.T.; Vijayasarathy, S.; Du, P.; Li, X.; Yao, H.; Mueller, J.F.; Thai, P.K. Occurrence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in wastewater of major cities across China in 2014 and 2016. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, N.; Ashima, Y.K. Toxicity and toxicokinetics of perfluorooctanoic acid in humans and animals. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 28, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Toxicology Program. Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Perfluorooctanoic Acid Administered in Feed to Sprague Dawley (Hsd: Sprague Dawley SD) Rats. Res. Triangle Park 2020, 598, NTP-TR-598. [Google Scholar]
- Field, J.A.; Seow, J. Properties, occurrence, and fate of fluorotelomer sulfonates. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 643–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xie, G.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Yang, B. Adverse bioeffect of perfluorooctanoic acid on liver metabolic function in mice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4787–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, A.; Masetti, R.; Gazzotti, T.; Zama, D.; Astolfi, A.; Veyrand, B.; Pession, A.; Pagliuca, G. Perfluoroalkyl substances in human milk: A first survey in Italy. Environ. Int. 2013, 51, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Dou, Y.; He, J.; Kong, D. Perfluoroalkyl substances in drinking water sources along the Yangtze River in Jiangsu Province, China: Human health and ecological risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 218, 112289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Ying, G.-G.; Hong, H.; Deng, W.-J. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the urine and hair of preschool children, airborne particles in kindergartens, and drinking water in Hong Kong. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Mair, D.C.; Church, T.R.; Ellefson, M.E.; Reagen, W.K.; Boyd, T.M.; Herron, R.M.; Medhdizadehkashi, Z.; Nobiletti, J.B.; Rios, J.A.; et al. Decline in Perfluorooctanesulfonate and Other Polyfluoroalkyl Chemicals in American Red Cross Adult Blood Donors, 2000—2006. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4989–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, E.; Li, Y.; Niu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X. Photocatalytic degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid over Pb-BiFeO3/rGo catalyst: Kinetics and mechanism. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, S.P.; Kah, M.; Padhye, L.P. A review of the occurrence, transformation, and removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2021, 199, 117187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Gong, C.; Li, M. Volatile fatty acids production from food waste: Effects of pH, temperature, and organic loading rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Saady, N.M.C.; Torrijos, M.; Thanikal, J.V.; Hung, Y.T. Sustainable Agro-Food Industrial Wastewater Treatment Using High Rate Anaerobic Process. Water 2013, 5, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mudhoo, A.; Kumar, S. Effects of heavy metals as stress factors on anaerobic digestion processes and biogas production from biomass. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Lichtfouse, E.; Li, Z.; Kumar, P.S.; Liu, J.; Feng, D.; Yang, Q.; Liu, F. Effect of Antibiotics on the Microbial Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion of Wastewater: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 611613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Peng, L.; Redina, M.M.; Gao, T.; Khan, A.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Perfluorooctane sulfonate decreases the performance of a sequencing batch reactor system and changes the sludge microbial community. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Yuan, R.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H. A review of responses of terrestrial organisms to perfluorinated compounds. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Liao, Y.; Su, C.; Tang, L.; Qi, Z.; Wei, L.; Wu, J.; Gao, S. Effects of PFOA on the physicochemical properties of anaerobic granular sludge: Performance evaluation, microbial community and metagenomic analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Wei, W.; Ni, B.-J. Unravelling the impacts of perfluorooctanoic acid on anaerobic sludge digestion process. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 149057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, N.; Yang, J.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Tang, L.; Xia, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; et al. Interaction between perfluorooctanoic acid and aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojanowicz, M.; Bojanowska-Czajka, A.; Bartosiewicz, I.; Kulisa, K. Advanced Oxidation/Reduction Processes treatment for aqueous perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS)—A review of recent advances. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 170–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Xu, R.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Xiao, E.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Gao, P.; Yang, Z.; Lin, H.; et al. Effects of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) on activated sludge microbial community under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 286, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesters, R.J.W.; Schröder, H.F. Perfluorooctane sulfonate—A quite mobile anionic anthropogenic surfactant, ubiquitously found in the environment. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 5, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA (American Public Health Association). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA (American Public Health Association): Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Maurines-Carboneill, C.; Pernelle, J.J.; Morin, L.; Sachon, G.; Leblon, G. Relevance of the INT response as an indicator of ETS activity in monitoring heterotrophic aerobic bacterial populations in activated sludges. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. A comparison study on membrane fouling in a sponge-submerged membrane bioreactor and a conventional membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 165, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Mao, R.; Li, X.; Song, S.; Zhao, J.; Yu, M.; Shi, Y.; et al. Biomanipulation impacts on per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances accumulation and trophic transfer in an eutrophic lake. Environ. Int. 2022, 160, 107057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, G.; Dzakpasu, M.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, R. New insights into the mechanisms underlying biochar-assisted sustained high-efficient co-digestion: Reducing thermodynamic constraints and enhancing extracellular electron transfer flux. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, M.; Fernández, R.; Gutiérrez, M.; Siles, J. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of pre-treated orange peel: Modelling of methane production. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Aihemaiti, A.; Meng, Y.; Yang, M.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zou, Q.; Chen, X. Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution using MgO-modified magnetic biochar derived from anaerobic digestion residue. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulders, M.; Estevez-Alonso, A.; Stouten, G.R. Volatile fatty acid product spectrum as a function of the solids retention time in an anaerobic granular sludge process. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zou, M.; Yang, X.; Tsang, Y.F.; Chen, H. Perfluorooctanoic acid triggers oxidative stress in anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Basu, S.; Balakrishnan, M. Comprehensive treatment scheme for distillery wastewater targeting recovery of water, antioxidant compounds and biogas. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Deng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, Q.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Sorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate on activated sludge. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavari, E.; Rouch, D.; Khudur, L.S.; Thomas, D.; Aburto-Medina, A.; Ball, A.S. Challenges and Current Status of the Biological Treatment of PFAS—Contaminated Soils. Microbiol. Physiol. Metab. 2021, 8, 602040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedt, O.; Mergelsberg, M.; Eisenreich, W.; Boll, M. Promiscuous Defluorinating Enoyl-CoA Hydratases/Hydrolases Allow for Complete Anaerobic Degradation of 2-Fluorobenzoate. Microbiol. Physiol. Metab. 2017, 8, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zhong, Y.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, L.; Yi, K.; Zeng, G. Enhanced dewaterability of waste activated sludge by Fe(II)—activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, H.Q.; Li, X.Y. Probing the contribution of extracellular polymeric substance fractions to activated-sludge bioflocculation using particle image velocimetry in combination with extended DLVO analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Wang, L.; Su, H. Role and influence of extracellular polymeric substances on the preparation of aerobic granular sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Kang, Y. Characterization of sulfate-reducing bacteria anaerobic granular sludge and granulometric analysis with grey relation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 1829–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, X.; Xi, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xie, T.; Liu, Y.; Quan, B.; Zhang, C.; et al. Insight the roles of loosely-bound and tightly-bound extracellular polymeric substances on Cu2+, Zn2+ and Pb2+ biosorption process with Desulfovibrio vulgaris. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 596, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Lin, X.; Chen, Z.; Su, C.; Zhu, F.; Yang, W.; Chen, Z.; Lu, P. Evaluation of characteristics and microbial community of anaerobic granular sludge under microplastics and aromatic carboxylic acids exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| PFOA Concentration (mg/L) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| Langmuir model R2 | 0.7926 | 0.6713 | 0.8221 | 0.8632 | 0.9079 |
| Freundlich model R2 | 0.9789 | 0.9898 | 0.9858 | 0.9902 | 0.9796 |
| Saturated adsorption capacity (ug/g·VSS) | 38.5182 | 84.8912 | 122.1567 | 161.8340 | 239.5228 |
| PFOA Concentration (mg/L) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 3.0 | |
| PFOA in sludge | Proportion (%) | 61.2 | 47.7 | 47.0 | 43.4 | 36.1 |
| Content (mg/L) | 0.307 | 0.477 | 0.705 | 0.868 | 1.084 | |
| PFOA in supernatant | Proportion (%) | 28.4 | 29.9 | 32.5 | 31.23 | 35.7 |
| Content (mg/L) | 0.142 | 0.299 | 0.488 | 0.624 | 1.072 | |
| Others | Proportion (%) | 10.4 | 22.4 | 20.5 | 25.37 | 28.2 |
| Content (mg/L) | 0.053 | 0.223 | 0.307 | 0.507 | 0.843 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, Z.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Y. Insight into the Impacts and Removal Pathways of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Anaerobic Digestion. Water 2022, 14, 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142255
Xie H, Chen Y, Wang Y, Kong Z, Cao W, Zhang Y. Insight into the Impacts and Removal Pathways of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Anaerobic Digestion. Water. 2022; 14(14):2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142255
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Hongyu, Yuqi Chen, Yuzheng Wang, Zhe Kong, Wenzhi Cao, and Yanlong Zhang. 2022. "Insight into the Impacts and Removal Pathways of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Anaerobic Digestion" Water 14, no. 14: 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142255
APA StyleXie, H., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Kong, Z., Cao, W., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Insight into the Impacts and Removal Pathways of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Anaerobic Digestion. Water, 14(14), 2255. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142255