Geochemical Characterization of Natural Groundwater on the Southern Slopes of the Caucasus Mountains on the Russian Black Sea Coast
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
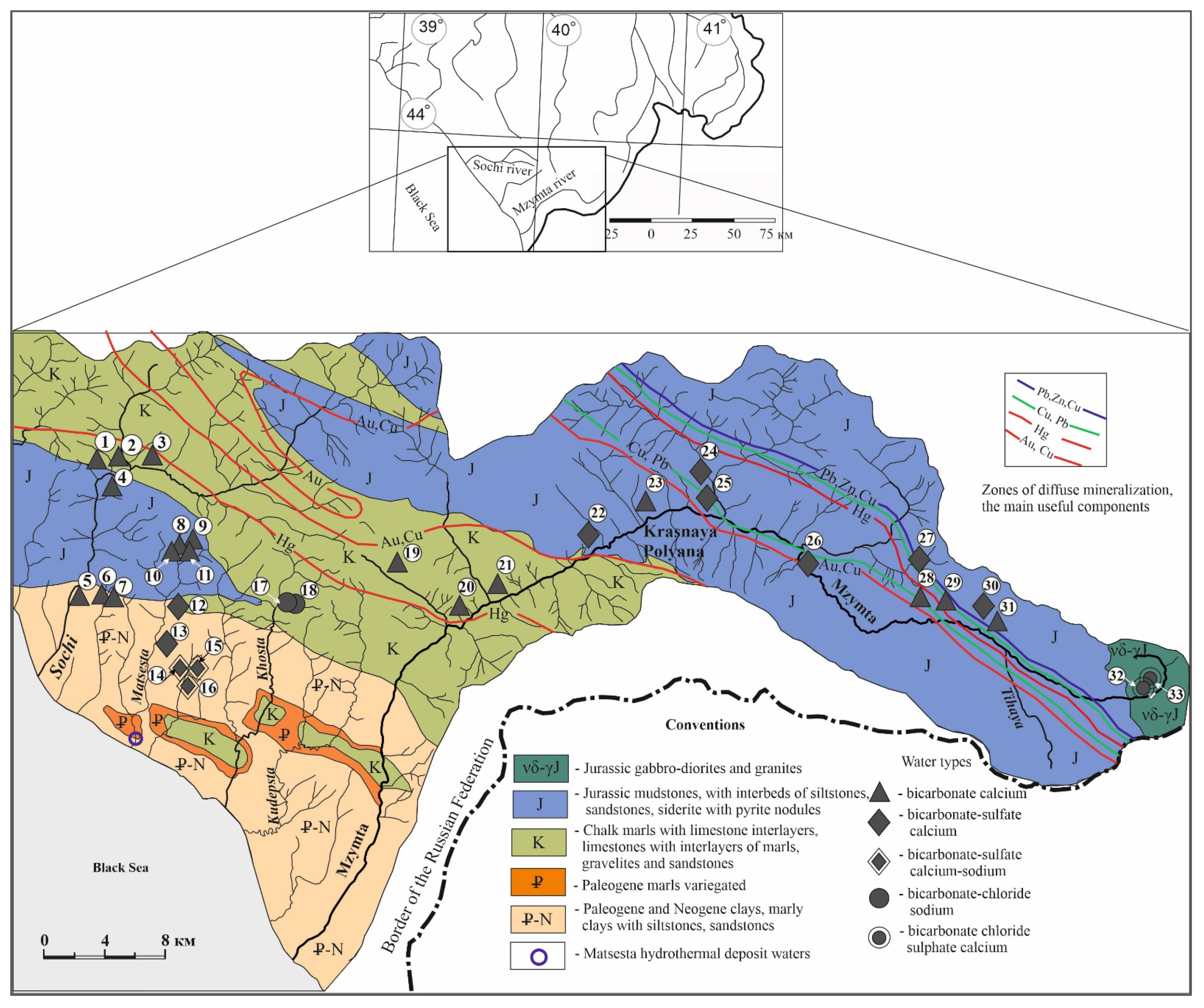
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Geological Conditions
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Geochemical Characterization and Statistical Analysis of Groundwater
3. Results
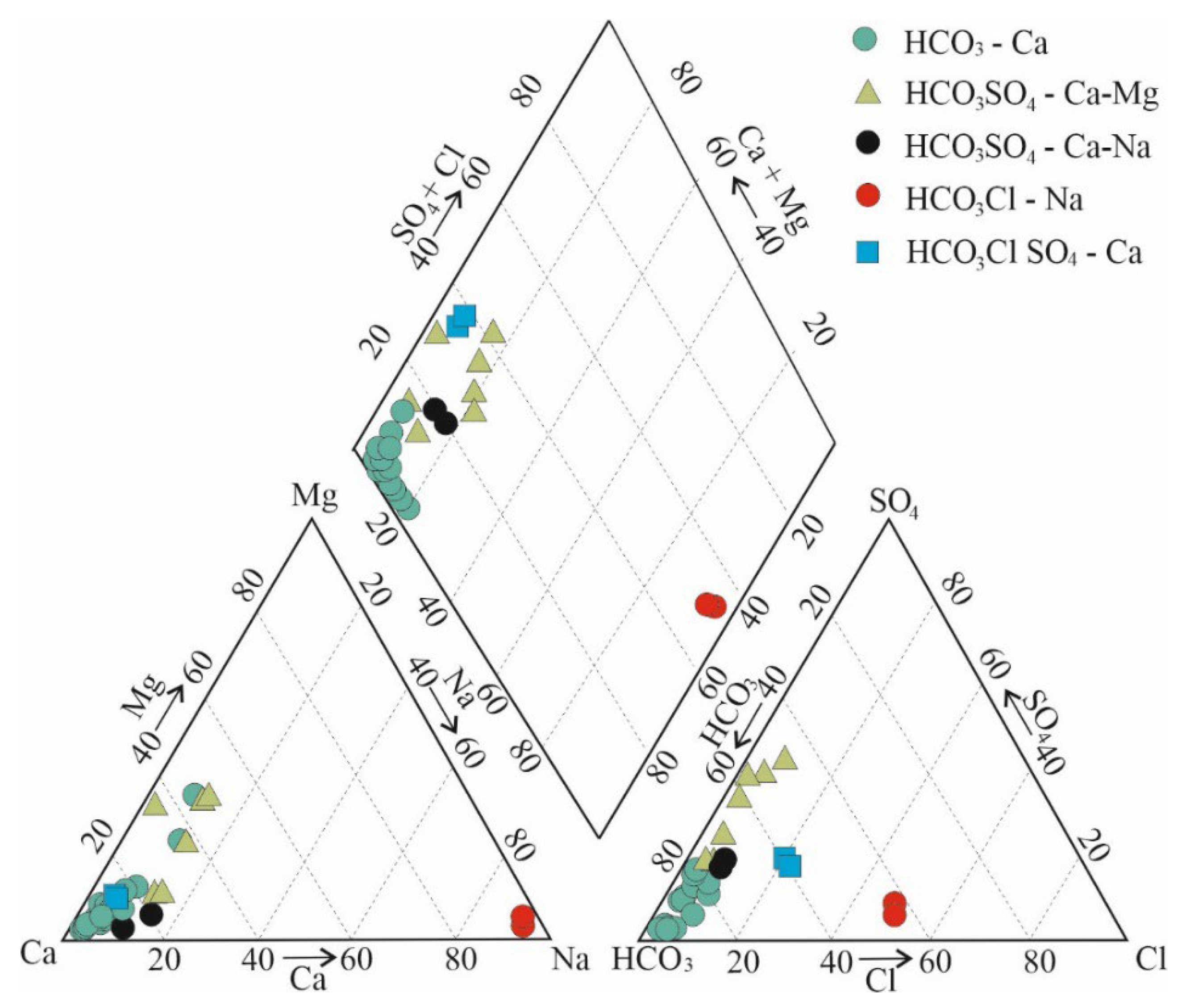
3.1. Macro-Elemental Chemical Composition of Groundwater
- bicarbonate-calcium;
- bicarbonate-sulfate calcium-magnesium;
- bicarbonate-sulfate calcium-sodium;
- bicarbonate-chloride sodium;
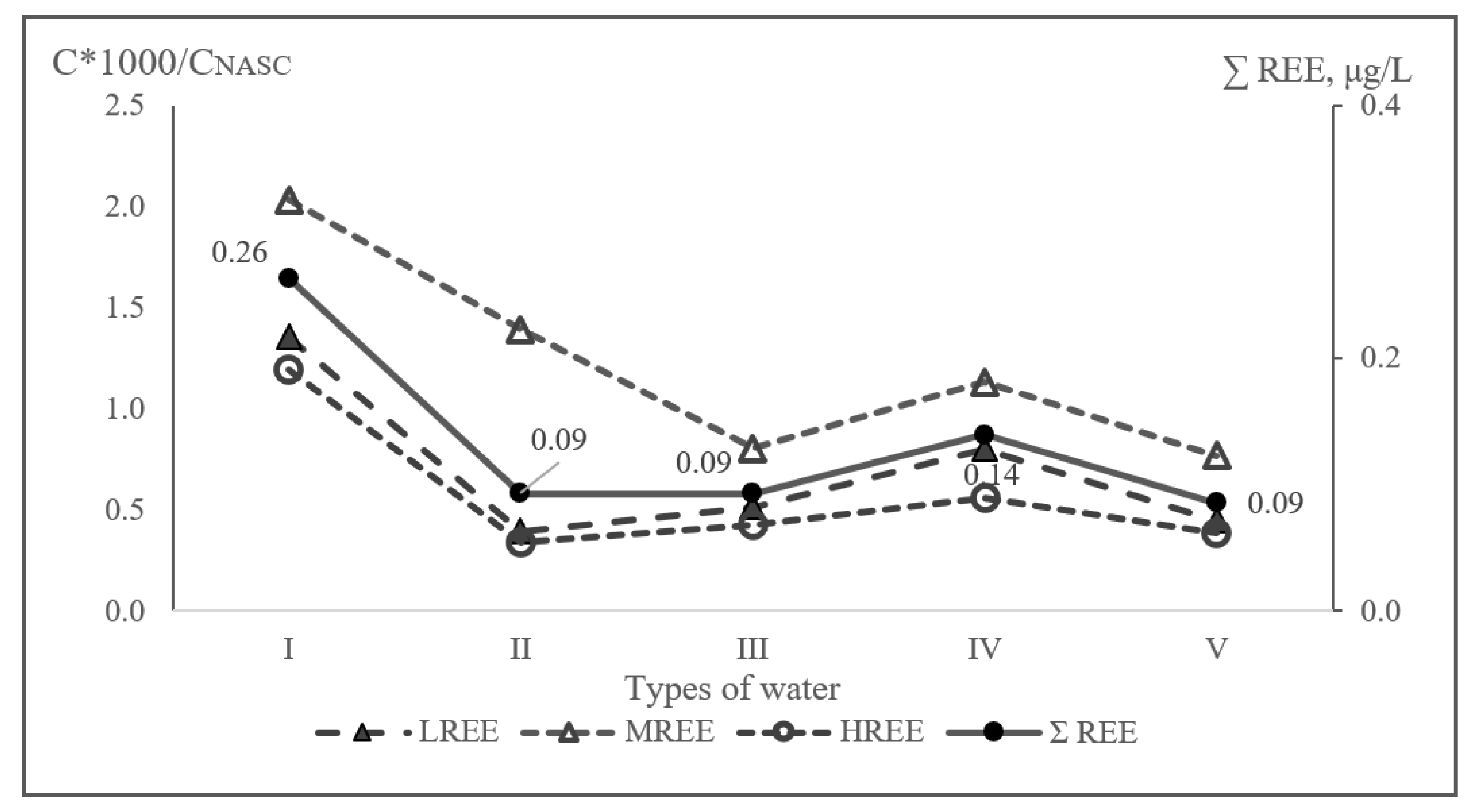
3.2. Groundwater Elemental Composition
3.3. Factor Analysis of the Elemental Composition of Groundwater
- Factor 1—31.8% K > 0.9 Re > 0.8 (Rb, Sr, U, Li, Ba, B, S) > 0.7 (Ca, Na) > 0.6
- (LREEs, MREEs, HREEs) > 0.5 (Mn, Mo, Cu, Al) > 0.4 (Y, Si) > 0.3
- Ag < −0.24
- Factor 2—18.2% (Y, Al, MREEs, LREEs) > 0.7 HREEs > 0.6 (Mn, Pb) > 0.4 Zn > 0.3
- (Cu, V) > 0.24
- (Mg, Si) < −0.5 (Li, S) < −0.4 (Cs, Sr) < −0.3 (Rb, Na,) < −0.24
- Factor 3—11.0% Ca > 0.4 Y > 0.3 (HREEs, V, MREEs) > 0.24
- (Pb, Ag, Zn) < −0.6 (Na, Cu, Mn, Sb) < −0.4 (Cs, B) < −0.3 Mo < −0.24
- Factor 4—7.8% Mo > 0.7 V > 0.6 Na > 0.4 Re > 0.3 (Sb, B) > 0.24
- (Zn, Ca) < −0.4 Ba < −0.3
- Factor 5—7.1% Sb > 0.7 Cs > 0.6 Mg > 0.4 Pb > 0.3 (Y, HREEs, Si) > 0.24
- B < −0.3 (Re, Ba) < −0.24
- Factor 6—4.4% Mo > 0.3 (S, Cu, U) > 0.24
- Si < −0.4 (Ag, Li, Na, Sr) < −0.24
4. Discussion
4.1. Macro-Elemental Chemical Composition of Groundwater
4.2. Groundwater Elemental Composition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, Z.; Chen, J.; Jiang, T.; Li, K.; Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Xie, Z. Identification of the dominant hydrogeochemical processes and characterization of potential contaminants in groundwater in Qingyuan, China, by multivariate statistical analysis. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 33243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wali, S.U.; Umar, K.J.; Dankani, I.M.; Abubakar, S.D.; Gada, M.A.; Umar, A.; Usman, A. Groundwater Hydrochemical Characterization in Urban Areas of Southwestern Sokoto Basin Nigeria. SF J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 1, 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Wali, S.U.; Umar, K.J.; Gada, M.A.; Usman, A.A. Evaluation of Shallow Groundwater in Cretaceous and Tertiary Aquifers of Northern Kebbi State, Nigeria. SF J Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 1, 1005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Lu, H. Analysis of the hydro-chemical characteristics and origin of the karst groundwater, East Jinan city. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 189, 32061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajil Kumar, P.J.; James, E.J. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes in the Coimbatore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embaby, A.; Razack, M.; Lecoz, M.; Porel, G. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Groundwater in the Precambrian Rocks, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2016, 8, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, J.; Su, C.; Rashid, A.; Yang, N.; Baloch, M.Y.J.; Talpur, S.A.; Ullah, Z.; Rahman, G.; Rahman, N.U.; Sajjad, M.M. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Groundwater and Suitability Analysis for Domestic and Agricultural Utility in Southern Punjab, Pakistan. Water 2021, 13, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteldjaoui, F.; Bessenasse, M.; Taupin, J.-D.; Kettab, A. Mineralization mechanisms of groundwater in a semi-arid area in Algeria: Statistical and hydrogeochemical approaches. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2020, 69, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yidana, S.M.; Bawoyobie, P.; Sakyi, P.; Fynn, O.F. Evolutionary analysis of groundwater flow: Application of multivariate statistical analysis to hydrochemical data in the Densu Basin, Ghana. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 138, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikhani, R.; Ghassemi Dehnavi, A.; Ahmadnejad, Z.; Kalantari, N. Hydrochemical characteristics and groundwater quality assessment in Bushehr Province. SW Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6265–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollaro, C.; Fuoco, I.; Bloise, L.; Calabrese, E.; Marini, L.; Vespasiano, G.; Muto, F. Geochemical Modeling of Water-Rock Interaction Processes in the Pollino National Park. Hindawi Geofluids 2021, 2021, 6655711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollaro, C.; Perri, F.; Borrelli, L.; Caloiero, T. The Role of Water-Rock Interaction Processes in Soil Formation: Geochemical, Mineralogical, Geomorphological, and Engineering-Geological Aspects. Hindawi Geofluids 2019, 2019, 8453136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzien, S.M.; Hamed, B.O. Rock-Water Interaction, Hydrochemical Facies and Salinity of Groundwaters from Al Bauga Area, River Nile State, Sudan. J. Res. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2016, 4, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M. Insights into hydrological and hydrochemical processes in response to water replenishment for lakes in arid regions. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuoco, I.; De Rosa, R.; Barca, D.; Figoli, A.; Gabriele, B.; Apollaro, C. Arsenic polluted waters: Application of geochemical modelling as a tool to understand the release and fate of the pollutant in crystalline aquifers. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, I.; Marini, L.; De Rosa, R.; Figoli, A.; Gabriele, B.; Apollaro, C. Use of reaction path modelling to investigate the evolution of water chemistry in shallow to deep crystalline aquifers with a special focus on fluoride. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollaro, C.; Vespasiano, G.; De Rosa, R.; Marini, L. Use of mean residence time and flowrate of thermal waters to evaluate the volume of reservoir water contributing to the natural discharge and the related geothermal reservoir volume. Application to Northern Thailand hot springs. Geothermics 2015, 58, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okbah, M.A.; El-Gammal, M.I.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Abokhder, S.A.M. Spatial Variations of Major Ion Chemistry and Hydrogeochemical Processes of Groundwater, Menoufia Governorate, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019, 23, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyene, G.; Aberra, D.; Fufa, F. Geochemical quality analysis of groundwater in Jimma Zone, Oromia, National Regional State, Ethiopia. J. Environ. Occup. Sci. 2017, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taucare, M.; Daniele, L.; Viguier, B.; Vallejos, A.; Arancibia, G. Groundwater resources and recharge processes in the Western Andean Front of Central Chile. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadi, A.N.; Tukur, A.; Okunlola, I.A.; Olasehinde, P.I.; Jimoh, M.O. Lithologic Influence on the Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in Zango, North-west Nigeria. Nat. Resour. Conserv. 2015, 3, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- De Uist, R.D. Hydrogeology with the basics of land hydrology. Peace 1965, 1, 312. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hem, J.D. Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water; Water Supply Paper; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; p. 2254. [Google Scholar]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Kanel, S.R.; Nakarmi, A. Groundwater pollution: Occurrence, detection, and remediation of organic and inorganic pollutants. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Pang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Fu, D.; Wang, X. Environmental remediation of heavy metal ions by novel-nanomaterials: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvinenko, Y.S.; Zakharikhina, L.V. Geochemistry and Radioecology of Waters and Bottom Sediments of the Mzymta River, the Black Sea Coast. Geochem. Int. 2022, 60, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogush, I.A.; Cherkashin, V.I. Metallogeny of the Jurassic sedimentary complexes of the Caucasus. Collection of articles based on the materials of the scientific and practical conference dedicated to the memory of the Honored Geologist of the Russian Federation, D.A. Mirzoev. Proc. Inst. Geol. DSC RAS 2012, 58, 7–13. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Karelina, E.V.; Markov, V.E.; Blokov, V.I. Potentiality of the Krasnopolyanensky district of the city of Sochi for precious metal mineralization. Bulletin of the Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia. Ser. Eng. Res. 2017, 18, 497–504. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gazeev, V.M.; Gurbanov, A.G.; Kondrashov, I.A. Paleogene basalt-trachyte formation of the Western Caucasus: Geochemical specificity, issues of petrogenesis, geodynamic typification, metallogeny. Geol. Geophys. South Russ. 2018, 4, 18–32. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Official Website of “Matsesta” Balneotherapeutic Health Resort. Available online: https://macesta-san-sochi.ru (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Osipov, Y.S. (Ed.) The Big Russian Encyclopedia; Big Russian Encyclopedia: Moscow, Russia, 2004; Volume 19. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Drozhzhina, K.V. Peculiarities of natural and climatic conditions of the Mzymta River basin for purposes of recreational activities. Young Sci. 2013, 5, 196–198. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Borisov, V.I. Rivers of Kuban; Kuban Publishing House: Krasnodar, Russia, 2005. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lavrishchev, V.А.; Prutsky, N.I.; Semenov, V.М. State Geological Map of the Russian Federation, Scale of 1: 200 000, Caucasus Series, Sheet К-37-V, 2nd ed.; Nauka: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2002. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- RD 52.24.495-2017 (Roshydromet Ruling Document). Hydrogen Index of Waters. Methods of Measurement by Potentiometric Method. Hydrogen ion Exponent (pH) of Water. Measuring Technique via Potentiometric Method. Available online: https://files.stroyinf.ru/Data2/1/4293739/4293739174.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022). (In Russian).
- All Union State Standard 18164-72. Drinking Water. Method for Determination of Total Solids Content. Available online: https://allgosts.ru/13/060/gost_18164-72.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022). (In Russian).
- All Union State Standard 4245-72. Drinking Water. Method for Determination of Chloride Content. Available online: http://gostrf.com/normadata/1/4294850/4294850721.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022). (In Russian).
- All Union State Standard 31940-2012. Drinking Water. Method for Determination of Sulfate Content). Available online: https://files.stroyinf.ru/Data2/1/4293785/4293785995.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022). (In Russian).
- All Union State Standard 31957-2012. Water. Methods for Determination of Alkalinity and Mass Concentration of Carbonates and Bicarbonates). Available online: https://files.stroyinf.ru/Data/564/56411.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022). (In Russian).
- All Union State Standard 23268.5-78. Drinking Medicinal, Medicinal-Table and Natural-Table Mineral Waters. Methods for Determination of Calcium and Magnesium Ions. Available online: https://www.testprom.ru/img_user/gosts/67/160/gost_23268.5-78.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022). (In Russian).
- RD 52.24.514-2002/ Methodological Instructions. Calculation of Total Sodium and Potassium Content and Total Ion Content in Surface Water of Land. All Union State standard 4245-72. Drinking Water. Method for Determination of Chloride Content. Available online: https://ohranatruda.ru/upload/iblock/7ae/4293829642.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022). (In Russian).
- Karandashev, V.K.; Leikin, A.Y.; Khvostiko, V.A.; Kutseva, N.K.; Pyrogov, S.V. Water analysis by mass spectrometry method with inductively-coupled plasma. Plant Laboratory. Mater. Diagn. 2015, 81, 5–18. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- 29 Component Trace Metals in 2% HNO3 + Tr HF. Available online: https://highpuritystandards.com/products/29-component-trace-metals-in-2-hno3-tr-hf/ (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Savenko, V.S. Biophilicity of chemical elements and its reflection in ocean chemistry. Moscow State University Bulletin, Series 5. Geographical 1997, 1, 3–7. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Cattell, R.B. The scree test for the number of factors. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1966, 1, 245–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belonin, M.D.; Golubeva, V.A.; Skublov, G.T. Factor Analysis in Geology; Nedra: Moscow, Russia, 1982. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vorobyev, S.A. Software Package of Integrated Processing of Geological-Geochemical Data—Gold Digger, Documentation and Description; MNR: Moscow, Russia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- All Union State Standard R 54316-2011. National standard of the Russian Federation. Drinking natural mineral waters. General specifications. 2011. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200085076 (accessed on 28 January 2022). (In Russian).
- Grigoriev, N.A. Average concentrations of chemical elements in rocks of the upper continental crust. Geochem. Int. 2003, 41, 711–718. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharikhina, L.V.; Sharafan, M.V. Behavior of rare earth elements in the soil and vegetation cover of the urban landscapes of Sochi. KRAUNTS. Ser. Earth Sci. 2021, 50, 48–58. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovov, A.P. Geochemical Methods of Prospecting for Mineral Deposits; Nedra: Moscow, Russia, 1985; p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Haskin, L.A.; Haskin, M.A.; Frey, F.A.; Wildman, T.R. Relative and Absolute Terrestrial Abundance’s of the Rare Earths. In Origin and Distribution of the Elements; Ahrens, L.H., Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1968; pp. 889–912. [Google Scholar]
- Gromet, L.P.; Dumek, R.F.; Haskin, L.A.; Korotev, R.L. The “North American shale composite”: Its composition, major and trace element characteristics. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 2469–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharikhina, L.V.; Rudev, P.V.; Paltseva, A.V. Chemical composition and morphology of the Mediterranean mussel, Black Sea coast of Russia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelman, A.I.; Kasimov, N.S. Landscape Geochemistry, Educational Guidance, 3rd ed.; Astrea: Moscow, Russia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
| Water Type | Number of Sampling Points | Statistical Characteristics | рН | Content, mg/L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Мtotal, mg/L | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | ||||
| I Bicarbonate calcium | 29 | Maximum | 7.9 | 366.0 | 7.33 | 99.75 | 6.72 | 1.82 | 51.50 | 333.49 |
| Minimum | 6.5 | 62.0 | 0.87 | 12.29 | 0.87 | 13.86 | 1.00 | 47.64 | ||
| Average | 7.3 ± 0.5 | 217.4 ± 8.7 | 3.07 ± 0.2 | 59.31 ± 3.6 | 2.84 ± 0.1 | 6.65 ± 0.4 | 16.12 ± 1.1 | 181.63 ± 5.4 | ||
| Standard deviation | 0.40 | 90.45 | 1.77 | 25.94 | 1.54 | 3.59 | 10.81 | 74.79 | ||
| II Bicarbonate-sulphate calcium-magnesium | 8 | Maximum | 7.75 | 362.0 | 6.37 | 111.3 | 12.78 | 10.50 | 125.0 | 216.16 |
| Minimum | 6.28 | 106.0 | 1.22 | 13.90 | 1.33 | 2.38 | 40.0 | 51.97 | ||
| Average | 7.05 ± 0.2 | 206.5 ± 10 | 4.00 ± 0.2 | 44.77 ± 1.3 | 6.32 ± 0.4 | 4.73 ± 0.1 | 76.08 ± 5.3 | 137.39 ± 6.9 | ||
| Standard deviation | 0.48 | 87.5 | 1.90 | 33.55 | 4.13 | 2.80 | 33.37 | 63.25 | ||
| III Bicarbonate-sulphate calcium-sodium | 4 | Maximum | 6.80 | 790.0 | 43.50 | 186.6 | 15.26 | 31.22 | 150.0 | 473.0 |
| Minimum | 6.67 | 574.0 | 37.33 | 151.2 | 7.44 | 10.08 | 130.0 | 368.1 | ||
| Average | 6.74 ± 0.3 | 633.3 ± 44 | 39.67 ± 1.6 | 161.4 ± 4.8 | 11.68 ± 0.6 | 15.84 ± 0.6 | 141.8 ± 5.7 | 427.9 ± 12.8 | ||
| Standard deviation | 0.06 | 104.7 | 2.74 | 16.95 | 3.22 | 10.27 | 8.88 | 46.44 | ||
| IV Bicarbonate-chloride sodium | 4 | Maximum | 8.10 | 1212 | 305.0 | 5.82 | 5.46 | 310.8 | 40.0 | 918.2 |
| Minimum | 7.09 | 1104 | 284.0 | 1.76 | 0.21 | 208.8 | 39.0 | 628.0 | ||
| Average | 7.58 ± 0.4 | 1160 ± 81 | 298.4 ± 15 | 3.61 ± 0.3 | 2.72 ± 0.1 | 275.0 ± 11 | 39.0 ± 2.7 | 754.7 ± 52.8 | ||
| Standard deviation | 0.52 | 46.04 | 9.96 | 2.09 | 2.90 | 45.18 | 0.60 | 160.4 | ||
| V Bicarbonate-chloride-sulphate calcium | 4 | Maximum | 8.12 | 332.8 | 0.54 | 10.75 | 0.76 | 10.68 | 21.60 | 46.34 |
| Minimum | 7.45 | 309.5 | 0.49 | 9.87 | 0.71 | 10.08 | 20.12 | 43.31 | ||
| Average | 7.83 ± 0.4 | 322.3 ± 16 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 10.40 ± 0.3 | 0.73 ± 0.1 | 10.45 ± 0.3 | 20.78 ± 0.8 | 45.02 ± 1.8 | ||
| Standard deviation | 0.34 | 12.30 | 0.04 | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.84 | 1.28 | ||
| Water Types | Cc ≥ 1 | Cc < 1 |
|---|---|---|
| I | Se(7.0)-Cs(3.3)-Eu(3.0)-Tb,Ho(2.0)-Sn,Ba(1.7)- Dy(1.6)- Sr, Pr, Gd(1.4)-Ca,Nd, Sm(1.3)-Ce(1.2)-Cd,La,Er,Lu,Tm,Lu (1.0) | Zn,Yb(0.8)-B,Si(0.5)-Pb(0.4)- V,Li,Ge,Cu(0.3)- As, S, Rb, Mo, K, Al (0.2)- Hg, Br, Mg, Na,Sb,Y,Ag,U,Mn,Fe(0.1)-Th,Zr,Tl(0.01) |
| II | Pr(5.4)-Se(3.2)-Tb(2.0)-Gd(1.9)-Sn(1.7) -Ba(1.3)-Cs(1.2)-Ca(1.1)-Sr,Eu,Ho,Tm,Lu(1.0) | Cd(0.7)-Si, Pb(0.6)-B,Li,Dy,Mo,La,Sm,Ce(0.4)-V,Cu,Er,Yb(0.3)-Rb,Nd,Ag(0.2)-Hg,K,Mg,Br,Na,As,Sb(0.1)- Al,U,Y,Mn,Fe,Th,Tl,Zr(0.01) |
| III | Ba(4.1)-Se(3.5)-Ca(3.4)-Sr(3.1)-Li(1.7)-Rb(1.3)-B(1.2)-Eu,Tb,Ho,Tm,Lu(1.0) | S(0.8)-Pr(0.7)-Si,Dy,K,Sn,Sm,Gd,Er,Cs,Ce(0.5)-Nd,Cu(0.4)-Na,V,Cd,La,Yb(0.3)-Mg,Zn(0.2)-Hg,Mn,U,Br,Mo,U,Br,Mo,Pb(0.1)-As,Al,Y,Sb,Ag,Fe,Th,Tl,Zr(0.01) |
| IV | Se(30.3)-Ge(21.6)-B(16.0)-Br(10.5)-Ba(7.6)-Na(6.6)-Li(4.1)-Sr(3.5)-Cr(1.3)-Mo(1.2)-Eu,Gd,Tb,Dy,Ho,Tm,Lu(1.0) | Sm,Ce,Pr(0.9)-Er(0.8)-Nd,Hg,Ni(0.7)-Ca,Cs,Si(0.6)-Yb,La(0.5)-Zn,Pb,V(0.4)-S,Rb,Cd,Cu(0.3)-K,Ag,Mn(0.2)-As,Sb,Fe,U,Al,Mg(0.1)-Y,Th,Zr,Tl(0.01) |
| V | Se(2.5)-Eu,Tb,Ho,Tm,Lu(1.0) | Dy,Cd,Pr(0.6)-Mo,Gd,Sn(0.5)-La,Zn,Sm,Pb(0.4)-Nd,Er,Ce,Yb,Mn,V(0.3)-Cu,Ca,Si,Ba,Hg(0.2)- B,Br,Ag,Rb,Sr,S(0.1)-As,Cs,Zr,K,Y,Al, Sb,U,Mg,Fe,Na,Th,Li,Tl(0.01) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakharikhina, L.; Litvinenko, Y.; Ryndin, A.; Saburov, R.; Shevelev, S.; Vareljyan, G. Geochemical Characterization of Natural Groundwater on the Southern Slopes of the Caucasus Mountains on the Russian Black Sea Coast. Water 2022, 14, 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142170
Zakharikhina L, Litvinenko Y, Ryndin A, Saburov R, Shevelev S, Vareljyan G. Geochemical Characterization of Natural Groundwater on the Southern Slopes of the Caucasus Mountains on the Russian Black Sea Coast. Water. 2022; 14(14):2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142170
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakharikhina, Lalita, Yury Litvinenko, Alexey Ryndin, Ruslan Saburov, Sergey Shevelev, and Georgy Vareljyan. 2022. "Geochemical Characterization of Natural Groundwater on the Southern Slopes of the Caucasus Mountains on the Russian Black Sea Coast" Water 14, no. 14: 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142170
APA StyleZakharikhina, L., Litvinenko, Y., Ryndin, A., Saburov, R., Shevelev, S., & Vareljyan, G. (2022). Geochemical Characterization of Natural Groundwater on the Southern Slopes of the Caucasus Mountains on the Russian Black Sea Coast. Water, 14(14), 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14142170





