Abstract
Studies on groundwater have traditionally been based on declining groundwater levels and associated ecological, environmental, and geological problems. However, due to extreme hydrometeorological events and human activities, rising groundwater levels have been observed in many areas. The daily groundwater levels from 2018 to 2020 for the Poyang Lake Basin (PLB) in Jiangxi Province were recorded. The statistical characteristics of abnormal groundwater level rising (AGLR) events and the factors influencing the dynamic changes in groundwater level were analyzed using geostatistical methods and outlier identification methods. The groundwater level in the lower terrain of the PLB has increased significantly in recent years. AGLR events identified by the median absolute deviation and interquartile range methods showed that AGLR events mainly occurred in the spring and summer and were mainly distributed near the surface water bodies. Correlation analysis of the factors influencing the groundwater level revealed that the correlation between precipitation and groundwater level was related to topography. In contrast, the correlation between river stage and groundwater level was related to runoff volume.
1. Introduction
As an essential source of water supply and a controlling element of the ecological environment, groundwater plays a role in ensuring drinking water safety, supporting economic and social development, and coping with increased demand for freshwater [1,2]. Studies have long focused on the decline in groundwater levels and associated ecological, environmental, and geological problems [3]. However, with extreme hydrometeorological events and human activities, many areas are already experiencing an increase in groundwater levels [4,5]. In 2020, the Yangtze, Taihu, and Huaihe River basins in China experienced major basin floods [6]. In 2021, historic heavy rainfall events affected New York City in the United States, Zhengzhou in China, and some Western European cities [7,8]. The historical records of the river stage are gradually being broken. Consequently, flood control and water resource scheduling in the basin challenge the protection of groundwater resources and ecological safety, which are closely linked to surface water hydraulics [9]. In contrast to normal rising, this study defines abnormal groundwater level rising (AGLR) as a significant increase in the rate, magnitude or duration of groundwater level rising. Therefore, in this study, AGLR is divided into two aspects: abnormal duration and abnormal rate. A conceptual model is shown in Figure 1.
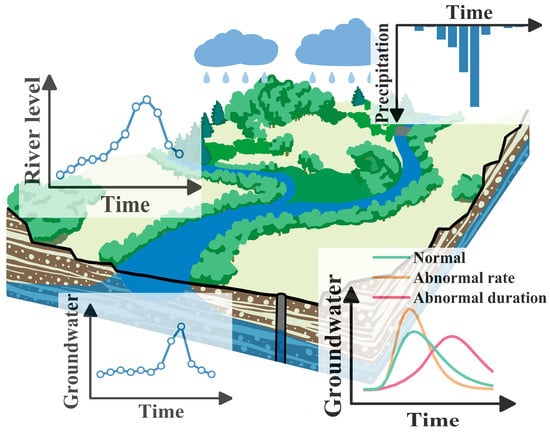
Figure 1.
Conceptual model of abnormal groundwater level rising (AGLR).
In 2020, the Poyang Lake Basin (PLB) in Jiangxi Province, China, experienced a heavy rainstorm that was more than a once-a-century event. The water level of Poyang Lake in 2020 exceeded the water level in 1998. The level became the highest in history, creating a rare opportunity to study the problem of AGLR. Poyang Lake is the largest freshwater lake in China, the largest natural flood storage area in the Yangtze River Basin, and a typical seasonal throughput lake. Its unique wetland ecosystem plays a significant role in biodiversity conservation in the Yangtze River Basin [10]. Poyang Lake has an apparent surface–groundwater interaction during wet and dry seasons [11]. During the wet season, the water level of Poyang Lake is relatively high, and surface water recharges the groundwater. During the dry season, the water level decreased, and the lake became a discharge area for groundwater. The change in the surface water level directly affects the change in the groundwater level near the surface. With the new water regime created by global changes, intensified human activities, and extreme hydrometeorological events, the AGLR has become more complicated. The resulting ecological and environmental effects have also become more prominent. The dynamic changes of groundwater have been studied using macro devices, including remote sensing and satellite data in the literature [12,13,14]. However, the problem of AGLR in the PLB urgently needs to be solved [15] and has not been systemically studied yet. In this regard, the phenomenon and influencing factors of AGLR in the PLB are investigated using the geostatistical method in this study.
To study the phenomenon and influencing factors of the AGLR in the PLB, it is feasible to quantify the spatial and temporal distributions of the groundwater level in the area at a macro level. Geostatistical methods are increasingly used in hydrology [16,17], which can accurately describe the spatial variability of the environment and reveal the spatial variability and spatial pattern of the study object. The methods are effective for studying the spatial and temporal distributions of groundwater. The use of geostatistical methods to study groundwater variability has been internationally explored. For example, Budiman et al. [18] used geostatistical methods to study the groundwater dynamics in Saudi Arabia. Seyedmohammadi et al. [19] applied kriging interpolation to analyze the spatial variation in groundwater storage in Iran. Lu et al. [20] applied geostatistical methods to analyze the dynamic changes in the spatiotemporal distribution of groundwater depths in the Northeast China Plain and North China Plain. Outliers are a well-known problem in scientific research, and their accurate identification plays a vital role in statistical analysis. Many techniques have been proposed for their detection and identification [21,22]. Current hydrological research commonly uses the three-sigma rule (3σ), median absolute deviation (MAD), and interquartile range (IQR) for outlier identification. The 3σ method is limited by assuming a Gaussian data distribution. In contrast, the MAD and IQR methods are more appropriate, as they take advantage of nonparametric statistics (i.e., median) instead of parametric measures (e.g., mean and standard deviation) [23].
The main objectives of this paper are to clarify the differences in statistical characteristics of AGLR relative to normal fluctuations in the PLB and to clarify the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of AGLR. This paper is organized as follows: the groundwater level data were first collected and collated from groundwater monitoring stations in the PLB. The geostatistical method revealed spatial distribution characteristics and dynamic changes in the groundwater level. Groundwater level time series were analyzed to determine the process of groundwater level rise and to identify characteristics, such as the duration, magnitude, and rate of groundwater level rising events. Statistical methods were then used to quantitatively identify AGLR events and characteristics. Finally, factors influencing AGLR were analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Poyang Lake is the largest freshwater lake in China. It is located in the northern part of Jiangxi Province, on the southern shore where the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River meet [24]. It is a natural throughput, seasonal lake, receiving water from five major rivers: Ganjiang, Fuhe, Xinjiang, Raohe, Xiushui, and other small rivers that flow into the lake alone [25]. The PLB (24°29′ N–30°04′ N, 113°34′ N–118°28′ N) is surrounded by mountains on three sides: Hunan to the west, Hubei and Anhui to the north, Zhejiang and Fujian to the east, and Guangdong to the south. The edges of the mountains and ridges form a natural provincial boundary and watershed, and the basin area overlaps with the administrative division of Jiangxi Province (Figure 2). Therefore, the administrative area of Jiangxi Province was analyzed instead of the PLB in this study [26].
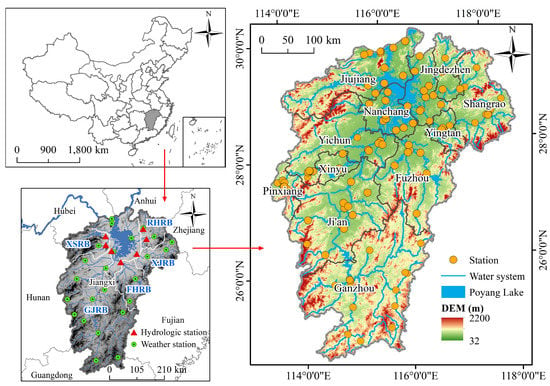
Figure 2.
Overview of the Poyang Lake Basin (PLB). Abbreviations, GJRB: Ganjiang River Basin; FHRB, Fuhe River Basin; XJRB: Xinjiang River Basin; RHRB: Raohe River Basin; XSRB: Xiushui River Basin.
The PLB is located in the East Asian monsoon region, which has a subtropical, warm, and humid climate. The annual average temperature is approximately 16.3–19.5 °C, and the average precipitation is 1341–1943 mm. The mountains in the PLB are mainly in the northeast–southwest trend. The topography is low in the middle and high in the surrounding areas, whereas the interior is high in the south and low in the north. This terrain plays a crucial role in the development of water systems and plains in basins [27]. The unique characteristics of climate change, geographical environment, and human activities in the PLB have resulted in frequent floods. The groundwater characteristics in the PLB are severely affected by hydrological conditions, showing significant intra-annual changes and prominent hydrometeorological event-driven characteristics [25].
2.2. Data Collection
The groundwater level and runoff data were obtained from the Jiangxi Provincial Hydrological Monitoring Center. Precipitation data were obtained from the China Meteorological Data Service Centre (data.cma.cn). The 1096-day study period was from 1 January 2018, to 31 December 2020. Seven hydrological stations, 24 weather stations, and 116 automatic groundwater monitoring stations located in the PLB were selected (Figure 2). The groundwater monitoring stations automatically recorded the daily groundwater levels at 8 a.m. Owing to the possible failure of groundwater monitoring stations or other problems, there may be missing data or abnormal values in the groundwater level time series records. Newton’s interpolation method was used to correct and interpolate the data [28]. Finally, 116 groundwater level time series and 1096 daily groundwater level datasets were obtained. Precipitation and runoff data for the same period were collected.
2.3. Methodology
The geostatistical method was used to study the spatial distribution characteristics of groundwater levels in the PLB. MATLAB (MATLAB R2018a, MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA) was used to identify the rising stage of the groundwater level and the characteristics of the rising rate and duration. Mathematical statistics theory was used to quantitatively identify the AGLR events and statistical characteristics and analyze the factors influencing the abnormal rise in the groundwater level.
2.3.1. Geostatistical Methods
The basic tools of geostatistical methods are the semi-variance function and kriging interpolation [29], which are used to quantitatively evaluate the spatiotemporal dynamics of groundwater levels in the PLB. The semi-variance function reflects the spatial relationship between a sampling point and its adjacent points. To quantitatively describe the various characteristics of the study area, a theoretical model of its semi-variance function must be determined. The most commonly used semi-variance function models are the spherical, exponential, Gaussian, and pure nugget effect models [30]. In comparison, the value of the semi-variance function of the groundwater level in the PLB fits better with the Gaussian model [31].
In this study, ordinary kriging interpolation was used to interpolate the groundwater level in the study area to evaluate the spatial distribution of groundwater level. The results of ordinary kriging interpolation are more accurate when the data variables are trained to follow a Gaussian distribution, and the Kolmogorov–Smirnov single-sample test (K–S test) was used to check whether the data conformed to a Gaussian distribution [32]. If the groundwater level dataset does not conform to a Gaussian distribution, some transformation of the dataset is required to make it conform to a Gaussian distribution before the ordinary kriging interpolation can be performed.
2.3.2. Outlier Identification
Most traditional outlier identification methods have been proposed for data suitable for Gaussian distribution. It is not easy to extend them to consider the variability of the data effectively, yet most of the data tend to be non-Gaussian distributed [23]. Traditional outlier identification methods commonly used in hydrology include the 3σ, MAD, and IQR methods [33]. Comparing these three traditional methods, the 3σ method is not suitable for anomaly identification in groundwater data because this method is limited by the assumption that the data are Gaussian distributed. However, the distribution of groundwater level data is usually non-Gaussian distributed. For comparison, the traditional MAD and IQR methods are more suitable for identifying AGLR.
MAD
The MAD method based on the median for outlier identification was proposed by Hampel [34]. Considering a series of independent random variables (X1, X2,…, Xn) and corresponding sample series {x1, x2,…, xn}, the median of the sample series is defined as
MAD is calculated as [35]:
where b is a model constant, usually b = 1.4826. Specifically, the MAD is calculated using the following steps: (a) calculate the median of the sample series {x1, x2,…, xn}; (b) each sample value xi is subtracted from the median of the sample series {x1, x2,…, xn} and calculate the absolute value to form a new sample series {x1, x2,…, xm}; (c) calculate the median of the new sample series{x1, x2,…, xm}; (d) multiply the median of the new sample series {x1, x2,…, xm} by 1.4826.
The calculation expression of the outlier identification coefficient for each sample value xi is:
When the outlier identification coefficient was greater than a given threshold, the sample value xi is considered an outlier. In general, it is more reasonable to choose the threshold of 2.5; that is, when A > 2.5, the sample value xi is determined to be an abnormal value.
IQR
IQR is a technique that allows the identification of outliers in continuously distributed data [36]. We arranged the sample series in order from smallest to largest and calculated the interquartile range of the series. The lower quartile (Q1), median (Q2), and upper quartile (Q3) were 25%, 50%, and 75% of the sorted sequences, respectively. The difference between Q3 and Q1 is defined as IQR, which is calculated as follows [37]:
In general, the threshold value of the IQR method is calculated as follows:
where a is generally determined by the individual and is usually set to 1.5, and data outside the IQR are considered abnormal data.
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Dynamic Characteristics of Groundwater Level
The groundwater level time series data of each groundwater monitoring station in the PLB did not follow a Gaussian distribution. However, after the logarithmic transformation process, all the groundwater level time series passed the K–S test. The results indicate that the log-transformed groundwater level time series conforms to a Gaussian distribution and can be analyzed through geostatistical analysis. The statistical values of the groundwater level in the PLB listed in Table 1, including the mean and median of the groundwater level, showed an overall increase with time. The variation pattern illustrates that the groundwater level in the PLB shows an overall increasing trend in 2018, 2019, and 2020.

Table 1.
Statistical characteristics of groundwater level, precipitation, and runoff in the study area.
Figure 3a shows the spatial distribution of the groundwater level in the PLB in 2018, including 11 prefecture-level cities, such as Nanchang, Jiujiang, Yichun, and Shangrao. The overall topography of the PLB is high in the surrounding areas and low in the middle, while the interior shows the characteristics of high in the south and low in the north, with the overall slope to the north. Previous studies have shown that influencing factors, such as topography, vegetation, and soil bedrock, control the spatial variation in groundwater levels because the dynamic change in groundwater level results from the combined effect of local recharge and discharge [38]. In contrast, the topography is often the driver of spatial variability in groundwater levels in mountainous catchments with shallow groundwater depths because gravitational potential energy is a significant component of total potential energy [39]. The groundwater level distribution in the PLB is consistent with the topography, showing the characteristics of a higher surrounding groundwater level, lower in the middle, and a self-flowing slope from the south to the north.
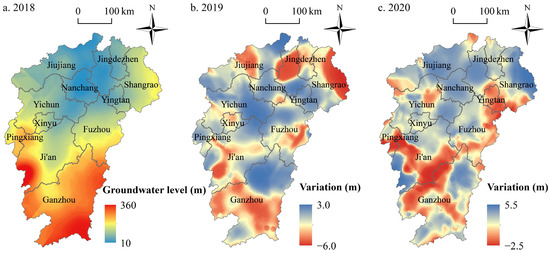
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of the groundwater level variation in the PLB. (a) Spatial distribution of groundwater level in the PLB in 2018; (b) Spatial distribution of groundwater level variation in PLB in 2019 relative to 2018; (c) Spatial distribution of groundwater level variation in PLB in 2020 relative to 2019.
Figure 3b shows the spatial distribution of groundwater level variation obtained by subtracting the spatial distribution of groundwater level in 2018 from the spatial distribution of groundwater level in 2019 in the PLB. Similarly, Figure 3c shows the spatial distribution of groundwater level variation in 2020 relative to 2019. In Figure 3b,c, cool colors indicate the area of rising groundwater level, and warm colors indicate the area of falling groundwater level. As shown in Figure 3b, compared to 2018, the groundwater level in most areas of the PLB showed an upward trend in 2019, and the rate of groundwater level rise reached a maximum of 3 m/a. In the central part of the study area, such as Nanchang, Yichun, Yingtan, and other cities with low terrain, there was a significant increase in groundwater level, while the groundwater level in most parts of Jingdezhen and Shangrao in the northeast showed a downward trend. In general, the rise in groundwater level was mainly concentrated in areas with lower elevations. It is noteworthy that in relatively high-altitude areas, such as Ganzhou, the northeastern region also shows a phenomenon of groundwater level rise.
In Figure 3c, compared with 2019, the groundwater level in the northern part of the PLB showed an overall increase in 2020, whereas the southern part showed a large decrease in area. The central part of the study area has been experiencing a groundwater level rise for two consecutive years, and there may be factors contributing to the continued rise in groundwater level. Jingdezhen and Shangrao cities in the northeastern part of the study area showed opposite changes in groundwater levels from 2019, indicating that stochastic factors may influence this part. For the southern part of the study area with a relatively high elevation (such as Ganzhou City), there is still a persisting phenomenon of groundwater level rise in parts of the northeast, which deserves further exploration.
3.2. Statistics of Groundwater Level Rising Events
The foregoing analyses of the spatiotemporal dynamics of the groundwater level in the PLB revealed that groundwater level rise does exist in some areas of the study area. To deeply understand the groundwater level rise in the PLB, mathematical and statistical analyses of all groundwater level rising events were performed. Based on the daily groundwater level monitoring data from 116 groundwater monitoring stations in the PLB from 2018 to 2020, all groundwater level rising events were identified and statistically distributed spatially (Figure 4). This study analyzed the time series of groundwater levels at each monitoring station. The continuous rise in groundwater level was treated as a rising event. Moreover, a slight decline may occur during the groundwater level rise. If the decline during the rising process did not exceed one-third of the last rising process, the entire process was regarded as a rising event. In terms of groundwater level rising events, 7457 groundwater level rising events occurred at all groundwater monitoring stations within 3 years. The highest frequency of rising events for each groundwater monitoring station was 136, whereas the minimum value was 0. In some stations without a significant groundwater level rise, the average frequency of rising events was 64.3 times.
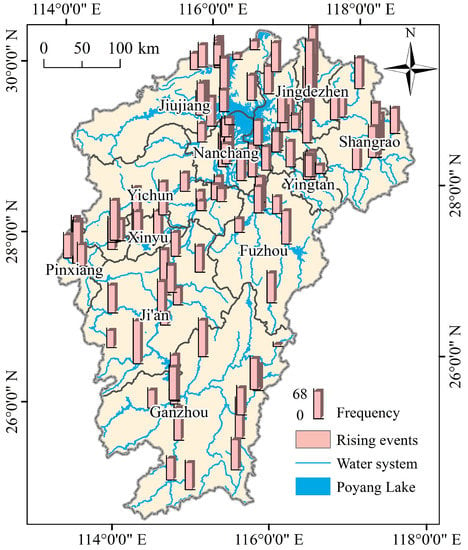
Figure 4.
Distribution of groundwater level rising events in the PLB from 2018 to 2020.
In this study, spatial and temporal statistical analyses of all groundwater level rising events in the study area were performed. The start of the groundwater level rising event was used as the time of the rising event in this study because of the long duration of some groundwater level rising events, which may exceed 1 or even 2 months. From the perspective of temporal distribution, Figure 5a shows a boxplot of rising groundwater levels in the PLB from 2018 to 2020. The average frequency of groundwater level rising events in each month at each groundwater monitoring station was 4.6–6.5 times. Rising events occurred mainly from April to August. Rising events in August were significantly more frequent than those in other months, with an average frequency of 6.5. March had the lowest frequency of rising events, with an average frequency of 4.6. The Q1 of January–March, June–July, and November in the study area was 3, indicating that only 25% of the stations had a low frequency of rising events during approximately half the year. The lowest value of the frequency of rising events each month was 1, whereas the highest value varied widely, with the highest in August (20) and the lowest in February (12). The outliers of the frequency of rising events were mainly concentrated from July to September. The collective findings indicate that the groundwater level rising events in the study area mainly occurred in spring and summer, which is consistent with the wet season in the study area. This laterally reflects that the groundwater recharge in the study area mainly depends on the infiltration recharge of precipitation and lateral recharge of runoff [40,41].
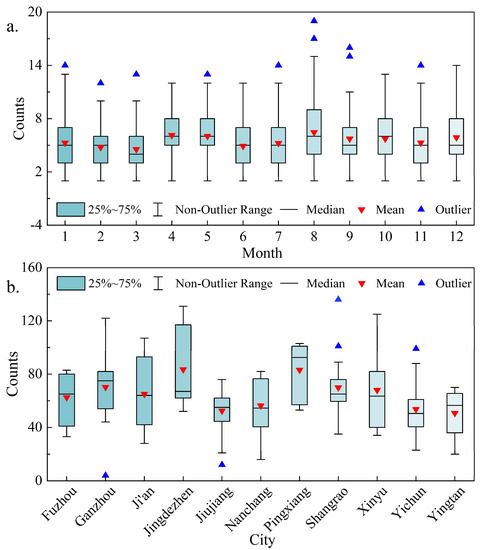
Figure 5.
Boxplot of groundwater level rising events in PLB from 2018 to 2020 by month (a) and by city (b).
It can be seen from Figure 3 that the frequency of groundwater level rising events in different regions of the PLB is quite different, so it is necessary to further analyze the frequency of rising events by region. From the perspective of spatial distribution, Figure 5b shows a boxplot of rising groundwater levels in each prefecture-level city in the PLB from 2018 to 2020. The average frequency of rising events occurring in groundwater monitoring stations in each city in the three years was 52.5–83.6 times. Significant differences were observed in the frequency of rising events and uneven spatial distributions. The frequency of rising events in Jingdezhen and Pingxiang was significantly higher than in other regions, with the frequency of rising events in Xinyu having the highest dispersion and that in Jiujiang and Shangrao having the lowest dispersion. The boxes for Jiujiang, Nanchang, and Shangrao were short, and the frequency of rising events was more concentrated. These three cities are located around the lake area, and their groundwater monitoring stations are mainly located around the lake area. Therefore, there may be some connection between the groundwater level and the lake level. Overall, the frequency of rising events is more concentrated in areas closer to the lake, and the frequency is more discrete in areas farther away from the lake.
3.3. Identification of AGLR Events
3.3.1. Identification of AGLR Events Using MAD
Dynamic changes in groundwater levels are influenced by seasonal surface hydrological processes and geographical location. The MAD method was used to identify the abnormal rising duration and rate of groundwater level events at each groundwater monitoring station. Figure 6a shows the spatial distribution of the AGLR events identified by the MAD method for each prefecture-level city. The analysis revealed AGLR events in all prefecture-level cities; most of the groundwater monitoring stations displayed only abnormal rising duration events in this case. The frequency of AGLR at a single station in southern Jiangxi Province was significantly higher than that in other regions. The frequency of AGLR at a single station in the plain area of northern Jiangxi Province was at a lower level. The distribution of AGLR events was highly consistent with the distribution of surface water, and the abnormal events were mainly distributed in Nanchang, Jiujiang, and Shangrao, which are adjacent to the Poyang Lake area.
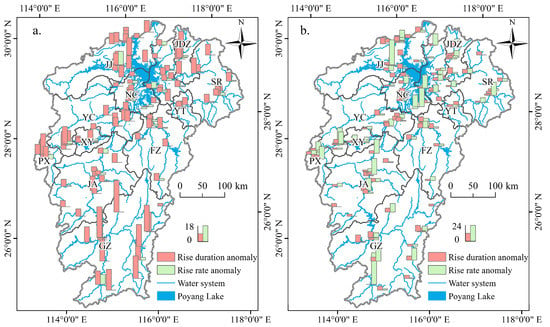
Figure 6.
Distribution of the AGLR events by city using the MAD method (a) and IQR method (b).
3.3.2. Identification of AGLR Events Using IQR
Similar to the MAD method, the IQR method identifies the duration and rate of AGLR events at each groundwater monitoring station. The analysis (Figure 6b) revealed that AGLR events in all prefecture-level cities, with a wide distribution of both types of AGLR. However, abnormal rising rate events have been more common. The stations around the lake area recorded AGLR events, but the frequency of the events in the three years of the study was low for individual stations. AGLR events occurred mainly at stations around surface water bodies, but their frequency was relatively low. For individual stations, the frequency of abnormal rising duration events was significantly higher at stations in the mountainous areas in the south of the basin than in the plains in the north, probably because groundwater in mountainous areas is mainly influenced by precipitation infiltration. In contrast, more complex factors, such as precipitation, runoff, and human activity, influence groundwater dynamics in the plains.
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Dynamics in Groundwater Level, River Stage, and Precipitation
The intra-annual distribution characteristics of precipitation and runoff volume in the five sub-basins within the PLB are listed in Table 1. The CV of precipitation was generally smaller than that of runoff volume, indicating a more uniform intra-annual distribution than that of the runoff volume. The CV values of precipitation in the five sub-basins were not significantly different, indicating that the intra-annual distribution of precipitation in each basin was not significantly different. In contrast, the CV of runoff volume in the Raohe and Fuhe River basins was larger than those in other basins, and the intra-annual distribution of runoff volume was more concentrated. The findings indicate that the intra-annual variability of the runoff volume is more dynamic and unstable than that of precipitation, and the unevenness of its intra-annual distribution is more prominent.
Figure 7 shows the change process lines of the daily groundwater level, river stage, and precipitation in the five sub-basins of the PLB from 2018 to 2020. The time series of the river stage is the daily data from the hydrological control stations of each sub-basin. In contrast, the time series of the groundwater level and precipitation was the arithmetic mean of the time series of all groundwater monitoring stations and meteorological stations in each sub-basin. The combined data of Table 1 and Figure 7 indicate that the maximum annual precipitation occurred in June and July, and the minimum annual precipitation occurred in October. The highest river stage and groundwater level values were concentrated in July, and the minimum values were in November. The distributions of precipitation and runoff volume were extremely uneven throughout the year.
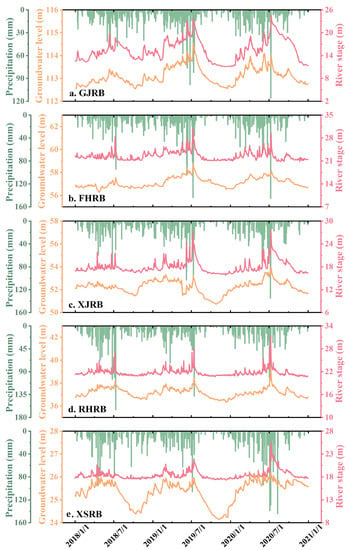
Figure 7.
Groundwater level, river stage, and precipitation in sub-basins of the PLB from 2018 to 2020. (a) GJRB, (b) FHRB, (c) XJRB, (d) RHRB and (e) XSRB.
The river stage in each basin was significantly influenced by precipitation, and the two trends were the same (Figure 7). However, the changes in runoff lagged slightly behind precipitation. Except for the Xiushui River Basin, the dynamic change in groundwater level in the remaining areas was highly consistent with the river stage and precipitation change process. However, the peak of the process line of the groundwater level slightly lagged behind the process line of the river stage, and the dynamic change in groundwater level in the basin was highly correlated with the change in precipitation and river stage. The river stage dynamically changes owing to the influence of precipitation, which directly affects the change in the groundwater level near the surface water [42]. The consistency of the processes of groundwater level change with river stage change was greatest in the Ganjiang River Basin. This may be because the Ganjiang River is the largest tributary in the PLB, surface water is more widely distributed in the basin, and groundwater is more significantly influenced by surface water. The annual runoff volume of the Xiushui River is smaller than that of the other tributaries, and the relationship between the variation in groundwater and surface water in the Xiushui River Basin is not significant.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Abnormal Thresholds Using MAD and IQR
The principles of outlier identification using the MAD and IQR methods are different, resulting in very different thresholds for outlier identification. Figure 8 shows the thresholds obtained using these two methods to identify the abnormal rise in the groundwater level. The two types are the abnormal threshold of the rising duration and the rising rate. Similarly, the abnormal rising threshold of the groundwater level was analyzed from the temporal and spatial perspectives. Overall, the abnormal threshold of the rising duration calculated by the IQR method was more significant than that of the MAD method, while the abnormal threshold of the rising rate was smaller than that of the MAD method, showing a relatively synchronous trend.
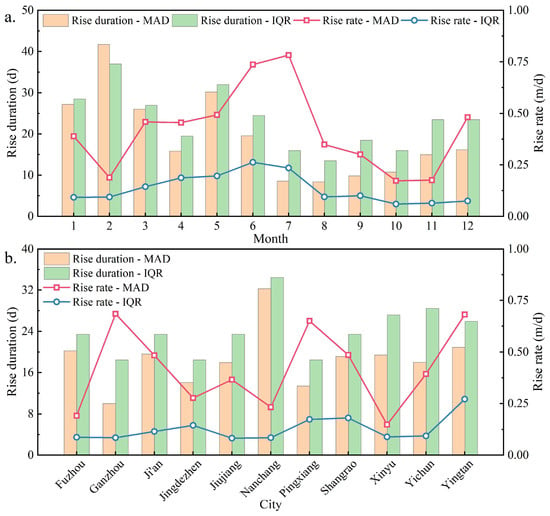
Figure 8.
Statistical chart of abnormal rising threshold of groundwater level by month (a) and by city (b).
Figure 8a shows the monthly distribution of the abnormally rising groundwater level threshold. It can be clearly seen that the abnormal threshold of the rising duration and the abnormal threshold of the rising rate showed opposite trends. From February to July, the abnormal threshold of the rising duration showed a decreasing trend as a whole, while the abnormal threshold of the rising rate continued to increase. From July to November, the abnormal threshold of the rising duration continued to increase, while the abnormal threshold of the rising rate continued to decrease. There was a brief reversal in January and December, showing a significant seasonal distribution. The minimum value of the abnormal threshold for the rising duration and the maximum value of the abnormal threshold for the rising rate occurred in summer. The respective values calculated by the MAD method were 8.4 days and 0.78 m/s, while those calculated by the IQR method were 13.5 days and 0.26 m/s. The maximum value of the abnormal threshold for the rising duration and the minimum value of the abnormal threshold for the rising rate appeared in winter. The respective values calculated by the MAD method were 41.7 days and 0.19 m/s, and those calculated by the IQR method were 37 days and 0.06 m/s. Abnormal rising rate events in spring and summer were more likely to occur, and the abnormal threshold was more significant because the change in groundwater level in this season is more easily affected by surface hydrological processes. More abnormal rising duration events occur in autumn and winter when the groundwater level rise is a slow cumulative process.
Figure 8b shows a statistical plot of the abnormal rising thresholds of groundwater levels in various cities and the relative synchronous changes in the abnormal thresholds calculated by the two methods. The maximum abnormal threshold of rising duration calculated by the two methods appeared in Nanchang: 32.3 days calculated by the MAD method and 34.5 days calculated by the IQR method. The minimum value of the abnormal threshold of the rising duration calculated by the MAD method was 10.0 days in Ganzhou, whereas the minimum value (18.5 days) of the abnormal threshold of the rising duration calculated by the IQR method appeared in Ganzhou, Jingdezhen, and Pingxiang. The maximum value of the abnormal threshold of the rising rate was in Yingtan: 0.68 and 0.27 m/s calculated by the MAD and IQR method, respectively. The minimum value of the abnormal threshold value of the rising rate was in Xinyu (0.16 and 0.09 m/s calculated by the MAD and IQR method, respectively). In general, the lower the altitude, the higher the abnormal threshold of the rising duration and the lower the rising rate threshold. The effect was more pronounced closer to the Poyang Lake area.
4.2. Analysis of Factors Affecting Abnormal Rising of Groundwater Level
The dynamic change in groundwater level is the result of the combined effects of natural and human factors. The natural factors include meteorological and hydrological factors. Among the meteorological factors, precipitation and evaporation significantly influence the dynamic changes in the groundwater level. Hydrological factors especially include infiltration and surface runoff. Human factors mainly refer to agricultural irrigation, groundwater extraction, and other human activities [43]. The land use of the study area is shown in Figure 9, which is mainly divided into six types, and the area proportions are forest (61.39%), cropland (26.41%), grass (4.31%), water (4.31%), residential (3.25%), and unused land (0.32%). The land use with the highest frequency of abnormal rising duration events is residential (7.48 times per year), and the land use with the highest frequency of abnormal rising rate events is water (4.38 times per year). The land use with the lowest frequency of abnormal rising duration events is grass (5.50 times per year), and the land use with the lowest frequency of abnormal rising rate events is unused land (0.00 times per year). In particular, it should be noted that both the shoaly land and the actual water are classified as waters according to the LUCC classification system. The AGLR mainly occurs in near-surface water bodies and agricultural irrigation areas. Analysis of data from the Jiangxi Provincial Water Resources Bulletin revealed that the PLB has abundant water resources. The amount of surface water resources has been much greater than that of groundwater resources (approximately four times in past years). The surface water dominated the water supply in the PLB. Nanchang and Shangrao had a slightly higher groundwater supply than other cities. Agricultural irrigation in the study area mainly uses surface water, with only part of the rural areas using groundwater resources for domestic water. Therefore, anthropogenic factors in the study area had little influence on dynamic changes in the groundwater level. As a result, meteorological and hydrological factors principally influence dynamic changes in the groundwater level from a macroscopic perspective that is potentially supported by Wang, et al. [11]. Therefore, as one of the types of dynamic changes, the phenomenon of AGLR could be correlated to meteorological and hydrological factors in temporal and spatial view, such as precipitation, river stage, and surface runoff. Then, these potential factors are further studied.
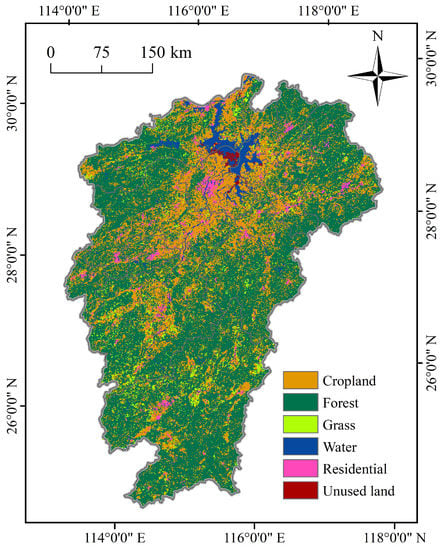
Figure 9.
Land use map of the PLB.
As for precipitation, the PLB is located on the south bank of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, with abundant precipitation, unique topography, and climate conditions that lead to frequent flood and drought disasters in the basin. The dynamic change in groundwater level is dramatic, and abnormal changes occur. During the summer flood season, the water levels of rivers and lakes tend to rise rapidly, flooding occurs, and groundwater levels rise frequently. However, during the winter dry season, precipitation decreases and the amount of water is low, resulting in a lack of abundant water resources [44]. In the Poyang Lake area during the study period, the water volume rose sharply when the water level was high during the flood season, and the water volume decreased sharply when the water level was low during the dry season. The interaction between groundwater and surface water was significant. Characteristics of the PLB include more rainfall processes, concentrated and continuous heavy rainfall processes, and high-intensity heavy rainfall. Temporally, precipitation is mainly concentrated from March to June. Spatially, precipitation in the northwest is more significant than in the south. In such a case, AGLR more possibly occurred in the PLB.
To analyze the degree of influence of precipitation and surface runoff on the groundwater level in different areas, the groundwater level was correlated with precipitation and river stage. The study area was divided into different Thiessen polygons according to the location of the weather station, and the Spearman correlation analysis was performed between the precipitation within each Thiessen polygon and the average groundwater level. The results are shown in Figure 10. The correlation coefficient between precipitation and groundwater level in the vast majority of areas in the PLB exceeded 0.5, with a significant correlation. Overall, the correlation coefficient between precipitation and groundwater level in the Raohe River Basin and Xiushui River Basin was the largest. Precipitation significantly affects dynamic changes in the groundwater level in these regions [40]. Furthermore, the correlation coefficient of the Poyang Lake area was lower because of the significant interaction between surface water and groundwater in the area. The groundwater level dynamics in the lake area were most affected by surface water, and precipitation had a relatively minor influence on the groundwater level. These data, combined with the topographic map of the PLB in Figure 1, revealed a more significant correlation between precipitation and groundwater levels in areas with higher altitudes. This result may occur because groundwater recharge in mountainous areas mainly comes from atmospheric precipitation, whereas groundwater recharge in plain areas has more complicated sources [24,25]. The correlation coefficients between the river stage and the average groundwater level in the sub-basin recorded by the hydrological control stations in the five sub-basins of the PLB were not quite the same. Correlation coefficients were 0.861 for the Ganjiang River Basin, 0.718 for the Fuhe River Basin, 0.689 for the Xinjiang River Basin, 0.860 for the Rao River Basin, and 0.582 for the Xiushui River Basin. The river stage in the Ganjiang River Basin correlated most strongly with the groundwater level because the Ganjiang River is the largest tributary of Poyang Lake, with a significant annual runoff volume. The surface runoff volume significantly influenced the groundwater level in this area. The correlation between river stage and groundwater level in the Xiushui River Basin was the lowest, which may be due to the small annual runoff volume of the Xiushui River. The interaction between groundwater and surface water in this basin was not significant, resulting in a low correlation.
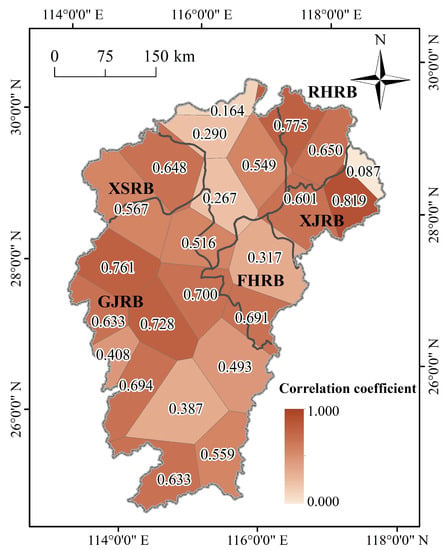
Figure 10.
Correlation coefficients between groundwater level and precipitation in the PLB.
5. Conclusions
This study used geostatistical and outlier identification methods to explore the spatial distribution and abnormal rise of groundwater levels in the PLB from 2018 to 2020. The main conclusions of this study are summarized below.
- The groundwater level distribution in the PLB was consistent with the topography, showing the characteristics of a higher surrounding groundwater level, lower in the middle, and a self-flowing slope from the south to the north. The groundwater monitoring stations in the PLB have the phenomenon of rising groundwater levels. Spatially, the AGLR events were mainly concentrated in the areas closer to the surface water bodies and temporally were mainly concentrated in the wet season.
- The results of the MAD and IQR methods for identifying AGLR were similar yet different. The MAD method identified more AGLR duration events, whereas the IQR method identified more AGLR rate events. The spatial and temporal distributions of these two AGLR event methods were similar. The abnormal threshold of the rising duration calculated by the IQR method was more significant than that of the MAD method. In contrast, the abnormal threshold of the rising rate was smaller than that of the MAD method.
- There were fundamental synchronous changes in groundwater level, river stage, and precipitation in the PLB. The correlation between precipitation and groundwater level was related to topography; the higher the elevation, the more significant was the correlation between precipitation and groundwater level. The correlation between river stage and groundwater level was related to runoff volume; the higher the runoff volume, the more significant was the correlation between the river stage and groundwater level.
Author Contributions
Z.S., software, formal analysis, writing—original draft; C.L., conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing—reviewing and editing, funding acquisition; Y.Z., validation, reviewing and editing; J.C., validation; W.L.: validation, reviewing and editing; B.L., investigation, project administration; L.S., conceptualization, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, grant number 2021YFC3200500; the Water Conservancy Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu, grant number 2018005; and the Science and Technology Program of Jiangxi Provincial Water Resources Department, grant number 202022YBKT11 and 202223YBKT26.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available due to institutional property rights.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the reviewers for their revision suggestions, and thanks to Vikas Narang for polishing the language.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| XSRB | Xiushui River Basin | ||
| PLB | Poyang Lake Basin | X1, X2,…, Xn | independent random variables series |
| AGLR | abnormal groundwater level rising | x1, x2,…, xn | original sample series |
| 3σ | the three-sigma rule | x1, x2,…, xm | new sample series |
| MAD | median absolute deviation | Z | the median of the sample series |
| IQR | interquartile range | b | model constant of MAD method |
| GJRB | Ganjiang River Basin | xi | sample value |
| FHRB | Fuhe River Basin | A | outlier identification coefficient |
| XJRB | Xinjiang River Basin | Max | maximum |
| RHRB | Raohe River Basin | Min | minimum |
References
- Famiglietti, J.S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.; Jin, Y.; Li, G.; Zheng, C.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.; Luo, J. Groundwater depletion and contamination: Spatial distribution of groundwater resources sustainability in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Gleeson, T. Regional strategies for the accelerating global problem of groundwater depletion. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essam, D.; Ahmed, M.; Abouelmagd, A.; Soliman, F. Monitoring temporal variations in groundwater levels in urban areas using ground penetrating radar. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 703, 134986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bob, M.; Rahman, N.A.; Elamin, A.; Taher, S. Rising Groundwater Levels Problem in Urban Areas: A Case Study from the Central Area of Madinah City, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Chen, J. A new era of flood control strategies from the perspective of managing the 2020 Yangtze River flood. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, L.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.; Song, F.; Leung, L.R.; Hao, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; et al. Abrupt emissions reductions during COVID-19 contributed to record summer rainfall in China. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachand, C.L.; Walsh, J.E. Extreme Precipitation Events in Alaska: Historical Trends and Projected Changes. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H. Extreme value analysis dilemma for climate change impact assessment on global flood and extreme precipitation. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.-Y.; Hong, Y.; Hardy, J.; Sun, Z. Examining the influence of river–lake interaction on the drought and water resources in the Poyang Lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Wu, J.; Wu, J. Variation of lake-river-aquifer interactions induced by human activity and climatic condition in Poyang Lake Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 126058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deoli, V.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, M.; Kuriqi, A.; Elbeltagi, A. Water spread mapping of multiple lakes using remote sensing and satellite data. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouttaki, I.; Khomalli, Y.; Maanan, M.; Bagdanavičiūtė, I.; Rhinane, H.; Kuriqi, A.; Pham, Q.; Maanan, M. A New Approach to Mapping Cultural Ecosystem Services. Environments 2021, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.; Kumar, S.; Malik, A.; Kuriqi, A. Artificial Neural Network Optimized with a Genetic Algorithm for Seasonal Groundwater Table Depth Prediction in Uttar Pradesh, India. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.; Dixon, A.; Newell, A.; Hallaways, A. Groundwater flooding within an urbanised flood plain. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2012, 5, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, M.; Sinha, R. Evaluating dynamic hydrological connectivity of a floodplain wetland in North Bihar, India using geostatistical methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2473–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, S.; Charles, C.; Degré, A. Geostatistical interpolation of daily rainfall at catchment scale: The use of several variogram models in the Ourthe and Ambleve catchments, Belgium. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2259–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budiman, J.S.; Al-Amri, N.S.; Chaabani, A.; Elfeki, A.M.M. Geostatistical based framework for spatial modeling of groundwater level during dry and wet seasons in an arid region: A case study at Hadat Ash-Sham experimental station, Saudi Arabia. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmohammadi, J.; Esmaeelnejad, L.; Shabanpour, M. Spatial variation modelling of groundwater electrical conductivity using geostatistics and GIS. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Song, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Si, H.; Liu, B.; Shu, L. Spatiotemporal variation and long-range correlation of groundwater depth in the Northeast China Plain and North China Plain from 2000∼2019. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 37, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Least Median of Squares Regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1984, 79, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, V.; Austin, J. A Survey of Outlier Detection Methodologies. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2004, 22, 85–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, J.; Park, E.; Han, W.S.; Kim, K.-Y.; Choung, S.; Chung, I.M. Identifying outliers of non-Gaussian groundwater state data based on ensemble estimation for long-term trends. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, H.; Wang, S.; Zheng, L.; Liao, M. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Water Body Changes and Their Influencing Factors in the Seasonal Lakes of the Poyang Lake Region. Water 2021, 13, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, S.; Guo, H.; Chen, G.; Jiang, T. Interactions of the Yangtze river flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Hörmann, G.; Fohrer, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, J. Streamflow Trends and Climate Variability Impacts in Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Gao, L.; Wei, J.; Ma, M.; Xu, L.; Fan, H.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Dang, H.; Chen, X.; et al. Contributions of climate change and human activities to runoff variations in the Poyang Lake Basin of China. Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts A/B/C 2021, 123, 103019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, W. Polynomial Interpolation: Lagrange versus Newton. Math. Comput. 1984, 43, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.H.; Sedghamiz, A. Application and evaluation of kriging and cokriging methods on groundwater depth mapping. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 138, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilonick, R.A. An Introduction to Applied Geostatistics; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kitanidis, P.K. Introduction to Geostatistics: Applications in Hydrogeology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, F.J., Jr. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test for Goodness of Fit. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1951, 46, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filzmoser, P.; Maronna, R.; Werner, M. Outlier identification in high dimensions. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 1694–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, F.R. The Influence Curve and Its Role in Robust Estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1974, 69, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leys, C.; Ley, C.; Klein, O.; Bernard, P.; Licata, L. Detecting outliers: Do not use standard deviation around the mean, use absolute deviation around the median. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 49, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riaz, M. On Enhanced Interquartile Range Charting for Process Dispersion. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2015, 31, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinderer, M.; van Meerveld, H.J.; Seibert, J. Topographic controls on shallow groundwater levels in a steep, prealpine catchment: When are the TWI assumptions valid? Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6067–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.G.; Burt, T.P. The role of topography in controlling throughflow generation. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 1978, 3, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Huang, D.; Wang, T. Isotopic signatures of precipitation, surface water, and groundwater interactions, Poyang Lake Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, G.; Shi, Z.; Liao, F.; Xue, Y. Spatiotemporal Variation of Groundwater Recharge in the Lower Reaches of the Poyang Lake Basin, China: Insights From Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, K.K.; Anantha, K.H.; Radha, A.V.; Dixit, S.; Singh, R.; Ragab, R. Impact of Rainwater Harvesting on Hydrological Processes in a Fragile Watershed of South Asia. Ground Water 2021, 59, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, J. Shallow groundwater dynamics in North China Plain. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Sun, R.; Xu, Z.; Tang, W. The Dynamic Change and Effect of Rainfall Induced Groundwater Flow. Water 2021, 13, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).