Effect of Ecosystem Degradation on the Source of Particulate Organic Matter in a Karst Lake: A Case Study of the Caohai Lake, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
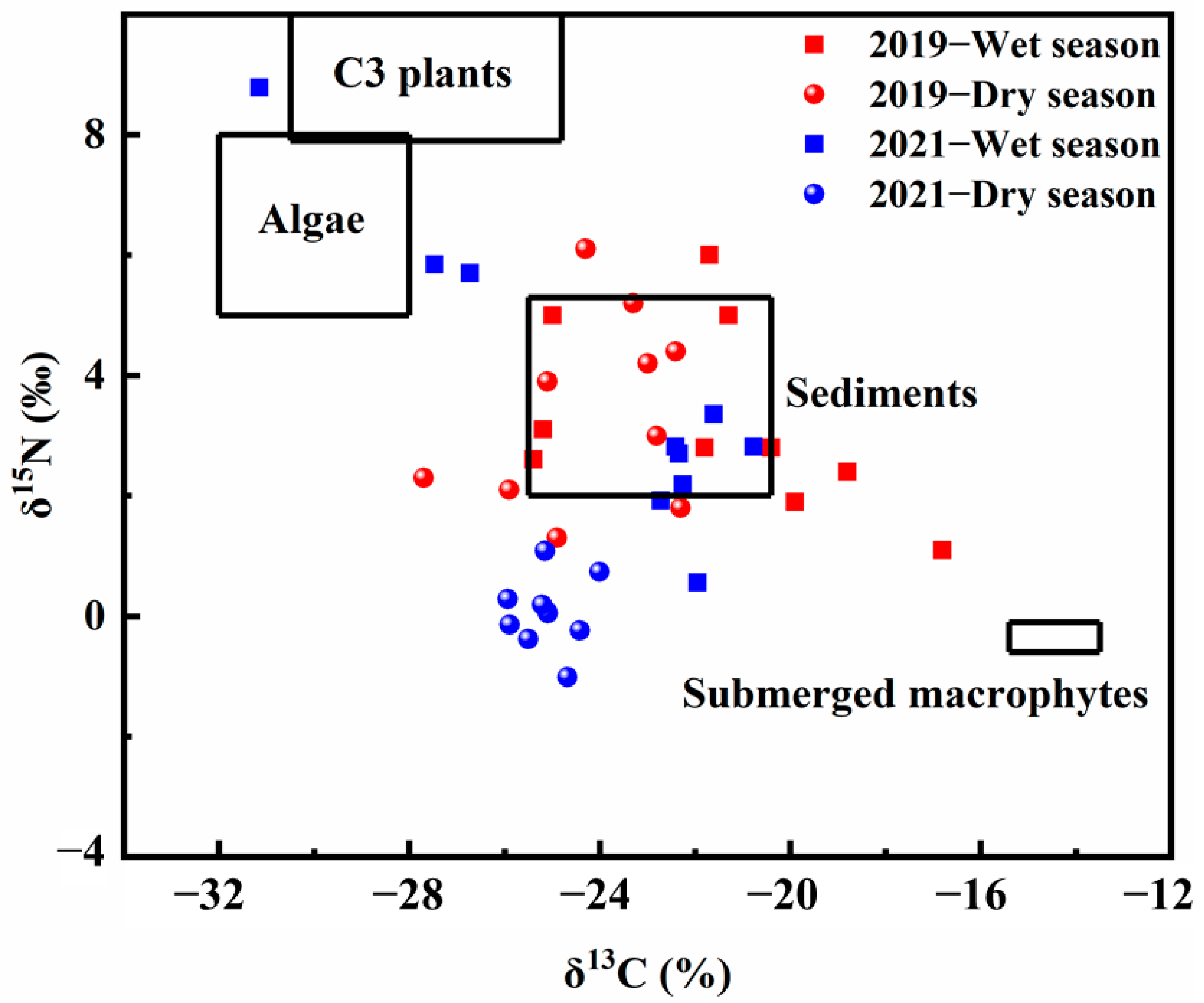
2.3. Isotopic Mixing Model
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
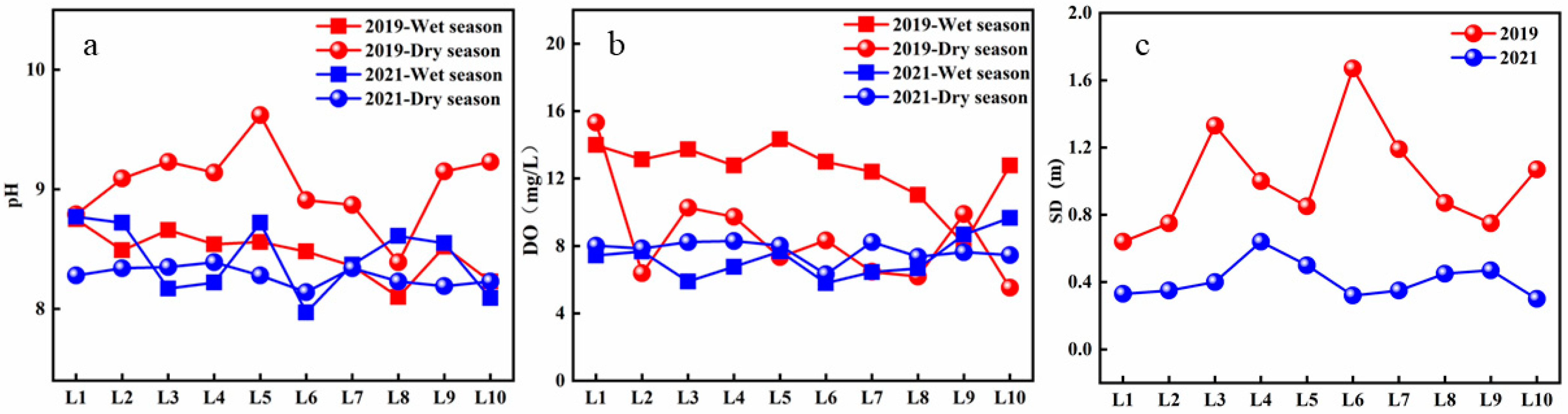
3.1. Water Quality Parameters
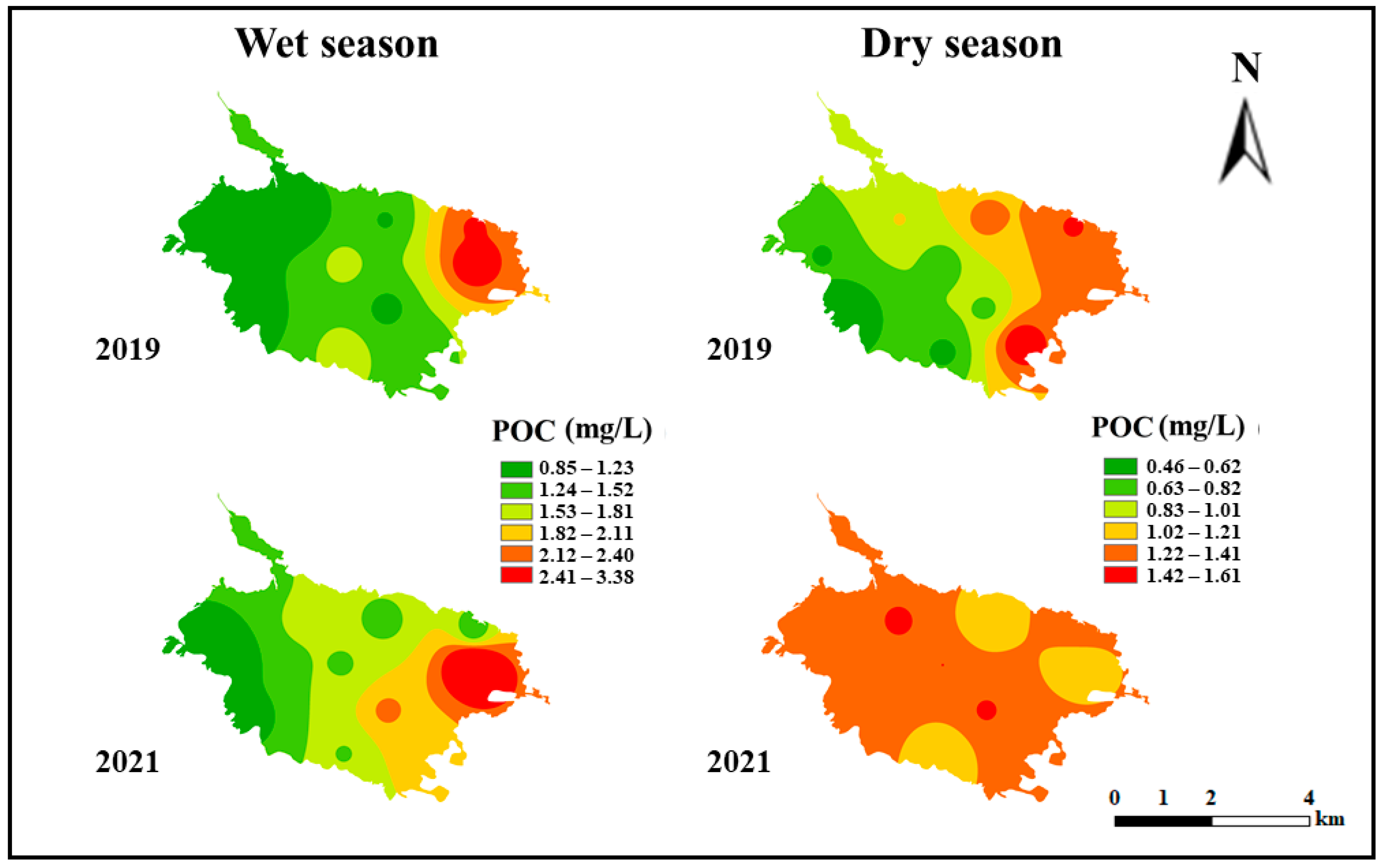
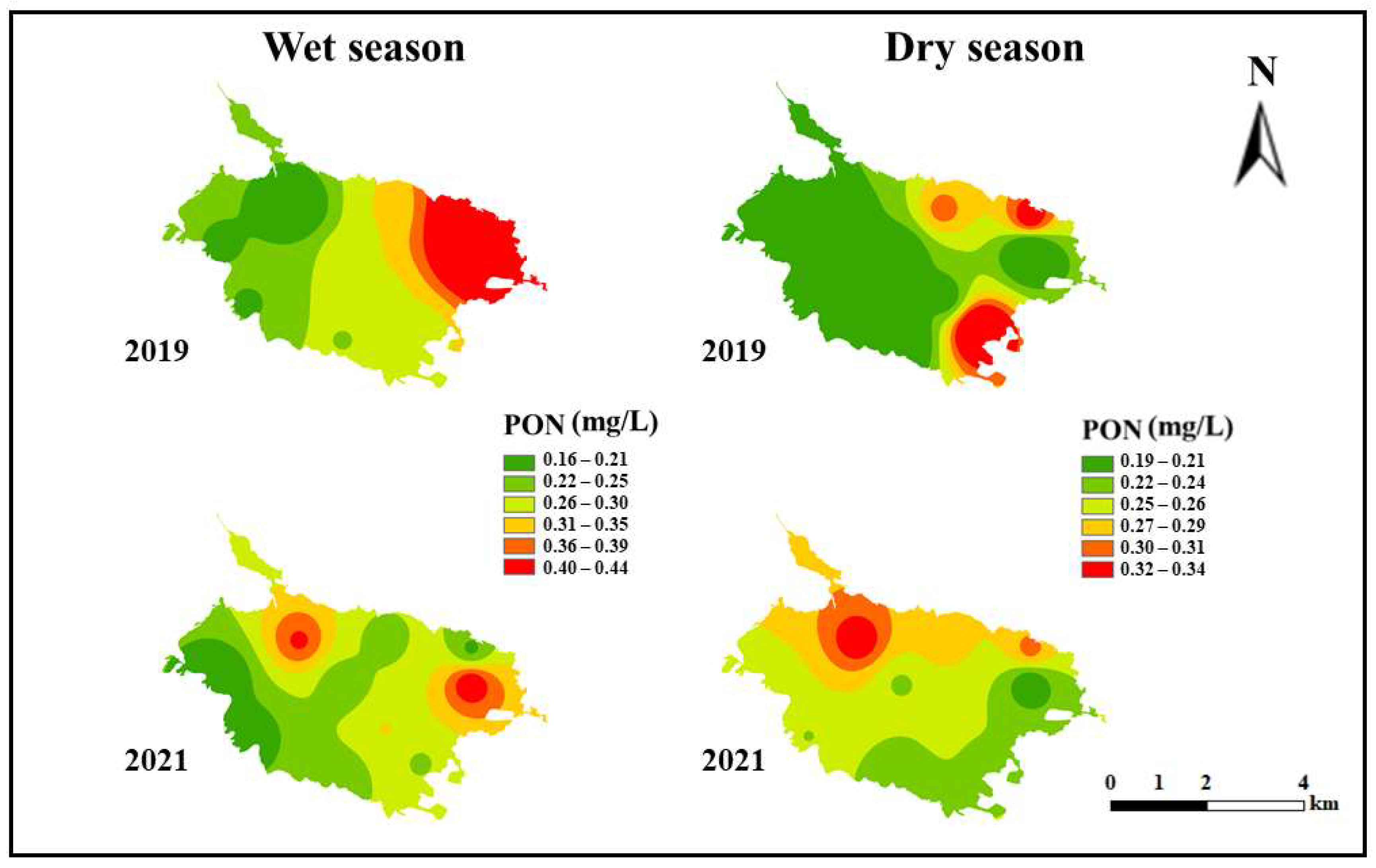
3.2. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of POM Concentrations in Water Prior to and after Ecosystem Degradation
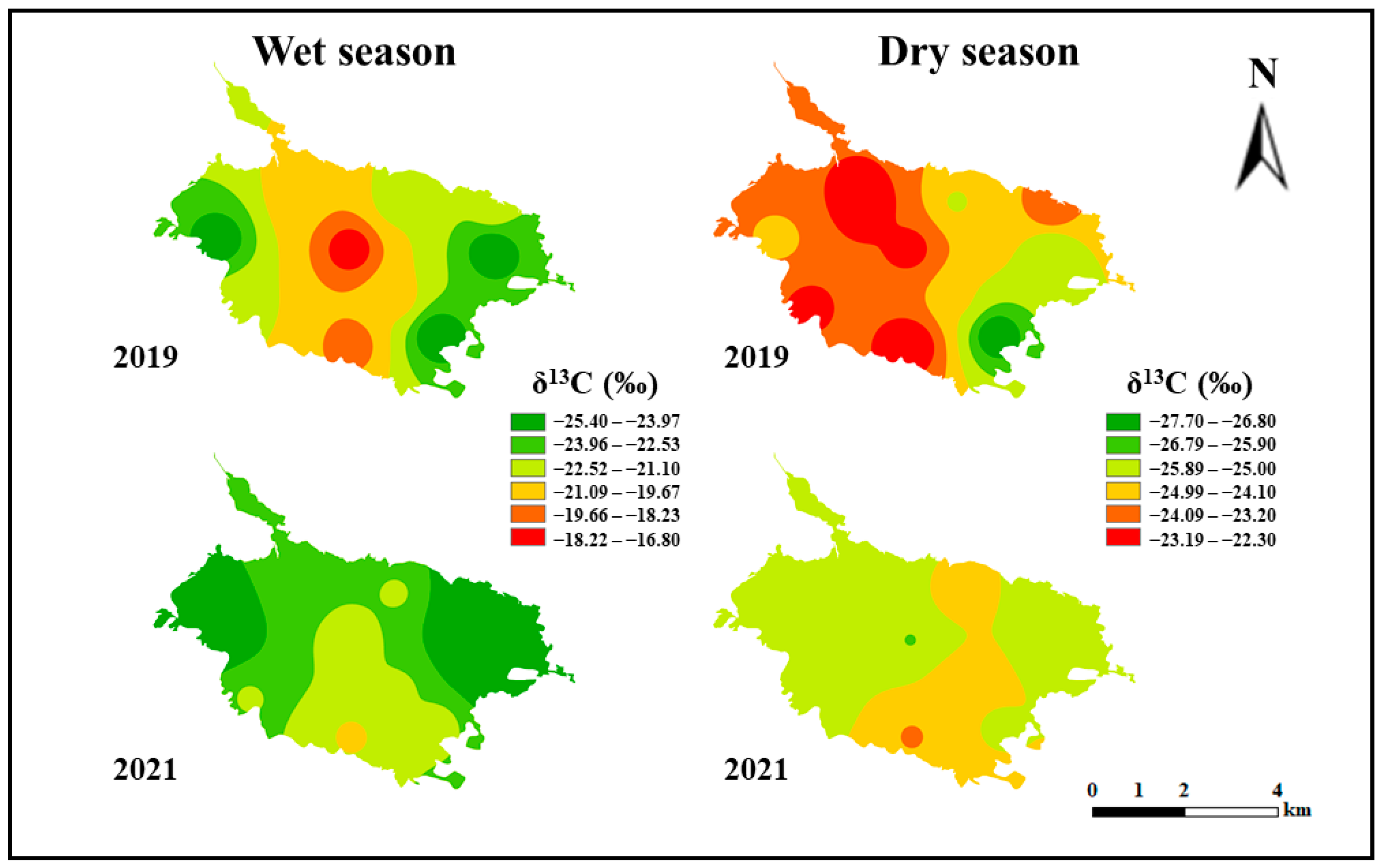
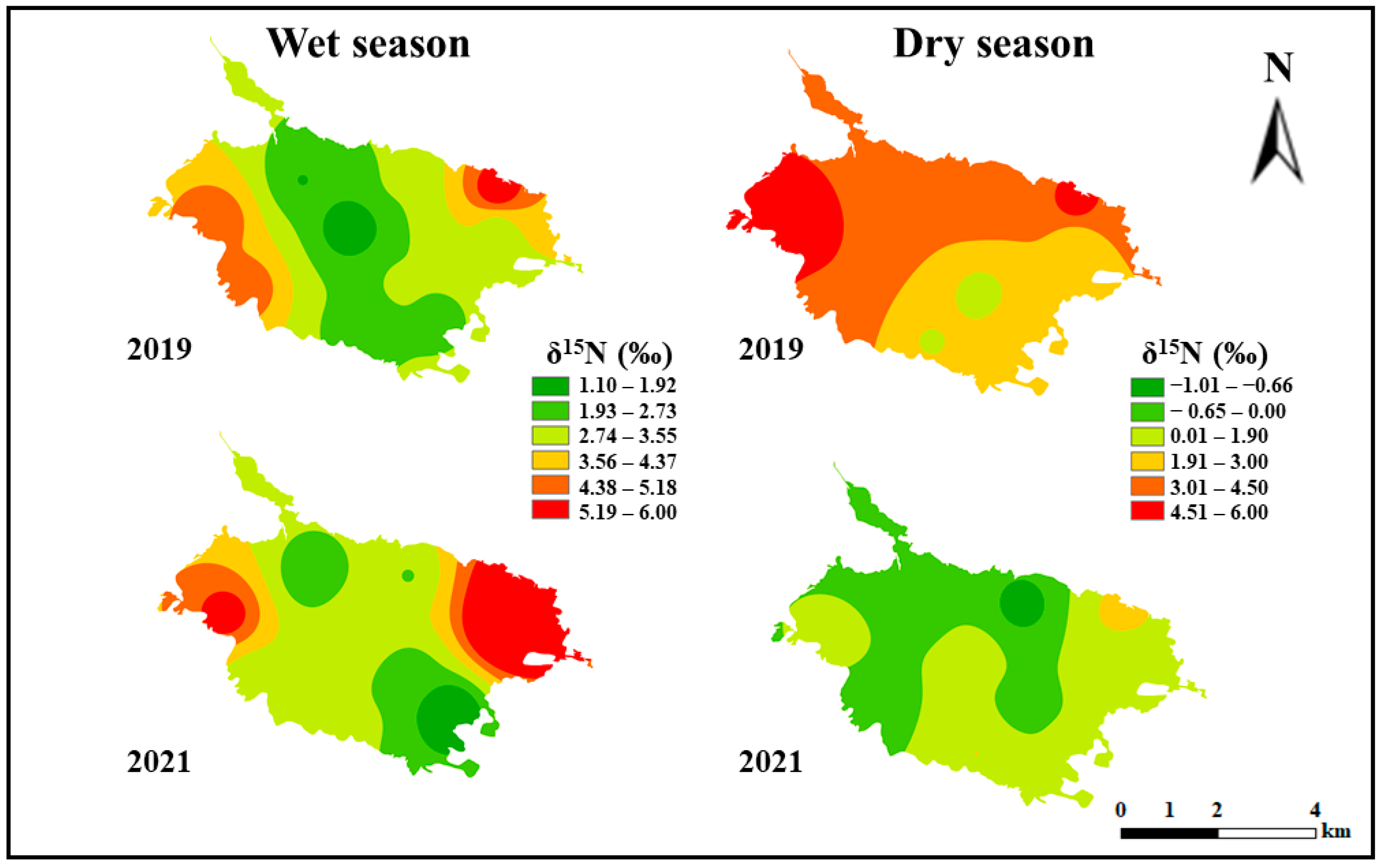
3.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of POM Carbon and Nitrogen Isotopes in Lake Water Prior to and after Ecosystem Degradation
| End Member | δ13C | δ15N | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range of δ13C | Mean ± SD | Range of δ15N | Mean ± SD | ||
| Sediment (n = 10) | −20.4 to −25.5 | −23.3 ± 1.7 | 2.0 to 5.3 | 3.3 ± 1.1 | this study |
| Submerged macrophytes (n = 5) | −13.5 to −15.4 | −14.9 ± 0.7 | −0.6 to −0.1 | −0.1 ± 0.4 | this study |
| Algae | −32.0 to −28.0 | −30.0 ± 2.0 | 5.0 to 8.0 | 6.5 ± 1.5 | [21,27] |
| C3 plants | −30.5 to −24.8 | −27.6 ± 2.0 | 7.9 to 12.8 | 10.3 ± 2.0 | [28,29] |
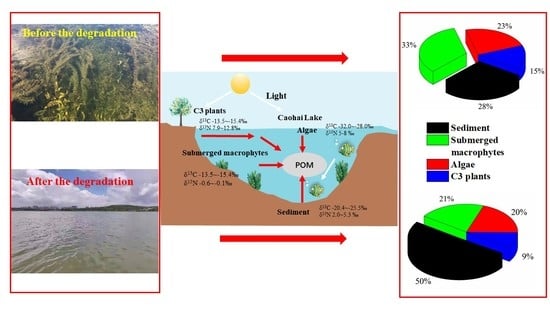
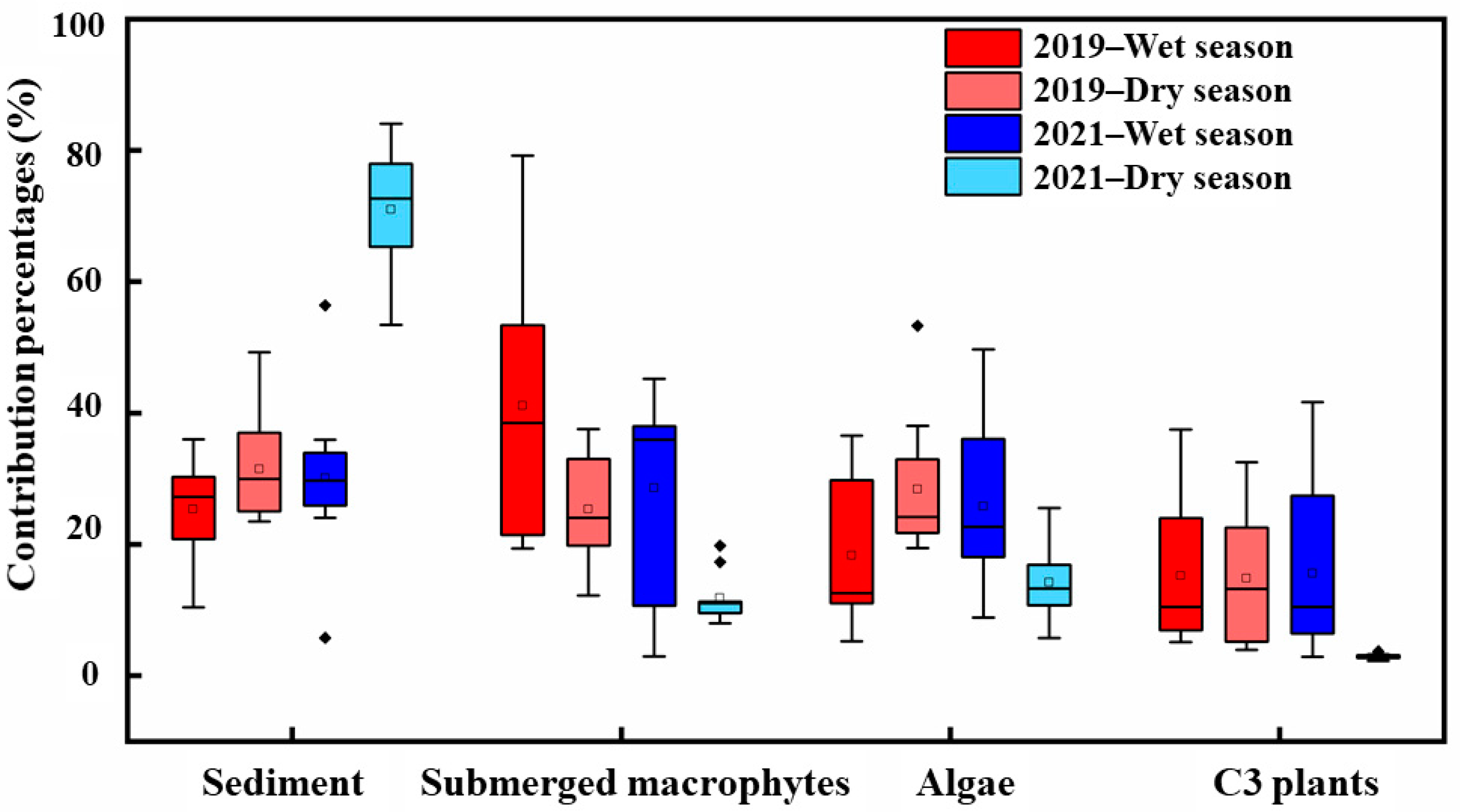
3.4. POM Source Characteristics and Their Drivers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheffer, M. Multiplicity of stable states in freshwater systems. In Biomanipulation Tool for Water Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.R. Catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems: Linking theory to observation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; van Nes, E.H. Mechanisms for marine regime shifts: Can we use lakes as microcosms for oceans? Prog. Oceanogr. 2004, 60, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, J.; Song, Y.; Ding, W. Combined use of radiocarbon and stable carbon isotope to constrain the sources and cycling of particulate organic carbon in a large freshwater lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Finlay, J.C.; Sterner, R.W. Isotopic composition of nitrogen in suspended particulate matter of Lake Superior: Implications for nutrient cycling and organic matter transformation. Biogeochemistry 2010, 103, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, D.; Unger, D.; Qiu, G. Particulate organic matter dynamics in coastal systems of the northern Beibu Gulf. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 82, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawade, L.; Krishna, M.; Sarma, V.; Hemalatha, K.; Rao, Y.V. Spatio-temporal variability in the sources of particulate organic carbon and nitrogen in a tropical Godavari estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 215, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Schelske, C.L.; Waters, M.N. Patterns and controls of seasonal variability of carbon stable isotopes of particulate organic matter in lakes. Oecologia 2011, 165, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Long, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Wu, P. Influence of different land use types on hydrochemistry and heavy metals in surface water in the lakeshore zone of the Caohai wetland, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, L. Influence of spatial variation in land-use patterns and topography on water quality of the rivers inflowing to Fuxian Lake, a large deep lake in the plateau of southwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ni, Z.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S. Climate change and human activities reduced the burial efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus in sediment from Dianchi Lake, China. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 274, 122839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Zhang, H.; Chang, F.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y. Isotopic constraints on sources of organic matter in surface sediments from two north–south oriented lakes of the Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yang, S.; Wu, P.; Liu, S.; Liao, J. Coupling stable isotopes to evaluate sources and transformations of nitrate in groundwater and inflowing rivers around the Caohai karst wetland, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 45826–45839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Jia, J.; Lu, Y.; Sun, K.; Ha, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, W. Vertically stratified water source characteristics and associated driving mechanisms of particulate organic carbon in a large floodplain lake system. Water Res. 2021, 209, 117963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, D.; Wu, Y.; Shirodkar, P.V.; Pradhan, U.K.; Zhang, J. Sources and implications of particulate organic matter from a small tropical river—Zuari River, India. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Gu, B. Global pattern of carbon stable isotopes of suspended particulate organic matter in lakes. Limnology 2012, 13, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, P.; Han, Z.; Zhang, S.; Tu, H. Sources, Spatial Distribution, and Seasonal Variation of Major Ions in the Caohai Wetland Catchment, Southwest China. Wetlands 2016, 36, 1069–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Y. Paleotemperature variations at Lake Caohai, southwestern China, during the past 500 years: Evidence from combined δ 18O analysis of cellulose and carbonates. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Jiang, J.; Hu, X.; Hu, J.; Ren, C.; Zhou, S. The response of microbial community structure and sediment properties to anthropogenic activities in Caohai wetland sediments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, S.; McManus, J. Application of Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Stable Isotope and C/N Ratios as Source Indicators of Organic Matter Provenance in Estuarine Systems: Evidence from the Tay Estuary, Scotland, Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1994, 38, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edje, B.O.; Ishaque, A.B.; Chigbu, P. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of δ13C and δ15N of Suspended Particulate Organic Matter in Maryland Coastal Bays, USA. Water 2020, 12, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Pu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Cao, J.; Pan, M. Sources, variations, and flux of settling particulate organic matter in a subtropical karst reservoir in Southwest. China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Zhong, J.; Bao, H.; Mostofa, K.M.; Xu, S.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Li, S.-L. The impacts of reservoirs on the sources and transport of riverine organic carbon in the karst area: A multi-tracer study. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saino, T.; Hattori, A. 15N natural abundance in oceanic suspended particulate matter. Nature 1980, 283, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ramesh, R.; Bhosle, N.B.; Sardesai, S.; Sheshshayee, M.S. Natural isotopic composition of nitrogen in suspended particulate matter in the Bay of Bengal. Biogeosciences 2004, 1, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, F.; Guo, W.; Shi, Z.; Jia, G.; Wei, G. Seasonal dynamics of particulate organic matter and its response to flooding in the Pearl River Estuary, China, revealed by stable isotope (δ13C and δ15N) analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 6835–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope composition of aquatic and terrestrial plants of the San Francisco Bay estuarine system. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 713–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter. Chem. Geol. 1994, 114, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Lyu, H.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Lei, S.; Bi, S.; Mu, M.; Du, C.; Zeng, S. Dual stable isotope tracing the source and composition of POM during algae blooms in a large and shallow eutrophic lake: All contributions from algae? Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, T.F.; Van de Broek, M.; Govers, G.; Silva, R.W.; Moraes, J.M.; Camargo, P.B.; Mazzi, E.A.; Martinelli, L.A. Runoff, soil loss, and sources of particulate organic carbon delivered to streams by sugarcane and riparian areas: An isotopic approach. Catena 2019, 181, 104083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barko, J.W.; Gunnison, D.; Carpenter, S.R. Sediment interactions with submersed macrophyte growth and community dynamics. Aquat. Bot. 1991, 41, 41–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaeda, T.; Fujino, T.; Manatunge, J. Morphological adaptations of emergent plants to water flow: A case study withTypha angustifolia, Zizania latifoliaandPhragmites australis. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Søndergaard, M.; Christoffersen, K. (Eds.) The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; p. 131. ISBN 0-387-98284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Moreno-Madriñán, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, X. Long-term change of total suspended matter in a deep-valley reservoir with HJ-1A/B: Implications for reservoir management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 3041–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Han, Y.; Li, Q.; Jeppesen, E.; Li, K.; Yu, J.; Liu, Z. Crucian Carp (Carassius carassius) Strongly Affect C/N/P Stoichiometry of Suspended Particulate Matter in Shallow Warm Water Eutrophic Lakes. Water 2019, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Li, Q.; He, H.; Gu, J.; Wu, Z.; Huang, X.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K. Effect of juvenile omni-benthivorous fish (Carassius carassius) disturbance on the efficiency of lanthanum-modified bentonite (LMB) for eutrophication control: A mesocosm study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 21779–21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, M.; Schmidt, C.; van Geldern, R.; Barth, J.A. Dissolved oxygen in water and its stable isotope effects: A review. Chem. Geol. 2017, 473, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Controlling cyanobacterial harmful blooms in freshwater ecosystems. Microb Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Como, S.; Magni, P.; Huang, L. Spatiotemporal variation in environmental features and elemental/isotopic composition of organic matter sources and primary producers in the Yundang Lagoon (Xiamen, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 13126–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Jeppesen, E.; Taylor, W.D.; Rudstam, L.G. Effects of benthic-feeding common carp and filter-feeding silver carp on benthic-pelagic coupling: Implications for shallow lake management. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Yu, W.; Yin, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, D.; Li, Q.; Chen, J. Effect of Ecosystem Degradation on the Source of Particulate Organic Matter in a Karst Lake: A Case Study of the Caohai Lake, China. Water 2022, 14, 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121867
Wu J, Yang H, Yu W, Yin C, He Y, Zhang Z, Xu D, Li Q, Chen J. Effect of Ecosystem Degradation on the Source of Particulate Organic Matter in a Karst Lake: A Case Study of the Caohai Lake, China. Water. 2022; 14(12):1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121867
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiaxi, Haiquan Yang, Wei Yu, Chao Yin, Yun He, Zheng Zhang, Dan Xu, Qingguang Li, and Jingan Chen. 2022. "Effect of Ecosystem Degradation on the Source of Particulate Organic Matter in a Karst Lake: A Case Study of the Caohai Lake, China" Water 14, no. 12: 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121867
APA StyleWu, J., Yang, H., Yu, W., Yin, C., He, Y., Zhang, Z., Xu, D., Li, Q., & Chen, J. (2022). Effect of Ecosystem Degradation on the Source of Particulate Organic Matter in a Karst Lake: A Case Study of the Caohai Lake, China. Water, 14(12), 1867. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14121867