Using Machine Learning Models for Predicting the Water Quality Index in the La Buong River, Vietnam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
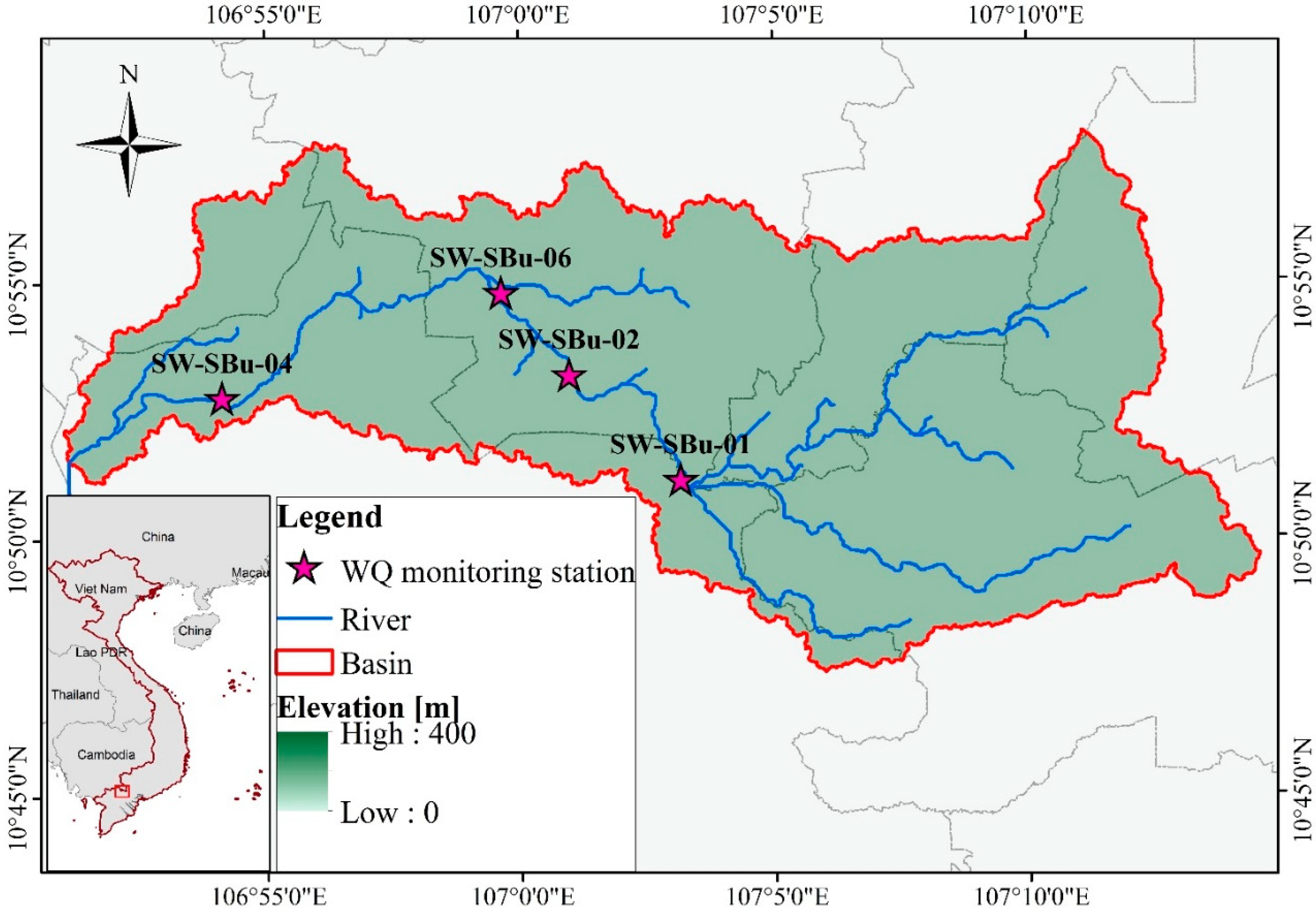
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data Collection and Processing
3.2. Machine Learning Models
3.2.1. Boosting-Based Algorithms
3.2.2. Decision Tree-Based Algorithms
3.2.3. ANN-Based Algorithms
3.3. Construction of ML Models
3.4. Performance Evaluation of ML Models
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Performance Evaluation of Boosting-Based Models
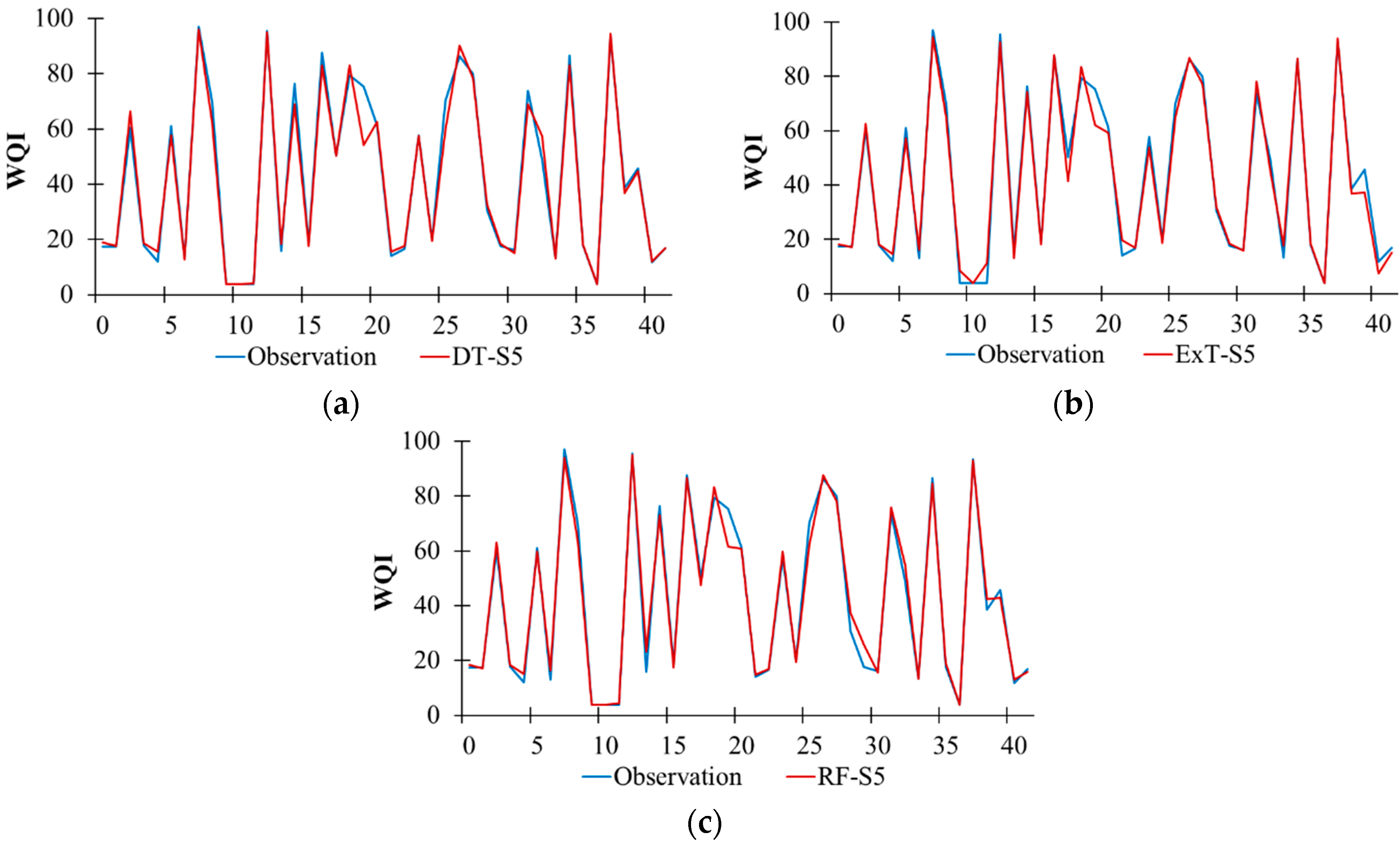
4.2. Performance Evaluation of Decision Tree-Based Models
4.3. Performance Evaluation of ANN-Based Models
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nouraki, A.; Alavi, M.; Golabi, M.; Albaji, M. Prediction of water quality parameters using machine learning models: A case study of the Karun River, Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 57060–57072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambade, B.; Sethi, S.S. Health Risk Assessment and Characterization of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon from the Hydrosphere. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2021, 25, 05020008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, B.; Sethi, S.S.; Giri, B.; Biswas, J.K.; Bauddh, K. Characterization, Behavior, and Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Estuary Sediments. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadollah, S.B.H.S.; Sharafati, A.; Motta, D.; Yaseen, Z.M. River water quality index prediction and uncertainty analysis: A comparative study of machine learning models. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.; Pasupuleti, S.; Singha, S.S.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S. Prediction of groundwater quality using efficient machine learning technique. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A water quality index-do we dare. Water Sew. Work. 1970, 117, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, D.T.; Khosravi, K.; Tiefenbacher, J.; Nguyen, H.; Kazakis, N. Improving prediction of water quality indices using novel hybrid machine-learning algorithms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyasha; Tung, T.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. A survey on river water quality modelling using artificial intelligence models: 2000–2020. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, G.S.; Kratzert, F.; Sampson, A.K.; Pelissier, C.S.; Klotz, D.; Frame, J.M.; Prieto, C.; Gupta, H.V. What Role does Hydrological Science Play in the Age of Machine Learning? Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bilali, A.; Taleb, A.; Brouziyne, Y. Groundwater quality forecasting using machine learning algorithms for irrigation purposes. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayan, A.-A.; Kibria, M.G.; Rahman, M.O.; Saha, J. River Water Quality Analysis and Prediction Using GBM. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Advanced Information and Communication Technology (ICAICT), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 28–29 November 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bedi, S.; Samal, A.; Ray, C.; Snow, D. Comparative evaluation of machine learning models for groundwater quality assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, N.; Pillai, A.S. Comparison of Water Quality Classification Models using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 10–12 June 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1183–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Mumtaz, R.; Hassan Zaidi, S.M. Analysis of water quality indices and machine learning techniques for rating water pollution: A case study of Rawal Dam, Pakistan. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3225–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naloufi, M.; Lucas, F.S.; Souihi, S.; Servais, P.; Janne, A.; Wanderley Matos De Abreu, T. Evaluating the Performance of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict the Microbial Quality of Surface Waters and to Optimize the Sampling Effort. Water 2021, 13, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaz, N.M.; Yusoff, M.K.; Aris, A.Z.; Juahir, H.; Ramli, M.F. Artificial neural network modeling of the water quality index for Kinta River (Malaysia) using water quality variables as predictors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2409–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, M.; Sharqi, S.S.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Afan, H.A.; Hussain, A.; Elshafie, A. Application of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques in water quality index prediction: A case study in tropical region, Malaysia. Neural Comput. Appl. 2017, 28, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, B.D.; Wang, C.; Ercan, M.B.; Culver, T.B.; Beling, P.A.; Goodall, J.L. Reinforcement learning-based real-time control of coastal urban stormwater systems to mitigate flooding and improve water quality. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.V.V.; Venkataramana, L.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Prasannamedha, G.; Harshana, S.; Srividya, S.J.; Harrinei, K.; Indraganti, S. Analysis and prediction of water quality using deep learning and auto deep learning techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MONRE. Decision No. 879/QD-TCMT on the Guidelines for Calculating Water Quality Index (WQI); Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2011.
- Khoi, D.N.; Nguyen, V.; Sam, T.T.; Nhi, P. Evaluation on Effects of Climate and Land-Use Changes on Streamflow and Water Quality in the La Buong River Basin, Southern Vietnam. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grayman, W.M.; Day, H.J.; Luken, R. Regional water quality management for the Dong Nai River Basin, Vietnam. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najah Ahmed, A.; Binti Othman, F.; Abdulmohsin Afan, H.; Khaleel Ibrahim, R.; Ming Fai, C.; Shabbir Hossain, M.; Ehteram, M.; Elshafie, A. Machine learning methods for better water quality prediction. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-H. Ensemble Methods: Foundations and Algorithms, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schapire, R.E. The Boosting Approach to Machine Learning: An Overview. In Nonlinear estimation and classification; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 149–171. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, W.; Jiao, X.; Guo, W.; Hamoud, Y.A. Comparison of five Boosting-based models for estimating daily reference evapotranspiration with limited meteorological variables. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, A.; Nasira, G.M. Data mining for meteorological applications: Decision trees for modeling rainfall prediction. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research, Coimbatore, India, 18–20 December 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.W.; Reynolds, J.; Rezgui, Y. Predictive modelling for solar thermal energy systems: A comparison of support vector regression, random forest, extra trees and regression trees. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, P.; Kamrava, S.; Bai, T.; Sahimi, M. Machine learning in geo- and environmental sciences: From small to large scale. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 142, 103619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Boyle, D.P.; Bäse, F. Comparison of different efficiency criteria for hydrological model assessment. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, D.; Khan, A.A. Machine learning techniques for monthly river flow forecasting of Hunza River, Pakistan. Earth Sci. Informatics 2020, 13, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, R.; Henderson, B.L. Estimation of nonlinear trends in water quality: An improved approach using generalized additive models. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W07420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Moyer, D.L. Estimation of nonlinear water-quality trends in high-frequency monitoring data. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadri, S.; Elbeltagi, A.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Kateb, S. Performance of machine learning methods in predicting water quality index based on irregular data set: Application on Illizi region (Algerian southeast). Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.-C.; Wu, T. Influence of water allocation on bioenergy production under climate change: A stochastic mathematical programming approach. Energy 2021, 231, 120955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.-C.; Mu, J.E. Prospect of China’s renewable energy development from pyrolysis and biochar applications under climate change. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 114, 109343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variables | Unit | Min | Max | Mean | Median | Std. Deviation | CV% |
| T | °C | 25.60 | 32.80 | 28.59 | 28.55 | 1.48 | 5.2% |
| pH | 5.84 | 8.42 | 7.03 | 7.07 | 0.39 | 5.6% | |
| DO | mg/L | 2.04 | 8.63 | 5.75 | 6.12 | 1.53 | 1.5% |
| BOD | mg/L | 2.00 | 24.00 | 6.40 | 5.00 | 3.66 | 3.6% |
| COD | mg/L | 3.00 | 113.00 | 19.87 | 16.00 | 14.91 | 15.6% |
| NH4+ | mg/L | 0.03 | 11.10 | 0.89 | 0.31 | 1.52 | 1.5% |
| PO43− | mg/L | 0.02 | 2.90 | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.41 | 0.4% |
| TSS | mg/L | 2.00 | 1402.00 | 85.48 | 31.00 | 156.52 | 153.9% |
| TUR | NTU | 2.00 | 1280.00 | 82.36 | 24.00 | 158.36 | 158.4% |
| Coliform | MPN/100 mL | 430.00 | 930,000.00 | 28,195.00 | 9300.00 | 96,766.23 | 343.2% |
| WQI | 3.02 | 98.30 | 42.72 | 33.91 | 31.86 | 79.3% |
| Variables | T | pH | DO | BOD | COD | NH4+ | PO43− | TSS | TUR | Coliform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.056 | 0.107 | 0.069 | 0.261 | 0.385 | 0.364 | 0.276 | 0.565 | 0.476 | 0.775 |
| Scenarios | Input Variables |
|---|---|
| S1 | Coliform |
| S2 | Coliform, TSS |
| S3 | Coliform, TSS, TUR |
| S4 | Coliform, TSS, TUR, COD |
| S5 | Coliform, TSS, TUR, COD, BOD |
| S6 | Coliform, TSS, TUR, COD, BOD, PO43− |
| S7 | Coliform, TSS, TUR, COD, BOD, PO43−, NH4+ |
| S8 | Coliform, TSS, TUR, COD, BOD, PO43−, NH4+, pH |
| S9 | Coliform, TSS, TUR, COD, BOD, PO43−, NH4+, pH, DO |
| S10 | Coliform, TSS, TUR, COD, BOD, PO43−, NH4+, pH, DO, T |
| Models | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AdaBoost | RMSE | 0.550 | 0.175 | 0.211 | 0.205 | 0.205 | 0.207 | 0.212 | 0.212 | 0.221 | 0.219 |
| R2 | 0.690 | 0.973 | 0.959 | 0.960 | 0.962 | 0.964 | 0.960 | 0.961 | 0.955 | 0.958 | |
| GBM | RMSE | 0.552 | 0.183 | 0.130 | 0.131 | 0.118 | 0.120 | 0.108 | 0.122 | 0.117 | 0.109 |
| R2 | 0.682 | 0.967 | 0.983 | 0.983 | 0.986 | 0.986 | 0.989 | 0.986 | 0.987 | 0.989 | |
| HGBM | RMSE | 0.542 | 0.183 | 0.203 | 0.204 | 0.202 | 0.203 | 0.198 | 0.198 | 0.197 | 0.200 |
| R2 | 0.695 | 0.967 | 0.958 | 0.957 | 0.958 | 0.958 | 0.960 | 0.960 | 0.960 | 0.959 | |
| LightGBM | RMSE | 0.545 | 0.166 | 0.138 | 0.155 | 0.152 | 0.119 | 0.160 | 0.158 | 0.143 | 0.167 |
| R2 | 0.691 | 0.973 | 0.981 | 0.976 | 0.977 | 0.986 | 0.974 | 0.975 | 0.979 | 0.972 | |
| XGBoost | RMSE | 0.552 | 0.179 | 0.133 | 0.127 | 0.121 | 0.112 | 0.120 | 0.119 | 0.107 | 0.111 |
| R2 | 0.683 | 0.968 | 0.982 | 0.984 | 0.986 | 0.988 | 0.986 | 0.987 | 0.989 | 0.988 | |
| DT | RMSE | 0.553 | 0.206 | 0.183 | 0.158 | 0.147 | 0.216 | 0.199 | 0.205 | 0.199 | 0.238 |
| R2 | 0.681 | 0.957 | 0.966 | 0.976 | 0.979 | 0.954 | 0.960 | 0.957 | 0.960 | 0.941 | |
| ExT | RMSE | 0.553 | 0.177 | 0.158 | 0.164 | 0.126 | 0.149 | 0.199 | 0.142 | 0.202 | 0.197 |
| R2 | 0.681 | 0.968 | 0.974 | 0.973 | 0.985 | 0.978 | 0.963 | 0.981 | 0.959 | 0.962 | |
| RF | RMSE | 0.554 | 0.162 | 0.126 | 0.127 | 0.121 | 0.123 | 0.125 | 0.123 | 0.123 | 0.129 |
| R2 | 0.680 | 0.974 | 0.984 | 0.984 | 0.986 | 0.985 | 0.985 | 0.985 | 0.985 | 0.984 | |
| MLP | RMSE | 0.532 | 0.153 | 0.192 | 0.132 | 0.141 | 0.196 | 0.928 | 0.307 | 0.996 | 0.515 |
| R2 | 0.711 | 0.976 | 0.964 | 0.984 | 0.980 | 0.961 | 0.127 | 0.901 | 0.080 | 0.768 | |
| RBF | RMSE | 0.620 | 0.360 | 0.385 | 0.511 | 0.595 | 0.562 | 0.632 | 0.728 | 0.845 | 0.803 |
| R2 | 0.679 | 0.887 | 0.858 | 0.760 | 0.687 | 0.689 | 0.607 | 0.516 | 0.276 | 0.370 | |
| DFNN | RMSE | 0.543 | 0.162 | 0.170 | 0.169 | 0.189 | 0.190 | 0.215 | 0.173 | 0.206 | 0.217 |
| R2 | 0.702 | 0.973 | 0.972 | 0.971 | 0.971 | 0.967 | 0.953 | 0.972 | 0.958 | 0.954 | |
| CNN | RMSE | 0.485 | 0.185 | 0.203 | 0.180 | 0.158 | 0.221 | 0.139 | 0.243 | 0.265 | 0.348 |
| R2 | 0.773 | 0.965 | 0.962 | 0.964 | 0.977 | 0.961 | 0.982 | 0.942 | 0.937 | 0.895 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khoi, D.N.; Quan, N.T.; Linh, D.Q.; Nhi, P.T.T.; Thuy, N.T.D. Using Machine Learning Models for Predicting the Water Quality Index in the La Buong River, Vietnam. Water 2022, 14, 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101552
Khoi DN, Quan NT, Linh DQ, Nhi PTT, Thuy NTD. Using Machine Learning Models for Predicting the Water Quality Index in the La Buong River, Vietnam. Water. 2022; 14(10):1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101552
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhoi, Dao Nguyen, Nguyen Trong Quan, Do Quang Linh, Pham Thi Thao Nhi, and Nguyen Thi Diem Thuy. 2022. "Using Machine Learning Models for Predicting the Water Quality Index in the La Buong River, Vietnam" Water 14, no. 10: 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101552
APA StyleKhoi, D. N., Quan, N. T., Linh, D. Q., Nhi, P. T. T., & Thuy, N. T. D. (2022). Using Machine Learning Models for Predicting the Water Quality Index in the La Buong River, Vietnam. Water, 14(10), 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101552








