Preparation of PANI Modified ZnO Composites via Different Methods: Structural, Morphological and Photocatalytic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PANI-ZnO Composites
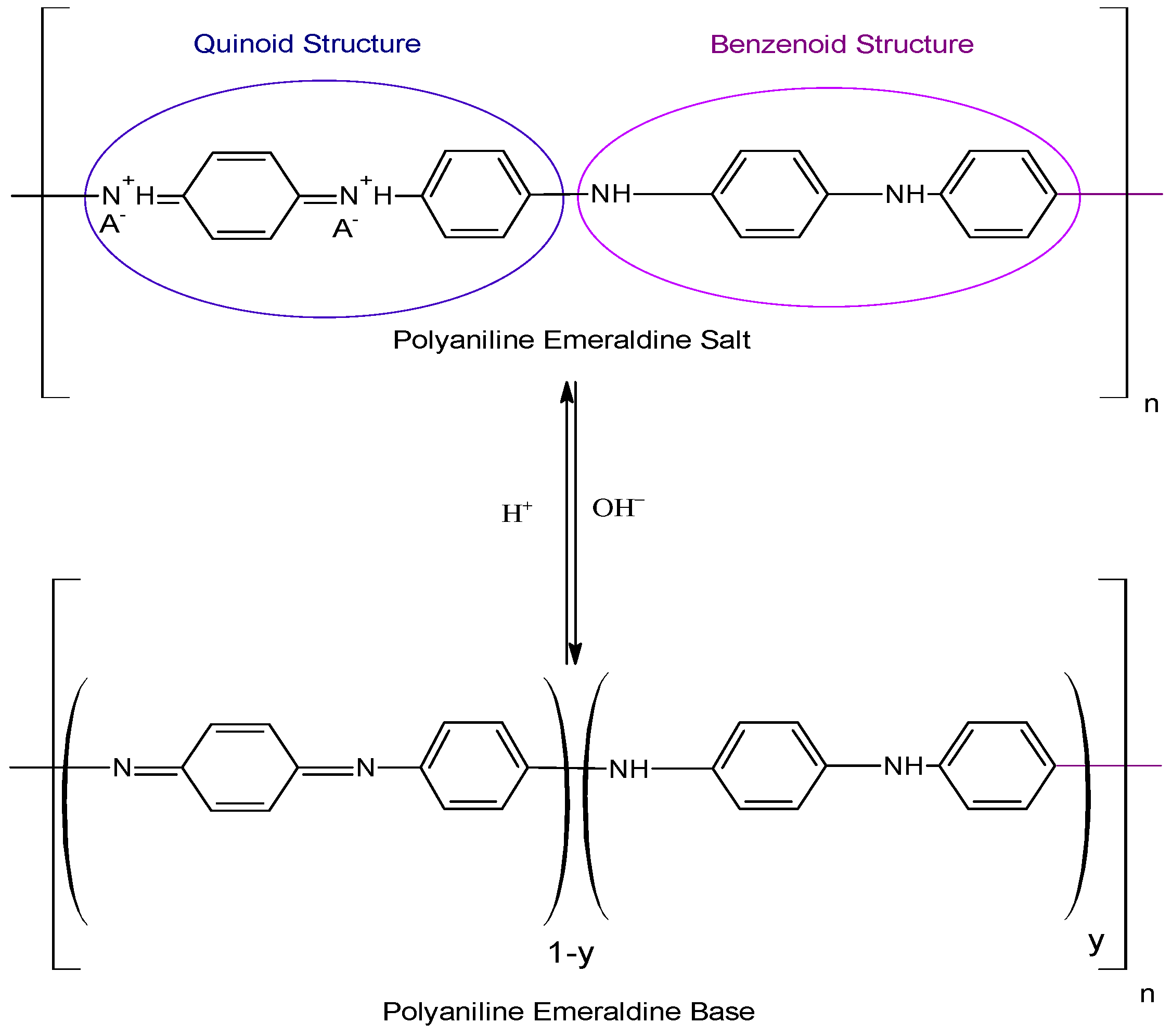
2.2.1. Preparation of PANI-ES and PANI-EB
2.2.2. In-Situ Chemical Oxidation Polymerization Method
2.2.3. Hybridization Method
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Photocatalytic Activity
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the PANI-ZnO Composites
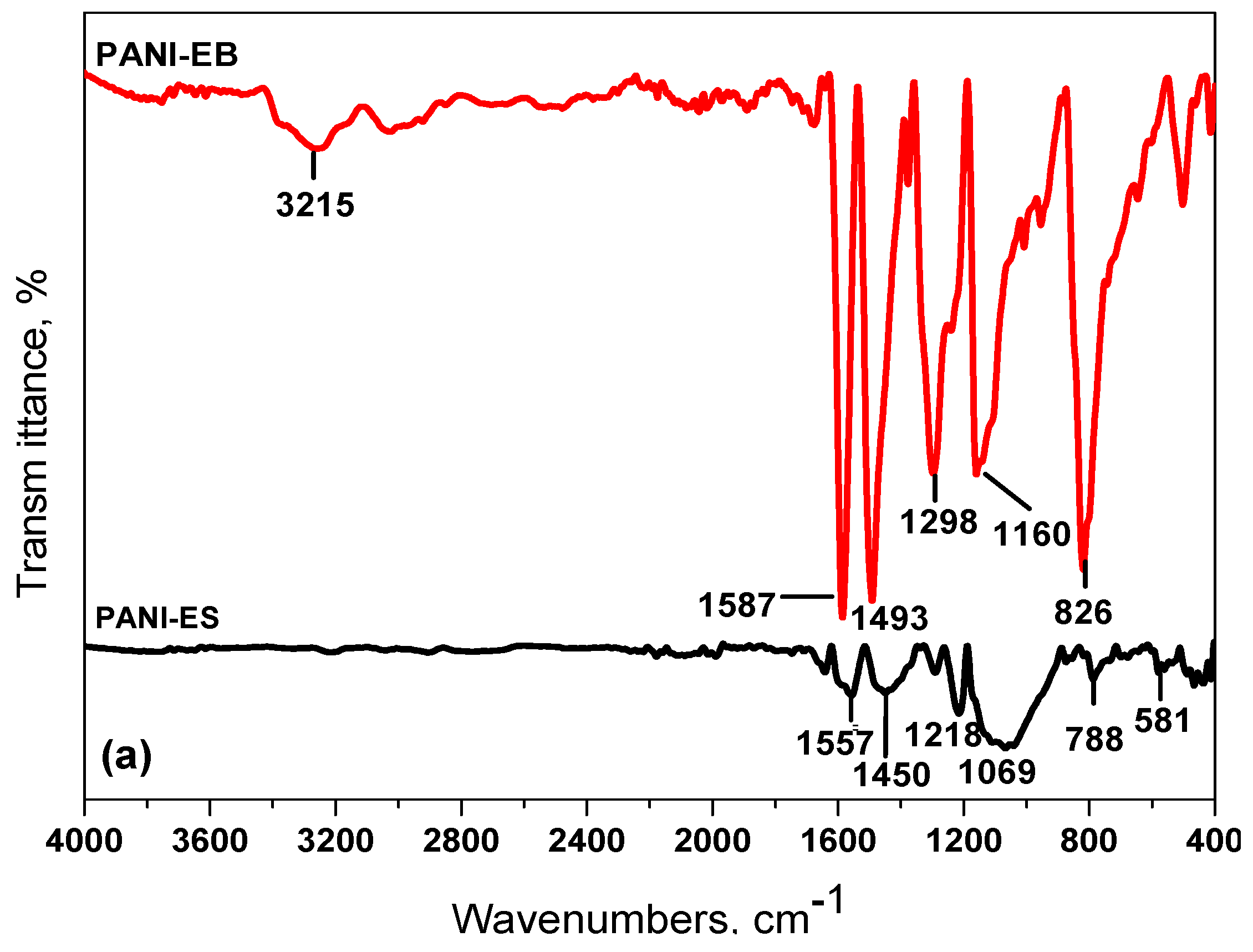
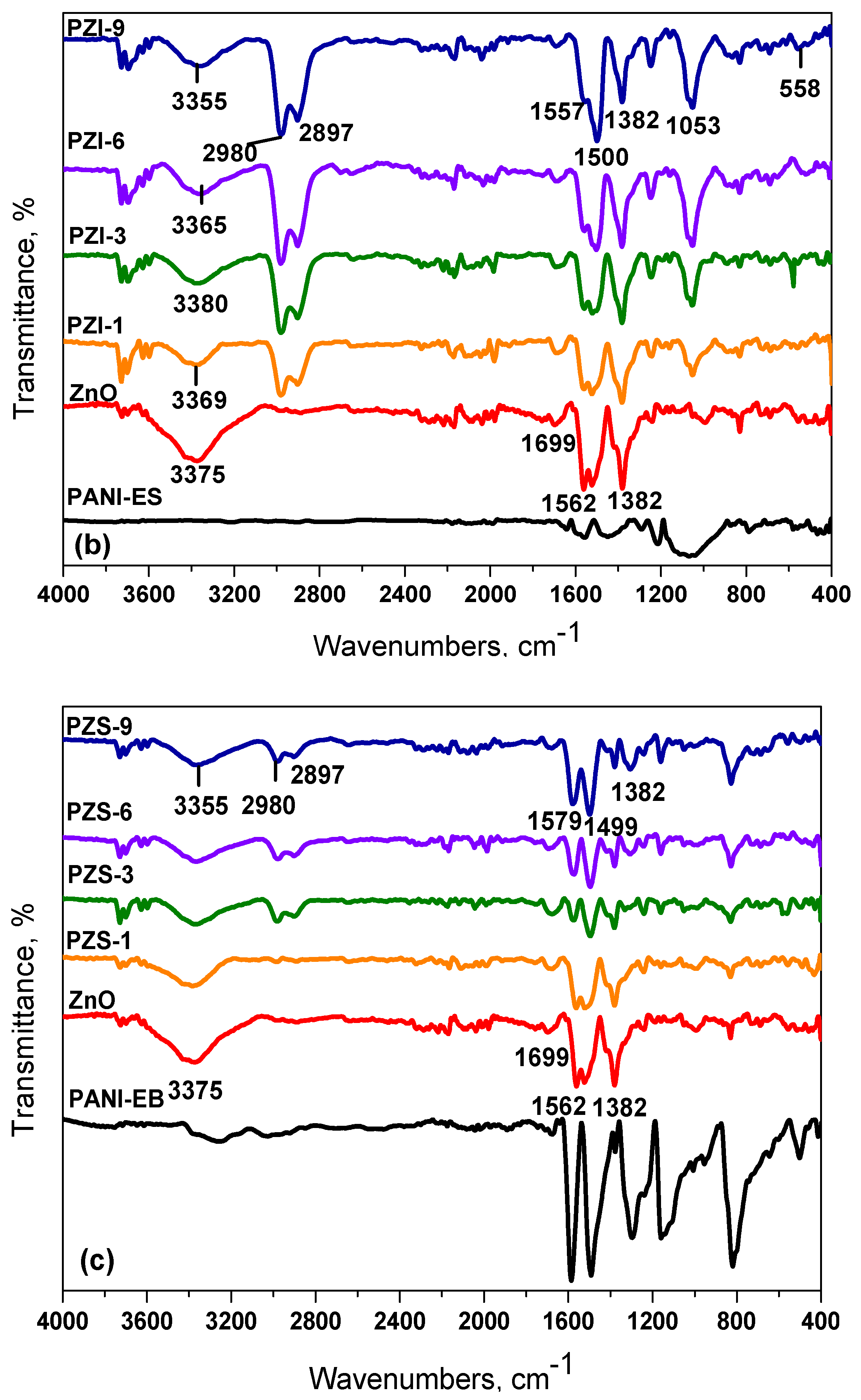
3.1.1. FT-IR Spectroscopy
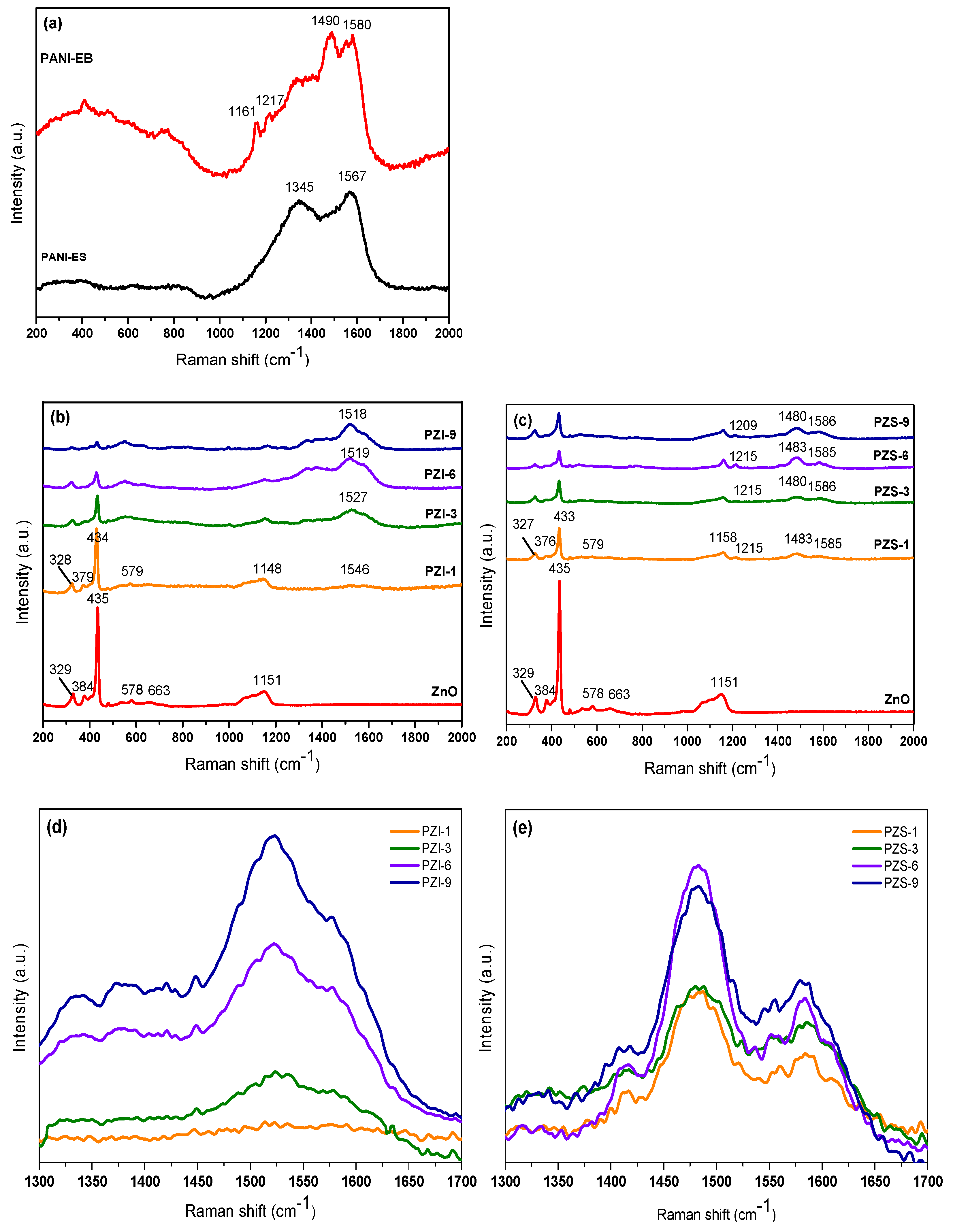
3.1.2. Raman Spectroscopy
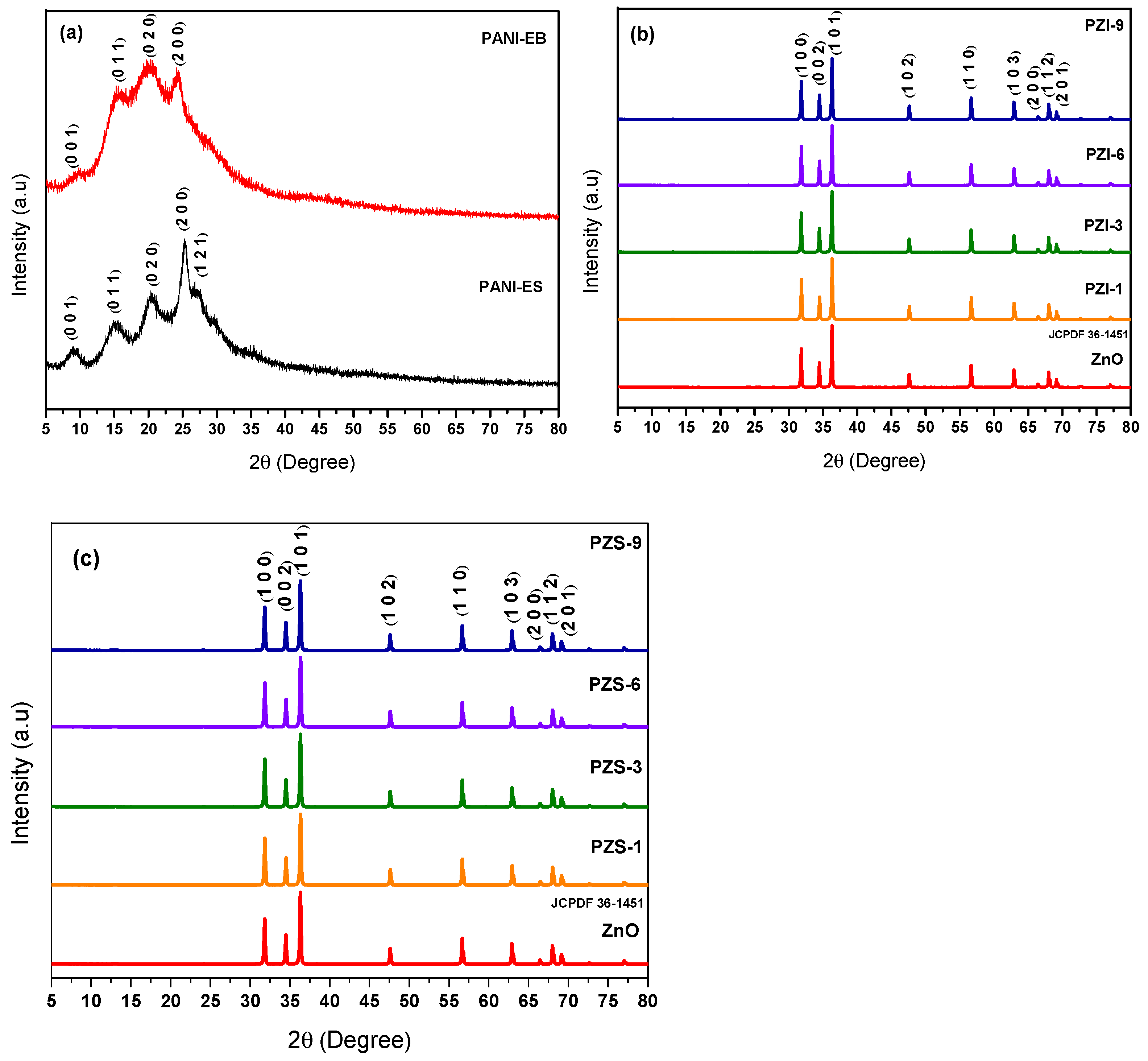
3.1.3. XRD Spectroscopy and Crystal Structure
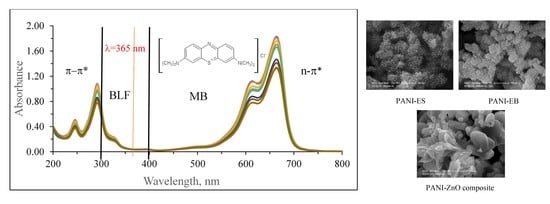
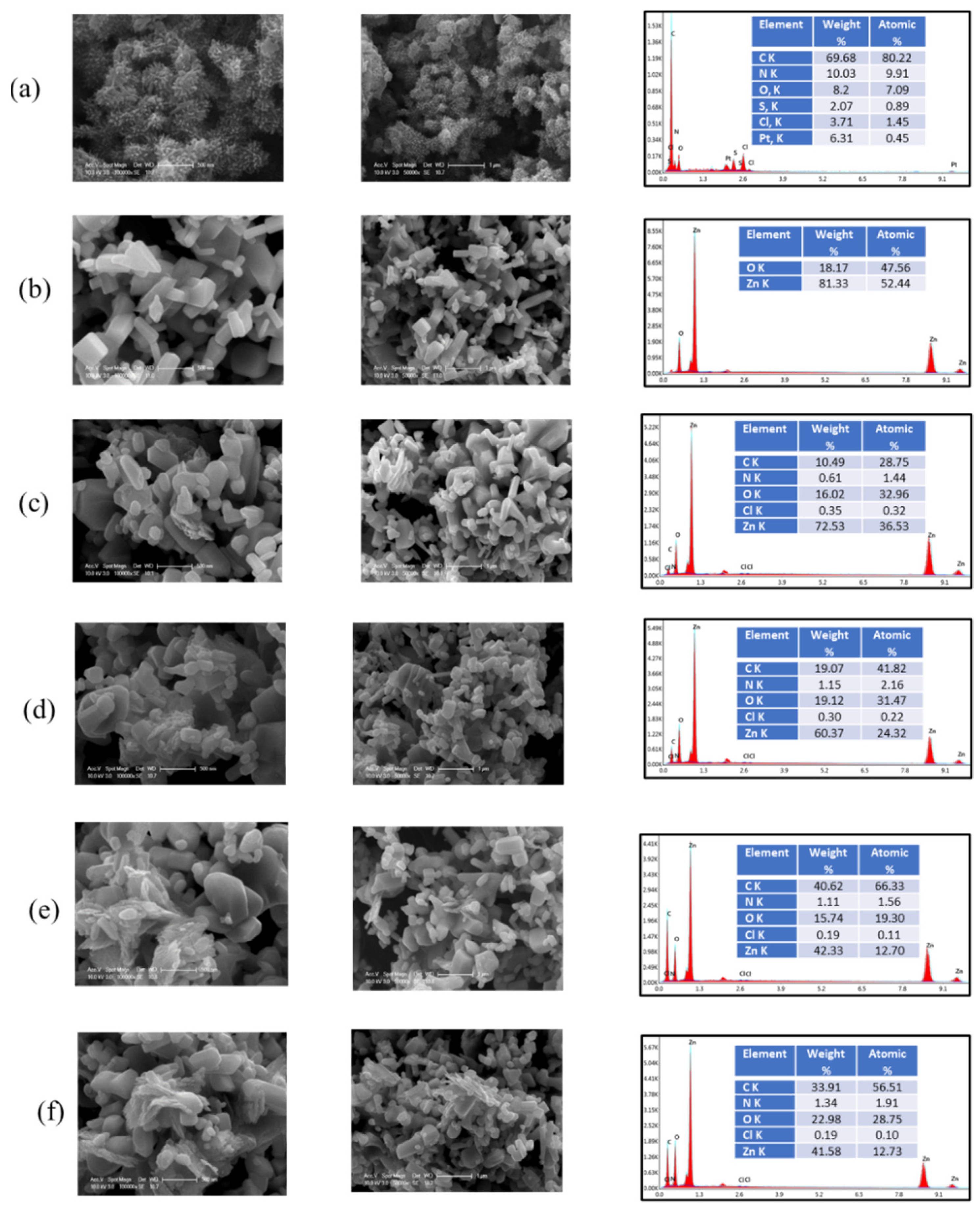
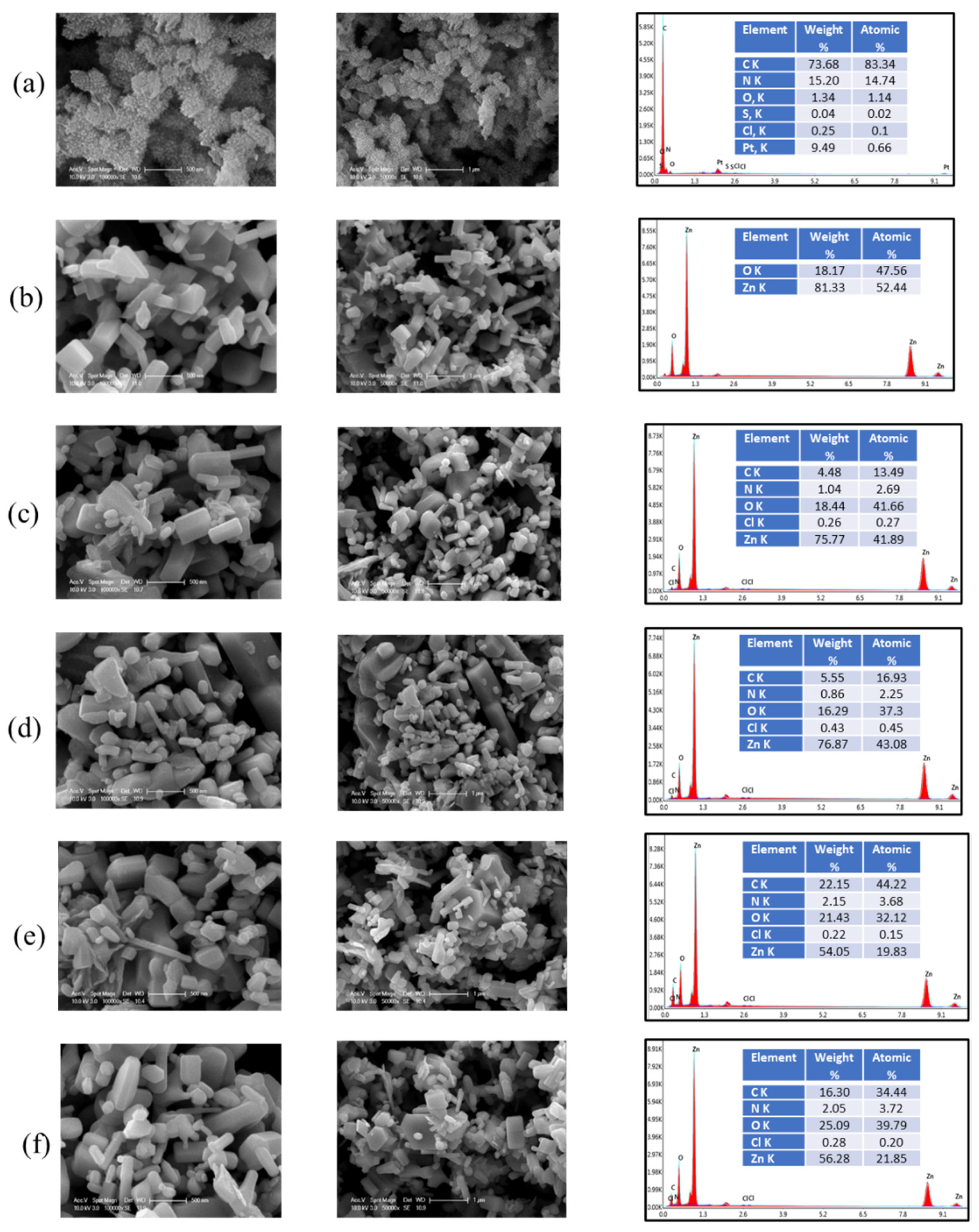
3.1.4. SEM-EDAX Analysis and Morphological Structure
3.2. Photocatalytic Activity Experiments
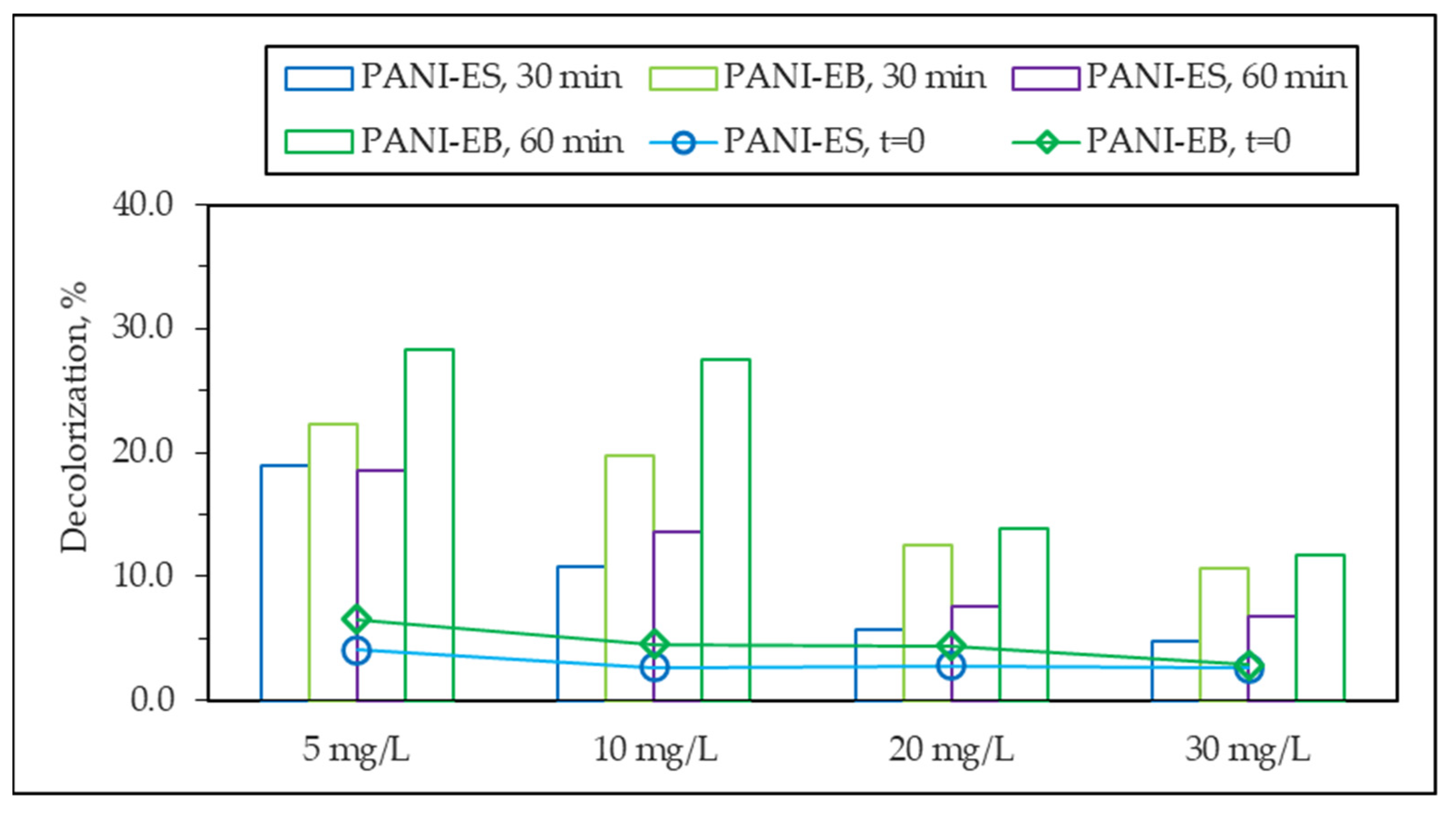
3.2.1. Direct Photolysis of MB
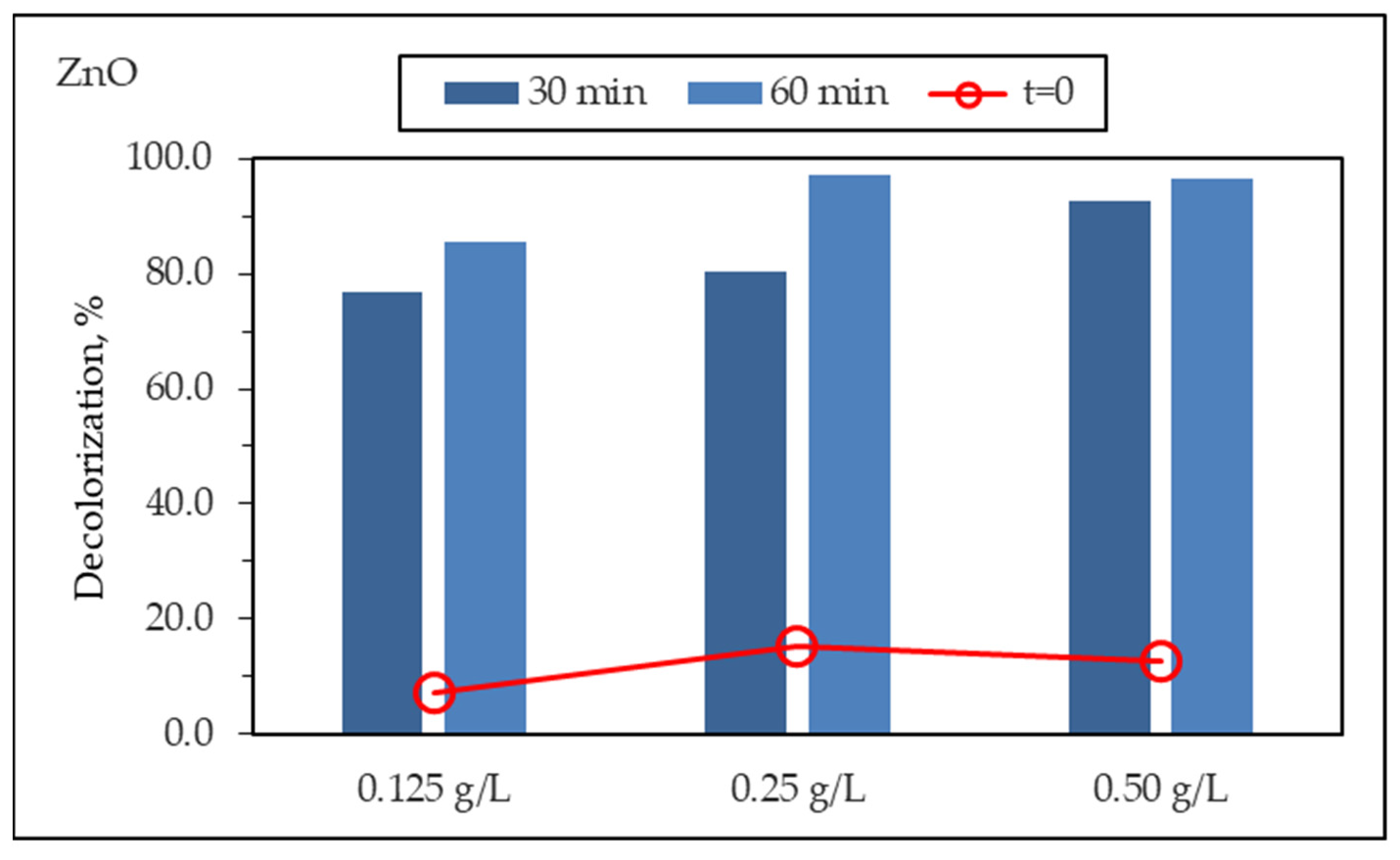
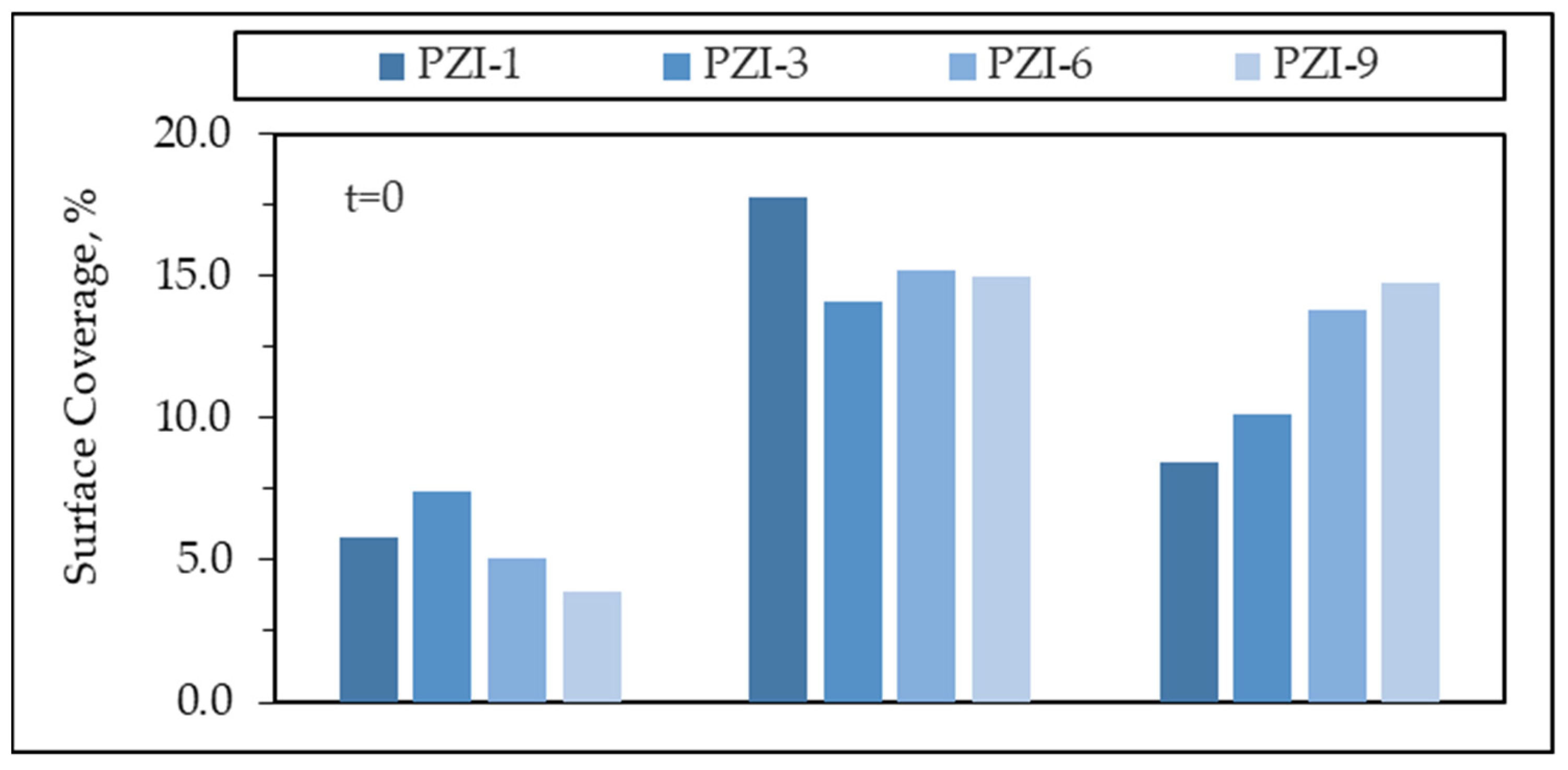
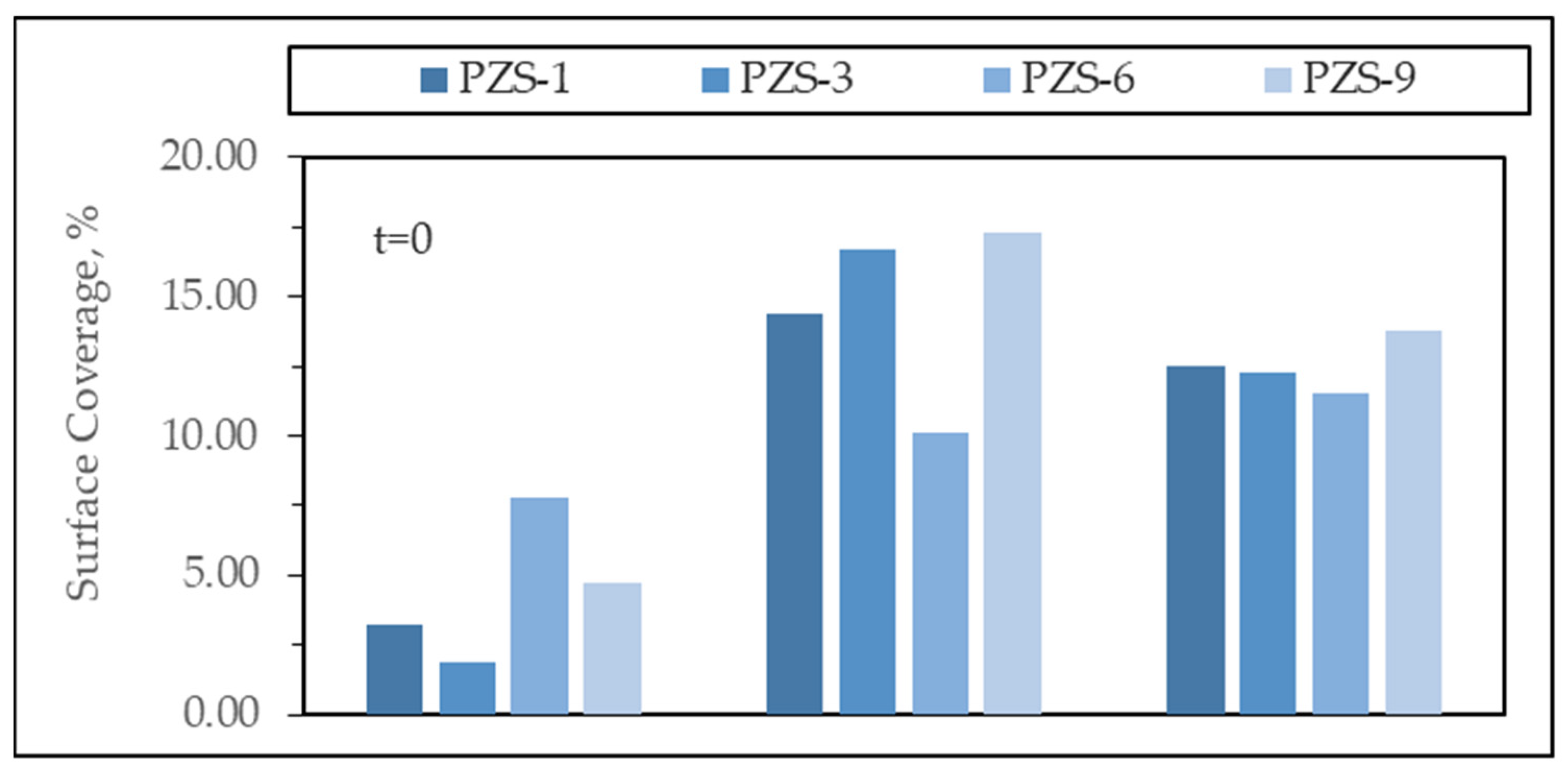
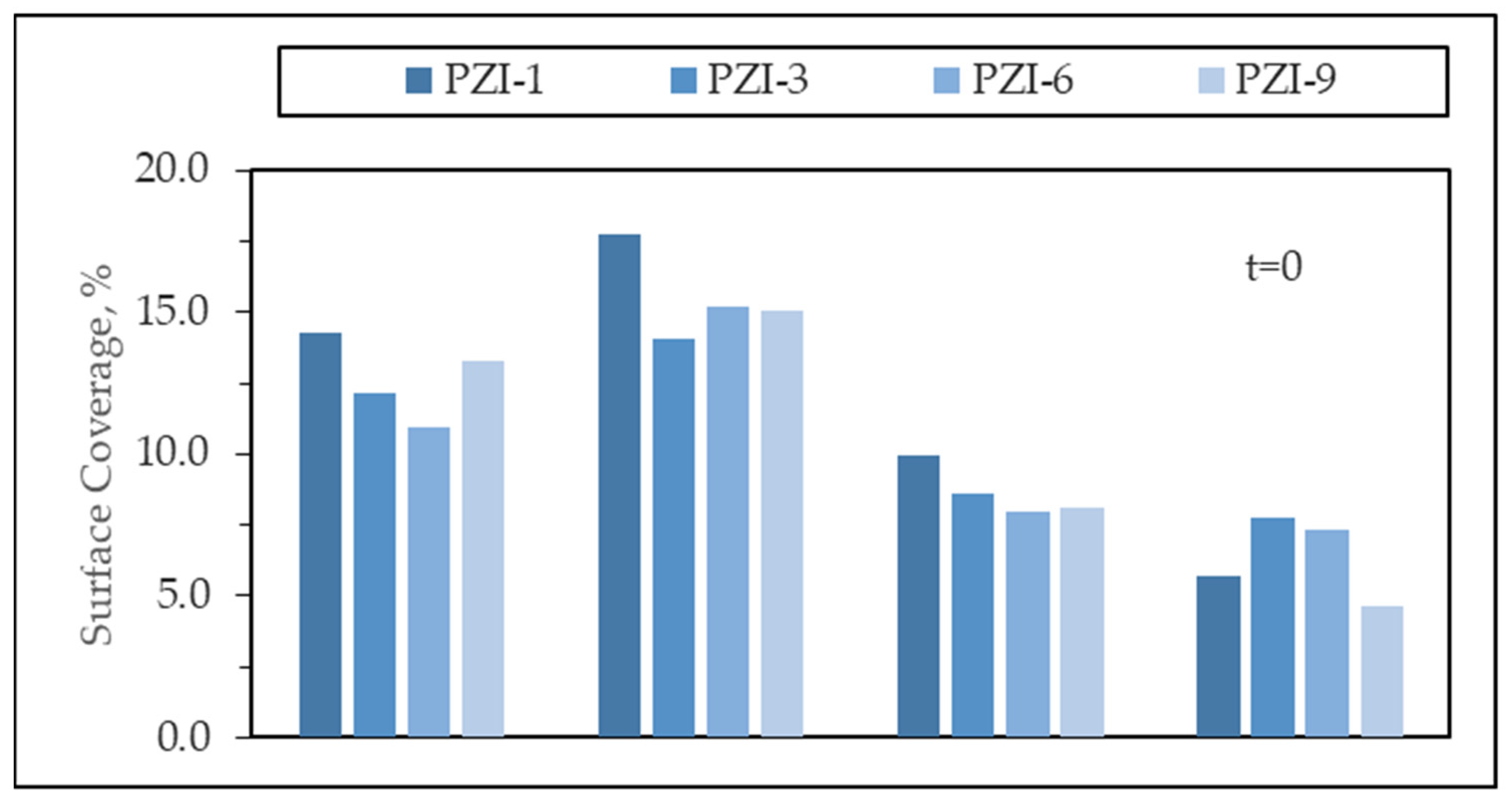
3.2.2. Adsorptive Interactions in the Absence of Light
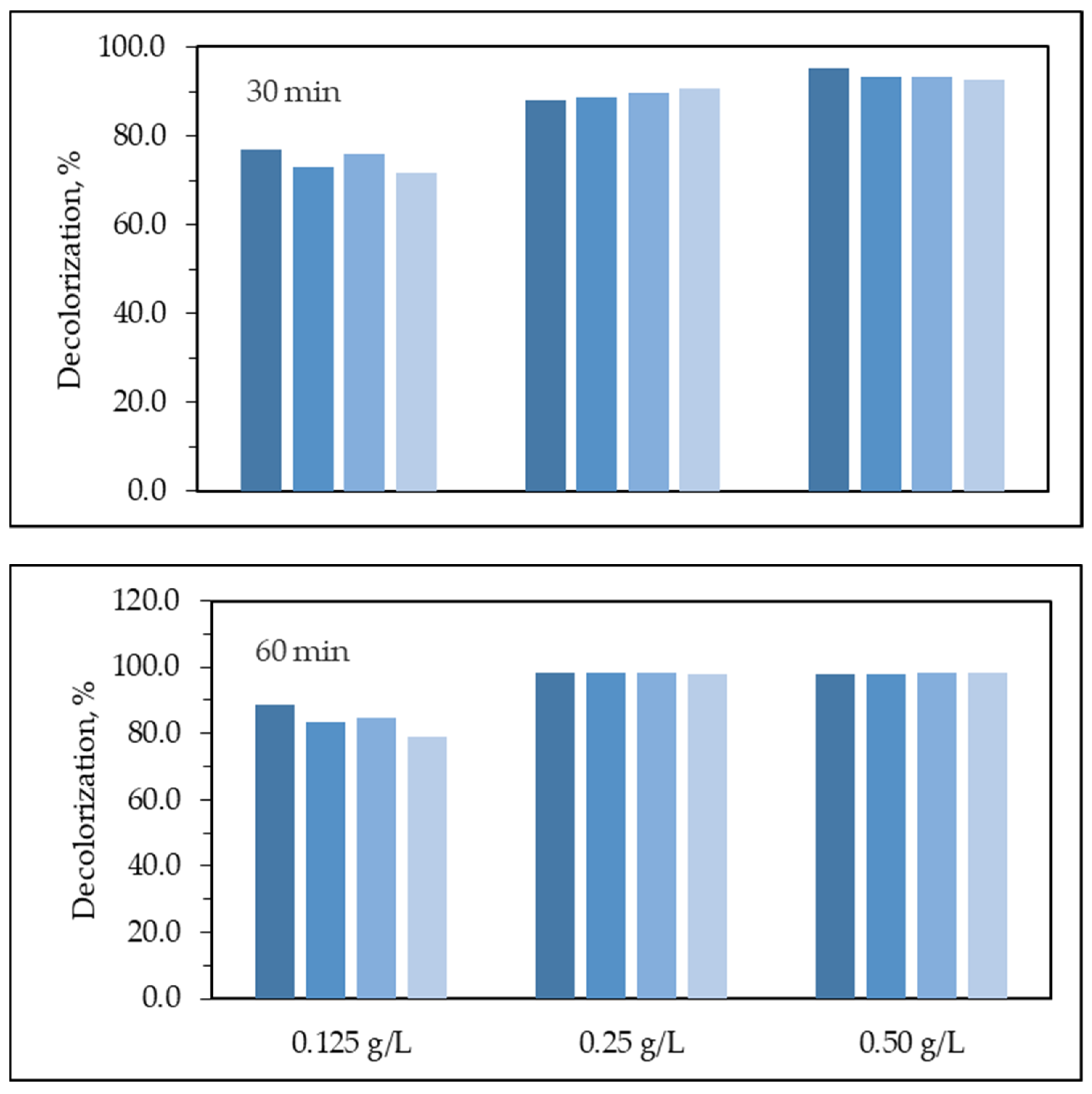
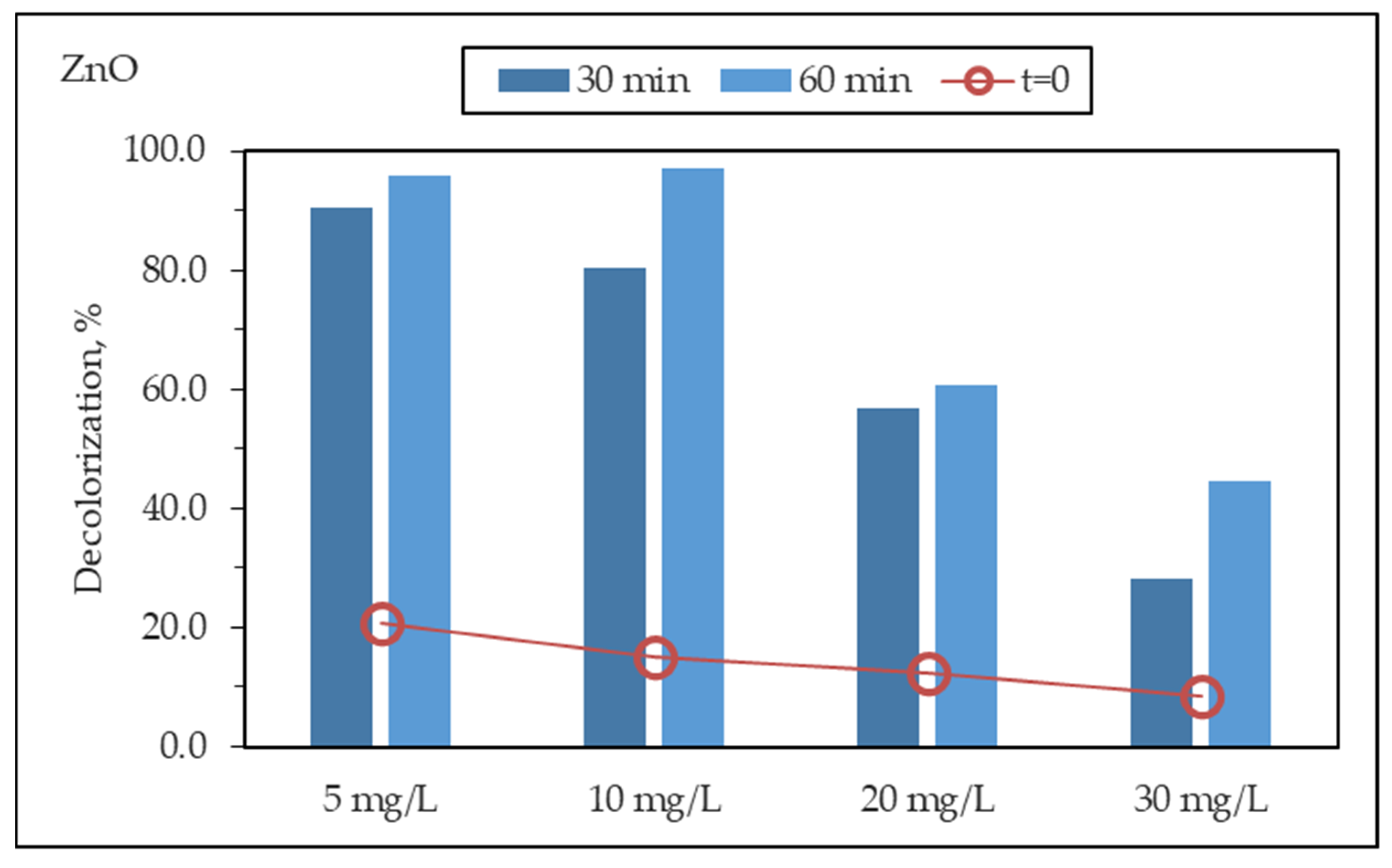
3.2.3. Photocatalytic Degradation of MB using PANI-ZnO Specimens
3.2.4. Kinetics of Photocatalytic Degradation
- R: pseudo first order rate (cm−1min−1),
- Ao: initial absorbance of MB expressed as A664,o, A292,o and A246,o,
- A: absorbance of MB expressed as A664, A292 and A246 at time t,
- t: irradiation time, min,
- k: pseudo first order reaction rate constant, min−1.
- Half-life (t1/2, min) could easily be calculated by the following equation, t1/2 = 0.692/k.
- Kinetic model parameters (R2 > 0.85) were presented in Table 1.
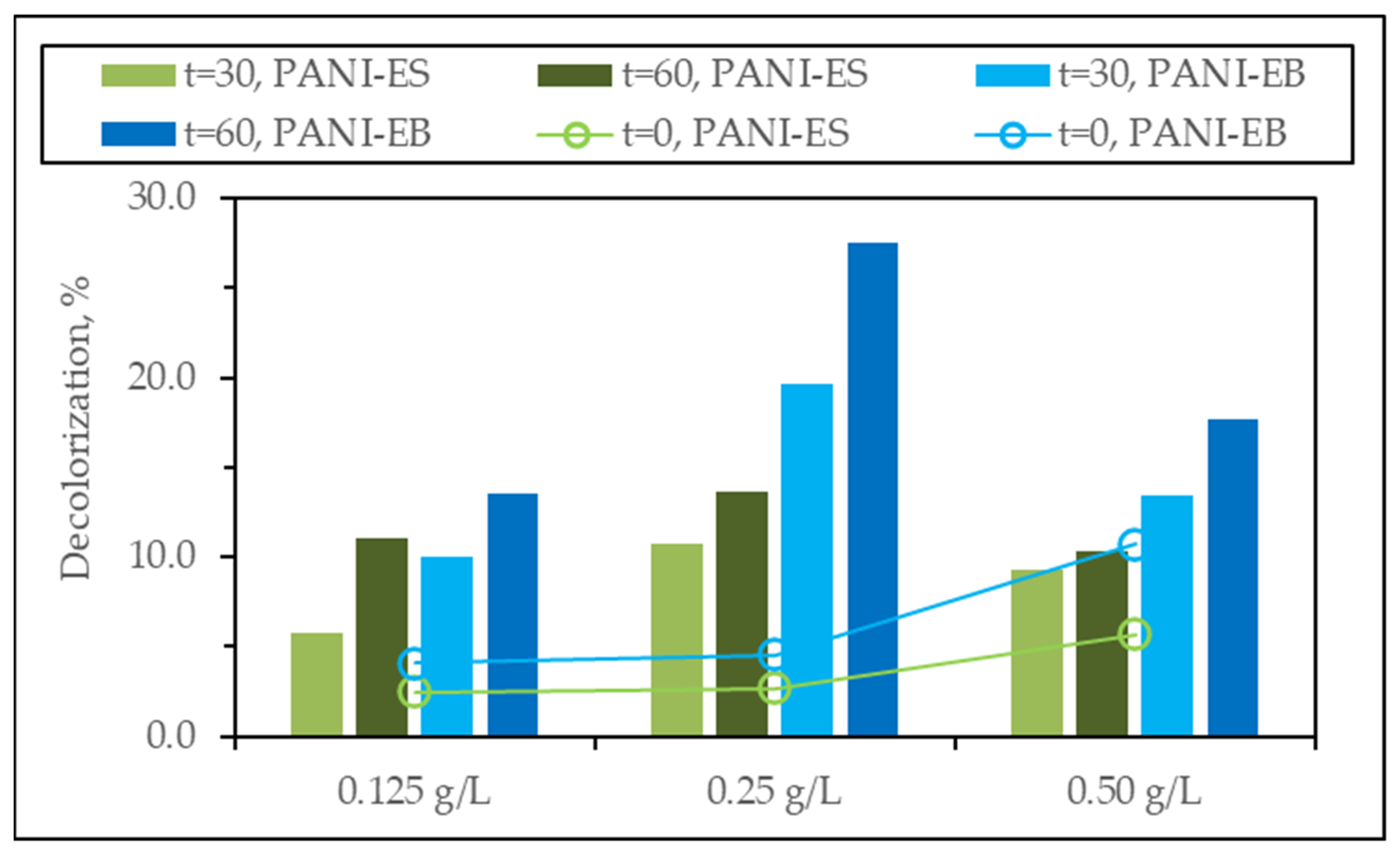
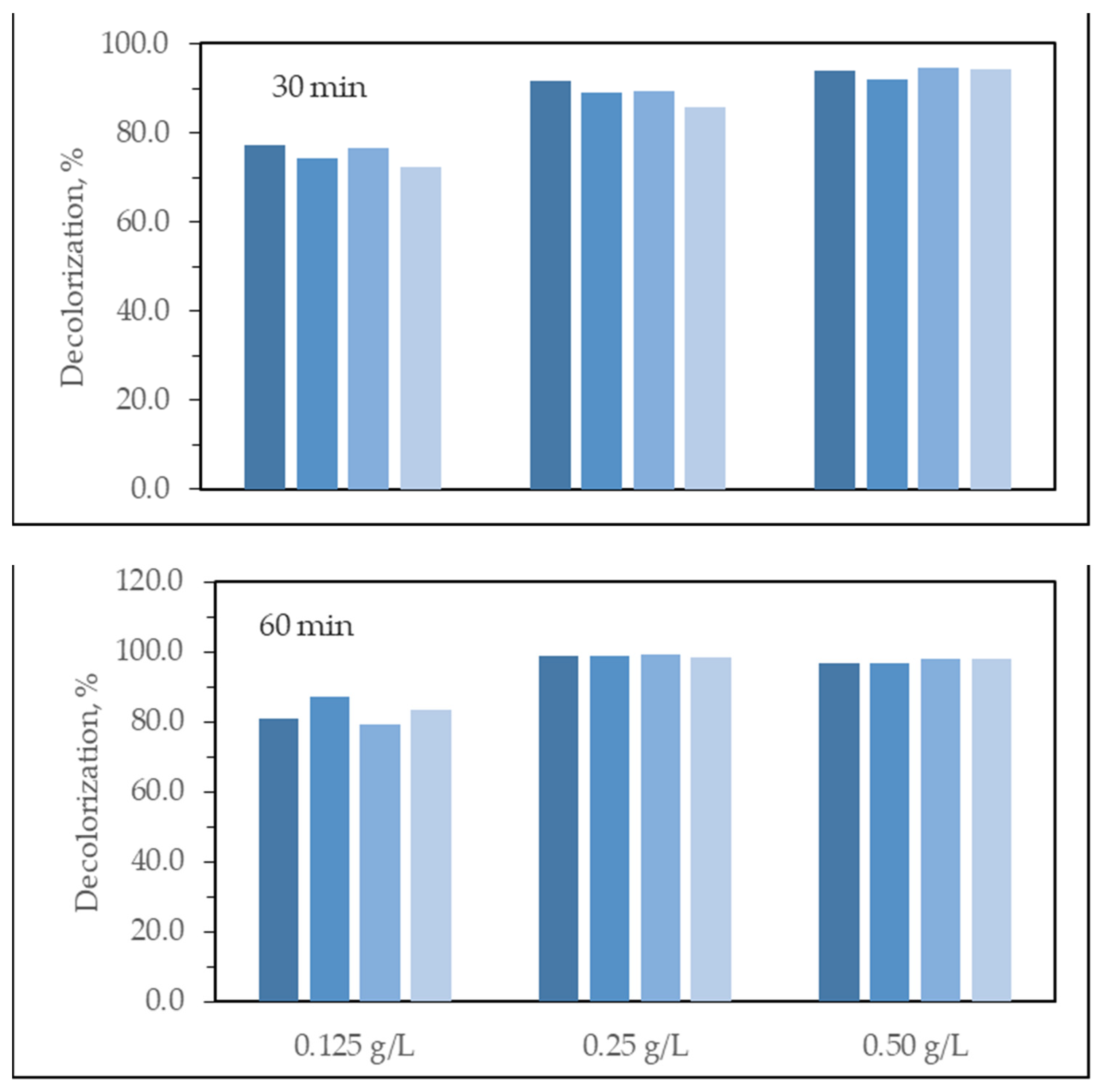
3.2.5. Photocatalyst Dose Effect
3.2.6. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Byrne, C.; Subramanian, G.; Pillai, S.C. Recent advances in photocatalysis for environmental applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3531–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Lai, C.W.; Ngai, K.S.; Juan, J.C. Recent developments of zinc oxide based photocatalyst in water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2016, 88, 428–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, M.; Zirak, M.; Naseri, A.; Khorashadizade, E.; Moshfegh, A.Z. Recent progress on doped ZnO nanostructures for visible-light photocatalysis. Thin Solid Films 2016, 605, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakthivel, S.; Neppolian, B.; Shankar, M.V.; Arabindoo, B.; Palanichamy, M.; Murugesan, V. Solar photocatalytic degradation of azo dye: Comparison of photocatalytic efficiency of ZnO and TiO2. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2003, 77, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Kumar, P.M.; Bhagavathiachari, M.; Nair, R.G. Hierarchical ZnO-TiO2 nanoheterojunction: A strategy driven approach to boost the photocatalytic performance through the synergy of improved surface area and interfacial charge transport. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 534, 147321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Manoli, K.; Shen, X.; Wang, J.; Ray, A.K. Solar photocatalytic degradation of caffeine with titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 377, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Chauhan, R.; Kumar, N.; Singh, V.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mohanty, P.; Mandal, T.K. Enhancing photocatalytic degradation of quinoline by ZnO:TiO2 mixed oxide: Optimization of operating parameters and mechanistic study. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 258, 110032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguti, L.; Dejene, F. Influence of annealing temperature on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of ZnO-TiO2 composites for application in dye removal in water. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2020, 24, 100594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štrbac, D.; Aggelopoulos, C.A.; Štrbac, G.; Dimitropoulos, M.; Novaković, M.; Ivetić, T.; Yannopoulos, S.N. Photocatalytic degradation of naproxen and methylene blue: Comparison between ZnO, TiO2 and their mixture. Process. Saf. Environ. 2018, 113, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkten, N.; Bekbolet, M. Photocatalytic performance of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide binary system on degradation of humic matter. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 401, 112748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, G.K.; Rajput, J.K.; Pathak, T.K.; Kumar, V.; Purohit, L.P. Synthesis of ZnO:TiO2 nanocomposites for photocatalyst application in visible light. Vacuum 2019, 160, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskizeybek, V.; Sarı, F.; Gülce, H.; Gülce, A.; Avcı, A. Preparation of the new polyaniline/ZnO nanocomposite and its photocatalytic activity for degradation of methylene blue and malachite green dyes under UV and natural sun lights irradiations. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 119, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilja, V.; Vrban, I.; Mandic, V.; Zic, M.; Hrnjak-Murgic, Z. Preparation of a PANI/ZnO composite for efficient photocatalytic degradation of acid blue. Polymers 2018, 10, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nosrati, R.; Olad, A.; Maramifar, R. Degradation of ampicillin antibiotic in aqueous solution by ZnO/polyaniline nanocomposite as photocatalyst under sunlight irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 2291–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowska, M.; Szczubiałka, K. Photoactive polymeric and hybrid systems for photocatalytic degradation of water pollutants. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 145, 120–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, U.; Ashraf, S.M.; Kashyap, J. Enhancement of photocatalytic properties of transitional metal oxides using conducting polymers: A mini review. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 71, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Liu, G.; Bao, C.; Chen, M.; Huang, Q. Improved stability and dispersity of ZnO@PANI nanocomposites aqueous suspension. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoičić, M.; Šaponjić, Z.; Janković, I.A.; Ćirić-Marjanović, G.; Ahrenkielc, S.P.; Čomor, M.I. Improvements to the photocatalytic efficiency of polyaniline modified TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S. Polyaniline blends, composites, and nanocomposites. In Polyaniline Blends, Composites, and Nanocomposites, 1st ed.; Visakh, P.M., Pina, C.D., Falletta, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 23–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ćirić-Marjanović, G. Recent advances in polyaniline research: Polymerization mechanisms, structural aspects, properties and applications. Synth. Met. 2013, 177, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J. Interaction of conducting polymers, polyaniline and polypyrrole, with organic dyes: Polymer morphology control, dye adsorption and photocatalytic decomposition. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.; Dong, H.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, J. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance of polyaniline modified mesoporous single crystal TiO2 microsphere. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, D.; Cheng, G.; Luo, Q.; An, J.; Wang, Y. Preparation of polyaniline-modified TiO2 nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity under visible light illumination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 81, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Min, S.X. TiO2/polyaniline composites: An efficient photocatalyst for the degradation of methylene blue under natural light. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2007, 18, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Dong, W.; Cui, G.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Xia, X.; Tang, B.; Wang, W. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of PANI/TiO2 due to their photosensitization-synergetic effect. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 247, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Su, Z. Preparation of PANI-TiO2 nanocomposites and their solid-phase photocatalytic degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zong, R.; Zhu, Y. Photocorrosion inhibition and photoactivity enhancement for zinc oxide via hybridization with monolayer polyaniline. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4605–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Wang, C.; Tan, R.; Song, W.; Cheng, Y. Preparation of pompon-like ZnO-PANI heterostructure and its applications for the treatment of typical water pollutants under visible light. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Mills, A.; Wells, N. Assessing photocatalytic activity using methylene blue without dye sensitization. Catal. Today 2018, 313, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatchard, C.G.; Parker, C.A. A new sensitive chemical actinometer—II. Potassium ferrioxalate as a standard chemical actinometer. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Proc. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1956, 235, 518–536. [Google Scholar]
- Bandgar, D.K.; Khuspe, G.D.; Pawar, R.C.; Lee, C.S.; Patil, V.B. Facile and novel route for preparation of nanostructured polyaniline (PANI) thin films. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 4, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdiryim, T.; Xiao-Gang, Z.; Jamal, R. Comparative studies of solid-state synthesized polyaniline doped with inorganic acids. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 90, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinova, N.V.; Stejskal, J.; Trchová, M.; Prokeš, J.; Omastová, M. Polyaniline and polypyrrole: A comparative study of the preparation. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trchová, M.; Šeděnková, I.; Stejskal, J. In-Situ polymerized polyaniline films 6. FTIR spectroscopic study of aniline polymerisation. Synth. Met. 2005, 154, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavian, M.A.; Moazezi, N. Removal of cadmium and zinc ions from industrial wastewater using nanocomposites of PANI/ZnO and PANI/CoHCF: A comparative study. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, M.; Muthukumaran, S. Microstructure, optical and FTIR studies of Ni, Cu co-doped ZnO nanoparticles by co-precipitation method. Opt. Mater. 2014, 37, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristovan, F.H.; Pereira, E.C. Polymeric varistor based on PANI/ABS composite. Synth. Met. 2011, 161, 2041–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Griffiths, P.R. Resolution enhancement of diffuse reflectance i.r. spectra of coals by Fourier self-deconvolution. Fuel 1985, 64, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maensiri, S.; Laokul, P.; Promarak, V. Synthesis and optical properties of nanocrystalline ZnO powders by a simple method using zinc acetate dihydrate and poly (vinyl pyrrolidone). J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 289, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Khan, H.; Biswas, I.; Jana, S. Polyaniline hybridized surface defective ZnO nanorods with long-term stable photoelectrochemical activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 383, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, M.; Shrivastava, S.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Annapoorni, S. Polyaniline mediated enhancement in band gap emission of zinc oxide. Compos. B Eng. 2013, 45, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Ding, L.; Lu, M.; Fan, Z.; Weng, S.; Hu, J.; Liu, P. Synergistic effect in polyaniline-hybrid defective ZnO with enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 9570–9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Hong, B.; Kerong, Z. An infrared and Raman spectroscopic study of polyanilines co-doped with metal ions and H+. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 66, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šćepanović, M.; Grujić-Brojčin, M.; Vojisavljević, K.; Bernik, S.; Srećković, T. Raman study of structural disorder in ZnO nanopowders. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, X. Preparation of TiO2/polyaniline nanocomposite from a lyotropic liquid crystalline solution. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 2525–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J.; Riede, A.; Hlavatá, D.; Prokeš, J.; Helmstedt, M.; Holler, P. The effect of polymerization temperature on molecular weight, crystallinity, and electrical conductivity of polyaniline. Synth. Met. 1998, 96, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, P. Estimation of the size and internal structure of colloidal particles by means of röntgen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen 1918, 2, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Wan, M.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic 3D microstructures assembled from 1D nanofibers of polyaniline. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łużny, W.; Śniechowski, M.; Laska, J. Structural properties of emeraldine base and the role of water contents: X-ray diffraction and computer modelling study. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.A.; Meetani, M.A.; Khaleel, A.; Ahmed, A. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue using a mixed catalyst and product analysis by LC/MS. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogi, C.; Kojima, K.; Wada, N.; Tokumoto, H.; Takai, T.; Mizoguchi, T.; Tamiaki, H. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by TiO2 film and Au particles-TiO2 composite film. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 5881–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Shahid, S.; Amura, I.; Sarihan, A.; Tiana, M.; Emanuelsson, E.A.C. Enhanced adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solutions by polyacid doped polyaniline. Synth. Met. 2018, 245, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhan, M.; Kaur, R. Nano-structured polyaniline as a potential adsorbent for methylene blue dye removal from effluent. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, K.; Deb, K.; Debnath, A.; Arun Bera, A.; Debnath, A.; Saha, B. Polaron localization in polyaniline through methylene blue dye interaction for tuned charge transport and optical properties. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Oyama, T.; Aoshima, A.; Hidaka, H.; Zhao, J.; Serpone, N. Photooxidative N-demethylation of methylene blue in aqueous TiO2 dispersions under UV irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol A Chem. 2001, 140, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.M.; John, J.; Zachariah, E.S.; Jose, J.; Titus, T.; Abraham, R.; Joseph, A.; Thomas, V. Metal free, phosphorus doped carbon nanodot mediated photocatalytic reduction of methylene blue. React. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2020, 129, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabnezhad, S. Study of catalytic reduction and photodegradation of methylene blue by heterogeneous catalyst. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 81, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Oyama, T.K.; Horikoshi, S.; Hidaka, H.; Zhao, J.; Serpone, N. Photocatalyzed N-demethylation and degradation of methylene blue in titania dispersions exposed to concentrated sunlight. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2002, 73, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Luo, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, P. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in aqueous solution by using ZnO-SnO2 nanocomposites. Mater. Sci Semicond. Process. 2018, 87, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcher, J.; Barth, N.; Schilde, C.; Kwade, A.; Bahnemann, D. Influence of TiO2 agglomerate and aggregate sizes on photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 52, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, F.; Pellutiè, L.; Sordello, F.; Minero, C.; Ortel, E.; Hodoroaba, V.-D.; Maurino, V. Influence of agglomeration and aggregation on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 216, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, M.; Zangenehtabar, S.; Homaeigohar, S. Overview of the Water Remediation Potential of Nanomaterials and Their Ecotoxicological Impacts. Water 2020, 12, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adochite, C.; Andronic, L. Aquatic Toxicity of Photocatalyst Nanoparticles to Green Microalgae Chlorella Vulgaris. Water 2021, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
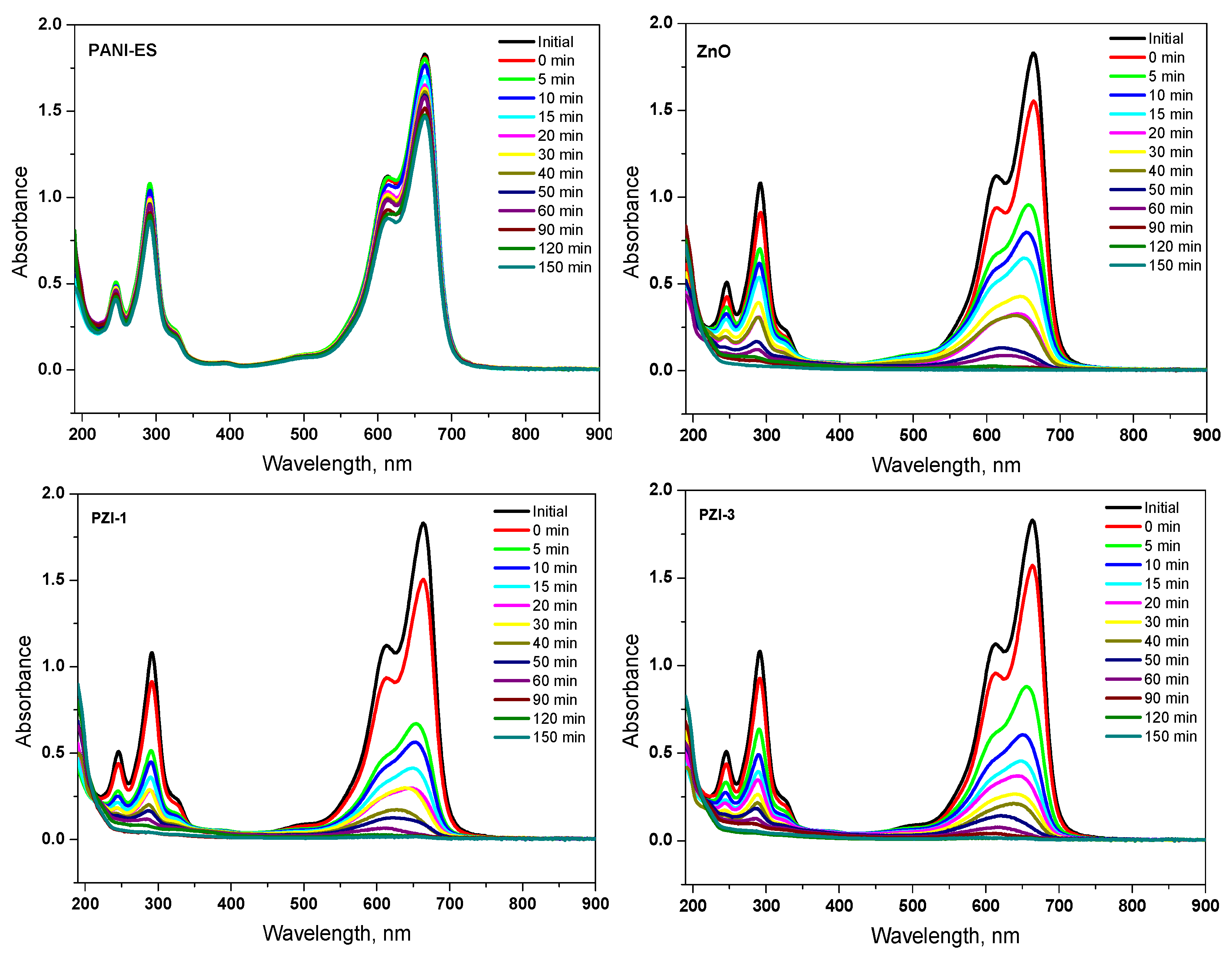
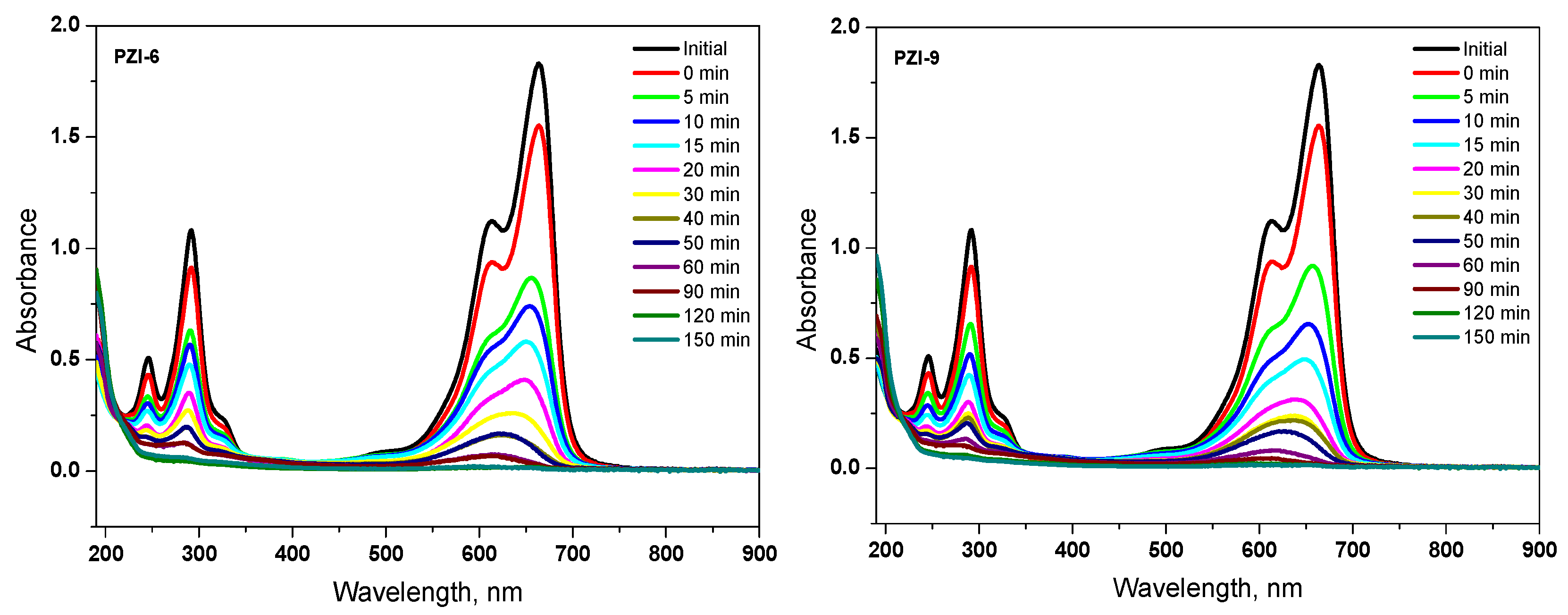
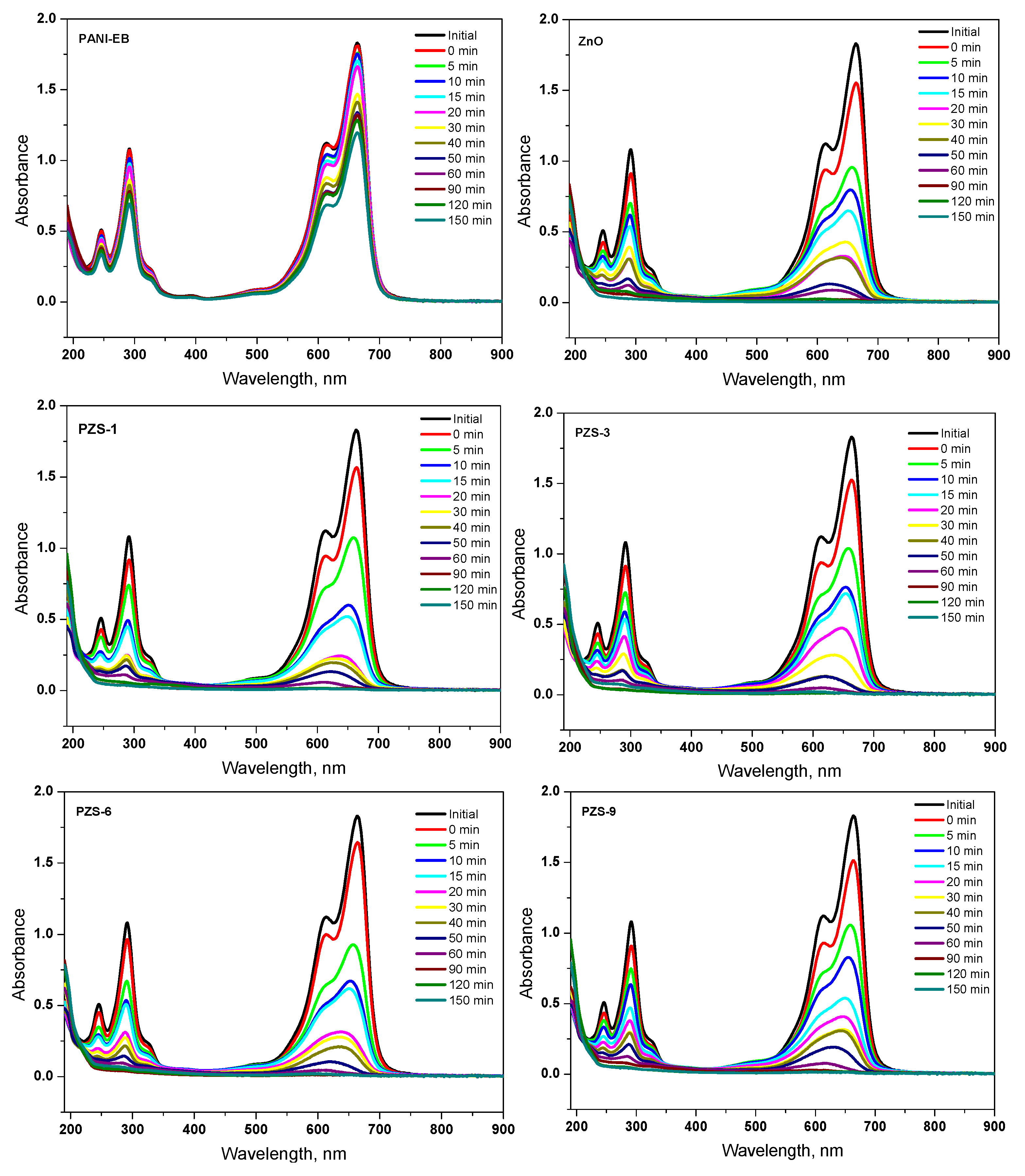
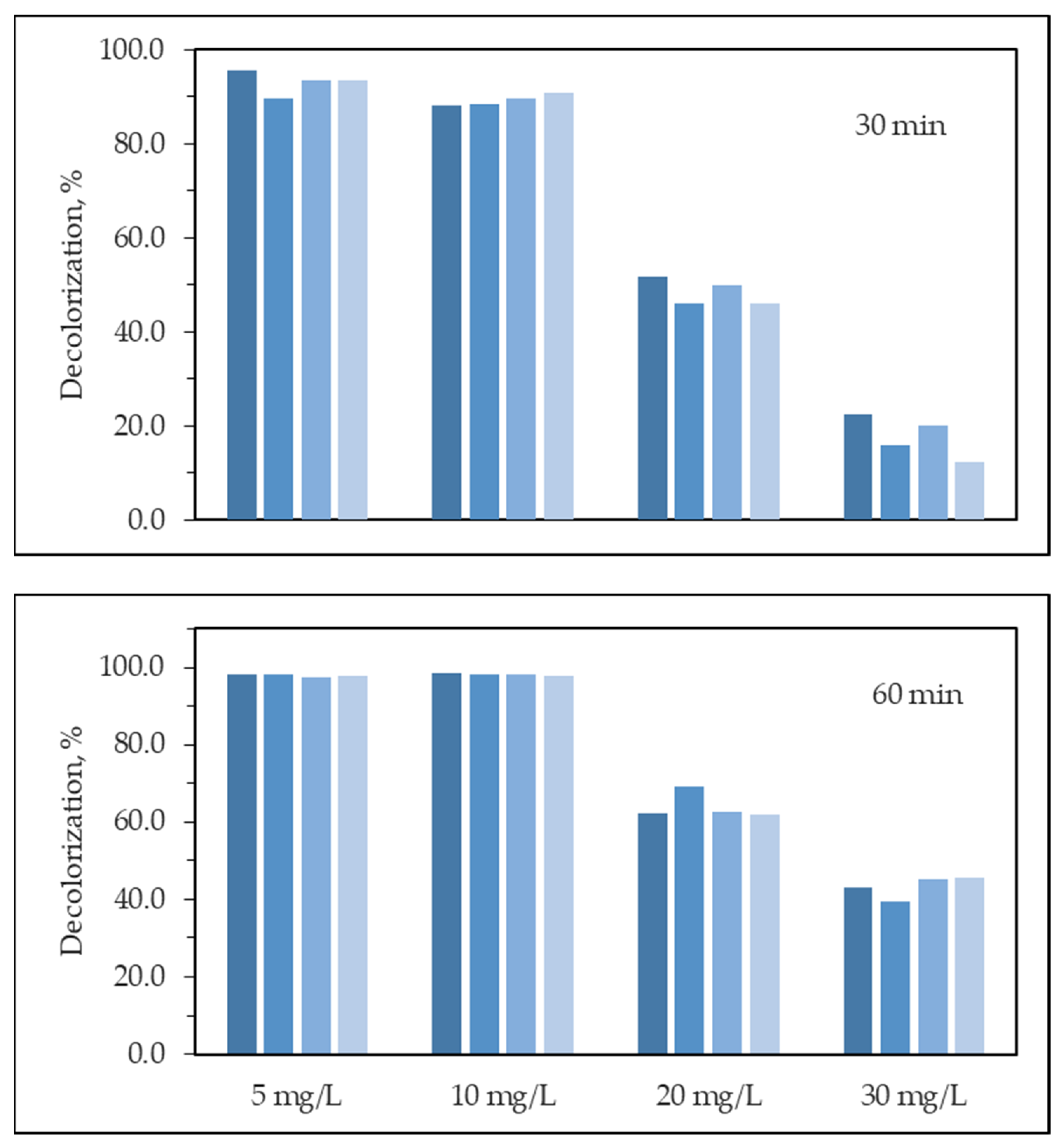
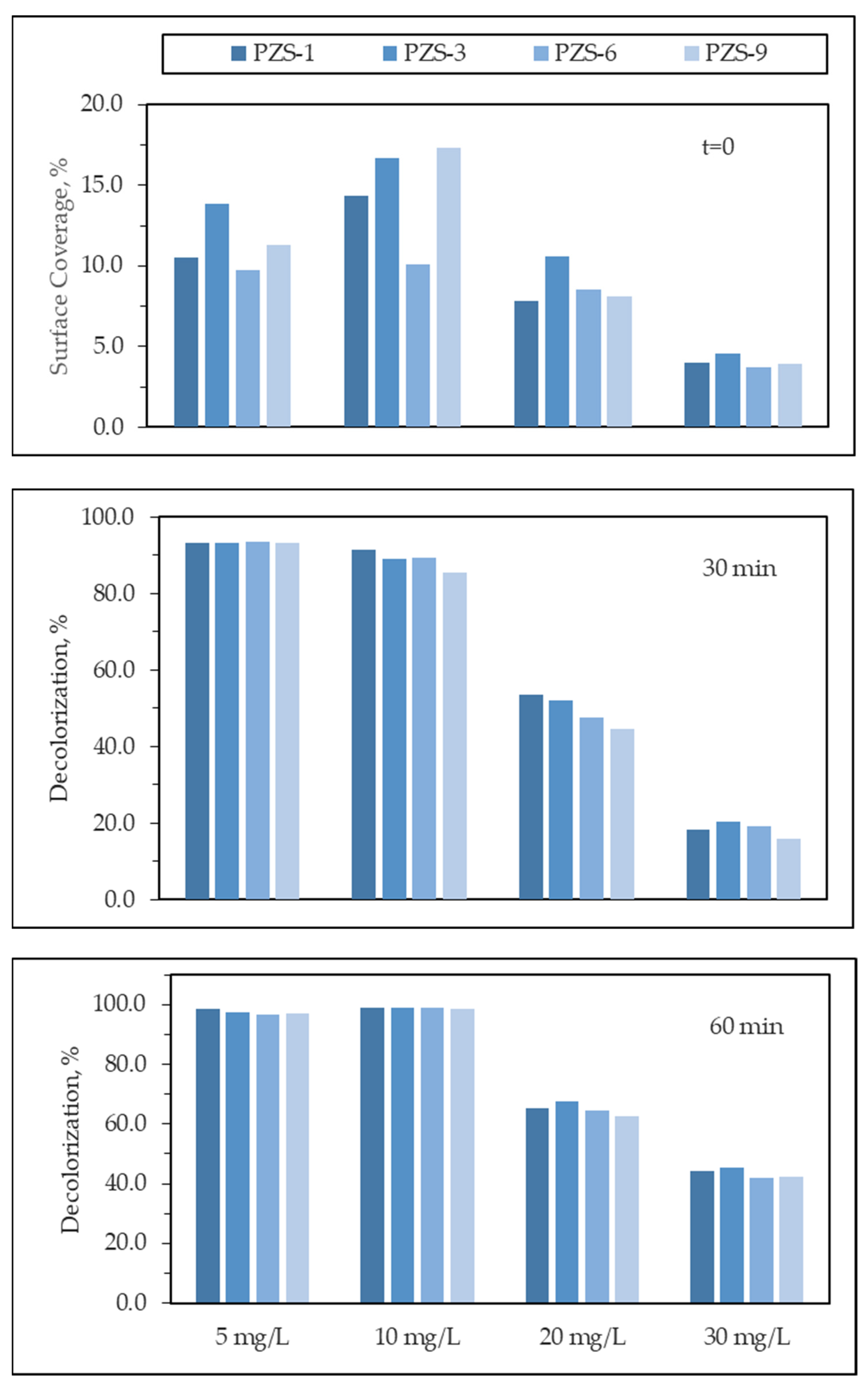
| First Order Kinetic Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| A664 | k × 10−2, min−1 | t1/2, min | Rate, cm−1 min−1 |
| ZnO | 5.39 | 12.9 | 0.0970 |
| PZI-1 | 5.73 | 12.1 | 0.105 |
| PZI-3 | 5.85 | 11.8 | 0.107 |
| PZI-6 | 6.14 | 11.3 | 0.112 |
| PZI-9 | 5.55 | 12.4 | 0.102 |
| PZS-1 | 6.47 | 10.7 | 0.118 |
| PZS-3 | 7.13 | 9.73 | 0.130 |
| PZS-6 | 6.82 | 10.2 | 0.125 |
| PZS-9 | 5.73 | 12.1 | 0.105 |
| A292 | |||
| ZnO | 3.32 | 20.9 | 0.0359 |
| PZI-1 | 3.18 | 21.8 | 0.0343 |
| PZI-3 | 3.22 | 21.5 | 0.0348 |
| PZI-6 | 3.34 | 20.7 | 0.0361 |
| PZI-9 | 3.12 | 22.2 | 0.0337 |
| PZS-1 | 3.51 | 19.8 | 0.0379 |
| PZS-3 | 3.87 | 17.9 | 0.0418 |
| PZS-6 | 3.82 | 18.1 | 0.0413 |
| PZS-9 | 3.28 | 21.1 | 0.0355 |
| A246 | |||
| ZnO | 2.36 | 29.4 | 0.0120 |
| PZI-1 | 1.93 | 35.9 | 0.00983 |
| PZI-3 | 2.07 | 33.6 | 0.0105 |
| PZI-6 | 2.10 | 33.0 | 0.0107 |
| PZI-9 | 2.00 | 34.7 | 0.0102 |
| PZS-1 | 2.24 | 30.9 | 0.0114 |
| PZS-3 | 2.43 | 28.5 | 0.0124 |
| PZS-6 | 2.48 | 27.9 | 0.0126 |
| PZS-9 | 2.19 | 31.7 | 0.0111 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turkten, N.; Karatas, Y.; Bekbolet, M. Preparation of PANI Modified ZnO Composites via Different Methods: Structural, Morphological and Photocatalytic Properties. Water 2021, 13, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081025
Turkten N, Karatas Y, Bekbolet M. Preparation of PANI Modified ZnO Composites via Different Methods: Structural, Morphological and Photocatalytic Properties. Water. 2021; 13(8):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081025
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurkten, Nazli, Yunus Karatas, and Miray Bekbolet. 2021. "Preparation of PANI Modified ZnO Composites via Different Methods: Structural, Morphological and Photocatalytic Properties" Water 13, no. 8: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081025