Using Multi-Factor Analysis to Predict Urban Flood Depth Based on Naive Bayes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
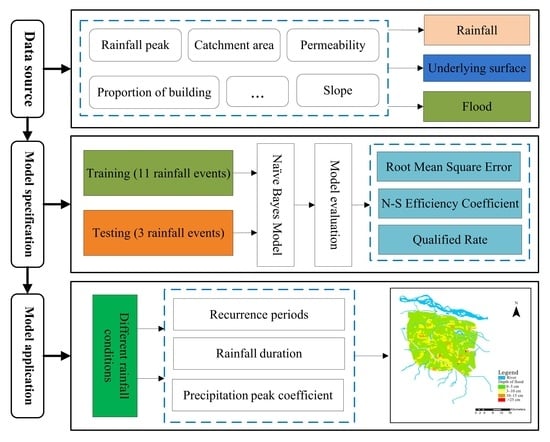
2. Materials and Methods
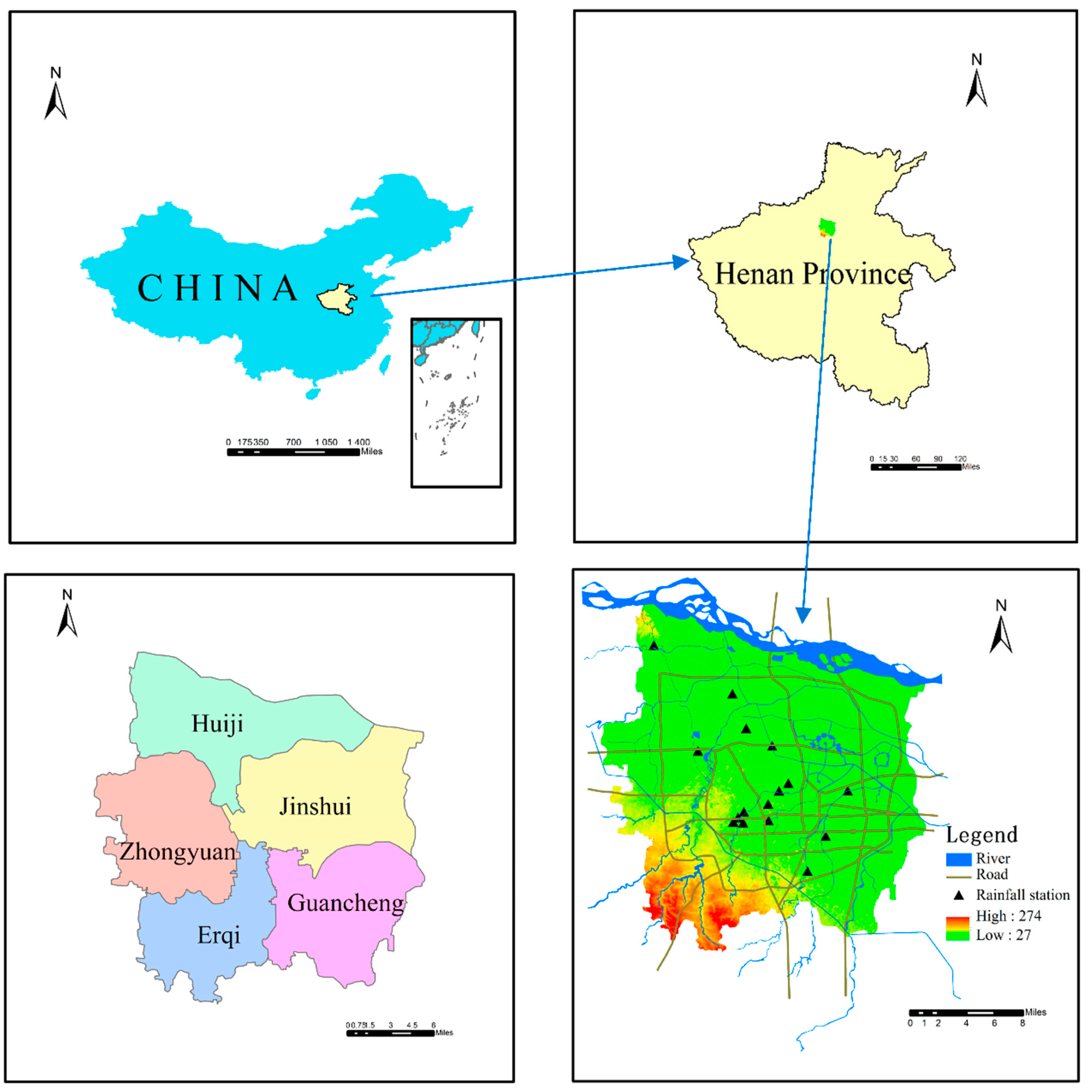
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Date and Material
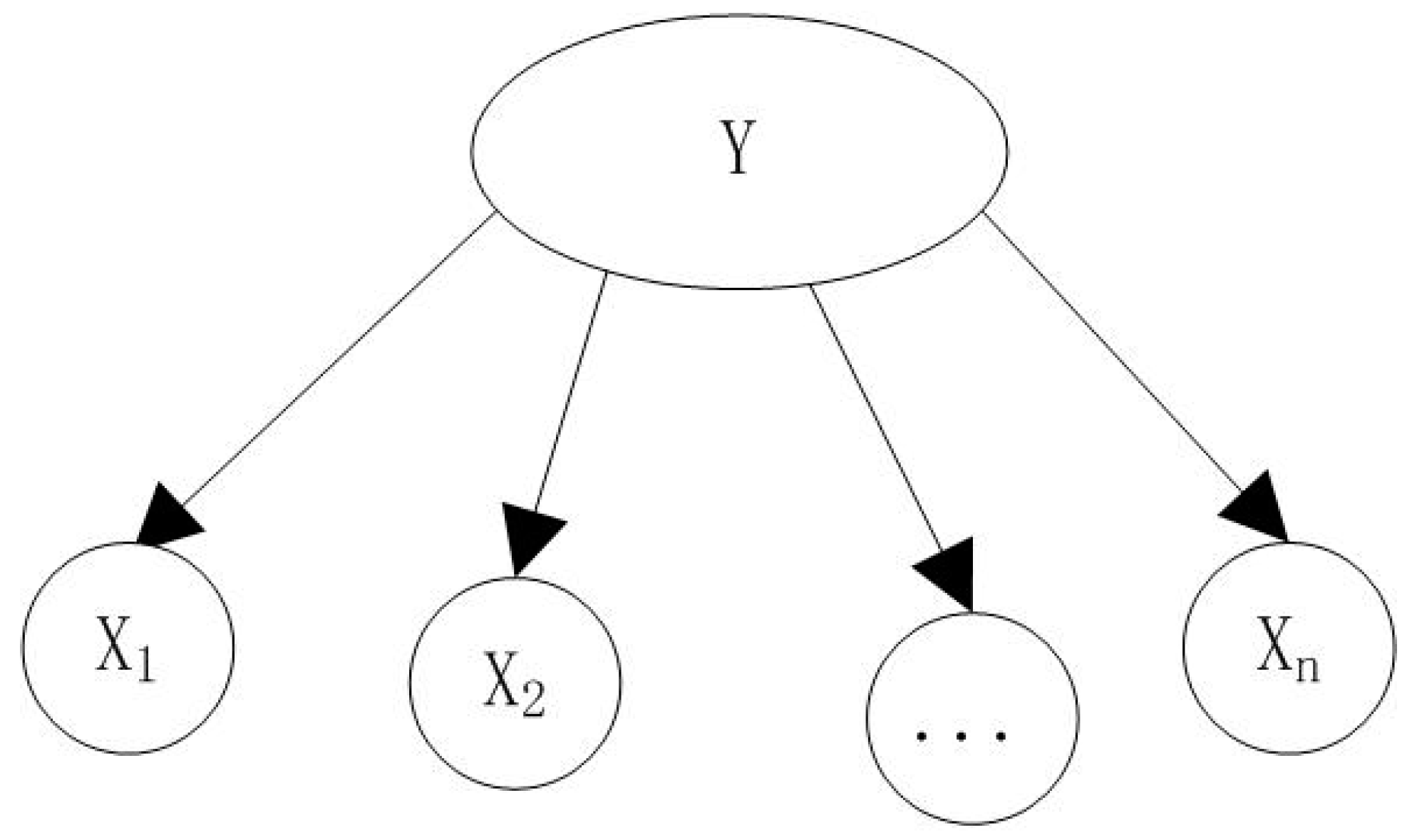
2.3. Naive Bayes Algorithms
2.4. Evaluation of Model Accuracy
3. Results and Discussions
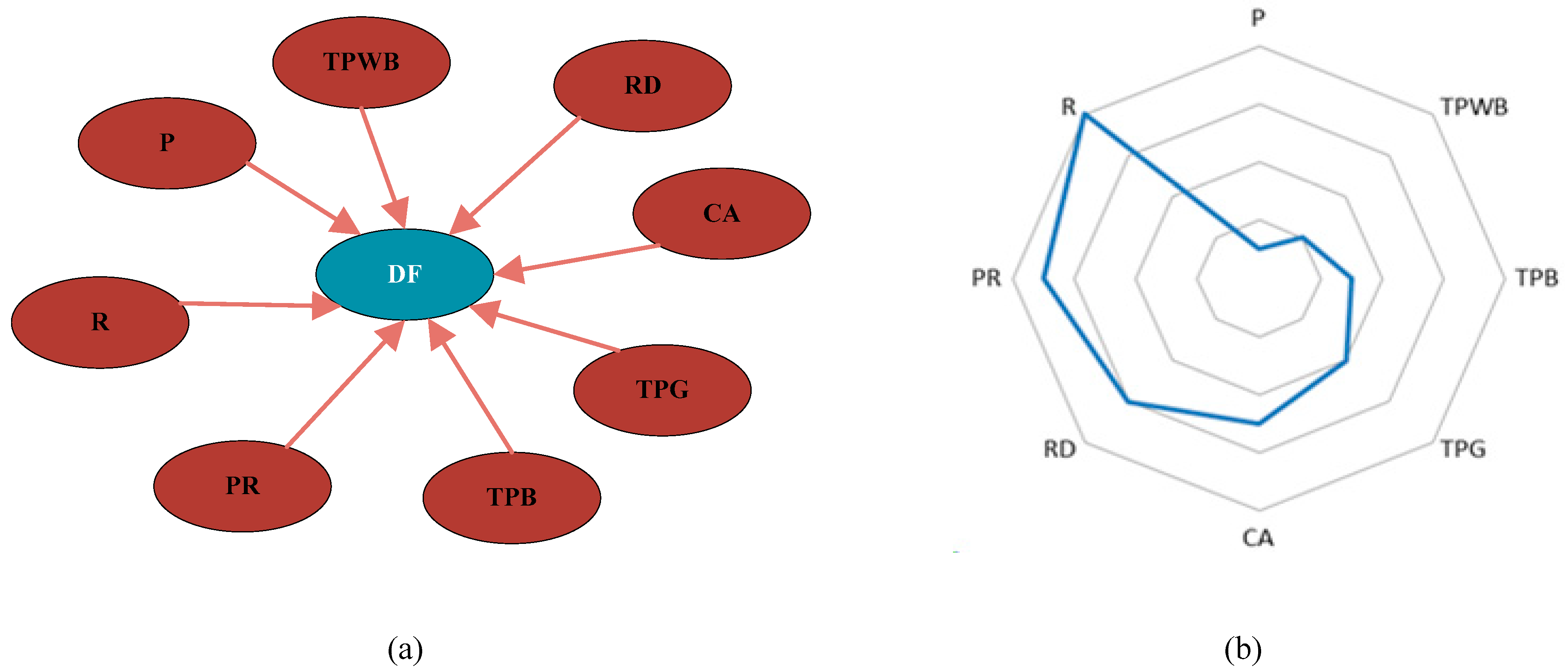
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. Forecasting Model of Urban Waterlogging Flood Depth Based on Naïve Bayes Algorithm
3.3. Evaluating the Performance of the Model
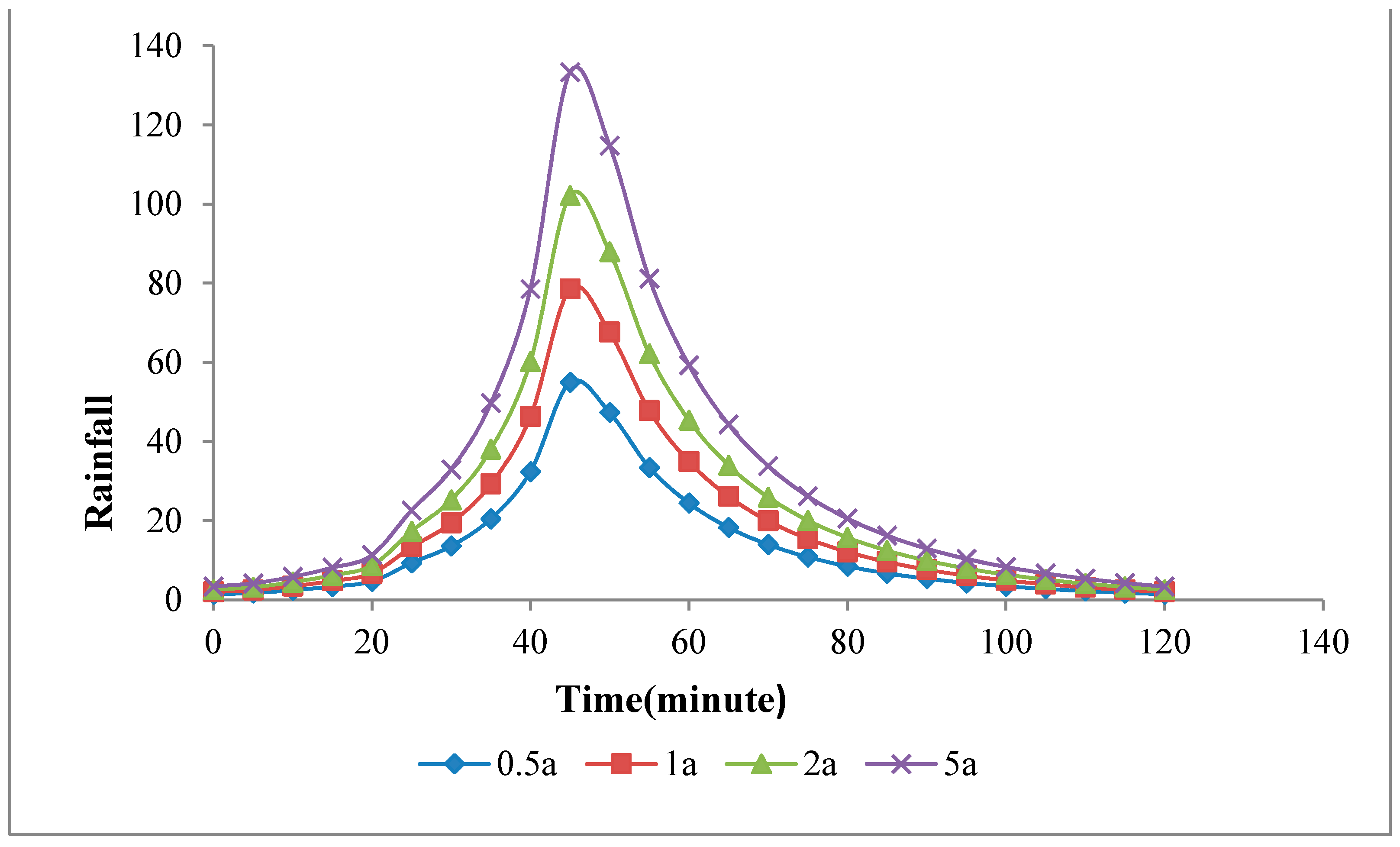
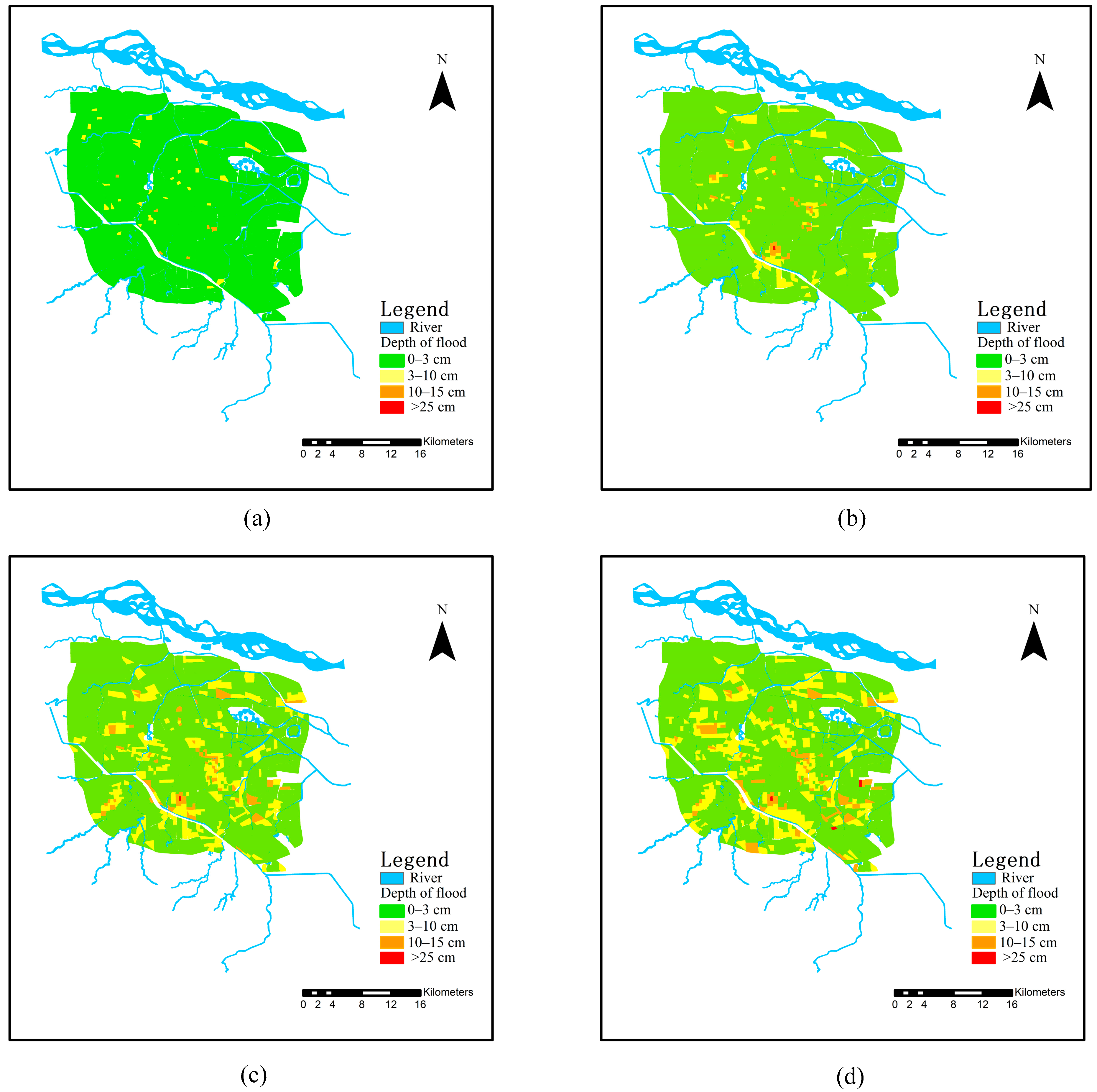
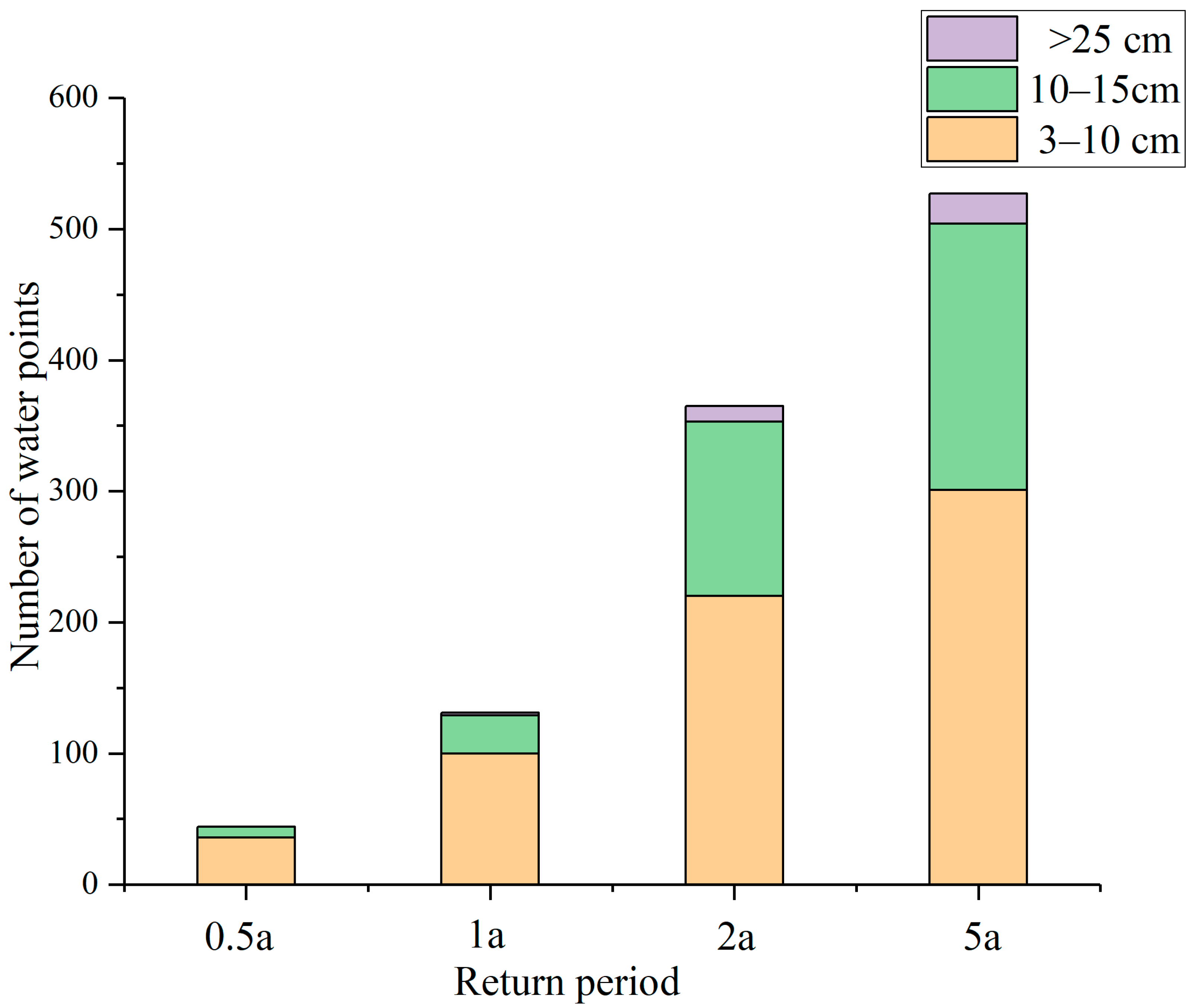
3.4. Waterlogging Prediction under Different Rainfall Conditions in Zhengzhou City Based on Naive Bayesian Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamali, B.; Löwe, R.; Bach, P.M.; Urich, C.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Deletic, A. A rapid urban flood inundation and damage assessment model. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, K.; Hettiarachchi, S.; Ou, Y.; Sharma, A. Can integrated green spaces and storage facilities absorb the increased risk of flooding due to climate change in developed urban environments? J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Hosseinpour, A.; Nazif, S. Improvement of Urban Drainage System Performance under Climate Change Impact: Case Study. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tan, H.; Zhou, J.; Yang, T.; Benjamin, A.; Wen, S.W.; Li, S.; Liu, A.; Li, X.; Fen, S.; et al. Flood hazard in Hunan province of China: An economic loss analysis. Nat. Hazards 2008, 47, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources, PRC. 2018 China Flood and Drought Disaster Bulletin; Water Resources and Hydropower Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Core Writing Team. Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Galuppini, G.; Quintilliani, C.; Arosio, M.; Barbero, G.; Ghilardi, P.; Manenti, S.; Petaccia, G.; Todeschini, S.; Ciaponi, C.; Martina, M.L.V.; et al. A unified framework for the assessment of multiple source urban flash flood hazard: The case study of Monza, Italy. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Tsangaratos, P.; Ilia, I.; Liu, J.; Zhu, A.-X.; Chen, W. Application of fuzzy weight of evidence and data mining techniques in construction of flood susceptibility map of Poyang County, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 625, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, Z. Interpretable spatio-temporal attention LSTM model for flood forecasting. Neurocomputing 2020, 403, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gironás, J.; Roesner, L.A.; Rossman, L.A.; Davis, J. A new applications manual for the Storm Water Management Model (SWMM). Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, H.J.; Troldborg, L.; Nyegaard, P.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Madsen, B. Methodology for construction, calibration and validation of a national hydrological model for Denmark. J. Hydrol. 2003, 280, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguez, M.G.; Battemarco, B.P.; De Sousa, M.M.; Rezende, O.M.; Veról, A.P.; Gusmaroli, G. Urban Flood Simulation Using MODCEL—An Alternative Quasi-2D Conceptual Model. Water 2017, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, W.; Hong, H. Flood susceptibility assessment based on a novel random Naïve Bayes method: A comparison between different factor discretization methods. Catena 2020, 190, 104536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajedi-Hosseini, F.; Choubin, B.; Solaimani, K.; Cerdà, A.; Kavian, A. Spatial prediction of soil erosion susceptibility using a fuzzy analytical network process: Application of the fuzzy decision making trial and evaluation laboratory approach. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3092–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-C.; Chen, P.-A.; Lu, Y.-R.; Huang, E.; Chang, K.-Y. Real-time multi-step-ahead water level forecasting by recurrent neural networks for urban flood control. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Meng, L.; Huang, C.; Shi, K. Spatial Attraction Models Coupled with Elman Neural Networks for Enhancing Sub-Pixel Urban Inundation Mapping. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.Y.; Chang, L.C. Online Multistep-Ahead Inundation Depth Forecasts by Recurrent NARX networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choubin, B.; Moradi, E.; Golshan, M.; Adamowski, J.; Sajedi-Hosseini, F.; Mosavi, A. An ensemble prediction of flood susceptibility using multivariate discriminant analysis, classification and regression trees, and support vector machines. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 651, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Lai, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Zhao, S.; Bai, X. Flood hazard risk assessment model based on random forest. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandhiani, S.M.; Sihag, P.; Bin Shabri, A.; Singh, B.; Pham, Q.B. Time-Series Prediction of Streamflows of Malaysian Rivers Using Data-Driven Techniques. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z. Depth prediction of urban flood under different rainfall return periods based on deep learning and data warehouse. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 716, 137077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Chan, P.W.; Zhang, W.-H. Dynamic spatial-temporal precipitation distribution models for short-duration rainstorms in Shenzhen, China based on machine learning. Atmos. Res. 2020, 237, 104861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftis, M.W.; Mortensen, P.B. Collaborating with the Machines: A Hybrid Method for Classifying Policy Documents. Policy Stud. J. 2018, 48, 184–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, S.A.; Moghaddam, D.D.; Kalantar, B.; Pradhan, B.; Kisi, O. A comparative assessment of GIS-based data mining models and a novel ensemble model in groundwater well potential mapping. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2017, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khosravi, K.; Shahabi, H.; Pham, B.T.; Adamowski, J.; Shirzadi, A.; Pradhan, B.; Dou, J.; Ly, H.-B.; Gróf, G.; Ho, H.L.; et al. A comparative assessment of flood susceptibility modeling using Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Analysis and Machine Learning Methods. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Miao, C.; Ye, X.; Min, M. Linking Heat Source–Sink Landscape Patterns with Analysis of Urban Heat Islands: Study on the Fast-Growing Zhengzhou City in Central China. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faccini, F.; Luino, F.; Paliaga, G.; Sacchini, A.; Turconi, L.; De Jong, C. Role of rainfall intensity and urban sprawl in the 2014 flash flood in Genoa City, Bisagno catchment (Liguria, Italy). Appl. Geogr. 2018, 98, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Priskos, G.; Skordoulis, M. Public perception of flood risk in flash flood prone areas of Eastern Mediterranean: The case of Attica Region in Greece. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 28, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, H.; Choubin, B.; Rahmati, O.; Haghighi, A.T.; Pradhan, B.; Kløve, B. Urban flood risk mapping using the GARP and QUEST models: A comparative study of machine learning techniques. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.H.; Rovini, E.; Dolciotti, C.; De Petris, G.; Bongioanni, P.; Carboncini, M.C.; Cavallo, F. Objective and automatic classification of Parkinson disease with Leap Motion controller. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y. Comprehensive Evaluation Method for Urban Flood Warning in Zhengzhou. Master’s Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Pang, B.; Xu, Z.; Peng, D.; Xu, L. Assessment of urban flood susceptibility using semi-supervised machine learning model. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 659, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Liu, G.-S. Up-to-date urban rainstorm intensity formulas considering spatial diversity in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keifer, C.J.; Chu, H.H. Synthetic Storm Pattern for Drainage Design. Hydraul. Div. 1957, 83, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.H. Analysis Flood Risk and Study Waterlogging Simulation in Zhengzhou. Master’s Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]

| Group | Factor | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| hydrometeorology factors | rainfall | R | the total amount of rainfall for a given rainfall |
| rainfall duration | RD | the duration of a rainfall from the beginning to the end | |
| peak rainfall | PR | peak on the rainfall intensity curve | |
| underlying surface factors | the proportion of roads | TPR | the ratio of road area to the overall regional area |
| the proportion of woodlands | TPW | the ratio of the area planted with trees to the overall regional area | |
| the proportion of grasslands | TPG | the ratio of the area planted with grasslands to the overall regional area | |
| the proportion of water bodies | TPWB | the ratio of the area of lakes, rivers and other water bodies in the region to the overall regional area | |
| the proportion of building | TPB | the ratio of district building area to the overall regional area | |
| permeability | P | the water permeability of the land within the area | |
| catchment area | CA | the area of the subregion | |
| slope | S | regional mean topographic inclination | |
| flood data | depth of the flood | DF | recorded value of the change in water level |
| The Label Number of the Sample Points | Simulated Depth of Sample Points/m | Measured Value of Sample Points/m | Absolute Error/m | Relative Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.27 | 0.28 | −0.01 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 0.13 | 0.132 | −0.002 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 0.24 | 0.27 | −0.03 | 11.1 |
| 4 | 0.13 | 0.132 | −0.002 | 1.5 |
| 5 | 0.139 | 0.142 | −0.003 | 2.1 |
| … | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| 3320 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0 | 0 |
| 3321 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 2.7 |
| 3322 | 0.32 | 0.33 | −0.01 | 3.1 |
| 3323 | 0.28 | 0.259 | 0.021 | 8.1 |
| 3324 | 0.24 | 0.26 | −0.02 | 7.6 |
| Index | RMSE (cm) | QR (%) | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 June 2014 | 0.065 | 83 | 0.92 |
| 5 August 2016 | 0.059 | 89 | 0.97 |
| 20 July 2017 | 0.061 | 85 | 0.94 |
| Average value | 0.062 | 86 | 0.94 |
| Method | Time Consumed by the Model (Second) | NSE |
|---|---|---|
| SWMM | 65 | 0.82 |
| NB | 2 | 0.95 |
| Return Period (Year) | Rainfall (mm) | Peak Rainfall (mm/h) | Rainfall Duration (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 27 | 54 | 120 |
| 1 | 38 | 78 | 120 |
| 2 | 51 | 102 | 120 |
| 5 | 66 | 133 | 120 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Using Multi-Factor Analysis to Predict Urban Flood Depth Based on Naive Bayes. Water 2021, 13, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040432
Wang H, Wang H, Wu Z, Zhou Y. Using Multi-Factor Analysis to Predict Urban Flood Depth Based on Naive Bayes. Water. 2021; 13(4):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040432
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huiliang, Hongfa Wang, Zening Wu, and Yihong Zhou. 2021. "Using Multi-Factor Analysis to Predict Urban Flood Depth Based on Naive Bayes" Water 13, no. 4: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040432