A Batch Experiment of Cesium Uptake Using Illitic Clays with Different Degrees of Crystallinity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clay Materials
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Cesium Uptake Experiments
2.4. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cesium Uptake Properties of Illitic Clays
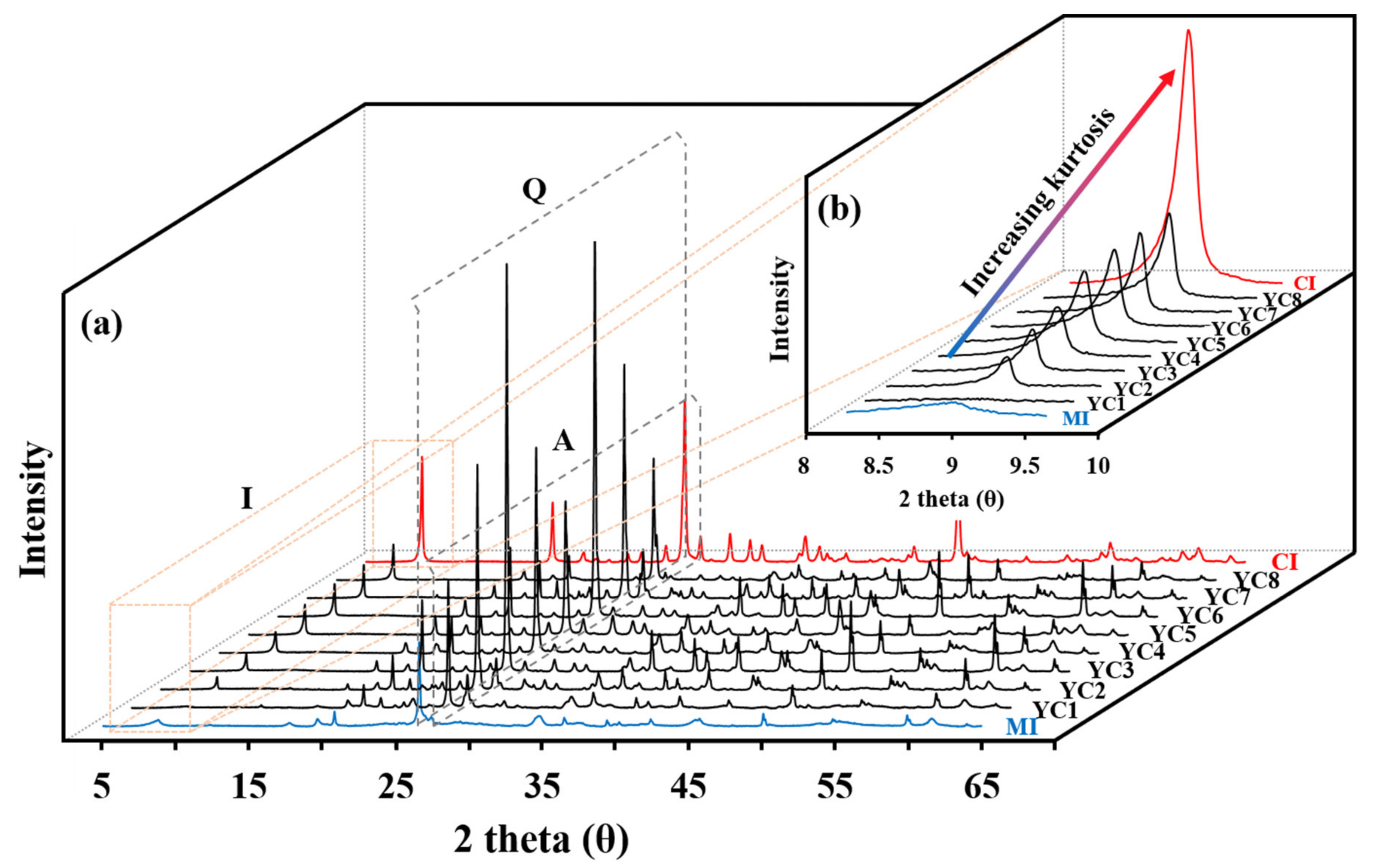
3.1.1. Material Characterization
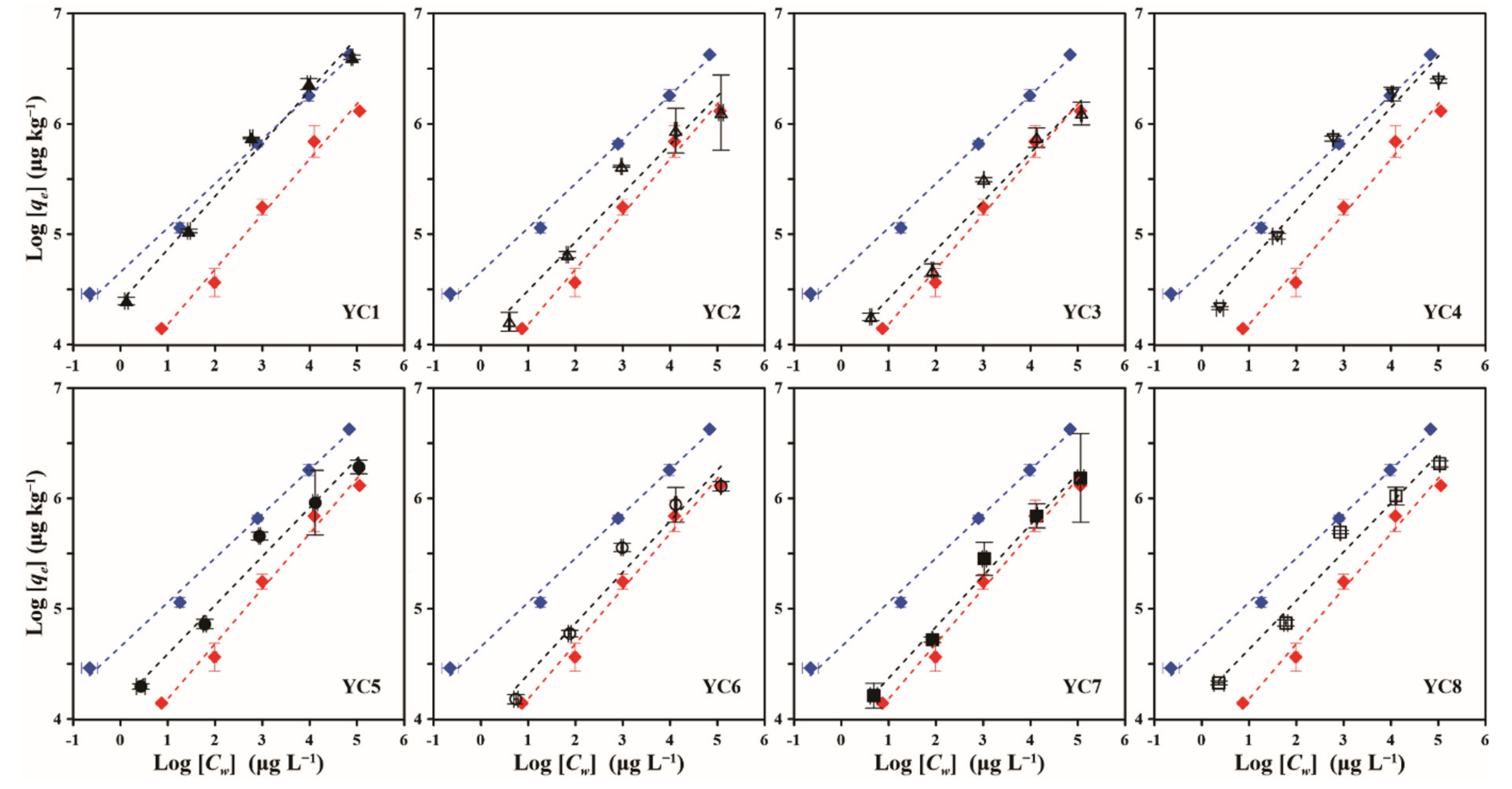
3.1.2. Cesium Uptake Isotherms
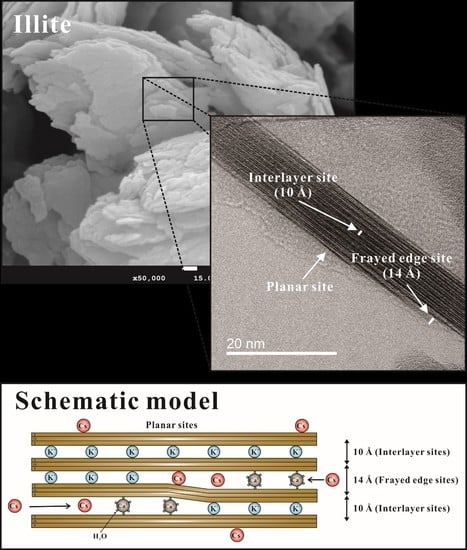
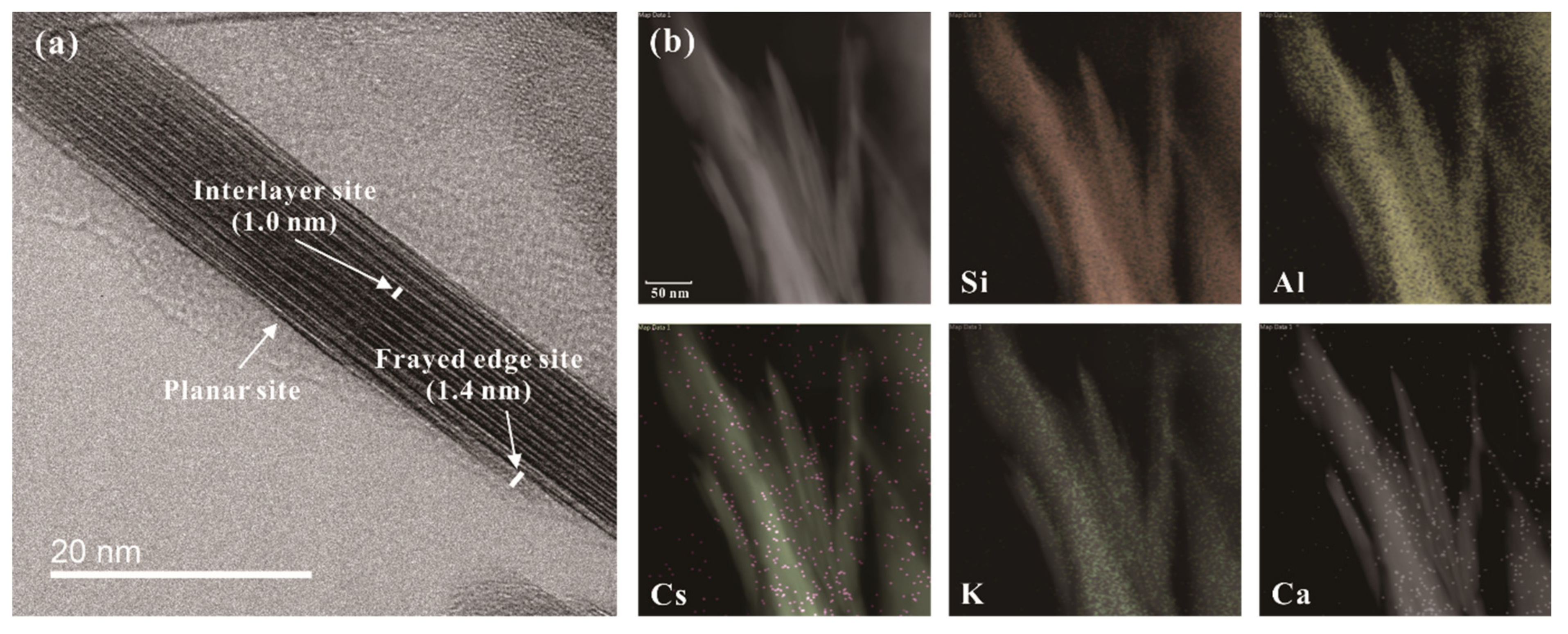
3.1.3. Uptake Mechanisms and Frayed Edge Sites
3.2. Correlation between Cesium Uptake and Crystallinity
3.2.1. Spearman’s Correlation Coefficients
3.2.2. Illite Classification by Crystallinity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kitajima, A.; Ogawa, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Kawasaki, T.; Kawatsu, Y.; Kawamoto, T.; Tanaka, H. Monitoring low-radioactivity caesium in Fukushima waters. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhauser, G.; Brandl, A.; Johnson, T.E. Comparison of the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear accidents: A review of the environmental impacts. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 470, 800–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwagami, S.; Tsujimura, M.; Onda, Y.; Nishino, M.; Konuma, R.; Abe, Y.; Hada, M.; Pun, I.; Sakaguchi, A.; Kondo, H.; et al. Temporal changes in dissolved 137Cs concentrations in groundwater and stream water in Fukushima after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 166, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanial, V.; Buesseler, K.O.; Charette, M.A.; Nagao, S. Unexpected source of Fukushima-derived radiocesium to the coastal ocean of Japan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11092–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Yang, Y.; Cai, T. Remediation of radiocesium-contaminated liquid waste, soil, and ash: A mini review since the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2249–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Hua, D.; Wu, N. Prussian blue analogue functionalized magnetic microgels with ionized chi-tosan for the cleaning of cesium-contaminated clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-H.; Li, M.-H.; Yeh, W.-C.; Wei, Y.-Y.; Teng, S.-P. Removal of cesium ions from aqueous solution by adsorption onto local Taiwan laterite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M. Adsorption of cesium on minerals: A review. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1993, 171, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Tanaka, M.; Tanaka, K.; Sakaguchi, A.; Takahashi, Y. An EXAFS study on the effects of natural organic matter and the expandability of clay minerals on cesium adsorption and mobility. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 135, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, H.; Hirose, A.; Motai, S.; Kikuchi, R.; Tanoi, K.; Nakanishi, T.M.; Yaita, T.; Kogure, T. Cesium adsorption/desorption behavior of clay minerals considering actual contamination conditions in Fukushima. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukai, H.; Motai, S.; Yaita, T.; Kogure, T. Identification of the actual cesium-adsorbing materials in the contaminated Fukushima soil. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 121, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinssot, C.; Baeyens, B.; Bradbury, M.H. Experimental and modelling studies of caesium sorption on illite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 3217–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, M.H.; Baeyens, B. A generalised sorption model for the concentration dependent uptake of caesium by argilla-ceous rocks. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2000, 42, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajec, P.; Šucha, V.; Eberl, D.D.; Środoń, J.; Elsass, F. Effect of illite particle shape on cesium sorption. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Wagai, R. Global distribution of clay-size minerals on land surface for biogeochemical and climatological studies. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedicto, A.; Missana, T.; Fernández, A.M. Interlayer Collapse Affects on Cesium Adsorption Onto Illite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4909–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostick, B.C.; Vairavamurthy, M.A.; Karthikeyan, K.; Chorover, J. Cesium adsorption on clay minerals: An EXAFS spec-troscopic investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, E.; Baeyens, B.; Maes, A.; Cremers, A. Cesium and Rubidium Ion Equilibria in Illite Clay. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, A.J.; Shaw, S.; Ward, M.B.; Haigh, S.J.; Mosselmans, J.F.W.; Peacock, C.L.; Stackhouse, S.; Dent, A.J.; Trivedi, D.; Burke, I.T. Caesium incorporation and retention in illite interlayers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 108, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, A.J.; Shaw, S.; Peacock, C.L.; Trivedi, D.; Small, J.S.; Abrahamsen, L.G.; Burke, I.T. Ionic strength and pH dependent multi-site sorption of Cs onto a micaceous aquifer sediment. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 40, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, M.A.; Martin-Garin, A.; Gérard, F.; Bildstein, O. A robust and parsimonious model for caesium sorption on clay minerals and natural clay materials. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 87, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lammers, L.N.; Bourg, I.C.; Okumura, M.; Kolluri, K.; Sposito, G.; Machida, M. Molecular dynamics simulations of cesium adsorption on illite nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 490, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Missana, T.; García-Gutiérrez, M.; Benedicto, A.; Ayora, C.; De-Pourcq, K. Modelling of Cs sorption in natural mixed-clays and the effects of ion competition. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 49, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerisit, S.; Okumura, M.; Rosso, K.M.; Machida, M. Molecular Simulation of Cesium Adsorption at the Basal Surface of Phyllosilicate Minerals. Clays Clay Miner. 2016, 64, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, S.-M.; Jeon, E.-K.; Baek, K. Selective and irreversible adsorption mechanism of cesium on illite. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 85, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots, P.; Renshaw, J.C.; Payne, T.; Comarmond, M.J.; Schellenger, A.E.P.; Pedrotti, M.; Calì, E.; Lunn, R.J. Geochemical evidence for the application of nanoparticulate colloidal silica gel for in situ containment of legacy nuclear wastes. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 1481–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.; Gil-Sotres, F. Potassium fixation in suspensions of soils of Galicia (N.W. Spain). Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 1995, 26, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawhney, B.L. Selective Sorption and Fixation of Cations by Clay Minerals: A Review. Clays Clay Miner. 1972, 20, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuki, T.; Kozai, N. Adsorption behavior of radioactive cesium by non-mica minerals. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.G.; Park, O.H.; Moon, D.H.; Do, J.Y.; Kim, S.O. Phosphate Adsorption of Youngdong Illite, Korea. J. Miner. Soc. Korea 2007, 20, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, S.-M. Geological formation environment and mineralization age of the Daehyun sericite deposits in Bonghwa-gun, Gyeongsangbuk-do: Introduction of the new type in South Korea. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2008, 44, 365–386. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, T.; Lee, Y.I. Thermal histories of the Cretaceous Pungam and Yeongdong basins, Korea based on apatite and zircon fission track analysis. Geosci. J. 2006, 10, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, J.W.; Walter, L.S.; Vergo, N. Mid-Infrared (2.1-25 um) Spectra of Minerals; 2331-1258; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1987; p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Jiang, W.H. Experimental Research on Ore Dressing of Sericite in Chuzhou, Anhui Province. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2002, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ouhadi, V.; Yong, R. Impact of clay microstructure and mass absorption coefficient on the quantitative mineral identifi-cation by XRD analysis. Appl. Clay Sci. 2003, 23, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Johnston, C.T.; Sumner, M.E. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods, 5.3; Series No. 5; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, D.; Lalhmunsiama; Choi, S.; Lee, S. Activated Sericite: An Efficient and Effective Natural Clay Material for Attenuation of Cesium from Aquatic Environment. Pedosphere 2014, 24, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Park, M.; Kim, J.; Oh, M.; Lee, E.-H.; Kim, K.-W.; Chung, D.-Y.; Moon, J.-K. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermo-dynamic study of cesium adsorption onto nanocrystalline mordenite from high-salt solution. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Cai, G.; Liu, S.; Puppala, A.J.; Zou, H. Correlations Between Electrical Resistivity and Geotechnical Parameters for Jiangsu Marine Clay Using Spearman’s Coefficient Test. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 15, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, N.; Uchida, S.; Tagami, K. Effects of Clay Minerals on Radiocesium Sorption Behavior onto Paddy Field Soils. Radioisotopes 2007, 56, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, H.; Uchida, S.; Muramatsu, Y.; Yoshida, S. Sorption of manganese, cobalt, zinc, strontium, and cesium onto ag-ricultural soils: Statistical analysis on effects of soil properties. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 83, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, R.; Fujimoto, K.; Kameda, J.; Hamahashi, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kimura, G.; Hamada, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Saito, S. Changes in illite crystallinity within an ancient tectonic boundary thrust caused by thermal, mechanical, and hydrothermal effects: An example from the Nobeoka Thrust, southwest Japan. Earth Planets Space 2014, 66, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harraden, C.L.; McNulty, B.A.; Gregory, M.J.; Lang, J.R. Shortwave Infrared Spectral Analysis of Hydrothermal Alteration Associated with the Pebble Porphyry Copper-Gold-Molybdenum Deposit, Iliamna, Alaska. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumm, S.; Buggisch, W. Sample preparation effects on illite crystallinity measurement: Grain-size gradation and particle orientation. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1991, 9, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kübler, B.; Jaboyedoff, M. Illite crystallinity. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences-Series IIA-Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 331, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremers, A.; Elsen, A.; De Preter, P.; Maes, A. Quantitative analysis of radiocaesium retention in soils. Nat. Cell Biol. 1988, 335, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, J.P.; Zachara, J.M.; Heald, S.M.; Dohnalkova, A.; Newville, M.G.; Sutton, S.R. Microscale Distribution of Cesium Sorbed to Biotite and Muscovite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, A.; Thiry, Y.; Funakawa, S.; Kosaki, T. Characterization of the frayed edge site of micaceous minerals in soil clays influenced by different pedogenetic conditions in Japan and northern Thailand. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2008, 54, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, M. Weathering of primary and secondary minerals in soils. Int. Congr. Soil Sci. Trans. 1968, 4, 281–292. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.; Hseung, Y.; Corey, R.; Evans, E.; Heuvel, R.V. Weathering Sequence of Clay-size Minerals in Soils and Sedi-ments: II. Chemical Weathering of Layer Silicates 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1952, 16, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
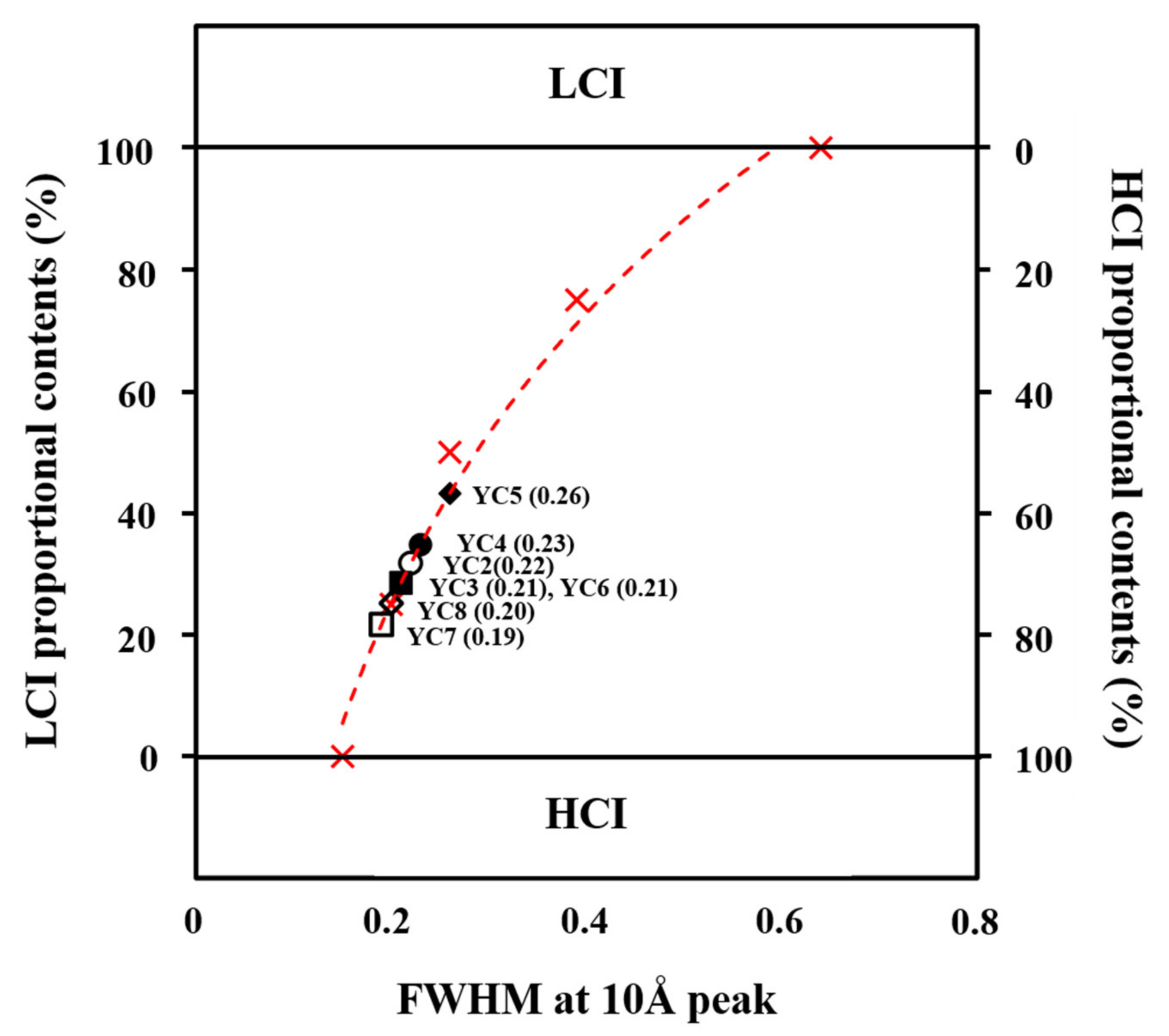
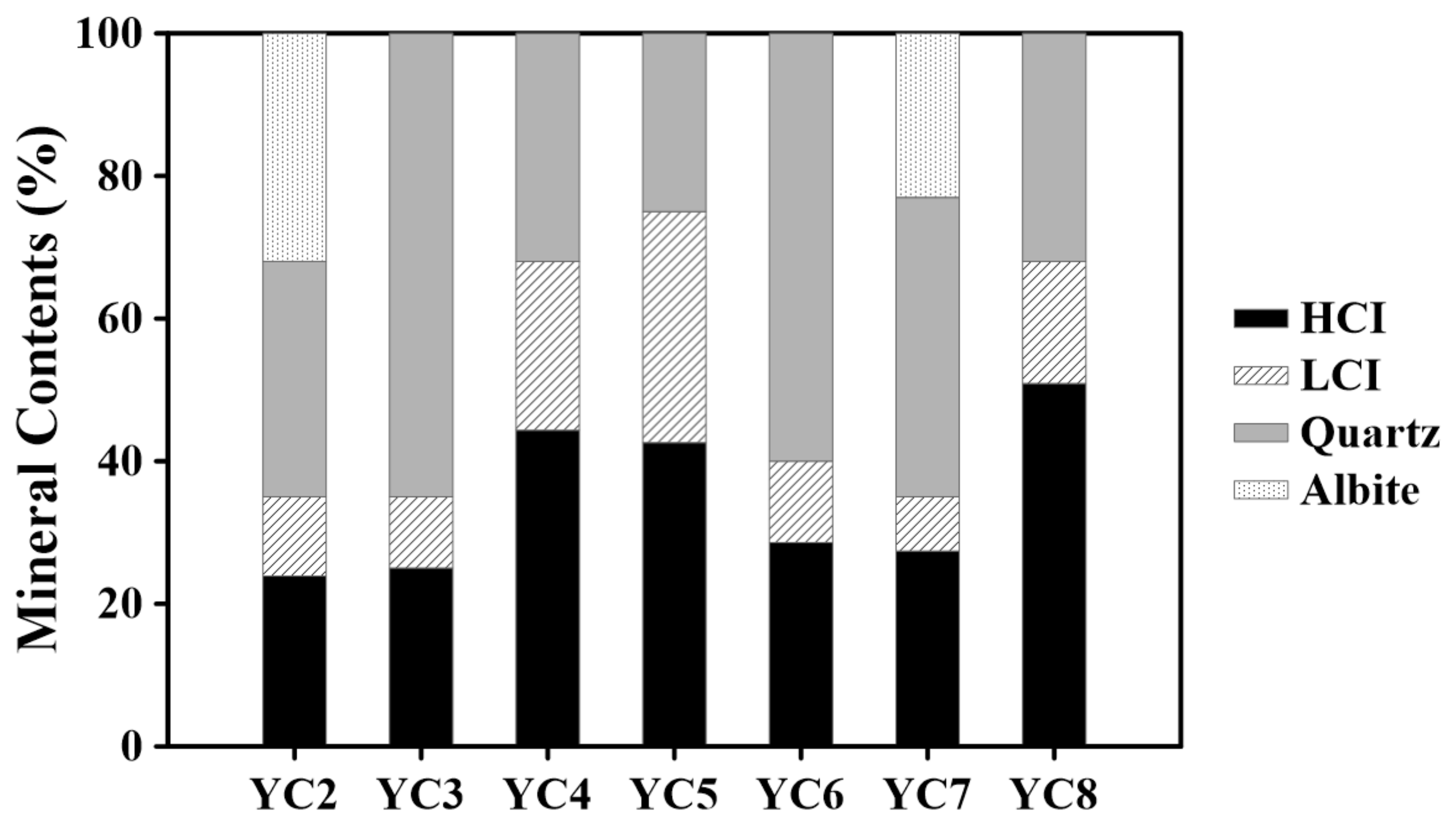
| (a) | Illite | Quartz | Albite | FWHM | BET | CEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (°) | (m2 g−1) | (eq kg−1) | |
| MI | ~100 | - | - | 0.64 | 29.3 | 0.147 |
| YC1 | <47 | 25 | 28 | 1.22 | 28.5 | 0.161 |
| YC2 | 35 | 33 | 32 | 0.22 | 5.9 | 0.040 |
| YC3 | 35 | 65 | - | 0.21 | 3.7 | 0.023 |
| YC4 | 68 | 32 | - | 0.23 | 7.5 | 0.060 |
| YC5 | 75 | 25 | - | 0.26 | 7.6 | 0.046 |
| YC6 | 40 | 60 | - | 0.21 | 2.6 | 0.031 |
| YC7 | 35 | 42 | 23 | 0.19 | 9.3 | 0.037 |
| YC8 | 68 | 32 | - | 0.20 | 2.1 | 0.087 |
| CI | ~100 | - | - | 0.15 | 7.3 | 0.035 |
| (b) | Illite Contents | FWHM | BET | CEC | ||
| Illite Contents | 1.000 | |||||
| FWHM | 0.180 | 1.000 | ||||
| BET | 0.303 | 0.559 | 1.000 | |||
| CEC | 0.432 | * 0.657 | 0.527 | 1.000 | ||
| Freundlich Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Kf [(μg kg−1)/(L μg−1)n] | n (-) | r2 | |
| MI | 4.5 × 104 | 0.401 | 0.995 |
| YC1 | 2.4 × 104 | 0.480 | 0.985 |
| YC2 | 1.1 × 104 | 0.436 | 0.954 |
| YC3 | 9.4 × 103 | 0.440 | 0.968 |
| YC4 | 1.9 × 104 | 0.466 | 0.946 |
| YC5 | 1.4 × 104 | 0.442 | 0.978 |
| YC6 | 8.7 × 103 | 0.463 | 0.960 |
| YC7 | 8.0 × 103 | 0.464 | 0.988 |
| YC8 | 1.6 × 104 | 0.441 | 0.976 |
| CI | 4.8 × 103 | 0.500 | 0.986 |
| Kd (L kg−1) at Ranged Cw (μg L−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × 10 | 1 × 102 | 1 × 103 | 1 × 104 | 1 × 105 | |
| Illite Contents | 0.303 | 0.352 | 0.259 | 0.414 | 0.605 |
| FWHM | * 0.742 | ** 0.809 | ** 0.827 | ** 0.821 | 0.565 |
| BET | 0.418 | 0.467 | 0.345 | 0.333 | * 0.636 |
| CEC | ** 0.855 | ** 0.915 | ** 0.867 | ** 0.842 | ** 0.903 |
| BET | CEC | Kd (L kg−1) at Ranged Cw (μg L−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × 10 | 1 × 102 | 1 × 103 | 1 × 104 | 1 × 105 | |||
| LCI | 0.285 | * 0.778 | ** 0.837 | ** 0.929 | ** 0.912 | ** 0.929 | * 0.695 |
| HCI | −0.333 | −0.017 | −0.217 | −0.183 | −0.100 | −0.067 | 0.167 |
| Quartz | −0.479 | −0.647 | −0.311 | −0.395 | −0.311 | −0.420 | * −0.672 |
| Albite | 0.160 | −0.091 | −0.297 | −0.183 | 0.274 | −0.479 | −0.342 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, J.; Choung, S.; Shin, W.; Han, W.S.; Chon, C.-M. A Batch Experiment of Cesium Uptake Using Illitic Clays with Different Degrees of Crystallinity. Water 2021, 13, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040409
Hwang J, Choung S, Shin W, Han WS, Chon C-M. A Batch Experiment of Cesium Uptake Using Illitic Clays with Different Degrees of Crystallinity. Water. 2021; 13(4):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040409
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Jeonghwan, Sungwook Choung, Woosik Shin, Weon Shik Han, and Chul-Min Chon. 2021. "A Batch Experiment of Cesium Uptake Using Illitic Clays with Different Degrees of Crystallinity" Water 13, no. 4: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13040409