Occurrence and Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Marine Surface Microlayer of an Industrialized Coastal Area in the Eastern Mediterranean
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Analytical Method and Quality Assurance
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentrations Patterns of PAHs
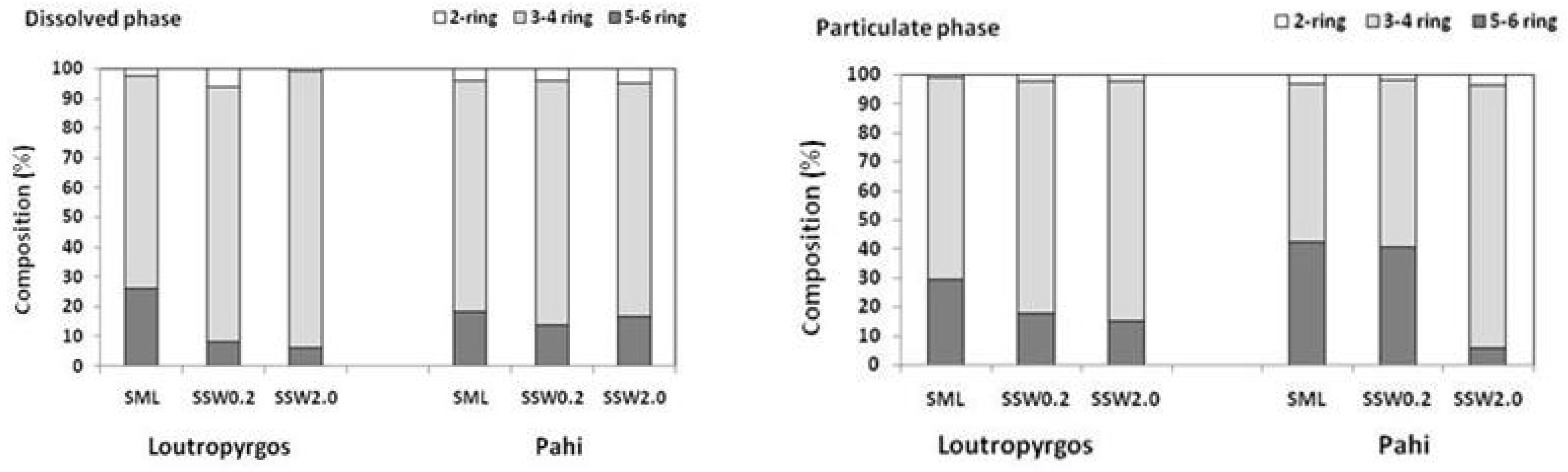
3.2. Composition and Partitioning of PAHs
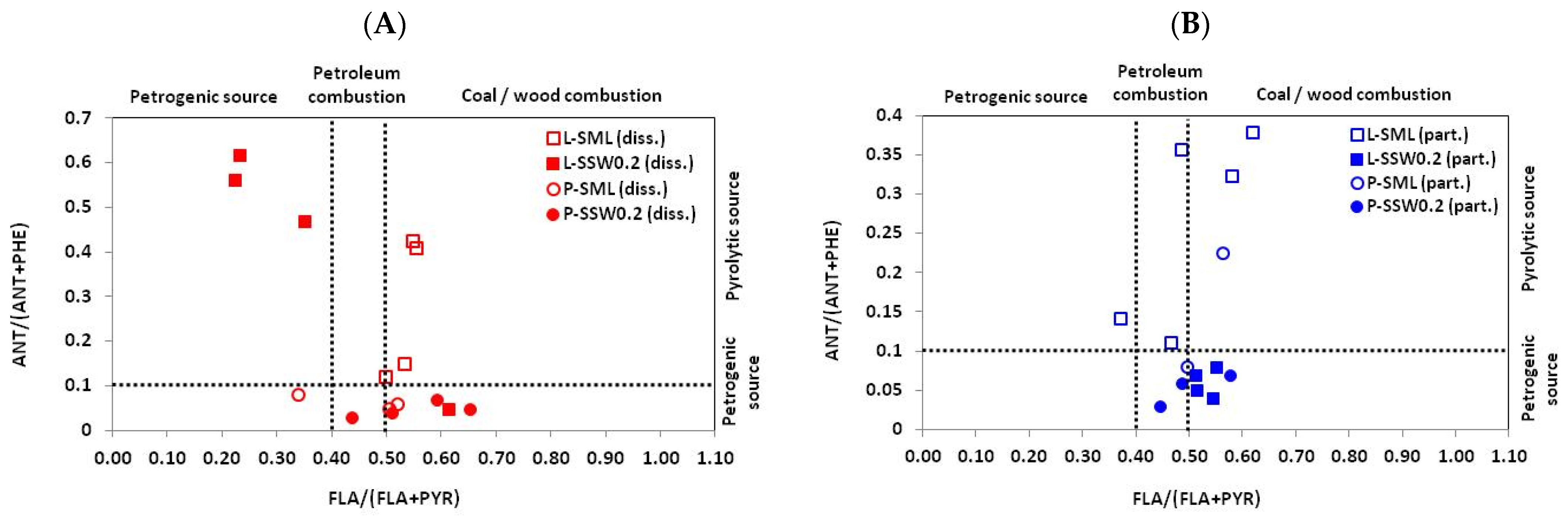
3.3. Possible Sources of PAHs
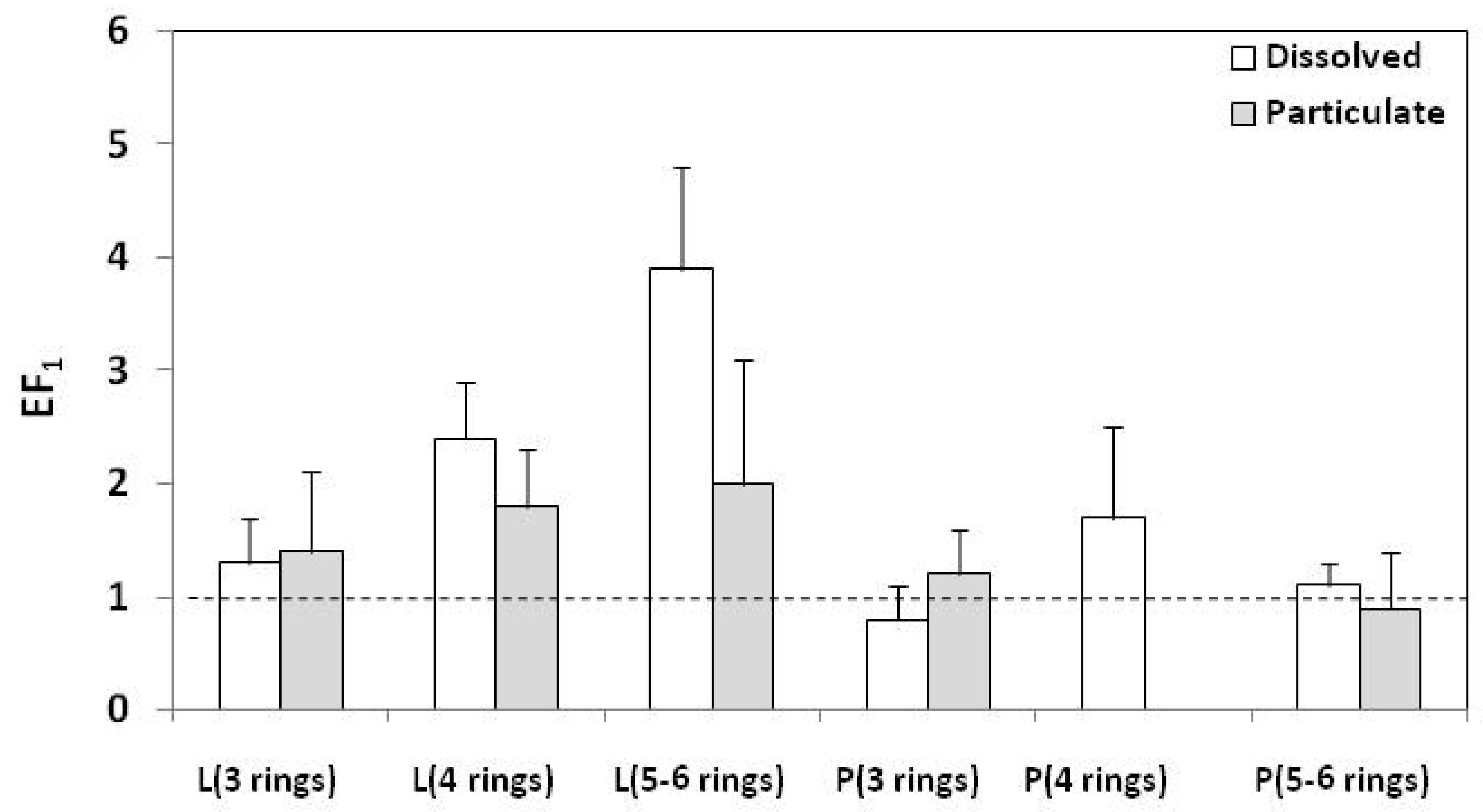
3.4. Assessment of Potential Enrichment of SML
3.5. Toxicity Assessment
3.6. PAHs Levels Reported in the SML of Other Marine Areas
| Area | na | SML (ng L−1) | SSW (ng L−1) | Sampling Year | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolved PAHs | Particulate PAHs | Dissolved PAHs | Particulate PAHs | ||||
| San Diego Bay, USA | 26 | 20.4–79.2 | 551–7540 | 1994 | [68] | ||
| Leghorn, Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy | 15 | 214–15,200 | 826–154,000 | 63–3050 b | 1999 | [5] | |
| Baltic Sea | 4.5–53 b | 1992–1998 | [69] | ||||
| Alexandria coast | 7 | 103–523 b | 13–120 b | 2002 | [23] | ||
| Barcelona, Spain | 14 | 11.9–93.4 | 4.9–19.9 | 2001 | [70] | ||
| Venice Lagoon, Italy | 20 | 8.32–138 | 30.3–163 | 6.31–259 | 5.68–45.2 | 2001–2003 | [37] |
| Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica | 13 | 4.67–7.79 | 5.68–14.1 | 2.24–4.01 | 1.65–3.65 | 1998–1999 | [71] |
| Singapore | 16 | 2.7–46.2 | 3.8–31.4 | 3.4–36.5 | 6.7–30.3 | 2005 | [44] |
| Barcelona, Spain | 16 | 4.6–41.7 | 2.3–31.2 | 3.6–30.7 | 0.5–5.7 | 2001–2002 | [9] |
| Banyuls-sur-Mer, France | 2.5–25.9 | 0.6–14.5 | 4.6–12.9 | 0.4–8.6 | |||
| Terra Nova, Antarctica | 13 | 4.25–8.11 | 3.07–15.8 | 2.14–2.85 | 2.81–4.66 | 2000–2001 | [60] |
| Barcelona, Spain | 16 | 16.7–35.7 | 2.3–16.7 | 4.4–17.7 | 0.5–0.8 | 2002–2003 | [42] |
| Banyuls-sur-Mer, France | 2.4–22.3 | 0.6–6.7 | 4.6–7.6 | 0.4–2.4 | |||
| Port-de Bouc, Marseilles, France | 1842 | 148 | 6.4 | 553 | 2008–2009 | [36] | |
| Marseilles, France | 17 | 50–217 | 6.0–1597 | 1.9–98 | 1.9–21 | 2009–2010 | [7] |
| Xiamen Island, China | 16 | 93.4–424 b | 42.3–279 b | 2005 | [35] | ||
| Lagos Lagoon, Nigeria | 17 | 9100–16,200 b | 8900–13,300 b | 2014 | [72] | ||
| Kaohsiung Harbor and adjacent area, Taiwan | 15 | 2.90–192 | 14.4–268 | 1.25–9.39 | 12.9–26.4 | 2014 | [46] |
| Saronicos gulf, Greece | 16 | 40.4–237 | 30.8–177 | 22.8–180 | 36.8–171 | 2018–2020 | This study |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liss, P.S.; Duce, R.A. The Sea Surface and Global Change; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 339–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Cai, W. Studies on the sea surface microlayer: II. The layer of sudden change of physical and chemical properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 264, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunliffe, M.; Murrell, J.C. The sea-surface microlayer is a gelatinous biofilm. ISME J. 2009, 3, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wurl, O.; Wurl, E.; Miller, L.; Johnson, K.; Vagle, S. Formation and global distribution of sea-surface microlayers. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cincinelli, A.; Stortini, A.M.; Perugini, M.; Checchini, L.; Lepri, L. Organic pollutants in sea surface microlayer and aerosol in the coastal environment of Leghorn–(Tyrrhenian Sea). Mar. Chem. 2001, 76, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunliffe, M.; Engel, A.; Frka, S.; Gasparovic, B.; Guitart, C.; Murrell, J.C.; Salter, M.; Stolle, C.; Upstill-Goddard, R.; Wurl, O. Sea surface microlayers: A unified physicochemical and biological perspective of the air-ocean interface. Prog. Oceanog. 2013, 109, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigue, C.; Tedetti, M.; Giorgi, S.; Goutx, M. Occurrence and distribution of hydrocarbons in the surface microlayer and subsurface water from the urban coastal marine area off Marseilles Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2741–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, D.J.; George, C. Sea-surface chemistry and its impact on the marine boundary layer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10385–10389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitart, C.; García-Flor, N.; Bayona, J.M.; Albaigés, J. Occurrence and fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the coastal surface microlayer. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, R.F.; Lee, C.L. Effects of anthropogenic surfactants on the conversion of marine dissolved organic carbon and microgels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neff, J.M. Bioaccumulation in marine organisms. In Effect of Contaminants from Oil Well Produced Water; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; 468p, ISBN 9780080527840. [Google Scholar]
- Green, G.; Skerratt, J.H.; Leeming, R.; Nichols, P.D. Hydrocarbon and coprostanol levels in seawater, sea-ice algae and sediments near Davis station in Eastern Antarctica: A regional survey and preliminary results for a field fuel spill experiment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1992, 25, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fingas, M.; Page, D.S. Oil spill identification. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 843, 369–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurl, O.; Obbard, J.P. A review of pollutants in the sea-surface microlayer (SML): A unique habitat for marine organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 1016–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, J.M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the aquatic environment, sources: Fates and biological effects. In Applied Science; Elsevier Science Pub Co.: London, UK, 1979; ISBN 0853348324/9780853348320. [Google Scholar]
- Howsam, M.; Jones, K.C. Sources of PAH in the environment. In PAHs and Related Compounds. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Neilson, A.H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 3, pp. 137–174. ISBN 978-3-642-08286-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, P.; Qiao, X.; Tian, F. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Dalian soils: Distribution and toxicity assessment. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; Grieken, R.V. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolosa, I.; Bayona, J.M.; Albaigés, J. Aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and sulfur/oxygen derivatives in Northwestern Mediterranean sediments: Spatial and temporal variability, fluxes, and budgets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiatou, E.; Tolosa, I.; Simó, R.; Bouloubassi, I.; Dachs, J.; Marti, S.; Sicre, M.A.; Bayona, J.M.; Grimalt, J.O.; Saliot, A.; et al. Mass budget and dynamics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Mediterranean Sea. Deep-Sea Res. II 1997, 44, 881–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namiesnik, J. PAH diagnostic ratios for the identification of pollution emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcher, W. Spectral Atlas of Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; Abd-Allah, A.M.A. Contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in microlayer and subsurface waters along Alexandria coast, Egypt. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porte, C.; Albaiges, J. Bioaccumulation patterns of hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in bivalves crustacean and fishes. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 26, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djomo, J.E.; Garrigue, P.; Narbonne, J.F. Uptake and depuration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from sedment by the zebrafish (Bracydanio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Triantafillaki, S.; Dassenakis, M.; Androutsos, F.; Scoullos, M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface seawater and in indigenous mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from coastal areas of the Saronikos Gulf (Greece). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklivagou, E.; Varnavas, S.P.; Hatzianestis, J. Aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from Elefsis Bay, Greece (Eastern Mediterranean). Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2001, 79, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklivagou, E.; Varnavas, S.P.; Hatzianestis, I.; Kanias, G. Assessment of aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and trace elements in coastal sediments of the Saronikos Gulf, Greece (Eastern Mediterranean). Mar. Georesour. Geotec. 2008, 26, 372–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzianestis, I.; Rori, N.; Sklivagou, E.; Rigas, F. PAH profiles in dated sediment cores from Elefsis bay, Greece. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2004, 13, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Parinos, C.; Hatzianestis, I.; Chourdaki, S.; Plakidi, E.; Gogou, A. Imprint and short-term fate of the AgiaZoni II tanker oil spill on the marine ecosystem of Saronikos Gulf. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, W.D. Collection of slick-forming materials from the sea surface. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1965, 10, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowska, L. Sea surface microlayer: A field evaluation of teflon plate, glass plate and screen sampling techniques. Part 2. Dissolved and suspended matter. Oceanologia 1999, 41, 223–240. [Google Scholar]
- Momzikoff, A.; Brinis, A.; Dallot, S.; Gondry, G.; Saliot, A.; Lebaron, P. Field study of the chemical characterization of the upper ocean surface using various samplers. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2004, 2, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavoltsos, S.; Sakellari, A.; Makarona, A.; Plavšić, M.; Ampatzoglou, D.; Bakeas, E.; Dassenakis, M.; Scoullos, M. Copper complexation in wet precipitation: Impact of different ligand sources. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, M.L.; Wang, X.H.; Wu, Y.L.; Ye, C.X.; Li, Y.Y. Enrichment and partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sea surface microlayer and subsurface water along the coast of Xiamen Island, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedetti, M.; Guigue, C.; Goutx, M. Utilization of a submersible UV fluorometer for monitoring anthropogenic inputs in the Mediterranean coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manodori, L.; Gambaro, A.; Piazza, R.; Ferrari, S.; Stortini, A.M.; Moret, I.; Capodaglio, G. PCBs and PAHs in sea-surface microlayer and sub-surface water samples of the Venice Lagoon (Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardy, J.T.; Crecelius, E.A.; Antrim, L.D.; Broadhurst, V.L.; Apts, C.W.; Gurtisem, J.M.; Fortman, T.J. The sea-surface microlayer of Puget-Sound: Part II. Concentrations of contaminants and relation to toxicity. Mar. Environ. Res. 1987, 23, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouloubassi, I.; Saliot, A. Composition and sources of dissolved and particulate PAHs in surface waters from the Rhone delta (NW Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 22, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Wang, X.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Hong, H.S. Occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in seawater from the Western Taiwan Strait, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Cai, H.; Van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M.; Luo, F.; Liu, F.; Yang, Q. Dynamics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water column of Pearl river estuary (China): Seasonal pattern, environmental fate and source implication. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 90, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitart, C.; García-Flor, N.; Miquel, J.C.; Fowler, S.W.; Albaigés, J. Effect of the accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sea surface microlayer on their coastal air-sea exchanges. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 79, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivella, À. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rainwater and surface waters of Lake Maggiore, a subalpine lake in Northern Italy. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.; Wurl, O.; Karuppiah, S.; Obbard, J.P. Atmospheric wet deposition of PAHs to the sea-surface microlayer. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporstol, S.; Gjos, N.; Lichtenthaler, R.G.; Gustavsen, K.O.; Urdal, K.; Oreldm, F.; Skei, J. Source identification of aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments using GC/MS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1983, 17, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Lin, B.S.; Lee, C.L.; Brimblecombe, P. Enrichment behavior of contemporary PAHs and legacy PCBs at the sea-surface microlayer in harbor water. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, D.; Callcott, D. Partitioning and physical chemical properties of PAHs. In PAHs and Related Compounds; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzinski, H.; Jones, I.; Bellocq, J.; Piérard, C.; Garrigues, P. Evaluation of sediment contamination by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Gironde estuary. Mar. Chem. 1997, 58, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, S.; Rocher, V.; Muller, M.; Moilleron, R.; Thevenor, D.R. Sources, distribution and variability of hydrocarbons and metals in atmospheric deposition in an urban area (Paris, France). Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 337, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.L.; Tao, S.; Liu, W.X.; Yang, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Liu, S.Z. Source diagnostics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons based on species ratios: A multimedia approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9109–9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouloubassi, I.; Saliot, A. Investigation of anthropogenic and natural organic inputs in estuarine sediments using hydrocarbon markers (NAH, LAB, PAH). Oceanol. Acta 1993, 16, 145–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ya, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Transport of terrigenous polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons affected by the coastal upwelling in the northwestern coast of South China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R.H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pies, C.; Hoffmann, B.; Petrowsky, J.; Yang, Y.; Ternes, T.A.; Hofmann, T. Characterization and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in river bank soils. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivwurie, W.; SnapeM, C.E.; Sun, C. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in vegetation samples from the UK by stable carbon isotope ratios measurement. Int. J. Trop. Agric. Food Syst. 2010, 4, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kucklick, J.R.; Bidleman, T.F. Organic contaminants in Winyah Bay, South Carolina I: Pesticides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in subsurface and microlayer waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 1994, 37, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.A.; Codi, S. Non-volatile hydrocarbon chemistry studies around a production platform on Australia’s Northwest Shelf. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1999, 49, 853–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, G.P.; Wu, G.W.; Gao, X.C.; Xia, Q.Y. Concentration and characterization of dissolved organic matter in the surface microlayer and subsurface water of the Bohai Sea, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 52, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Dickhut, R.M. Surface microlayer enrichment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in southern Chesapeake Bay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2777–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stortini, A.M.; Martellini, T.; Del Bubba, M.; Lepri, L.; Capodaglio, G.; Cincinelli, A. n-Alkanes, PAHs and surfactants in the sea surface microlayer and sea water samples of the Gerlache Inlet sea (Antarctica). Microchem. J. 2009, 92, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berrojalbiz, N.; Dachs, J.; Ojeda, M.J.; Valle, M.C.; Castro-Jimenez, J.; Wollgast, J.; Ghiani, M.; Hanke, G.; Zaldivar, J.M. Biogeochemical and physical controls on concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and plankton of the Mediterranean and Black Seas. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2011, 25, GB4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro-Jimenez, J.; Berrojalbiz, N.; Wollgast, J.; Dachs, J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Mediterranean Sea: Atmospheric occurrence, deposition and decoupling with settling fluxes in the water column. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 166, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Smith, S.L.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, R.C. Consensus sediment quality guidelines for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, J.D.; Carrier, W.L.; Gucinski, H.; Olla, B.L.; Yoshida, H.; Fujimura, R.K.; Wicklund, R.I. DNA as a solar dosimeter in the ocean. Photochem. Photobiol. 1992, 56, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.T.; Crecelius, E.A.; Antrim, L.D.; Kiesser, S.L.; Broadhust, V.L. Aquatic surface microlayer contamination in Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Chem. 1990, 28, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.N.; Hardy, J.T.; Hose, J.E.; Hershelman, G.P.; Antrim, L.D.; Gosett, R.W.; Creselius, E.A. Contaminant concentrations and toxicity of sea-surface microlayer near Los Angeles, California. Mar. Environ. Res. 1987, 23, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, E.Y.; Vista, C.L. Organic pollutants in the coastal environment off San Diego, California. 1. Source identification and assessment by compositional indices of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, G. Occurrence and transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the water bodies of the Baltic Sea. Mar. Chem. 2002, 79, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitart, C.; García-Flor, N.; Dachs, J.; Bayona, J.M.; Albaigés, J. Evaluation of sampling devices for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface microlayer coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 48, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cincinelli, A.; Stortini, A.M.; Checchini, L.; Martellini, T.; Del Bubba, M.; Lepri, L. Enrichment of organic pollutants in the sea surface microlayer (SML) at Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica: Influence of SML on superficial snow composition. J. Environ. Monit. 2005, 7, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benson, N.U.; Essien, J.P.; Asuquo, F.E.; Eritobor, A.L. Occurrence and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface microlayer and subsurface seawater of Lagos Lagoon, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5519–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Date | Sampling Time, h | Weather Conditions | Solar Irradiation, W m−2 | Tair, oC | Wind Speed, m s−1 | State of the Sea b | Tsea, oC | pH | Salinity, ppt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loutropyrgos SML a | 13.02.2018 | 7:45–9:15 | Sunny with light fog | 24,000 | 14.5 | 1.30 | 0 | 13.8 | 7.85 | 38.2 |
| Loutropyrgos SSW0.2 | 13.7 | 7.84 | 38.3 | |||||||
| Pahi SML a | 10:45–12:00 | Sunny with light clouding | 38,500 | 13.6 | 1.15 | 1 | 13.9 | 7.82 | 38.2 | |
| Pahi SSW0.2 | 13.8 | 7.83 | 38.2 | |||||||
| Loutropyrgos SML a | 16.05.2018 | 7:30–8:50 | Sunny with light clouding | 28,000 | 19.5 | 0.90 | 0 | 16.8 | 7.98 | 38.3 |
| Loutropyrgos SSW0.2 | 16.7 | 7.99 | 38.1 | |||||||
| Loutropyrgos SSW2.0 | 16.1 | 7.97 | 38.1 | |||||||
| Pahi SML a | 10:00–12:30 | Sunny with light clouding | 45,000 | 22.0 | 0.50 | 0 | 17.0 | 7.96 | 38.6 | |
| Pahi SSW0.2 | 16.8 | 8.00 | 38.5 | |||||||
| Pahi SSW2.0 | 16.6 | 7.99 | 38.4 | |||||||
| Loutropyrgos SML a | 05.09.2018 | 9:00–10:30 | Sunny | 41,500 | 29.3 | 5.2 | 1 | 23.6 | 8.08 | 38.5 |
| Loutropyrgos SSW0.2 | 23.6 | 8.09 | 38.5 | |||||||
| Loutropyrgos SSW2.0 | 23.2 | 8.06 | 38.3 | |||||||
| Pahi SML a | 13:00–14:30 | Sunny | 75,000 | 33.6 | 3.5 | 2 | 23.4 | 8.10 | 38.4 | |
| Pahi SSW0.2 | 23.5 | 8.14 | 38.4 | |||||||
| Pahi SSW2.0 | 23.2 | 8.15 | 38.2 | |||||||
| Loutropyrgos SML a | 06.07.2019 | 7:10–8:45 | Sunny | 32,000 | 29.0 | 1.80 | 1 | 22.8 | 8.05 | 38.1 |
| Loutropyrgos SSW0.2 | 22.8 | 8.07 | 38.0 | |||||||
| Loutropyrgos SSW2.0 | 22.6 | 8.03 | 38.0 | |||||||
| Pahi SML a | 9:55–11:50 | Sunny | 85,000 | 30.0 | 0.70 | 0 | 23.0 | 8.02 | 38.7 | |
| Pahi SSW0.2 | 22.9 | 8.04 | 38.6 | |||||||
| Pahi SSW2.0 | 22.7 | 8.05 | 38.5 | |||||||
| Loutropyrgos SML a | 11.01.2020 | 7:30–9:00 | Sunny | 19,000 | 16.0 | 0.60 | 1 | 14.0 | 7.76 | 38.0 |
| Loutropyrgos SSW0.2 | 13.8 | 7.81 | 38.0 | |||||||
| Loutropyrgos SSW2.0 | 13.7 | 7.83 | 37.9 | |||||||
| Pahi SML a | 10:20–12:55 | Sunny | 44,000 | 19.2 | 0.50 | 0 | 15.2 | 7.71 | 38.3 | |
| Pahi SSW0.2 | 15.2 | 7.74 | 38.3 | |||||||
| Pahi SSW2.0 | 15.0 | 7.72 | 38.2 |
| February 2018 | May 2018 | September 2018 | July 2019 | January 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolved phase | |||||
| Loutropyrgos SML | 177 | 237 | 162 | 67.1 | 42.9 |
| Loutropyrgos SSW0.2 | 113 | 128 | 180 | 42.6 | 22.8 |
| Loutropyrgos SSW2.0 | - * | 52.3 | 93.8 | 20.2 | 24.9 |
| Pahi of Megara SML | 133 | 181 | 181 | 75.2 | 40.4 |
| Pahi of Megara SSW0.2 | 118 | 92.6 | 126 | 69.0 | 81.3 |
| Pahi of Megara SSW2.0 | - | 98.3 | 145 | 53.4 | 15.5 |
| Particulate phase | |||||
| Loutropyrgos SML | 118 | 101 | 102 | 57.0 | 177 |
| Loutropyrgos SSW0.2 | 66.7 | 48.3 | 78.1 | 43.0 | 119 |
| Loutropyrgos SSW2.0 | - | 24.5 | 68.3 | 25.2 | 7.78 |
| Pahi of Megara SML | 140 | 30.8 | 72.6 | 39.7 | 57.3 |
| Pahi of Megara SSW0.2 | 171 | 42.0 | 69.6 | 36.8 | 145 |
| Pahi of Megara SSW2.0 | - | 47.9 | 33.7 | 10.8 | 5.79 |
| Loutropyrgos | Pahi of Megara | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolved | Particulate | Dissolved | Particulate | |||||
| EF1 a | EF2 b | EF1 | EF2 | EF1 | EF2 | EF1 | EF2 | |
| 13 February 2018 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 0.8 | ||||
| 16 May 2018 | 1.8 | 4.5 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 4.1 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| 5 September 2018 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 2.2 |
| 6 July 2019 | 1.6 | 3.3 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 3.7 |
| 11 January 2020 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 22.7 | 0.4 | 9.9 |
| Mean ± st dev | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 2.8 ± 1.4 | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 7.6 ± 10 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 4.1 ± 4.1 |
| Concentration (ng g−1) | SML | SSW0.2 | SSW2.0 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERL a | ERM b | nc > ERL | n > ERM | n > ERL | n > ERM | n > ERL | n > ERM | |
| ACY | 44 | 640 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| ACE | 16 | 500 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| FL | 19 | 540 | 7 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| PHE | 240 | 1500 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| ANT | 85.3 | 1100 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| FLA | 600 | 5100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| PYR | 665 | 2600 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BaA | 261 | 1600 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DahA | 63.4 | 260 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Total PAHs | 4022 | 44,792 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakellari, A.; Karavoltsos, S.; Moutafis, I.; Koukoulakis, K.; Dassenakis, M.; Bakeas, E. Occurrence and Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Marine Surface Microlayer of an Industrialized Coastal Area in the Eastern Mediterranean. Water 2021, 13, 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223174
Sakellari A, Karavoltsos S, Moutafis I, Koukoulakis K, Dassenakis M, Bakeas E. Occurrence and Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Marine Surface Microlayer of an Industrialized Coastal Area in the Eastern Mediterranean. Water. 2021; 13(22):3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223174
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakellari, Aikaterini, Sotirios Karavoltsos, Ipek Moutafis, Konstantinos Koukoulakis, Manos Dassenakis, and Evangelos Bakeas. 2021. "Occurrence and Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Marine Surface Microlayer of an Industrialized Coastal Area in the Eastern Mediterranean" Water 13, no. 22: 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223174
APA StyleSakellari, A., Karavoltsos, S., Moutafis, I., Koukoulakis, K., Dassenakis, M., & Bakeas, E. (2021). Occurrence and Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Marine Surface Microlayer of an Industrialized Coastal Area in the Eastern Mediterranean. Water, 13(22), 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223174







