Risk Analysis of Instability Failure of Earth–Rock Dams Based on the Fuzzy Set Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Uncertain Factors Affecting the Stability of Earth–Rock Dams
- Uncertainty of human factors
- Uncertainty of the calculation model
- Uncertainty of parameters
2.2. Fuzzy Analysis of the Instability Risk of Earth–Rock Dams
2.2.1. Calculation Model of Fuzzy Risk
2.2.2. Method for Eliminating Fuzziness
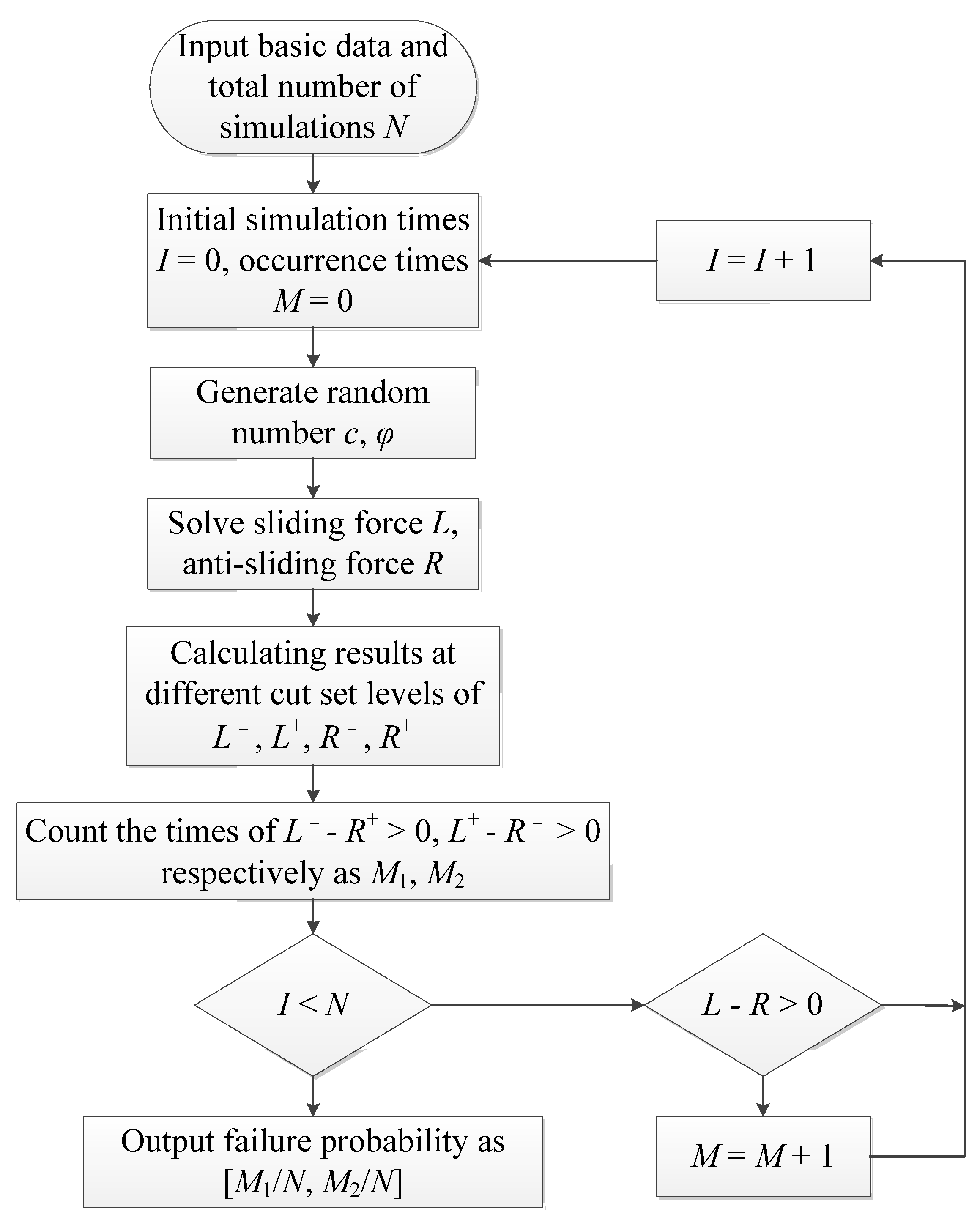
2.2.3. Fuzzy Risk Calculation
- 1.
- The solution of
- 2.
- The solution of
- 3.
- Limit state equation
2.3. Risk Standard for Instability Failure of Earth–Rock Dams
3. Case Study: The Longxingsi Reservoir
3.1. Basic Data
3.2. Fuzzy Risk Calculation of the Earth–Rock Dam Instability
3.2.1. Calculation of Interval Frequency
3.2.2. Calculation of
3.2.3. Fuzzy Risk Calculation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, W.; Sun, H.Q.; Zhang, H.X.; Li, Z.K.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.Y.; Qin, Y.P.; Gao, W.X.; Gelder, P.V. Economic risk criteria for dams considering the relative level of economy and industrial economic contribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Jiao, Y.T.; Sun, H.Q.; Li, Z.K.; Zhang, H.X.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.S.; Gelder, P.V. A method for fast evaluation of potential consequences of dam breach. Water 2019, 11, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mouyeaux, A.; Carvajal, C.; Bressolette, P.; Peyrasa, L.; Breul, P.; Bacconnet, C. Probabilistic analysis of pore water pressures of an earth dam using a random finite element approach based on field data. Eng. Geol. 2019, 259, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Qin, Y.P.; Li, Z.K.; Zhang, H.X.; Gao, W.X.; Guo, X.Y.; Song, Z.Y.; Li, W.; Gelder, P.V. An innovative methodology for establishing societal life risk criteria for dams: A case study to reservoir dam failure events in China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Yao, S.M.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.H.; Chen, D. Review on overtopping failure and flood evolution of earth–rock dams. Adv. Water Sci. 2020, 31, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.K.; Ge, W.; Wang, J.; Li, W. Strategic consideration of dam safety management and risk management in China. Adv. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, Z.H.; Jiang, J.P. An analysis on laws of reservoir dam defects and breaches in China. Sci. Sin. Tech. 2017, 47, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.S.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.J. Slope reliability analysis using length-based representative slip surfaces. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 9065–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinyol, N.M.; Alonso, E.E.; Corominas, J.; Moya, J. Canelles landslide: Modelling rapid drawdown and fast potential sliding. Landslides 2012, 9, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wu, C.Z.; Gu, X.; Liu, H.L.; Mei, G.X.; Zhang, W.G. Probabilistic stability analysis of earth dam slope under transient seepage using multivariate adaptive regression splines. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Li, J.J.; Kang, F. Risk analysis of dam based on artificial bee colony algorithm with fuzzy c -means clustering. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2011, 38, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.N.; Kao, H.P. An evaluation approach to logistics service using fuzzy theory, quality function development and goal programming. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2014, 68, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.W.; Zhang, H.G.; Wang, Z.S.; Liu, J.H. Synchronization analysis for complex networks with coupling delay based on T–S fuzzy theory. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 6215–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; You, J.X.; Duan, C.Y. An integrated approach for failure mode and effect analysis under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 207, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Gu, C.S.; Su, H.Z.; Qin, X.N. Risk Analysis of Earth–rock Dam Failures Based on Fuzzy Event Tree Method. Int. J. Env. Res. Pub. He. 2018, 15, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, R.; Lodwick, W.A. Interval analysis and fuzzy set theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2003, 135, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Um, J.G.; Woo, I.; Kim, J.W. Application of fuzzy set theory to evaluate the probability of failure in rock slopes. Eng. Geol. 2012, 125, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canal, M.D.D.L.; Ferraris, I.C. Risk analysis holistic approach as a base for decision making under uncertainties. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 33, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, A.; Ayati, A.H. Stability analysis of gravity dams under uncertainty using the fuzzy sets theory and a many-objective GA. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 30, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.E.; Ma, G.Z.; Wang, F.; Rong, W.J.; He, Y.J. Analysis of dam failure trend of China from 2000 to 2018 and improvement suggestions. Hydro Sci. Eng. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, N.H.; Niu, Y.G. Accident statistics and analysis of earth rock dam. Dam Saf. 2001, 1, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.J.; Yu, Z.B.; Li, Y.P.; Han, D.W.; Zhao, L.L.; Chu, Q. Calculation method and application of loss of life caused by dam break in China. Nat. Hazards 2017, 85, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Wang, Y.Z. Cognition in the uncertainty and equifinality of hydrological model: A systematic review. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 49, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chai, J.R.; Cao, J.; Xu, Z.G.; Qin, Y.; Xian, M.T. Numerical Analysis of Seepage for Concrete Face Rockfill Dam with Cracks Based on Block Equivalent Continuum Method. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wen, L.F.; Shi, N. A Prediction Model for Deformation Behavior of Concrete Face Rockfill Dams Based on the Threshold Regression Method. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.X.; Yin, Y.P.; Li, B.; Wang, W.P. Research on the colluvial landslide stability during reservoir water level fluctuation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 48, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.Z.; Wen, Z.P. Interval risk analysis for gravity dam instability. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 33, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanss, M.; Turrin, S. A fuzzy-based approach to comprehensive modeling and analysis of systems with epistemic uncertainties. Struct. Saf. 2010, 32, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.D.; Sheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.K.; Zhang, Z.P. Computation of the safety factor for slope stability using discontinuous deformation analysis and the vector sum method. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 92, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Tang, W.; Wen, L.F.; Wang, J. Study on seismic failure probability of high earth–rock dam considering dam body deformation and slope stability. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Bao, T.F.; Shu, X.S.; Chen, Z.X.; Gao, Z.X.; Zhang, K. A Hybrid Model Integrating Principal Component Analysis, Fuzzy C-Means, and Gaussian Process Regression for Dam Deformation Prediction. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Wang, X.W.; Li, Z.K.; Zhang, H.X.; Guo, X.Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, W.X.; Lin, C.N.; Gelder, P.V. Interval analysis of loss of life caused by dam failure. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2021, 147, 04020098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.H.; Sun, Y.F.; Li, M.C. Dam break threshold value and risk probability assessment for an earth dam. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, X.H.; Zhou, J.Z.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.S.; Dai, L. Real-time flood control risk estimation of reservoir and analysis on the interoperability of storage capacity of multi–reservoir regulation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 50, 209–217+224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Z.K.; Ge, W.; Wu, S. Risk Evaluation Model of Life Loss Caused by Dam-Break Flood and Its Application. Water 2019, 11, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.K.; Wang, T.; Ge, W.; Wei, D.; Li, H.Y. Risk Analysis of Earth–rock Dam Breach Based on Dynamic Bayesian Network. Water 2019, 11, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Chen, C.; Lu, X.; Pei, L.; Zhang, L.M. Discussion on the allowable safety factor of slope stability for high rockfill dams in China. Eng. Geol. 2020, 272, 105666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Li, Z.; Liang, R.Y.; Li, W.; Cai, Y.C. Methodology for Establishing Risk Criteria for Dams in Developing Countries, Case Study of China. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 4063–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.H.; Fan, Z.W. Earth–rockfill dam safety classification and risk rate assessment on flood control. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 39, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Z.; Yun, J.; Si, Z.; Li, S.Y. Analysis on overtopping failure risk of earth–rock dam based on random-fuzziness of reservoir inflow flood. Eng. J. Wuhan Univ. 2020, 53, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.F. Analysis of fuzzy risk of earth dams. Master’s Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Cheng, Y.M.; Yu, J.D. Slope Stability Analysis Based on GeoStudio. Value Eng. 2016, 35, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam Safety Management of Ministry of Water Resources, Nanjing Water Conservancy Research Institute, Hohai University. SL 258–2017, Guideline of Dam Safety Evaluation; Ministry of Water Resources: Beijing, China, 2017.

| Dam Grade | Coefficient of Variation | Risk Rate Pfa | Risk Rate Pfb |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | δR = δS = 0.1 | 7.5 × 10−8 | 1.4 × 10−6 |
| δR = δS = 0.2 | 9.2 × 10−6 | 4.1 × 10−5 | |
| 2 | δR = δS = 0.1 | 8.2 × 10−7 | 3.0 × 10−5 |
| δR = δS = 0.2 | 3.6 × 10−5 | 1.7 × 10−4 | |
| 3 | δR = δS = 0.1 | 6.9 × 10−6 | 1.0 × 10−4 |
| δR = δS = 0.2 | 1.1 × 10−4 | 4.2 × 10−4 |
| Soil Parameter | Saturation Density (g/cm3) | Floating Density (g/cm3) | Wet Density (g/cm3) | Internal Friction Angle (°) | Cohesive Force (KPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum value | 2.376 | 1.376 | 2.20 | 13.0 | 27.5 |
| Minimum value | 1.854 | 0.854 | 1.60 | 10.5 | 21.5 |
| Mean Value | 2.236 | 1.236 | 1.90 | 11.2 | 26 |
| Recommended value | 2.236 | 1.236 | 1.90 | 11.2 | 26 |
| Variable | Distribution Type | Mean Value | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cohesive Force C | Extreme value type I | 26 (KPa) | 0.46 |
| Tanφ | Lognormal | 0.198 | 0.25 |
| Water Level Interval (m) | 286.8~284.41 | 284.41~283 | 283~281 | 281~279 | 279~277 | 277~275 | 275~273 | 273~271 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interval Probability (%) | 0.19 | 1.68 | 7.49 | 19.26 | 13.7 | 25.36 | 8.19 | 3.75 |
| Reservoir Water Level (m) | The Most Dangerous Sliding Surface | Minimum Safety Factor Kmin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X0 (m) | Y0 (m) | R (m) | ||
| 286.8 | 25.47 | 75.47 | 76.05 | 1.1073 |
| 284.41 | 25.64 | 76.28 | 76.46 | 1.1081 |
| 283.0 | 25.76 | 75.62 | 76.11 | 1.1091 |
| 281.0 | 24.95 | 78.43 | 78.18 | 1.1109 |
| 279.0 | 26.33 | 73.79 | 74.76 | 1.1141 |
| 277.0 | 26.27 | 73.96 | 74.88 | 1.1187 |
| 275.0 | 26.84 | 72.23 | 73.63 | 1.1247 |
| 273.0 | 27.04 | 71.55 | 73.16 | 1.1295 |
| 271.0 | 26.91 | 71.63 | 73.24 | 1.1387 |
| Reservoir Water Level (m) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 286.8~284.41 | 0.0221 | 0.0259 | 0.0019 | 0.00004 | 0.00005 |
| 284.41~283 | 0.0071 | 0.0089 | 0.0168 | 0.00012 | 0.00015 |
| 283~281 | 0.0023 | 0.0041 | 0.0749 | 0.00017 | 0.00031 |
| 281~279 | 0.0051 | 0.0066 | 0.1926 | 0.00098 | 0.00127 |
| 279~277 | 0.0018 | 0.0026 | 0.137 | 0.00025 | 0.00036 |
| 277~275 | 0.0011 | 0.002 | 0.2536 | 0.00028 | 0.00051 |
| 275~273 | 0.0084 | 0.0058 | 0.0819 | 0.00069 | 0.00048 |
| 273~271 | 0.0049 | 0.0006 | 0.0375 | 0.00018 | 0.00002 |
| Total | 0.00272 | 0.00314 | |||
| α | Fuzzy Risk Probability | Mean Value |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | [0.00197,0.00390] | 0.00294 |
| 0.1 | [0.00196,0.00392] | 0.00294 |
| 0.2 | [0.00213,0.00371] | 0.00292 |
| 0.3 | [0.00211,0.00357] | 0.00284 |
| 0.4 | [0.00234,0.00343] | 0.00289 |
| 0.5 | [0.00272,0.00314] | 0.00293 |
| 0.6 | [0.00225,0.00306] | 0.00265 |
| 0.7 | [0.00232,0.00306] | 0.00269 |
| 0.8 | [0.00261,0.00304] | 0.00283 |
| 0.9 | [0.00262,0.00294] | 0.00278 |
| 1.0 | [0.00267,0.00267] | 0.00267 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Song, Z.; Ge, W.; Han, R.; Wang, T. Risk Analysis of Instability Failure of Earth–Rock Dams Based on the Fuzzy Set Theory. Water 2021, 13, 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213088
Zhang H, Li Z, Li W, Song Z, Ge W, Han R, Wang T. Risk Analysis of Instability Failure of Earth–Rock Dams Based on the Fuzzy Set Theory. Water. 2021; 13(21):3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213088
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hexiang, Zongkun Li, Wei Li, Ziyuan Song, Wei Ge, Ruifang Han, and Te Wang. 2021. "Risk Analysis of Instability Failure of Earth–Rock Dams Based on the Fuzzy Set Theory" Water 13, no. 21: 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213088
APA StyleZhang, H., Li, Z., Li, W., Song, Z., Ge, W., Han, R., & Wang, T. (2021). Risk Analysis of Instability Failure of Earth–Rock Dams Based on the Fuzzy Set Theory. Water, 13(21), 3088. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213088







