Projected Streamflow and Sediment Supply under Changing Climate to the Coast of the Kalu River Basin in Tropical Sri Lanka over the 21st Century
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
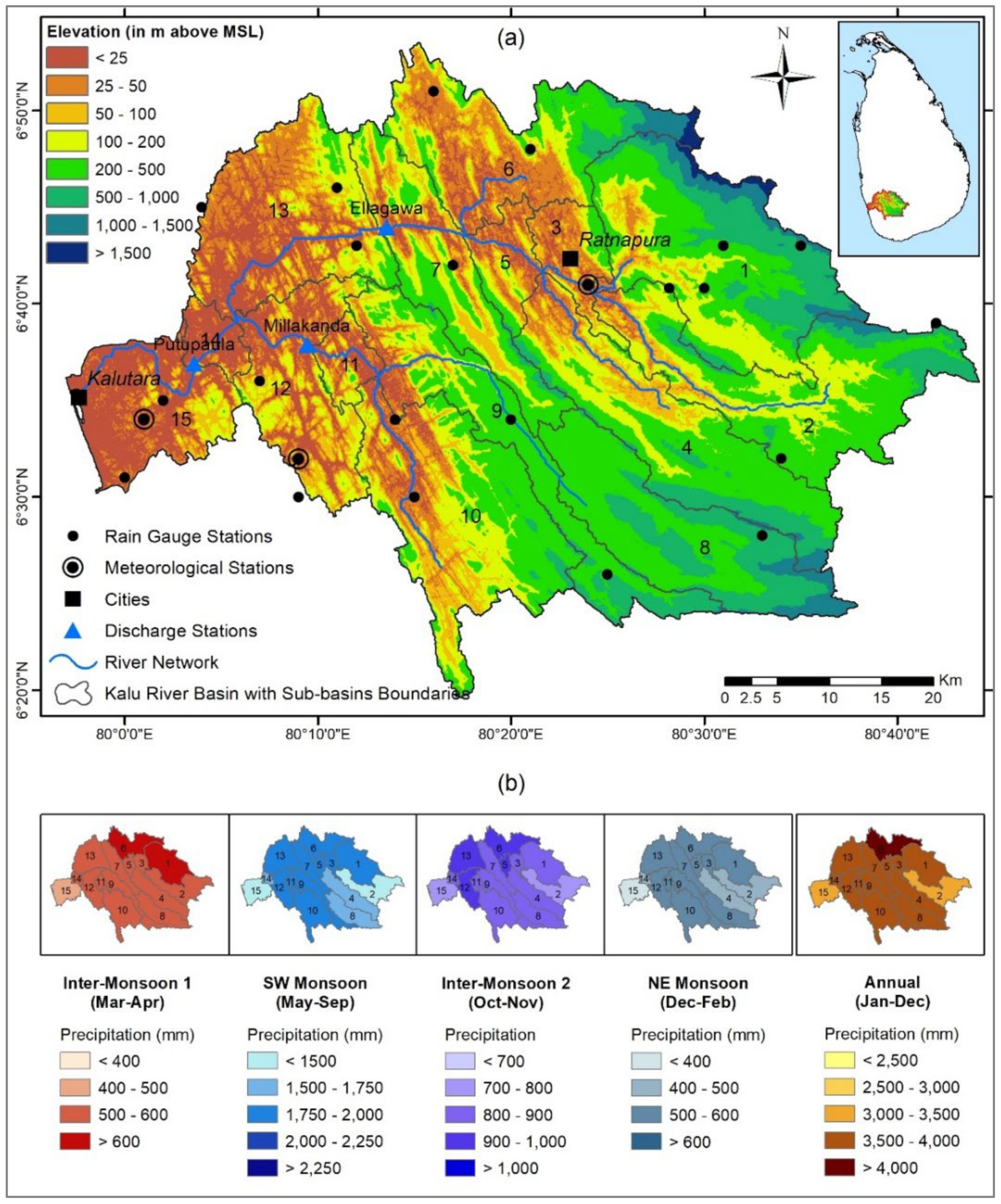
2.1. Data Used in This Study
2.2. Hydrological Model (SWAT) Setup and Calibration
2.3. Climate Projections and Bias Correction
3. Results and Discussion
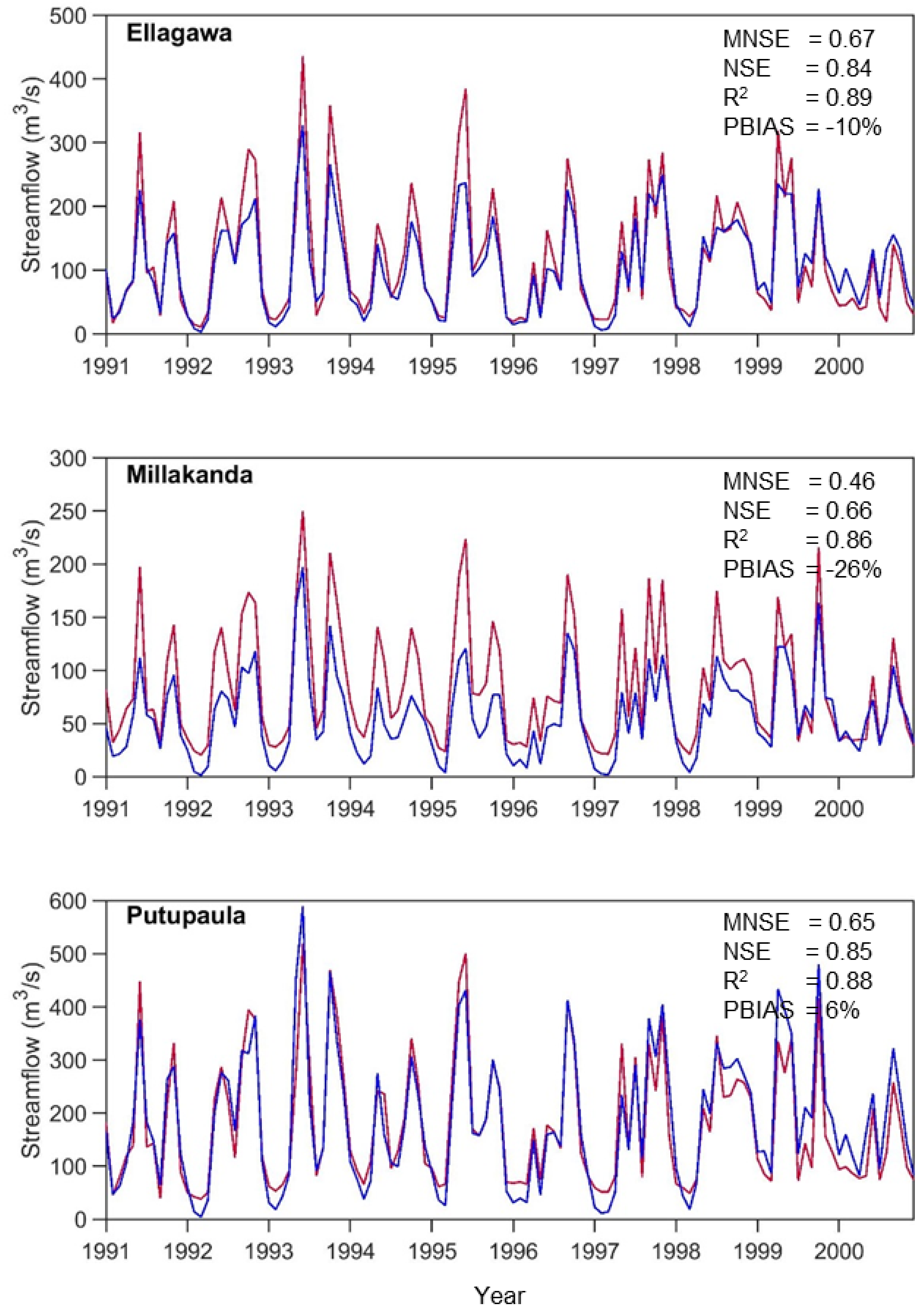
3.1. Calibration of the Hydrological Model Using Observed Data (1991–2000)
3.2. Model Simulations for the Baseline Period Using Bias-Corrected RCMs Data
3.2.1. Streamflow
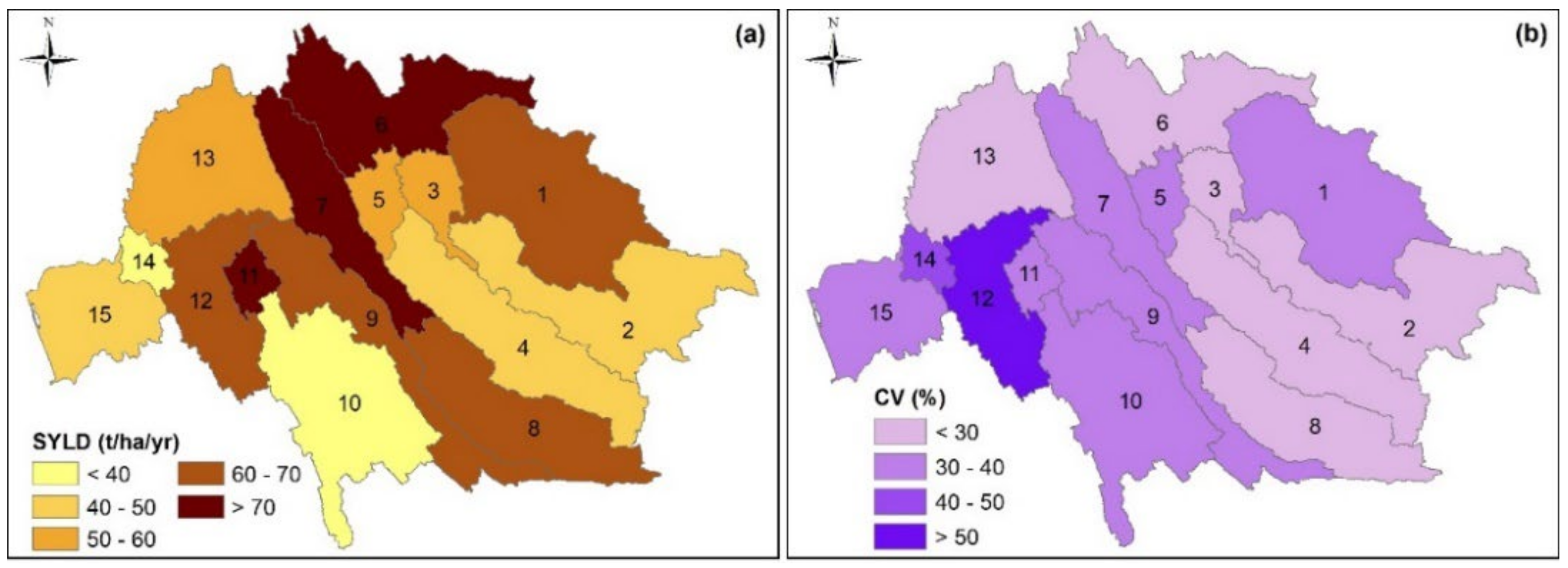
3.2.2. Sediment Loads
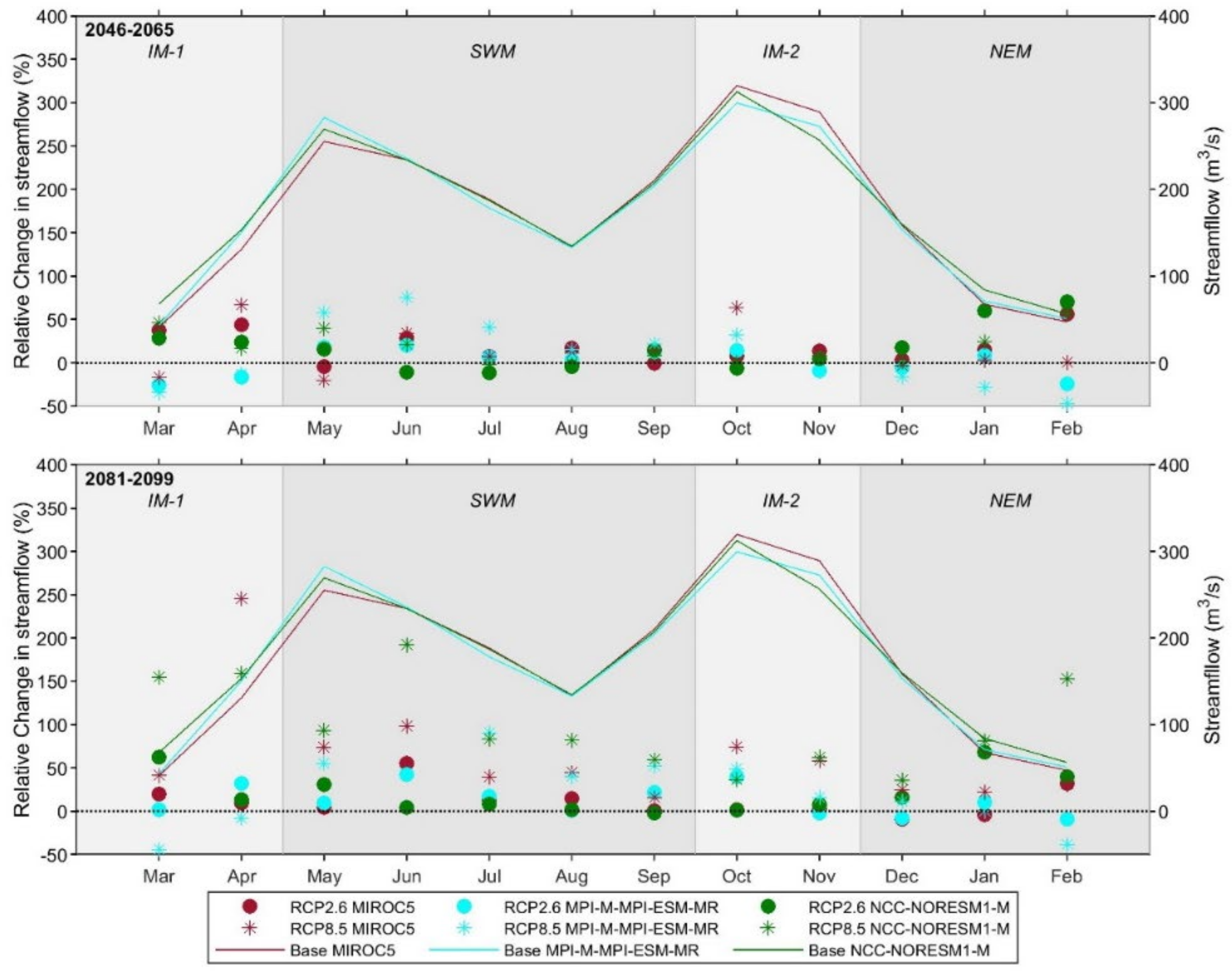
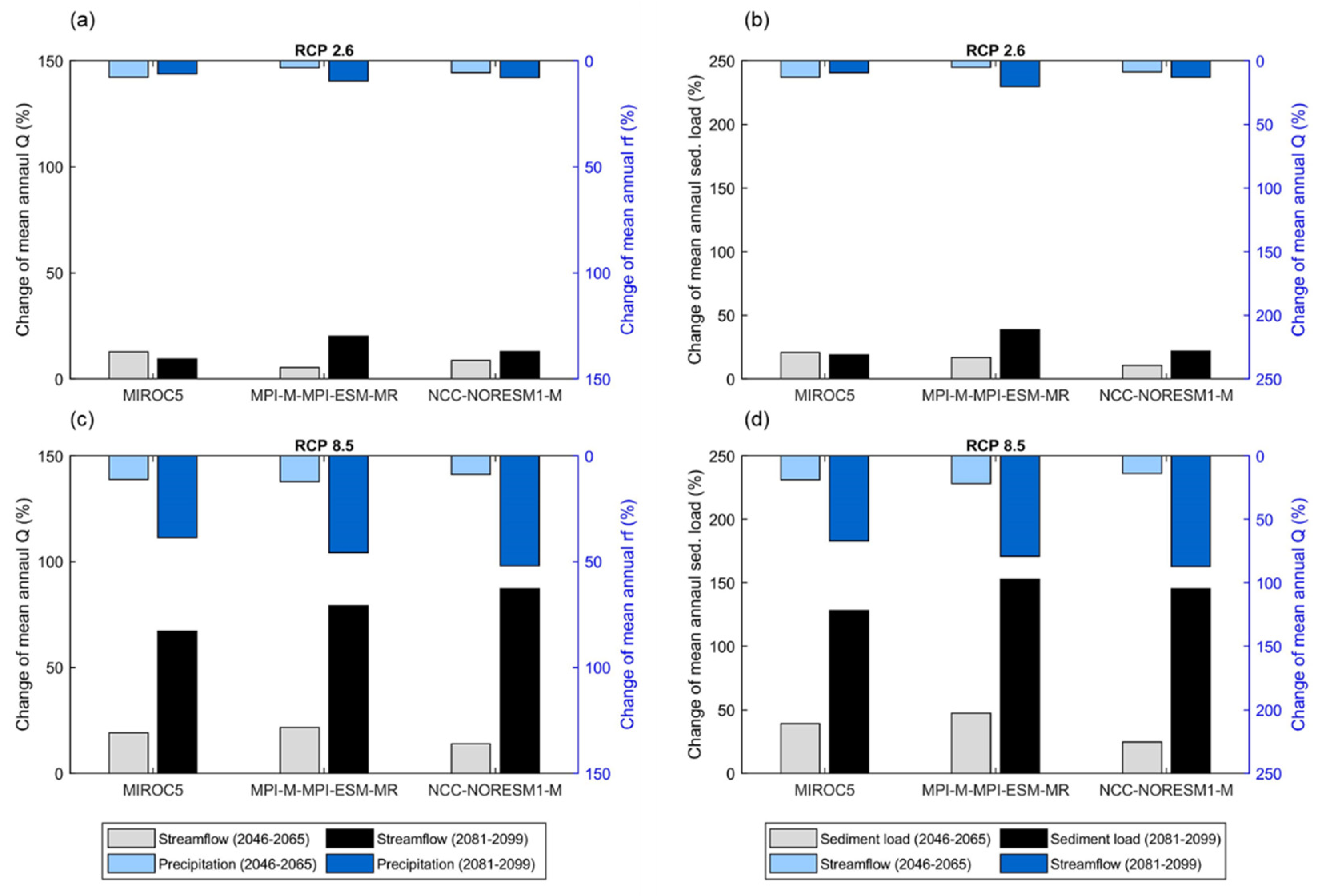
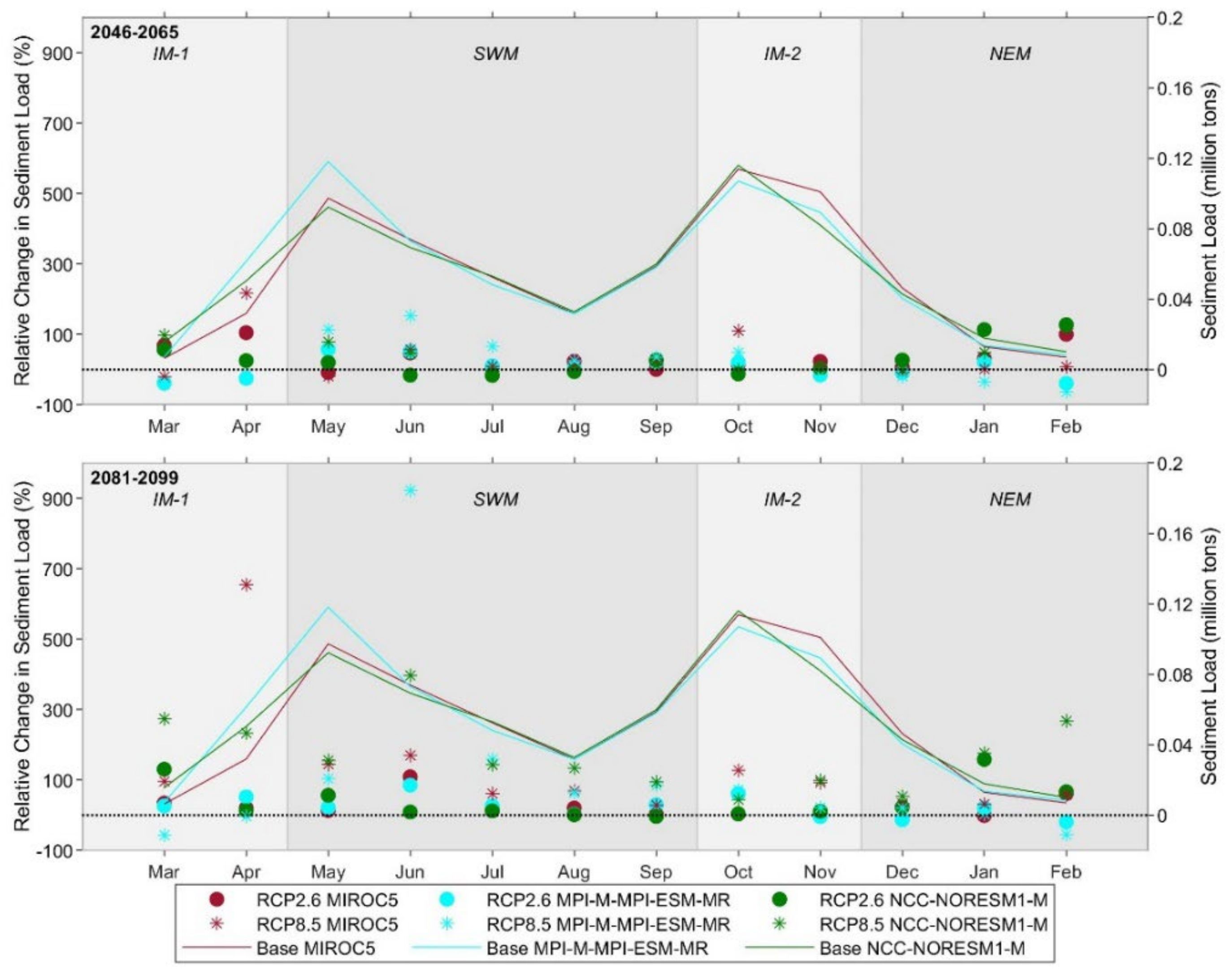
3.3. Future Projections of Climate and Hydrology Using Bias-Corrected RCM Data under RCP 2.6 and 8.5
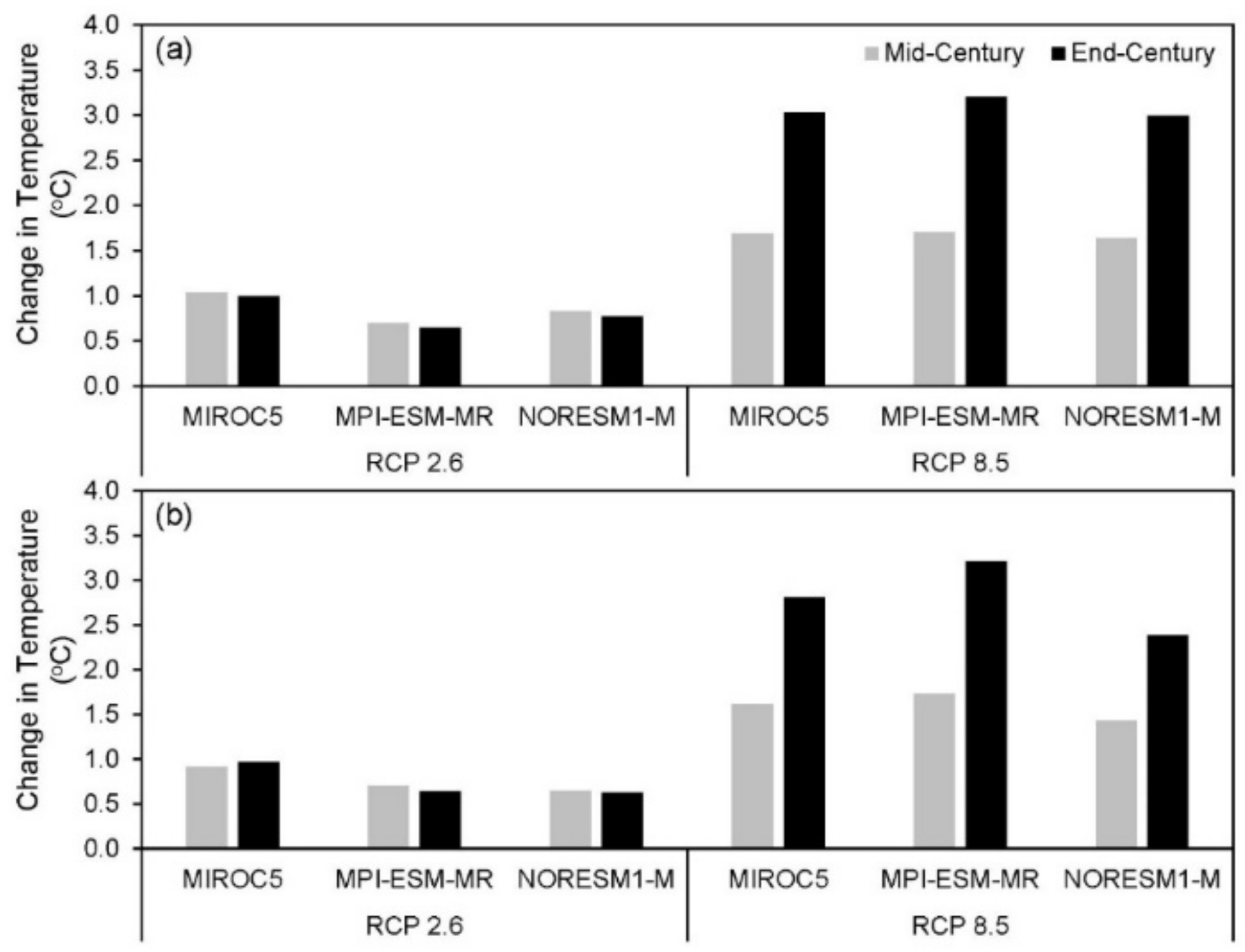
3.3.1. Changes in Future Climate
3.3.2. Changes in Hydrology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. (Eds.) IPCC Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Buendia, E.C.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Zhai, P.; Slade, R.; Connors, S.; van Diemen, R. (Eds.) IPCC Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Core Writing Team; Pachauri, R.K.; Meyer, L.A. (Eds.) IPCC Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. ISBN 9789291691432. [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein, D.; Dorsch, L.; Fischer, L. Global Climate Risk Index 2020; Germanwatch e.V.: Bonn, Germany, 2019; ISBN 9783943704044. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, N. Sinking the Pearl of the Indian Ocean: Climate Change in Sri Lanka. Glob. Major. E-J. 2010, 1, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Turn Down the Heat: Climate Extremes, Regional Impacts, and the Case for Resilience; International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- De Costa, W.A.J.M. Climate change in Sri Lanka: Myth or reality? Evidence from long-term meteorological data. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2008, 36, 63–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriyagama, N.; Smakhtin, V. Observed and projected climatic changes, their impacts and adaptation options for Sri Lanka: A review. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Water, Food Security and Climate Change, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 9–11 June 2009; pp. 99–117. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrapala, L. Long-term Trends of Rainfall and Temperature in Sri Lanka. In Climate Variability and Agriculture; Abrol, Y.P., Gadgil, S., Pant, G.B., Eds.; Narosa Publishing House: New Delhi, India, 1996; pp. 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ampitiyawatta, A.D.; Guo, S. Precipitation Trends in the Kalu Ganga Basin in Sri. J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 4, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriyagama, N.; Smakhtin, V.; Chandrapala, L.; Fernando, K. Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources and Agriculture in Sri Lanka: A Review and Preliminary Vulnerability Mapping; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nandalal, K.D.W. Use of a hydrodynamic model to forecast floods of Kalu River in Sri Lanka. Spec. Issue J. Flood Risk Manag. Integr. Flood Manag. 2009, 2, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Zhang, X.J.; Chen, H.; Guo, S.; Zhao, Y. Bias correcting climate model multi-member ensembles to assess climate change impacts on hydrology. Clim. Chang. 2019, 153, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Das Gupta, A.; Babel, M.S. Spatial disaggregation of bias-corrected GCM precipitation for improved hydrologic simulation: Ping River Basin, Thailand. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1373–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smitha, P.S.; Narasimhan, B.; Sudheer, K.P.; Annamalai, H. An improved bias correction method of daily rainfall data using a sliding window technique for climate change impact assessment. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological CC-impact studies_Review and evaluation of different methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456–457, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyunt, C.T.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Nemoto, T.; Kitsuregawa, M.; Koike, T. Application of bias-correction and downscaling method to Kalu Ganga Basin in Sri Lanka. Annu. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 56, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, L.; Kingston, D.G. GCM-related uncertainty in river flow projections at the threshold for “dangerous” climate change: The Kalu Ganga river, Sri Lanka. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment Part I: Model development. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil & Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, A.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E.; Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-Filled SRTM for the Globe Version 4. 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 1 August 2016).
- FAO. The Digital Soil Map of the World (Version 3.6); FAO/UNESCO: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Maskey, S. HyKit: A Tool for Grid-Based Interpolation of Hydrological Variables, User’s Guide (Version 1.3); IHE Delft Institute for Water Education: Delft, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J.R.; Haney, E.B.; Neitsch, S.L. Soil & Water Assessment Tool: Input/output documentation. Version 2012. Texas Water Resour. Inst. 2012, TR-439, 650. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, K.C. SWAT-Calibration and Uncertainty Programs (CUP); Eawag—Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology: Duebendorf, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 9780975840047. [Google Scholar]
- Sirisena, T.A.J.G.; Maskey, S.; Ranasinghe, R.; Babel, S. Effects of different precipitation inputs on streamflow simulation in the Irrawaddy River Basin, Myanmar. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 19, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masih, I.; Maskey, S.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Smakhtin, V. Assessing the impact of areal precipitation input on streamflow simulations using the SWAT model. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2011, 47, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, J.; Maximov, I.; Siber, R.; Bogner, K.; Mieleitner, J.; Zobrist, J.; Srinivasan, R. Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre-alpine/alpine Thur watershed using SWAT. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisena, T.A.J.G.; Maskey, S.; Ranasinghe, R. Hydrological Model Calibration with Streamflow and Remote Sensing Based Evapotranspiration Data in a Data Poor Basin. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Babel, M.S.; Maskey, S.; Van Griensven, A.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Green, A.; Akkharath, I. Impact of climate change on sediment yield in the Mekong River basin: A case study of the Nam Ou basin, Lao PDR. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Rouholahnejad, E.; Vaghefi, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H.; Kløve, B. A continental-scale hydrology and water quality model for Europe: Calibration and uncertainty of a high-resolution large-scale SWAT model. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legates, D.R.; McCabe, G.J., Jr. Evaluating the use of “Goodness of Fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpalatha, R.; Perrin, C.; Moine, N.L.; Andréassian, V. A review of efficiency criteria suitable for evaluating low-flow simulations. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420–421, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCD. Gazette Extraordinary of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka 2006; Coast Conservation Department: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2006; pp. 1–58.
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Binger, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Coppola, E.; Solmon, F.; Mariotti, L.; Sylla, M.B.; Bi, X.; Elguindi, N.; Diro, G.T.; Nair, V.; Giuliani, G.; et al. RegCM4: Model description and preliminary tests over multiple CORDEX domains. Clim. Res. 2012, 52, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teichmann, C.; Jacob, D.; Remedio, A.R.; Remke, T.; Buntemeyer, L.; Hoffmann, P.; Kriegsmann, A.; Lierhammer, L.; Bülow, K.; Weber, T.; et al. Assessing mean climate change signals in the global CORDEX-CORE ensemble. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 1269–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ranasinghe, R.; Maskey, S.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M.; Vrijling, J.K. Comparison of empirical statistical methods for downscaling daily climate projections from CMIP5 GCMs: A case study of the Huai River Basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; Buishand, A.; Van Deursen, W. Estimates of future discharges of the river Rhine using two scenario methodologies: Direct versus delta approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidli, J.; Frei, C.; Vidale, P.L. Downscaling from GCM precipitation: A benchmark for dynamical and statistical downscaling methods. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewawasam, T. Effect of land use in the upper Mahaweli catchment area on erosion, landslides and siltation in hydropower reservoirs of Sri Lanka. J. Natn. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2010, 38, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, C.B.; Rupasinghe, M.S. Environmental impact of mining, erosion and sedimentation in Sri Lanka. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1996, 51, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Suphachalasai, S. Assessing the Costs of Climate Change and Adaptation in South Asia; Asian Development Bank: Manila, Philippines, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Imbulana, N.; Gunawardana, S.; Shrestha, S.; Datta, A. Projections of extreme precipitation events under climate change scenarios in Mahaweli River Basin of Sri Lanka. Curr. Sci. 2018, 114, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Charles, S.; Podger, G. Future climate and runoff projections across South Asia from CMIP5 global climate models and hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 18, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.J.; Xiao, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H. Climate Change Impacts on Flow and Suspended Sediment Yield in Headwaters of High-Latitude Regions—A Case Study in China’s Far Northeast. Water 2017, 9, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirisena, T.A.J.G.; Maskey, S.; Bamunawala, J.; Ranasinghe, R. Climate change and reservoir impacts on 21st-century streamflow and fluvial sediment loads in the Irrawaddy River, Myanmar. Front. Earth Sci. Hydrosph. 2021, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| RegCM4 RCMs | Resolution | Average Annual Precipitation (mm) | Average of Daily TEMPERATURE (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | |||
| MIROC5 | 25 × 25 km2 | 7090 | 22.4 | 26.4 |
| MPI-M-MPI-ESM-MR | 25 × 25 km2 | 6630 | 22.4 | 26.6 |
| NCC-NORESM1-M | 25 × 25 km2 | 4490 | 21.9 | 26.9 |
| Observed | 3800 * | 22.7 ** | 31.5 ** | |
| Description | Observed (m3/s) | Simulated (Driven by RegCM4 Data, m3/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIROC5 | MPI-ESM | NorESM | ||
| Mean monthly flow | ||||
| January | 92 (41) | 60 (24) | 67 (20) | 81 (31) |
| February | 66 (20) | 45 (19) | 43 (23) | 54 (36) |
| March | 64 (14) | 42 (15) | 44 (17) | 61 (45) |
| April | 137 (93) | 121 (32) | 98 (64) | 156 (168) |
| May | 231 (114) | 183 (55) | 226 (203) | 293 (89) |
| June | 301 (144) | 199 (78) | 212 (108) | 258 (56) |
| July | 188 (99) | 169 (65) | 174 (51) | 205 (93) |
| August | 134 (42) | 121 (44) | 123 (33) | 135 (54) |
| September | 218 (113) | 203 (73) | 185 (23) | 200 (77) |
| October | 315 (92) | 314 (94) | 296 (100) | 298 (178) |
| November | 262 (109) | 293 (103 | 252 (87) | 250 (102) |
| December | 132 (67) | 143 (68) | 156 (54) | 148 (28) |
| Mean annual flow | 178 (29) | 158 (22) | 157 (36) | 179 (38) |
| Description | Observed * (Million tons/yr) | Simulated (Driven by RegCM4, Million tons/yr) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIROC5 | MPI-ESM | NorESM | ||
| Mean | 0.696 | 0.634 | 0.657 | 0.642 |
| Standard deviation | 0.092 | 0.198 | 0.265 | 0.194 |
| Year 1991 | 0.672 | 0.594 | 0.918 | 1.084 |
| Year 2001 | 0.576 | 0.846 | 0.742 | 0.487 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sirisena, T.A.J.G.; Maskey, S.; Bamunawala, J.; Coppola, E.; Ranasinghe, R. Projected Streamflow and Sediment Supply under Changing Climate to the Coast of the Kalu River Basin in Tropical Sri Lanka over the 21st Century. Water 2021, 13, 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213031
Sirisena TAJG, Maskey S, Bamunawala J, Coppola E, Ranasinghe R. Projected Streamflow and Sediment Supply under Changing Climate to the Coast of the Kalu River Basin in Tropical Sri Lanka over the 21st Century. Water. 2021; 13(21):3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213031
Chicago/Turabian StyleSirisena, T.A.J.G., Shreedhar Maskey, Janaka Bamunawala, Erika Coppola, and Roshanka Ranasinghe. 2021. "Projected Streamflow and Sediment Supply under Changing Climate to the Coast of the Kalu River Basin in Tropical Sri Lanka over the 21st Century" Water 13, no. 21: 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213031
APA StyleSirisena, T. A. J. G., Maskey, S., Bamunawala, J., Coppola, E., & Ranasinghe, R. (2021). Projected Streamflow and Sediment Supply under Changing Climate to the Coast of the Kalu River Basin in Tropical Sri Lanka over the 21st Century. Water, 13(21), 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213031








