Synthesis and Characterization of a Nano-Adsorbent Derivative Derived from Grape Seeds for Cadmium Ion Removal in an Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Adsorbant
2.3. Biosynthesis of Grape Seeds Iron Oxide Nanoparticles GS-IONPs
2.4. Characterization of the Prepared Grape Seeds Iron Oxide Nanoparticles GS-IONPs
2.5. Adsorption Studies
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
3. Results and Discussion
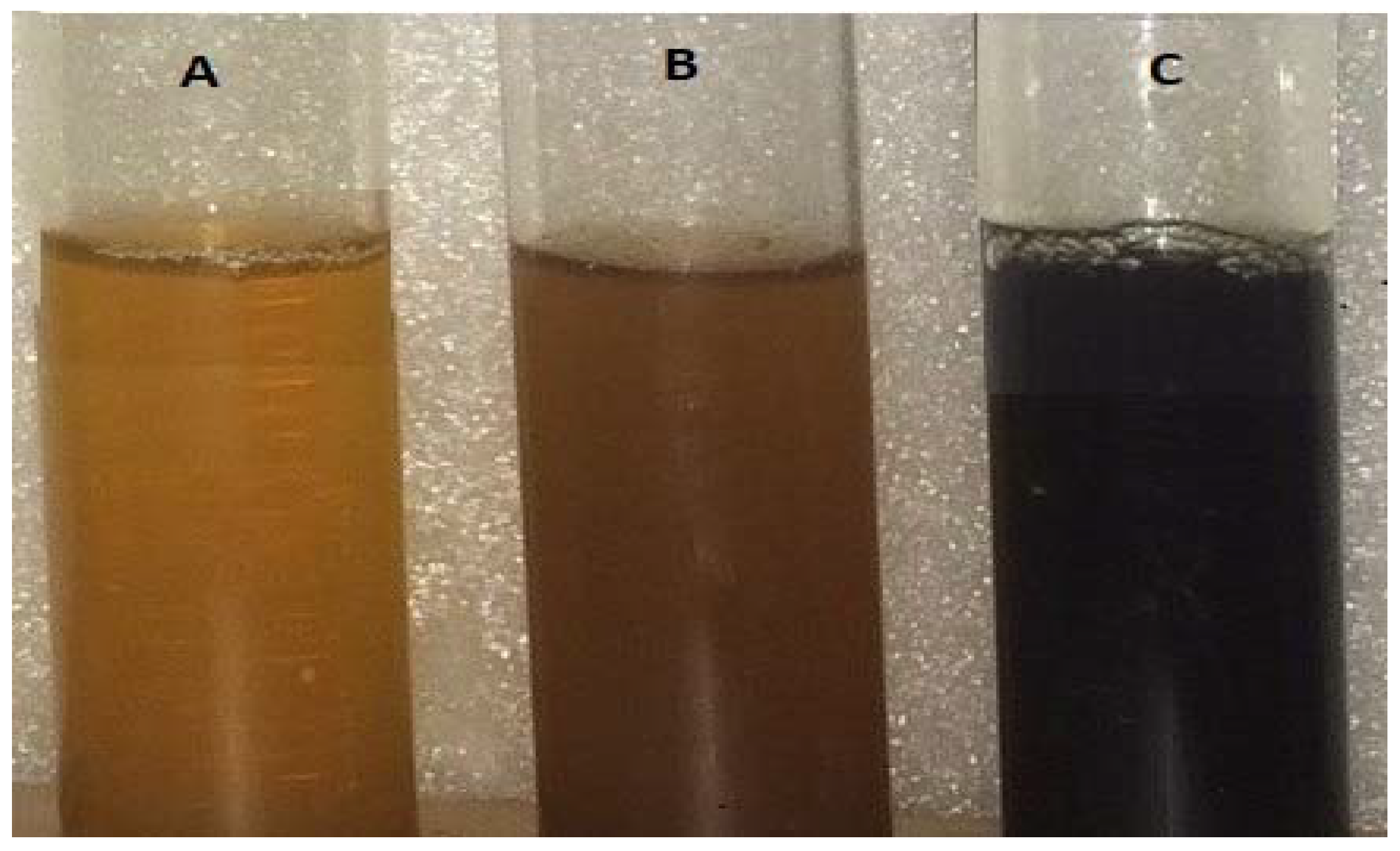
3.1. Color Change
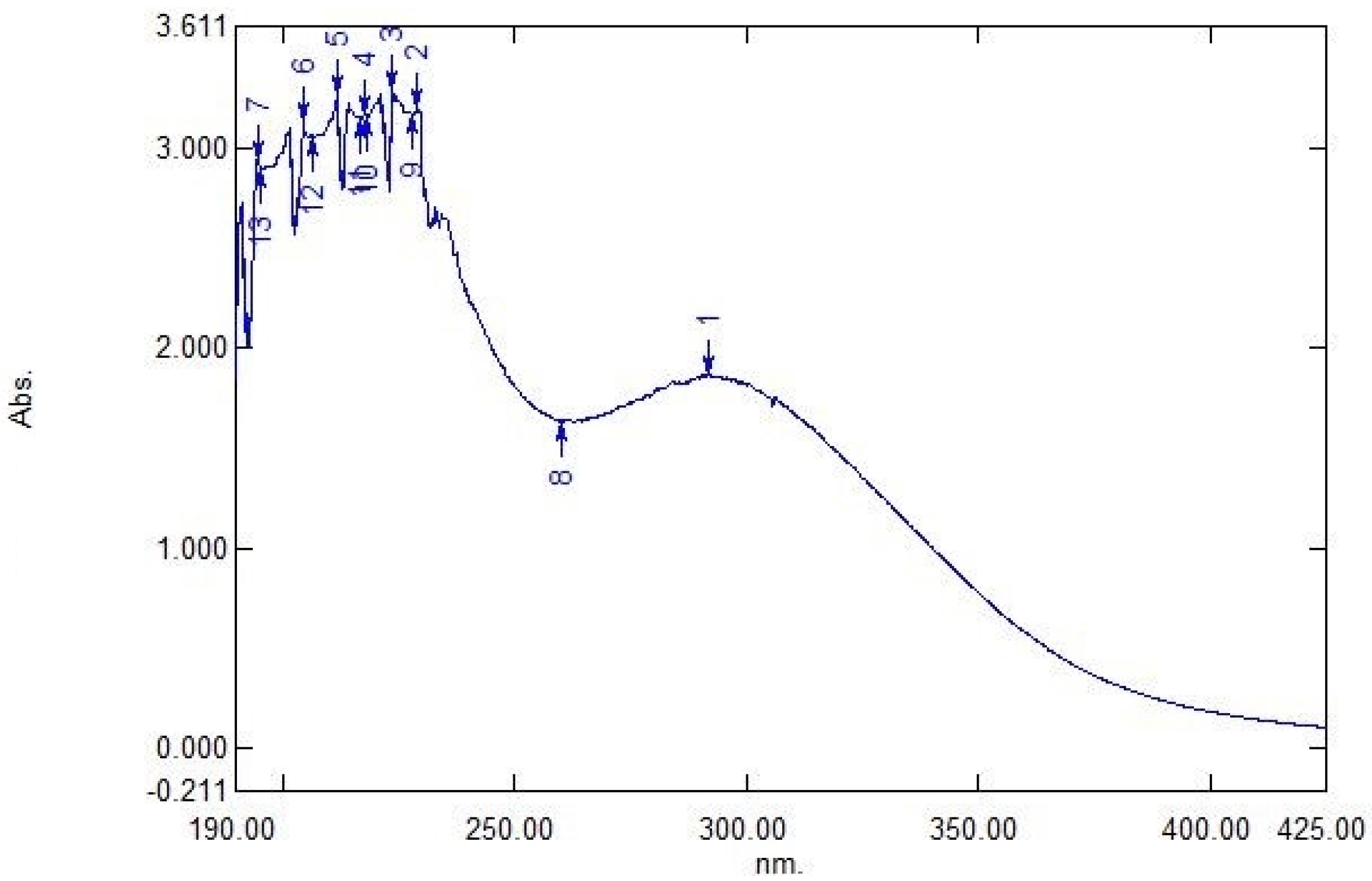
3.2. Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy Analysis
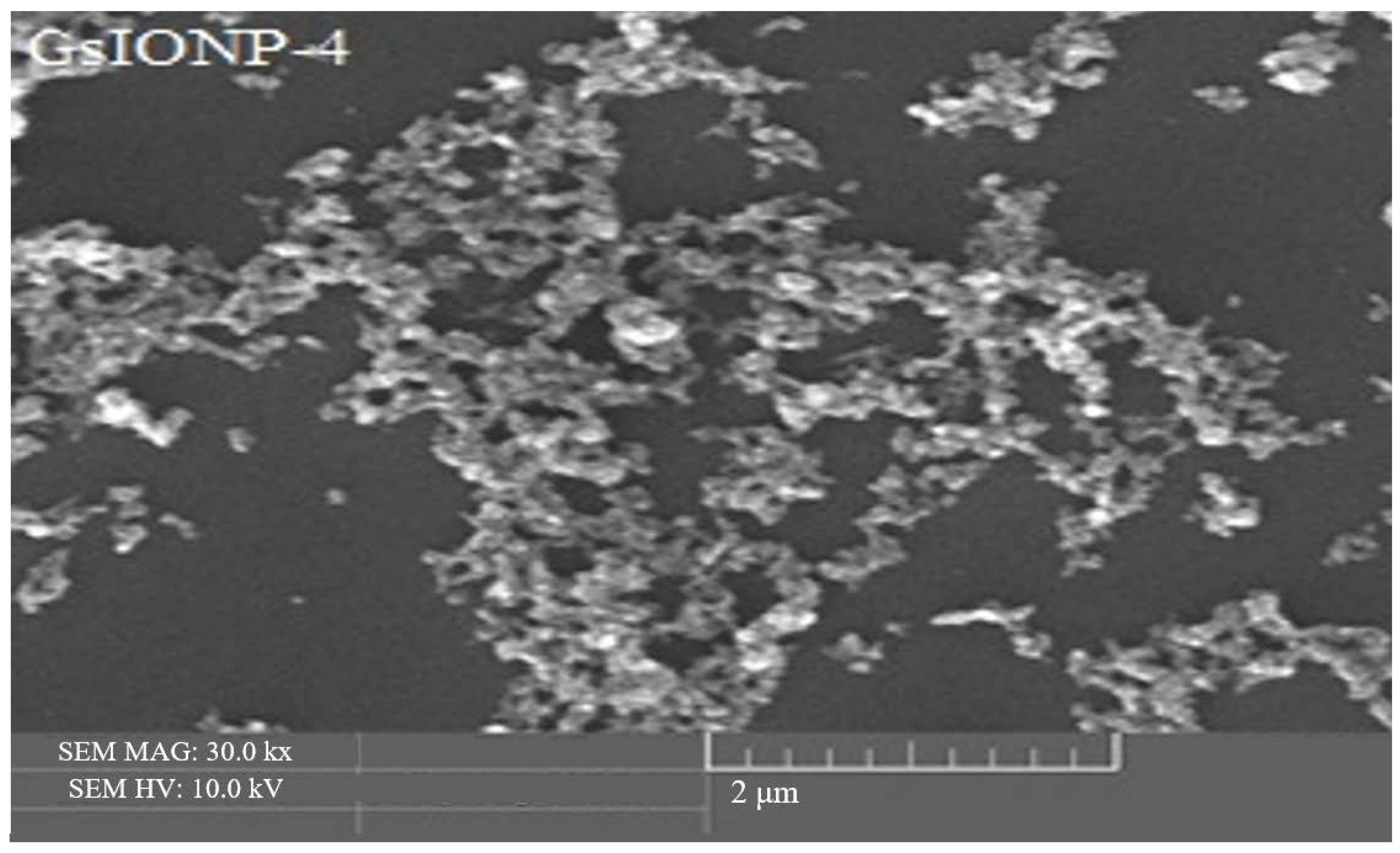
3.3. Surface Morphology Analysis
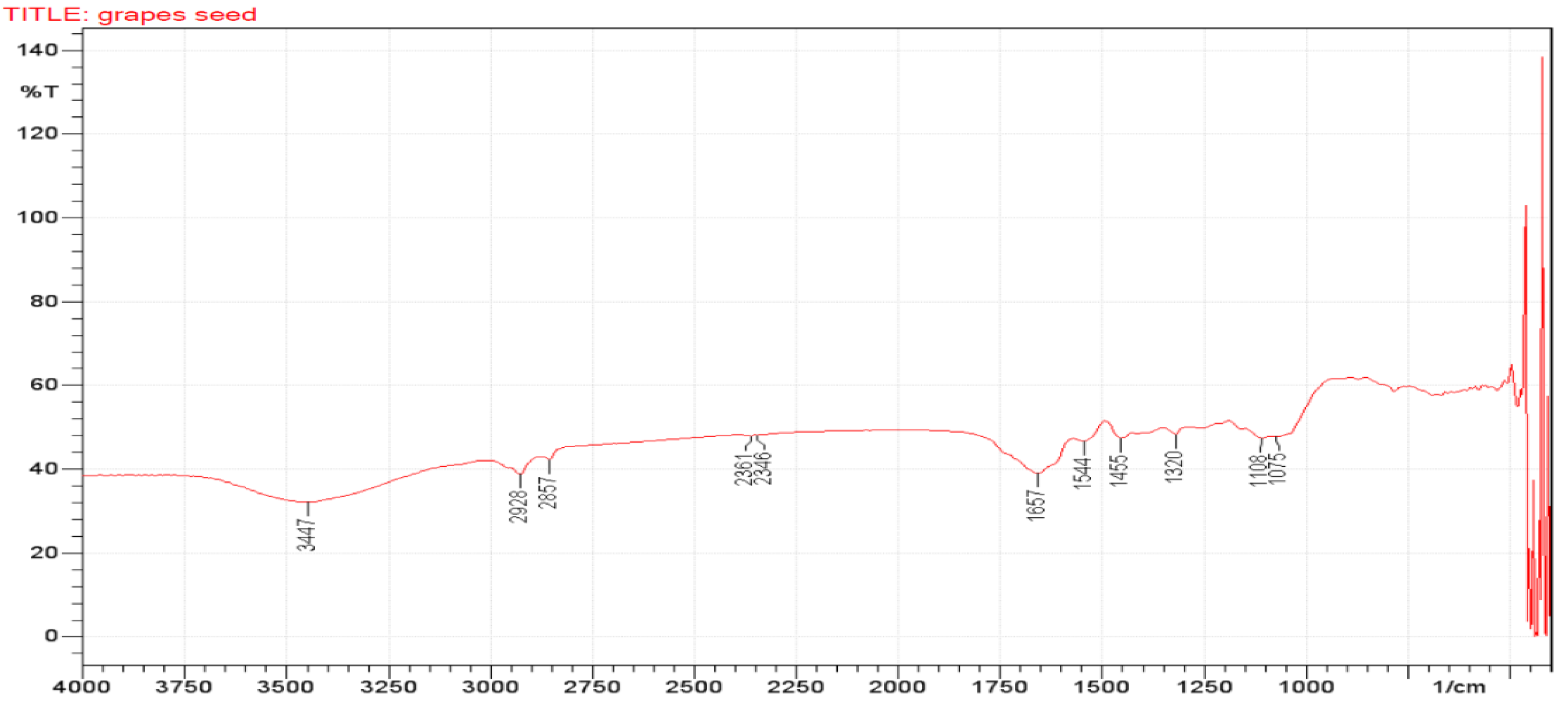
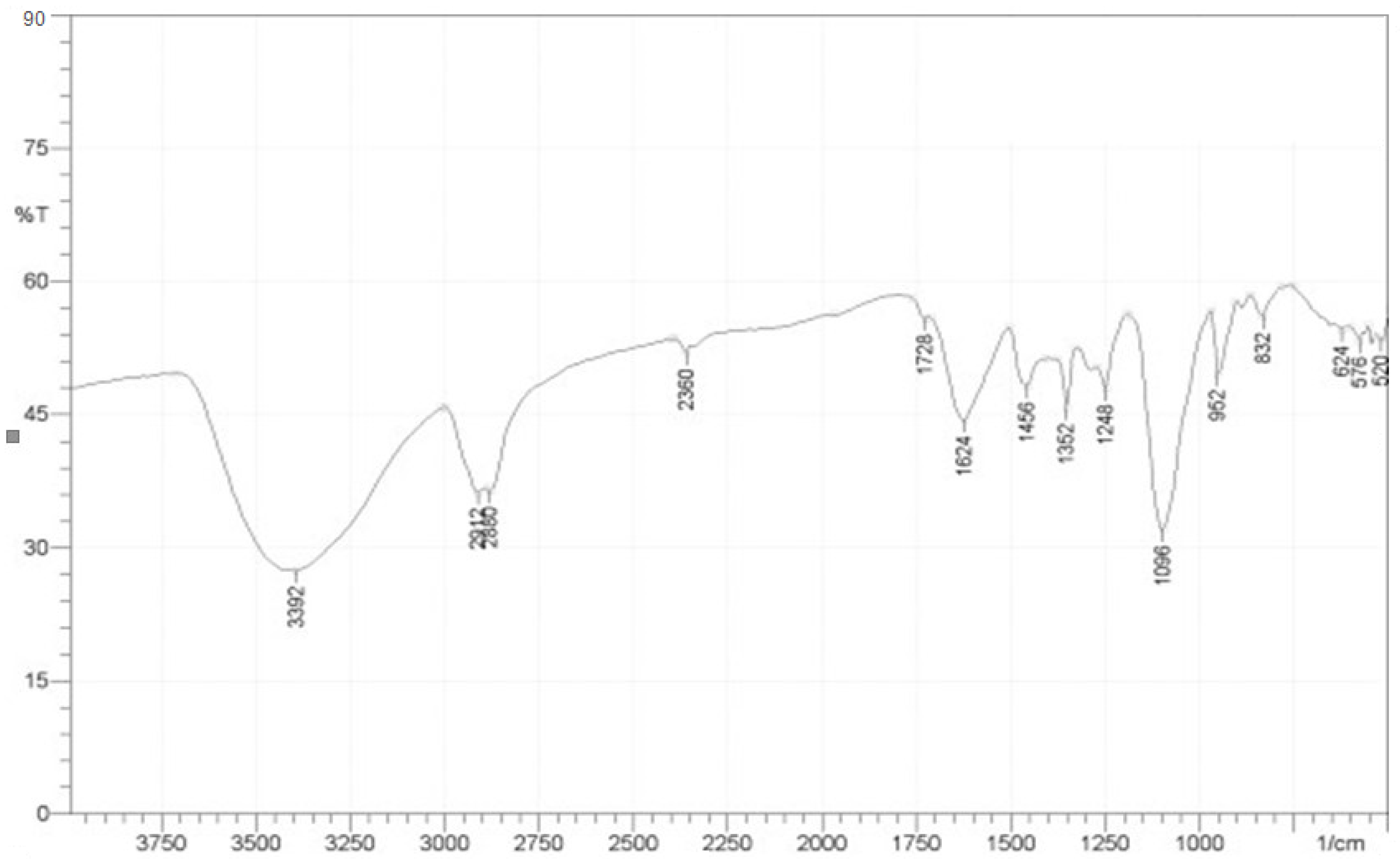
3.4. Fourier Transforms Infrared (FTIR) Analyses
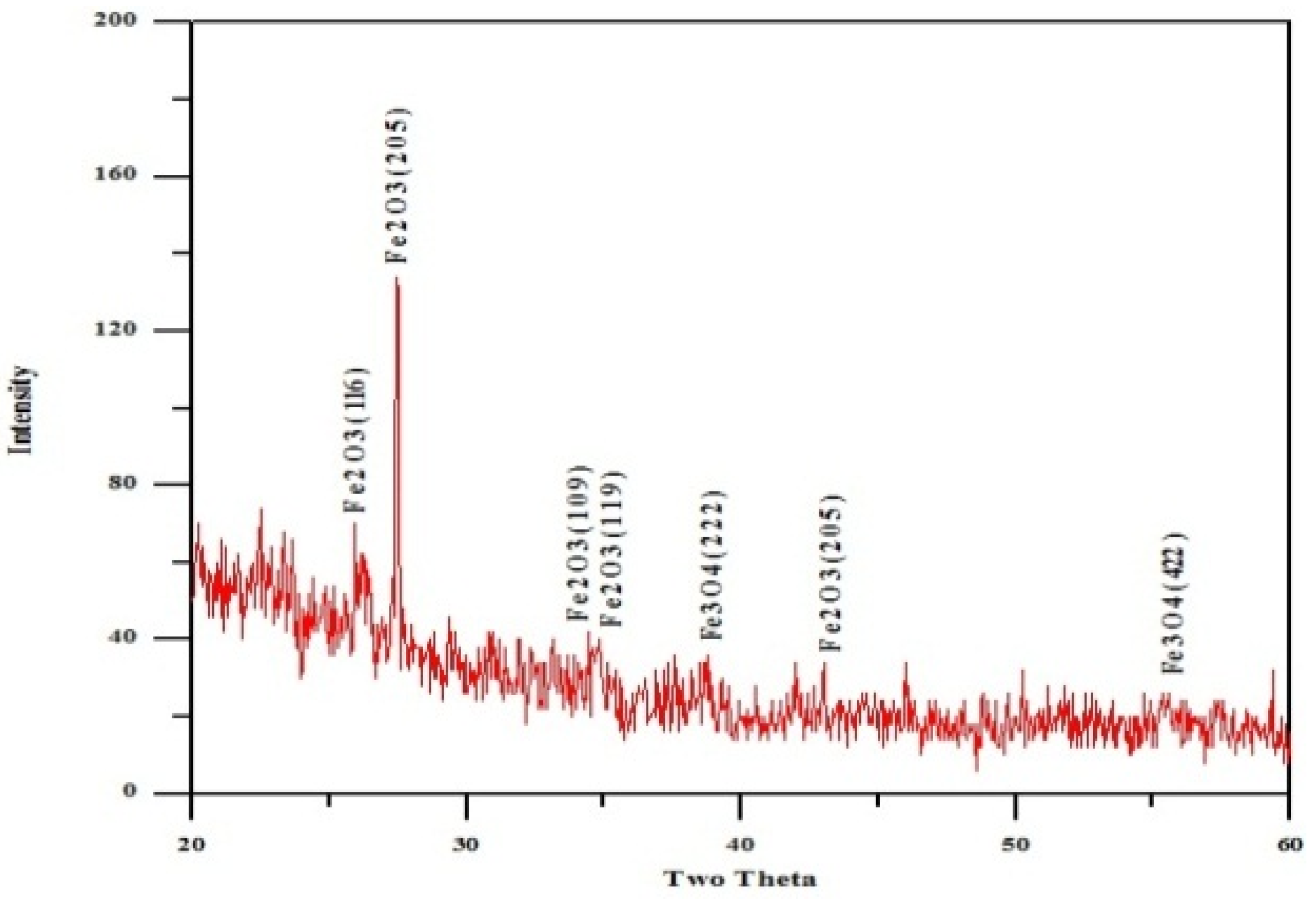
3.5. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
3.6. Adsorption Isotherms
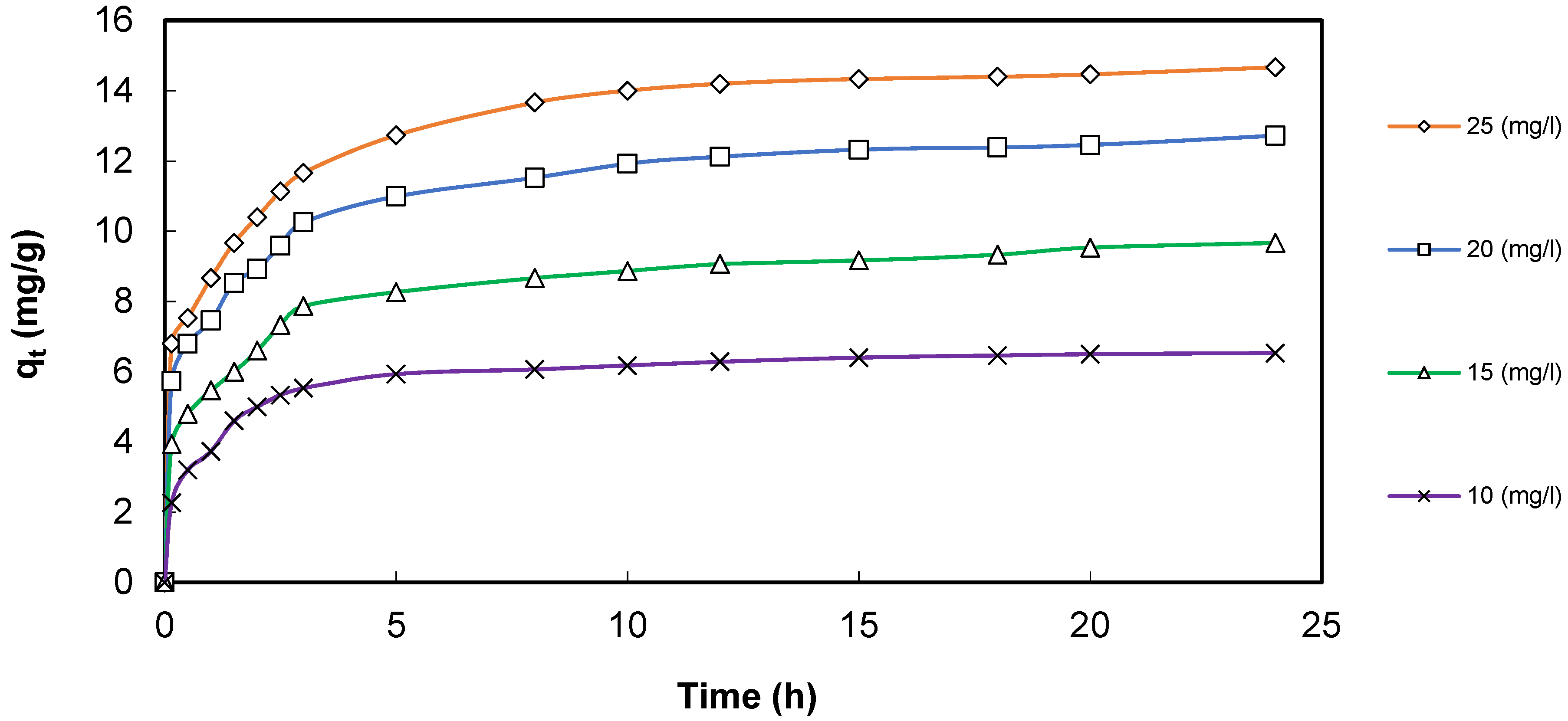
3.7. Cadmium Adsorption Effects onto GS-Fe2O3-NPs
3.8. Comparison of Cadmium Adsorption onto Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashraf, M.W. Levels of Heavy Metals in Popular Cigarette Brands and Exposure to These Metals via Smoking. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 729430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamarque, J.-F.; Shindell, D.T.; Josse, B.; Young, P.J.; Cionni, I.; Eyring, V.; Bergmann, D.; Cameron-Smith, P.; Collins, W.J.; Doherty, R.; et al. The Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Model Intercomparison Project (ACCMIP): Overview and description of models, simulations and climate diagnostics. Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 6, 179–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ite, A.E.; Ubong, U.U.; Etesin, U.M.; Nsi, E.W.; Ukpong, E.J.; Ekanem, A.N.; Ufrt, U.F.; Udo, A.I. Heavy metals in Epiphytic Lichens and Mosses of Producing Communities of Ekel and Ibeno, Akwo Ibom State—Nigeria. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Wu, P.; Yang, F.; Sun, D.-L.; Zhang, D.-X.; Zhou, Y.-K. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks in urban soils around an electronics manufacturing facility. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 630, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ite, A.E.; Udousoro, I.I.; Ibok, U.J. Distribution of Some Atmospheric Heavy Metals in Lichen and Moss Samples Collected from Eket and Ibeno Local Government Areas of Akwa Ibom State, Nigeria. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 2, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeola, A.A.; Kelechi, L.N.; Modupe, O.A. Assessment of Heavy Metals Pollution in Soils and Vegetation around Selected Industries in Lagos State, Nigeria. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2015, 3, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Rouf, Z.; Dar, I.Y.; Javaid, M.; Dar, M.Y.; Jehangir, A. Volatile Organic Compounds Emission from Building Sector and Its Adverse Effects on Human Health. In Ecological and Health Effects of Building Materials; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 67–86. [Google Scholar]
- Duruibe, J.O.; Ogwuegbu, M.O.C.; Egwurugwu, J.N. Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2007, 2, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Chioma, J.O.; Eka, B.E.; Matthew, O.W. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination for Population via Consumption of Selected Vegetables and Tubers Grown in Farmlands in Rivers State, South-South Nigeria. J. Anal. Pharm. Res. 2016, 3, 00077. [Google Scholar]
- Maciej, B.; Przemyslaw, R.; Moritz, F. Tapping Freshwaters for Methane and Energy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4183–4189. [Google Scholar]
- Jinming, L.; Kaixing, F.; Deyou, Y.; Kiril, D.; Paul, W.; John, C. Review of Advances in Engineering Nanomaterial Adsorbents for Metal Removal and Recovery from Water: Synthesis and Microstructure Impacts. ACS ES T Eng. 2021, 1, 623–661. [Google Scholar]
- Deyou, Y.; Yijia, W.; Minghua, W.; Lu, Z.; Lili, W.; Huagang, N. Surface functionalization of cellulose with hyperbranched polyamide for efficient adsorption of organic dyes and heavy metals. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 774–783. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi, S.; Jalali, M.; Afkhami, A. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using Fe3O4, ZnO, and CuO nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Marwani, H.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Alamry, A.K. An assessment of zinc oxide nanosheets as a selective adsorbent for cadmium. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghiloufi, I.; EI Ghoul, J.; Modwi, A.; EI Mir, L. Ga-doped ZnO for adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 42, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, J.G.; Smith, D.C. Distribution of Mining-Related Trace Elements in Streambed and Flood-Plain Sediment along the Middle Big River and Tributaries in the Southeast Missouri Barite District, 2012–15; U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2018-5103; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.N. Cadmium—Market trends and influences. In Cadmium 87. Proceedings of the 6th International Cadmium Conference; Cadmium Association: London, UK, 1988; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, B.; Russell, C.; Hedley, M.; Clothier, B. Cadmium adsorption by rhizobacteria: Implications for New Zealand pastureland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 87, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TapVan, H.; HuongNguyen, L.; DangNguyen, V.; HoanNguyen, X.; HaiNguyen, T.; VinhNguyen, T.; Vigneswaran, S.; Rinklebe, J.; NguyenTran, H. Characteristics and mechanisms of cadmium adsorption onto biogenic aragonite shells-derived biosorbent: Batch and column studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 535–548. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga-Díaz, S.J.; Meramo-Hurtado, S.I.; León-Pulido, J.; Zuorro, A.; González-Delgado, A.D. Environmental Assessment of Large Scale Production of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles via Coprecipitation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuorro, A.; Iannone, A.; Natali, S.; Lavecchia, R. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Bilberry and Red Currant Waste Extracts. Processes 2019, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nitin, N.; LaConte, L.; Zurkiya, O.; Hu, X.; Bao, G. Functionalization and peptide-based delivery of magnetic nanoparticles as an intracellular MRI contrast agent. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 9, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriannan, B.; Ewa, S.; Urban Margareta, H. Hydroxyapatite with magnetic core: Synthesis methods, properties, adsorption and medical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 291, 102401. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, M.J.; Pyzhev, V. Recent Modifications to Langmuir Isotherms. Acta Physiochim. URSS 1940, 12, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Skwarek, E.; Janusz, W. Adsorption of Cd(II) ions at the hydroxyapatite/electrolyte solution interface. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorota, K.; Ewa, S.; Zbigniew, H.; Władysław, J. The effect of adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions in the presence of EDTA on characteristic of electrical double layer at the ion exchanger/NaCl electrolyte solution interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 333, 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, U.; Bandyopadhyay, M. Sorption of cadmium from aqueous solution using pretreated rice husk. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taty-Costodes, V.; Fauduet, H.; Porte, C.; Delacroix, A. Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions, from aqueous solutions, by adsorption onto sawdust of Pinus sylvestris. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 105, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, Y.; Tez, Z. Removal of heavy metal ions by modified sawdust of walnut. Fresen Environ. Bull. 2003, 12, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrasbi, M.R.; Farahmandkia, Z.; Taghibeigloo, B.; Taromi, A. Adsorption of Lead and Cadmium from Aqueous Solution by Using Almond Shells. Water, Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 199, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimi, A.W.N.; Norain, I.; Aziyah, N.B.; Izza, N.H.; Vicinisvarri, I.; Hakim, M.H. Utilization of base modified oil palm fiber for removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solution. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2014, 18, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Haris, M.R.H.M.; Wahab, N.A.A.; Reng, C.W.; Azahari, B.; Sathasivam, K. The sorption of Cd(II) ions on mercerized rice husk and activated carbon. Turk. J. Chem. 2011, 35, 939–950. [Google Scholar]
- Tangjunak, S.; Insuk, N.; Tontrakoon, J.; Udeye, V. Adsorption of Pb(ii) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption on activated carbon prepared from cashew nut shells. Int. Sci. Ind. 2009, 3, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Heavy Metals | M.C. in Air (ppm) | M.C. in Soil (ppm) | M.C. in Drinking Water (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.1–0.2 | 85 | 0.005 |
| Pb | - | 420 | 0.01 |
| Zn | 1.5 * | 7500 | 5.00 |
| Hg | - | ≤1 | 0.002 |
| Ca | 5 | Tolerable | 50 |
| Ag | 0.01 | - | 0.0 |
| AS | - | - | 0.1 |
| RL Value | Nature of Adsorption Process |
|---|---|
| RL = 0 | Irreversible |
| RL = 1 | Linear |
| RL > 1 | Unfavorable |
| 0 < RL < 1 | Favorable |
| Isotherm Models | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grape seeds-IONPs (GS-IONPs) | ||||
| Langmuir | qm (mg/g) | Ka (L/mg) | R2 | |
| 16.13 | 3.425 | 0.999 | ||
| Freundlich | KF (mg/g(L/mg)1/n) | 1/n | R2 | |
| 2.632 | 0.2999 | 0.913 | ||
| Temkin | A (L/g) | B | R2 | |
| 2.725 | 2.382 | 0.72 | ||
| Commercial charcoal (CC) | ||||
| Langmuir | qm (mg/g) | Ka (L/mg) | R2 | |
| 11.124 | 0.177 | 0.97 | ||
| Freundlich | KF (mg/g(L/mg)1/n) | 1/n | R2 | |
| 2.731 | 0.481 | 0.91 | ||
| Temkin | A (L/g) | B | R2 | |
| 2.722 | 0.419 | 0.95 | ||
| No. | Low-Cost Adsorbent | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Isotherm Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rice husk | 8.85 | L | [31] |
| 2 | Sawdust | 9.29 | L | [32] |
| 3 | Walnut sawdust | 4.51 | R-P | [33] |
| 4 | Rice husk | 7 | L | [32] |
| 5 | Almond shell | 7 | L | [34] |
| 6 | oil palm fiber | 6.84 | L | [35] |
| 7 | Rice husk | 8.24 | L | [34] |
| 8 | cashew nut shell | 14.29 | L | [35] |
| 9 | Commercial charcoal (CC) | 11.12 | L | This study |
| 10 | Grape seeds-Iron oxide Nanoparticles | 16.3 | L | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammed, A.J.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Salman, J.M. Synthesis and Characterization of a Nano-Adsorbent Derivative Derived from Grape Seeds for Cadmium Ion Removal in an Aqueous Solution. Water 2021, 13, 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202896
Mohammed AJ, Ibrahim MH, Zulkifli SZ, Salman JM. Synthesis and Characterization of a Nano-Adsorbent Derivative Derived from Grape Seeds for Cadmium Ion Removal in an Aqueous Solution. Water. 2021; 13(20):2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202896
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammed, Alaa Jasim, Mohd Hafiz Ibrahim, Syaizwan Zahmir Zulkifli, and Jasim Mohammed Salman. 2021. "Synthesis and Characterization of a Nano-Adsorbent Derivative Derived from Grape Seeds for Cadmium Ion Removal in an Aqueous Solution" Water 13, no. 20: 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202896
APA StyleMohammed, A. J., Ibrahim, M. H., Zulkifli, S. Z., & Salman, J. M. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of a Nano-Adsorbent Derivative Derived from Grape Seeds for Cadmium Ion Removal in an Aqueous Solution. Water, 13(20), 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13202896






