Adsorption of EDCs on Reclaimed Water-Irrigated Soils: A Comparative Analysis of a Branched Nonylphenol, Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Isothermal Adsorption Experiment
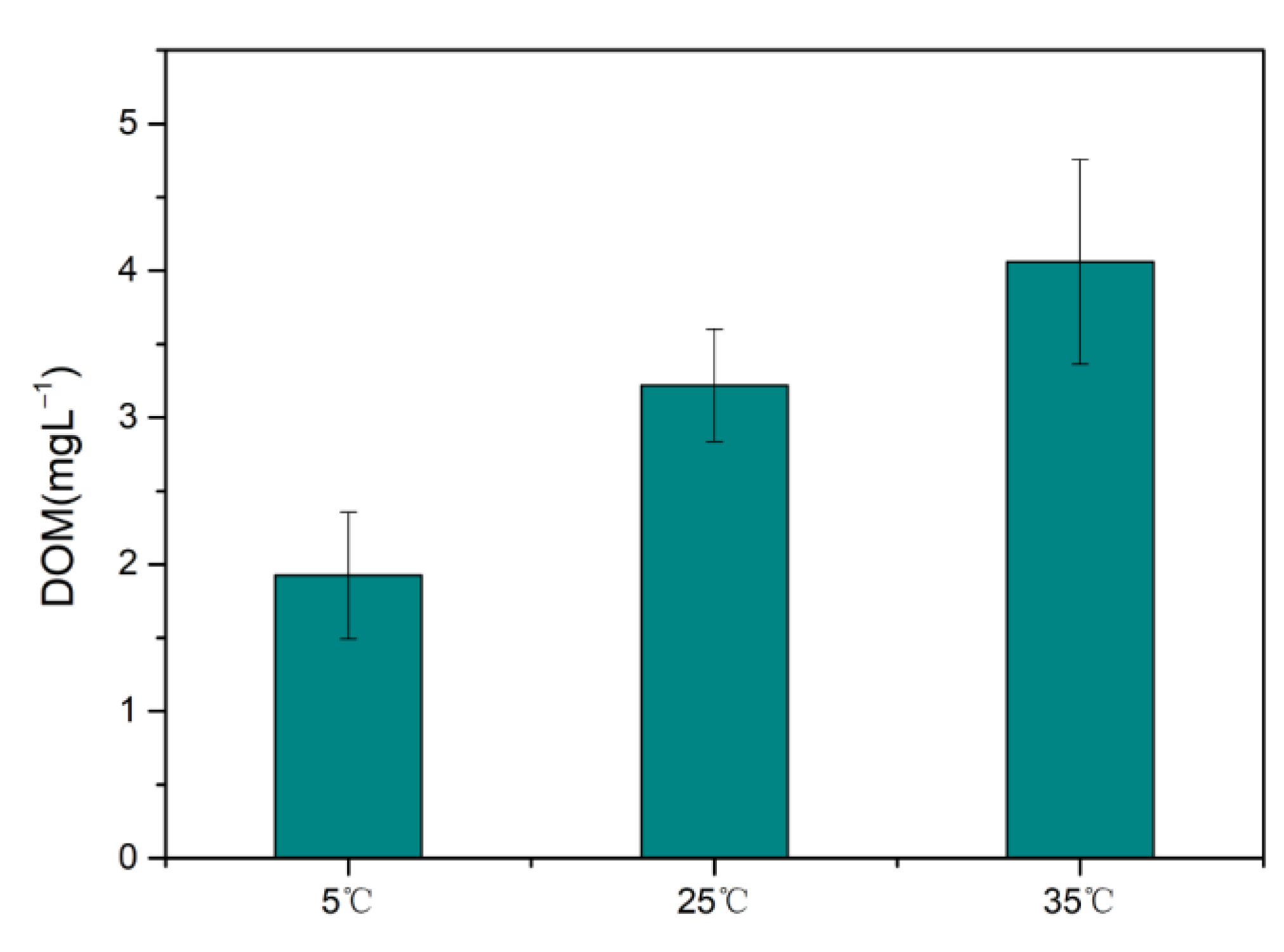
2.3. Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM)
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Linear Adsorption Model
2.4.2. Langmuir Adsorption Model
2.4.3. Freundlich Adsorption Model
2.4.4. Organic Carbon Adsorption Constants
2.4.5. Determination of NP and BPA
2.4.6. FTIR Analysis
2.4.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
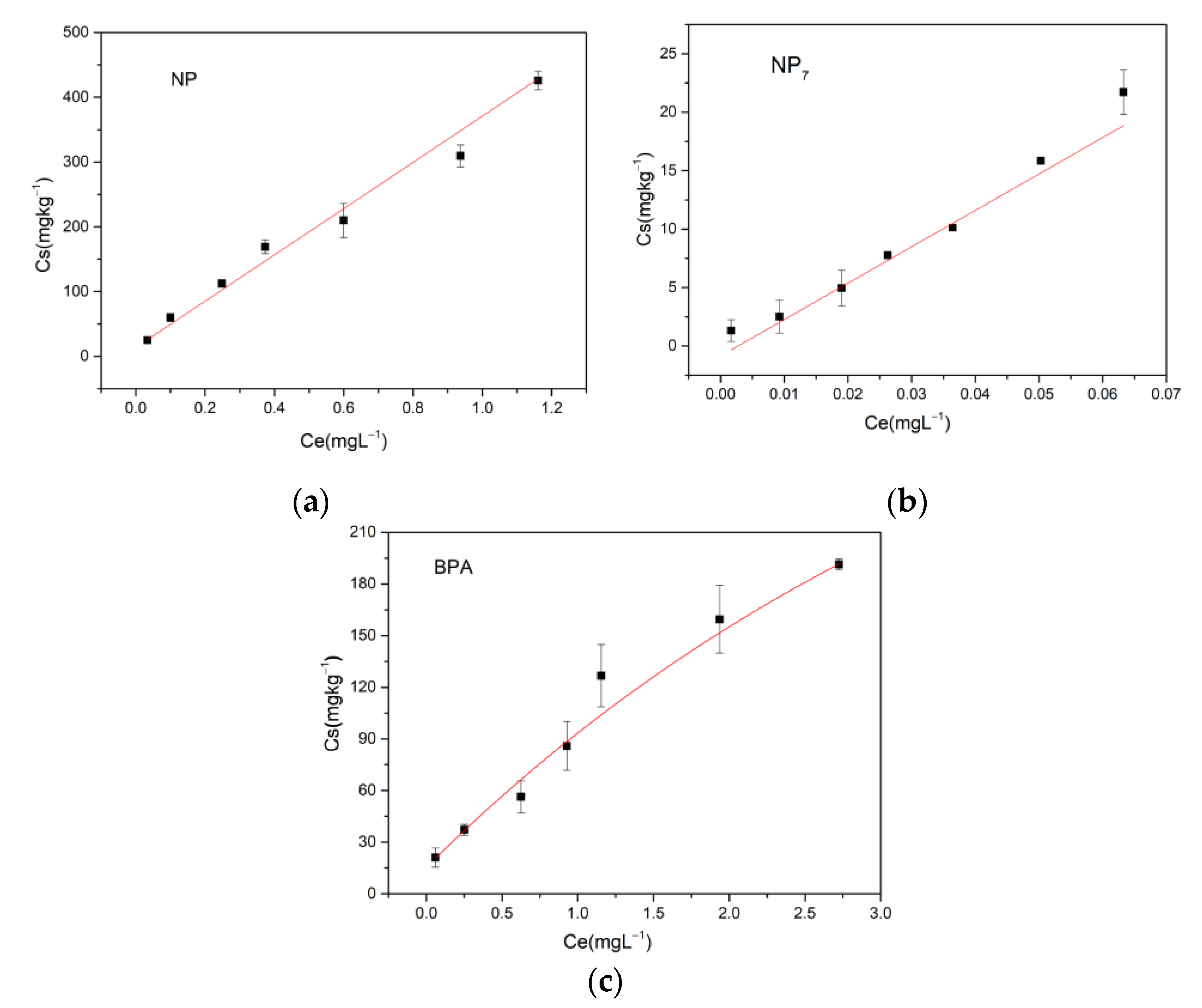
3.1. Isothermal Adsorption
3.2. Environmental Factors of Adsorption
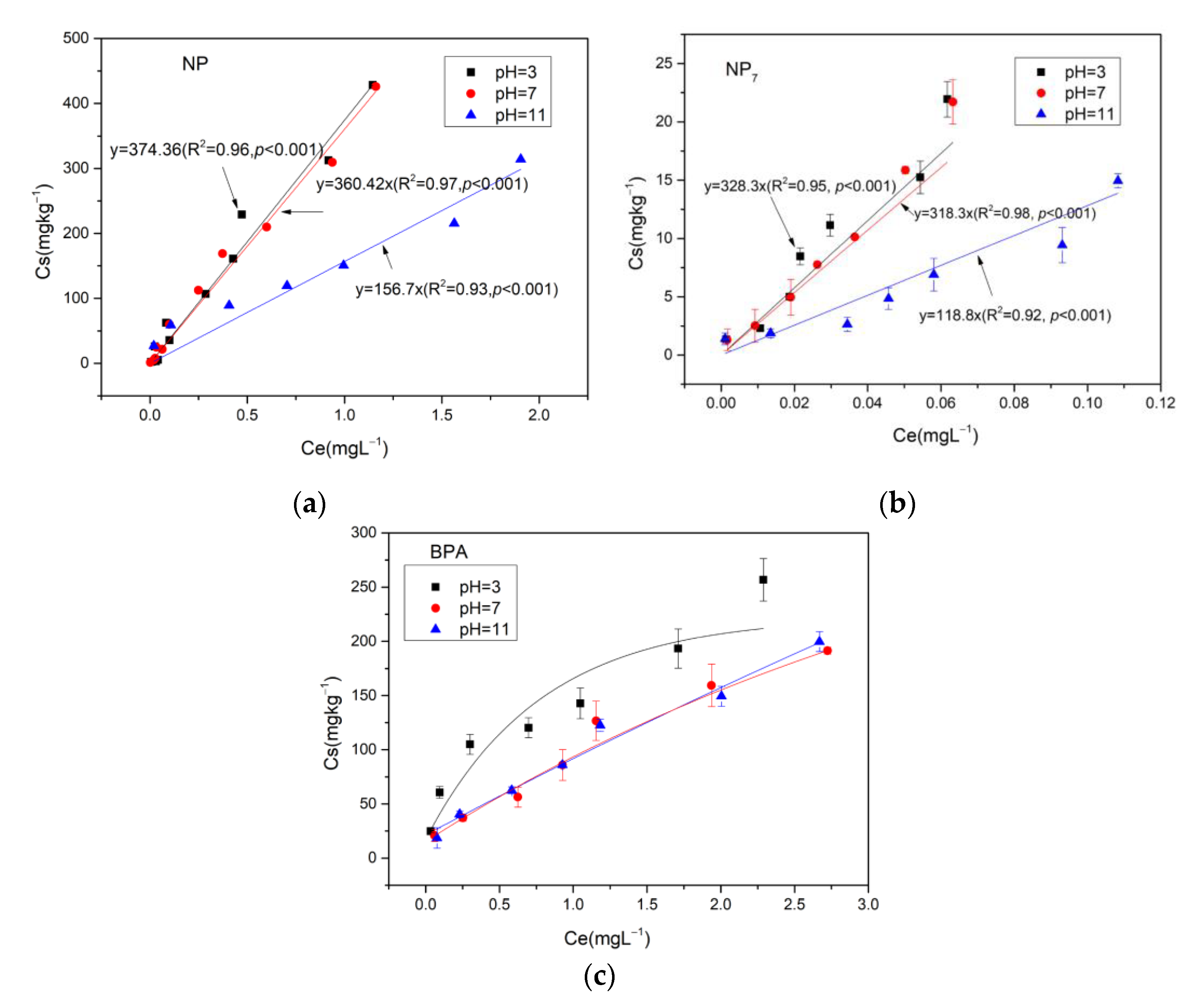
3.2.1. pH
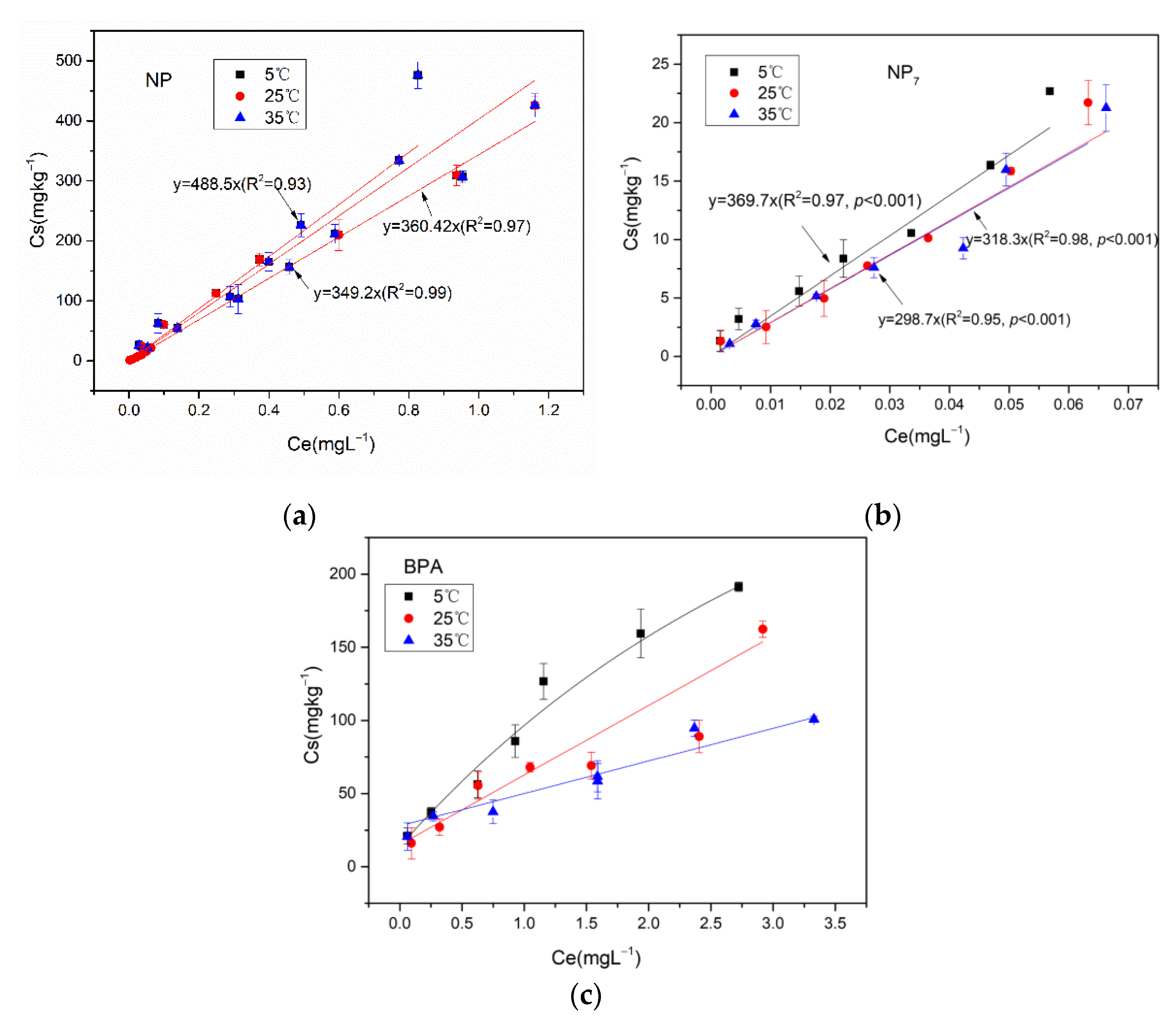
3.2.2. Temperature
3.2.3. Effects of Different Polyvalent Metal Ions
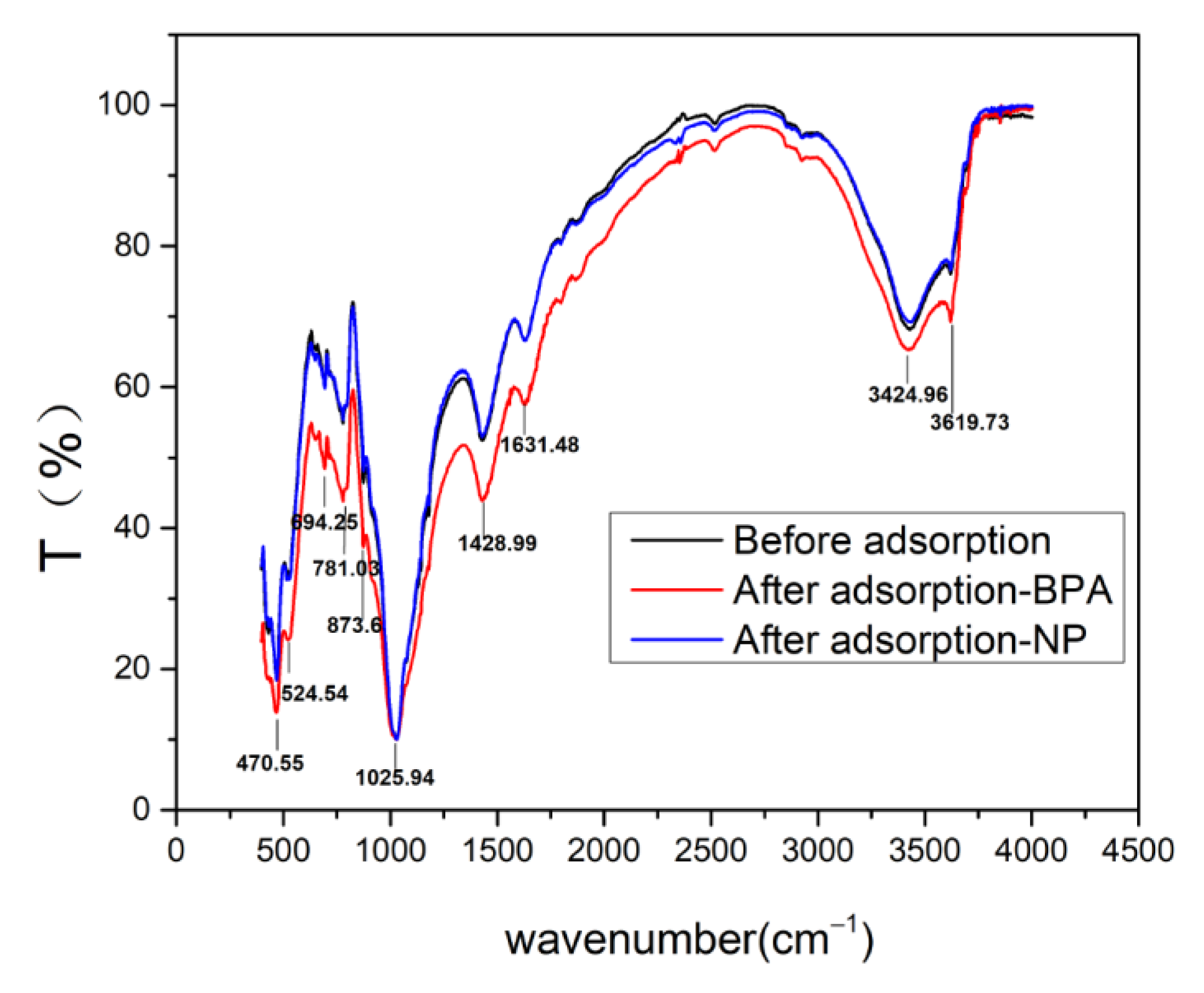
3.3. FTIR Spectra Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. FAO Water Reports 38, Coping with Water Scarcity: An Action Framework for Agriculture and Food Security; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.W.; Oh, W.-Y.; Yi, S.H.; Ku, B.; Lee, M.-Y.; Cho, Y.H.; Yang, M. Estimation of bisphenol A human toxicity by 3d cell culture arrays, high throughput alternatives to animal tests. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 259, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, H.; Ashafaq, M.; Parvez, S.; Raisuddin, S. Role of melatonin in mitigating nonylphenol-induced toxicity in frontal cortex and hippocampus of rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 104, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, H.; Eskicioglu, C. Fate of estrogenic hormones in wastewater and sludge treatment: A review of properties and analytical detection techniques in sludge matrix. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5813–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ömeroğlua, S.; Murdochb, F.K.; Sanina, F.D. Investigation of nonylphenol and nonylphenolethoxylates in sewage sludge samples from a metropolitan wastewater treatment plant in Turkey. Talanta 2015, 131, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhaj, D.; Athmouni, K.; Jerbi, B.; Kallel, M.; Ayadi, H.; Zhou, J.L. Estrogenic compounds in Tunisian urban sewage treatment plant: Occurrence, removal and ecotoxicological impact of sewage discharge and sludge disposal. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biel-Maeso, M.; Corada-Fernández, C.; Lara-Martin, P.A. Removal of personal care products (PCPs) in wastewater and sludge treatment and their occurrence in receiving soils. Water Res. 2019, 150, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykova, Y.; Björklund, K.; Strömvall, A.M.; Blom, L. Partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, alkylphenols, bisphenol A and phthalates in landfill leachates and stormwater. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Yang, L.; Nie, Z. Accumulation of steroid hormones in soil and its adjacent aquatic environment from a typical intensive vegetable cultivation of North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Stoffella, P.J.; Wilson, P.C. Uptake and distribution of bisphenol A and nonylphenol in vegetable crops irrigated with reclaimed water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.Y.; Li, X.O.; Wu, W.Y.; Liu, F. Sorption and Desorption Behavior of 4-Nonylphenol and a Branched Isomer on Soils with Long-Term Reclaimed Water Irrigation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeppert, N.; Dror, I.; Berkowitz, B. Fate and transport of free and conjugated estrogens during soil passage. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, H.S.; Wilson, P.C.; O’Connor, G.A. Endocrine-disrupting compounds in reclaimed water and residential ponds and exposure potential for dislodgable residues in turf irrigated with reclaimed water. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeel, M.; Song, X.M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Francis, D.; Yang, Y.S. Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeel, M.; Yang, Y.S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Song, X.M.; Arslan Ahmad, M.; Rogers, H.J. Uptake and transformation of steroid estrogens as emerging contaminants influence plant development. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Careghini, A.; Mastorgio, A.F.; Saponaro, S.; Sezenna, E. Bisphenol A, nonylphenols, benzophenones, and benzotriazoles in soils, groundwater, surface water, sediments, and food: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5711–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.Y.; Liu, F.; Wu, W.Y.; Hu, Y.Q.; Liao, R.K.; Chen, G.T.; Wang, J.L.; Li, J.L. Migration and health risks of nonylphenol and bisphenol A in soil-winter wheat systems with long-term reclaimed water irrigation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 158, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.P.; Zhang, C.X.; Yao, L.L.; Li, J.L.; Liu, M.; Xu, L.; Evalde, M. Sorption behavior of nonylphenol (NP) on sewage-irrigated soil: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Wu, W.Y.; Liu, F.; Yin, S.Y.; Bao, Z.; Liu, H.L. Spatial distribution and migration of nonylphenol in groundwater following long-term wastewater irrigation. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 177–178, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J., II; Moon, J.; Kim, D.; Cui, R.X.; An, Y.J. Species Sensitivity Distributions for Nonylphenol to Estimate Soil Hazardous Concentration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13957–13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruin, W.d.; Kritzingerbc, Q.; Bornmanc, R.; Korsten, L. Ocurrence, fate and toxic effects of the industrial endocrine disrupter, nonylphenol, on plants—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, R.; Durán-Álvarez, J.C.; Estrada, K.L.; Chávez, A.; Cisneros, B.J. Accumulation and leaching potential of some pharmaceutical and potential endocrine disruptors in soils irrigated with wastewater in the Tula Valley, Mexico. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Bisphenol A Action Plan; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoumas, A.; Honvault, N.; Houben, D.; Fontaine, J.; Meglouli, H.; Laruelle, F.; Tisserant, B.; Faucon, M.-P.; Sahraoui, A.L.H.; Firmin, S. Contrasting Response of Nutrient Acquisition Traits in Wheat Grown on Bisphenol A-Contaminated Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 23, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish EPA. Toxicological Evaluation and Limit Values for Nonylphenol, Nonylphenol Ethoxylates, Tricresyl, Phosphates and Benzoic Acid—Environmental Project no. 512. 2000. Available online: http://www.statensnet.dk/pligtarkiv/fremvis.pl?vaerkid=6944&reprid=0&filid= 0&iarkiv=1 (accessed on 15 December 2014).
- USEPA-IRIS Bisphenol, A. Quickview. Available online: http://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/index.cfm?fuseaction=iris.show Quickview&substance_nmbr= 0356 (accessed on 15 November 2014).
- Gabriel, F.L.P.; Routledge, E.J.; Heidlberger, A.; Rentsch, D.; Guenther, K.; Giger, W.; Sumpter, J.P.; Kohler, H.-P.E. Isomer specific degradation and endocrine disrupting activity of nonylphenols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6399–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.J.; Gan, J. Isomer-specific biodegradation of nonylphenol in river sediments and structure-biodegradability relationship. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schick, D.; Oellig, C. Screening for estrogen active nonylphenols in surface waters by planar solid phase extraction–planar yeast estrogen screen. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 6767–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Katase, T.; Horii, Y.; Yamashita, N.; Makino, M.; Uchiyama, T.; Fujimoto, Y.; Inou, T. Estrogen equivalent concentration of individual isomer-specific 4-nonylphenol in Ariake sea water, Japan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.J.; Gan, J. Analysis, toxicity, occurrence and biodegradation of nonylphenol isomers: A review. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, A.T.; Morra, M.J. Estrogens: Properties, behaviors, and fate in dairy manure-amended soils. Environ. Rev. 2017, 25, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bautista-Toledo, I.; Ferro-Garcia, M.A.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Vegas Fernandez, F.J. Bisphenol A removal from water by activated carbon. ffect of carbon characteristics and solution chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6246–6250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stumpe, B.; Marschner, B. Dissolved organic carbon from sewage sludge and manure can affect estrogen sorption and mineralization in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.P.; Ding, H.Y.; Cao, X.Y.; Ding, Q.Y. Sorption behavior of nonylphenol on marine sediments: Effect of temperature, medium, sediment organic carbon and surfactant. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2362–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, H.; Padmaja, P. Palm shell based activated carbon for removal of bisphenol A: An equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.M.; Li, Y.M. Removal of bisphenol A and 4-n-nonylphenol coupled to nitrate reduction using acclimated activated sludge under anaerobic conditions. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2014, 89, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Cheng, Y.; Hua, Z.L.; Yuan, C.; Wang, X.J. The Effect of dissolved organic matter (DOM) on the release and distribution of endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) from sediment under hydrodynamic forces, A Case Study of Bisphenol A (BPA) and Nonylphenol (NP). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Zeng, D.; Chen, Y.; Belzile, N.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, J. Adsorption behaviors of phenanthrene and bisphenol A in purple paddy soils amended with straw-derived DOM in the West Sichuan Plain of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Chen, H.H.; Hao, Z.Y.; Shi, Y.B.; Ma, F.S. Effect of regulation and storage engineering on groundwater salinity in reclaimed water irrigation district. Trans. CSAE 2009, 25, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z. Research on Pollution Risk of Heavy Metals in Soil and Groundwater under Reclaimed Water Irrigation; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. SW-846 Test Method 3550C: Ultrasonic Extraction. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-3550c-ultrasonic-extraction (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Düring, R.A.; Krahe, S.; Gäth, S. Sorption behavior of nonylphenol in terrestrial soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4052–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo-Torres, R.; Durán-Álvarez, J.C.; Prado, B.; Jiménez-Cisneros, B.E. Sorption and mobility of two micropollutants in three agricultural soils: A comparative analysis of their behavior in batch and column experiments. Geoderma 2012, 189–190, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martz, M.; Heil, J.; Marschner, B.; Stumpe, B. Effects of soil organic carbon (SOC) content and accessibility in subsoils on the sorption processes of the model pollutants nonylphenol (4-n-NP) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.A.; Roberts, K.J.; Beman, J.M.; Santoro, A.E.; Oakley, B.B. Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, J.H.; Li, J.Z.; Xin, J.; Li, M.; Liu, X. Sorption and desorption of 17α-ethinyl estradiol and 4-n-nonylphenol in Soil. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.B.; Li, X.S.; Xu, Y.X.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, J. Sorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solution by modified fabric peat. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 34, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.; Li, Y.X.; Zhang, F.S.; Chen, X.C.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, B.Y.; Zhang, X.L. Adsorption of 17β-estradiol onto humic-mineral complexes and effects of temperature, pH, and bisphenol A on the adsorption process. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Jin, J.; Gao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Xu, D.; Zhao, Y. Sorption of 17α-ethinyl estradiol, bisphenol A and phenanthrene to different size fractions of soil and sediment. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karickho, S.W. Semi-empirical estimation of sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments and soils. Chemosphere 1981, 10, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Hyun, S.; Pignatello, J.J.; Lee, L.S. Evidence for Π-Π electron donor acceptor interactions between-donor aromatic compounds and Π-acceptor sites in soil organic matter through pH effects on sorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4361–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yates, S.R. Dissolved organic matter and estrogen interactions regulate estrogen removal in the aqueous environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 641, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Huang, B.; Yang, B.Q.; Pan, X.J.; Dionysiou, D.D. Mitigating 17α-ethynylestradiol water contamination through binding and photosensitization by dissolved humic substances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 327, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Yang, Z.L.; Li, Z.; Ren, H.J. Degradation and Sorption of Nonylphenol in Soils. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2011, 30, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Milinovic, J.; Lacorte, S.; Rigol, A.; Vidal, M. Sorption behaviour of nonylphenol and nonylphenol monoethoxylate in soils. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, T.; Nishiyama, H.; Nakashima, A. Distribution and behavior of nonylphenol, octylphenol and nonylphenol monoethoxylate in Tokyo metropolitan area: Their association with aquatic particles and sedimentary distributions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.G.; Sun, H.W.; Gao, Y. Sorption of small metabolites of nonylphenol polyethoxylates in single and complex systems on aquatic suspended particulate matter. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Endo, S.; Gocht, T.; Barth, J.A.C.; Lacorte, S.; Barceló, D. Sorption of alkylphenols on Ebro River sediments: Comparing isotherms with field observations in river water and sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ji, R.; Schäffer, A.; Sequaris, J.M.; Amelung, W.; Vereecken, H.; Klumpp, E. Sorption of a branched nonylphenol and perfluorooctanoic acid on Yangtze River sediments and their model components. J. Environ. Monitor. 2012, 14, 2653–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collins, C.D.; Martin, I.; Doucette, W. Organic Xenobiotics and Plants: From mode of action to Ecophysiology. In Plant Uptake of Xenobiotics; Schroder, P., Collins, C.D., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sadmani, A.H.M.A.; Andrews, R.C.; Bagley, D.M. Nanofiltration of pharmaceutically active and endocrine disrupting compounds as a function of compound interactions with DOM fractions and cations in natural water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadmani, A.H.M.A.; Andrews, R.C.; Bagley, D.M. Rejection of pharmaceutically active and endocrine disrupting compounds by nanofiltration as a function of source water humic substances. J. Water. Process. Eng. 2014, 2, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Pan, S.; Cheng, H.; Sweetman, A.J.; Zhang, H.; Jones, K.C. Diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) for in situ sampling of selected endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in waters. Water Res. 2018, 137, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shchegolikhina, A.; Mouvenchery, Y.K.; Woche, S.K.; Bachmann, J.; Schaumann, G.E.; Marschner, B. Cation treatment and drying-temperature effects on nonylphenol and phenanthrene sorption to a sandy soil. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2014, 177, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.H.; Wu, L.; Letey, J. Effects of soil and water properties on anionic polyacrylamide sorption. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzer, M.; Scinner, S. Organo-metallic interactions in soil.4. Carboxyl and hydroxyl groups in organic matter and metal retention. Soil Sci. 1965, 99, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- Kunhi Mouvenchery, Y.; Kuèerík, J.; Diehl, D.; Schaumann, G.E. Cation-mediated cross-linking in natural organic matter: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.F.; Pignatello, J.J. Sorption of apolar aromatic compounds to soil humic acid particles affected by aluminum (III) ion cross-linking. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadachari, C.; Chattopadhyay, T.; Ghosh, K. Complexation of humic substances with oxides of iron and aluminium. Soil Sci. 1997, 162, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Sowa, M.G.; Mantsch, H.H. Infrared spectroscopy: A new frontier in medicine. Biophys. Chem. 1997, 68, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, A.; Perromat, A.; Deleris, G. Pharmacologic application of Fourier transform IR spectroscopy: In vivo toxicity of carbon tetrachloride on rat liver. Biopolym. (Biospectroscopy) 2000, 57, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severcan, F.; Sahin, I.; Kazanci, N. Melatonin strongly interacts with zwitterionic model membranes-evidence from Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1668, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L. The Behavior of 17α-Ethinyl Estradiol and 4-n-nonylphenol in Soil by Groundwater Recharge with Reclaimed Water; Tsinghua University: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| pH | 8.1 |
| OM (g/kg) | 4.41 |
| OC (%) | 0.47 |
| SSA (m2/g) | 4.79 |
| Clay (%) | 15 |
| CEC (cmol/kg) | 3.09 |
| NO3− (mg/kg) | 103.86 |
| PO43− (mg/kg) | 8.57 |
| Ca (g/kg) | 24 |
| Mg (g/kg) | 6.16 |
| Na (g/kg) | 0.143 |
| Linear | Freundlich | Langmuir | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kd (mg·kg−1) | R2 | Kf (mg1–1/n·L1/n/kg) | 1/n | R2 | KL (L·mg−1) | Qmax (mg·kg−1) | R2 | |
| NP | 360.42 | 0.97 | 342.41 | 0.77 | 0.99 | - | - | - |
| NP7 | 318.30 | 0.98 | 137.00 | 0.77 | 0.93 | - | - | - |
| BPA | 81.65 | 0.81 | 103.28 | 0.61 | 0.95 | 4 | 125 | 0.90 |
| Organic Carbon Sorption Constant | NP | NP7 |
|---|---|---|
| Koc (L·kg−1) | 7.56 × 104 | 6.67 × 104 |
| pH | Kf (mg1−1/n·L1/n/kg) | 1/n | R2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 157.76 | 0.49 | 0.96 | <0.001 |
| 7 | 103.28 | 0.613 | 0.95 | <0.001 |
| Temperature (°C) | Kf (mg1−1/n·L1/n/kg) | 1/n | R2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 120.20 | 0.57 | 0.93 | <0.001 |
| 25 | 103.28 | 0.613 | 0.95 | <0.001 |
| 35 | 63.53 | 0.61 | 0.94 | <0.001 |
| Metal Ions | Kf (mg1−1/n·L1/n/kg) | 1/n | R2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 16.69 | 1.26 | 0.93 | <0.001 |
| Ca2+ | 24.25 | 1.10 | 0.91 | <0.001 |
| As(III) | 32.25 | 1.16 | 0.95 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, F.; Liang, C.; He, L.; Jiao, W.; Wu, W. Adsorption of EDCs on Reclaimed Water-Irrigated Soils: A Comparative Analysis of a Branched Nonylphenol, Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A. Water 2021, 13, 2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182532
Wang S, Zhang J, Zhou F, Liang C, He L, Jiao W, Wu W. Adsorption of EDCs on Reclaimed Water-Irrigated Soils: A Comparative Analysis of a Branched Nonylphenol, Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A. Water. 2021; 13(18):2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182532
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shiyu, Junnan Zhang, Fada Zhou, Cunzhen Liang, Liao He, Wentao Jiao, and Wenyong Wu. 2021. "Adsorption of EDCs on Reclaimed Water-Irrigated Soils: A Comparative Analysis of a Branched Nonylphenol, Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A" Water 13, no. 18: 2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182532
APA StyleWang, S., Zhang, J., Zhou, F., Liang, C., He, L., Jiao, W., & Wu, W. (2021). Adsorption of EDCs on Reclaimed Water-Irrigated Soils: A Comparative Analysis of a Branched Nonylphenol, Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A. Water, 13(18), 2532. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182532







