Spontaneous Imbibition in a Fractal Network Model with Different Wettabilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
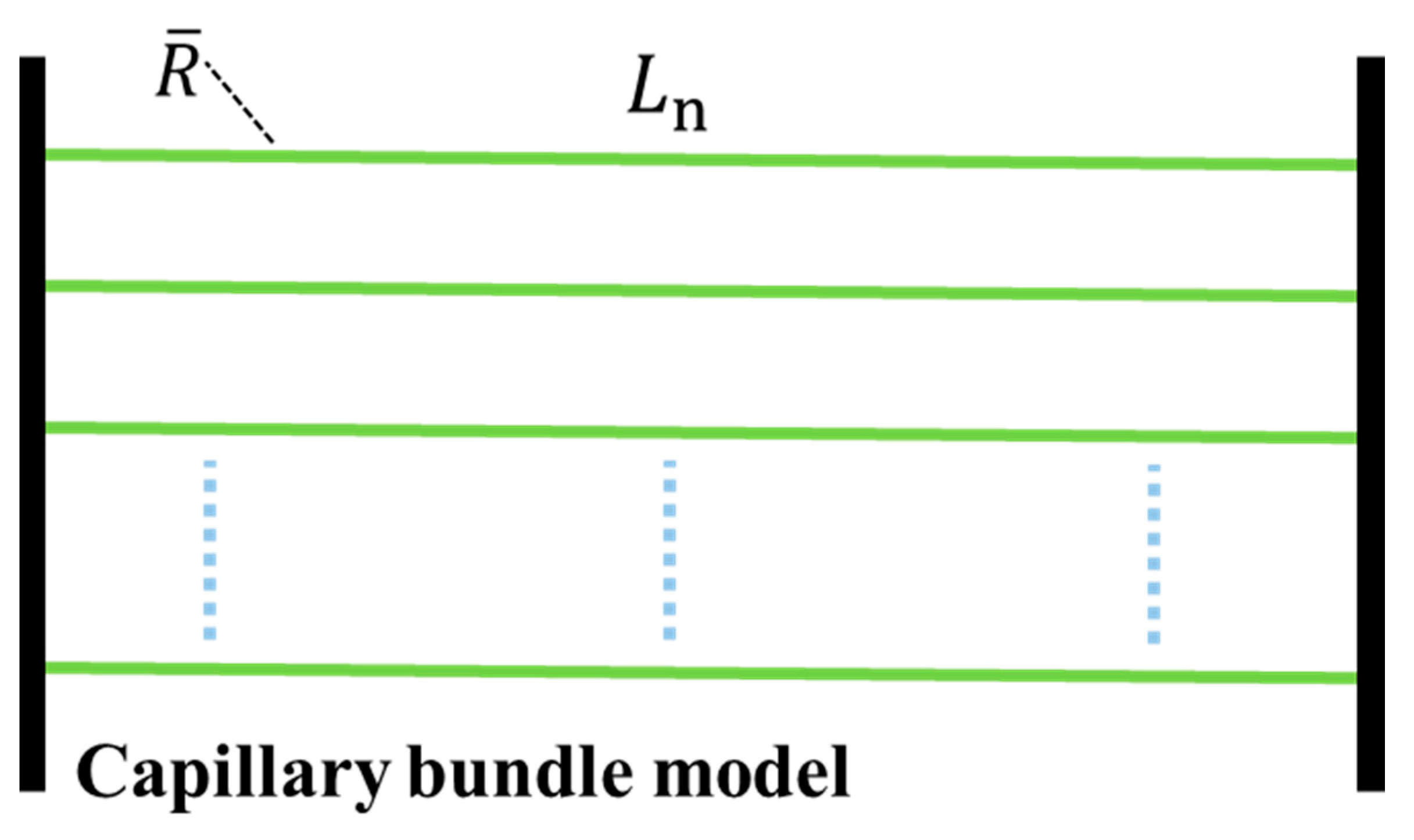
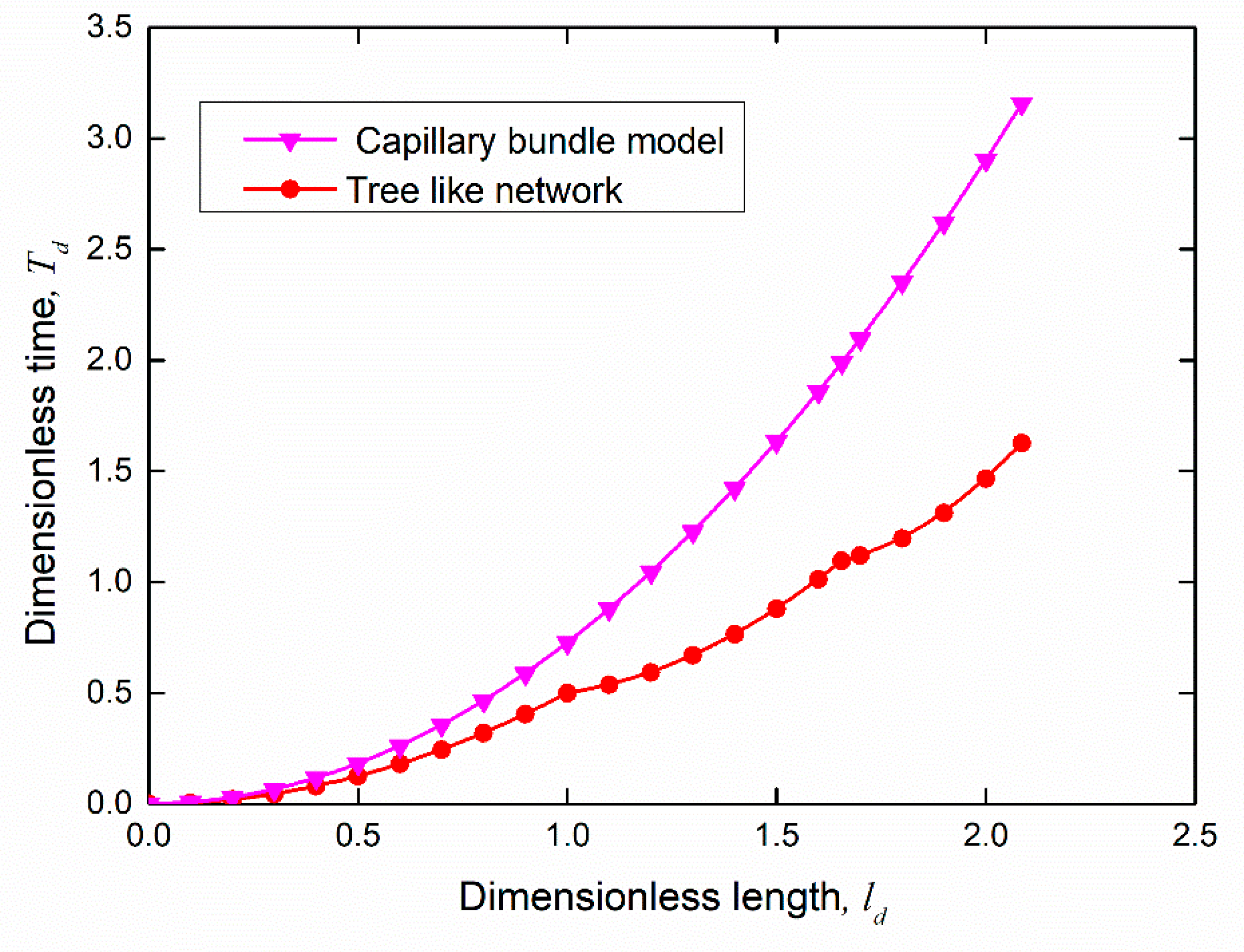
2. Assumptions and Models
- The total length of the capillary tube is the same as that of the Y-shaped branching model;
- The specific surface area of the capillary bundle model is equal to that of the Y-shaped branching model, and the radius of the capillary bundle model is determined by this feature;
- The porosity of the capillary bundle model is equal to that of the Y-shaped branching model. According to the same porosity, the number of capillaries is determined;
- The permeability of the capillary bundle model is equal to that of the Y-shaped branching model. By keeping the specific surface area and porosity of the two models equal, the permeability of the two models is approximately equal.
3. Derivation and Calculation
3.1. Model Features
3.2. Derivation of Flow Process
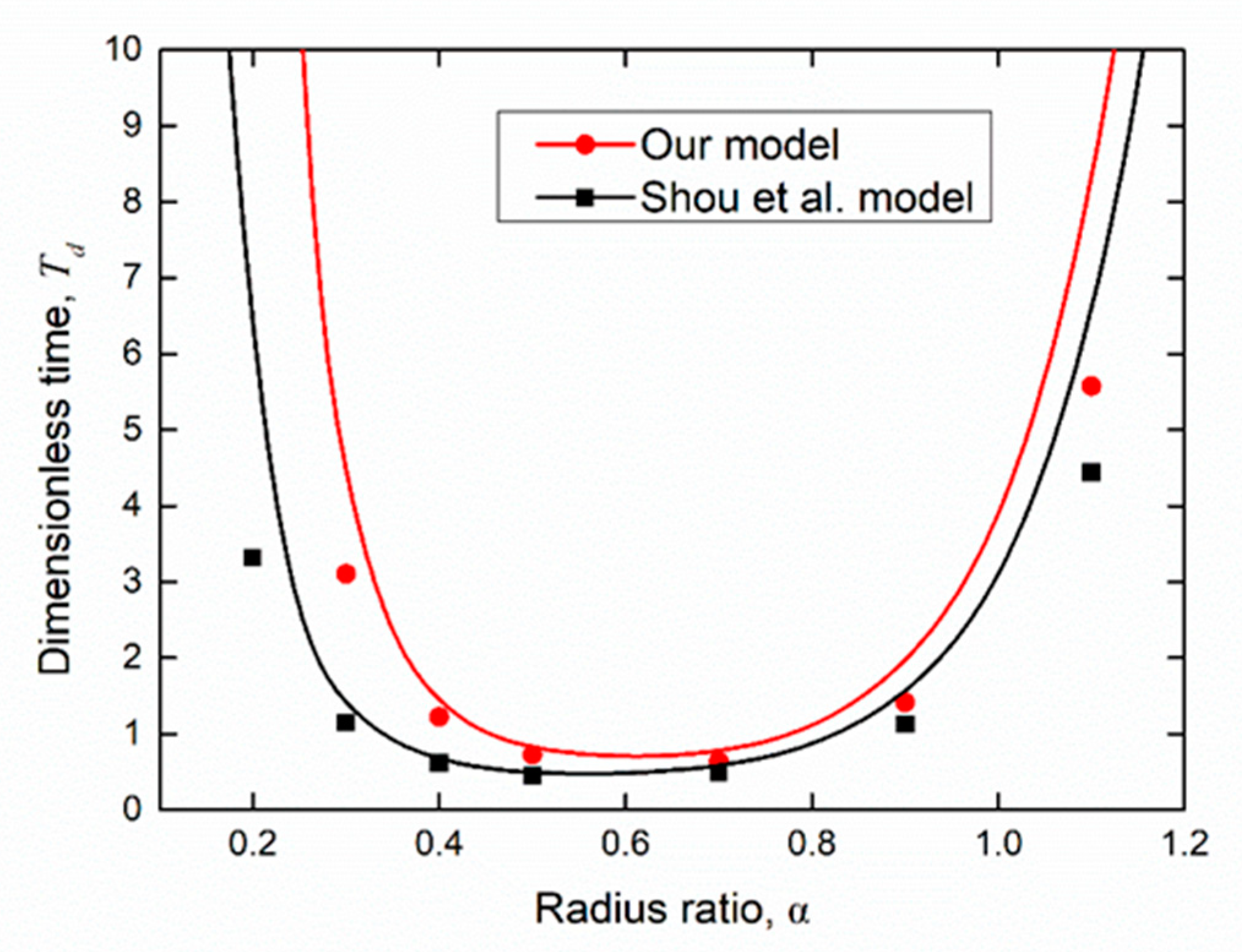
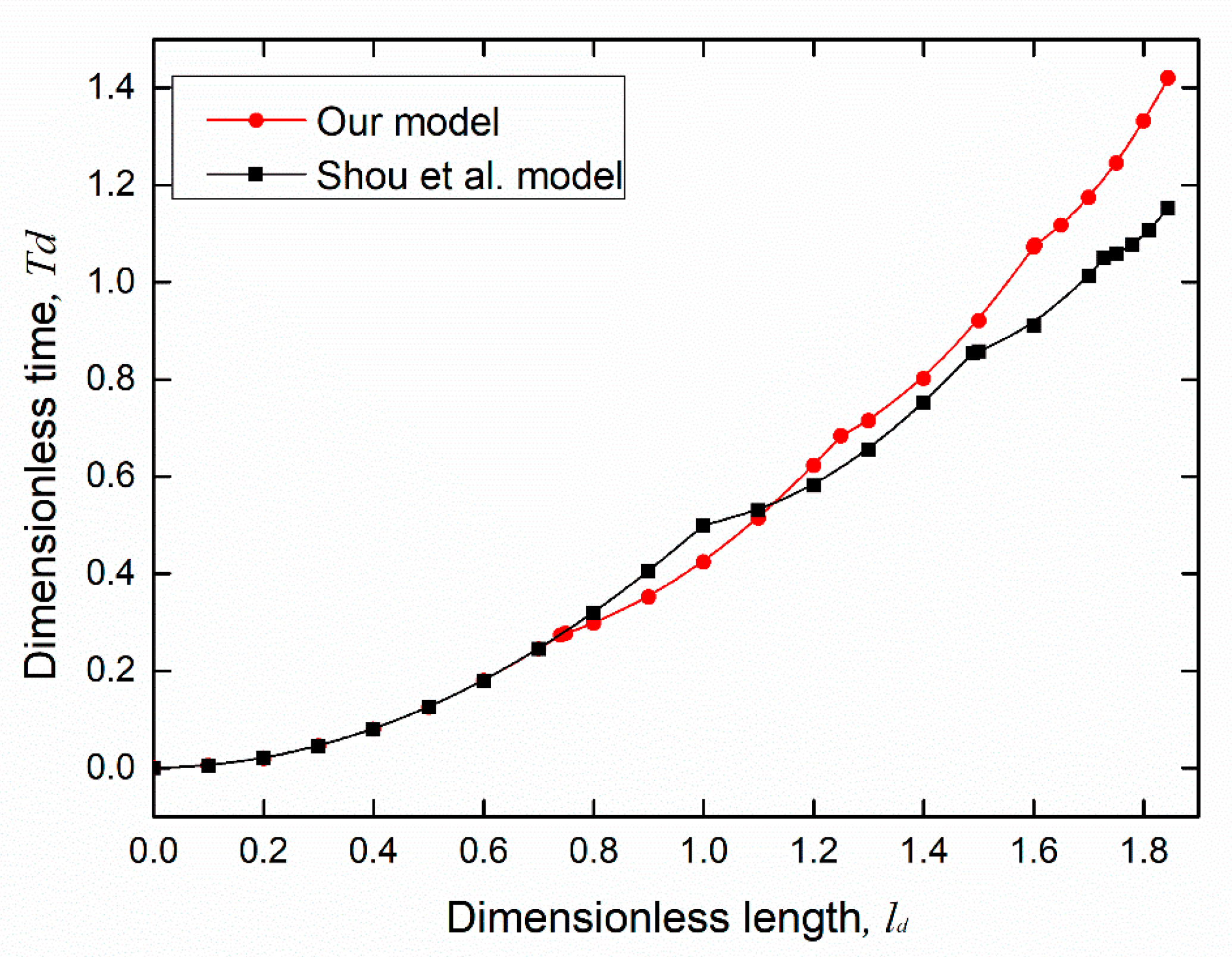
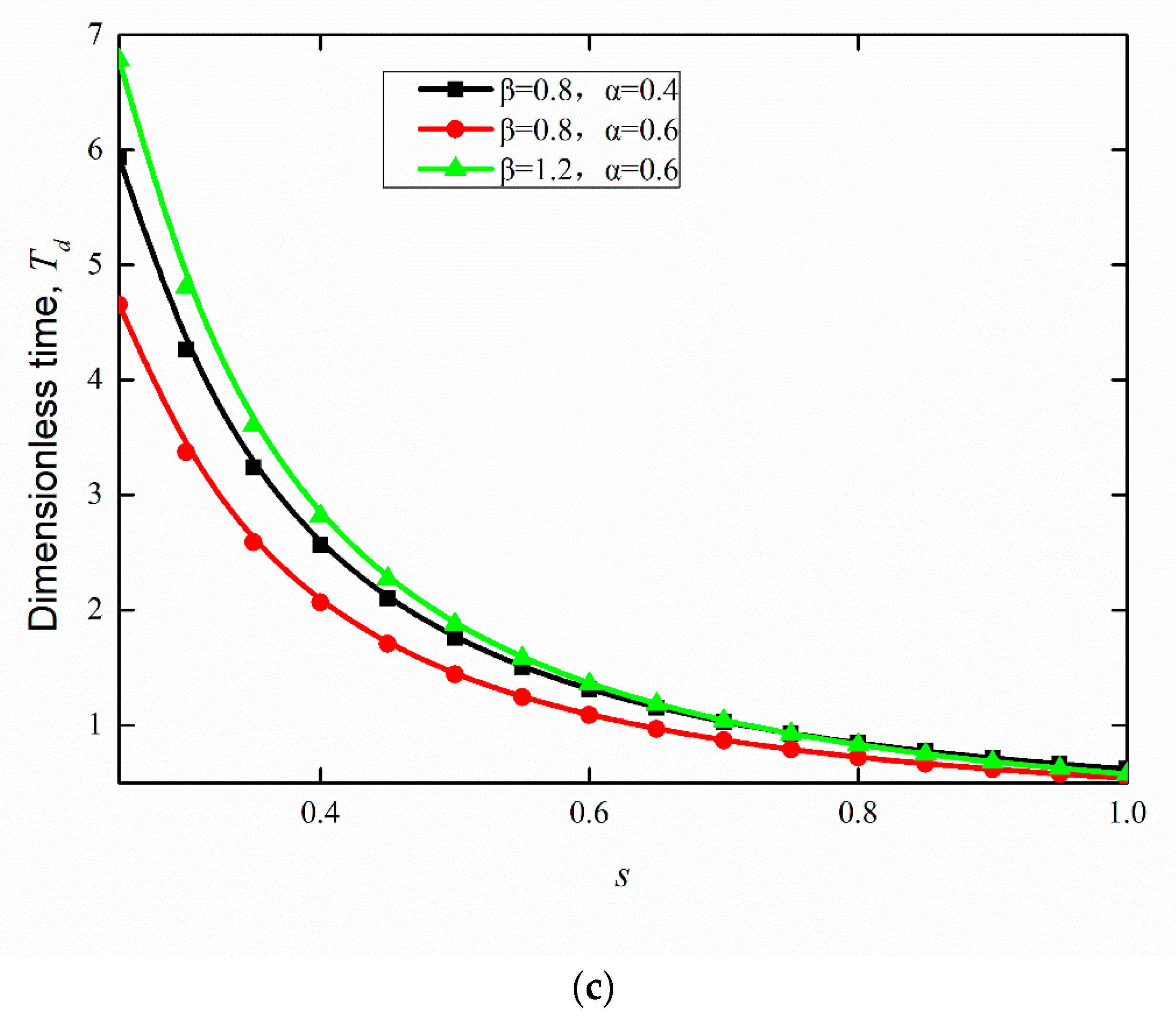
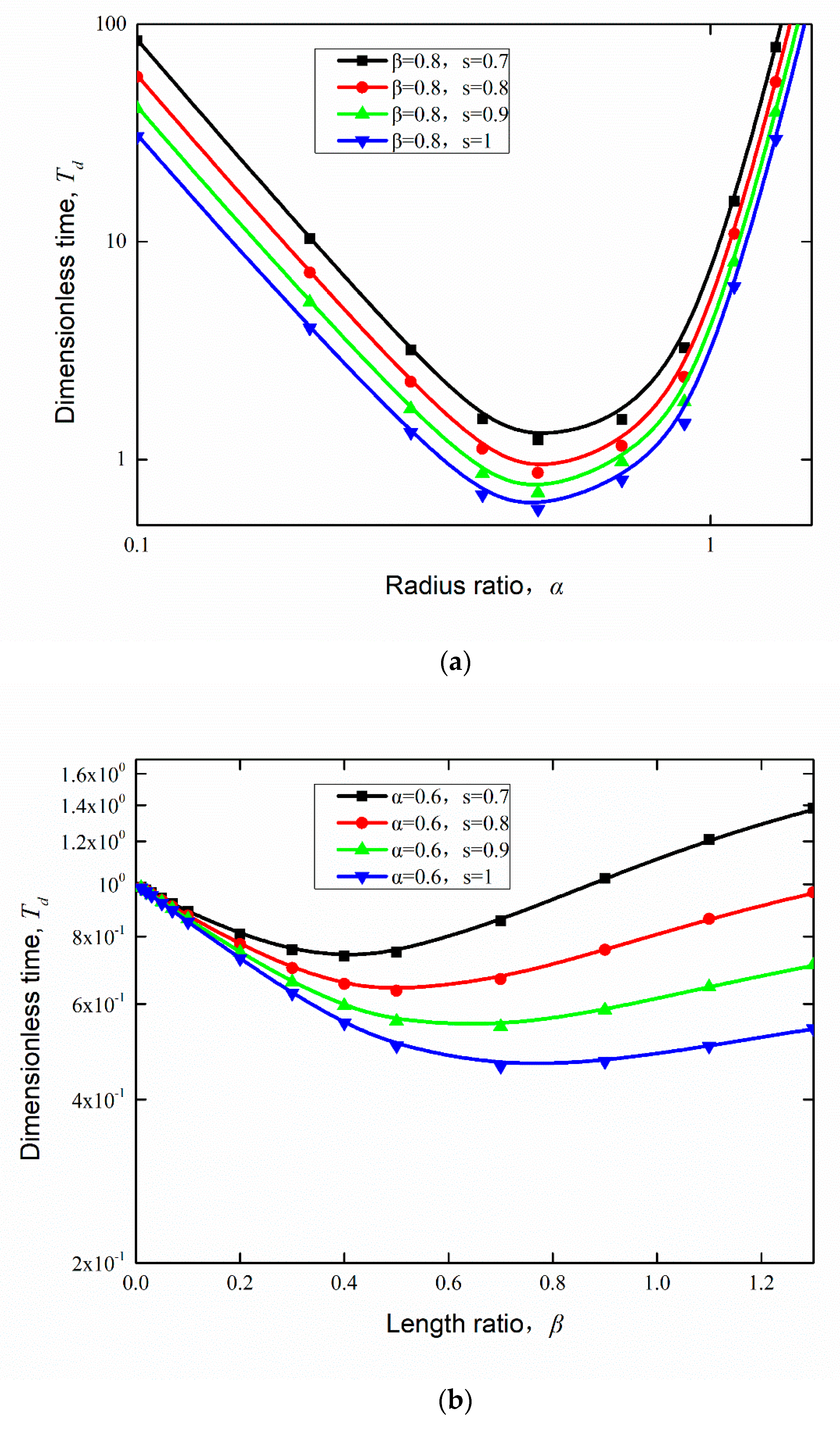
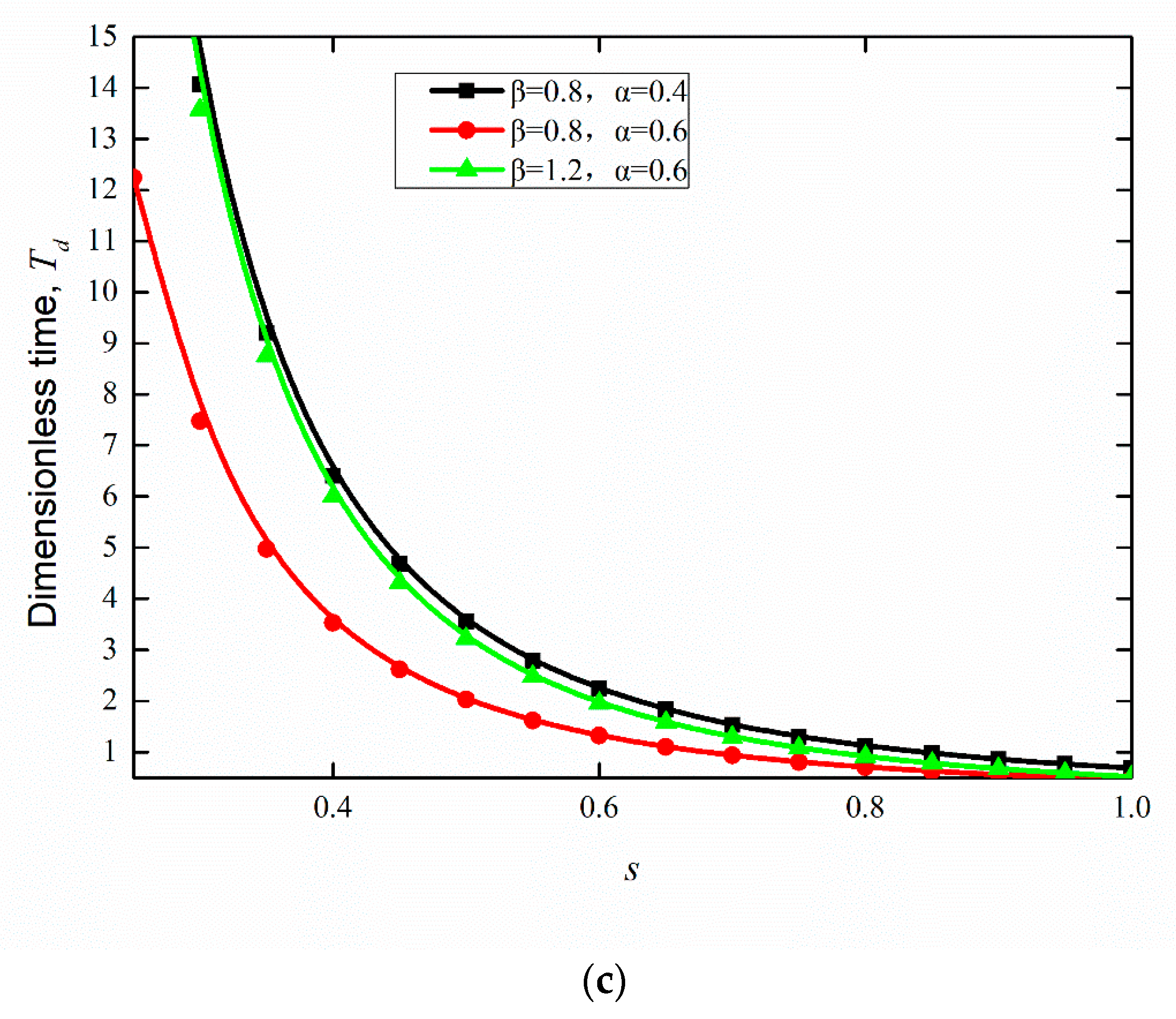
4. Results and Discussions
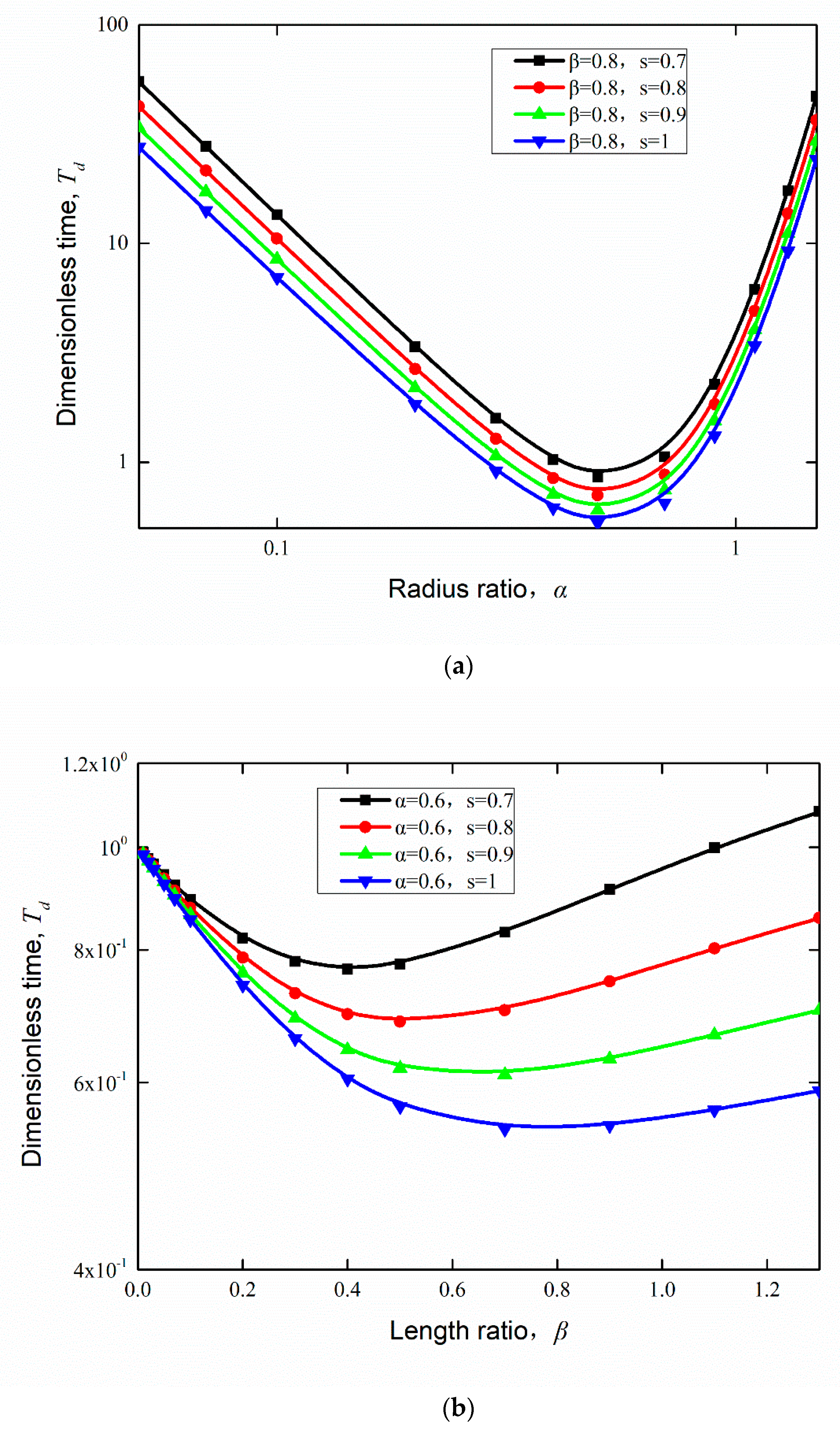
4.1. Effect of Proportional Variation in Wetting Strength on the Flow
4.2. Effect of Random Variation in Wetting Strength on Flow
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Berkowitz, B.; Ewing, R.P. Percolation Theory and Network Modeling Applications in Soil Physics. Surv. Geophys. 1998, 19, 23–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, G.; Cai, S.; Wang, X.; Jing, W.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Yao, J. The Effect of Surface Roughness on Immiscible Displacement Using Pore Scale Simulation. Transp. Porous Media 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Liu, J.; Yao, J.; Kou, J.L.; Li, Z.; Wu, T.H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H. Adsorption behaviors of shale oil in kerogen slit by molecular simulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Yang, H.Y.; Tao, L.; Yao, J. Microscopic Determination of Remaining Oil Distribution in Sandstones With Different Permeability Scales Using Computed Tomography Scanning. J. Energy Resour. Technol.-Trans. ASME 2019, 141, 092903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Yao, J.; Wang, C.C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; An, S.Y.; Song, W.H. New pore space characterization method of shale matrix formation by considering organic and inorganic pores. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balberg, I.; Berkowitz, B.; Drachsler, G.E. Application of a percolation model to flow in fractured hard rocks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1991, 96, 10015–10021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Regenauer-Lieb, K. Application of percolation theory to microtomography of rocks. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 214, 103519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Jin, T.; Kou, J.; Zou, S.; Xiao, J.; Meng, Q. Lucas-Washburn Equation-Based Modeling of Capillary-Driven Flow in Porous Systems. Langmuir 2021, 37, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Cai, J. Recent advances in spontaneous imbibition with different boundary conditions. Capillarity 2018, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jing, W.L.; Yang, Y.F.; Yang, H.N.; Guo, Y.H.; Sun, H.; Zhao, J.L.; Yao, J. The Investigation of Permeability Calculation Using Digital Core Simulation Technology. Energies 2019, 12, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parteli, E.J.R.; da Silva, L.R.; Andrade, J.S., Jr. Self-organized percolation in multi-layered structures. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2010, 2010, P03026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuuskraa, V.; Stevens, S.H.; Moodhe, K.D. Technically Recoverable Shale Oil and Shale Gas Resources: An Assessment of 137 Shale Formations in 41 Countries outside the United States; Adiministation, U.S. Energy Information: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Li, N.; Ran, Q.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.-S. A Multiple-Continuum Model for Simulation of Gas Production from Shale Gas Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the All Days, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 16 September 2013; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.F.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, K.; Ma, J.S. Pore-scale simulation of shale oil flow based on pore network model. Fuel 2019, 251, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, J.; Lu, S. Dynamic capillary pressure analysis of tight sandstone based on digital rock model. Capillarity 2020, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yang, Z.; Shi, Y. Experimental study on spontaneous imbibition characteristics of tight rocks. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2018, 2, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Yu, B. Advances in studies of spontaneous imbibition in porous media. Adv. Mech. 2012, 42, 735–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. A critical review on fundamental mechanisms of spontaneous imbibition and the impact of boundary condition, fluid viscosity and wettability. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2017, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R. Rate of capillary ascension of liquids. Kolloid Z. 1918, 23, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, E.W. The Dynamics of Capillary Flow. Phys. Rev. 1921, 17, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K. Theoretical Soil Mechanics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Handy, L.L. Determination of Effective Capillary Pressures for Porous Media from Imbibition Data. Trans. AIME 1960, 219, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuiec, L.E.; Bourbiaux, B.; Kalaydjian, F. Oil recovery by imbibition in low-permeability chalk. SPE Form. Eval. 1994, 9, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, H.; Gilman, J.R.; Eisharkawy, A.M. Analytical and numerical solution of oil recovery from fractured reservoirs with empirical transfer functions. SPE Reserv. Eng. 1992, 7, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.W.; Horne, R.N. An analytical scaling method for spontaneous imbibition in gas/water/rock systems. SPE J. 2004, 9, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.W.; Horne, R.N. Generalized scaling approach for spontaneous imbibition: An analytical model. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2006, 9, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattax, C.C.; Kyte, J.R. Imbibition Oil Recovery from Fractured, Water-Drive Reservoir. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1962, 2, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouxiang, M.; Morrow, N.R.; Zhang, X. Generalized scaling of spontaneous imbibition data for strongly water-wet systems. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1997, 18, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, D.; Lock, P.; Del Cura, M.A.G.; Ordonez, S. Predicting the capillary imbibition of porous rocks from microstructure. Transp. Porous Media 2002, 49, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventis, A.; Verganelakis, D.A.; Halse, M.R.; Webber, J.B.; Strange, J.H. Capillary Imbibition and Pore Characterisation in Cement Pastes. Transp. Porous Media 2000, 39, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, D.; Niu, B. Prediction of spontaneous imbibition in fractal porous media based on modified porosity correlation. Capillarity 2021, 4, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; Times Books: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcraft, S.W.; Tyler, S.W. An explanation of scale-dependent dispersivity in heterogeneous aquifers using concepts of fractal geometry. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.C.; Yu, B.M.; Zou, M.Q.; Luo, L. Fractal Characterization of Spontaneous Co-current Imbibition in Porous Media. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.D.; Su, Y.L.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, G.L.; Ren, L. Analysis of the Complex Fracture Flow in Multiple Fractured Horizontal Wells with the Fractal Tree-Like Network Models. Fractals-Complex Geom. Patterns Scaling Nat. Soc. 2015, 23, 1550014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shen, Y.; Ge, H.; Su, S.; Yang, Z. Analysis of Spontaneous Imbibition in Fractal Tree-Like Network System. Fractals 2016, 24, 1650035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, D.; Ye, L.; Fan, J. Treelike networks accelerating capillary flow. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2014, 89, 053007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Wang, J.; Yuan, B.; Shen, Y. Review on gas flow and recovery in unconventional porous rocks. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2017, 1, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.S.; Liu, Y. Some mechanisms of crude oil/brine/solid interactions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1998, 20, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.P.; Kou, J.S.; Yao, B.W.; Wu, Y.S.; Yao, J.; Sun, S.Y. Thermodynamically consistent modelling of two-phase flows with moving contact line and soluble surfactants. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 879, 327–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.P.; Kou, J.S.; Yao, J.; Li, A.F.; Sun, S.Y. A phase-field moving contact line model with soluble surfactants. J. Comput. Phys. 2020, 405, 109170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cai, S.; Yao, J.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, K.; Song, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Lisitsa, V. Pore-scale simulation of remaining oil distribution in 3D porous media affected by wettability and capillarity based on volume of fluid method. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2021, 143, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



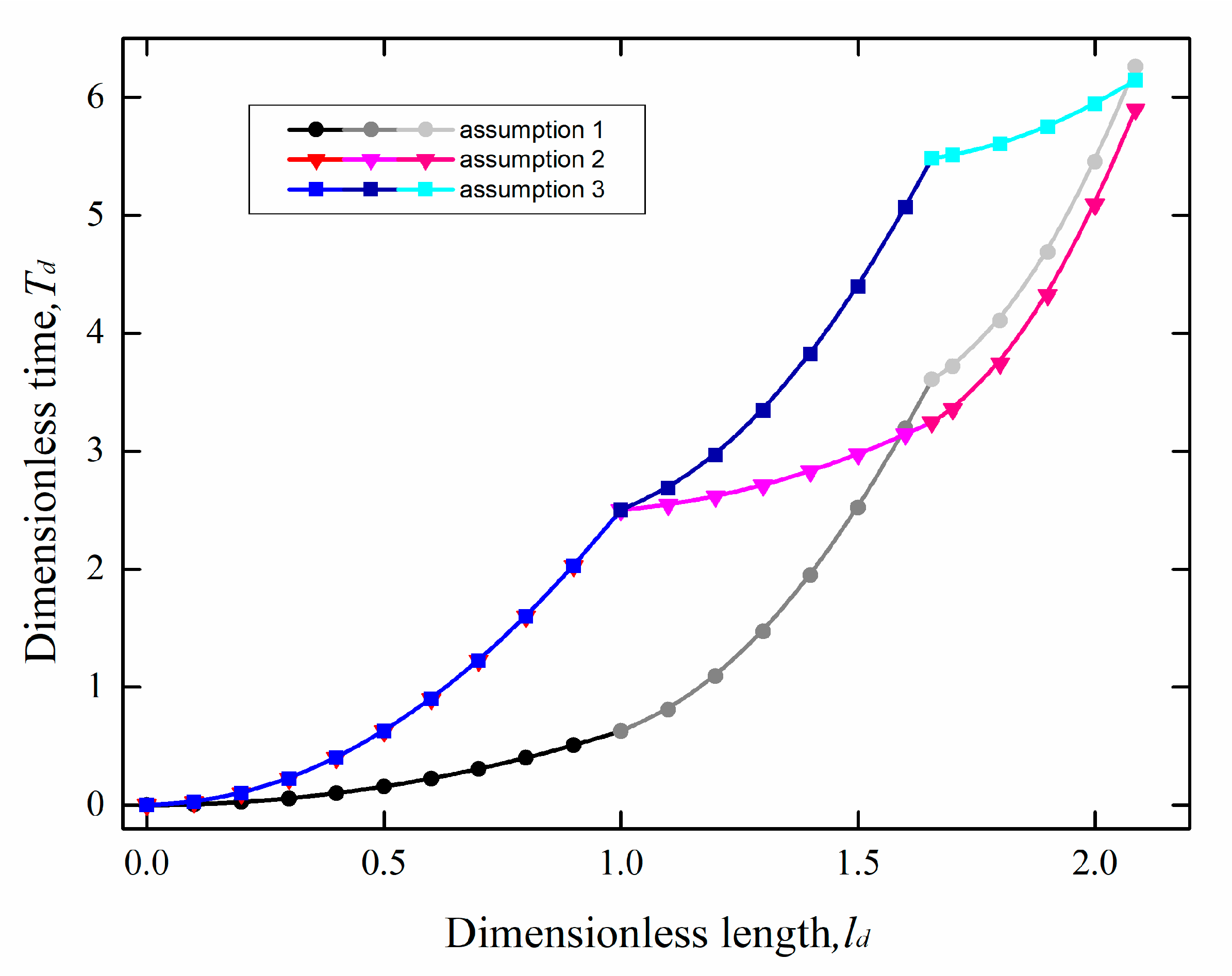
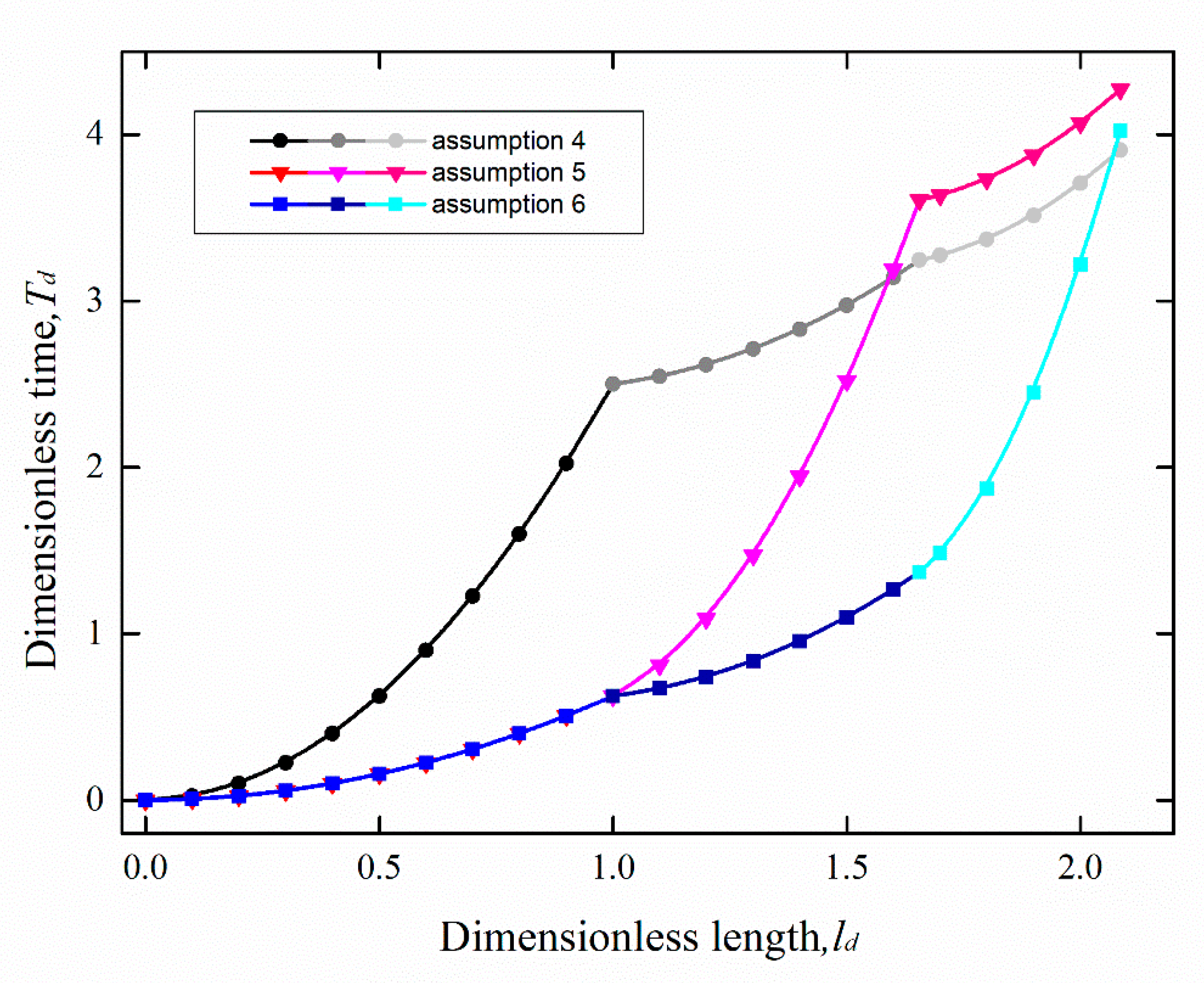
| Case No. | cosθ1 | cosθ2 | cosθ3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Group | #1 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| #2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | |
| #3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | |
| Second Group | #4 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| #5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.8 | |
| #6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, S.; Zhang, L.; Kang, L.; Yang, Y.; Jing, W.; Zhang, L.; Xu, C.; Sun, H.; Sajjadi, M. Spontaneous Imbibition in a Fractal Network Model with Different Wettabilities. Water 2021, 13, 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172370
Cai S, Zhang L, Kang L, Yang Y, Jing W, Zhang L, Xu C, Sun H, Sajjadi M. Spontaneous Imbibition in a Fractal Network Model with Different Wettabilities. Water. 2021; 13(17):2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172370
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Shaobin, Li Zhang, Lixin Kang, Yongfei Yang, Wenlong Jing, Lei Zhang, Chao Xu, Hai Sun, and Mozhdeh Sajjadi. 2021. "Spontaneous Imbibition in a Fractal Network Model with Different Wettabilities" Water 13, no. 17: 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172370
APA StyleCai, S., Zhang, L., Kang, L., Yang, Y., Jing, W., Zhang, L., Xu, C., Sun, H., & Sajjadi, M. (2021). Spontaneous Imbibition in a Fractal Network Model with Different Wettabilities. Water, 13(17), 2370. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172370








