Science and Binational Cooperation: Bidirectionality in the Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program in the Arizona-Sonora Border Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Principles for Analyzing Groundwater Governance
2.2. Analyzing the Science–Policy Interface in Transboundary Groundwater Governance
3. Materials and Methods
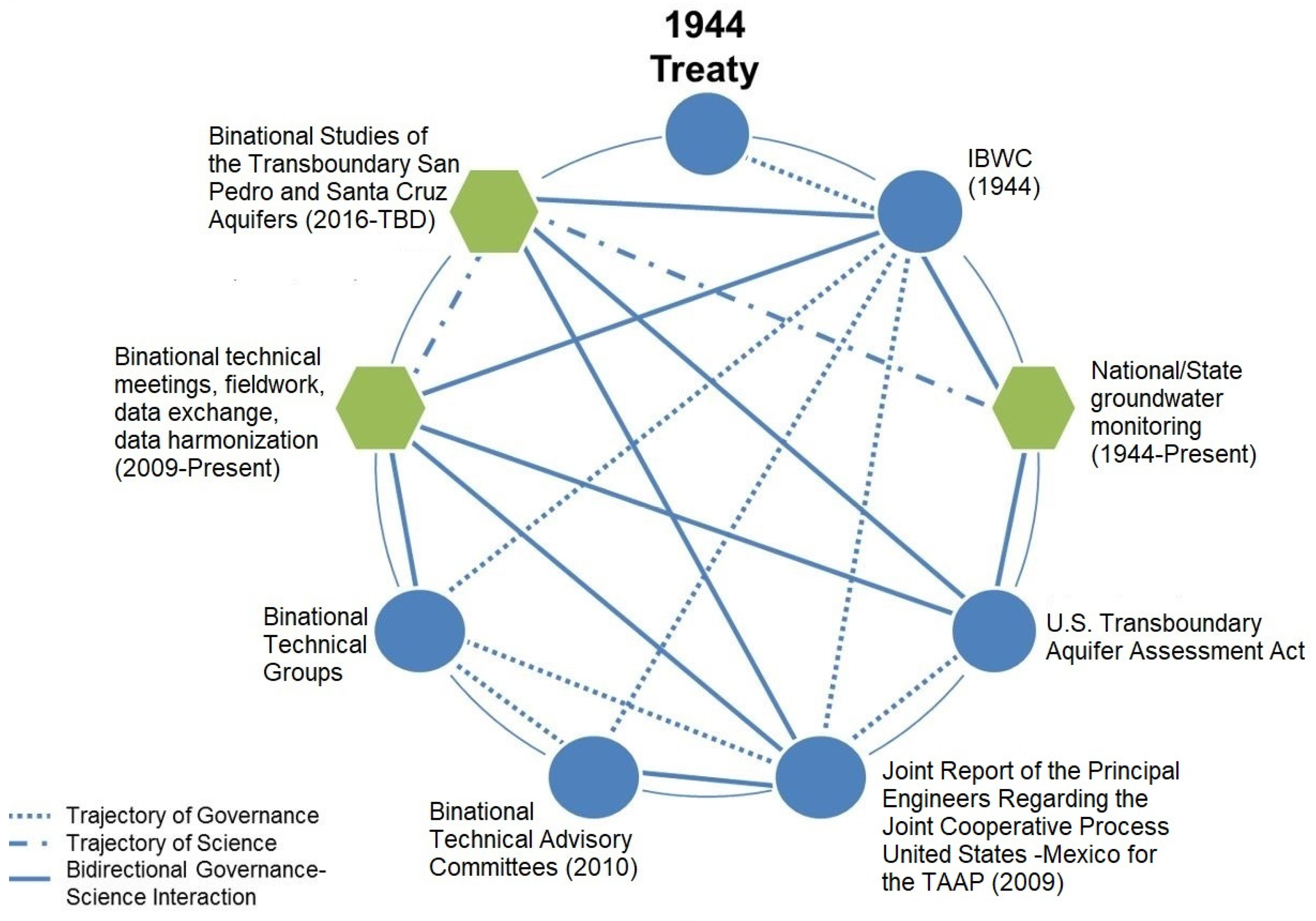
4. Results
4.1. Water Management and Governance on Both Sides of the Border
4.2. Binational Water Management
4.3. Establishment of the TAAP
4.4. Summary of Governance Principles Present
4.5. Summary of Attributes for Information to Be Used in Decision-Making
4.6. Interview Results
5. Bidirectionality and the Science–Policy Interface
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pagán, B.R.; Ashfaq, M.; Rastogi, D.; Kendall, D.R.; Kao, S.-C.; Naz, B.S.; Mei, R.; Pal, J.S. Extreme Hydrological Changes in the Southwestern US Drive Reductions in Water Supply to Southern California by Mid Century. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 094026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Lankao, P.; Smith, J.B.; Davidson, D.J.; Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Kinney, P.L.; Kirshen, P.; Kovacs, P.; Villers Ruiz, L. North America. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Barros, V.R., Field, C.B., Dokken, D.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Mach, K.J., Eren Billir, T., Chatterjee, M., Ebie, K.L., Otsuki Estrada, Y., Genova, R.C., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1439–1498. ISBN 978-1-107-05816-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wilder, M.; Garfin, G.; Ganster, P.; Eakin, H.; Romero-Lankao, P.; Lara-Valencia, F.; Cortez-Lara, A.A.; Mumme, S.P.; Neri, C.; Muñoz-Arriola, F.; et al. Climate change and U.S.-Mexico border communities. In Assessment of Climate Change in the Southwest United States: A Report Prepared for the National Climate Assessment; Garfin, G., Jardine, A., Merideth, R., Black, M., LeRoy, S., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 340–384. ISBN 978-1-61091-446-8. [Google Scholar]
- Meixner, T.; Manning, A.H.; Stonestrom, D.A.; Allen, D.M.; Ajamie, H.; Blasch, K.W.; Brookfield, A.E.; Castro, C.L.; Clark, J.F.; Gochis, D.J.; et al. Implications of projected climate change for groundwater recharge in the western United States. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamir, E.; Megdal, S.B.; Carillo, C.; Castro, C.L.; Chang, H.-I.; Chief, K.; Corkhill, F.E.; Eden, S.; Georgakakos, K.P.; Nelson, K.M.; et al. Climate change and water resources management in the Upper Santa Cruz River, Arizona. J. Hydrol. 2015, 521, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamir, E.; Tapia-Villaseñor, E.M.; Cruz-Ayala, M.B.; Megdal, S.B. A review of climate change impacts on the USA-Mexico transboundary Santa Cruz River Basin. Water 2021, 13, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.; Eckstein, G. Aquifers shared between Mexico and the United States: Management perspectives and their transboundary nature. Groundw 2017, 55, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Groundwater Resources Assessment Centre (IGRAC). Transboundary Aquifers of the World. Special Edition for the 7th World Water Forum. 2015. Available online: https://www.un-igrac.org/resource/transboundary-aquifers-world-map-2015 (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Burchi, S. Legal frameworks for the governance of international transboundary aquifers: Pre- and post-ISARM experience. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 20, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megdal, S.B.; Petersen-Perlman, J.D. Groundwater governance and assessment in a transboundary setting. In Lake Governance, 1st ed.; Grover, V., Krantsberg, G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 38–60. ISBN 9781138633759. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhala, L. Process tracing in the study of environmental politics. Glob. Environ. Politics 2017, 17, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashwan, P. Forest policy, institutions, and REDD+ in India, Tanzania, and Mexico. Glob. Environ. Politics 2015, 15, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, C.; Mann, P. Scaling up Buen Vivir: Globalizing local environmental governance from Ecuador. Glob. Environ. Politics 2014, 14, 40–58. [Google Scholar]
- Milman, A.; MacDonald, A. Focus on interactions between science-policy in groundwater systems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 090201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Boundary and Water Commission-Comision Internacional de Limites y Agua (IBWC). Welcome. Available online: http://www.ibwc.gov/home.html (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Dunn, G.; Brown, R.R.; Bos, J.J.; Bakker, K. The role of science-policy interface in sustainable urban water transitions: Lessons from Rotterdam. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 73, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.; Bos, J.J.; Brown, R.R. Mediating the science-policy interface: Insights from the urban water sector in Melbourne, Australia. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 82, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowski, J. A “new water culture” on the Iberian Peninsula? Evaluating epistemic community impact on water resources management policy. Environ. Plan. C 2016, 35, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, D.; de Loë, R.C.; Morris, M.; Edwards, T.W.D.; Gerlak, A.K.; Hall, R.I.; Huitema, D.; Ison, R.; Livingstone, D.; MacDonald, G.; et al. Science-policy processes for transboundary water governance. Ambio 2015, 44, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, A.T.; Yoffe, S.B.; Giordano, M. International waters: Identifying basins at risk. Water Policy 2003, 5, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blomquist, W.; Ingram, H.M. Boundaries seen and unseen: Resolving transboundary groundwater problems. Water Int. 2003, 28, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegary, J.B.; Megdal, S.B.; Tapia-Villaseñor, E.M.; Minjárez-Sosa, I.; Petersen-Perlman, J.D.; Monreal, R.; Gray, F.; Grijalva Noriega, F. Findings and lessons learned from the assessment of the Mexico-United States transboundary San Pedro and Santa Cruz aquifers: The utility of social science in applied hydrologic research. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 20, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udall, S.L.; Varady, R.G. Environmental conflict and the world’s new international borders. Transbound Resour Rep. 1994, 7, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Varady, R.G.; Morehouse, B.J. Moving borders from the periphery to the center: River basins, political boundaries, and water management policy. In Water: Science, Policy, and Management; Lawford, R., Fort, D., Hartmann, H., Eden, S., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 143–160. ISBN 978-0875903200. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, E.; Bakker, K. Drivers and Barriers of Cooperation in Transboundary Water Governance: A Case Study of Western Canada and the United States; Report to the Walter and Duncan Gordon Foundation. 2005. Available online: https://watergovernance.ca/2017/07/15/drivers-and-barriers-of-cooperation-in-transboundary-water-governance-a-case-study-of-western-canada-and-the-united-states/ (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Megdal, S.B.; Scott, C.A. The importance of institutional asymmetries to the development of binational aquifer assessment programs: The Arizona-Sonora experience. Water 2011, 3, 949–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albrecht, T.R.; Varady, R.G.; Zuniga-Teran, A.A.; Gerlak, A.K.; De Grenade, R.R.; Lutz-Ley, A.; Martín, F.; Megdal, S.B.; Meza, F.; Ocampo Melgar, D.; et al. Unraveling transboundary water security in the arid Americas. Water Int. 2018, 43, 1075–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Norman, E.S. Renegotiating the Columbia River Treaty: Transboundary governance and indigenous rights. Glob. Environ. Politics 2018, 18, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen-Perlman, J.D.; Wolf, A.T. Getting to the first handshake: Enhancing security by initiating cooperation in transboundary river basins. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 1688–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, T.; Detges, A. International water cooperation and environmental peacemaking. Glob. Environ. Politics 2018, 18, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Chaisemartin, M.; Varady, R.G.; Megdal, S.B.; Conti, K.I.; van der Gun, J.; Merla, A.; Nijsten, G.-J.; Scheibler, F. Addressing the groundwater governance challenge. In Freshwater Governance for the 21st Century; Karar, E., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 205–227. ISBN 978-3-319-43350-9. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, M. Global groundwater? Issues and solutions. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megdal, S.B. Invisible water: The importance of good groundwater governance and management. NPJ Clean. Water 2018, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theesfeld, I. Institutional challenges for national groundwater governance: Policies and issues. Groundwater 2010, 48, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Megdal, S.B.; Gerlak, A.K.; Varady, R.G.; Huang, L.-Y. Groundwater governance in the United States: Common priorities and challenges. Groundwater 2015, 53, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, K.I. Cooperation over transboundary aquifers: Lessons learned from 10 years of experience. In Free Flow: Reaching Water Security through Cooperation; Griffiths, J., Lambert, R., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 40–44. ISBN 978-92-3-104256-0. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.K.; Tortajada, C. Future water governance: Problems and perspectives. In Improving Water Policy and Governance; Tortajada, C., Biswas, A., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–13. ISBN 978-0415606288. [Google Scholar]
- Akhmouch, A.; Clavreul, D. Assessing and monitoring groundwater governance. In Advances in Groundwater Governance, Vilholth, K.G., López-Gunn, E., Conti, K., Garrido, A., van der Gun, J., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2018; pp. 247–265. ISBN 978-1138029804. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, T.R.; Varady, R.G.; Zuniga-Teran, A.A.; Gerlak, A.K.; Staddon, C. Governing a shared hidden resource: A review of governance mechanisms for transboundary groundwater security. Water Secur. 2017, 2, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiparsky, M.; Milman, A.; Owen, D.; Fisher, A.T. The importance of institutional design for distributed local-level governance of groundwater: The case of California’s Sustainable Groundwater Management Act. Water 2017, 9, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varady, R.G.; Zuniga-Teran, A.A.; Gerlak, A.K.; Megdal, S.B. Modes and approaches of groundwater governance: A survey of lessons learned from selected cases across the globe. Water 2016, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciplet, D.; Adams, K.M.; Weikmans, R.; Timmons Roberts, J. The transformative capability of transparency in global environmental governance. Glob. Environ. Politics 2018, 18, 130–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, S.; Appelgren, B.; Arnold, G.; Aureli, A.; Burchi, S.; Burke, J.; Margat, J.; Pallas, P. Internationally Shared (Transboundary) Aquifer Resources Management: Their Significance and Sustainable Management; Non Serial Document, SC-2001/WS/40; Puri, S., Ed.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- Puri, S.; Aureli, A. Transboundary aquifers: A global program to assess, evaluate, and develop policy. Groundwater 2005, 43, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movilla Pateiro, L. Ad hoc legal mechanisms governing transboundary aquifers: Current status and future prospects. Water Int. 2016, 41, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H. The Guarani Aquifer System, highly present but not high profile: A hydropolitical analysis of transboundary groundwater governance. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 83, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sindico, F.; Hirata, R.; Manganelli, A. The Guarani Aquifer System: From a beacon of hope to a question mark in the governance of transboundary aquifers. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 20, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.; Menga, F.; Greco, F. Monitoring transboundary water cooperation in SDG 6.5. 2: How a critical hydropolitics approach can spot inequitable outcomes. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferragina, E.; Greco, F. The Disi project: An internal/external analysis. Water Int. 2008, 33, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hove, S. A rationale for science-policy interfaces. Futures 2007, 39, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. Governing the Commons: The Evolution of Institutions for Collective Action; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; ISBN 0-521-40599-8. [Google Scholar]
- Margat, J.; van der Gun, J. Groundwater around the World: A Geographic Synopsis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780367576509. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, J.; Brooks, D.B. Governance of transboundary aquifers: New challenges and new opportunities. Water Int. 2011, 36, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Ait-Kadi, M. Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM): How does groundwater fit in? Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, M.; Shah, T. From IWRM back to integrated water resources management. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2014, 30, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varady, R.G.; van Weert, F.; Megdal, S.B.; Gerlak, A.K.; Abdalla Iskandar, C.; House-Peters, L. GEF-FAO Groundwater Governance Project: A Global Framework for Country Action. Thematic Paper No. 5: Groundwater Policy and Governance; With Major Editing by Dellinger McGovern, E. 2013. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281824294_Groundwater_Governance_A_Global_Framework_for_Country_Action (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Cash, D.; Clark, W.C.; Alcock, F.; Dickson, N.M.; Eckley, N.; Jäger, J. Salience, credibility, legitimacy and boundaries: Linking research, assessment and decision making. In KSG Working Papers Series RWP02-046; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; p. 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemos, M.C.; Kirchhoff, C.J.; Ramprasad, V. Narrowing the climate information usability gap. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.S.; Stringer, L.C.; Fazey, I.; Evely, A.C.; Kruijsen, J.H.J. Five principles for the practice of knowledge exchange in environmental management. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirchhoff, C.J.; Lemos, M.C.; Dessai, S. Actionable knowledge for environmental decision making: Broadening the usability of climate science. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2013, 38, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milman, A.; Ray, I. Interpreting the unknown: Uncertainty and the management of transboundary groundwater. Water Int. 2011, 36, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshall, A.S.; Tsai, F.T.-C. Constructive epistemic modeling of groundwater flow with geological structure and boundary condition uncertainty under Bayesian paradigm. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilling, L.; Lemos, M.C. Creating usable science: Opportunities and constraints for climate knowledge use and their Implications for science policy. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2011, 21, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkki, S.; Tinch, R.; Niemelä, J.; Heink, U.; Waylen, K.; Timaeus, J.; Young, J.; Watt, A.; Neßhöver, C.; van den Hove, S. Adding ‘iterativity’ to the credibility, relevance, legitimacy: A novel scheme to highlight dynamic aspects of science-policy interfaces. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugg, Z.P.; Varady, R.G.; Gerlak, A.K.; de Grenade, R. Transboundary groundwater governance in the Guarani Aquifer System: Reflections from a survey of global and regional experts. Water Int. 2015, 40, 377–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, C.I.; Soliman, S.M. The transboundary non-renewable Nubian Aquifer System of Chad, Egypt, Libya, and Sudan: Classical groundwater questions and parsimonious hydrogeologic analysis and modeling. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 441–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahane, Y. The Turonian-Cenomanian Aquifer. In Management of Shared Groundwater Resources: The Israeli-Palestinian Case with an International Perspective; Feitelson, E., Haddad, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 83–106. ISBN 978-0-7923-7254-7. [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson, E.; Haddad, M. Identification of Joint Management Structures for Shared Aquifers: A Cooperative Palestinian-Israeli Effort; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; Volume 415, ISBN 0-8213-4307-6. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, K.I. Factors Enabling Transboundary Aquifer Cooperation: A Global Analysis; UN-IGRAC: Delft, The Netherlands, 2014; p. 108. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, M. Cooperation on Africa’s international waterbodies: Information needs and the role of information-sharing. In Transboundary Water Management in Africa: Challenges for Development Cooperation; Scheumann, W., Neubert, S., Eds.; Deutsches Institut für Entwicklungspolitick: Bonn, Germany, 2006; pp. 173–236. ISBN 3-88985-326-9. [Google Scholar]
- Milman, A.; Gerlak, A.K.; Albrecht, T.R.; Colosimo, M.; Conca, K.; Kittikhoun, A.; Kovács, P.; Moy, R.; Schmeier, S.; Wentling, K.; et al. Addressing knowledge gaps for transboundary environmental governance. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2020, 64, 102162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendy, E.; Flessa, K.W.; Schlatter, K.J.; de la Parra, C.A.; Hinojosa Huerta, O.M.; Carrillo-Guerrero, Y.K.; Guillen, E. Leveraging environmental flows to reform water management policy: Lessons learned from the 2014 Colorado River Delta pulse flow. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, A.H.; Scott, C.A. Interbasin water transfers at the US–Mexico border city of Nogales, Sonora: Implications for aquifers and water security. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2014, 30, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varady, R.G.; Moote, M.A.; Merideth, R. Water allocation options for the Upper San Pedro basin: Assessing the social and institutional landscape. Nat. Resour. J. 2000, 40, 223–235. [Google Scholar]
- Milman, A.; Scott, C.A. Beneath the surface: Intranational institutions and management of the United States—Mexico transboundary Santa Cruz Aquifer. Environ. Plan. C Politics Space 2010, 28, 528–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNabb, D.E. Water resource management comes of age. In Water Resource Management; Palgrave MacMillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 163–185. ISBN 978-3-319-54816-6. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, R.H. Legal convergence of East and West in contemporary American water law. Environ. Law 2012, 42, 65–92. [Google Scholar]
- Megdal, S.B. Arizona groundwater management. Water Rep. 2012, 104, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Arizona Town Hall. Keeping Arizona’s Water Glass Gull. 2015. Available online: https://aztownhall.org/resources/Documents/107%20Keeping%20Arizona’s%20Water%20Glass%20Full%20FINAL%20Report%20web.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Mumme, S.P. Innovation and reform in transboundary resource management: A critical look at the International Boundary and Water Commission, United States and Mexico. Nat. Resour. J. 1993, 33, 93–120. [Google Scholar]
- Mumme, S.P. Minute 242 and beyond: Challenges and opportunities for managing transboundary groundwater on the Mexico-U.S. border. Nat. Resour. J. 2000, 40, 341–378. [Google Scholar]
- Wilder, M.O.; Varady, R.G.; Gerlak, A.K.; Mumme, S.P.; Flessa, K.W.; Zuniga-Teran, A.A.; Scott, C.A.; Pineda Pablos, N.; Megdal, S.B. Hydrodiplomacy and adaptive governance at the U.S.-Mexico border: 75 years of tradition and innovation in transboundary water management. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 112, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBWC. Minute 242: Permanent and Definitive Solution to the International Problem of Salinity of the Colorado River. 1973. Available online: https://www.usbr.gov/lc/region/pao/pdfiles/min242.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Hatch Kuri, G. A joint management of transboundary aquifers: From asymmetries to environmental protection. Front. Norte 2018, 30, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownell, H.; Eaton, S.D. The Colorado River salinity problem with Mexico. Am. J. Int. Law 1975, 69, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumme, S.P.; Collins, K. The La Paz Agreement 30 years on. J. Environ. Dev. 2014, 23, 303–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.M. Five-Year Interim Report of the United States—Mexico Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program: 2007–2012. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2013/1059/pdf/ofr2013-1059.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- IBWC. Joint Report of the Principal Engineers Regarding the Joint Cooperative Process United States-Mexico for the Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program. 2009. Available online: https://www.ibwc.gov/Files/Minutes/Joint_Report_TAAP_081909.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Rojo, H.A.; Bredehoeft, J.; Lacewell, R.; Price, J.; Stromberg, J.; Thomas, G.A. Sustaining and Enhancing Riparian Migratory Bird Habitat on the Upper San Pedro River: Public Review Draft. 1998. Available online: https://searchworks.stanford.edu/view/4782615 (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Eckstein, G.E. Managing buried treasure across frontiers: The International Law of Transboundary Aquifers. Water Int. 2011, 36, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memorandum of Understanding between City of Juárez, Mexico Utilities and the El Paso Water Utilities Public Services Board and the City of El Paso, Texas (MOU). 1999. Available online: http://www.internationalwaterlaw.org/documents/regionaldocs/Local-GW-Agreements/El-Paso-JuarezMoU.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Pool, D.R.; Dickinson, J.E. Ground-Water Flow Model of the Sierra Vista Subwatershed and Sonoran Portions of the Upper San Pedro Basin, Southeastern Arizona, United States, and Northern Sonora, Mexico; No. 2006-5228; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2007.
- Wallace, C.S.A.; Villarreal, M.L.; Norman, L.M. Development of a High-Resolution Binational Vegetation Map of the Santa Cruz River Riparian Corridor and Surrounding Watershed, Southern Arizona and Northern Sonora, Mexico; No. 2011-1143; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011.
- Villareal, M.L.; Norman, L.M.; Wallace, C.S.A.; Van Riper, C. A Multitemporal (1979–2009) Land-Use/Land-Cover Dataset of the Binational Santa Cruz Watershed; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011.
- Callegary, J.B.; Heilman, J.A.; Tapia-Villaseñor, E.M.; Knight, J.E. San Pedro River Aquifer Data Release—Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program (TAAP); U.S. Geological Survey Data Release: Reston, VA, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Dirks, K.T. Trust in leadership and team performance: Evidence from NCAA basketball. J. Appl Psychol. 2000, 85, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Megdal, S.B. The cooperative framework for the Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program: A model for collaborative transborder studies. Water Resour. Impact 2018, 20, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mechlem, K. Past, present and future of the International Law of Transboundary Aquifers. Int. Community Law Rev. 2011, 13, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Villaseñor, E.M.; Megdal, S.B. The U.S.-Mexico Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program as a model for transborder groundwater collaboration. Water 2021, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, M.C. Blaze in Nogales, Sonora Battled from Both Sides of the Border. Nogales International (Nogales, AZ). 10 May 2012. Available online: https://www.nogalesinternational.com/news/blaze-in-nogales-sonora-battled-from-both-sides-of-the/article_3267761e-9b0d-11e1-85e7-001a4bcf887a.html (accessed on 6 August 2021).
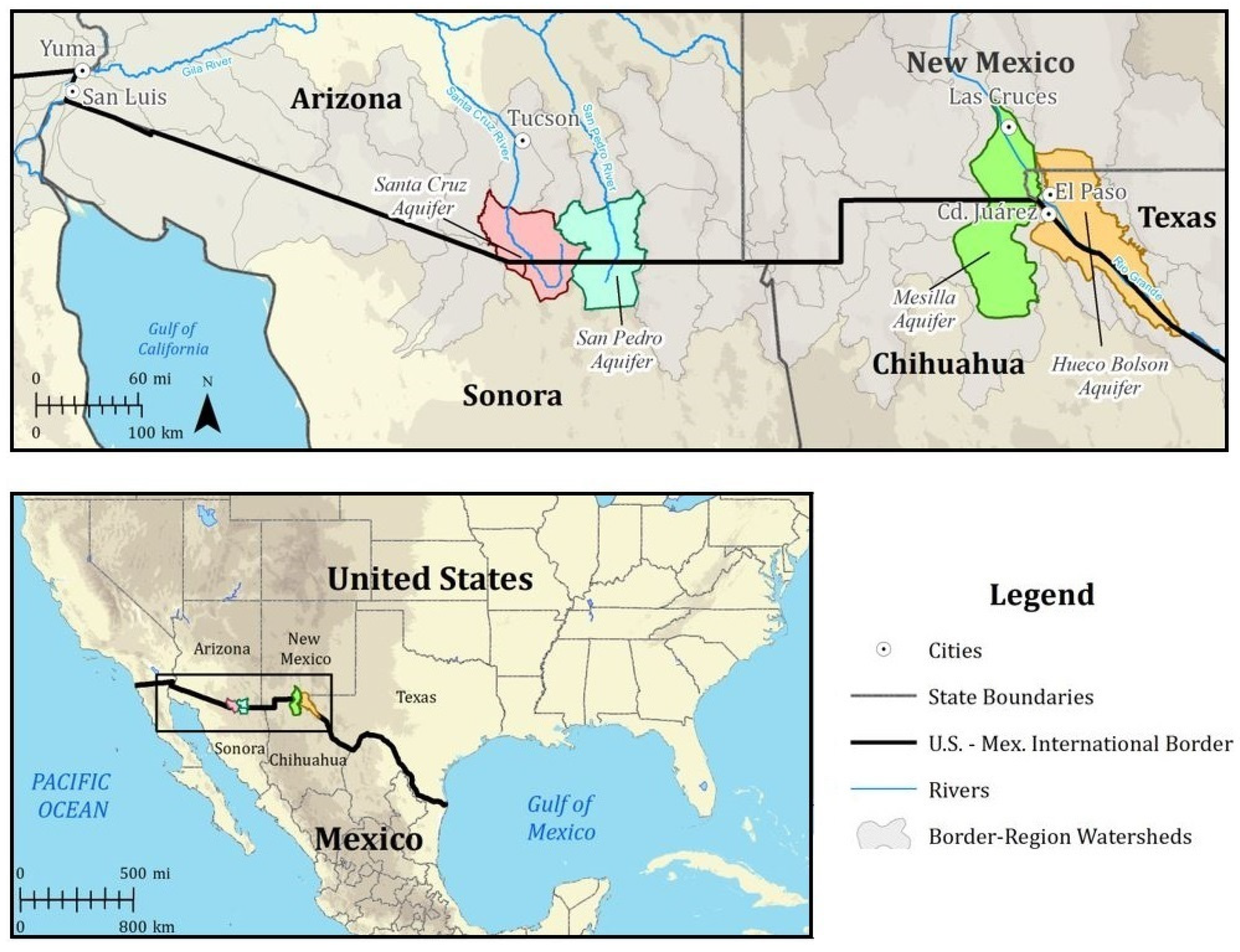
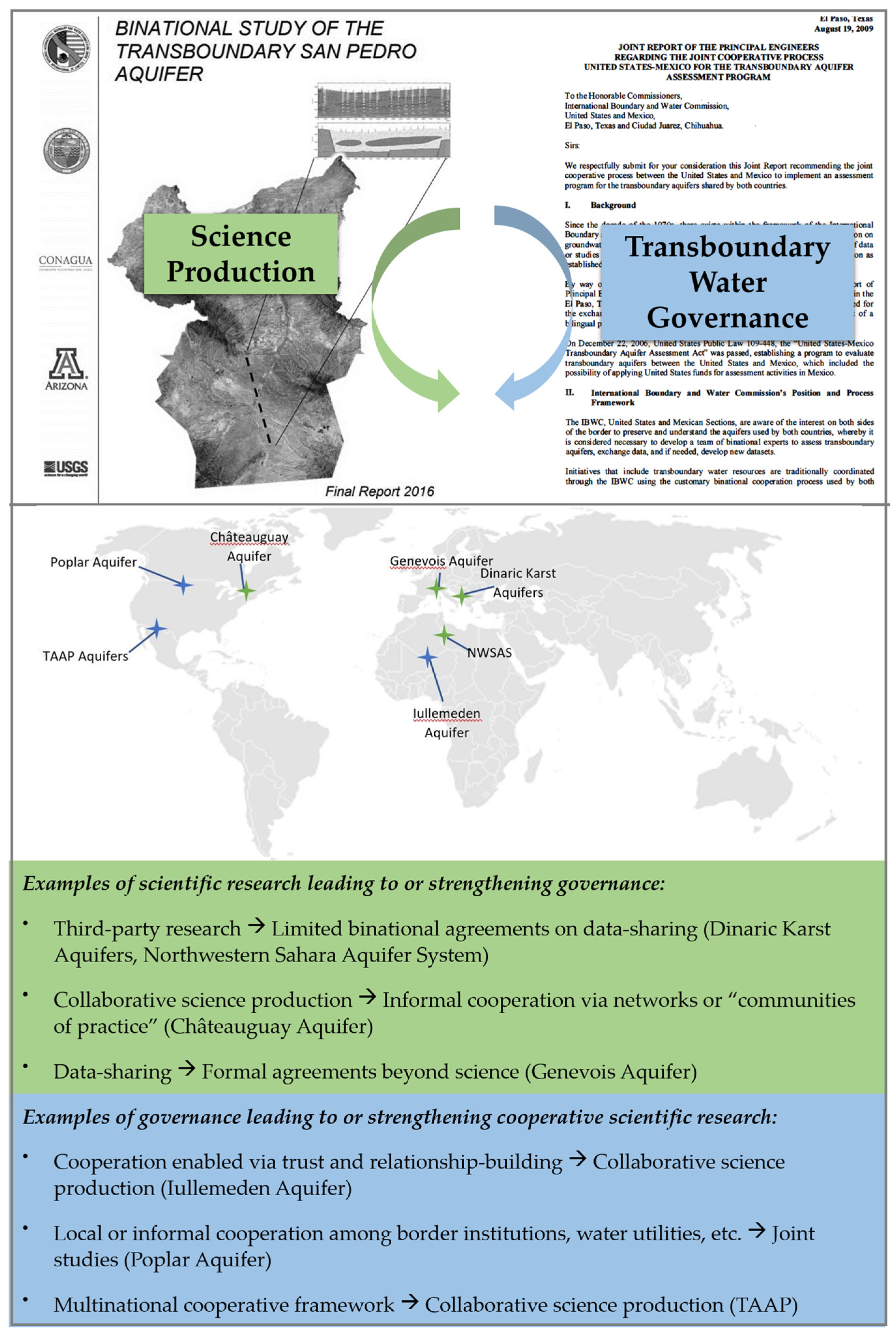
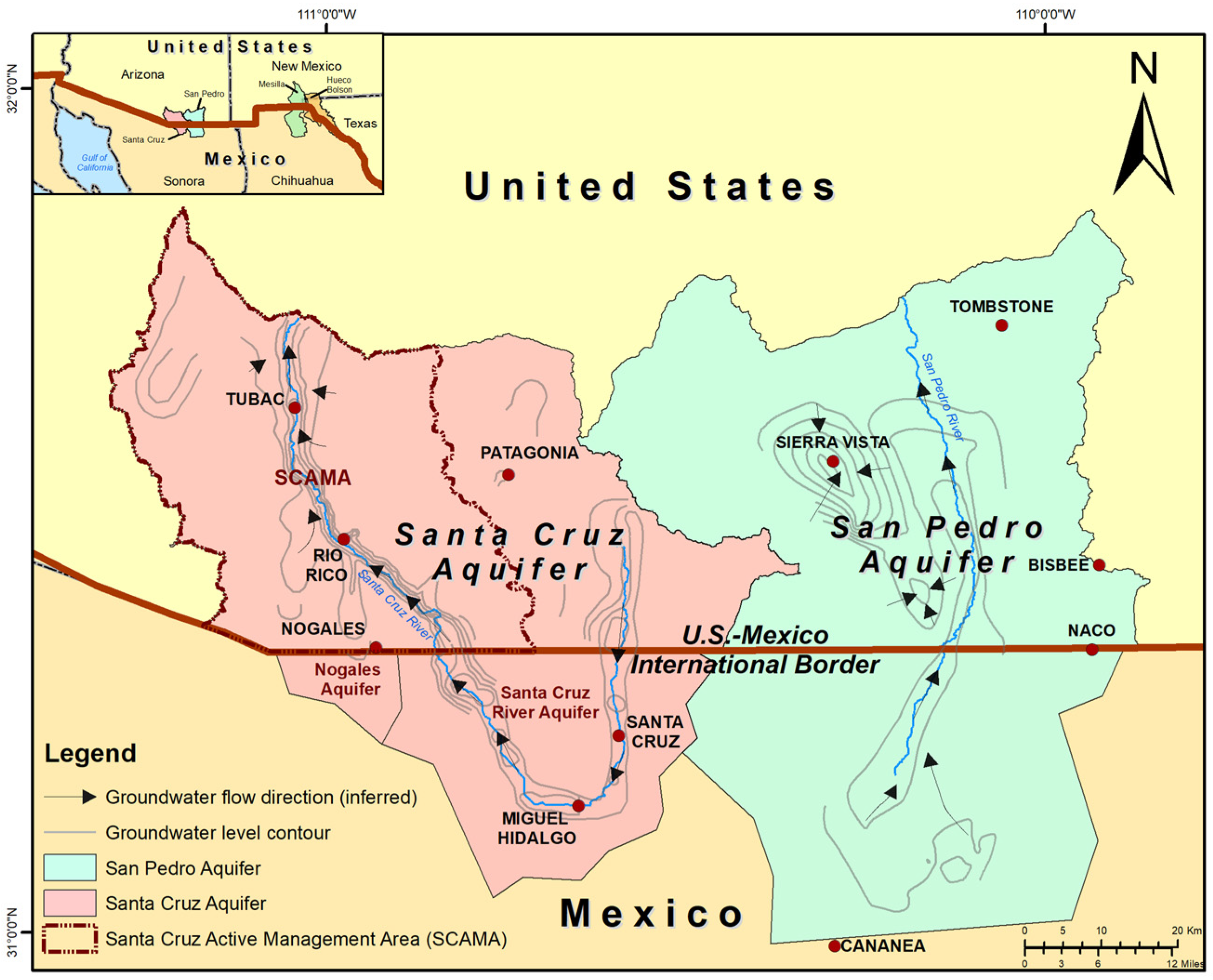
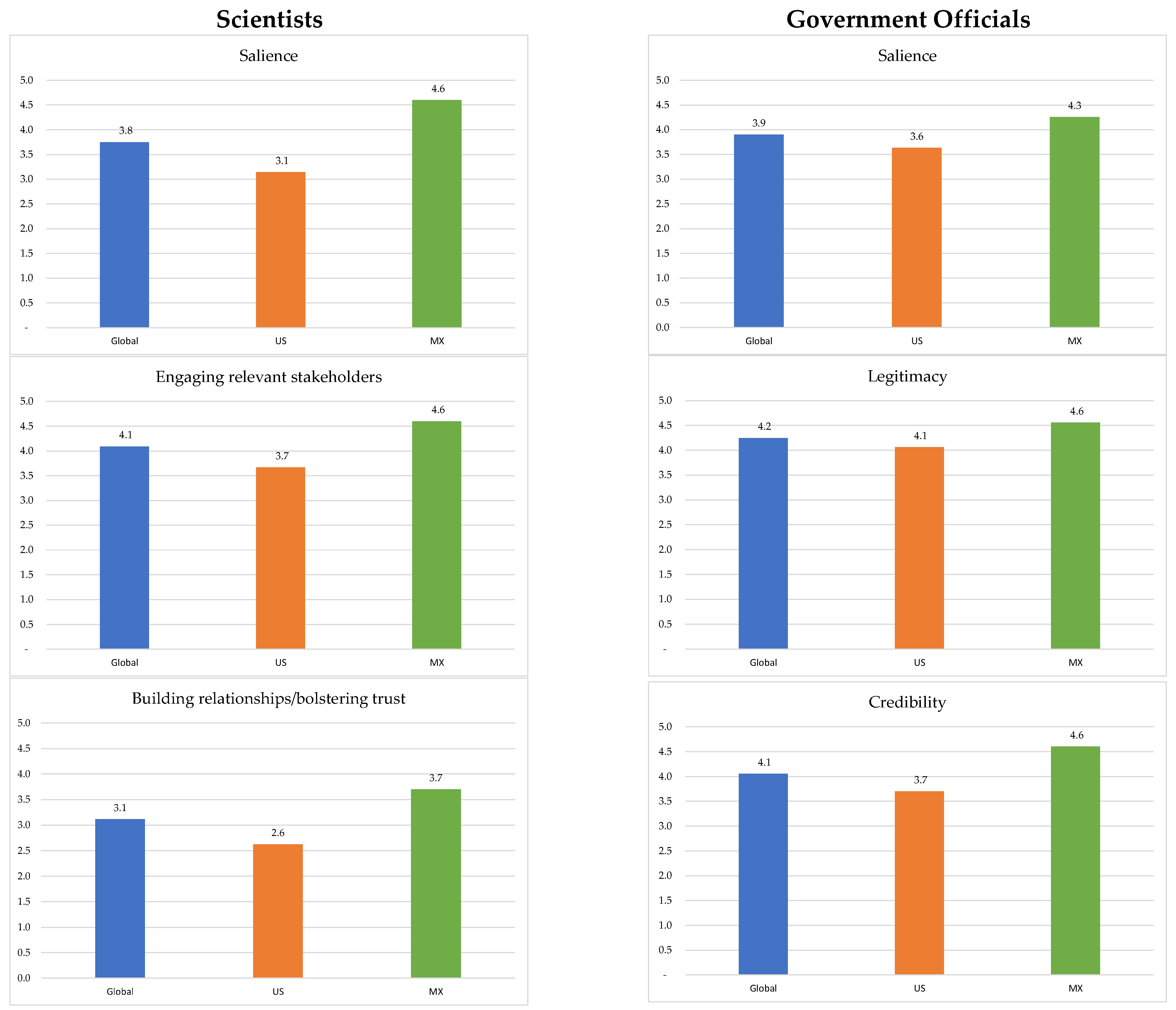
| Features of Science Production | Relevant Attributes of Science Outputs |
|---|---|
| Binational development of research aims and focus areas through Binational Technical Group meetings | Legitimacy, salience, iteration |
| Investment of funding or in-kind investments from both countries | Legitimacy |
| Involvement of binational experts in knowledge production | Credibility, iteration |
| Stakeholder involvement in planning | Salience, legitimacy, iteration |
| Integration and harmonization of data from both nations | Salience, iteration |
| Bilingual reporting of results (Binational Studies of the San Pedro and Santa Cruz Aquifers) | Legitimacy |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petersen-Perlman, J.D.; Albrecht, T.R.; Tapia-Villaseñor, E.M.; Varady, R.G.; Megdal, S.B. Science and Binational Cooperation: Bidirectionality in the Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program in the Arizona-Sonora Border Region. Water 2021, 13, 2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172364
Petersen-Perlman JD, Albrecht TR, Tapia-Villaseñor EM, Varady RG, Megdal SB. Science and Binational Cooperation: Bidirectionality in the Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program in the Arizona-Sonora Border Region. Water. 2021; 13(17):2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172364
Chicago/Turabian StylePetersen-Perlman, Jacob D., Tamee R. Albrecht, Elia M. Tapia-Villaseñor, Robert G. Varady, and Sharon B. Megdal. 2021. "Science and Binational Cooperation: Bidirectionality in the Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program in the Arizona-Sonora Border Region" Water 13, no. 17: 2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172364
APA StylePetersen-Perlman, J. D., Albrecht, T. R., Tapia-Villaseñor, E. M., Varady, R. G., & Megdal, S. B. (2021). Science and Binational Cooperation: Bidirectionality in the Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program in the Arizona-Sonora Border Region. Water, 13(17), 2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13172364







