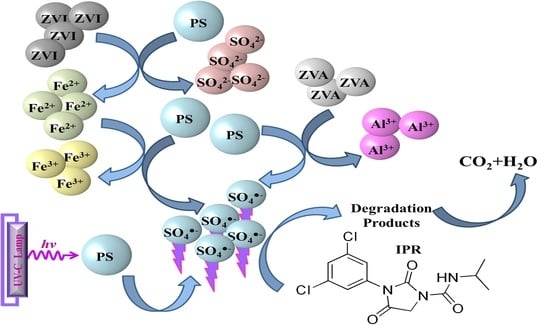
Iprodione Removal by UV-Light-, Zero-Valent Iron- and Zero-Valent Aluminium-Activated Persulfate Oxidation Processes in Pure Water and Simulated Tertiary Treated Urban Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.3. Analytical and Instrumental Procedures
3. Results
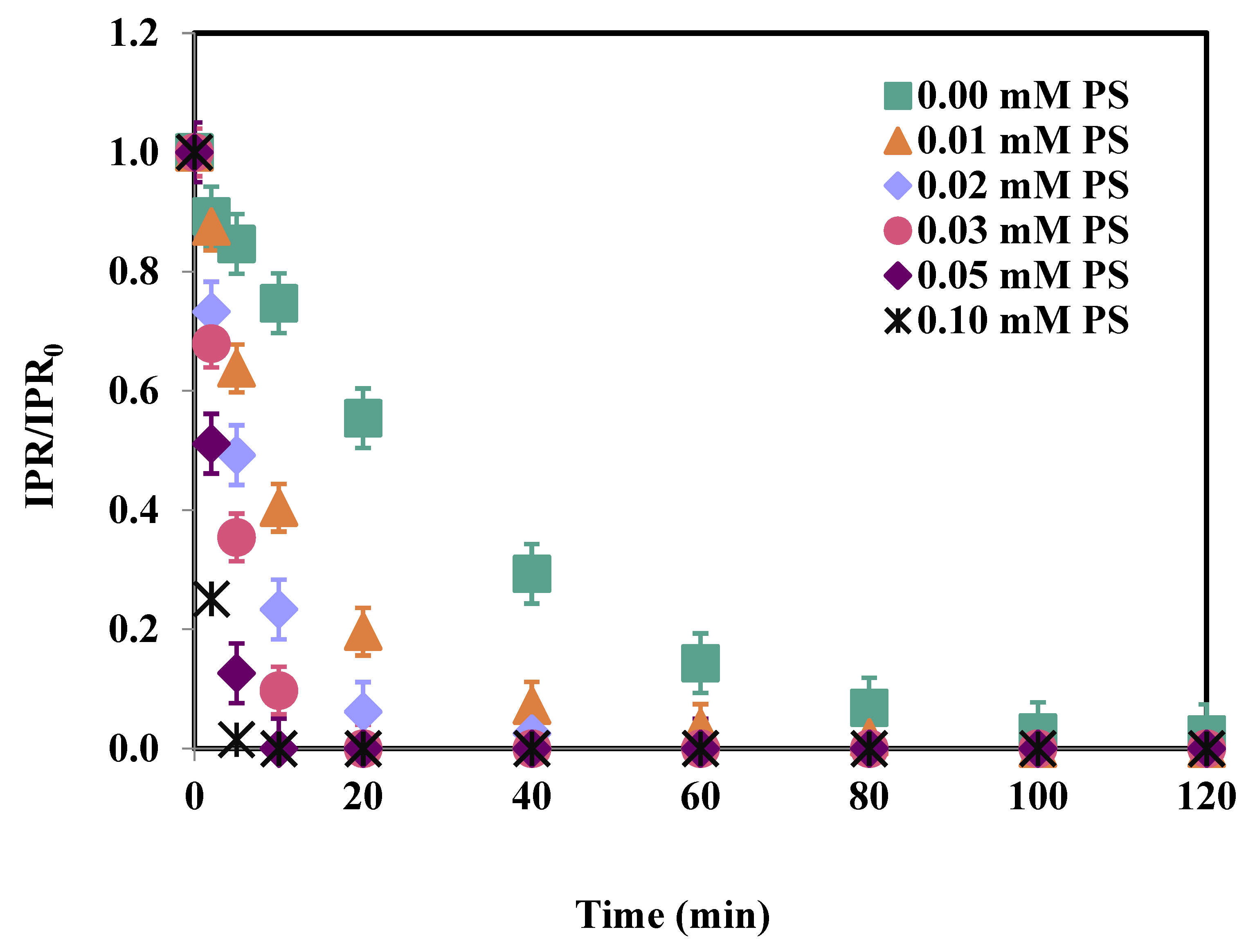
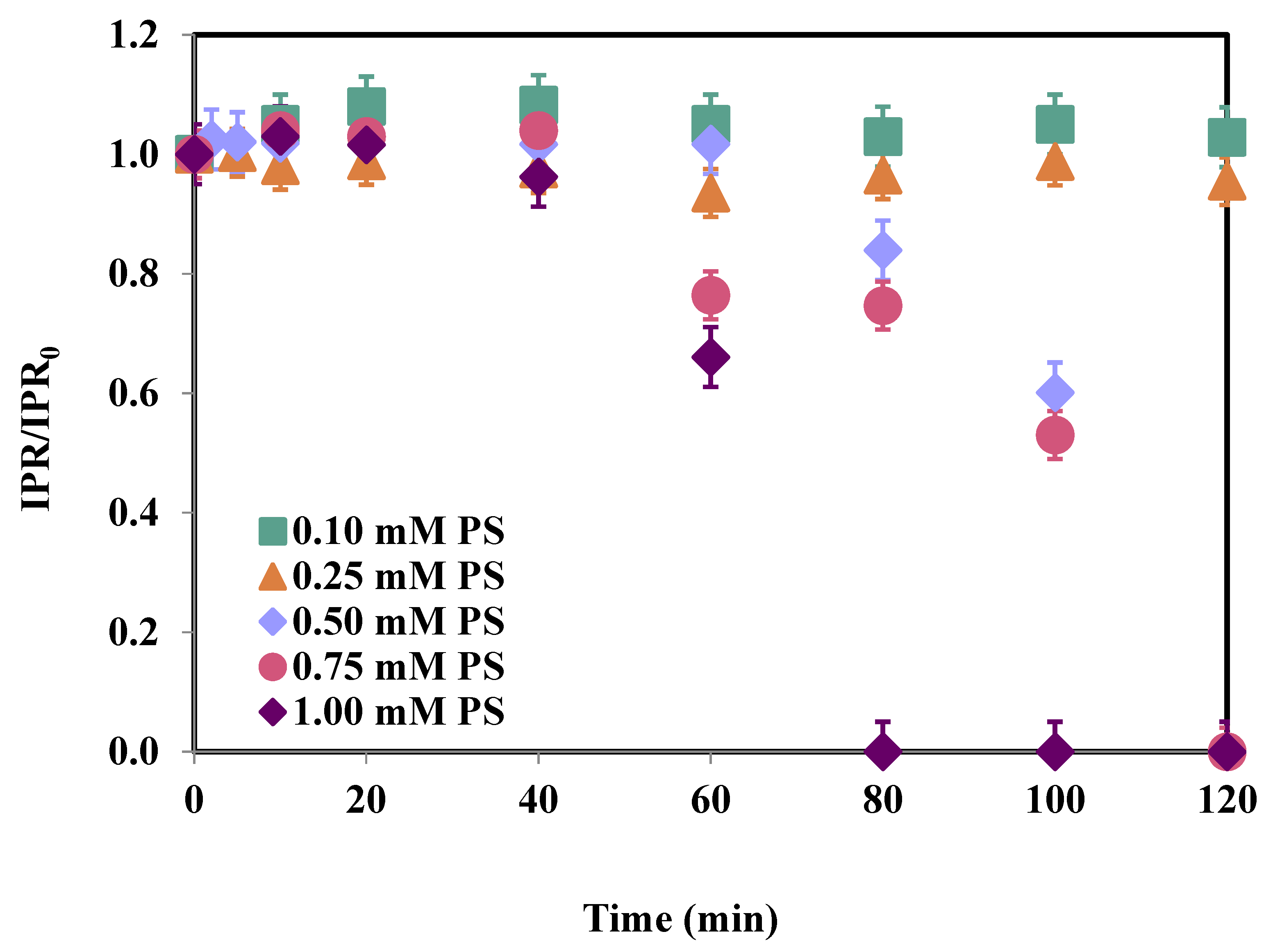
3.1. Effect of PS Concentration
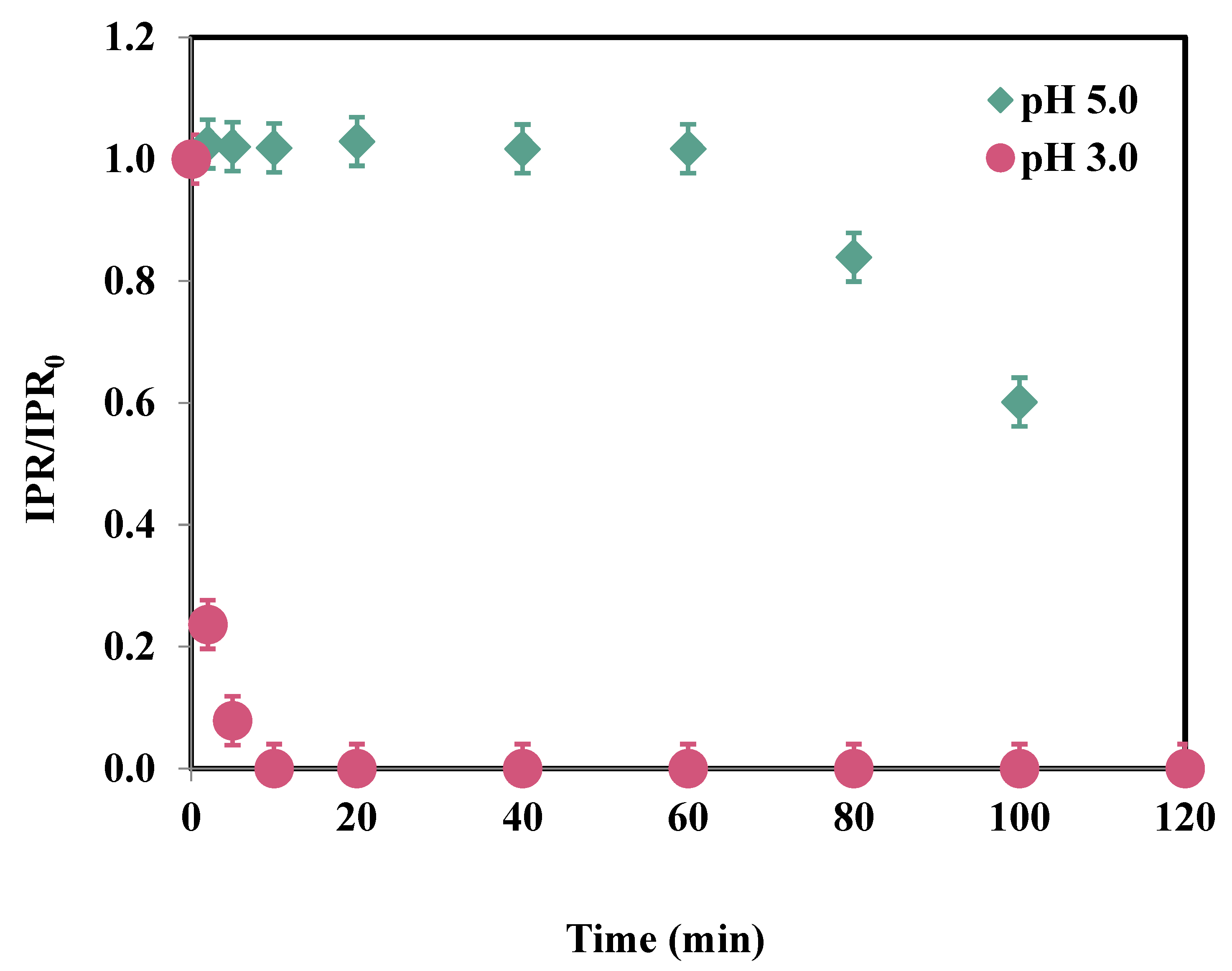
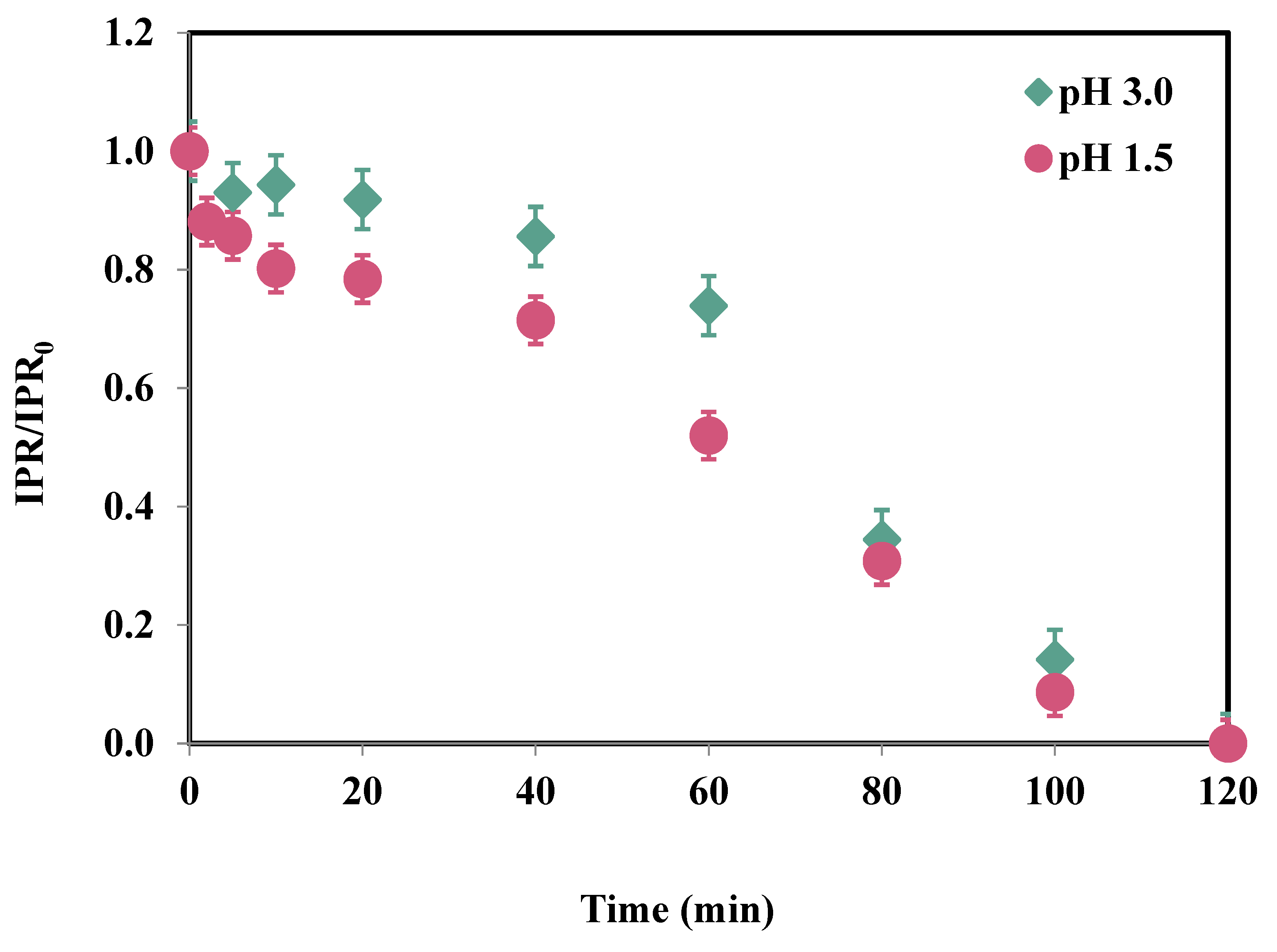
3.2. Effect of pH
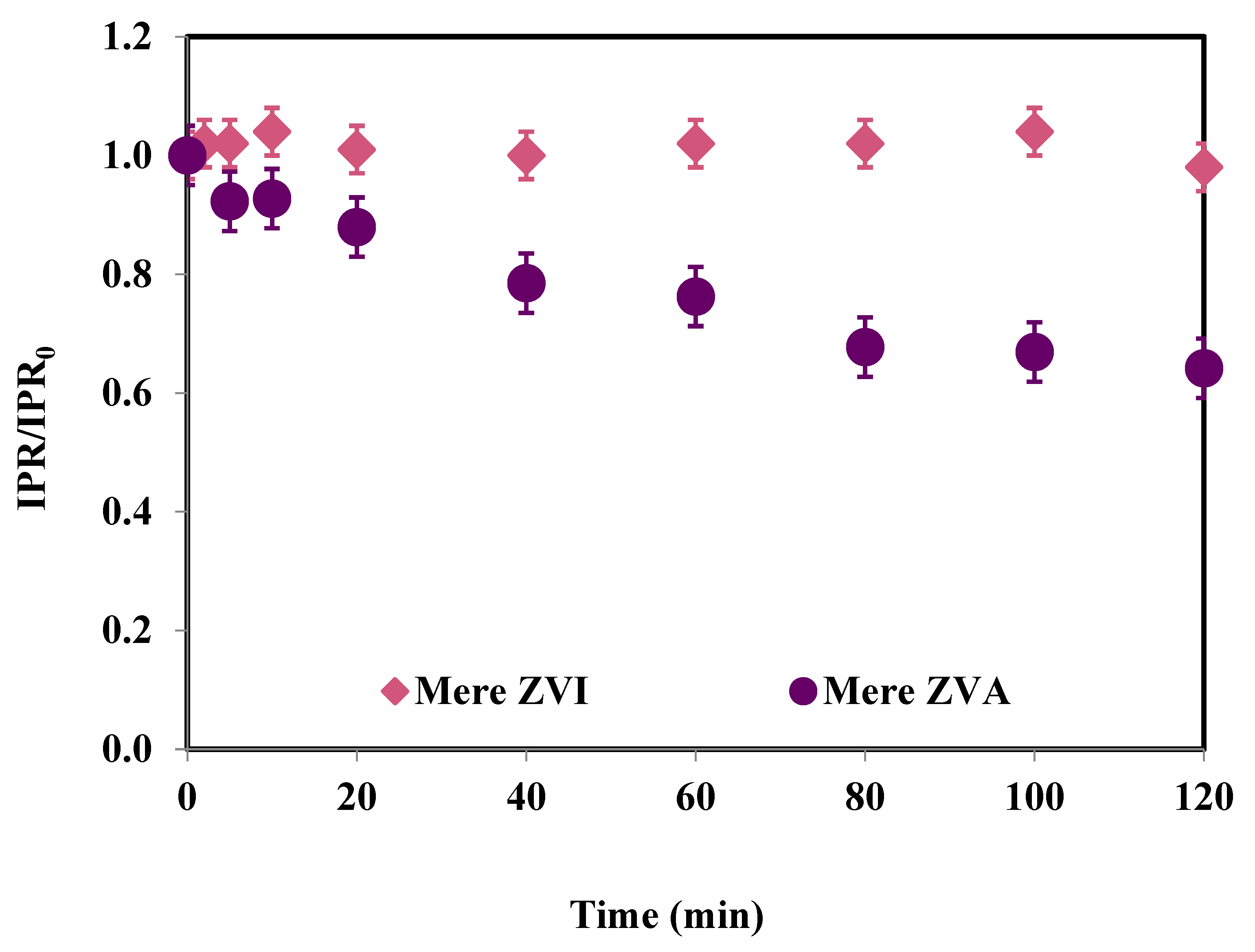
3.3. Metal (Fe, Al) Release and PS Consumption for Heterogeneous Oxidation Processes
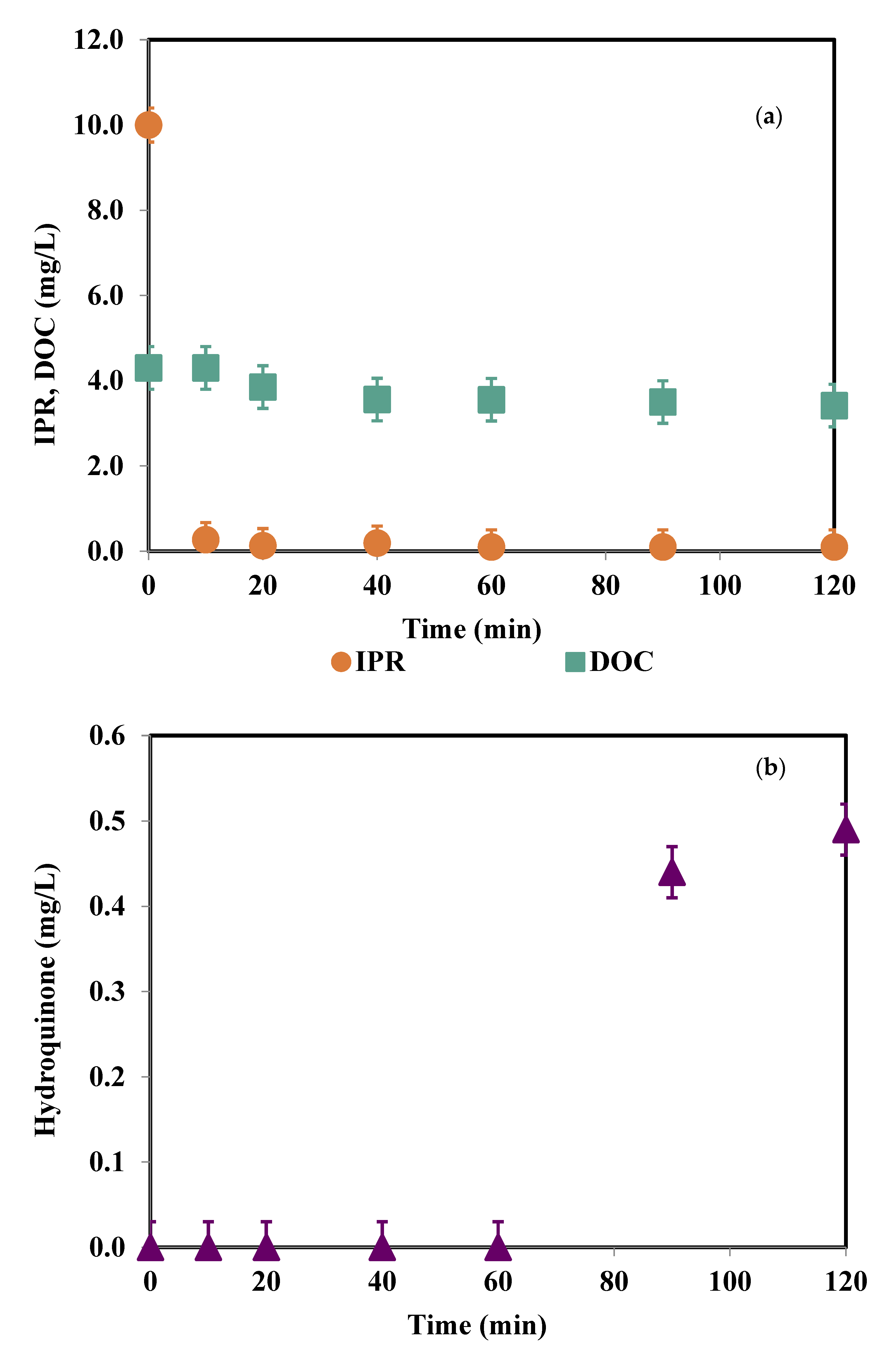
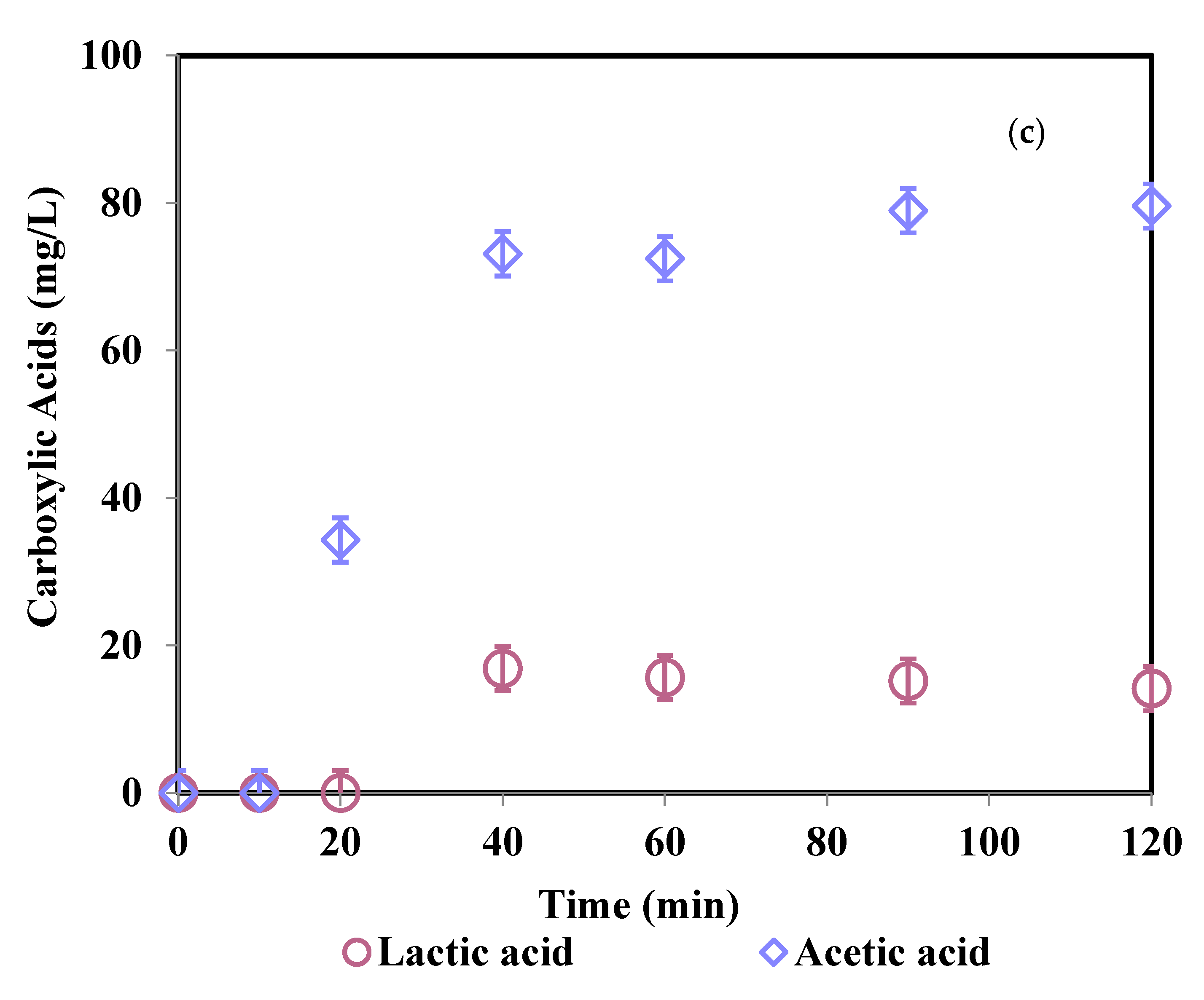
3.4. Degradation Products and Mineralization Rates
3.5. Experiments in Simulated Tertiary Wastewater
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimizu, T. Studies on the Use of Hydantoin-Related Compounds as Slow Release Fertilizers. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1986, 32, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belafdal, O.; Bergon, M.; Calmon, J.P. Mechanism of hydantoin ring opening in iprodione in aqueous media. Pestic. Sci. 1986, 17, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrioli, N.B.; Chaufan, G. Dose-independent genotoxic response in A549 cell line exposed to fungicide Iprodione. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Meng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, K.; Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, H. Development toxicity and cardiotoxicity in zebrafish from exposure to iprodione. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbalah, A.; Nakatani, N.; Sakugawa, H. Distribution, seasonal pattern, flux and contamination source of pesticides and nonylphenol residues in Kurose River water, Higashi-Hiroshima, Japan. Geochem. J. 2003, 37, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequinatto, L.; Reichert, J.M.; Dos Santos, D.R.; Reinert, D.J.; Copetti, A.C.C. Occurrence of agrochemicals in surface waters of shallow soils and steep slopes cropped to tobacco. Química Nova 2013, 36, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garbin, J.R.; Milori, D.; Simões, M.L.; da Silva, W.T.; Neto, L.M. Influence of humic substances on the photolysis of aqueous pesticide residues. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Xu, Z. Effects of fungicide iprodione and nitrification inhibitor 3, 4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate on soil enzyme and bacterial properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauret-Szczepanski, N.; Mirabel, P.; Wortham, H. Development of an SPME–GC–MS/MS method for the determination of pesticides in rainwater: Laboratory and field experiments. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, P.M.; Andrade-Vieira, L.F.; Aragão, F.B.; Ferreira, A.; Ferreira, M.F.D.S. Toxicological effects of comercial formulations of fungicides based on procymidone and iprodione in seedlings and root tip cells of Allium cepa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 21013–21021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radice, S.; Ferraris, M.; Marabini, L.; Grande, S.; Chiesara, E. Effect of iprodione, a dicarboximide fungicide, on primary cultured rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2001, 54, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blystone, C.R.; Lambright, C.S.; Furr, J.; Wilson, V.S.; Grayjr, L.E., Jr. Iprodione delays male rat pubertal development, reduces serum testosterone levels, and decreases ex vivo testicular testosterone production. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 174, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, J.M.; Shadung, J.M.; Wepener, V. Prioritizing agricultural pesticides used in South Africa based on their environmental mobility and potential human health effects. Environ. Int. 2014, 62, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission (EC). Regulation EU 2091 Concerning the Non-Renewal of Approval of the Active Substance Iprodione, in Accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning the Placing of Plant Protection Products on the Market, and Amending Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 540/2011; Official Journal of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; pp. 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhuan, R. Degradation of antibiotics by advanced oxidation processes: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 135023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Yao, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Yi, K.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Wang, D. Recent advances in photo-activated sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for refractory organic pollutants removal in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Xu, L.J. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: Formation of Hydroxyl Radical and Application. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 251–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacławek, S.; Lutze, H.V.; Grübel, K.; Padil, V.V.T.; Černík, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewil, R.; Mantzavinos, D.; Poulios, I.; Rodrigo, M.A. New perspectives for Advanced Oxidation Processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Fernández-González, C. Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Removal of Antibiotics from Water: An Overview. Water 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, S.; Cheng, M.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, Q. Iron-mediated activation of persulfate and peroxymonosulfate in both homogeneous and heterogeneous ways: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-S.; Su, Y.-C. Removal of dinitrotoluenes in wastewater by sono-activated persulfate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Su, H.-W. Identification of Sulfate and Hydroxyl Radicals in Thermally Activated Persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolthoff, I.M.; Miller, I.K. The Chemistry of Persulfate. I. The Kinetics and Mechanism of the Decomposition of the Persulfate Ion in Aqueous Medium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 3055–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical Review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (OH/O− in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dogliotti, L.; Hayon, E. Flash photolysis of per[oxydi]sulfate ions in aqueous solutions. The sulfate and ozonide radical anions. J. Phys. Chem. 1967, 71, 2511–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Shin, W.S.; Hwang, I. Activation of Persulfate by Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron (NZVI): Mechanisms and Transformation Products of NZVI. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yue, R.; Li, X.; Lei, M. Activation of persulfate by stability-enhanced magnetic gra-phene oxide for the removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 707, 135656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Liu, P.; Shao, S.; Wang, M.; Zhan, X.; Gao, S. An efficient graphene supported copper salen catalyst for the activation of persulfate to remove chlorophenols in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; He, H.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Zeng, G.; Wu, B.; He, S.; Lu, L. Insights into atrazine degradation by persulfate activation using composite of nanoscale zero-valent iron and graphene: Performances and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.-Q.; Li, C.; Gao, N.-Y.; Yin, D.-Q. Persulfate activation by nano zero-valent iron for the degradation of metoprolol in water: Influencing factors, degradation pathways and toxicity analysis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20991–20999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.; Khatri, J.; Singh, T.A.; Gandhimathi, R.; Ramesh, S. Review of zero-valent aluminium based water and wastewater treatment methods. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.-Y.; Kang, S.-G.; Chiu, P.C. Degradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3464–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-W.; Park, J.-M.; Park, H.-S.; Yoon, C. Oxidation of polyvinyl alcohol by persulfate activated with heat, Fe2+, and zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Alaton, I.; Olmez-Hanci, T.; Korkmaz, G.; Sahin, C. Removal of iopamidol, an iodinated X-ray contrast medium, by zero-valent aluminum-activated H2O2 and S2O82−. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 318, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, B.; Ucun, O.K.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Olmez-Hanci, T. UV-C-activated persulfate oxidation of a commercially im-portant fungicide: Case study with iprodione in pure water and simulated tertiary treated urban wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karci, A.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Bekbolet, M.; Ozhan, G.; Alpertunga, B. H2O2/UV-C and Photo-Fenton treatment of a nonylphenol polyethoxylate in synthetic freshwater: Follow-up of degradation products, acute toxicity and genotoxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 241, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucun, O.K.; Montazeri, B.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Olmez-Hanci, T. Degradation of 3,5-dichlorophenol by UV-C photolysis and UV-C-activated persulfate oxidation process in pure water and simulated tertiary treated urban wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuger, J. Pesticides in stream water within an agricultural catchment in southern Sweden, 1990–1996. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 216, 227–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatis, N.; Hela, D.; Konstantinou, I. Occurrence and removal of fungicides in municipal sewage treatment plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessergenev, V.; Mateus, M.; Morgado, I.; Hantusch, M.; Burkel, E. Photocatalytic reactor, CVD technology of its preparation and water purification from pharmaceutical drugs and agricultural pesticides. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Alvarez, B.; Villegas-Guzman, P.; Peñuela, G.A.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Degradation of a Toxic Mixture of the Pesticides Carbofuran and Iprodione by UV/H2O2: Evaluation of Parameters and Implications of the Degradation Pathways on the Synergistic Effects. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassalle, Y.; Jellouli, H.; Ballerini, L.; Souissi, Y.; Nicol, É.; Bourcier, S.; Bouchonnet, S. Ultraviolet–vis degradation of iprodione and estimation of the acute toxicity of its photodegradation products. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1371, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwack, W.; Bourgeois, B.; Walker, F. Fungicides and photochemistry photodegradation of the dicarboximide fungicide iprodione. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 2993–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S. Degradation of aniline with zero-valent iron as an activator of persulfate in aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3502–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Du, X. Degradation of p-chloroaniline by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messele, S.A.; Bengoa, C.; Stüber, F.E.; Giralt, J.; Fortuny, A.; Fabregat, A.; Font, J. Enhanced Degradation of Phenol by a Fenton-Like System (Fe/EDTA/H2O2) at Circumneutral pH. Catalysts 2019, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Water Quality—Application of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)—Part 2: Determination of 62 Elements; 17294-2; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Villegas, E.; Pomeranz, Y.; Shellenberger, J. Colorimetric determination of persulfate with alcian blue. Anal. Chim. Acta 1963, 29, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokare, A.D.; Choi, W. Zero-valent aluminum for oxidative degradation of aqueous organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7130–7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Alaton, I.; Olmez-Hanci, T.; Ozturk, T. Effect of inorganic and organic solutes on zero-valent aluminum-activated hydrogen peroxide and persulfate oxidation of bisphenol A. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34938–34949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Ji, Y.; Kong, D.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, X. Simultaneous removal of bisphenol A and phosphate in zero-valent iron activated persulfate oxidation process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Alaton, I.; Olmez-Hanci, T.; Dogan, M.; Ozturk, T. Zero-valent aluminum-mediated degradation of Bisphenol A in the presence of common oxidants. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2455–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temiz, K.; Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I. Zero-valent iron-activated persulfate oxidation of a commercial alkyl phenol polyethoxylate. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing surface corrosion of zero-valent aluminum (ZVAl) and electron transfer process for the degradation of trichloroethylene with the presence of persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; Mackay, A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Organic Contaminant Destruction Based on the Fenton Reaction and Related Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni Soon, A.; Hameed, B. Heterogeneous catalytic treatment of synthetic dyes in aqueous media using Fenton and photo-assisted Fenton process. Desalination 2011, 269, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, G.; Jorfi, S.; Zarezade, V.; Khatebasreh, M.; Mehdipour, F.; Ghanbari, F. 4-Chlorophenol degradation using ultrasound/peroxymonosulfate/nanoscale zero valent iron: Reusability, identification of degradation intermediates and potential application for real wastewater. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Gao, N.; Li, C.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, L. Zero-valent iron (ZVI) activation of persulfate (PS) for oxidation of bentazon in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Chen, S. Enhanced oxidation of 4-chlorophenol using sulfate radicals generated from zero-valent iron and peroxydisulfate at ambient temperature. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, B.; Liu, W.; Lin, K.; Feng, J. Oxidative removal of acetaminophen using zero valent aluminum-acid system: Efficacy, influencing factors, and reaction mechanism. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Cao, B.; Lin, K.; Gan, J. Oxidative removal of bisphenol A using zero valent aluminum–acid system. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1872–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wan, J.; Ma, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y. New insights into the role of zero-valent iron surface oxidation layers in persulfate oxidation of dibutyl phthalate solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 250, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittke, K.; Hajimiragha, H.; Dunemann, L.; Begerow, J. Determination of dichloroanilines in human urine by GC–MS, GC–MS–MS, and GC–ECD as markers of low-level pesticide exposure. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 755, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turci, R.; Barisano, A.; Balducci, C.; Colosio, C.; Minoia, C. Determination of dichloroanilines in human urine by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry: Validation protocol and establishment of Reference Values in a population group living in central Italy. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2621–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Gao, X.; Geng, J.; Li, S.; Wu, G.; Ren, H. Degradation of three nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs by UV/persulfate: Degradation mechanisms, efficiency in effluents disposal. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zeng, Y.; He, D.; Pan, X. Application of iron-based materials in heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

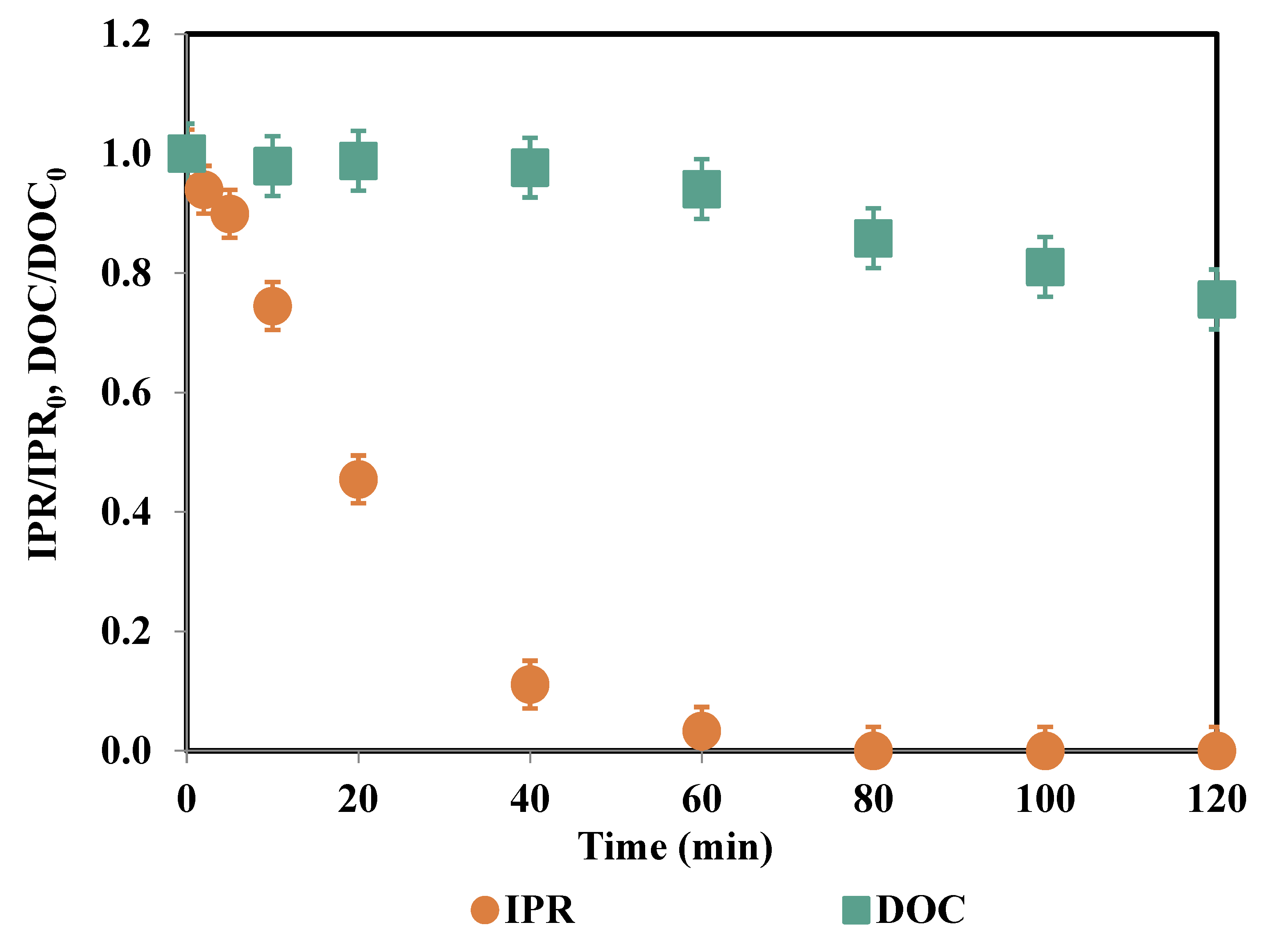
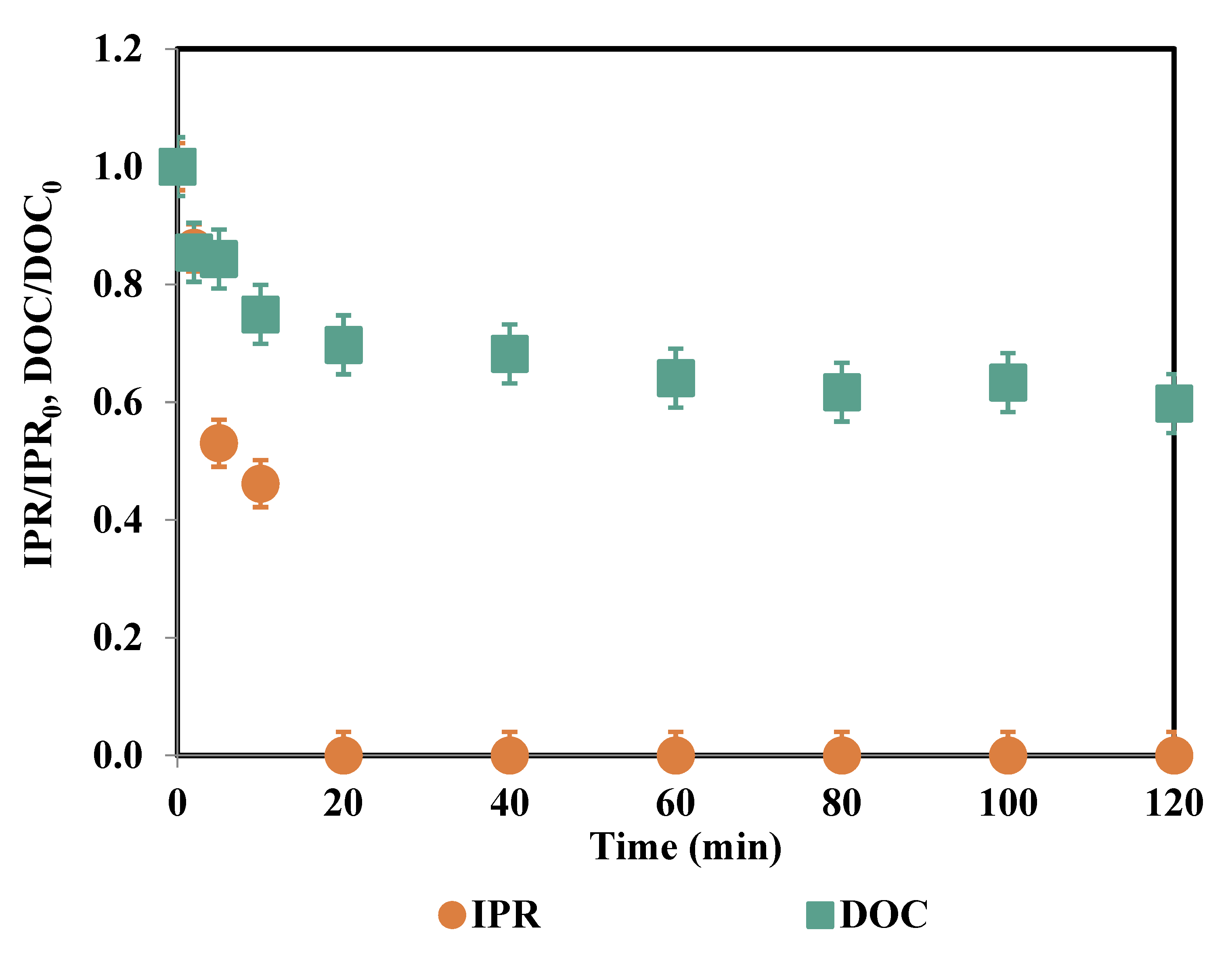

| Time (min) | IPR (mg/L) | Fe (μg/L) | PS Consumption (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.16 | <10 | 10 |
| 10 | 0 | <10 | 13 |
| 30 | 0 | <10 | 20 |
| 60 | 0 | 88 | 68 |
| 120 | 0 | 129 | 95 |
| Time (min) | IPR (mg/L) | Al (μg/L) | PS Consumption (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1.90 | - | - |
| 10 | 1.87 | 299 | 5 |
| 30 | 1.79 | 324 | 7 |
| 60 | 1.49 | 353 | 10 |
| 120 | 0 | 499 | 15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montazeri, B.; Koba-Ucun, O.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Olmez-Hanci, T. Iprodione Removal by UV-Light-, Zero-Valent Iron- and Zero-Valent Aluminium-Activated Persulfate Oxidation Processes in Pure Water and Simulated Tertiary Treated Urban Wastewater. Water 2021, 13, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121679
Montazeri B, Koba-Ucun O, Arslan-Alaton I, Olmez-Hanci T. Iprodione Removal by UV-Light-, Zero-Valent Iron- and Zero-Valent Aluminium-Activated Persulfate Oxidation Processes in Pure Water and Simulated Tertiary Treated Urban Wastewater. Water. 2021; 13(12):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121679
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontazeri, Bahareh, Olga Koba-Ucun, Idil Arslan-Alaton, and Tugba Olmez-Hanci. 2021. "Iprodione Removal by UV-Light-, Zero-Valent Iron- and Zero-Valent Aluminium-Activated Persulfate Oxidation Processes in Pure Water and Simulated Tertiary Treated Urban Wastewater" Water 13, no. 12: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121679
APA StyleMontazeri, B., Koba-Ucun, O., Arslan-Alaton, I., & Olmez-Hanci, T. (2021). Iprodione Removal by UV-Light-, Zero-Valent Iron- and Zero-Valent Aluminium-Activated Persulfate Oxidation Processes in Pure Water and Simulated Tertiary Treated Urban Wastewater. Water, 13(12), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121679