Abstract
The study was aimed at the determination of the dynamics of spatial distribution of moisture front, caused by pointwise application of water under conditions of high pressure. This was effected through a series of simulations of water injection to a porous material with particle size distribution corresponding to that of sand. The study was composed of six independent experimental series in which the sand monolith was supplied with water doses of 250, 500, 750, 1000, 1250, and 1500 cm3 under pressure (4 bar). At the same time, measurements of volumetric moisture were conducted with the use of TDR sensors, which were positioned within the soil in a regular grid pattern. It was demonstrated that the primary cause of water movement at the moment of injection is the pressure potential gradient of water molecules. The spatial reach of moisture change in relation to the injected water dose was also defined. It was also observed that in the course of water injection there is a risk of disturbing the structure of the porous material. The correctness of the adopted method was verified through the calculation of the water balance.
1. Introduction
Fresh water is a fundamental element of the natural environment and ensures the continuity of life on Earth [1]. It is estimated that the current annual world water consumption is approximately four thousand km3, 16.7% of which is used by industry, 15.6% is household consumption, and as much as 67.7% is used in agriculture [2]. Therefore, special attention should be paid to the segment related directly to food production [3]. Water consumption in agriculture relates a.o. to the use of irrigation systems, and a measurable effect of their use is an increase in the level of yields [4,5,6]. For this reason, in open field cultivations there is an extensive application of such irrigation systems as mobile or fixed sprinkler systems, which are used globally on an area of approximately 35 million ha [7]. An increasing popularity is also observed in the case of water-saving drip lines, for which the area of use in 2030 will be doubled relative to that of 2000 [8]. Selected features of those irrigation systems became the base point for a concept of an injection irrigation system for crop plants, which is being realized within the framework of the project “Mobile system of injection irrigation and fertilisation meeting the individual requirements of the plant” by the consortium Mobile Irrigation and Fertilisation (MSINiN) [9,10,11]. The concept consists in subsurface application of a specific dose of water, within soil space containing plant root systems, which is characteristic of the subsurface drip line. In addition, the application of water is to proceed in a mobile manner, and that will allow the use of the system on the largest possible area, which is an advantage of mobile sprinkler irrigation systems (Figure 1) [12]. According to this idea, a one-time injection for one plant should last several seconds at maximum. Such an approach to irrigation is in conformance with the idea and solutions of “precision agriculture” [13,14]. One of the issues that should be addressed during the research and development work on this concept is to determine the form of the body of moisture that is formed during pointwise application of water to soil under high pressure of the liquid.
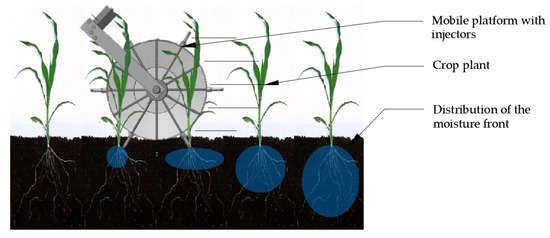
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of the concept of a platform for injection irrigation with a possibility of fertilization [9].
1.1. Distribution of Soil Moisture Dynamics during Injection Irrigation
The fundamental difference between the process of injection irrigation and the irrigation systems used so far is the method of water application and the dynamic of an increase of soil moisture within the root system of the crop plant. In the case of the conventional methods of irrigation, the phenomenon of moisture dynamics can be defined as water movement within the aeration zone, caused primarily by the heterogeneity of the sum of gravity potential and pressure equivalent of soil water potential. The gravity potential is related with the effect of gravity on water, while the pressure equivalent is defined by the difference between pressure in water and the atmospheric pressure in the environment of the water particle (so-called matrix or pressure potential) [15,16]. The unique concept of injection irrigation relates to the case when a dose of water is applied to soil in the conditions of a high hydraulic pressure (at the intensity of several hundreds of cm3 of water within a few seconds). Therefore, the dynamics of volumetric moisture in the soil monolith is not determined by the gravity gradient and the pressure equivalent, but solely by the hydraulic pressure of the injected liquid [17]. After the process of injection, the hydraulic pressure disappears and water movement takes place as a result of the difference in the total potential composed mainly of the gravity potential and the pressure equivalent.
Whereas the problem of moisture dynamics caused by the gradient of the sum of the potentials mentioned above has been described by the Richards equation, whose basis is the description of the soil medium by means of physical and empirical parameters [18], the solution is arrived at using a method of finite differences or elements, with the use of explicit or implicit schemes [19,20]. In the case of water application to soil under pressure, there are many aspects which no equation describing water movement in soils (the Richards equation included) takes into account. These include, e.g., the appearance of water potential resulting from hydraulic pressure, soil structure deformation, the necessity of describing the phenomenon within a small space, i.e., the necessity of dividing the entire space into small elements and also with a very short time step. Taking the above assumptions into account makes it difficult to maintain stability in a mathematical model.
In addition, the character of moisture changes caused by injection irrigation depends on the kind of soil into which the liquid is applied. Distinct differences were demonstrated in water distribution in sandy and loamy media [21]. Porous media with various particle size distributions are characterised by various physical parameters such as porosity, structure, filtration coefficient, hydraulic conductivity, or retention capacity [22]. All of those physical properties have a direct impact on the parameters which are used in the numerical description of water movement in soil [23]. Another important variable is the pressure at which the liquid is applied to the ground. As mentioned earlier, one of the components of the total potential of water molecules is the pressure potential. The higher the gradient of the potential, the more dynamic the character of the changes [24]. The dose of applied water is still another important variable. In the case of the drip line systems, the range of moisture changes is proportional to the water dose applied [25].
In the study presented here the experiments were conducted on a physical model. Therefore, before the actual experiment, we should take into account the issues defined in the project as standards of injection irrigation [9]. These aspects are presented in the next section.
1.2. Standards of Injection Irrigation of Field Cultivations
1.2.1. Plant Spacing in Cultivations Dedicated for Injection Irrigation
The functionality of the mobile irrigation machine consists in, among other things, that the modules of the machine move between plant rows and supply water, through injectors, into the vicinity of plant roots systems (Figure 1). This means that this irrigation system will be dedicated only for specific plant species, grown in systematic spacing, such as vegetables or root crops and excluding cereals. The crop plant species selected within the scope of the MSINiN project include, e.g., species of leek, root celeriac, or sugar beet [9]. In the cultivation of those species, plant spacing depends on a number of factors, such as the time of planting or sowing—early/late cultivars, area dedicated for the cultivation, possibility of using agricultural machinery. In the case of leek, plants can be spaced within rows at distances from 10 to as much as 20 cm, depending on the cultivar (early-late), with row spacing being 25–50 cm [26,27,28]. In the case of celeriac, plant spacing within rows is 30–50 cm, depending on the cultivar (strong-weak), with row spacing of 30–50 cm [29,30]. Examples of plant spacing within rows of sugar beet are 15-20-25-30-35 cm, optimal yields being obtained at plant spacing of 15 cm. Row spacing in sugar beet cultivation is 35 cm [31]. Based on the above, a widely used row spacing is 45 cm and plant spacing is 20 cm. Therefore, it was decided that 40 cm × 45 cm should be sufficient dimensions for the physical model (plan view).
1.2.2. Irrigation Dose in the Case of Injection Irrigation
To determine the dose of applied water, reference should be made to the conventional description of irrigation doses. Generally, one-time irrigation dose depends on the water requirements of the plant, irrigation frequency, the soil capacity for water retention, and irrigation techniques [32,33]. In practice, a single irrigation dose in the case of a sprinkler irrigation system varies from 10 to 30 mm [33]. However, from the aspect of water economy, a technique closer to injection irrigation is the use of subsurface drip lines. One-time irrigation doses in the case of such irrigation systems amount to 5–15 mm. This is a starting point for the determination of water doses for injection application, but one should keep in mind the fundamental difference relating to the irrigation time which in the case of drip lines is several hours, and in the case of the injection method is several seconds. For this reason, one should not attempt direct comparison of the two irrigation techniques.
The aspect of individualisation of water application for a specific plant means that the unit of water dose is not the water column height but the water dose volume which can be expressed with the following formula:
where: —water dose volume in the case of injection irrigation (cm3), —water dose determined as liquid column height in the case of irrigation using a sprinkler system or a drip line (mm H2O), —surface area per a single plant (cm2), 10—unit correction number (−).
Surface area per a single plant was established based on the shorter spacing between plants. The area of 20 cm× 20 cm was adopted for the calculations. Assuming water doses at the level of the previously described irrigation systems, i.e., 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 mm, water doses for injection irrigation, for the above plant spacing, and thus for a single plant, amount to 200, 400, 600, 800, 1000, 1200 cm3, respectively.
1.2.3. Depth of Water Injection Relative to Ground Surface
In order to determine the depth of the injection irrigation, reference should again be made to the technique of applying water via a subsurface drip line. Installation depth of subsurface drip lines varies from 5 to as much as 30 cm and depends on the kind of soil, crop plant species, and cultivation technique (flat or in ridges) [34,35,36]. This is related with the fundamental condition in the determination of the depth of drip line installation, i.e., avoidance of water evaporation from the soil [37]. In addition, consideration should be given to the reach of the rhizosphere, i.e., the zone of the soil ecosystem containing plant roots. As an example, after 60 days from leek planting, the main root mass of the plants is situated at a depth of 15–45 cm [38]. However, such information applies to a specific case (plant, soil, cultivation technique, irrigation system). In turn, in a study on the growth of the root mass of maize in the conditions of pot experiments, it was demonstrated that the reach of the root system depends on soil compaction and on irrigation frequency. As an example, maize plants watered at 3-day intervals were characterised by almost double the reach of the root system compared to plants watered every day [39]. When determining the depth of injection, one should take into consideration also the engineering recommendations which relate, among other things, to the strength of ground resistance that must be overcome by the injector during the penetration beneath the ground surface. Taking the above into account, it was decided that, within the scope of the experiment, water would be injected at the depth of 10 cm.
1.3. Research Objective
The objective of the study was the identification of the dynamics of the front of volumetric moisture during pointwise application of water to the soil profile under pressure. In addition, the scope of the study included the verification of the correctness of results obtained experimentally, with the use of a calculation of the water balance. The results obtained from the present work can provide a basis for verification and validation of a numerical model describing water movement in a porous medium under injection irrigation conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scope and Run of the Experiment
To analyse the dynamics of volumetric moisture caused by injection application of water to the porous medium, a series of experiments were conducted on the laboratory scale. The experiments were conducted at the Laboratory of Soil Physics and Modelling of Environmental Processes, Institute of Environmental Protection and Management, Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences. A physical model was prepared, the main elements of which were a sand monolith, a water injection device, and sensors of volumetric moisture (Figure 2). The monolith had the form of a cuboid with dimensions of 45 cm × 40 cm × 30 cm. The base and the side walls of the monolith were limited by impermeable barriers, and the upper surface was exposed to contact with atmospheric air. The particle size distribution of the mineral parts of the material used for the construction of the monolith was determined with the sieve method, and according to the USDA classification it corresponded to that of sand (100% of sand fraction, 0.050–2.000 mm) [40]. Such a choice of material ensured the homogeneity of the system. The bulk density of the monolith was 1.70 g∙cm−3, and porosity was 0.425 (–) [41].
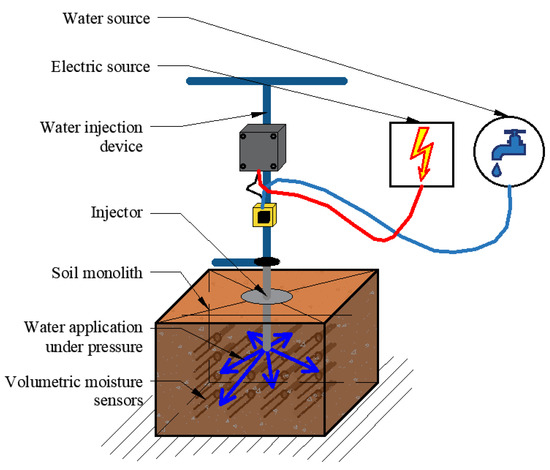
Figure 2.
Schematic presentation of the experiment setup.
Water application to the porous medium under high pressure was conducted with the use of a unique device developed by the MSINiN project team [11,42]. The device allows precise dosage of water with the accuracy of ±10% of the volume of the injected liquid [43], at a pressure corresponding to the conditions of the water supply network. The key element of the device is the injector, with length of 20 cm, outer diameter of 1 cm, and inner diameter of 0.5 cm. On the side of the injector, 1 cm from its tip, there is the nozzle hole with diameter of 0.5 cm. At distances of 5, 10, 15, and 20 cm from the nozzle there are incisions meant to help when inserting the injector to a desired depth. The device also provides the intensity of liquid outflow from injector nozzle of 144 cm3∙s−1 (±10%) and under pressure of 4 bar, which is in conformance with the concept of injection irrigation presented in the introduction.
The design of the experiment in every trial included: preparing the sand material (drying), installing sensors monitoring the status of water content, pouring sand material, inserting the injector to the preset depth (10 cm), performing the injection and monitoring of volumetric moisture (measurement period: 12 h). The experiment was conducted in six independent replicates. Each replicate involved the injection of one of the following water volumes—250, 450, 750, 1000, 1250, and 1500 cm3. The dimensions of the monolith, injection depth, and the volume of the applied water doses with the required outflow intensity were determined on the basis of the theoretical considerations presented in the introduction and verified in pilot experiments.
2.2. Monitoring of Volumetric Water Content
The main requirements imposed on the choice of measurement technique were the small dimensions of the sensor (to minimise the effect of the sensors on the conditions of water filtration) and the highest possible frequency of measurements (water injection is a process with a dynamic character). These conditions can be met by a number of measurement techniques: neutron, gammascopic, capacitive, TDR (time domain reflectrometry) or FDR (frequency domain reflectometry) technique, resistance, and telemetric [44,45,46,47,48]. In the experiments conducted within the scope of the study, the monitoring of volumetric moisture was performed with the use of sensors type LP/ms (laboratory probe/moisture salinity) which make use of the TDR technique [49,50,51,52]. The sensors are characterised by a high correlation coefficient (>0.9) in relation to the basic technique of moisture determination—the gravimetric method [53,54]. Correct operation of TDR sensors has also been demonstrated in measurements in sandy soils, i.e., such as those used in the experiment described herein [55].
When conducting experiments, apart from the choice of the type of sensors, one should also determine the optimal frequency of observations. The process of injection irrigation is dynamic in character. It was determined that the application of the dose of 1000 cm3 of water to the soil profile lasts about 7 s. In addition, the filtration coefficient of sand is in the range from 10−6 to 10−3 m∙s−1 [56]. For this reason it was decided that the measurements would be taken at the highest possible frequency for apparatus calibrated for those parameters, i.e., at 30-s intervals.
In the case of laboratory and field experiments aimed at the identification of the dynamics of moisture caused by the operation of an irrigation system, an aspect that must be determined is the spacing of moisture sensors. The optimum spacing of the sensors is one that ensures the highest possible number of such measurement points. This guarantees more accurate identification of the process. At the same time, the number of sensors installed in the sand should not have any impact on water movement in the porous medium. In the case of using a sprinkler irrigation system, it is sufficient to analyse the vertical direction of water movement [57,58]. The vertical orientation (1D) plays a particularly important role in moisture dynamics caused by the operation of sprinkler systems, because the wetting of the soil profile takes place through its top surface, in a descending movement. Whereas, in the case of point-wise application of water, like with the use of drip lines, 2D descriptions are employed [59,60]. For such cases, analyses are performed especially for a vertical section through the soil profile, and through the main plant root mass [61,62]. In such cases it is assumed that water movement relative to the vertical axis, along which the emitter is situated, is symmetrical (under the condition that the soil structure is homogeneous).
The above assumptions, however, are not sufficient in the case of water injection under high pressure, where the outflow of water is aimed in any horizontal direction. It is then necessary to take into account the point of insertion of the injector nozzle and also the orientation and sense of injection. The adopted solution was determined in reference to the space presented in Figure 3. In the analysed space there is a point 0, which is the origin of the XYZ system, and point 0i—the origin of the XiYiZi system, which is the location of the tip of the injector nozzle oriented along the 0Yi axis. The fundamental condition is that the moisture sensors cover the entire space XYZ, dividing it into equal elementary volumes. Thus, the space was divided into 5 cm cubes. This creates the possibility of analysing the volumetric moisture in every direction (not only in directions 0iXi, 0iYi, and 0iZi), and also allows the construction of water balance which verifies the correctness of the adopted method. In relation to the above, in the experiment conducted within the scope of this study the LP/ms sensors were distributed in a regular grid. The adopted solution can be compared to the grid of the calculation area in the finite difference method. It is a numerical method used for the solution of differential equations [63], such as the Richards equation, used for the description of soil water movement [64].
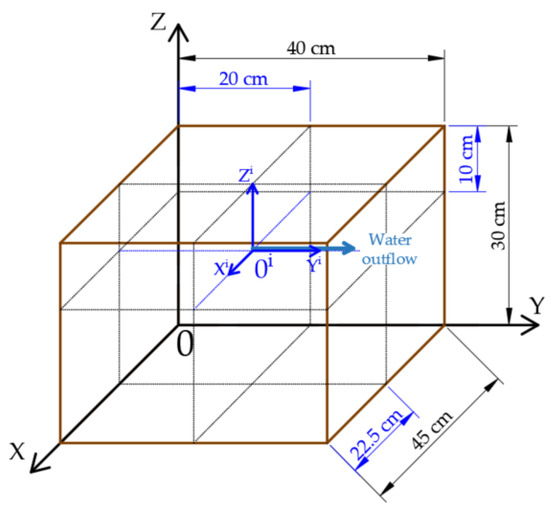
Figure 3.
The space of the physical model in dimetric projection.
In parallel, the distances between the LP/ms sensors were determined. It was assumed that at the initial stage of injection application of water to the porous medium, a spherical moisture front is formed, its centre point being situated at the point of water outflow from the injector. It was also assumed that within the radius of the sphere the pores are fully saturated with water. Therefore, the radius of such a sphere is:
where: —radius of the sphere (cm), —volume of applied dose (cm3), —moisture of the solid after injection, moisture in the saturated zone for coarse-grained sand is = 0.425 cm3∙cm−3 [65], —initial moisture, = 0.1 cm3∙cm−3.
With the minimal water dose of 250 cm3, the radius of the sphere is 5.7 cm, while for the maximal dose of 1500 cm3, the radius is 10.3 cm. In relation to the above it was assumed that, for the analysed water doses, changes in moisture should be expected at distances of approximately 5–15 cm from the injection point. For this reason, in the adopted distribution of the TDR sensors the distances between neighbouring sensors were 5 cm.
A potential shortcoming of the adopted solution is the risk of an excessive interference of the LP/ms sensors with the structure of the model. The volume of the body of a TDR sensor type LP/ms is about 0.027 cm3 [66]. The adoption of sand monolith dimensions of 40 cm × 45 cm × 30 cm and the division of the model into elementary volumes in the form of cubes with dimensions of 5 cm × 5 cm × 5 cm resulted in 432 sensors that should be placed within the model. The resultant total volume of the sensors relative to the entire volume of the model would be 0.026%. However, symmetry of moisture distribution in planes normal in relation to axis 0Yi was assumed, due to which the number of sensors was reduced. Such an assumption is typical in the study of the spatial and temporal distribution of moisture during the operation of drip lines [21]. The distribution of the sensors was therefore simplified, which is presented in Figure 4. The figure presents also the division of the monolith into columns (along axis 0X), rows (along axis 0Y), and layers (along axis 0Z). The localization of individual spaces in relation to the assigned axis is very important. As an example, the spaces situated along a horizontal line identical with the direction of water injection (axis 0Yi) were also presented. The centre points of volumes h, g, f, e are situated at distances of 17.5, 12.5, 7.5, and 2.5 cm from the point of injection, and distributed in the direction of water outflow from the injector, and points d, c, b, a at distances of 2.5, 7.5, 12.5, 17.5 cm, respectively, and oriented in the opposite direction.
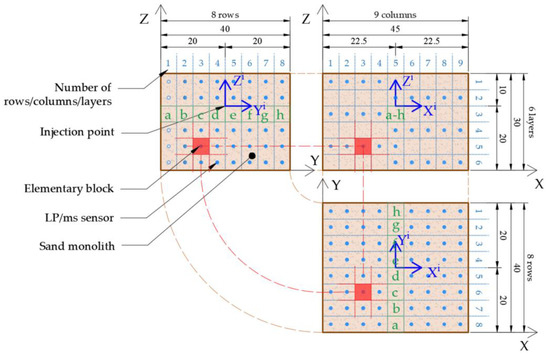
Figure 4.
Schematic of the sensor distribution within the physical model and the division of the sand monolith into columns, rows, and layers. Dimensions in centimetres.
The proposed TDR sensors distribution allowed the visualisation of the spatial layout of volumetric moisture at any moment in time. The surface distributions were generated in the program Surfer®10 [25], on the basis of 48, 54 (vertical planes), and 72 (horizontal plane) measurement points. Between the indicated points, the values of volumetric moisture were interpolated with the kriging method. It is a geostatistical method of interpolation which was applied a.o. for the presentation of changes of volumetric moisture in selected sections with the use of a drip line [67]. Kriging is also used in the monitoring of moisture changes caused by the operation of sprinkler irrigation systems [68].
2.3. Water Balance
One of the methods of verifying the accuracy of measurement data obtained from a physical model is to perform calculations aimed at the analysis of water balance. Calculations of the volume of water in the sand monolith were performed on the basis of measurements of volumetric moisture, with the use of the TDR technique, within representative points of the elementary volumes [45]. The basis for the assumption of the water balance construction is the law of conservation of mass expressed by the continuity equation. The law relates to, among other things, the physical interactions within an isolated system—such as the physical model analysed in this study. Irrespective of the intensity of changes on the boundaries and within the analysed area, the mass of the system remains constant [69,70]. Correctness of the water balance not only informs about the goodness of the adopted experimental assumptions, but also constitutes the basis for the analysis of stability and convergence of numerical computations allowing the description of water movement in a porous medium [71,72,73]. Applying the law of conservation of mass to the process of injection—the volume of water supplied to the porous medium should be related to an increase in the readings of volumetric moisture. The current volume of water in a monolith can be calculated on the basis of knowledge of moisture dynamics:
where: —current volume of water in porous monolith at moment (cm3), —elementary i-th volume, representative for TDR sensor type LP/ms (cm3), —volumetric moisture of i-th volume at moment (cm3∙cm−3), —number of elementary volumes of the monolith (−).
Knowing the current total volume of water in the porous monolith at moment and at moment we can calculate the change in that volume within time . It is expressed by the formula:
where: —change of water volume in the physical model (cm3), —volumetric moisture in i-th volume at moment (cm3∙cm−3), —volumetric moisture in i-th volume at moment (cm3∙cm−3), remaining symbols as in the formula above.
In the case of injection irrigation, the formula defining the change in water content in the porous monolith assumes the form:
where: —increase of water volume in the physical model caused by injection irrigation, calculated on the basis of measurements with TDR sensors (cm3), —volumetric moisture in i-th volume immediately after injection, (cm3∙cm−3), —volumetric moisture in i-th volume immediately prior to injection, (cm3∙cm−3). The value of can then be compared with the actual dose of water applied by the injector.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dynamics of the Volumetric Moisture
The dynamics of volumetric moisture in an elementary volume in the case of injection of 1500 cm3 of water is presented in Figure 5. This is the dynamics of moisture for a point which is 2.5 cm distant from the injector nozzle and which is situated in accordance with the orientation and sense of injection. In other words, this is the first encountered moisture sensor on the path of the water outflow from the injector nozzle. Prior to the start of water application under pressure, in a 30-min period lasting from moment t1 to t2, the volumetric moisture was constant at = 0.11 cm3∙cm−3. In the period from moment t2 to t3, lasting for 12 s, the injector delivered to the physical model 1500 cm3 of water under high pressure. This caused a jump increase of volumetric moisture, from = 0.11 cm3∙cm−3 to = 0.47 cm3∙cm−3. The mean rate of moisture increase was as much as 18 cm3∙cm−3∙min−1. Such an intensive increase of volumetric moisture is not observed in the case of other irrigation systems. As an example, Mmolawa and Or [74] studied the changes in water content in soil during the operation of a surface drip line. For a point situated 5 cm beneath the emitter, an increase of moisture from 0.25 cm3∙cm−3 to 0.42 cm3∙cm−3 was noted. That moisture increase was observed as late as after about 3 h (the intensity of water outflow from the emitter was 1.6 L∙h−1). To elucidate such a jump in soil moisture, we need to reach for the theory of soil water movement. Water movement in soil is due to differences in the total potential which is the sum of the matrix, gravity, osmotic, and pressure potentials [16]. In the course of injection, the cause of the jump increase of moisture is the gradient of the pressure potential resulting from the pressure of the liquid applied. The remaining gradients can be left out. However, this is a hypothesis which needs to be verified. The maximum measured volumetric moisture of = 0.47 cm3∙cm−3 is higher than the value of = 0.425 cm3∙cm−3 defined as moisture at the state of full saturation in the case of sand [65]. This is evidence of a disturbance of the structure of the porous medium, caused by the high pressure of liquid from the injector nozzle. This is supported by the fact that during injection the surface of the monolith building the model became deformed—the surface in the area of the fixed injector moved up. In addition, after the injection was completed, the surface settled down. The observed phenomenon of ground settlement is a known process which takes place at the moment of saturation of pores with water to the level of and subsequent decrease of volumetric moisture [75]. The period from moment t3 to t4, lasting for 3 min, is a period of rapid decrease of moisture. During that time the volumetric moisture dropped from 0.47 cm3∙cm−3 to 0.22 cm3∙cm−3, i.e., by 0.25 cm3∙cm−3, at an average rate of 0.083 cm3∙cm−3∙min−1. Therefore, the rate of volumetric moisture decrease in that stage is over 20-fold lower than the rate of moisture increase in the period from moment t2 to t3. In the next 3-min period, from moment t4 to t5, the rate of moisture decrease is lower still and amounts to only 0.007 cm3∙cm−3∙min−1. The process of slow decrease of volumetric moisture lasts till the end of the experiment (12 h), and it is now caused by a difference of total potential which is the sum of the gravity potential and the pressure equivalent [15].
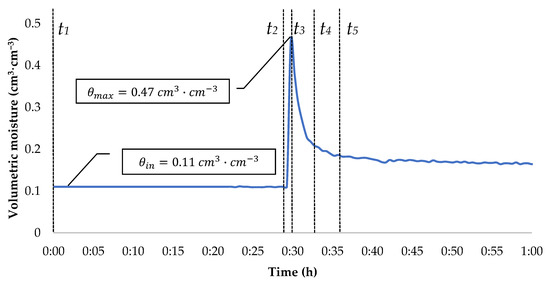
Figure 5.
Dynamics of volumetric moisture in a selected elementary volume during injection of 1500 cm3 of water.
The moisture changes in eight elementary volumes, caused by the injection of 1500 cm3 of water, is presented in Figure 6. The elementary spaces were described and visualized in Figure 4. Prior to the application of water, the volumetric moisture in those elementary volumes was in the range of 0.10–0.12 cm3∙cm−3. In volumes d, e, and f the run of changes of volumetric moisture was similar in character to that presented in Figure 5. In elementary volume g there was a jump increase of moisture, but not to the level of full saturation of pores with water. The maximum moisture in that volume was ca. 0.25 cm3∙cm−3. After the injection, no dynamic decrease of water content was noted but only a slow decrease of volumetric moisture. In volumes a, b, c, and h the content of water did not change in the course of the experiment. Therefore, the range of the effect of injection along the analysed axis 0Yi is 12.5 cm in the direction of water outflow, and only 2.5 cm in the opposite direction. The results of measurements for the analysed elementary volumes indicate that volumetric moisture changes caused by injection irrigation are not homogeneous, and their intensity decreases with increasing distance from the injector nozzle. A similar character of moisture change is noted also in the case of other irrigation systems. Naglić et al. studied the propagation of water in a sandy soil (with moisture of 0.12 cm3∙cm−3) irrigated with the use of a surface drip line [21]. The emitters of the line dosed water with the intensity of 2 L∙h−1, which resulted in an increase of the volumetric moisture of the soil. The character of the increase just under the soil surface was as follows: at the distance of 10 cm from the emitter the moisture was 0.38 cm3∙cm−3, at 20 cm it was 0.28 cm3∙cm−3, and at 30 cm it was only 0.16 cm3∙cm−3. Badr and Abuarab determined soil moisture changes for a subsurface drip line, installed in a sandy soil at the depth of 30 cm [25]. The results had an identical character—the rate of soil moisture increase decreased with increasing distance from water emitters. Also, a similar character of the volumetric moisture changes was obtained during measuring the intensity of evaporation caused by induced irrigation [11]. In this work, the moisture content of the top layer of the monolith during a water injection was measured. For example, when 1000 cm3 of water was implemented into sand, the sensor located 8 cm from the injection site showed an increase in volumetric moisture by 0.07 cm3∙cm−3 at the time of injection.
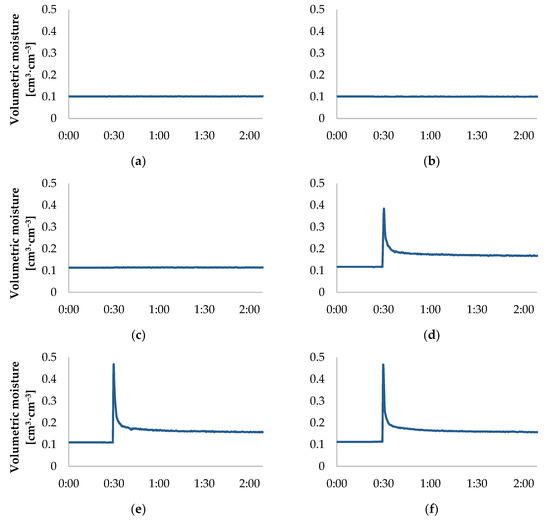
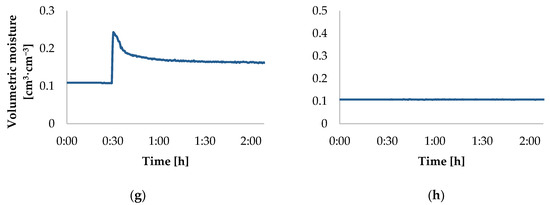
Figure 6.
Dynamics of volumetric moisture in eight elementary volumes with centre points situated on the line of water outflow from the injector—axis 0Yi (dose of 1500 cm3). Elements (a–h) were described in Figure 4.
Figure 7 presents volumetric moisture distributions in two vertical planes, perpendicular to each other, containing axes 0Xi and 0Yi, and in a horizontal plane containing axis 0Zi. The visualisations have been prepared on the basis of data from measurements taken at the moment of injection termination (t3). Based on the visualisations of the shape and extent of the moisture front in the figure below, one can conclude that the range of changes of the volumetric moisture is proportional to the volume of the applied water doses. As an example, in the case of the injection of 250 cm3 of water, the maximum volumetric moisture was noted at 3.5 cm from the injector nozzle and it amounted to 0.47 cm3∙cm−3. In turn, for the dose of 1500 cm3, the maximum moisture was as high as 0.65 cm3∙cm−3 and it was recorded at the distance of 12.8 cm from the injector nozzle. The recorded maximum moisture content was higher than the initial porosity of the monolith due to the disturbance of the porous structure by the water jet injected at high pressure. In every case, the maximum values of moisture at the moment of injection were noted in the direction of water outflow from the injector nozzle. The proportion between the intensity of changes in water content and the volume of water applied to the monolith is visible also in the analysis of the dynamics of moisture caused by the operation of other irrigation systems. An example can be the spatial reach of moisture changes in the case of irrigation with the use of a subsurface drip line [76]. When the water dose applied to the soil profile was 1 dm3, the front of soil moisture with the value of 0.33 cm3∙cm−3, in the horizontal direction, could have the reach of 6.7 cm, while for the dose of 5 dm3 it was as much as 16 cm, and for 10 dm3—even 21 cm. In the cited study, the determination of soil moisture dynamics was conducted with the use of TDR probes. Numerical models (Hydrus software) also confirm that in a sandy soil formation the spatial extent of changes in volumetric moisture depends on the volume of water supplied to the porous medium [77].
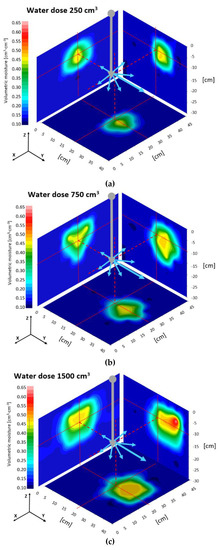
Figure 7.
Distributions of moisture in selected sections for doses of 250 (a), 750 (b), and 1500 (c) cm3.
3.2. Water Balance in the Physical Model
The results of measurements of volumetric moisture provide a basis for the calculation of the water balance in the physical model. Each TDR sensor is representative of an elementary volume—a cube with the side of 5 cm. The sum of water volumes in the cubes is the volume of water in the entire physical model (formula 3). The initial half-hour of the measurements was the period before injection, during which no moisture changes were observed. In the course of the series of experiments, after the 30-min period, water injection took place. The effect was a jump increase of water content in the monolith—. The value of increased with an increase in the injection dose (Table 1). As an example, in the case of the application of 450 cm3 of water the increase was 435 cm3, and for the dose of 1250 cm3–1200 cm3. The increments should be comparable with the volumes of water planned for injection—. However, according to the instructions from the manufacturer of the water injection device, the accuracy of the liquid dose applied is ± 10% [43].

Table 1.
Increase of water content at the moment of injection for the analysed water doses.
As can be seen from Table 1, in the case of doses of 250 and 1500 cm3 the 10% relative error between the water volume calculated on the basis of the water balance and the planned water dose was exceeded slightly. The causes of that can be potential error in the amount of injected water and the change of the structure of the porous medium mentioned earlier.
The graphs in Figure 8 present changes of water content in sand monolith during water injections. At the beginning, increases of water content are observable, which, then, irrespective of the passage of time, should remain at a constant level. In practice, however, already a moment after the injections, a gradual decrease of water content in the monolith is observed. What is more, the tendency resembles the runs of moisture dynamics presented in Figure 5 and Figure 6. After 12 h of measurements, the loss of water resulting from the water balance calculation for the doses of 250, 450, 750, 1000, 1250, and 1500 cm3 was 110, 209, 412, 357, 495, and 346 cm3, respectively. Assuming the correctness of the measurements and the calculations, the results clearly indicate an outflow of water from the analysed space. To localise the flow boundary, one should analyse the values of changes in the water balance in time, for the individual layers of the monolith, and also for the rows and columns (Figure 4). Taking into account the greatest changes in water content, the analysis was performed for the results of water balance calculations for the injection of 750 cm3 of water (Figure 9).
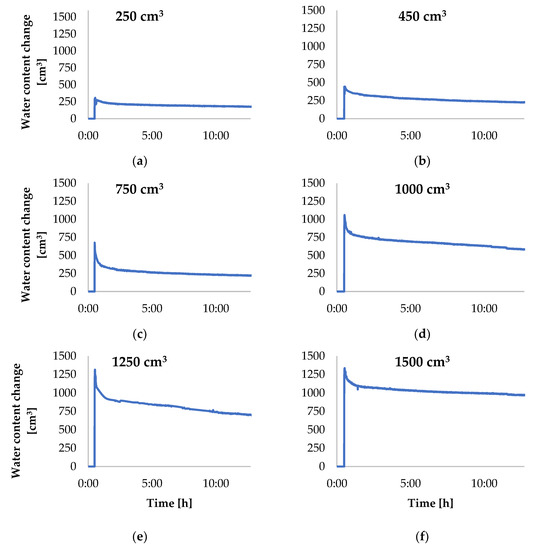
Figure 8.
Changes of water content in sand monolith during the injection of 250 (a), 450 (b), 750 (c), 1000 (d), 1250 (e), and 1500 (f) cm3 of water, in a 12-h time interval.
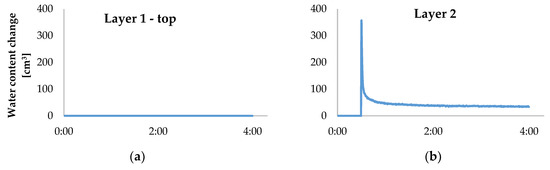
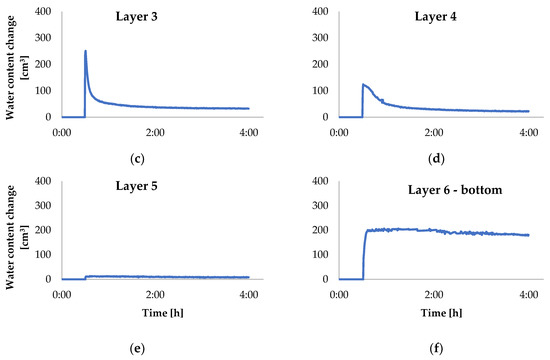
Figure 9.
Changes of water content in sand monolith during the injection of 750 cm3 of water, in a 4-h time interval, in the individual layers: (a)—layer 1, (b)—layer 2, (c)—layer 3, (d)—layer 4, (e)—layer 5, (f)—layer 6. The layers were presented in Figure 4.
The base and the side walls of the structure of the experimental setup were impermeable barriers, and the upper surface was exposed to contact with atmospheric air (Figure 2). Therefore, the first possible explanation for the decrease of water content is the appearance of the phenomenon of evaporation [37]. However, the partial results of the water balance presented in Figure 9 contradict this hypothesis. The graphs illustrate the changes in water content in division of the monolith into layers. The highest positioned first layer did not show any changes in this respect, both before and after water injection. This means that no process of evaporation took place. In fact, it could not, even if only due to the phenomenon of capillary rise in porous material of this type. In sands, the value of capillary rise after 12 h is only approximately 1.1 cm [78]. In layers 2, 3, and 4 the content of water increased within several seconds—by 266, 251, 120 cm3, respectively—but after 4 h there was a decrease of water content, by 232, 218, and 98 cm3, respectively. This indicates a nearly total evacuation of water from those volumes. In layer 5 no major changes were recorded in water content. Whereas, in the deepest situated, 6th layer, an increase of water content was noted, but it was much less violent than in the higher parts of the sand profile. Within 8 min the increase amounted to 200 cm3. What is more, the subsequent decrease of water content was very slight. After 4 h a decrease by 22 cm3 was noted. Changes of water content over time, but in a division into columns and rows, were also analysed. Changes in water content were noted only in the central rows and columns, i.e., in the immediate vicinity of the point of injection. The run of the changes can be compared to the moisture dynamics noted in layers 2, 3, and 4. In the extreme rows and columns no changes in water content were observed. This indicates that there was no water escape through the extreme vertical barriers of the monolith.
Among the characteristics presented above, the relationship shown in Figure 9 for changes in water content in the lowest, 6th, layer of the monolith, is characterised by the smallest decrease of water content. There is a possibility that the water supplied through injection migrated, due to gravity, to the bottom of the monolith. Taking into account the kind of porous material used, which is characterised by a high filtration coefficient (10−6–10−3 m∙s−1 [56]), high porosity (0.425 (−) [65]), low maximum capillary rise (3 cm [78]), and small retention capacity [79], it is certain that the orientation and sense of water flow was identical to the orientation and sense of the force of gravity. In the 6th layer, the TDR sensors were situated 2.5 cm above the impermeable bottom. The zone of sensitivity of TDR sensors type LP/ms in saturated soil has the form of a cylinder with dimensions of 5.5 cm along the sensor rods and 0.5 and 0.8 cm in the cross-section of the rods [80]. This means that above the vertically installed sensors there is a layer with a maximum thickness of 2.25 cm, which is included in the volumes represented by the LP/ms sensors, but in which moisture changes are not recorded in reality. Taking into account the section of the volumes in the plan view (5 cm × 5 cm) and 2.25 cm of thickness, the volume isolated for a single elementary volume, in which the moisture sensors do not register moisture dynamics, amounts to as much as 56.25 cm3. What is more, the results of measurements demonstrated that, depending on the injected water dose, the moisture jump in the bottom, 6th, layer was noted in varying numbers of volumes. Based on this, it is possible to calculate the volume of pores in which there could have been water not registered by the TDR sensors:
where: —volume of pores available on the bottom of the monolith, containing a part of the injected water dose, which has not been registered by the TDR sensors (cm3), —number of elementary volumes in 6th layer, where an increase of volumetric moisture was noted during the 12 h period of the experiment (−), —part of the volume of the isolated space, for which no volumetric moisture was recorded (cm3), —volumetric moisture in the saturated zone, 0.425 cm3∙cm−3 [65], —initial volumetric moisture immediately before injection, 0.10 cm3∙cm−3.
As can be seen in Table 2, at every injection under analysis the following relationship is noted: . The sole exception is the injection of 750 cm3. This means that in the bottom layer, with a thickness of 2.25 cm, beneath the sensors which registered an increase of volumetric moisture, there is a sufficient volume in the form of free pores than can accommodate water migrating down under gravity from the upper layers of the monolith. This is the basis for the acceptance of the method employed in the experiment as correct for the determination of the dynamics of the moisture front caused by injection irrigation. There is a possibility of independent verification of the correctness of the measurements—with the use of mathematical modelling [19,81]. Even conducting an identical experiment with the use of a soil formation with a percentage of silt and clay particles should ensure the maintenance of water balance at the level from the moment of injection. Heavier soil formations are characterised by a notably lower filtration coefficient, lower porosity, and higher capillary rise. The above hypotheses will be the subject of future research.

Table 2.
Difference between the volume of pores available on the bottom of the sand monolith and the decrease of water content over time, for various water injection doses.
4. Conclusions
The study presented the character of moisture changes in relation to the injected water to sand material. In the course of injection irrigation, the resultant water movement can be divided into stages (Figure 5). In the first stage, an increase of volumetric moisture in the sand monolith is caused by the application of a given dose of water under a high hydraulic pressure (period t2–t3). After the process of injection (maximum several seconds), the hydraulic pressure ceases and there takes place a decrease of moisture, the intensity of which reduces with the passage of time (period t3–t4–t5). Within the scope of the experiment, the spatial reach of the changes was also determined. As an example, in the case of the injection of 250 cm3 of water, the maximum volumetric moisture was noted at 3.5 cm from the injector nozzle, and it amounted to 0.47 cm3∙cm−3. For the dose of 1500 cm3, the maximum moisture was as high as 0.65 cm3∙cm−3 and it was registered at the distance of 12.8 cm from the injector nozzle (Figure 7). It was also observed that during water injection there is a risk of disturbing the sand structure.
The correctness of the adopted methodology was demonstrated through calculations of the water balance, the basis for which was the division of the monolith into elementary volumes, represented by LP/ms sensors. At the moment of injection (t3), the calculation of the water balance showed that the amounts of water applied to the monolith were comparable to the planned water doses (with the accuracy of ±10%). The water balance calculations revealed, however, that the content of water decreased with the passage of time (Figure 8). There was no possibility of water outflow from the monolith, as it was enclosed in impermeable barriers. Also, no evaporation from the surface was noted (Figure 9). The cause of the decrease of the content of water was its migration, conforming with the orientation and sense of the force of gravity, below the zone of sensitivity of the lowest positioned layers of moisture sensors (Table 2). In future research, it is planned to focus on the determination of moisture dynamics through mathematical modelling, and to extend the scope of the research into other types of soil.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.J., A.W.; methodology, A.W., G.J.; software, A.W.; validation, A.W., G.J., A.S.; formal analysis, A.W., G.J.; investigation, A.W., G.J.; resources, A.W.; data curation, A.W.; writing—original draft preparation, A.W.; writing—review and editing, G.J., A.S., G.P., A.W.; visualization, A.W.; supervision, A.S., G.J., G.P.; project administration, A.W.; funding acquisition, G.J., G.P., A.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financed by the National Centre for Research and Development (Warszawa, Poland) as part of the project “A mobile system for precision injection irrigation and fertilisation meeting the individual requirements of plants”. MSINiN—Polish acronym for the project title. Grant number: BIOSTRATEG3/343547/8/NCBR/2017.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Jackson, R.B.; Carpenter, S.R.; Dahm, C.N.; McKnight, D.M.; Naiman, R.J.; Postel, S.L.; Running, S.W. Issues in Ecology. WATER A Chang. WORLD 2001, 11, 1027–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, Y.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Sustainability of global water use: Past reconstruction and future projections. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 104003–104020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, A. The Use of World Water Resources in the Irrigation of Field Cultivations. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, M.; Kanber, R.; Şenyigit, U.; Onaran, H.; Diker, K. Trickle and sprinkler irrigation of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in the Middle Anatolian Region in Turkey. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 79, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Wang, F.X.; Liu, H.J.; Yuan, B.Z. Potato evapotranspiration and yield under different drip irrigation regimes. Irrig. Sci. 2004, 23, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyśko, J.; Kaniszewski, S. Effect of drip irrigation, n-fertigation and cultivation methods on the yield and quality of carrot. Veg. Crop. Res. Bull. 2007, 67, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S. Innovative Technologies for Water Saving in Irrigated Agriculture. Int. J. Water Resour. Arid Environ. 2011, 1, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, T.; Havlík, P.; Schneider, U.A.; Schmid, E.; Kindermann, G.; Obersteiner, M. Agriculture and resource availability in a changing world: The role of irrigation. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, G.; Walczak, A.; Dawid, M.; Pokładek, R.; Adamczewska-Sowińska, K.; Wolski, K.; Sowiński, J.; Gronostajski, Z.; Reiner, J.; Kaszuba, M.; et al. Innovative Conception of Irrigation and Fertilization—Section in Monography; Agricultural Advisory Center in Brwinów: Brwinów, Poland, 2013; ISBN 978-83-88082-18-4. [Google Scholar]
- Janik, G.; Kłosowicz, I.; Walczak, A.; Adamczewska-Sowińska, K.; Jama-Rodzeńska, A.; Sowiński, J. Application of the TDR technique for the determination of the dynamics of the spatial and temporal distribution of water uptake by plant roots during injection irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 252, 106911–106923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, A.; Lipiński, M.; Janik, G. Application of the tdr sensor and the parameters of injection irrigation for the estimation of soil evaporation intensity. Sensors 2021, 21, 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczyński, P.; Kaszuba, M.; Dworzak, Ł. Obrotowy Rozdzielacz Hydrauliczny Obrotowy do Iniekcyjnego Nawadniania Gruntów. Polish Patent P.436556, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- McBratney, A.; Whelan, B.; Ancev, T.; Bouma, J. T. Future Directions of Precision Agriculture. Precis. Agric. 2005, 6, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbers, R.; Adamchuk, V.I. Precision Agriculture and Food Security Published by: American Association for the Advancement. Precis. Agric. Food Secur. 2017, 327, 828–831. [Google Scholar]
- Shock, C.C.; Wang, F.X. Soil water tension, a powerful measurement for productivity and stewardship. HortScience 2011, 46, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittelli, M. Measuring soil water potential forwater management in agriculture: A review. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1226–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, B.A.; Bjorneberg, D.L. Characterizing droplet kinetic energy applied by moving spray-plate center-pivot irrigation sprinklers. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. A pressure-membrane extraction apparatus for soil solution. Soil Sci. 1941, 51, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Šejna, M. Hydrus: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar]
- List, F.; Radu, F.A. A study on iterative methods for solving Richards’ equation. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 20, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naglič, B.; Kechavarzi, C.; Coulon, F.; Pintar, M. Numerical investigation of the influence of texture, surface drip emitter discharge rate and initial soil moisture condition on wetting pattern size. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W.D.; Bowman, B.T.; Drury, C.F.; Tan, C.S.; Lu, X. Indicators of good soil physical quality: Density and storage parameters. Geoderma 2002, 110, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puértolas, J.; Alcobendas, R.; Alarcón, J.J.; Dodd, I.C. Long-distance abscisic acid signalling under different vertical soil moisture gradients depends on bulk root water potential and average soil water content in the root zone. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, A.E.; Abuarab, M.E. Soil moisture distribution patterns under surface and subsurface drip irrigation systems in sandy soil using neutron scattering technique. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfstrand, S.; Båth, B.; Mårtensson, A. Influence of various forms of green manure amendment on soil microbial community composition, enzyme activity and nutrient levels in leek. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 36, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, D.T.; Bastiaans, L.; Kropff, M.J. Competition and crop performance in a leek-celery intercropping system. Crop Sci. 2001, 41, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilde, D. Phytophthora Porri in Leek: Epidemiology and Resistance; Wageningen University & Research: Wageningen, Netherlands, 1996; ISBN 9789054855071. [Google Scholar]
- Borowy, A. Effect of Celeriac-Leek Intercropping on Weeds, Insects and Plant Growth. In Second European Allelopathy Symposium “Allelopathy—from understanding to application”; Institute of Soil Science and Plant Cultivation State Research Institute: Puławy, Poland, 2003; pp. 119–120. [Google Scholar]
- Niemiec, M.; Cupiał, M.; Szeląg-Sikora, A. Efficiency of Celeriac Fertilization with Phosphorus and Potassium Under Conditions of Integrated Plant Production. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 7, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogut, T.; Arioglu, H. Plant density and sowing date effects on sugarbeet yield and quality. J. Agron. 2004, 3, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; You, X. Estimating parameters of van genuchten model for soil water retention curve by intelligent algorithms. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2013, 7, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaloglou, S.; Diamantopoulos, E. Soil water dynamics under surface trickle irrigation as affected by soil hydraulic properties, discharge rate, dripper spacing and irrigation duration. Irrig. Drain. 2010, 59, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbat, G.; Cufí, S.; Duran-Ros, M.; Pinsach, J.; Puig-Bargués, J.; Pujol, J.; de Cartagena, F.R. Modeling approaches for determining dripline depth and irrigation frequency of subsurface drip irrigated rice on different soil textures. Water 2020, 12, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y. Water and nitrate distributions as affected by layered-textural soil and buried dripline depth under subsurface drip fertigation. Irrig. Sci. 2011, 29, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.S.; Jha, B.K.; Singh, R.; Meena, M. Bitter Gourd Response to Surface and Subsurface Drip Irrigation under Different Fertigation Levels. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliński, J.; Horabik, J.L.J. Encyclopedia of Agrophyscis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, A.L.; Zuin, A. Root growth dynamics of Brussels sprouts (Brassica olearacea van gemmifera ) and leeks (Allium porrum L.) as reflected by root length, root colour and UV fluorescence. Plant Soil 2021, 185, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossne, A.J.; Jesus Méndez, N.; Leonett, F.A.; Meneses, J.E.; Gil, J.A. Maize root growth under regular water content, subjected to compaction, irrigation frequencies, and shear stress. Rev. Fac. Nac. Agron. Medellin 2016, 69, 7867–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gaines, R.A.; Frankenstein, S. USCS and the USDA Soil Classification System: Development of a Mapping Scheme. United States Army Corps of Engineers: Washington DC, USA, 2015; 37. [Google Scholar]
- Sulewska, M.J. Neural modelling of compactibility characteristics of cohesionless soil. Comput. Assist. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2010, 17, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczyński, P.J.; Kaszuba, M.D.; Dworzak, Ł.J.; Hawryluk, M. Iniektor do Nawadniania Gruntu 2019. nr W.128720, Polish Patent Office: Warszawa, Poland. Available online: https://ewyszukiwarka.pue.uprp.gov.pl/search/pwp-details/W.128720?lng=en.
- Isweek.com. YF-B Series Water Flow Sensor Description. Available online: https://www.isweek.com/product/water-flow-sensor-yf-b1-b2-b3-b7_2430.html (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Bianchi, A.; Masseroni, D.; Thalheimer, M.; de Medici, L.O.; Facchi, A. Field irrigation management through soil water potential measurements: A review. Ital. J. Agrometeorol. 2017, 22, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Evett, S. Coaxial Multiplexer for time domain rflectometry measurement of soil water content and bulk electrical conductivity. Encylopedia Water Sci. 2003, 41, 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.B.; Sheng, W.; Xu, J.; Robinson, D.A. Electromagnetic Sensors for Water Content: The Need for International Testing Standards. In Proceedings of the 2018 12th International Conference on Electromagnetic Wave Interaction with Water and Moist Substances (ISEMA), Lublin, Poland, 4–7 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Šarec, P.; Šarec, O.; Prošek, V.; Dobek, T.K. Description of new design of an instrument measuring soil humidity. Inżynieria Rol. 2008, 11, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Susha Lekshmi, S.U.; Singh, D.N.; Shojaei Baghini, M. A critical review of soil moisture measurement. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2014, 54, 92–105. [Google Scholar]
- Malicki, M.A.; Plagge, R.; Roth, C.H. Improving the calibration of dielectric TDR soil moisture determination taking into account the solid soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skierucha, W. Accuracy of soil moisture measurement by TDR technique. Int. Agrophys. 2000, 14, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Skierucha, W.; Wilczek, A.; Alokhina, O. Calibration of a TDR probe for low soil water content measurements. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 147, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skierucha, W.; Wilczek, A.; Szypłowska, A.; Sławiński, C.; Lamorski, K. A TDR-based soil moisture monitoring system with simultaneous measurement of soil temperature and electrical conductivity. Sensors 2012, 12, 13545–13566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoel, C.; Vaz, P.; Hopmans, J.W. with a Combined Penetrometer—TDR Moisture Probe. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Cao, Q.; Sun, Z. The effects of soil bulk density, clay content and temperature on soil water content measurement using time-domain reflectometry. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 3601–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.P.; Chen, Y.M.; Xu, W.; Yu, X. Measurement of electrical conductivity of pore water in saturated sandy soils using time domain reflectometry (TDR) measurements. Can. Geotech. J. 2012, 47, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telichenko, V.; Rimshin, V.; Eremeev, V.; Kurbatov, V. Mathematical modeling of groundwaters pressure distribution in the underground structures by cylindrical form zone. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 196, 02025. Available online: https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/abs/2018/55/matecconf_rsp2018_02025/matecconf_rsp2018_02025.html (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Karlberg, L.; Jansson, P.E.; Gustafsson, D. Model-based evaluation of low-cost drip-irrigation systems and management strategies using saline water. Irrig. Sci. 2007, 25, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumanov, K.S.; Hopmans, J.W.; Schwankl, L.W. Soil Water Dynamics in the Root Zone of a Micro-Sprikler Irrigated Almond Tree. Available online: https://www.ishs.org/ishs-article/664_46 (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Alomran, A.M. Management of Irrigation Water Salinity in Greenhouse Tomato Production under Calcareous Sandy Soil and Drip Irrigation. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 14, 939–950. [Google Scholar]
- Simionesei, L.; Ramos, T.B.; Brito, D.; Jauch, E.; Leitão, P.C.; Almeida, C.; Neves, R. Numerical Simulation of Soil Water Dynamics Under Stationary Sprinkler Irrigation With Mohid-Land. Irrig. Drain. 2016, 65, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnesr, M.N.; Alazba, A.A. Computational evaluations of HYDRUS simulations of drip irrigation in 2D and 3D domains (i-Surface drippers). Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Schulze Lammers, P.; Grantz, D.A.; Xue, X.; Wang, Z. A horizontal mobile dielectric sensor to assess dynamic soil water content and flows: Direct measurements under drip irrigation compared with HYDRUS-2D model simulation. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 179, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipnikov, K.; Manzini, G.; Shashkov, M. Mimetic finite difference method. J. Comput. Phys. 2014, 257, 1163–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Negrete, C.; Domínguez-Mota, F.J.; Santana-Quinteros, D. Numerical solution of Richards’ equation of water flow by generalized finite differences. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 101, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, C.W.; Bennett, R.H.; Hulbert, M.H.; Curry, K.J.; Faas, R.W. Comparative study of sand porosity and a technique for determing porosity of undisturbed marine sediment. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2004, 22, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E-TEST Sp. z o.o. Innovative Measurement Techniques for Environment and Soil Science. Available online: https://www.e-test.eu/ (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Douh, B.; Boujelben, A.; Khila, S.; Bel Haj Mguidiche, A. Effect of Subsurface Drip Irrigation System Depth on Soil Water Content Distribution At Different Depths and Different Times After Irrigation. Larhyss. J. 2013, 13, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, J.B.; Franz, T.E.; Heeren, D.M.; Neale, C.M.U.; Luck, J.D. Soil water content monitoring for irrigation management: A geostatistical analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 188, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J. The General Conservation Principle. In Dynamics of fluids in porous media; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 74–113. [Google Scholar]
- Sahimi, M. The Mass Conservation Equation. In Flow and Transport in Porous Media and Fractured Rock: From Classical Methods to Modern Approaches; John Wiley and Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Quinones, H.; Ruelle, P.; Nemeth, I. Comparison of three calibration procedures for tdr soil moisture sensors. Irrig. Drain. 2003, 52, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfletschinger, H.; Engelhardt, I.; Piepenbrink, M.; Königer, F.; Schuhmann, R.; Kallioras, A.; Schüth, C. Soil column experiments to quantify vadose zone water fluxes in arid settings. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, G.; Wolski, K.; Daniel, A.; Albert, M.; Skierucha, W.; Wilczek, A.; Szyszkowski, P.; Walczak, A. TDR technique for estimating the intensity of evapotranspiration of turfgrasses. Sci. World J. Hindawi 2015, 2015, 626545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mmolawa, K.; Or, D. Root zone solute dynamics under drip irrigation: A review. Plant Soil 2000, 222, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, G.; Dawid, M.; Walczak, A.; Słowińska-Osypiuk, J.; Skierucha, W.; Wilczek, A.; Daniel, A. Application of the TDR technique for the detection of changes in the internal structure of an earthen flood levee. J. Geophys. Eng. 2017, 14, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiuy, M.L.C.; Dos Santos, L.N.S.; De Sousa, A.C.M.; Souza, C.F.; Matsura, E.E. Wet bulbs from the subsurface drip irrigation with water supply and treated sewage effluent. Eng. Agric. 2015, 35, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saefuddin, R.; Saito, H.; Šimůnek, J. Experimental and numerical evaluation of a ring-shaped emitter for subsurface irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka, M.; Szypcio, Z.; Tymosiak, D. The speed of capillary raise in granular soils. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2013, 4, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Hewelke, P.; Gnatowski, T.; Hewelke, E.; Tyszka, J.; Żakowicz, S. Analysis of water retention capacity for select forest soils in Poland. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, G.; Szpila, M.; Slowinska, J.; Brej, G.; Turkiewicz, M.; Skierucha, W.; Pastuszka, T. Method for the determination of the sensitivity zone of the probe. Acta Agrophys. 2011, 18, 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah, R. A review of models for predicting soil water dynamics during trickle irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).