Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter Dynamics Relative to Sediment Resuspension Induced by the Tidal Cycle in Macrotidal Estuaries, Kyushu, Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
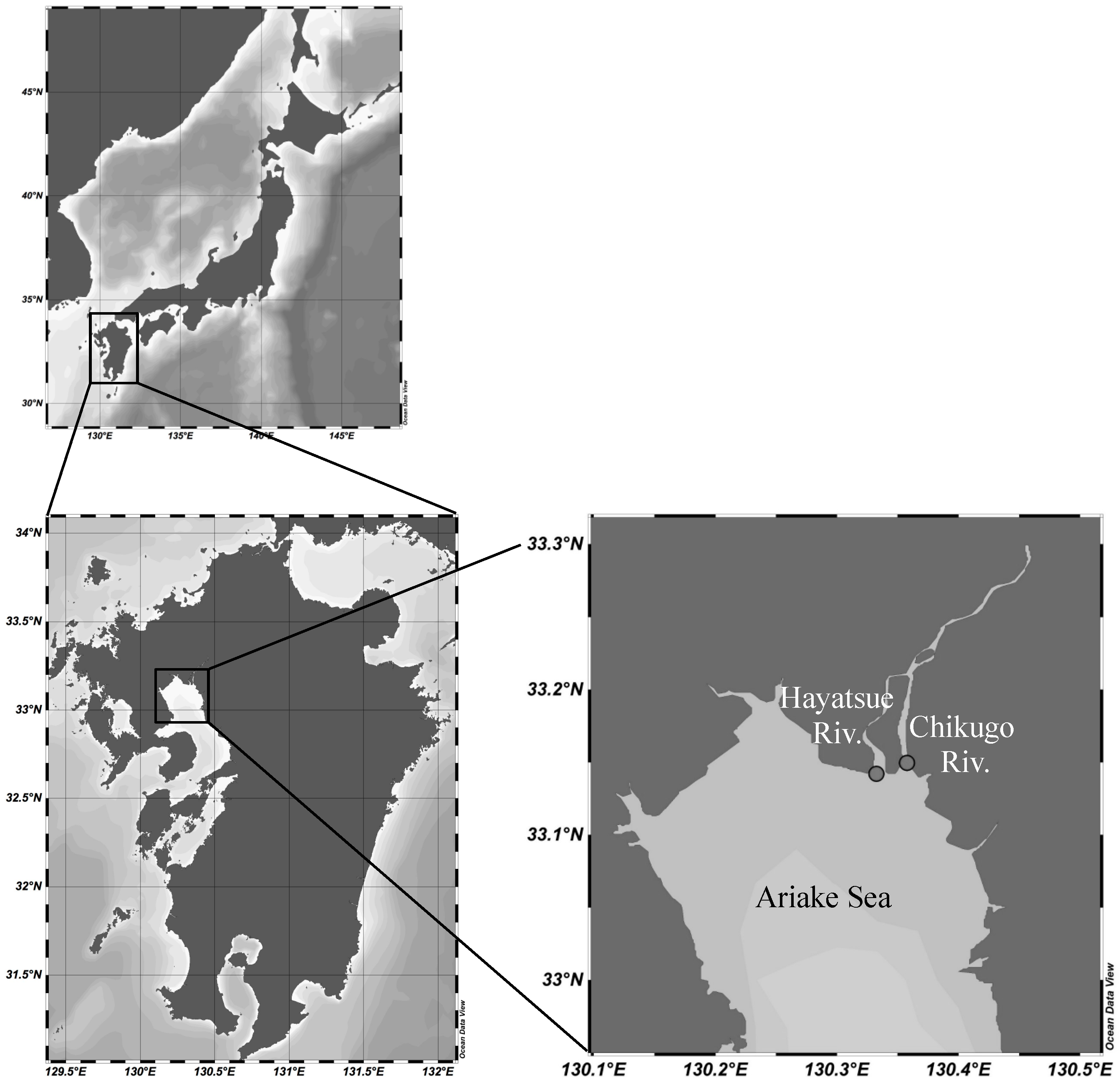
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gattuso, J.P.; Frankignoulle, M.; Wollast, R. Carbon and carbonate metabolism in coastal aquatic ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1998, 29, 405–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, S.; Pace, M.; Lints, D. Variability and transport of suspended sediment, particulate and dissolved carbon in the tidal freshwater Hudson River. Biogeochemistry 1991, 12, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, T.S. Biogeochemistry of Estuaruaries; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 706. [Google Scholar]
- Etcheber, H.; Taillez, A.; Abril, G.; Garnier, J.; Servais, P.; Moatar, F.; Commarieu, M.V. Particulate organic carbon in the estuarine turbidity maxima of the Gironde, Loire and Seine estuaries: Origin and lability. Hydrobiologia 2007, 588, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, J.; Andersson, A.; Johansson, S.; Wikner, J. Pelagic food web structure and carbon budget in the northern Baltic Sea: Potential importance of terrigenous carbon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 268, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, P.; Ask, J.; Andersson, A.; Karlsson, J.; Giesler, R. Allochthonous organic matter supports benthic but not pelagic food webs in shallow coastal ecosystems. Ecosystems 2018, 21, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Pinckney, J.L.; Fear, J.M.; Peierls, B.L. Ecosystem responses to internal and watershed organic matter loading: Consequences for hypoxia in the eutrophying Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina, USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 166, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Keil, R.G.; Benner, R. What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochelle-Newall, E.J.; Pizay, M.-D.; Middelburg, J.J.; Boschker, H.T.S.; Gattuso, J.-P. Degradation of riverine dissolved organic matter by seawater bacteria. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 37, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, K.; Lu, K.; Dai, M.; Liu, Z. The bioavailability of riverine dissolved organic matter in coastal marine waters of southern Texas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 231, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerringa, L.J.A. Aerobic degradation of organic matter and the mobility of Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe and Mn in marine sediment slurries. Mar. Chem. 1990, 29, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdige, D.J.; Zheng, S. The biogeochemical cycling of dissolved organic nitrogen in estuarine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 1796–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauwet, G.; Mackenzie, F.T. Carbon inputs and distribution in estuaries of turbid rivers: The Yang Tze and Yellow rivers (China). Mar. Chem. 1993, 43, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.W.; Kasai, A.; Nakayama, K.; Tanaka, M. Year-round accumulation of particulate organic matter in the estuarine turbidity maximum: Comparative observations in three macrotidal estuaries (Chikugo, Midori, and Kuma Rivers), southwestern Japan. J. Oceanogr. 2012, 68, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Hamada, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Hayami, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Ohgushi, K. Effects of hypoxia and organic enrichment on estuarine macrofauna in the inner part of Ariake Bay. Hydrobiologia 2010, 652, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.W.; Sugimoto, R.; Kasai, A.; Nakayama, K.; Tanaka, M. Dynamics of particulate organic matter in the estuarine turbidity maximum of the Chikugo River estuary, Ariake Sea, in summer: Influence of the fluctuation of freshwater discharge. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. Oceanogr. 2009, 73, 149–160, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, K.; Inomata, H.; Tahara, S.; Takasu, H. Contribution of organic matter decomposition in water column to oxygen consumption in the inner part of the Ariake Sea. J. Jpn. Soc. Water Environ. 2019, 42, 195–200, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Tanoue, E. Dissolved organic matter in oceanic waters. J. Oceanogr. 2003, 59, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawano, S. Morphodynamics and transport of sediment phosphorus in the northeast part of tha Arieka Sea and the estuarine channel of the Chikugogawa River. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. B 2008, 64, 366–370, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Welschmeyer, N.A. Fluorometric analysis of chlorophyll-a in the presence of chlorophyll-b and pheopigments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, L.M.; Schick, L.L.; Loder, T.C., III. Dissolved protein fluorescence in two Maine estuaries. Mar. Chem. 1999, 64, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, K.; Morimura, Y.; Shintani, T.; Yokoyama, K. Three-dimentional numerical simulation of saline intrusion in Chikugo River estuary. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. B1 2017, 73, I_1039–I_1044, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hayami, Y.; Wada, M.; Umezawa, Y.; Fujii, N.; Nakamura, A.; Mori, F. Hypoxic water mass in the highly turbid well-mixed macrotidal Rokkaku River Estuary, Ariake Sea, Japan. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 219, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.C.; Ketchum, B.H.; Richards, F.A. The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. In The Sea: Ideas and Observations on Progress in the Study of the Seas; Hill, M.N., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1963; Volume 2, pp. 26–77. [Google Scholar]
- Deines, P. The isotopic composition of reduced organic carbon. In Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry; The Terrestrial Environment; Fritz, P., Fontes, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980; Volume 1, pp. 329–406. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, B.; Sherr, E.B. δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Contrib. Mar. Sci. 1984, 27, 13–47. [Google Scholar]
- Fontugne, M.R.; Jouanneau, J.M. Modulation of the particulate organic carbon flux to the ocean by a macrotidal estuary: Evidence from measurements of carbon isotopes in organic matter from the Gironde system. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1987, 24, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P.A. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter. Chem. Geol. 1994, 114, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Murashige, S.; Ohnishi, Y.; Yuzawa, A.; Miyasaka, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Komiyama, H. Decomposition of phytoplankton in seawater. Part I. Kinetic analysis of the effect of organic matter concentration. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoye, N.; David, V.; Morisseau, F.; Etcheber, H.; Abril, G.; Billy, I.; Charlier, K.; Oggian, G.; Derriennic, H.; Sautour, B. Origin and composition of particulate organic matter in a macrotidal turbid estuary: The Gironde Estuary, France. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 108, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.F.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Barbieri, A.; McKenzie, J.A. Preservation of organic matter and alteration of its carbon and nitrogen isotope composition during simulated and in situ early sedimentary diagenesis. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliot, A.; Tronczynski, J.; Scribe, P.; Letolle, R. The application of isotopic and biogeochemical markers to the study of the biochemistry of organic matter in a macrotidal estuary, the Loire, France. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1988, 27, 645–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Herman, P.M.J. Organic matter processing in tidal estuaries. Mar. Chem. 2007, 106, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.; Song, H.; Ryu, J.S.; Ock, G.; Shin, K.H. Temporal variation in riverine organic carbon concentrations and fluxes in two contrasting estuary systems: Geum and Seomjin, South Korea. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Variables | Sal | Chl.a | Turb | POC | PON | δ13C | DOC | Protein | Humic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sal | |||||||||
| Chl.a | 0.67 ❊❊❊ | ||||||||
| Turb | −0.25 | −0.25 | |||||||
| POC | 0.01 | −0.08 | 0.58 ❊ | ||||||
| PON | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.47 ❊ | 0.98 ❊❊❊ | |||||
| δ13C | 0.76 ❊❊❊ | 0.76 ❊❊❊ | −0.26 | 0.11 | −0.18 | ||||
| DOC | −0.55 ❊ | −0.46 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.05 | −0.71 ❊❊❊ | |||
| Protein | −0.39 | −0.21 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.20 | −0.38 | −0.61 ❊❊ | ||
| Humic | −0.84 ❊❊❊ | −0.62 ❊❊ | 0.41 | 0.24 | 0.14 | −0.87 ❊❊❊ | −0.89 ❊❊❊ | −0.54 ❊ |
| Variables | Sal | Chl.a | Turb | POC | PON | δ13C | DOC | Protein | Humic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sal | |||||||||
| Chl.a | 0.67 ❊❊❊ | ||||||||
| Turb | 0.01 | 0.09 | |||||||
| POC | −0.56 ❊ | −0.42 | 0.02 | ||||||
| PON | −0.21 | −0.02 | 0.24 | 0.82 ❊❊❊ | |||||
| δ13C | 0.74 ❊❊❊ | 0.91 ❊❊❊ | −0.12 | −0.54 ❊ | −0.34 | ||||
| DOC | −0.81 ❊❊❊ | −0.62 ❊❊ | −0.07 | 0.48 ❊ | 0.14 | −0.71 ❊❊❊ | |||
| Protein | −0.41 | −0.34 | −0.01 | 0.26 | 0.23 | −0.47 ❊ | 0.38 | ||
| Humic | −0.95 ❊❊❊ | −0.71 ❊❊❊ | −0.14 | 0.54 ❊ | 0.16 | −0.80 ❊❊❊ | 0.91 ❊❊❊ | 0.40 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takasu, H.; Uchino, K.; Mori, K. Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter Dynamics Relative to Sediment Resuspension Induced by the Tidal Cycle in Macrotidal Estuaries, Kyushu, Japan. Water 2020, 12, 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092561
Takasu H, Uchino K, Mori K. Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter Dynamics Relative to Sediment Resuspension Induced by the Tidal Cycle in Macrotidal Estuaries, Kyushu, Japan. Water. 2020; 12(9):2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092561
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakasu, Hiroyuki, Koji Uchino, and Koichiro Mori. 2020. "Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter Dynamics Relative to Sediment Resuspension Induced by the Tidal Cycle in Macrotidal Estuaries, Kyushu, Japan" Water 12, no. 9: 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092561
APA StyleTakasu, H., Uchino, K., & Mori, K. (2020). Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter Dynamics Relative to Sediment Resuspension Induced by the Tidal Cycle in Macrotidal Estuaries, Kyushu, Japan. Water, 12(9), 2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092561





