Exploring How Cyanobacterial Traits Affect Nutrient Loading Thresholds in Shallow Lakes: A Modelling Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Model Selection
2.2. Model Adaptation
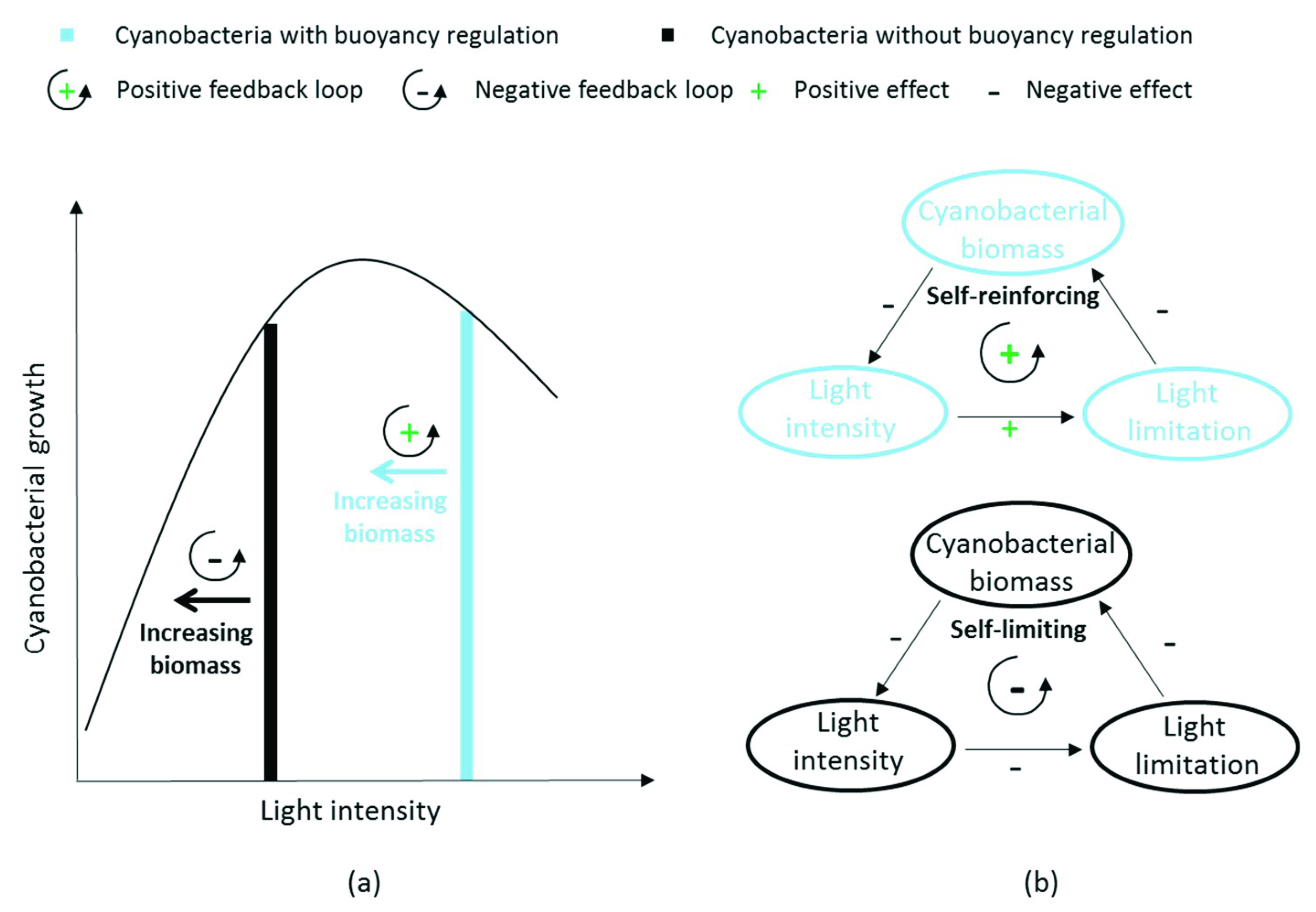
2.2.1. Buoyancy Regulation
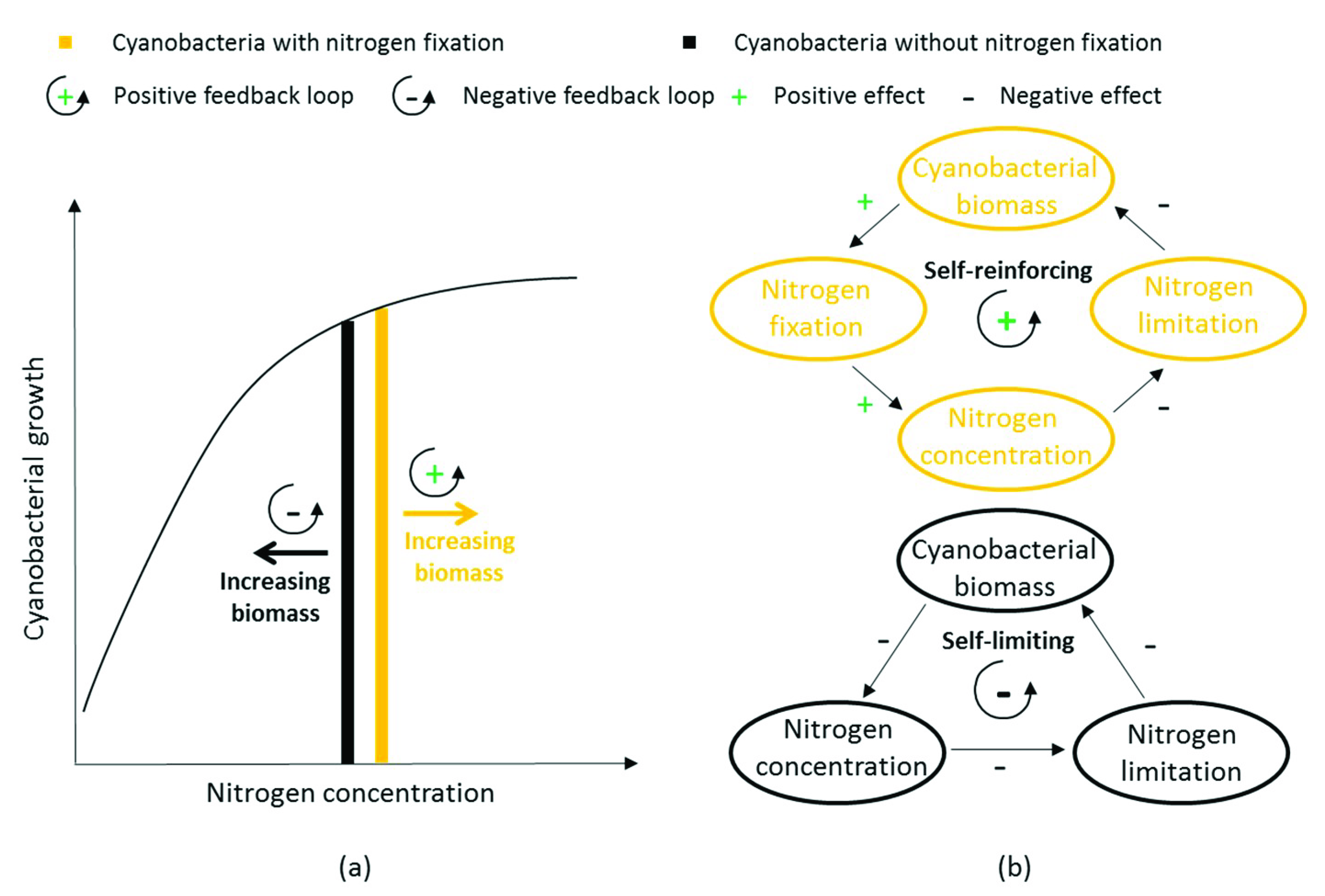
2.2.2. Nitrogen Fixation
2.3. Bifurcation Analyses
3. Results
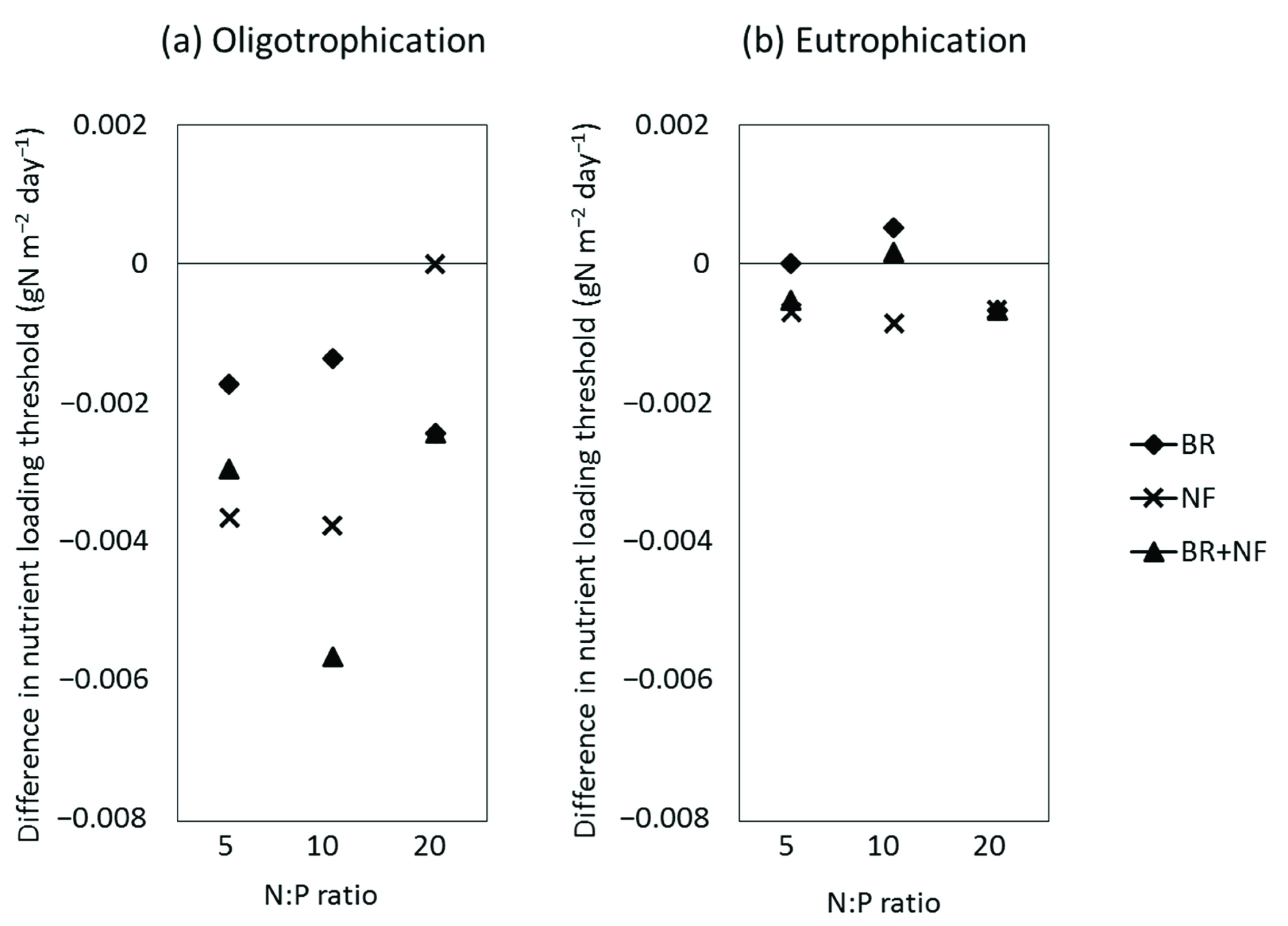
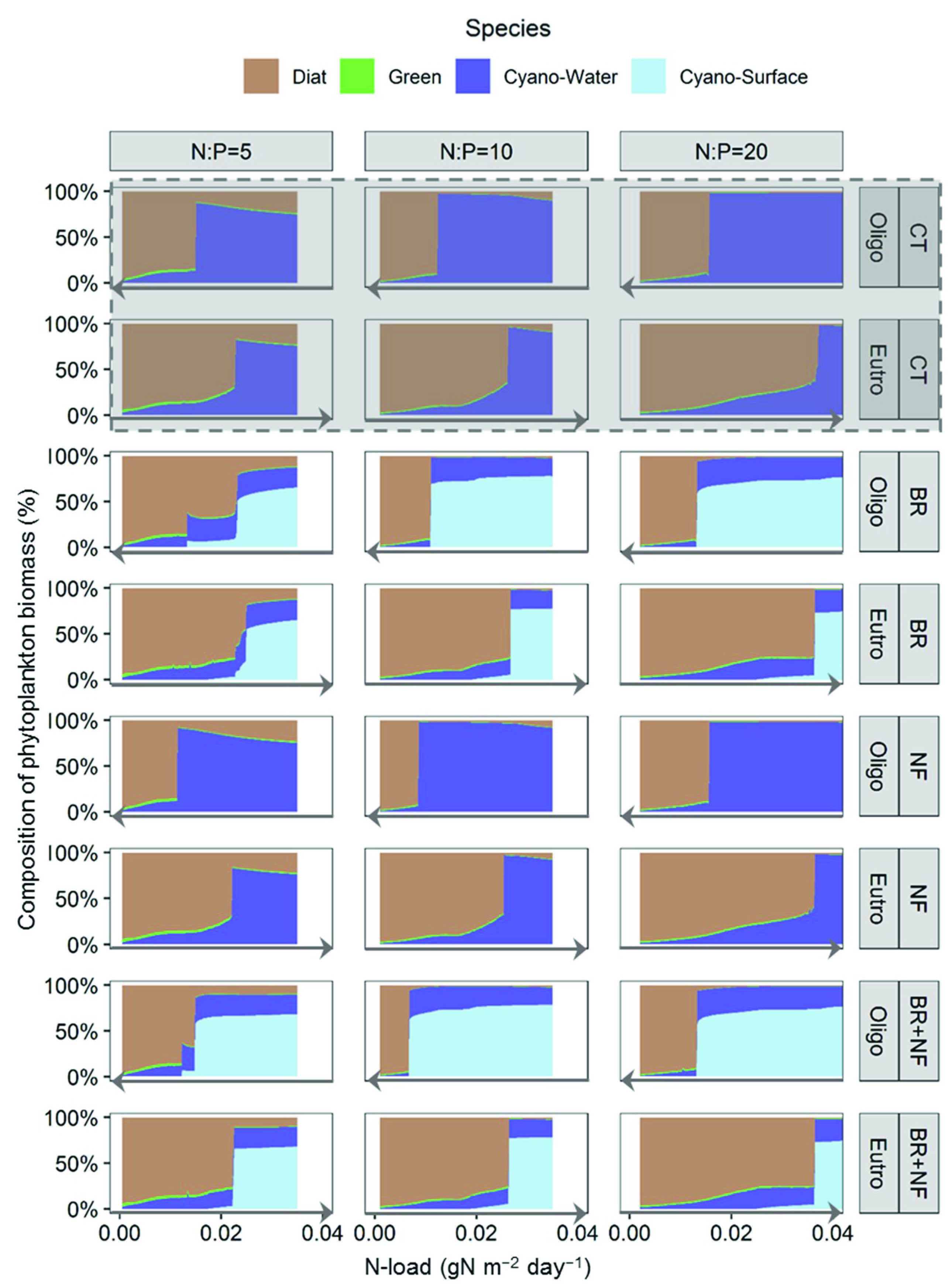
3.1. Effect of Buoyancy Regulation (BR Scenario)
3.2. Effect of Nitrogen Fixation (NF Scenario)
3.3. Synergistic Effect of Buoyancy Regulation and Nitrogen Fixation (BR + NF Scenario)
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect on Nutrient Loading Threshold
4.1.1. Feedback Loops due to Buoyancy Regulation
4.1.2. Feedback Loops due to Nitrogen Fixation
4.1.3. Feedback Loops due to the Combination of the Two Traits
4.1.4. Effect on Lake Nutrient Loading Thresholds during Eutrophication
4.2. Comparison to Natural Conditions
4.3. Modelling as a Tool for Lake Managers
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallegraeff, G.M. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.C.; Dortch, Q.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paerl, H.W. Nuisance phytoplankton blooms in coastal, estuarine, and inland waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Falconer, I.R.; Salas, H.J.; Bartram, J. Health risks caused by freshwater cyanobacteria in recreational waters. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2000, 3, 323–347. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. Wires Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, R.W.; Hoyer, M.V.; Canfield, D.E. The restoration of Lake Apopka in relation to alternative stable states. Hydrobiologia 1999, 394, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, S.; Brothers, S.; Jeppesen, E.; Veraart, A.J.; Kosten, S. Translating Regime Shifts in Shallow Lakes into Changes in Ecosystem Functions and Services. BioScience 2017, 67, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; Hilt, S.; Kosten, S.; de Klein, J.J.M.; Paerl, H.W.; van de Waal, D.B. Shifting states, shifting services: Linking regime shifts to changes in ecosystem services of shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Meerhoff, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jensen, J.P. Shallow lake restoration by nutrient loading reduction—Some recent findings and challenges ahead. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Hosper, S.; Meijer, M.; Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.R.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B.J. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suding, K.N.; Gross, K.L.; Houseman, G.R. Alternative states and positive feedbacks in restoration ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.S.; Wu, Y. Determining Critical Nutrient Thresholds Needed to Control Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms in Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; de Jager, V.C.; Janse, J.H.; Kong, X.; Liu, S.; Ye, Q.; Mooij, W.M. Spatial identification of critical nutrient loads of large shallow lakes: Implications for Lake Taihu (China). Water Res. 2017, 119, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Liere, L.; Janse, J.H.; Arts, G.H. Setting critical nutrient values for ditches using the eutrophication model PCDitch. Aquat. Ecol. 2007, 41, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse, J.H.; Domis, L.N.D.S.; Scheffer, M.; Lijklema, L.; van Liere, L.; Klinge, M.; Mooij, W.M. Critical phosphorus loading of different types of shallow lakes and the consequences for management estimated with the ecosystem model PCLake. Limnologica 2008, 38, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janse, J.H.; Scheffer, M.; Lijklema, L.; van Liere, L.; Sloot, J.S.; Mooij, W.M. Estimating the critical phosphorus loading of shallow lakes with the ecosystem model PCLake: Sensitivity, calibration and uncertainty. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Gragnani, A.; Mur, L.R.; van Nes, E.H. On the dominance of filamentous cyanobacteria in shallow, turbid lakes. Ecology 1997, 78, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate change: A catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Mur, L.R.; Walsby, A.E. Diurnal changes in buoyancy and vertical distribution in populations of Microcystis in two shallow lakes. J. Plankton Res. 1991, 13, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Sharples, J.; Stroom, J.M.; Visser, P.M.; Kardinaal, W.E.A.; Verspagen, J.M.; Sommeijer, B. Changes in turbulent mixing shift competition for light between phytoplankton species. Ecology 2004, 85, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dokulil, M.T.; Teubner, K. Cyanobacterial dominance in lakes. Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms: Causes, Consequences, and Controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsby, A.E. Gas vesicles. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1994, 58, 94–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Oliver, R.L.; Walsby, A.E. Cyanobacterial dominance: The role of buoyancy regulation in dynamic lake environments. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1987, 21, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Hall, N.S.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. The persistence of cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms throughout winter in Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agawin, N.S.R.; Rabouille, S.; Veldhuis, M.J.W.; Servatius, L.; Hol, S.; van Overzee, H.M.J.; Huisman, J. Competition and facilitation between unicellular nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and non—nitrogen-fixing phytoplankton species. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 2233–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paerl, H.W. Physiological ecology and regulation of N2 fixation in natural waters. In Advances in Microbial Ecology; Springer: Bostom, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 305–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferber, L.R.; Levine, S.N.; Lini, A.; Livingston, G.P. Do cyanobacteria dominate in eutrophic lakes because they fix atmospheric nitrogen? Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 690–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothe, H.; Schmitz, O.; Yates, M.G.; Newton, W.E. Nitrogen Fixation and Hydrogen Metabolism in Cyanobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 529–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paerl, H.W.; Pinckney, J.L.; Steppe, T.F. Cyanobacterial–bacterial mat consortia: Examining the functional unit of microbial survival and growth in extreme environments. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 2, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogg, G. Nitrogen fixation in lakes. Plant Soil 1971, 35, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Cassman, K.; Cleveland, C.; Crews, T.; Field, C.B.; Grimm, N.B.; Howarth, R.W.; Marino, R.; Martinelli, L.; Rastetter, E.B. Towards an ecological understanding of biological nitrogen fixation. In The Nitrogen Cycle at Regional to Global Scales; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.S.; Driscoll, C.T.; Stoddard, J.L.; Richer, E.E. Empirical Critical Loads of Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition for Nutrient Enrichment and Acidification of Sensitive US Lakes. BioScience 2011, 61, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capon, S.J.; Lynch, A.J.J.; Bond, N.; Chessman, B.C.; Davis, J.; Davidson, N.; Finlayson, M.; Gell, P.A.; Hohnberg, D.; Humphrey, C.; et al. Regime shifts, thresholds and multiple stable states in freshwater ecosystems; a critical appraisal of the evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 534, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gsell, A.S.; Scharfenberger, U.; Özkundakci, D.; Walters, A.; Hansson, L.-A.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Nõges, P.; Reid, P.C.; Schindler, D.E.; Van Donk, E. Evaluating early-warning indicators of critical transitions in natural aquatic ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8089–E8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilt, S.; Alirangues Nuñez, M.M.; Bakker, E.S.; Blindow, I.; Davidson, T.A.; Gillefalk, M.; Hansson, L.-A.; Janse, J.H.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Jeppesen, E.; et al. Response of Submerged Macrophyte Communities to External and Internal Restoration Measures in North Temperate Shallow Lakes. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, T.; Hatton, K.; O’Connor, M.; Connor, L.; Moss, B. Effects of nitrate load on submerged plant biomass and species richness: Results of a mesocosm experiment. Fundam. Appl. Limnol./Arch. Hydrobiol. 2008, 173, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.I.A.; Dossena, M.; Bohan, D.A.; Jeppesen, E.; Kordas, R.L.; Ledger, M.E.; Meerhoff, M.; Moss, B.; Mulder, C.; Shurin, J.B.; et al. Chapter Two—Mesocosm Experiments as a Tool for Ecological Climate-Change Research. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2013, 48, 71–181. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, M.; Teurlincx, S.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Janse, J.H.; Troost, T.A.; van Wijk, D.; Mooij, W.M.; Janssen, A.B.G. A Generically Parameterized model of Lake eutrophication (GPLake) that links field-, lab- and model-based knowledge. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottingham, K.L.; Ewing, H.A.; Greer, M.L.; Carey, C.C.; Weathers, K.C. Cyanobacteria as biological drivers of lake nitrogen and phosphorus cycling. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Andersen, T.; Baron, J.S.; Bergström, A.-K.; Jansson, M.; Kyle, M.; Nydick, K.R.; Steger, L.; Hessen, D.O. Shifts in lake N: P stoichiometry and nutrient limitation driven by atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Science 2009, 326, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; Teurlincx, S.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Rost, J.; Schipper, A.M.; Seelen, L.M.S.; Mooij, W.M.; Janse, J.H. PCLake+: A process-based ecological model to assess the trophic state of stratified and non-stratified freshwater lakes worldwide. Ecol. Model. 2019, 396, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse, J.H. Model Studies on the Eutrophication of Shallow Lakes and Ditches; Wageningen Universiteit: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mellios, N.; Kofinas, D.; Laspidou, C.; Papadimitriou, T. Mathematical Modeling of Trophic State and Nutrient Flows of Lake Karla using the PCLake Model. Environ. Process. 2015, 2, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mooij, W.M.; Janse, J.; Domis, L.D.S.; Hülsmann, S.; Ibelings, B.W. Predicting the effect of climate change on temperate shallow lakes with the ecosystem model PCLake. Shallow Lakes A Chang. World 2007, 584, 443–454. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gerven, L.; Brederveld, R.J.; de Klein, J.J.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Downing, A.S.; Faber, M.; Gerla, D.J.; Hoen, J.t.; Janse, J.H.; Janssen, A.B.G. Advantages of concurrent use of multiple software frameworks in water quality modelling using a database approach. Fundam. Appl. Limnol./Arch. Hydrobiol. 2015, 186, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooij, W.M.; Brederveld, R.J.; de Klein, J.J.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Downing, A.S.; Faber, M.; Gerla, D.J.; Hipsey, M.R.; Janse, J.H.; Janssen, A.B.G. Serving many at once: How a database approach can create unity in dynamical ecosystem modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 61, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ploug, H.J.L. Cyanobacterial surface blooms formed by Aphanizomenon sp. and Nodularia spumigena in the Baltic Sea: Small-scale fluxes, pH, and oxygen microenvironments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janse, J.H. A model of ditch vegetation in relation to eutrophication. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Vonk, M.; Los, H.F.; van der Molen, D.T.; Mooij, W.M. Fuzzy modeling of cyanobacterial surface waterblooms: Validation with noaa-avhrr satellite images. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 1456–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, B.; Yang, G.; Ma, J.; Deng, J.; Li, W.; Wu, T.; Liu, L.; Gao, G.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y. Dynamics of variability and mechanism of harmful cyanobacteria bloom in Lake Taihu, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 759–770. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Kong, F. Effects of light and wind speed on the vertical distribution of Microcystis aeruginosa colonies of different sizes during a summer bloom. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2009, 94, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Luo, L.; Ding, Y.; Bian, G. Dynamics of cyanobacterial bloom formation during short-term hydrodynamic fluctuation in a large shallow, eutrophic, and wind-exposed Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8546–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.H.; Walsby, A.E. The Effect of Temperature on Recovery of Buoyancy by Microcystis. Microbiology 1986, 132, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfeifer, F. Distribution, formation and regulation of gas vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, P.M.; Ibelings, B.W.; Mur, L.R. Autunmal sedimentation of Microcystis spp. as result of an increase in carbohydrate ballast at reduced temperature. J. Plankton Res. 1995, 17, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Fao, G. Hypothesis on cyanobacteria bloom-forming mechanism in large shallow eutrophic lakes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 589–595. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Visser, P.M.; Passarge, J.; Mur, L.R. Modelling vertical migration of the cyanobacterium Microcystis. Hydrobiologia 1997, 349, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, E.A.; Uittenbogaard, R.; van de Wiel, B.J.H.; Pires, L.M.D.; Clercx, H.J.H. An alternative explanation for cyanobacterial scum formation and persistence by oxygenic photosynthesis. Harmful Algae 2016, 60, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, U. An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Kong, F.; Luo, L.; Shi, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tao, Y. Effects of wind and wind-induced waves on vertical phytoplankton distribution and surface blooms of Microcystis aeruginosa in Lake Taihu. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2006, 21, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, I.T.; Hutchinson, P.A. Effect of wind on the distribution of phytoplankton cells in lakes revisited. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.R.; Meyer, D.L.; Waite, A.M.; Ivey, G.N.; Hamilton, D.P. Disaggregation of Microcystis aeruginosa colonies under turbulent mixing: Laboratory experiments in a grid-stirred tank. Hydrobiologia 2004, 519, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gao, J.; Hörmann, G. Hydrodynamic-phytoplankton model for short-term forecasts of phytoplankton in Lake Taihu, China. Limnologica 2012, 42, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, B.B.; Bailey, M.C.; Hamilton, D.P. Simulation of vertical position of buoyancy regulating Microcystis aeruginosa in a shallow eutrophic lake. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 62, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.C.; Ibelings, B.W.; Hoffmann, E.P.; Hamilton, D.P.; Brookes, J.D. Eco-physiological adaptations that favour freshwater cyanobacteria in a changing climate. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.; Webster, I.T. A model for the light-limited growth of buoyant phytoplankton in a shallow, turbid waterbody. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1994, 45, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.; Walsby, A. Water-blooms. Biol. Rev. 1975, 50, 437–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromkamp, J.; Walsby, A.E. A computer model of buoyancy and vertical migration in cyanobacteria. J. Plankton Res. 1990, 12, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormans, M.; Sherman, B.; Webster, I. Is buoyancy regulation in cyanobacteria an adaptation to exploit separation of light and nutrients? Mar. Freshw. Res. 1999, 50, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Li, G.; Li, D. The decline process and major pathways of Microcystis bloom in Taihu Lake, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Kellar, P.E. Nitrogen-Fixing Anabaena: Physiological Adaptations Instrumental in Maintaining Surface Blooms. Science 1979, 204, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severin, I.; Stal, L.J. Light dependency of nitrogen fixation in a coastal cyanobacterial mat. ISME J. 2008, 2, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S.N.; Lewis, W.M., Jr. A numerical model of nitrogen flxation and its application to Lake Valencia, Venezuela. Freshw. Biol. 1987, 17, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseleva, T.; Wagener, F.O.O. Bifurcations of optimal vector fields in the shallow lake model. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2010, 34, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsygankov, A.A. Nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria: A review. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2007, 43, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Tucker, J.; Bland, P.T. Carotenoid enhancement and its role in maintaining blue-green algal (Microcystis aeruginosa) surface blooms 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1983, 28, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Bland, P.T.; Bowles, N.D.; Haibach, M.E. Adaptation to high-intensity, low-wavelength light among surface blooms of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Dreher, T.W.; Li, R. An overview of diversity, occurrence, genetics and toxin production of bloom-forming Dolichospermum (Anabaena) species. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shan, K.; Song, L.; Chen, W.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, L. Analysis of environmental drivers influencing interspecific variations and associations among bloom-forming cyanobacteria in large, shallow eutrophic lakes. Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; Hall, N.S.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Wu, Y.; Rossignol, K.L.; Dong, L.; McCarthy, M.J.; Joyner, A.R. Controlling cyanobacterial blooms in hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China: Will nitrogen reductions cause replacement of non-N 2 fixing by N 2 fixing taxa? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huisman, J.; Matthijs, H.; Visser, P. Harmful Cyanobacteria Springer Aquatic Ecology Series 3; Spinger: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, S.N.; Schindler, D.W. Influence of nitrogen to phosphorus supply ratios and physicochemical conditions on cyanobacteria and phytoplankton species composition in the Experimental Lakes Area, Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 56, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, J.M.; Özkundakci, D.; Hamilton, D.P.; Jones, J.R. Latitudinal variation in nutrient stoichiometry and chlorophyll-nutrient relationships in lakes: A global study. Fundam. Appl. Limnol./Arch. Hydrobiol. 2012, 181, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratt, A.; Finlay, J.; Welter, J.; Vculek, B.; Van Allen, R. Co-limitation by N and P Characterizes Phytoplankton Communities Across Nutrient Availability and Land Use. Ecosystems 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerla, D.J.; Mooij, W.M.; Huisman, J. Photoinhibition and the assembly of light-limited phytoplankton communities. OIKOS 2011, 120, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilzer, M.M. Light-dependence of photosynthesis and growth in cyanobacteria: Implications for their dominance in eutrophic lakes. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1987, 21, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Maberly, S.C. Photoinhibition and the availability of inorganic carbon restrict photosynthesis by surface blooms of cyanobacteria. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, J.D.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Heckathorn, S.A.; Krause, A.E. Role of suspended sediments and mixing in reducing photoinhibition in the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2012, 4, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichtenberg, M.; Cartaxana, P.; Kühl, M. Vertical Migration Optimizes Photosynthetic Efficiency of Motile Cyanobacteria in a Coastal Microbial Mat. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waajen, G.; van Oosterhout, F.; Douglas, G.; Lürling, M. Management of eutrophication in Lake De Kuil (The Netherlands) using combined flocculant—Lanthanum modified bentonite treatment. Water Res. 2016, 97, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Janssen, A.B.G.; de Klein, J.J.; Kroeze, C.; Strokal, M.; Ma, L.; Zheng, Y. Modeling nutrients in Lake Dianchi (China) and its watershed. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teurlincx, S.; van Wijk, D.; Mooij, W.M.; Kuiper, J.J.; Huttunen, I.; Brederveld, R.J.; Chang, M.; Janse, J.H.; Woodward, B.; Hu, F.; et al. A perspective on water quality in connected systems: Modelling feedback between upstream and downstream transport and local ecological processes. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 40, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, A.S.; Chang, M.; Kuiper, J.J.; Campenni, M.; Hayha, T.; Cornell, S.; Svedin, U.; Mooij, W.M. Learning from generations of sustainability concepts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Description | Reference Value | Applied Value | Unit | Model Notation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HW | Transition constant of wind speed | 3–4 [55,65,66,67], 2 [68,69], 2–3 [56], 4 [28] | 3 | m s−1 | cVWindThrBlue |
| HT | Transition constant of temperature | 12–18 [60,70] | 15 | °C | cTmThrBlue |
| HB | Transition constant of cyanobacterial biomass (expressed as chl-a level) | 10–100 [55], 100 [71], 20 [16] | 10 | mg chl-a m−3 | cChlaThrBlue |
| Wmax | Maximum floating speed | 1–10 [71], 4.5 [72], 6 [73], 0.2–250 [74], 10 [75] | 10 | m day−1 | cVFloMaxBlueW |
| Parameter | Description | Reference Value * | Applied Value | Model Notation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS | Nitrogen fixation rate at light saturation | 366 nmol N2 (106 heterocysts)−1 h−1 | 60 µgN mgChl−1 day−1 | cNfixMaxBlue |
| D | Nitrogen fixation rate in the dark | 58 nmol N2 (106 heterocysts)−1 h−1 | 9.5 µgN mgChl−1 day−1 | cNfixDarkBlue |
| NS−1 | Auxiliary parameter for nitrogen fixation–light curve | 2.16 (Ei m−2)−1 | 0.036 (J m−2 s−1)−1 | cAlphNfix |
| Iave | The average of integral light through depth | dynamically calculated (Ei m−2) | dynamically calculated (J m−2 s−1) | aLPARAveSurf, aLPARAveEpi, aLPARAveHyp |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, M.; Teurlincx, S.; Janse, J.H.; Paerl, H.W.; Mooij, W.M.; Janssen, A.B.G. Exploring How Cyanobacterial Traits Affect Nutrient Loading Thresholds in Shallow Lakes: A Modelling Approach. Water 2020, 12, 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092467
Chang M, Teurlincx S, Janse JH, Paerl HW, Mooij WM, Janssen ABG. Exploring How Cyanobacterial Traits Affect Nutrient Loading Thresholds in Shallow Lakes: A Modelling Approach. Water. 2020; 12(9):2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092467
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Manqi, Sven Teurlincx, Jan H. Janse, Hans W. Paerl, Wolf M. Mooij, and Annette B. G. Janssen. 2020. "Exploring How Cyanobacterial Traits Affect Nutrient Loading Thresholds in Shallow Lakes: A Modelling Approach" Water 12, no. 9: 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092467
APA StyleChang, M., Teurlincx, S., Janse, J. H., Paerl, H. W., Mooij, W. M., & Janssen, A. B. G. (2020). Exploring How Cyanobacterial Traits Affect Nutrient Loading Thresholds in Shallow Lakes: A Modelling Approach. Water, 12(9), 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092467






