Response of Soil Water Dynamics to Rainfall on A Collapsing Gully Slope: Based on Continuous Multi-Depth Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Dynamics of Soil Water
3.2. Responses of the Dynamics of Soil Water to Typical Rainfall Events
3.3. Soil Water Storage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.X. Benggang erosion: The influencing factors. Catena 1996, 27, 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.L.; Qiu, J.N.; Zhang, D.L. Characteristics of slope runoff and soil water content in benggang colluviums under simulated rainfall. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voarintsoa, N.R.G.; Cox, R.; Razanatseheno, M.O.M.; Rakotondrazafy, A.F.M. Relation between bedrock geology, topography and lavaka distribution in Madagascar. S. Afr. J. Geol. 2012, 115, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacellar, L.A.P.; Netto, A.L.C.; Lacerda, W.A. Controlling factors of gullying in the Maracujá Catchment, Southeastern Brail. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2005, 30, 1369–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, S.; Rodolfi, G. A typical “calanchi” landscape on the Eastern Apennine margin (Atri, Central Italy) geomorphological features and evolution. Catena 2000, 40, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Z.W.; Chang, X.F.; He, J.J.; Nie, X.D.; Liu, L.; Xiao, H.B.; Wang, D.Y.; Peng, H.; Zeng, G.M. Soil carbon and nitrogen sources and redistribution as affected by erosion and deposition processes: A case study in a loess hilly-gully catchment, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 253, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J.; Wells, R.R. Gully erosion processes, disciplinary fragmentation, and technological innovation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ning, D.; Pan, X. Characteristics and management of Benggang in red soil region of southern China. Soil Water Conserv. China 2009, 1, 31–34, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.S.; Zheng, M.G.; Li, D.Q.; Wu, X.L.; Liang, C.; Nie, X.D.; Huang, B.; Xie, Z.Y.; Yuan, Z.J.; Tang, C.Y. Relationship of benggang number, area, and hypsometric integral values at different landform developmental stages. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart, F.; Marignani, M.; Pérez-Gallego, N.; Santi, E.; Maccherini, S. Thirty years of studies on badlands, from physical to vegetational approaches: A succinct review. Catena 2013, 106, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J. Soil erosion science: Reflections on the limitations of current approaches. Catena 2006, 68, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.S.; Yuan, Z.J.; Zhuo, M.N.; Huang, B.; Nie, X.D.; Xie, Z.Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Li, D.Q. Coupling effects of erosion and surface roughness on colluvial deposits under continuous rainfall. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, C.; Huang, B.; Liu, T.; Guo, T.L.; Yuan, Z.J.; He, B.; Li, D.Q. Flow hydraulic responses to near-soil surface components on vegetated steep red soil colluvial deposits. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.S.; Huang, Y.H.; Wang, M.K.; Lin, J.S.; Zhao, G.; Ge, H.L. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on steep colluvial deposit erosion in Southeast China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xu, Y.C.; Yang, Q.C. Is the “ecological and economic approach for the restoration of collapsed gullies” in Southern China really economic? Sustain. Sci. 2015, 7, 10308–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; He, Y.B.; Duan, X.Q.; Zou, Z.Q.; Lin, L.R.; Chen, J.Z. Preferential flows and soil moistures on a Benggang slope: Determined by the water and temperature co-monitoring. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.G.; Zhong, C.Z. The mechanism and types of the hillockcollapsing forming in Guangdong province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 1990, 10, 8–16, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.H.; Ling, X.C. Characteristics of slope Benggang and its monitoring technology in Southern China. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 3, 31–34, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Glaoss, R.J.; Nicholl, M.J.; Pringle, S.E.; Wood, T.R. Unsaturated flow through a fracture-matrix network: Dynamic preferential pathways in mesoscale laboratory experiments. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.S.; Ding, S.W.; Liu, C.M.; Xia, D.; Zhang, X.M.; Lv, G.A. Soil moisture characteristics of collapsing gully wall in granite area of southeastern Hubei. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 29, 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Farrick, K.K.; Branfireun, B.A. Soil water storage, rainfall and runoff relationships in a tropical dry forest catchment. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 9236–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadat, F.M.; Taimeh, A.Y. Effect of rainfall intensity, slope, land use and antecedent soil moisture on soil erosion in an arid environment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarrón-Galeote, M.A.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Quesada, M.A. Influence of aspect in soil and vegetation water dynamics in dry Mediterranean conditions: Functional adjustment of evergreen and semi-deciduous growth forms. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhuo, M.N.; Xie, Z.Y.; Yuan, Z.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Huang, B.; Liao, Y.S.; Li, D.Q.; Wang, Y. Effects of near soil surface components on soil erosion on steep granite red soil colluvial deposits. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliano, P.N.; Whitworth-Hulse, J.I.; Baldi, G. Interception, throughfall and stemflow partition in drylands: Global synthesis and meta-analysis. J. Hydrol. 2018, 568, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieskovský, J.; Kenderessy, P. Modelling the effect of vegetation cover and different tillage practices on soil erosion in VineyArds: A case study in Vráble (Slovakia) using WATEM/SEDEM. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; Malvar, M.C.; Serpa, D.; González-Pelayo, O.; Keizer, J.J. Do wildfire and slope aspect affect soil water repellency in eucalypt plantations? —A two-year high resolution temporal dataset. Catena 2020, 189, 104471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Ke, T.; Li, S.X.; Deng, S.Q.; An, X.L.; Ma, X.; Philippis, R.D.; Chen, L.Z. Induced biological soil crusts and soil properties varied between slope aspect, slope gradient and plant canopy in the Hobq desert of China. Catena 2020, 190, 104559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Murillo, J.F.; Gabarrón-Galeote, M.A.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D. Soil water repellency in Mediterranean rangelands under contrasted climatic, slope and patch conditions in southern Spain. Catena 2013, 110, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, S.; Horton, R.; Shao, M.A. Effects of vegetation and slope aspect on water budget in the hill and gully region of the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2011, 87, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.B.; Woods, R.A.; McDonnell, J.J. Hillslope threshold response to rainfall: (1) A field based forensic approach. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, J.A.; Wilcox, B.P.; Breshears, D.D.; Tongway, D.J.; Imeson, A.C. Vegetation patches and runoff-erosion as interacting ecohydrological processes in semiarid landscapes. Ecology 2005, 86, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, L.; las Heras, M.M.; Espigares, T.; Nicolau, J.M. Overland flow directs soil moisture and ecosystem processes at patch scale in Mediterranean restored hillslopes. Catena 2015, 133, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.H.; Tao, W.H.; Qin, G.H.; Hopkins, I.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.J.; Lin, H.; Guo, L. Soil micro-climate variation in relation to slope aspect, position, and curvature in a forested catchment. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 290, 107999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. The influence of geomorphological position and vegetation cover on the erosional and hydrological processes on a Mediterranean hillslope. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Cerdà, A.; Tarolli, P. Soil water erosion on Mediterranean vineyards: A review. Catena 2016, 141, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.S.; Yuan, Z.J.; Zheng, M.G.; Li, D.Q.; Nie, X.D.; Wu, X.L.; Huang, B.; Xie, Z.Y.; Tang, C.Y. The spatial distribution of Benggang and the factors that influence it. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 2323–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Wu, H.W.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhao, G.Q.; Wei, J.Q. Linking spatial distributions of the patchy grass Achnatherum splendens with dynamics of soil water and salt using electromagnetic induction. Catena 2017, 149, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro-Díaz, P.; Ochoa-Sánchez, A.; Célleri, R. Impact of tussock grasses removal on soil water content dynamics of a tropical mountain hillslope. Ecohydrology 2019, 12, e2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor, Á.G.; Bautista, S.; Small, E.E.; Dixon, M.; Bellot, J. Measurement of the connectivity of runoff source areas as determined by vegetation pattern and topography: A tool for assessing potential water and soil losses in drylands. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W10423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.M.; Wang, W.L.; Wang, T.C.; Wang, W.X.; Kang, H.L. Impacts of different vegetation restoration options on gully head soil resistance and soil erosion in loess tablelands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2020, 45, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.H.; Gao, J.E.; Huang, Y.F.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, M.J. Effects of vegetation stems on hydraulics of overland flow under varying water discharges. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, G.H.; Zhang, X.C.; Li, Z.W.; Su, Z.L.; Yi, T.; Shi, Y.Y. Effects of near soil surface characteristics on soil detachment by overland flow in a natural succession grassland. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.V.; Zhang, T.Y.; Wells, R.R.; Liu, B.Y. Consolidation effects on relationships among soil erosion properties and soil physical quality indicators. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ela, S.D.; Gupta, S.C.; Rawls, W.J. Macropore and surface seal interactions affecting water infiltration into soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zheng, F.L.; Jia, L.; Jia, Y.F.; Zhang, X.C.; Hu, F.N.; Zhang, J.Q. Interactive effects of raindrop impact and groundwater seepage on soil erosion. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, E.; Abdi, E.; Saravi, M.M.; Nieber, J.L.; Majnounian, B.; Chirico, G.B.; Wilson, B.; Nazaririad, M. Soil water dynamics under different forest vegetation cover: Implications for hillslope stability. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 2106–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbino, G.; Nicotera, M.V. Unsaturated soil mechanics in rainfall-induced flow landslides. Eng. Geol. 2013, 165, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannoppen, W.; Vanmaercke, M.; De Baets, S.; Poesen, J.A. Review of the mechanical effects of plant roots on concentrated flow erosion rates. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Zhou, M.; Lin, J.S.; Jiang, F.S.; Huang, B.F.; Xu, M.K.; Ge, H.L.; Huang, Y.H. Comparison of soil physicochemical properties and mineralogical compositions between noncollapsible soils and collapsed gullies. Geoderma 2018, 317, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
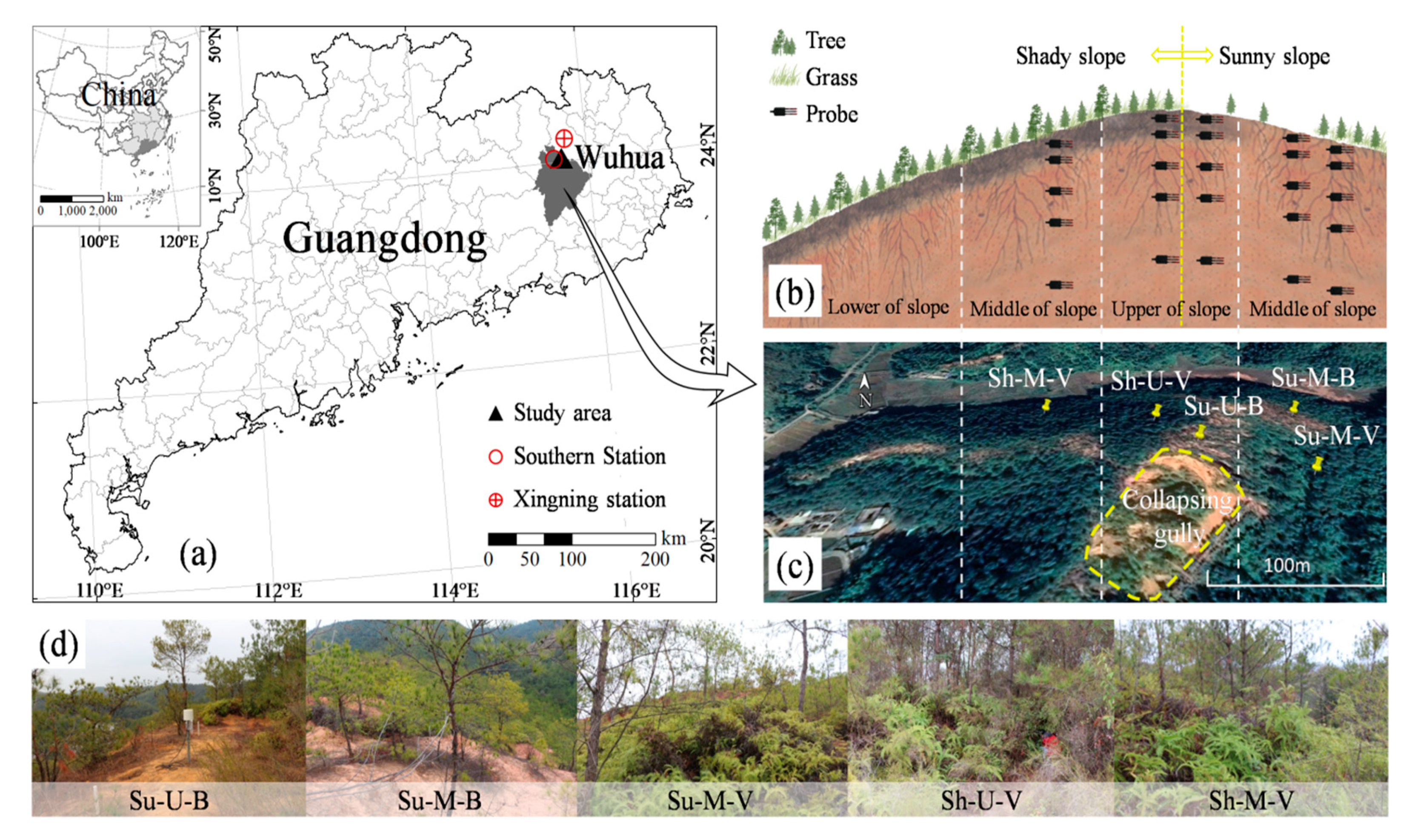

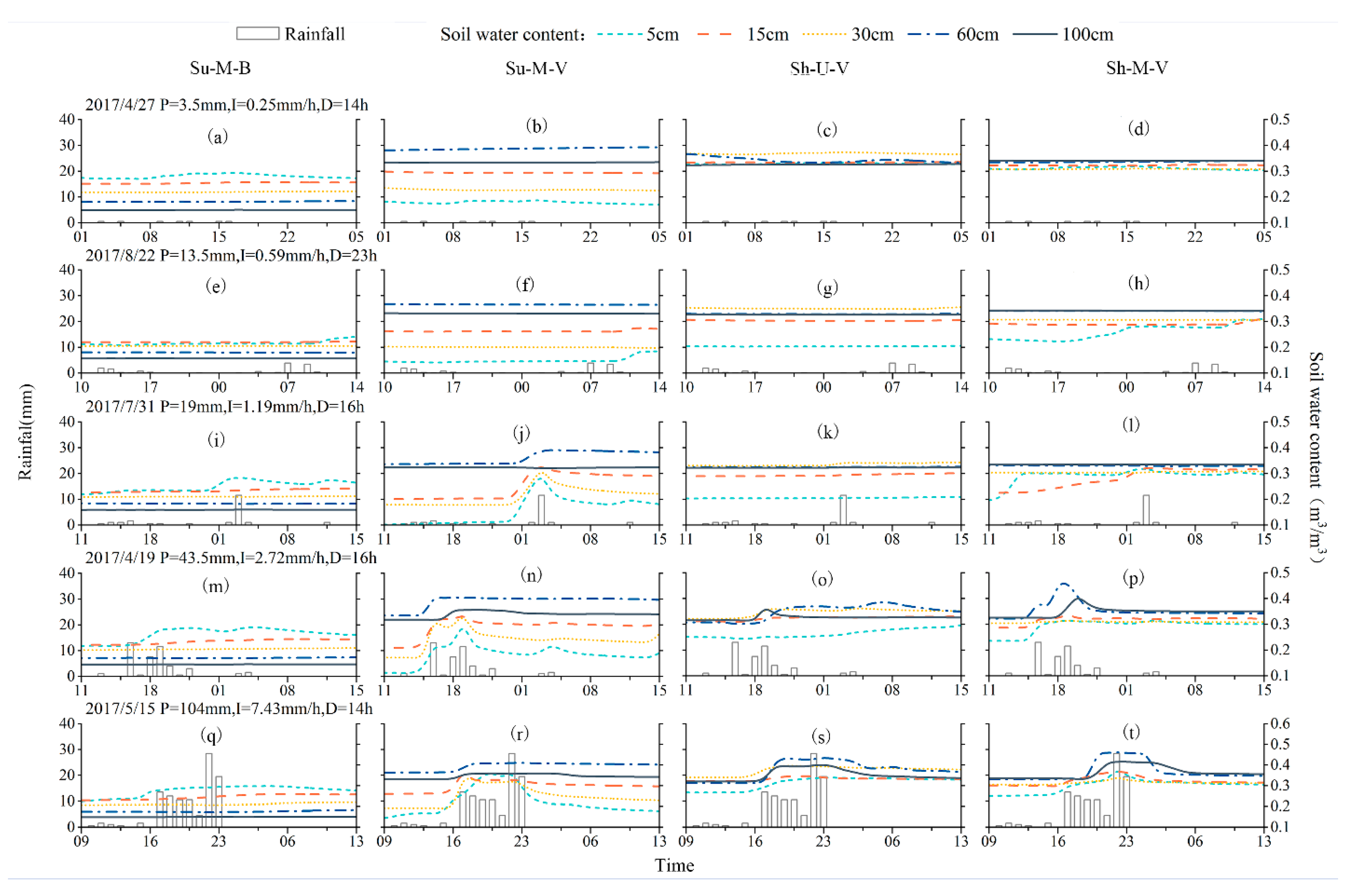

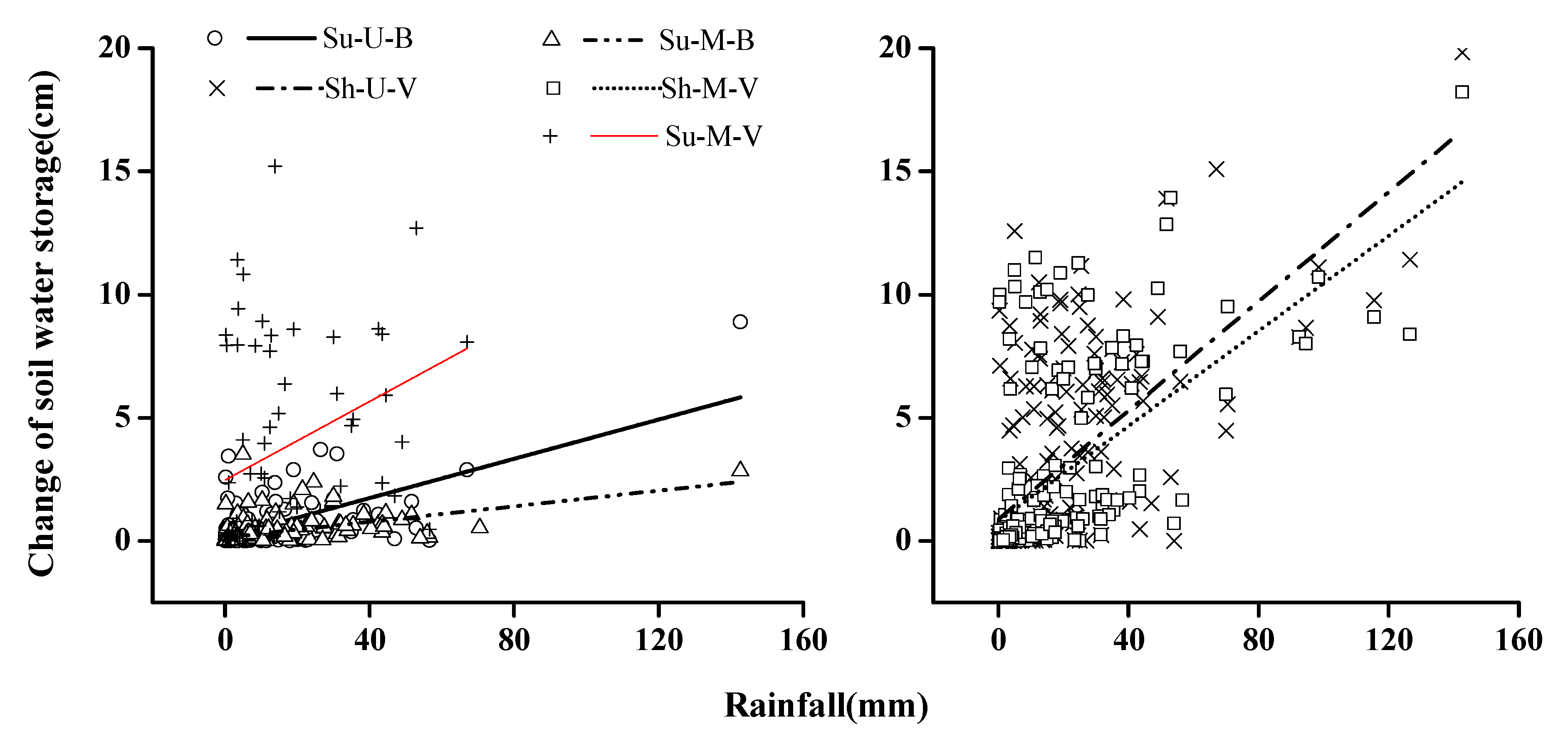
| Sites | Slope Aspect | Slope Position | Dominant Species | Undergrowth Coverage (%) | Particle Size Composition (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | Silt | Sand | |||||
| (<0.002 mm) | (0.002–0.05 mm) | (0.05–2 mm) | |||||
| Su-U-B | Sunny slope | Upper of slope | Bare land | 5 ± 1.3 | 27.66 ± 4.45 | 29.10 ± 4.83 | 43.24 ± 6.39 |
| Su-M-B | Sunny slope | Middle of slope | Bare land | 5 ± 2.1 | 5.49 ± 1.12 | 46.86 ± 7.63 | 47.65 ± 4.39 |
| Su-M-V | Sunny slope | Middle of slope | P. massoniana, D. dichotoma | 75 ± 13.5 | 38.51 ± 6.38 | 33.02 ± 5.77 | 28.47 ± 3.44 |
| Sh-U-V | Shady slope | Upper of slope | P. massoniana, D. dichotoma, B. frutescens, R. tomentosa. | 80 ± 17.6 | 42.48 ± 10.65 | 14.63 ± 3.82 | 42.89 ± 5.36 |
| Sh-M-V | Shady slope | Middle of slope | P. massoniana, D. dichotoma, B. frutescens, R. tomentosa. | 96 ± 16.2 | 51.64 ± 9.12 | 23.53 ± 1.09 | 24.83 ± 2.17 |
| Year | 0–10 mm | 10–30 mm | 30–60 mm | 60–100 mm | >100 mm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Rainfall mm/ Percentage% | Frequency | Rainfall mm/ Percentage% | Frequency | Rainfall mm/ Percentage% | Frequency | Rainfall mm/ Percentage% | Frequency | Rainfall mm/ Percentage% | |
| 2017 | 100 | 243.4/21.6 | 21 | 338.8/30.1 | 11 | 439.6/39.0 | 0 | 0/0 | 1 | 104.0/9.2 |
| 2018 | 74 | 157.4/10.3 | 34 | 595.9/38.9 | 12 | 475.8/31.1 | 2 | 159.2/10.4 | 1 | 142.8/9.3 |
| 2019 | 75 | 201.5/10.8 | 33 | 615.0/33.0 | 11 | 450.5/24.1 | 4 | 356/19.1 | 2 | 242.5/13.0 |
| Average | 83 | 200.8/13.3 | 29 | 516.6/34.3 | 11 | 455.3/30.2 | 2 | 171.7/11.4 | 1 | 163.1/10.8 |
| Sites | Soil Depth | Average | Maximum | Minimum | SD | CV | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (m3/m3) | (m3/m3) | (m3/m3) | (m3/m3) | (%) | ||
| Su-U-B | 5 | 0.233c | 0.325 | 0.181 | 0.034 | 14.6% | 6670 |
| 15 | 0.223b | 0.317 | 0.175 | 0.035 | 15.6% | 6670 | |
| 30 | 0.241d | 0.334 | 0.205 | 0.033 | 13.8% | 6670 | |
| 60 | 0.192a | 0.239 | 0.158 | 0.025 | 13.0% | 6508 | |
| 100 | 0.280e | 0.298 | 0.234 | 0.020 | 7.0% | 6670 | |
| Su-M-B | 5 | 0.200d | 0.301 | 0.158 | 0.031 | 15.7% | 6670 |
| 15 | 0.209e | 0.259 | 0.176 | 0.023 | 11.0% | 6670 | |
| 30 | 0.194c | 0.223 | 0.171 | 0.015 | 7.8% | 6670 | |
| 60 | 0.170b | 0.193 | 0.156 | 0.010 | 6.1% | 6670 | |
| 100 | 0.156a | 0.177 | 0.142 | 0.009 | 6.0% | 6670 | |
| Su-M-V | 5 | 0.107a | 0.447 | 0.048 | 0.044 | 41.0% | 6670 |
| 15 | 0.180c | 0.382 | 0.092 | 0.074 | 41.3% | 6670 | |
| 30 | 0.158b | 0.378 | 0.075 | 0.056 | 35.5% | 6670 | |
| 60 | 0.268d | 0.412 | 0.148 | 0.093 | 34.6% | 6670 | |
| 100 | 0.292e | 0.361 | 0.243 | 0.035 | 12.1% | 6670 | |
| Sh-U-V | 5 | 0.201a | 0.356 | 0.155 | 0.048 | 23.9% | 6670 |
| 15 | 0.276c | 0.348 | 0.233 | 0.036 | 13.0% | 6670 | |
| 30 | 0.281d | 0.411 | 0.205 | 0.061 | 21.6% | 6670 | |
| 60 | 0.256b | 0.438 | 0.148 | 0.043 | 16.8% | 6598 | |
| 100 | 0.292e | 0.400 | 0.251 | 0.031 | 10.6% | 6670 | |
| Sh-M-V | 5 | 0.202a | 0.381 | 0.133 | 0.058 | 28.6% | 6670 |
| 15 | 0.228b | 0.370 | 0.151 | 0.065 | 28.5% | 6670 | |
| 30 | 0.301c | 0.343 | 0.291 | 0.006 | 1.9% | 6670 | |
| 60 | 0.303d | 0.463 | 0.251 | 0.035 | 11.5% | 6670 | |
| 100 | 0.311e | 0.416 | 0.263 | 0.028 | 9.1% | 6670 |
| Sites | Average | Maximum | Minimum | SD | CV | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (cm) | (cm) | (cm) | (%) | ||
| Su-U-B | 27.73 | 34.48 | 22.03 | 3.71 | 16.80% | 6508 |
| Su-M-B | 21.17 | 23.95 | 18.94 | 1.30 | 6.53% | 6670 |
| Su-M-V | 27.91 | 44.91 | 18.50 | 7.04 | 33.26% | 6670 |
| Sh-U-V | 31.94 | 47.74 | 24.29 | 6.16 | 25.29% | 6598 |
| Sh-M-V | 34.71 | 49.00 | 29.11 | 3.70 | 12.66% | 6670 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-D.; Zhang, S.-Y.; He, B.; Zhao, X.-L.; Kong, F.-L.; Feng, D.; Zeng, Y.-C. Response of Soil Water Dynamics to Rainfall on A Collapsing Gully Slope: Based on Continuous Multi-Depth Measurements. Water 2020, 12, 2272. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082272
Jiang Z-Y, Wang X-D, Zhang S-Y, He B, Zhao X-L, Kong F-L, Feng D, Zeng Y-C. Response of Soil Water Dynamics to Rainfall on A Collapsing Gully Slope: Based on Continuous Multi-Depth Measurements. Water. 2020; 12(8):2272. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082272
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Zhi-Yun, Xue-Dan Wang, Si-Yi Zhang, Bin He, Xiao-Li Zhao, Fan-Ling Kong, Dan Feng, and Yu-Chao Zeng. 2020. "Response of Soil Water Dynamics to Rainfall on A Collapsing Gully Slope: Based on Continuous Multi-Depth Measurements" Water 12, no. 8: 2272. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082272
APA StyleJiang, Z.-Y., Wang, X.-D., Zhang, S.-Y., He, B., Zhao, X.-L., Kong, F.-L., Feng, D., & Zeng, Y.-C. (2020). Response of Soil Water Dynamics to Rainfall on A Collapsing Gully Slope: Based on Continuous Multi-Depth Measurements. Water, 12(8), 2272. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082272






