Abstract
The removal of antibiotics from the aquatic environment has received great interest. The aim of this study is to examine degradation of oxytetracycline (OTC), tetracycline (TC), chlortetracycline (CTC), amoxicillin (AMO), sulfamethazine (SMZ), sulfamethoxazole (SMX), sulfadimethoxine (SDM) in sludge. Four antibiotic-degrading bacterial strains, SF1 (Pseudmonas sp.), A12 (Pseudmonas sp.), strains B (Bacillus sp.), and SANA (Clostridium sp.), were isolated, identified and tested under aerobic and anaerobic conditions in this study. Batch experiments indicated that the addition of SF1 and A12 under aerobic conditions and the addition of B and SANA under anaerobic conditions increased the biodegradation of antibiotics in sludge. Moreover, the results of repeated addition experiments indicated that the efficiency of the biodegradation of antibiotics using the isolated bacterial strains could be maintained for three degradation cycles. Two groups of potential microbial communities associated with the aerobic and anaerobic degradation of SMX, AMO and CTC in sludge were revealed. Twenty-four reported antibiotics-degrading bacterial genera (Achromobacter, Acidovorax, Acinetobacter, Alcaligenes, Bacillus, Burkholderia, Castellaniella, Comamonas, Corynebacterium, Cupriavidus, Dechloromonas, Geobacter, Gordonia, Klebsiella, Mycobacterium, Novosphingobium, Pandoraea, Pseudomonas, Rhodococcus, Sphingomonas, Thauera, Treponema, Vibrio and Xanthobacter) were found in both the aerobic and anaerobic groups, suggesting that these 24 bacterial genera may be the major antibiotic-degrading bacteria in sludge.
1. Introduction
Antibiotics are discharged from animals (and humans) and enter wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) through the sewage system [1]. In general, antibiotics are not easy for wastewater treatment facilities to remove [2]. The release and persistence of antibiotics in the environments may lead to an increase in antibiotic-resistant bacteria [3]. Tetracycline antibiotics (TCs), such as tetracycline (TC), oxytetracycline (OTC), and chlortetracycline (CTC), are broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis [4]. Sulfonamide antibiotics (SAs) act against most Gram-positive and many Gram-negative bacteria. SAs act as competitive inhibitors of p-aminobenzoic acid in the folic acid synthetic pathway to inhibit the growth of bacteria [5]. Three sulfonamides, sulfamethoxazole (SMX), sulfadimethoxine (SDM), and sulfamethazine (SMZ), are found in sludge in many WWTPs and rivers [6,7,8]. Amoxicillin (AMO) is a β-lactam family antibiotic drug. This class of antibiotics disrupts bacterial cell walls during bacterial growth [9]. AMO in the environment may lead to an increase in antibiotic-resistant bacteria [10].
Several methods for antibiotic removal from wastewater sludge have been proposed. These approaches include chemical oxidation methods such as UV- and solar-based procedures (UV/H2O2, solar/H2O2), ozonation, photocatalysis by Fe2+ or Fe3+/H2O2 and TiO2 photocatalysis [11]. Antibiotic degradation by fungal extracellular enzymes extracted from spent mushroom composts has also been reported [12]. Thermal hydrolysis/anaerobic digestion [13] and the use of aerobic granular sludge treated with manganese oxides [14,15] have also been proposed. Nevertheless, many antibiotics continue to be detected in wastewater sludge [16,17,18]. The use of microorganisms to eliminate antibiotics is a promising strategy [19,20,21]. The aerobic degradation of antibiotics has been observed in pure bacterial cultures and microbial consortiums. Rhodococcus rhodochrous and Aspergillus niger degrade pharmaceuticals via cometabolism [22]. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia DT1 biotransforms tetracycline [23]. Klebsiella sp. SQY5 degrades tetracycline (TEC) [24]. Sulfamethoxazole is biodegraded by individual and mixed bacteria [25,26]. Antibiotic sulfanilamide biodegradation is performed by acclimated microbial populations [27]. Chlortetracycline can be used as the sole carbon and nitrogen source by the acclimated microbiota [28].
The aim of this study was to examine the degradation of antibiotics in sludge by antibiotic-degrading bacteria under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The microbial communities involved in the aerobic and anaerobic degradation of antibiotics in sludge are revealed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
SMX, SDM, SMZ, TC, OTC, CTC, AMO (Table S1) of 99.0% purity and all other chemicals were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Solvents were purchased from Mallinckrodt (Paris, KY, USA).
2.2. Sludge Sample and Medium
The sludge was a semisolid slurry (total solids 0.87 g/L, pH 6.7) that was produced as sewage sludge from the Dihus wastewater treatment plant in Taipei, Taiwan. Fresh sludge was used for antibiotic adaptation. The temperature of the sampling site was 30 °C. The medium used in aerobic experiments contained the following chemicals (mg/L): K2HPO4, 65.3; KH2PO4, 25.5; Na2HPO4·12 H2O, 133.8; NH4Cl, 5.1; CaCl2, 82.5; MgSO4·7H2O, 67.5; and FeCl3·6H2O, 0.75. The medium used in anaerobic experiments contained the following chemicals (mg/L): NH4Cl, 2.7; MgCl2•6H2O, 0.1; CaCl2•2H2O, 0.1; FeCl2•4H2O, 0.02; K2HPO4, 0.27; KH2PO4, 0.35 and resazurin, 0.001. The pH of the medium was adjusted to 7.0 using potassium hydroxide or nitric acid. Resazurin is an indicator, which exhibits red color under aerobic conditions and is colorless under anaerobic conditions. Titanium citrate of 0.9 mM was used as a reducing reagent. All anaerobic operations were performed in an anaerobic glove box.
2.3. Sludge Adaptation
Aerobic adaptation was performed by adding 1 mg/L CTC, SMX and AMO, simultaneously, to 1000 mL serum bottles containing 450 mL of aerobic medium, 50 mL sludge, and incubated on a rotary shaker (120 rpm) at 30 °C without light for 6 months. Anaerobic adaptation was performed by adding 1 mg/L CTC, SMX and AMO, simultaneously, to 1000 mL serum bottles containing 450 mL of anaerobic medium, 50 mL sludge and capped with butyl rubber stoppers and crimp seals, wrapped in aluminum foil, and then incubated without shaking at 30 °C without light for 6 months. All anaerobic operations were performed in an anaerobic glove box. In this paper, the sludge was referred to as antibiotic-adapted sludge.
2.4. Enrichment, Isolation, and Identification of Antibiotic-Degrading Bacteria
The enrichment procedure was performed using 5 mL of antibiotic-adapted sludge in a 125-mL serum bottle containing 45 mL of aerobic or anaerobic medium, with CTC, SMX and AMO of final concentration of 0.2 mg/L, simultaneously, and incubated at 30 °C. The second to the fourth enrichment transfers were amended with gradually increasing concentrations of CTC, SMX and AMO from 0.2 to 1 mg/L. An elevated concentration is commonly used for enrichment to ensure that the CTC, SMX and AMO degraders are selected. After the fourth enrichment, aerobic or anaerobic medium agar plates containing CTC, SMX and AMO (1 mg/L) were inoculated with 100 μL of the liquid part of the sludge by streaking to isolate pure strains of bacteria. The AnaeroPack system was used for anaerobic cultivation, including AnaeroPack®-Anaero and AnaeroPouch®-Anaero. All anaerobic operations were performed in the anaerobic glove box. To confirm that the bacterial strains were antibiotic degraders, degradation experiments were performed using 5 mL (106 CFU/mL) of bacterial culture and 45 mL of medium with 1 mg/L antibiotics on a shaker (120 rpm) at 30 °C in the dark. Samples were taken periodically to analyze residual CTC, SMX and AMO.
The 16S rRNA gene of the isolated bacterial strains were amplified by PCR with the 5′-primer F8 (5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′) and the 3′-primer R1510 (5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′). The PCR parameters included initial denaturation at 94 °C for 10 min, followed by 35 cycles of 45 s at 94 °C, 1 min at 60 °C, and 1 min at 72 °C, with a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The PCR products were sequenced on an ABI Prism automatic sequencer. The 3′-end sequence was converted into the reverse complementary sequence. The overlapping parts of sequences from the 5′ and 3′-ends were identified with the Align Sequences Nucleotide BLAST tool at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) website. Finally, the two sequences were assembled into a single contig sequence based on the overlapping sequences. The 16S rRNA sequences of the four isolates have been submitted to Genbank; accession number: A12: MT678104, B: MT678105, SANA: MT678106, SF1: MT678107. The 16S rRNA gene sequences of the four isolated bacterial strains were used to search the NCBI 16S rRNA database with the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLASTn). The top five sequences (with the highest scores) in the Blast results for each 16S rRNA sequence were retrieved and used to construct the phylogenetic tree. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using Clustal X 2.0 with 1000 bootstrapping repetitions [29]. The neighbor-joining algorithm was used to construct the phylogenetic tree.
2.5. Settings of Batch and Readdition Experiments
Two sets of experiments (batch and continuous addition) were performed under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. In the batch experiments, the aerobic experiments were performed in 125 mL serum bottles with the following contents: 45 mL of medium, 5 g of sludge, 5 mL (106 CFU/mL) of bacterial culture, and 2 mg/L SAs (SMX, SDM, SMZ), TCs (TC, OTC, CTC) or AMO, and which were incubated on a rotary shaker (120 rpm) at 30 °C in the dark. The anaerobic experiments were performed in 125 mL serum bottles containing 45 mL of medium, 5 g of sludge, 5 mL (106 CFU/mL) of bacterial culture, and 2 mg/L SAs (SMX, SDM, SMZ), TCs (TC, OTC, CTC) or AMO, and were conducted in an anaerobic glove box. The bottles were capped with butyl rubber stoppers and crimp seals, wrapped in aluminum foil, and then incubated without shaking at 30 °C. Inoculated controls containing 45 mL of medium, 5 g of sludge, and 2 mg/L SAs (SMX, SDM, SMZ), TCs (TC, OTC, CTC) or AMO, and were incubated without degrading bacteria at 30 °C. Sterile controls containing 45 mL of medium and 5 g of sludge were autoclaved at 121 °C for 30 min. SAs (SMX, SDM, SMZ), TCs (TC, OTC, CTC) or AMO were added at 2 mg/L after autoclaving. The remaining percentage of the original antibiotic content in the sludge ranged from 98.5 to 96.8%, indicating that the aerobic and anaerobic antibiotic degradation observed in all of the following experiments was due to microbial activity. Each experiment was repeated three times.
For the repeated addition experiments, sludge samples were used by adding 2 mg/L CTC, SMX and AMO three times under aerobic or anaerobic conditions. Aerobic experiments were conducted using 1000 mL bottles containing 450 mL of aerobic medium, and 50 g of sludge, with or without 50 mL (106 CFU/mL) of mixed bacterial culture. Anaerobic experiments were filled using 1000 mL bottles containing 450 mL of anaerobic medium, and 50 g of sludge, with or without 50 mL (106 CFU/mL) of mixed bacterial culture. CTC, SMX and AMO was readded into each medium when antibiotics were decreased to an undetectable level. The aerobic experiments were aerated by an air diffuser and the mixtures were stirred. The anaerobic experiments were conducted in an anaerobic glove box; capped with butyl rubber stoppers and crimp seals, wrapped in aluminum foil, and then incubated without shaking. The repeated addition experiments were performed at 30 °C.
2.6. Analytical Methods
SAs were extracted twice from the samples with an extraction solution of 10:3:1 water (containing 0.1% formic acid): acetonitrile:methanol. The extracts were analyzed using an Agilent 1260 HPLC system equipped with a 4.6 × 250 mm column (Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with photodiode array detector monitoring at 270 nm. The mobile phase was 30%:70% acetonitrile:water (containing 0.1% formic acid). TCs were extracted twice from the samples with an extraction solution of 4:1 water (containing 0.1% HCl): acetonitrile. The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile and water (containing 0.1% HCl); AMO was extracted twice from the samples with methanol. TCs, and AMO were quantified with an Agilent 1260 HPLC equipped with a 4.6 × 100 mm column (Poroshell 120 EC-C18, Agilent) with a photodiode array detector monitoring at 270 nm and 229 nm. The recovery percentages for TC, OTC, CTC, SDM, SMX, SMZ, and AMO were 91.2%, 95.5%, 89.3%, 94.7%, 93.4%, 90.3% and 92.6%, respectively. The detection limit was 0.1 mg/L in all cases. The remaining percentage and removal percentage were computed using the following formula: remaining percentage [%] = (residue concentration/initial concentration) × 100; removal percentage [%] = [1 − (residue concentration/initial concentration) × 100]. The degradation data collected in this study fit well with first-order kinetics (i.e., t = −ln(C/C0)/k, where C0 is the initial concentration, C is the concentration, t is the time period, t1/2 is the half-life, and k is the degradation rate constant). The coefficient of determinations (R2) ranged from 0.923 to 0.982.
2.7. Microbial Community Analysis
Total DNA was extracted from the sludge at the end of the readdition experiments using a PowerSoil DNA Isolation kit (QIAGEN, Venlo, Netherlands). The purified DNA was used as a template for the amplification of the 16S rRNA gene sequence containing the V5-V8 variable regions using a 5′-primer containing an Illumina adaptor and a 16S rRNA gene-specific sequence (5′-CCTACGGGNBGCASCAG-3′). The sequence of the 3′-primer contained an Illumina adaptor and a 16S rRNA gene-specific sequence (5′-GACTACNVGGGTATCTAATCC-3′). PCR was performed as previously described [30,31]. Next generation sequencing (NGS) was performed at the Genome Center of National Yang-Ming University, Taiwan, using the MiSeq platform (Illumina, Inc, San Diego, CA, USA.). A chimera check was used to analyze the 16S rRNA gene sequences to remove chimeras. The remaining sequences were subsequently analyzed using the classifier software of the Ribosomal Database Project (http://pyro.cme.msu.edu/) for phylogenetic assignment. Similarity (95%) was used for bacterial grouping. Xenobiotic biodegradation-associated bacteria were identified using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database [32]. A cluster analysis of the bacterial community compositions was performed using the Heatmap function in the ComplexHeatmap package of R (www.r-project.org).
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
Sludge samples were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline for 2 h at 4 °C and postfixed in 1% osmium tetroxide in the same buffer for 1 h. The samples were dehydrated in a graded ethyl alcohol series, critical point-dried, gold coated, and viewed under a JSM-5410 scanning electron microscope (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Antibiotic-Degrading Bacteria
Twelve and eight bacterial strains with the ability to use CTC, AMO and SMX as carbon sources under aerobic and anaerobic conditions were isolated from the sludge samples. The five aerobic isolates showing the greatest degrading capability were strains SF1, SF2, SF3, SF4 and A12. When the bacterial counts increased, the level of CTC, AMO and SMX decreased. The order of CTC, AMO and SMX degradation was strain SF1 > strain A12 > strain SF2 > strain SF3 > strain SF4. Strains SF1 and A12 exhibited the greatest aerobic degradation capability. The degradation of CTC, AMO and SMX by strain SF1 after 8 days of incubation was equal to 81.6, 89.1, and 95.9%, respectively (Table 1). The degradation of CTC, AMO and SMX by strain A12 after 8 days of incubation was equal to 69.4, 81.4, and 89.6%, respectively. The degradation of CTC, AMO and SMX by strains SF1 and A12 after 8 days of incubation was equal to 89.4, 93.4, and 99.3%, respectively. The order of the efficiency of the aerobic degradation of antibiotics was as follows: strains SF1 and A12 > strain SF1 > strain A12.

Table 1.
Remaining percentages (%) of chlortetracycline (CTC), amoxicillin (AMO) and sulfamethoxazole (SMX) after incubation with antibiotic-degrading bacteria.
Five anaerobic isolates exhibited the greatest antibiotic-degradation capability were strains B, SANA, SANB, SANC, SANC, and SAND. When the bacterial counts increased, the level of CTC, AMO and SMX decreased. The order of CTC, AMO and SMX degradation is strain B > strain SANA > strain SANB > strain SANC > strain SAND. Strains B and SANA exhibited the greatest antibiotic degradation capability under anaerobic conditions among the five tested isolates (B, SANA, SANB, SANC, SANC, and SAND). The degradation of CTC, AMO and SMX by strain B after 15 days of incubation was equal to 81.6, 89.1, and 95.1%, respectively (Table 1). The degradation of CTC, AMO and SMX by strain SANA after 15 days of incubation was equal to 59.4, 81.4, and 89.6%, respectively. The degradation of CTC, AMO and SMX by strain B and SANA after 15 days of incubation was equal to 89.6, 93.4, and 99.5%, respectively. The order of the efficiency of the anaerobic degradation of antibiotics was as follows: strains B and SANA > strain B > strain SANA. Yang et al. (2019) reported that the cocultures of strains M10 and M12 can enhance malachite green degradation in milkfish pond sediments. The addition of both bacterial strains M10 and M12 produced better results than each of the single cultures [31]. The aerobic stains SF1 and A12 and the anaerobic strains B and SANA were used in subsequent studies.
The colony morphology and scanning electron micrographs of the four bacterial strains are shown in Figure 1. All of them were Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria.
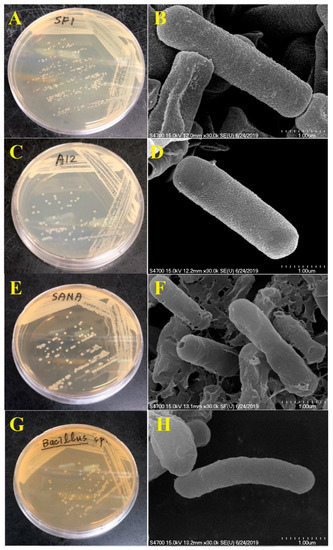
Figure 1.
Colony morphology and scanning electron micrographs of isolated bacterial strains SF1 (Pseudmonas sp.) (A,B), A12 (Pseudmonas sp.) (C,D), SANA (Clostridium sp.) (E,F), and B (Bacillus sp.) (G,H).
Phylogenetic analysis of strains A12, SF1, B and SANA, based on the 16S rRNA gene, is shown in Figure 2. The strains A12, SF1, B and SANA are closely related to Pseudmonas pseudoalcaligenes (99%), Pseudmonas taiwanensis (96%), Bacillus flexus (99%) and Clostridium butyricum (99%), respectively. Pseudomonas bacteria are widespread in various natural environments, such as soil, plants, animals, air and water. Pseudmonas taiwanensis is an aerobic Gram-negative, rod-shaped, motile, nonspore-forming bacterial strain isolated from soil [33]. Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes is an aerobic Gram-negative bacterium. It is able to use cyanide as a nitrogen source, and can be used for bioremediation [34]. Bacillus flexus is a Gram-positive, rod-shaped, endospore-forming bacterium. This bacterium may be isolated from feces and soil. Bacillus flexus has been shown to exert activity mainly against polyvinyl chloride additives and exhibits a low biodegradation rate of polyvinyl chloride polymers [35]. Clostridium butyricum is a strictly anaerobic endospore-forming Gram-positive bacillus. This bacterium has been studied for its efficiency in decolorizing various remazol reactive dyes [36].
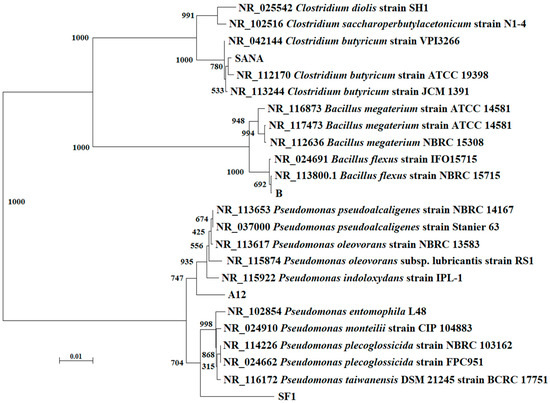
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA genes of the four bacterial strains (A12, B, SF1, SANA). Bootstrapping values at branch points indicate the number of times that the same branch was observed out of 1000 repeats of the phylogenetic reconstruction.
3.2. Degradation of Antibiotics in Sludge with Isolated Bacteria
The antibiotic concentrations in the sterile controls were first examined at the end of the 10th or 15th day incubation periods, under aerobic or anaerobic conditions, respectively. The remaining percentages of antibiotics ranged from 91.7 to 95.3%. Therefore, it was concluded that the antibiotic degradation that occurred in all of the following experiments was due to microbial action.
The aerobic and anaerobic degradation of the antibiotics in sludge containing the isolated bacterial strains is shown in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5. The degradation of the antibiotics was increased in sludge containing the isolated bacterial strains. As shown in Figure 3A, Figure 4A and Figure 5A, the aerobic degradation half-lives of OTC, TC, CTC, SDM, SMX, SMZ and AMO were 3.0, 4.6, 2.3, 2.5, 3.1, 1.7 and 2.0 days, respectively. The anaerobic degradation half-lives of OTC, TC, CTC, SDM, SMX, SMZ and AMO were 4.4, 7.0, 3.4, 4.1, 6.8, 2.4 and 3.0 days, respectively (Figure 3B, Figure 4B and Figure 5B). The order of the degradation rates of the antibiotics was CTC > OTC > TC> AMO > SMX > SDM > SMZ.
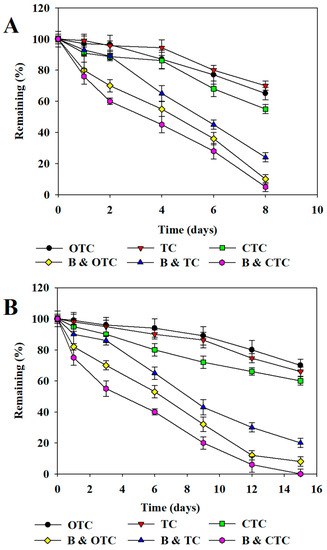
Figure 3.
Degradation of tetracyclines with and without degrading bacteria in sludge. Aerobic (A) and anaerobic (B) degradation of TCs. TC: tetracycline, CTC: chlortetracycline, OTC: oxytetracycline. B: isolated antibiotic-degrading bacteria. Data from three independent experiments are presented as the means ± SE.
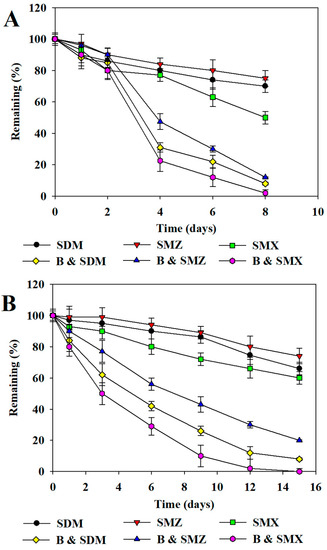
Figure 4.
Degradation of sulfonamides with and without degrading bacteria in sludge. Aerobic (A) and anaerobic (B) degradation of SAs. SMZ: sulfamethazine, SMX: sulfamethoxazole, SDM: sulfadimethoxine. B: isolated antibiotic-degrading bacteria. Data from three independent experiments are presented as the means ± SE.
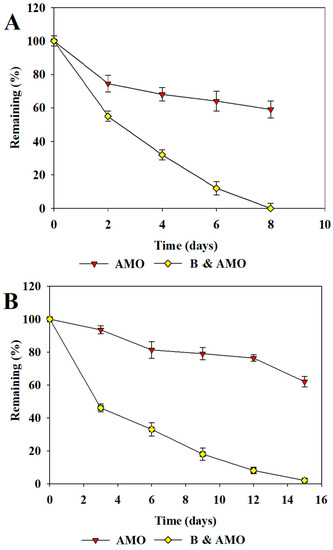
Figure 5.
Degradation of amoxicillin with and without degrading bacteria in sludge. Aerobic (A) and anaerobic (B) degradation of AMO. AMO: amoxicillin. B: isolated antibiotic-degrading bacteria. Data from three independent experiments are presented as the means ± SE.
The order of SA degradation rates in sludge was SMX > SDM > SMZ. Similar trends were observed in a study by Yang et al. (2016) in which fungal enzymes were used to increase the degradation of SAs in sludge [37]. The order of the TC degradation rates in sludge was CTC > OTC > TC. Similar results were reported by Suda et al. (2012) from a study in which TC antibiotics were treated with the laccase enzyme in the presence of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole [38]. The order of the antibiotic degradation rates was TCs > AMO > SAs. Antibiotics with lower molecular weights are easier to degrade than those with higher molecular weights. Larger functional groups may hinder degradation by affecting the interactions between target compounds and the bacteria or enzymes [39]. Moreover, the degradation of compounds with complex structures may require more reaction steps.
3.3. Repeated Addition of Antibiotics and Their Degradation in Sludge
To test the long-term degradation ability of aerobic strains SF1 and A12 and anaerobic strains B and SANA in sludge, experiments involving the repeated addition of antibiotics were performed (Table 2).

Table 2.
The removal rates (%) after the first (1st), second (2nd), and third (3rd) additions of antibiotics.
In the first addition experiments, in the sludge under aerobic conditions, 46.3, 41.6 and 35.6% of SMX, AMO and CTC initially present at 2 mg/L was degraded, respectively. In the sludge under anaerobic conditions, 42.2, 37.4 and 33.5% of SMX, AMO and CTC initially present at 2 mg/L was degraded, respectively. In the sludge under aerobic conditions containing aerobic strains SF1 and A12, 90.6, 88.2 and 82.6% of SMX, AMO and CTC initially present at 2 mg/L was degraded, respectively. In the sludge under anaerobic conditions containing anaerobic strains B and SANA, 92.3, 88.1 and 85.2% of SMX, AMO and CTC initially present at 2 mg/L was degraded, respectively. In the third addition experiments, in the sludge under aerobic conditions, 52.5, 50.4 and 46.1% of SMX, AMO and CTC initially present at 2 mg/L was degraded, respectively. In the sludge under anaerobic conditions, 50.4, 46.4 and 42.7% of SMX, AMO and CTC initially present at 2 mg/L was degraded, respectively. In the sludge under aerobic conditions containing aerobic strains SF1 and A12, 97.5, 95.3 and 90.3% of SMX, AMO and CTC initially present at 2 mg/L was degraded, respectively. In the sludge under anaerobic conditions containing anaerobic strains B and SANA, 98.1, 96.4 and 92.4% of SMX, AMO and CTC initially present at 2 mg/L was degraded, respectively. These results suggest that the degradation rate increased with the repeated addition of SMX, AMO and CTC. The repeated addition of antibiotics might increase the abundance of antibiotic-degrading microbes. These findings are similar to the results of our previous study of SA degradation in sludge [38].
3.4. Microbial Communities in the Repeated Addition Experiments
To obtain deeper insight into the conditions in the repeated addition experiments, the microbial communities in the repeated addition experiments were analyzed. As shown in Figure 6, the five experimental conditions (original sludge, sludge in aerobic conditions after the 3rd addition, sludge and bacteria in aerobic conditions after the 3rd addition, sludge in anaerobic conditions after the 3rd addition, sludge and bacteria in anaerobic conditions after the 3rd addition) exhibited differences in the composition of the major microbial communities (46, 45, 24, 33 and 26 microbial genera). The lists of the five groups of major microbial genera in the five experimental conditions are listed in Table S2.
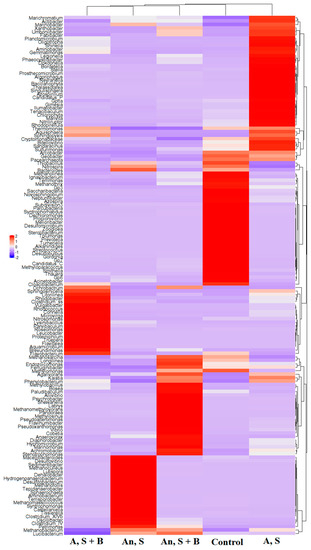
Figure 6.
Major microbial communities (genus level) in sludge after the 3rd repeated addition experiment. Control: original sludge. A, S: aerobic conditions, sludge only. A, S + B: aerobic conditions, sludge + bacteria. An, S: anaerobic conditions, sludge only. An, S + B: anaerobic conditions, sludge + bacteria. The major microbial genera (red color in heatmap) under the five experimental conditions are listed in Table S2.
For validation, a list of xenobiotic biodegradation-associated bacteria/archaea in the KEGG database was used to identify bacteria/archaea with xenobiotic degradation ability in the repeated addition experiments. The identified bacterial/archaeal genera were used as key words to perform text mining using the NCBI PubMed database. Under aerobic conditions, 25 of the 63 identified bacterial/archaeal genera have been reported to be antibiotic-degrading bacteria/archaea (Figure 7A). Under anaerobic conditions, 25 of the 63 identified bacterial/archaeal genera have been reported to be antibiotic-degrading bacteria/archaea (Figure 7B).
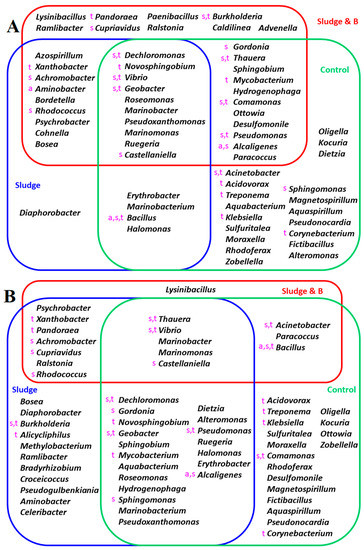
Figure 7.
Xenobiotic biodegradation-associated bacteria after the 3rd repeated addition experiment under aerobic (A) and anaerobic (B) conditions. Control: original sludge. Sludge and B: sludge containing the isolated bacterial strains. a: amoxicillin-degrading bacteria. s: sulfonamide-degrading bacteria. t: tetracycline-degrading bacteria.
In total, 24 reported antibiotic-degrading bacterial genera (Achromobacter, Acidovorax, Acinetobacter, Alcaligenes, Bacillus, Burkholderia, Castellaniella, Comamonas, Corynebacterium, Cupriavidus, Dechloromonas, Geobacter, Gordonia, Klebsiella, Mycobacterium, Novosphingobium, Pandoraea, Pseudomonas, Rhodococcus, Sphingomonas, Thauera, Treponema, Vibrio and Xanthobacter) are common to the aerobic and anaerobic groups. These results suggest that the 24 bacterial genera may be the major antibiotic-degrading bacteria in sludge. The PubMed ID, title and abstract of these reports are collected and summarized in Table S3.
The distribution of the number of major microbial genera exhibiting different aromatic compound degradation pathways is shown in Figure 8. Most of the microbial genera were associated with six reaction modules: M00548 (benzene degradation, benzene ≥ catechol), M00551 (benzoate degradation, benzoate ≥ catechol/methylbenzoate ≥ methylcatechol), M00568 (catechol ortho-cleavage, catechol ≥ 3-oxoadipate), M00569 (catechol meta-cleavage, catechol ≥ acetyl-CoA/4-methylcatechol ≥ propanoyl-CoA), M00623 (phthalate degradation, phthalate ≥ protocatechuate) and M00638 (salicylate degradation, salicylate ≥ gentisate). Moreover, more microbial genera associated with aromatic compound degradation were identified in the sludge with isolated antibiotic-degrading bacteria than in the sludge without the bacteria. These results provide explanations for the increased antibiotic-degrading effects associated with the addition of isolated antibiotic-degrading bacteria in sludge observed in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 and Table 2.
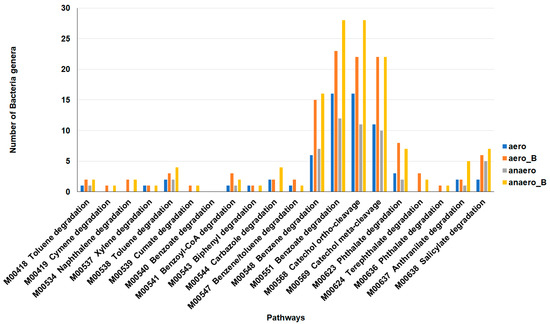
Figure 8.
Xenobiotic biodegradation-associated microbial genera after the 3rd repeated addition experiment under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Mxxxxx are Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database module IDs. aero: sludge under aerobic conditions. anaero: sludge under anaerobic conditions. aero_B: sludge with antibiotic-degrading bacteria under aerobic conditions. anaero: sludge with antibiotic-degrading bacteria under anaerobic conditions.
Yin et al. (2020) identified a TC-degrading strain, TR5, that could degrade TC quickly (~90% within 36 h) when the initial TC concentration was 200 mg/L [40]. Its efficiency is much higher than those of the TC-degrading bacteria identified in this study. However, TR5 was identified as Klebsiella pneumoniae according to 16S rRNA gene sequencing and biochemical properties. Great care must be taken in the application of pathogenic bacteria in wastewater treatment. Wu et al. (2020) identified two TC-degrading strains, Raoultella sp. XY-1 and Pandoraea sp. XY-2, which degraded 81.72% TC within 12 days in lysogeny broth (LB) medium [41]. The bacterial strains identified in this study exhibit a higher TC-degrading efficiency than Raoultella sp. XY-1 and Pandoraea sp. XY-2. Wen et al. reported that 95% of the doxycycline (50 mg/L) was degraded by the recombinant strain Escherichia coli ETD-1, with tetX, within 48 h [42]. Although the doxycycline-degrading ability of recombinant Escherichia coli is very significant, great care must be taken in the application of microorganisms carrying recombinant genes in the environment. Sodhi et al. (2020) identified the AMO-degrading bacterium, Alcaligenes sp. MMA, which was able to remove up to 84% of amoxicillin in 14 days in M9 minimal media [43]. The bacterial strains identified in this study exhibit a higher AMO-degrading efficiency than Alcaligenes sp. MMA. Liang et al. (2019) reported that Achromobacter sp. JL9 was able to utilize SMX as its sole nitrogen source for growth, with an SMX biodegradation efficiency of 63.10% [44]. Moreover, Nguyen et al. (2019) showed that SMX and sodium acetate could be cometabolized as carbon sources, with the highest removal efficiencies of 82.44%, 80.2%, and 79.45% for NH4+-N, NO3--N, and SMX, respectively [45]. The bacterial strains identified in this study exhibit a higher SMX-degrading efficiency than Achromobacter sp. Wang et al. (2018) demonstrated that Acinetobacter sp. could mineralize 98.8% of SMX, but only 17.5% and 20.5% of sulfadiazine and SMZ, respectively [46]. The bacterial strains identified in this study could degrade 98%, 91% and 88% SMX, SDM and SMZ, respectively. Overall, the antibiotic-degrading efficiency of the bacterial strains identified in this study is very good. Moreover, these bacterial strains exhibit the ability to degrade multiple antibiotics.
4. Conclusion
The removal efficiency of antibiotics in wastewater sludge was enhanced using the bacterial strains isolated in this study. Batch experiments indicated that the combination of two bacterial strains enhanced the biodegradation of antibiotics in sludge to a greater extent than the application of a single bacterial strain under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The efficiency was comparable between the aerobic and anaerobic settings. However, anaerobic biodegradation required a longer incubation time (by 2-fold) than aerobic biodegradation. The results of repeated addition experiments indicated that the efficiency of the biodegradation of antibiotics using bacterial strains could be maintained for at least three degradation runs. The added antibiotic-degrading bacteria not only degraded antibiotics directly but also changed the composition of the microbial community in the sludge. As a consequence, the composition of the xenobiotic degradation pathways and the antibiotic degradation capacity were changed.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/12/8/2147/s1, Table S1: Chemicals structures of target compounds, Table S2: five groups of major microbial genera in the five experimental conditions, Table S3: The PubMed ID, title and abstract of iterature reported antibiotics-degrading bacterial genera.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, C.L.; Funding acquisition, B.-V.C.; Methodology, C.-W.Y. and C.L.; Project administration, B.-V.C.; Visualization, C.-W.Y.; Writing—original draft, C.-W.Y. and B.-V.C.; Writing—review and editing, C.-W.Y. and B.-V.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (grant no. MOST 107-2313-B-031-002).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Salgado, R.; Noronha, J.P.; Oehmen, A.; Carvalho, G.; Reis, M.A. Analysis of 65 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in 5 wastewater treatment plants in Portugal using a simplified analytical methodology. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 2862–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.B.; Keefe, S.H.; LeBlanc, D.R.; Bradley, P.M.; Chapelle, F.H.; Meyer, M.T.; Loftin, K.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Rubio, F. Fate of sulfamethoxazole, 4- nonylphenol, and 17ß-estradiol in groundwater contaminated by wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4843–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.G. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gzyl, K.E.; Wieden, H.J. Tetracycline does not directly inhibit the function of bacterial elongation factor Tu. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, P.; Spiteller, M. Sulfonamides in the environment as veterinary drugs. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 187, pp. 67–101. [Google Scholar]
- Gobel, A.; Thomsen, A.; McArdell, C.S.; Joss, A.; Giger, W. Occurrence and sorption behavior of sulfonamides, macrolides, and trimethoprim in activated sludge treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3981–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, A.; Borrull, F.; Pocurull, E.; Marce, R.M. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and hormones in sewage sludge. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamek, E.; Baran, W.; Sobczak, A. Assessment of the biodegradability of selected sulfa drugs in two polluted rivers in Poland: Effects of seasonal variations, accidental contamination, turbidity and salinity. J. Hazard Mater. 2016, 313, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghapour, M.A.; Shirdarreh, M.R.; Faramarzian, M. Amoxicillin removal from aqueous solutions using submerged biological aerated filter. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 54, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilescu, M.; Demnerova, K.; Aamand, J.; Agathos, S.; Fava, F. Emerging pollutants in the environment: Present and future challenges in biomonitoring, ecological risks and bioremediation. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael-Kordatou, I.; Karaolia, P.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. The role of operating parameters and oxidative damage mechanisms of advanced chemical oxidation processes in the combat against antibiotic-resistant bacteria and resistance genes present in urban wastewater. Water Res. 2018, 129, 208–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.V.; Fan, S.N.; Tsai, Y.C.; Chung, Y.L.; Tu, P.X.; Yang, C.W. Removal of emerging contaminants using spent mushroom compost. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Qin, W.; Wen, X. Responses of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and mobile genetic elements in sewage sludge to thermal hydrolysis pre-treatment and various anaerobic digestion conditions. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X. Enhanced performance of tetracycline treatment in wastewater using aerobic granular sludge with in-situ generated biogenic manganese oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Yuan, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R. Impacts of long-term exposure to tetracycline and sulfamethoxazole on the sludge granules in an anoxic-aerobic wastewater treatment system. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, P.; Tomei, M.C.; Karaolia, P.; Langenhoff, A.; Almeida, C.M.; Felis, E.; Gritten, F.; Andersen, H.R.; Fernandes, T.; Manaia, C.M.; et al. Performance of secondary wastewater treatment methods for the removal of contaminants of emerging concern implicated in crop uptake and antibiotic resistance spread: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1052–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisognin, R.P.; Wolff, D.B.; Carissimi, E.; Prestes, O.D.; Zanella, R. Occurrence and fate of pharmaceuticals in effluent and sludge from a wastewater treatment plant in Brazil. Environ. Technol. 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzariai, A.; Hafidi, M.; Khadra, A.; Aemig, Q.; El Fels, L.; Barret, M.; Merlina, G.; Patureau, D.; Pinelli, E. Human and veterinary antibiotics during composting of sludge or manure: Global perspectives on persistence, degradation, and resistance genes. J. Hazard Mater. 2018, 359, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonnorat, J.; Kanyatrakul, A.; Prakhongsak, A.; Honda, R.; Panichnumsin, P.; Boonapatcharoen, N. Effect of hydraulic retention time on micropollutant biodegradation in activated sludge system augmented with acclimatized sludge treating low-micropollutants wastewater. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nas, B.; Argun, M.E.; Dolu, T.; Ateş, H.; Yel, E.; Koyuncu, S.; Dinç, S.; Kara, M. Occurrence, loadings and removal of EU-priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in wastewater and sludge by advanced biological treatment, stabilization pond and constructed wetland. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaz, M.; Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Eswaranandam, S.; Zhang, W.; Jones, S.M.; Watts, M.J.; Qian, X. Investigation into micropollutant removal from wastewaters by a membrane bioreactor. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, H.; Yargeau, V.; Cooper, D.G. Biodegradation of pharmaceuticals by Rhodococcus rhodochrous and Aspergillus niger by co-metabolism. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Y.; Bao, J.; Chang, G.; Zheng, H.; Li, X.; Du, J.; Snow, D. Biotransformation of tetracycline by a novel bacterial strain Stenotrophomonas maltophilia DT1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. Biodegradation mechanism of tetracycline (TEC) by strain Klebsiella sp. SQY5 as revealed through products analysis and genomics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 85, 109676–109683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, S.; Yargeau, V. Biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole by individual and mixed bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Microbial degradation of sulfamethoxazole in the environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3573–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Li, B.; Zou, R.; Xie, S.; Yuan, B. Antibiotic sulfanilamide biodegradation by acclimated microbial populations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zou, R.; Li, B.; Tong, T.; Xie, S.; Yuan, B. Biodegradation of chlortetracycline by acclimated microbiota. Process Saf. Environ. 2017, 109, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.V.; Chang, Y.T.; Chao, W.L.; Yeh, S.L.; Kuo, D.L.; Yang, C.W. Effects of sulfamethoxazole and sulfamethoxazole-degrading bacteria on water quality and microbial communities in milkfish ponds. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Chao, W.L.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chang, B.V. Biodegradation of malachite green in milkfish pond sediments. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.T.; Tai, C.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, Y.B.; Lee, F.L.; Wang, S.L. Pseudomonas taiwanensis sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2010, 60, 2094–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huertas, M.J.; Luque-Almagro, V.M.; Martinez-Luque, M.; Blasco, R.; Moreno-Vivian, C.; Castillo, F.; Roldan, M.D. Cyanide metabolism of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes CECT5344: Role of siderophores. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomucci, L.; Raddadi, N.; Soccio, M.; Lotti, N.; Fava, F. Polyvinyl chloride biodegradation by Pseudomonas citronellolis and Bacillus flexus. New Biotechnol. 2019, 52, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekambaram, S.P.; Perumal, S.S.; Annamalai, U. Decolorization and biodegradation of remazol reactive dyes by Clostridium species. 3 Biotech. 2016, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Hsiao, W.C.; Chang, B.V. Biodegradation of sulfonamide antibiotics in sludge. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Hata, T.; Kawai, S.; Okamura, H.; Nishida, T. Treatment of tetracycline antibiotics by laccase in the presence of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, L.L.; Gerba, C.P.; Gentry, T.J. Environmental microbiology. In Microorganisms and Organic Pollutant; Maier, M.M., Gentry, T.J., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 377–413. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Xia, D.; Shen, M.; Zhu, D.; Cai, H.; Wu, M.; Zhu, Q.; Kang, Y. Tetracycline degradation by Klebsiella sp. strain TR5: Proposed degradation pathway and possible genes involved. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gu, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, H.; Amanze, C.; Shen, L.; Zeng, W. Construction of a Tetracycline Degrading Bacterial Consortium and Its Application Evaluation in Laboratory-Scale Soil Remediation. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Huang, J.; Cao, J.; Xu, J.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, B.; Zou, Y.; Liao, X.; Liang, J.B.; et al. Heterologous expression of the tetracycline resistance gene tetX to enhance degradability and safety in doxycycline degradation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, D.K. Potential application in amoxicillin removal of Alcaligenes sp. MMA and enzymatic studies through molecular docking. Arch. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.H.; Hu, Y. Simultaneous sulfamethoxazole biodegradation and nitrogen conversion by Achromobacter sp. JL9 using with different carbon and nitrogen sources. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.Y.; Silva, A.F.; Reis, A.C.; Nunes, O.C.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Rodrigues, J.E.; Cardoso, V.V.; Benoliel, M.J.; Reis, M.A.; Oehmen, A.; et al. Bioaugmentation of membrane bioreactor with Achromobacter denitrificans strain PR1 for enhanced sulfamethoxazole removal in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J. Biodegradation of typical pharmaceutical compounds by a novel strain Acinetobacter sp. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).