Riverbed Changes of the Uppermost Atchafalaya River, USA—A Case Study of Channel Dynamics in Large Man-Controlled Alluvial River Confluences
Abstract
1. Introduction
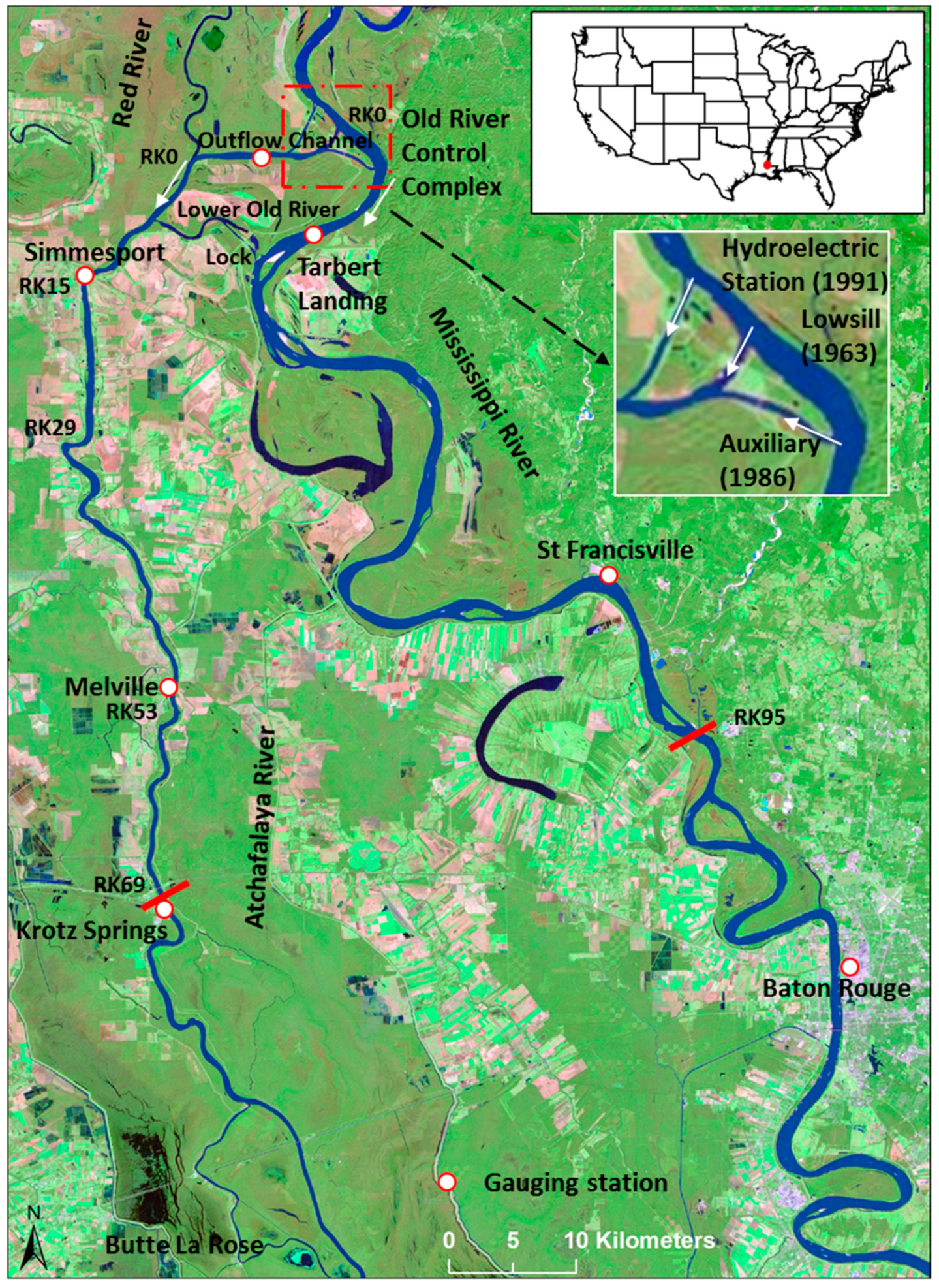
2. Case Study Site
3. Material and Methods
3.1. River Bathymetry and Hydrologic Data
3.2. Riverbed Deformation Analysis
3.3. Hydraulic Analysis
4. Results
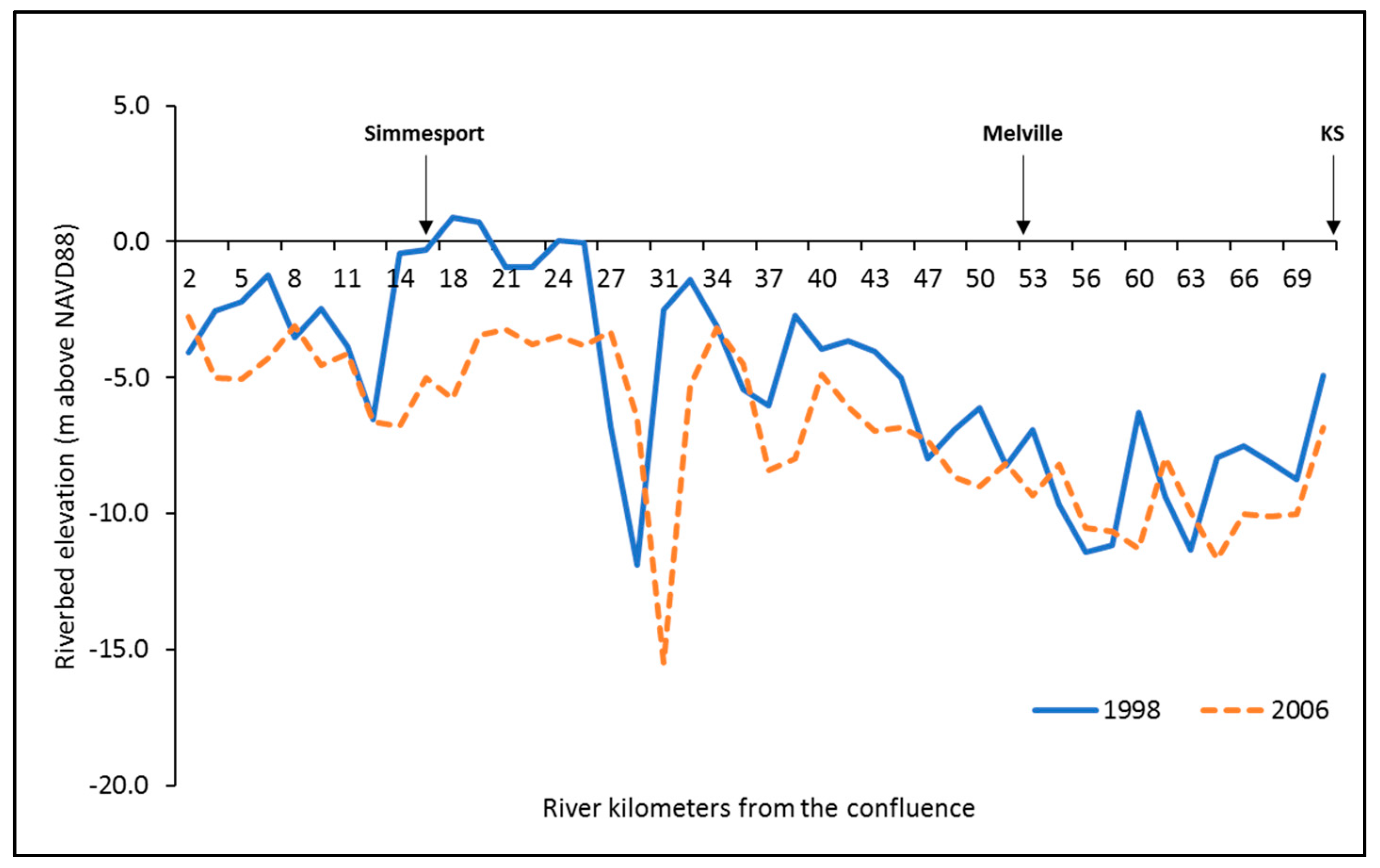
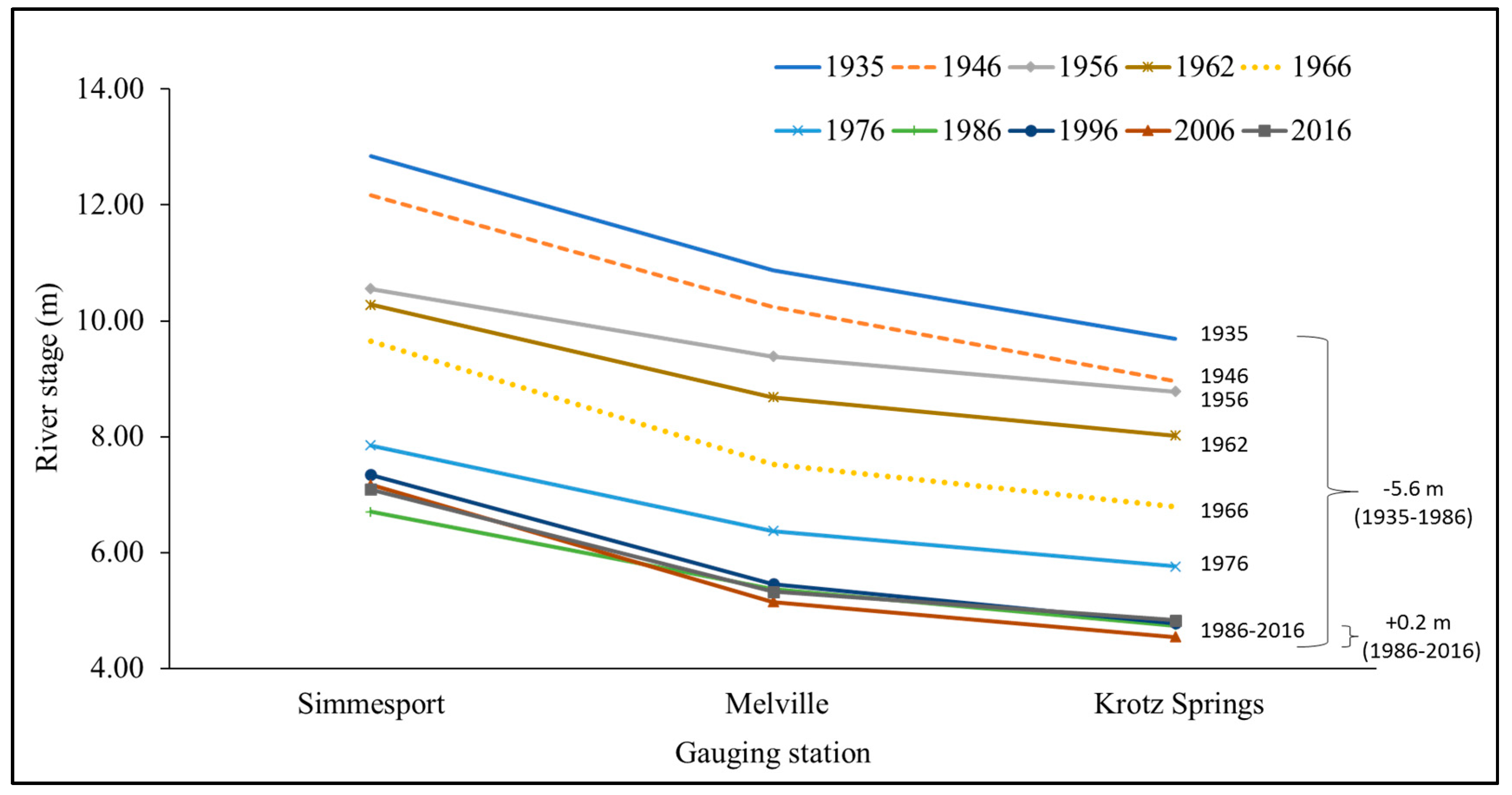
4.1. Changes in Thalweg and Riverbed Elevation
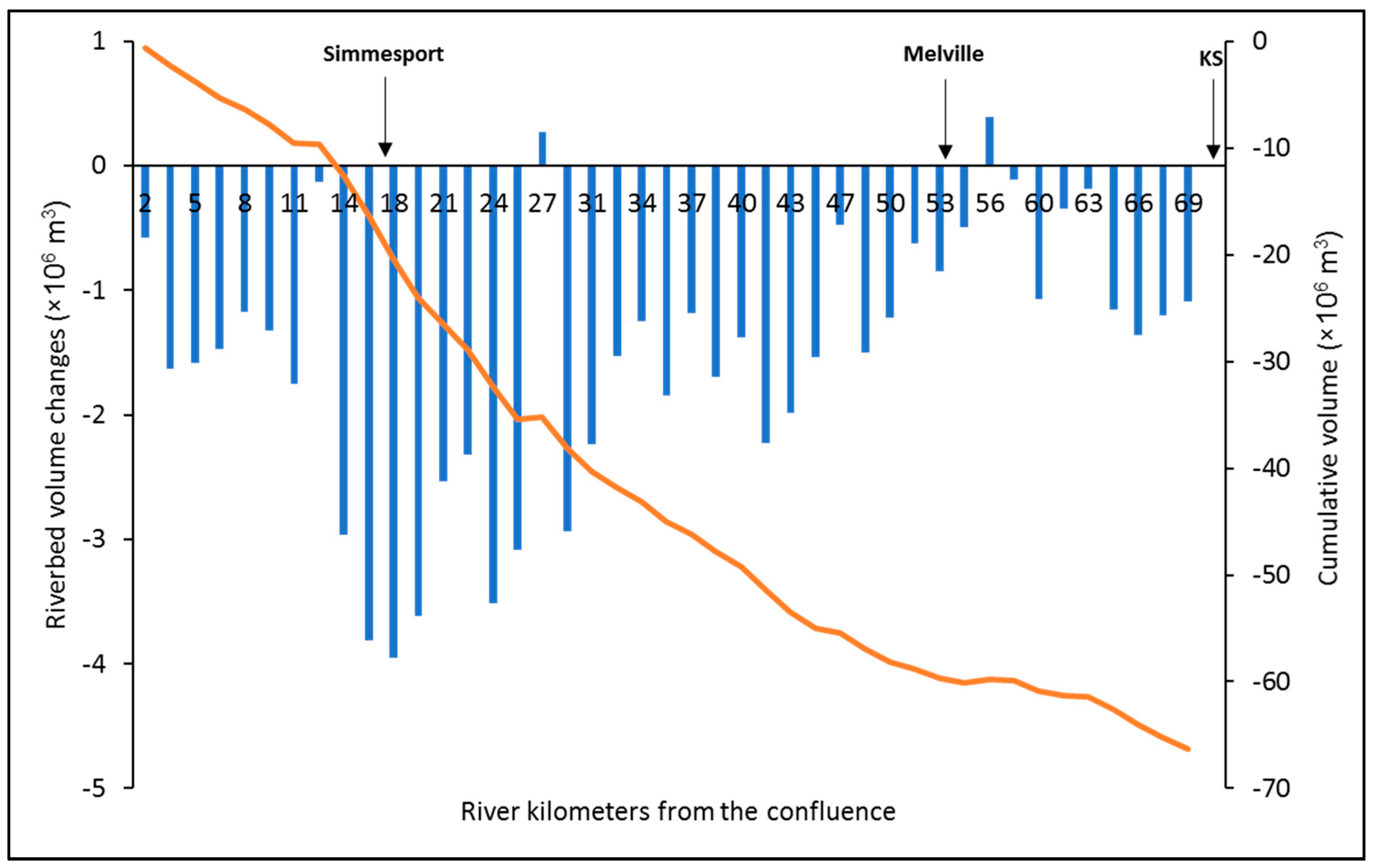
4.2. Volume Change of the Riverbed Sediment
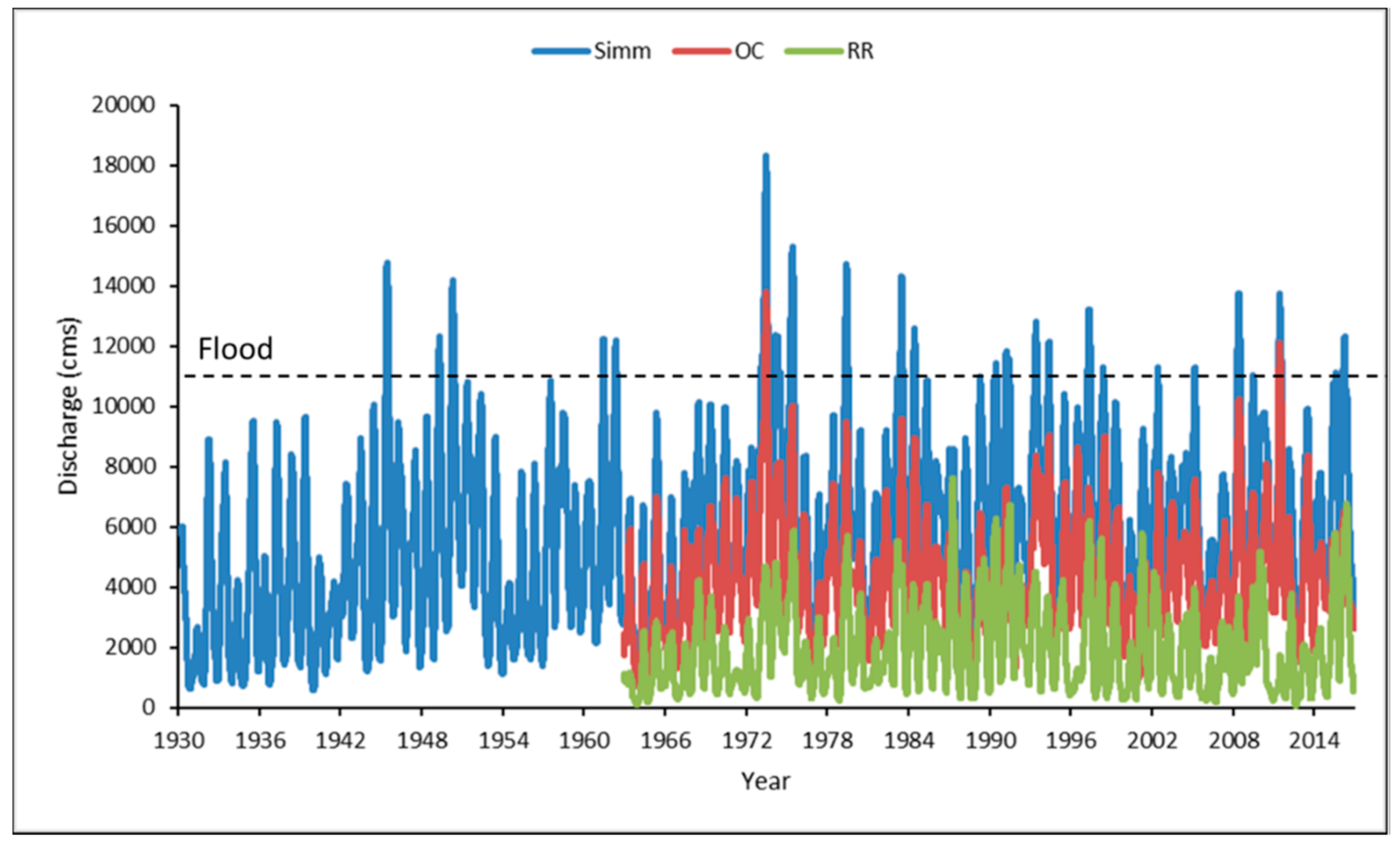
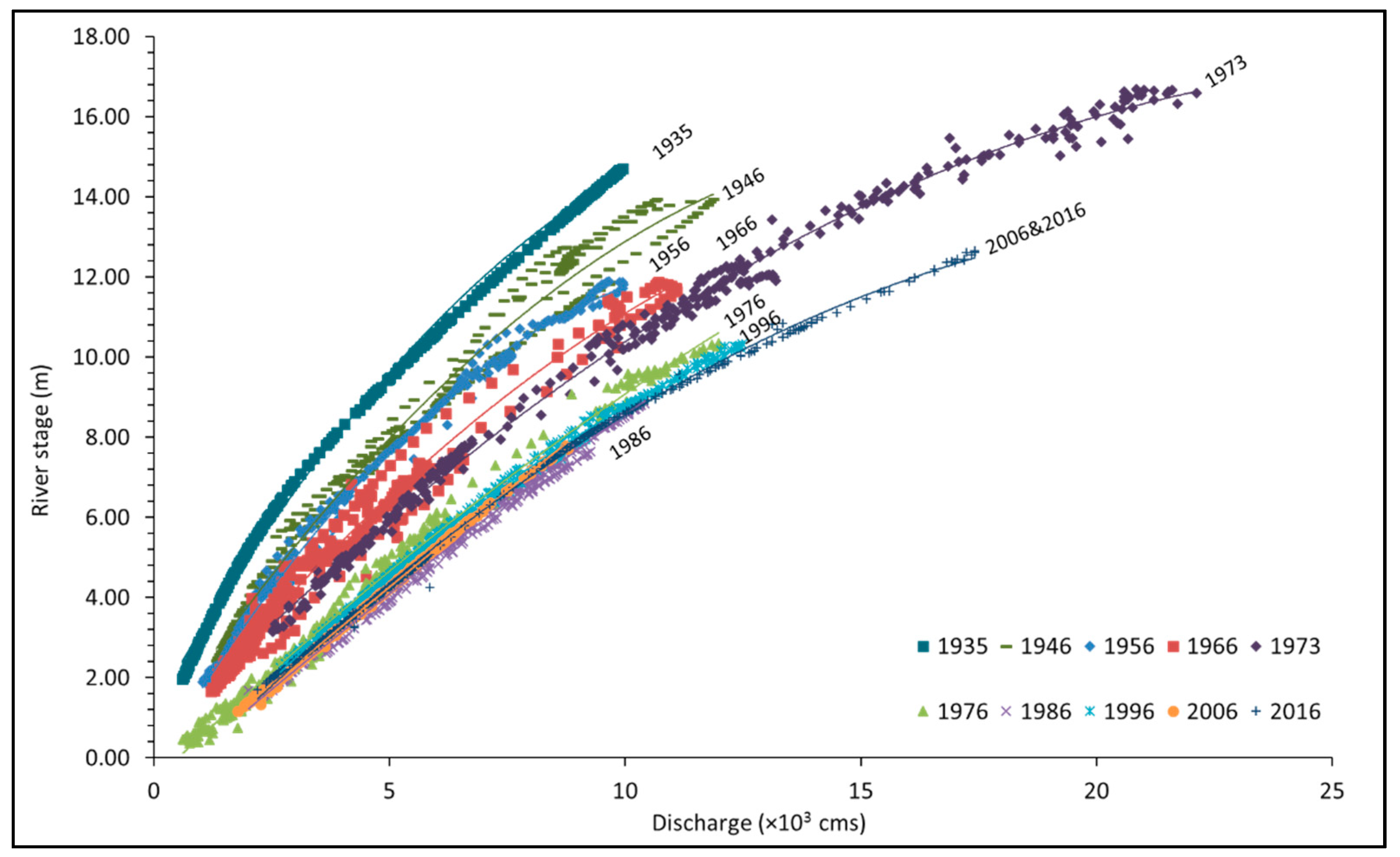
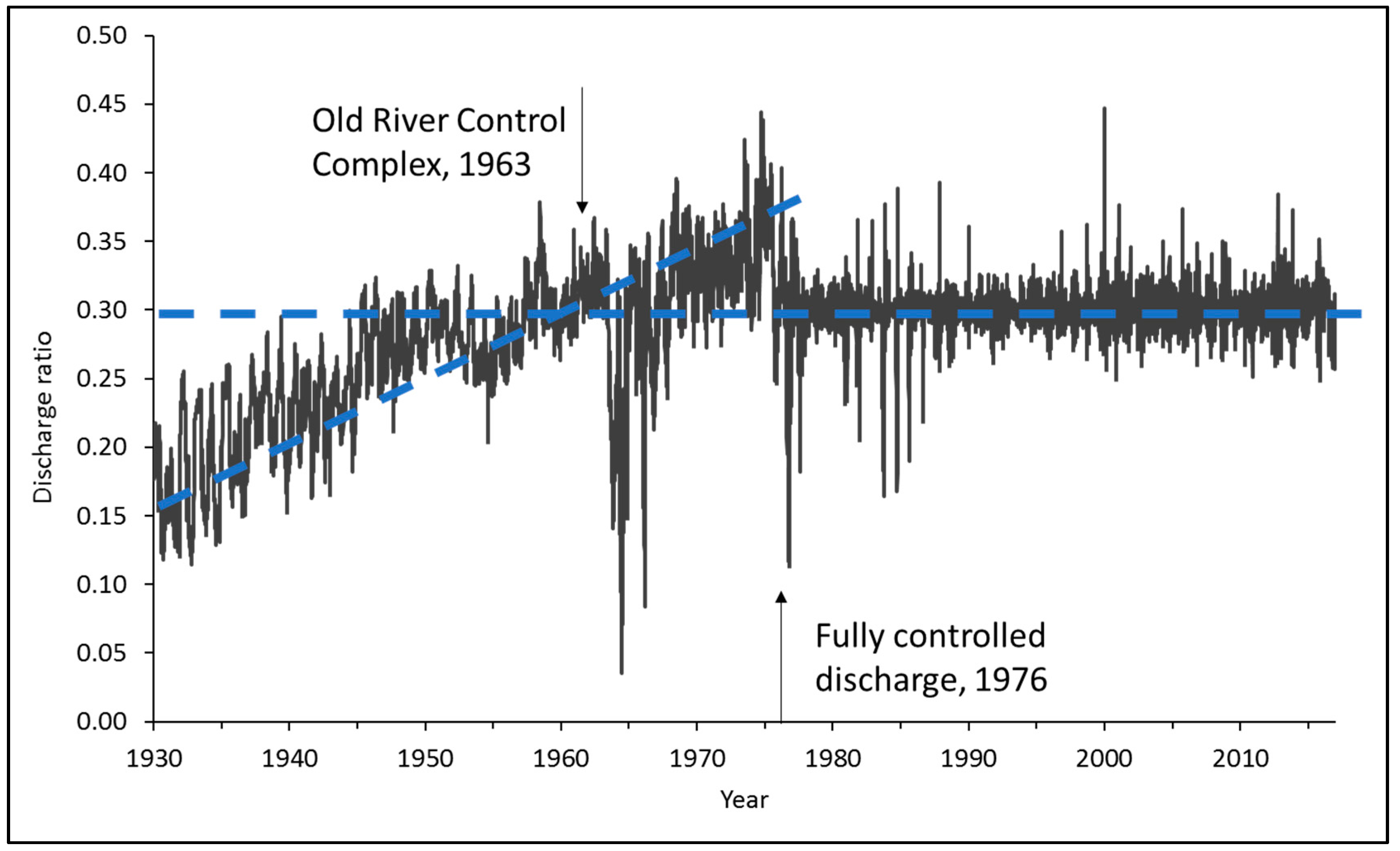
4.3. Long-Term River Flow and Changes in Water Surface Gradient
4.4. Reynolds Number, Bed Shear Stress, and Froude Number
5. Discussion
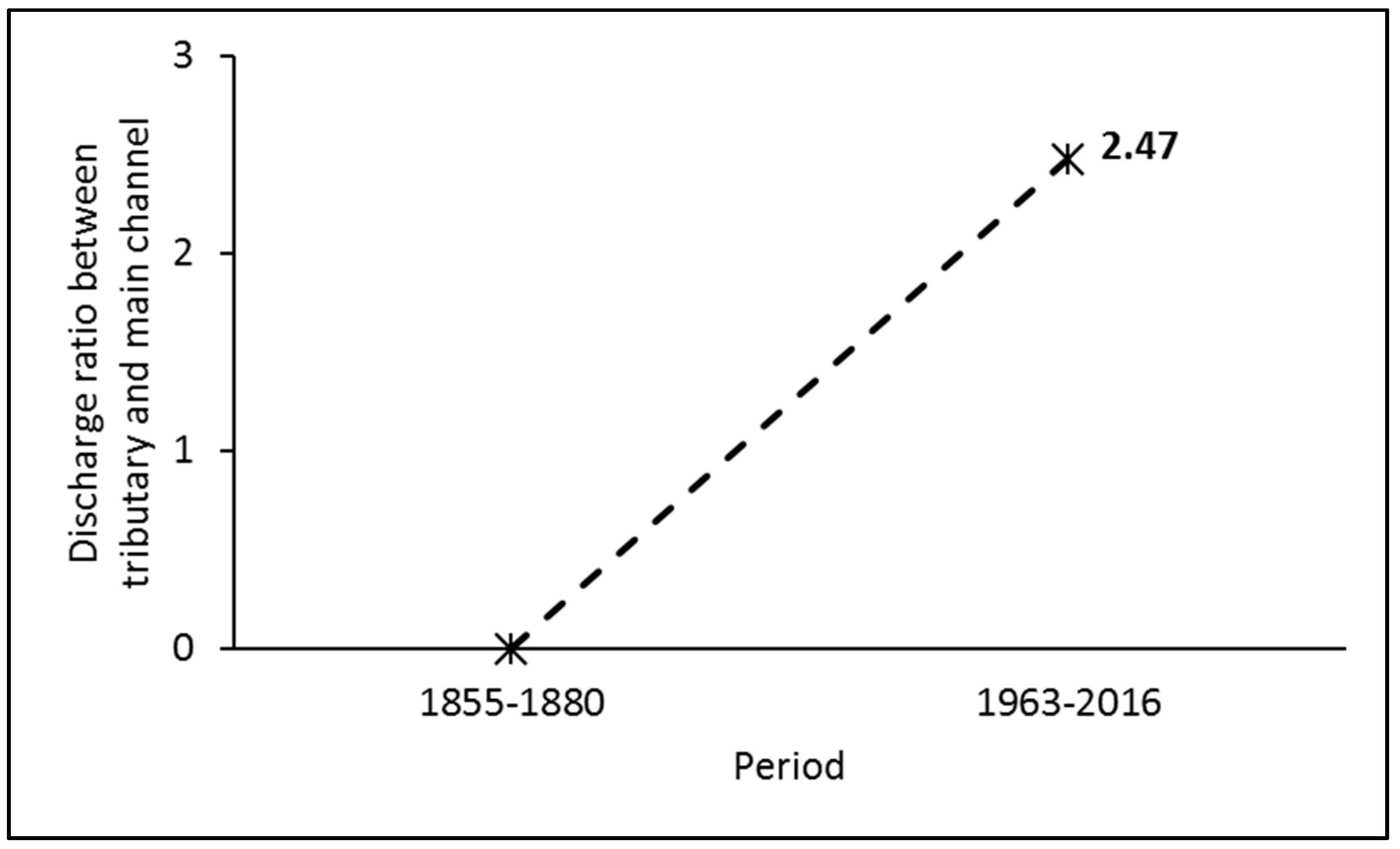
5.1. Indication of the Continuous Decline of Water Surface Gradient in the Past 80 Years
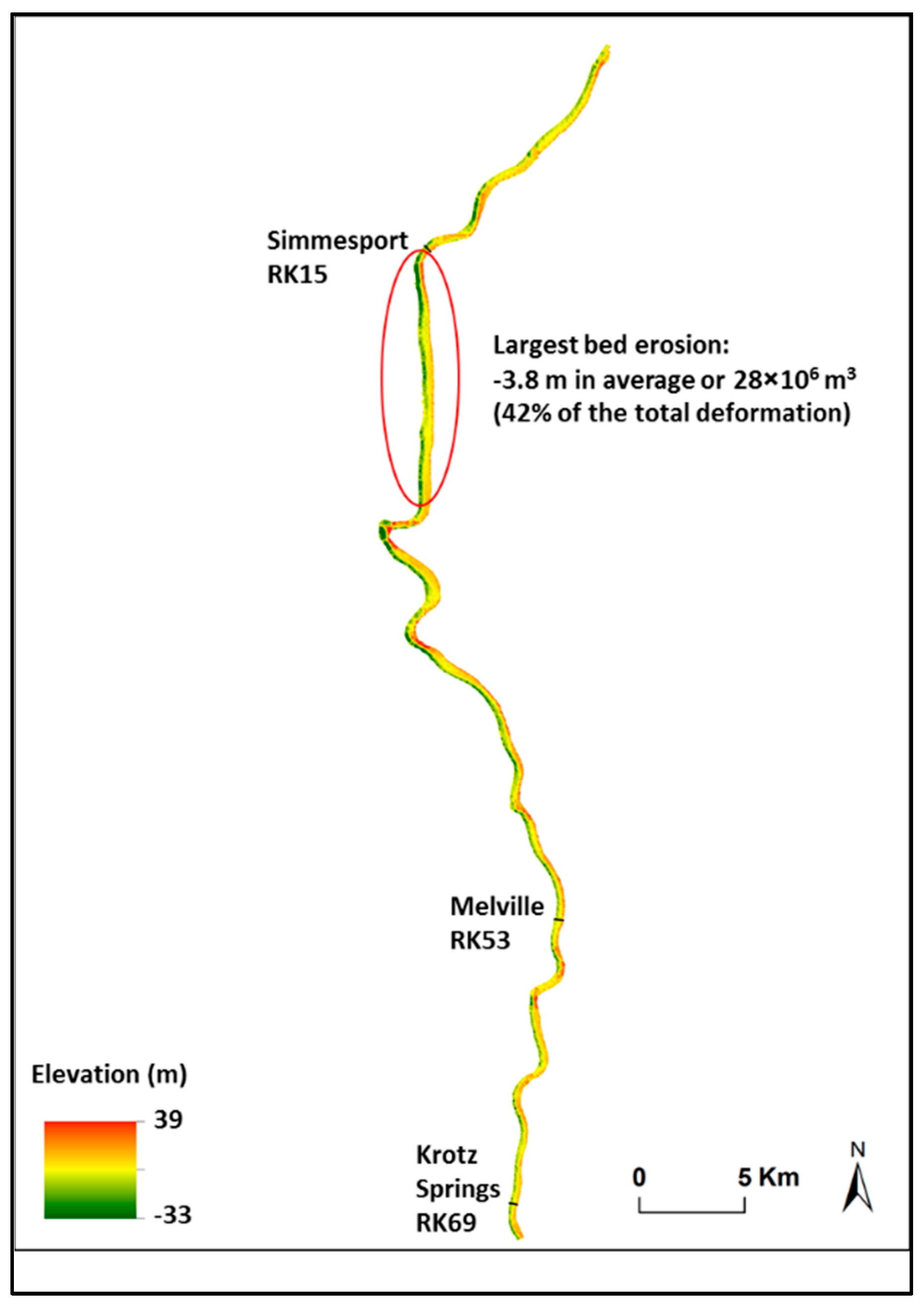
5.2. Riverbed Erosion during 1998–2006
5.3. Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosley, M.P. An experimental study of channel confluences. J. Geol. 1976, 84, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.S. A note on changes in channel geometry at tributary junctions. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, P.; Parker, G. Confluence scour in coarse braided streams. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.L. Flow dynamics at river channel confluences; implications for sediment transport and bed morphology. Spec. Publ. Soc. Econ. Paleontol. Mineral. 1987, 39, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Best, J.L.; Reid, I. Separation zone at open-channel junctions. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.L. The morphology of river channel confluences. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1986, 10, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.; Roy, A.G.; Best, J.L.; Boyer, C.J. Bed morphology and sedimentology at the confluence of unequal depth channels. Geomorphology 1993, 8, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, B.L.; Kenworthy, S.T. Flow structure at an asymmetrical stream confluence. Geomorphology 1995, 11, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.; Best, J.L.; Roy, A.G. Effects of bed discordance on flow dynamics at open channel confluences. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 1996, 122, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.N.; Biron, P.M.; Bradbrook, K.F.; Butler, J.B.; Chandler, J.H.; Crowell, M.D.; McLelland, S.J.; Richards, K.S.; Roy, A.G. Three-dimensional measurement of river channel flow processes using acoustic doppler velocimetry. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 1247–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.M.; Ramamurthy, A.S.; Han, S. Three-dimensional numerical modeling of mixing at river confluences. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 2004, 130, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Vide, J.P.; Plana-Casado, A.; Sambola, A.; Capapé, S. Bedload transport in a river confluence. Geomorphology 2015, 250, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.L. Sediment transport and bed morphology at river channel confluences. Sedimentology 1988, 35, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.L.; Blanckaert, K.; Roy, A.G.; Schleiss, A.J. Flow and sediment dynamics in channel confluences. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, C.; Roy, A.G.; Best, J.L. Dynamics of a river channel confluence with discordant beds: Flow turbulence, bed load sediment transport, and bed morphology. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, E.S.; dos Santos, M.L.; Cremon, E.H.; Stevaux, J.C. Floodplain evolution in a confluence zone: Parana and ivai rivers, brazil. Geomorphology 2016, 257, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Sambrook Smith, G.H.; Best, J.L.; Nicholas, A.P.; Bull, J.M.; Vardy, M.E.; Sarker, M.H.; Goodbred, S. The planform mobility of river channel confluences: Insights from analysis of remotely sensed imagery. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 176, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, P.E. Laboratory modelling of gravel braided stream morphology. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1982, 7, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, P.J. Mid-channel bar growth and its relationship to local flow strength and direction. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1996, 21, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, P.J.; Ferguson, R.I.; Powell, M.D. Bedload Transport and Sorting in Braided Channels; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 497–515. [Google Scholar]
- McLelland, S.J.; Ashworth, P.J.; Best, J.L. The Origin and Downstream Development of Coherent Flow Structures at Channel Junctions; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 459–490. [Google Scholar]
- Lach, J.; Wyzga, B. Channel incision and flow increase of the upper wisloka river, southern poland, subsequent to the reafforestation of its catchment. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2002, 27, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M. Hungry water: Effects of dams and gravel mining on river channels. Environ. Manag. 1997, 21, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petts, G.E.; Gurnell, A.M. Dams and geomorphology: Research progress and future directions. Geomorphology 2005, 71, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.J. Influence of the three gorges dam on downstream delivery of sediment and its environmental implications, yangtze river. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Finlayson, B.; Chen, J.; Yin, D.W. Implications of flow control by the three gorges dam on sediment and channel dynamics of the middle yangtze (changjiang) river, china. Geology 2010, 38, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B. Channel responses to declining flow on the rio-grande between ft quitman and presidio, texas. Geomorphology 1993, 6, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzuto, J.E. Channel adjustments to changing discharges, powder river, montana. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1994, 106, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, R.A.; Schweizer, C.W. The Atchafalaya River Study; A Report Based Upon Engineering and Geological Studies of the Enlargement of Old and Atchafalaya Rivers; Army Corps of Engineers, Mississippi River Commission: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Mossa, J. The changing geomorphology of the Atchafalaya River, Louisiana: A historical perspective. Geomorphology 2016, 252, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, T.; Xu, Y.J. Estimation of sedimentation rates in the distributary basin of the mississippi river, the atchafalaya river basin, USA. Hydrol. Res. 2015, 46, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J. Long-term sediment transport and delivery of the largest distributary of the mississippi river, the atchafalaya, USA. IAHS AISH Publ. 2010, 337, 282–290. [Google Scholar]
- Fisk, H.N. Geological Investigation of the Atchafalaya Basin and the Problem of Mississippi River Diversion; Wterways Experiment Station: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1952; p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- Mossa, J. Historical changes of a major juncture: Lower old river, louisiana. Phys. Geogr. 2013, 34, 315–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mize, S.V.; Murphy, J.C.; Diehl, T.H.; Demcheck, D.K. Suspended-sediment concentrations and loads in the lower mississippi and atchafalaya rivers decreased by half between 1980 and 2015. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, Y.J. Decadal-scale riverbed deformation and sand budget of the last 500 km of the mississippi river: Insights into natural and river engineering effects on a large alluvial river. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2018, 123, 874–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galler, J.J.; Bianchi, T.S.; Alison, M.A.; Wysocki, L.A.; Campanella, R. Biogeochemical implications of levee confinement in the lowermost mississippi river. EosTrans. Am. Geophys. Union 2003, 84, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Mossa, J.; Mao, L.; Almulla, M. Comparison of different spatial interpolation methods for historical hydrographic data of the lowermost mississippi river. Ann. GIS 2019, 25, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheaton, J.M.; Brasington, J.; Darby, S.E.; Kasprak, A.; Sear, D.; Vericat, D. Morphodynamic signatures of braiding mechanisms as expressed through change in sediment storage in a gravel-bed river. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2013, 118, 759–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheaton, J.M.; Brasington, J.; Darby, S.E.; Sear, D.A. Accounting for uncertainty in dems from repeat topographic surveys: Improved sediment budgets. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 136–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, P.Y. Erosion and Sedimentation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, T.; Xu, Y.J. A hydrograph-based sediment availability assessment: Implications for mississippi river sediment diversion. Water 2014, 6, 564–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, S.A. River Variability and Complexity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Xu, Y.J. Estimating bed material fluxes upstream and downstream of a controlled large bifurcation—The mississippi-atchafalaya river diversion. Hydrol. Process. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvillion, B.R.; Barras, J.A.; Steyer, G.D.; Sleavin, W.; Fischer, M.; Beck, H.; Trahan, N.; Griffin, B.; Heckman, D. Land Area Change in Coastal Louisiana from 1932 to 2010: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 3164; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2011; p. 12.
- Rouse, L.J., Jr.; Roberts, H.H.; Cunningham, R.H.W. Satellite observation of the subaerial growth of the atchafalaya delta, louisiana. Geology 1978, 6, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, T.; Xu, Y.J. Recent decadal growth of the atchafalaya river delta complex: Effects of variable riverine sediment input and vegetation succession. Geomorphology 2013, 194, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barras, J.A. Land Area Change in Coastal Louisiana after the 2005 Hurricanes—A Series of Three Maps: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 06-1274; US Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Farris, G.S.; Smith, G.J.; Crane, M.P.; Demas, C.R.; Robbins, L.L.; Lavoie, D.L. (Eds.) Science and the Storms—The Usgs Response to the Hurricanes of 2005: U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1306; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2007; p. 283.
- Walker, N.D. Tropical storm and hurricane wind effects on water level, salinity, and sediment transport in the river-influenced atchafalaya-vermilion bay system, louisiana, USA. Estuaries 2001, 24, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.B.; Sasser, C.E.; Gosselink, J.G. Succession of vegetation in an evolving river delta, atchafalaya bay, louisiana. J. Ecol. 1985, 73, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carle, M.V.; Sasser, C.E.; Roberts, H.H. Accretion and vegetation community change in the wax lake delta following the historic 2011 mississippi river flood. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 31, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.H.; Coleman, J.M.; Bentley, S.J.; Walker, N. An embryonic major delta lobe; a new generation of delta studies in the atchafalaya-wax lake delta system. Trans. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. 2003, 53, 690–703. [Google Scholar]
- Nittrouer, J.A.; Shaw, J.; Lamb, M.P.; Mohrig, D. Spatial and temporal trends for water-flow velocity and bed-material sediment transport in the lower mississippi river. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2012, 124, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, M.P.; Nittrouer, J.A.; Mohrig, D.; Shaw, J. Backwater and river plume controls on scour upstream of river mouths: Implications for fluvio-deltaic morphodynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatanantavet, P.; Lamb, M.P.; Nittrouer, J.A. Backwater controls of avulsion location on deltas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L01402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltares. Delft3d-Flow Simulation of Multi-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Flows and Transport Phenomena, Including Sediments User Manual; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, R.C.; Tate, J.N.; Brown, G.L.; Savant, G. Guidelines for Solving Two Dimensional Shallow Water Problems with the Adaptive Hydraulics (ADH) Modeling System; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Engineering Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]



| Period | Simmesport (m) | Melville (m) | KS (m) | Average (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1935–1946 | −0.7 | −0.6 | −0.7 | −0.7 |
| 1946–1956 | −1.6 | −0.9 | −0.2 | −0.9 |
| 1956–1966 | −0.9 | −1.9 | −2.0 | −1.6 |
| 1966–1976 | −1.8 | −1.2 | −1.0 | −1.3 |
| 1976–1986 | −1.1 | −1.0 | −1.0 | −1.1 |
| 1986–1996 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 |
| 1996–2006 | −0.2 | −0.3 | −0.2 | −0.2 |
| 2006–2016 | −0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Total | −5.8 | −5.6 | −4.9 | −5.4 |
| Period | River Stage Change (m) | Stage Change Rate (m year−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 1935–1946 | −1.8 | −0.15 |
| 1946–1956 | −0.6 | −0.05 |
| 1956–1966 | −1.1 | −0.10 |
| 1966–1976 | −2.1 | −0.19 |
| 1976–1986 | −0.6 | −0.05 |
| 1986–1996 | 0.4 | 0.04 |
| 1996–2006 | −0.1 | −0.01 |
| 2006–2016 | −0.1 | −0.01 |
| Location | Flow | Discharge (m3 s−1) | Velocity (m s−1) | Re (×106) | Re’ (×106) | Shear Stress (N m−2) | Fr | Fr’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simmesport | H | 8014 | 1.3 | 16.1 | 627 | 8.5 | 0.11 | 17.96 |
| M | 5550 | 1 | 11.7 | 517 | 4.7 | 0.10 | 14.83 | |
| L | 3058 | 0.7 | 6.8 | 366 | 2.6 | 0.08 | 10.50 | |
| Melville | H | 8014 | 1.3 | 16.3 | 634 | 8.5 | 0.11 | 18.17 |
| M | 5550 | 1.1 | 11.8 | 549 | 4.5 | 0.10 | 15.73 | |
| L | 3058 | 0.7 | 6.9 | 350 | 2.7 | 0.07 | 10.04 | |
| Krotz Springs | H | 8014 | 1.2 | 17.8 | 604 | 9.8 | 0.10 | 17.32 |
| M | 5550 | 0.9 | 13 | 457 | 5.9 | 0.08 | 13.11 | |
| L | 3058 | 0.6 | 7.4 | 296 | 3.5 | 0.05 | 8.48 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Xu, Y.J.; Xu, W.; Cheng, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W. Riverbed Changes of the Uppermost Atchafalaya River, USA—A Case Study of Channel Dynamics in Large Man-Controlled Alluvial River Confluences. Water 2020, 12, 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082139
Wang B, Xu YJ, Xu W, Cheng H, Chen Z, Zhang W. Riverbed Changes of the Uppermost Atchafalaya River, USA—A Case Study of Channel Dynamics in Large Man-Controlled Alluvial River Confluences. Water. 2020; 12(8):2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082139
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bo, Y. Jun Xu, Wei Xu, Heqin Cheng, Zhongyuan Chen, and Weiguo Zhang. 2020. "Riverbed Changes of the Uppermost Atchafalaya River, USA—A Case Study of Channel Dynamics in Large Man-Controlled Alluvial River Confluences" Water 12, no. 8: 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082139
APA StyleWang, B., Xu, Y. J., Xu, W., Cheng, H., Chen, Z., & Zhang, W. (2020). Riverbed Changes of the Uppermost Atchafalaya River, USA—A Case Study of Channel Dynamics in Large Man-Controlled Alluvial River Confluences. Water, 12(8), 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12082139







