Water Use Strategies of Dominant Species (Caragana korshinskii and Reaumuria soongorica) in Natural Shrubs Based on Stable Isotopes in the Loess Hill, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
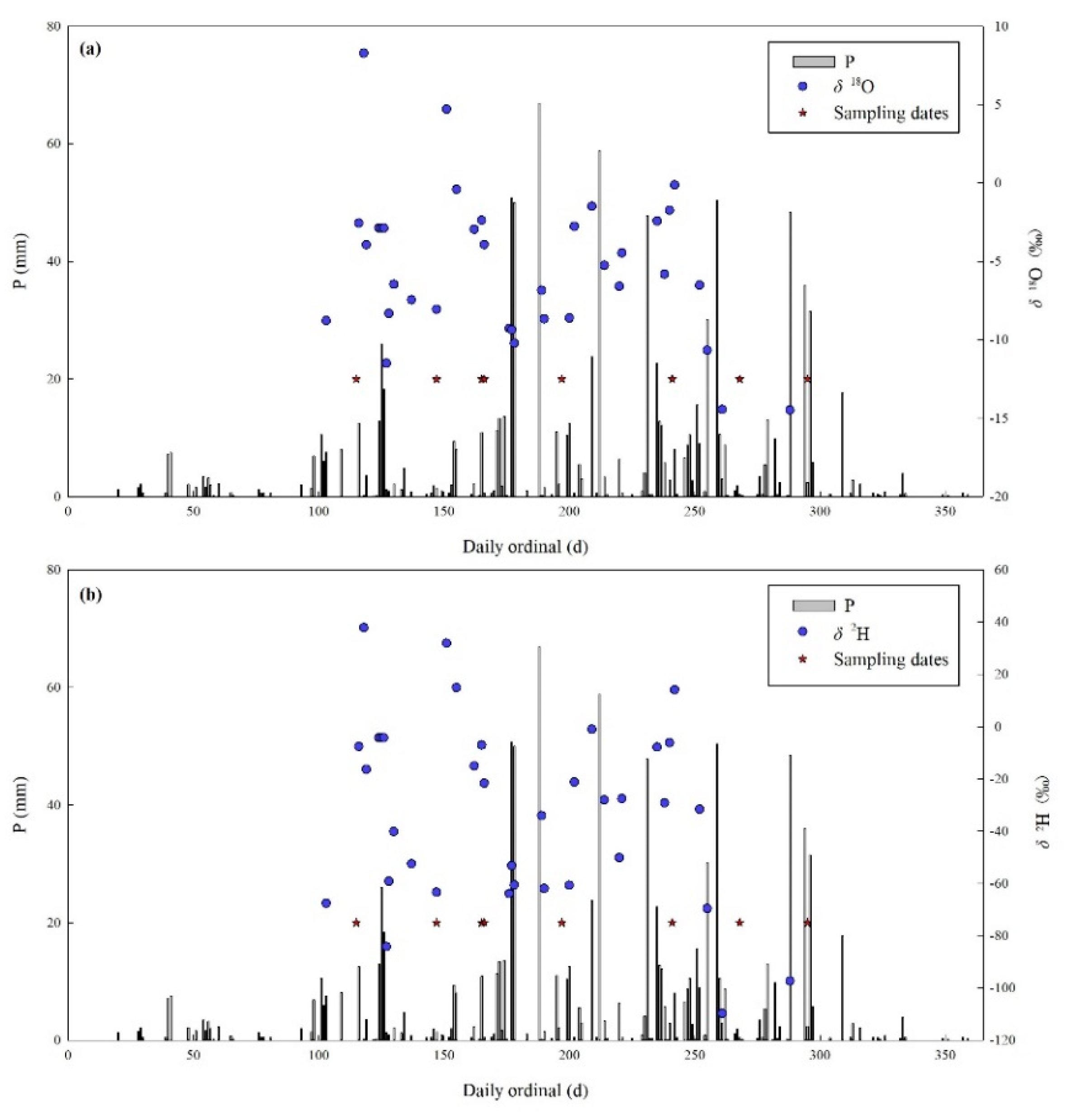
2.2. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Isotopic Analyses
2.4. Data Analyses
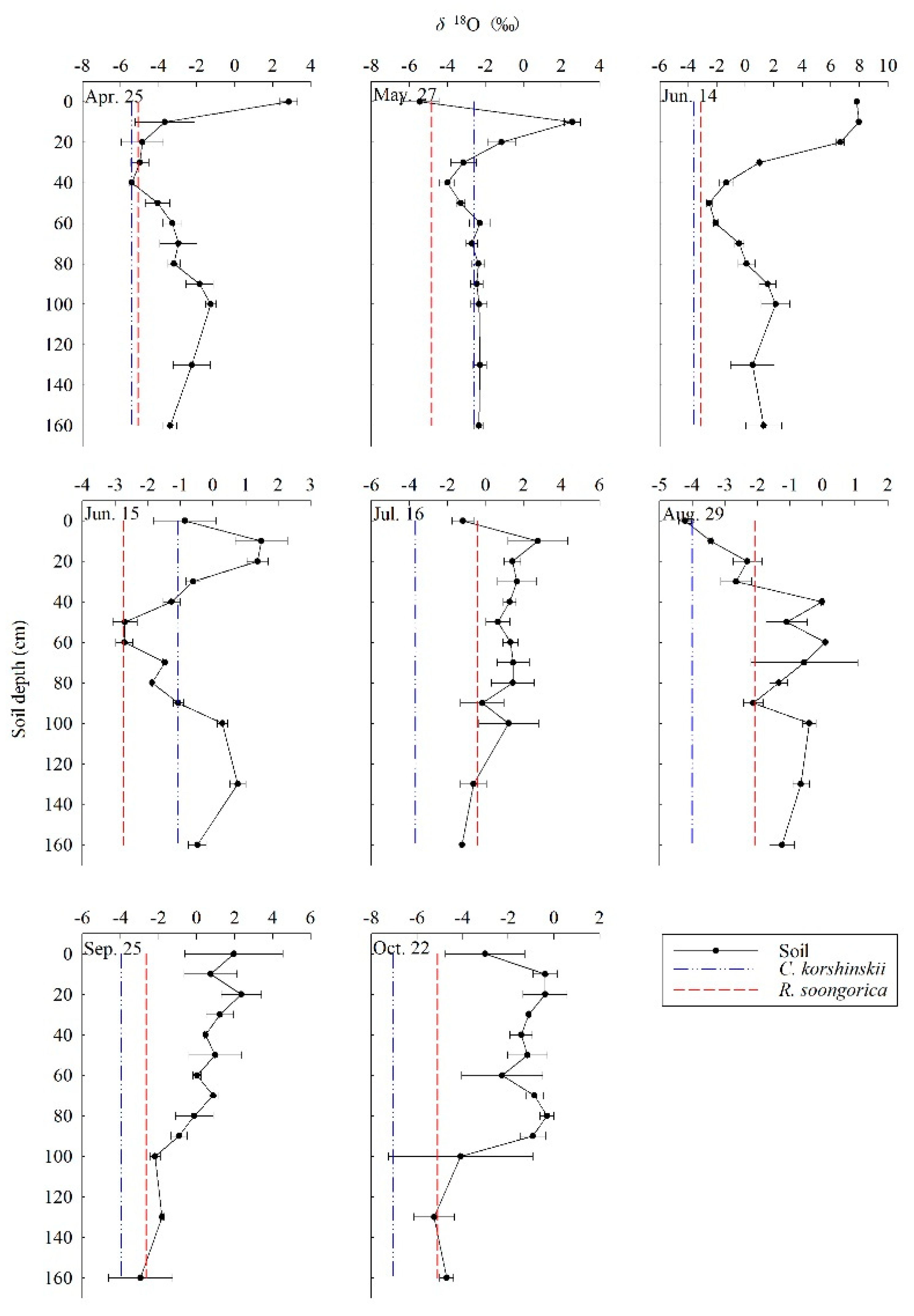
- Surface soil layer (0–10 cm): the isotopic ratios in soil water and SWC had greater variability and were vulnerable to rainfall pulse, irrigation and evaporation with season.
- Shallow soil layer (10–40 cm): the SWC was variable with obviously differences with changing seasons.
- Middle soil layer (40–100 cm): the isotopic ratios in soil water and SWC had gentle variations and milder monthly changes than those in the shallow soil layer.
- Deep soil layer (100–160 cm): the isotopic ratios in soil water and SWC showed relatively stable variations.
3. Results
3.1. Precipitation, Irrigation Water and Isotopic Composition
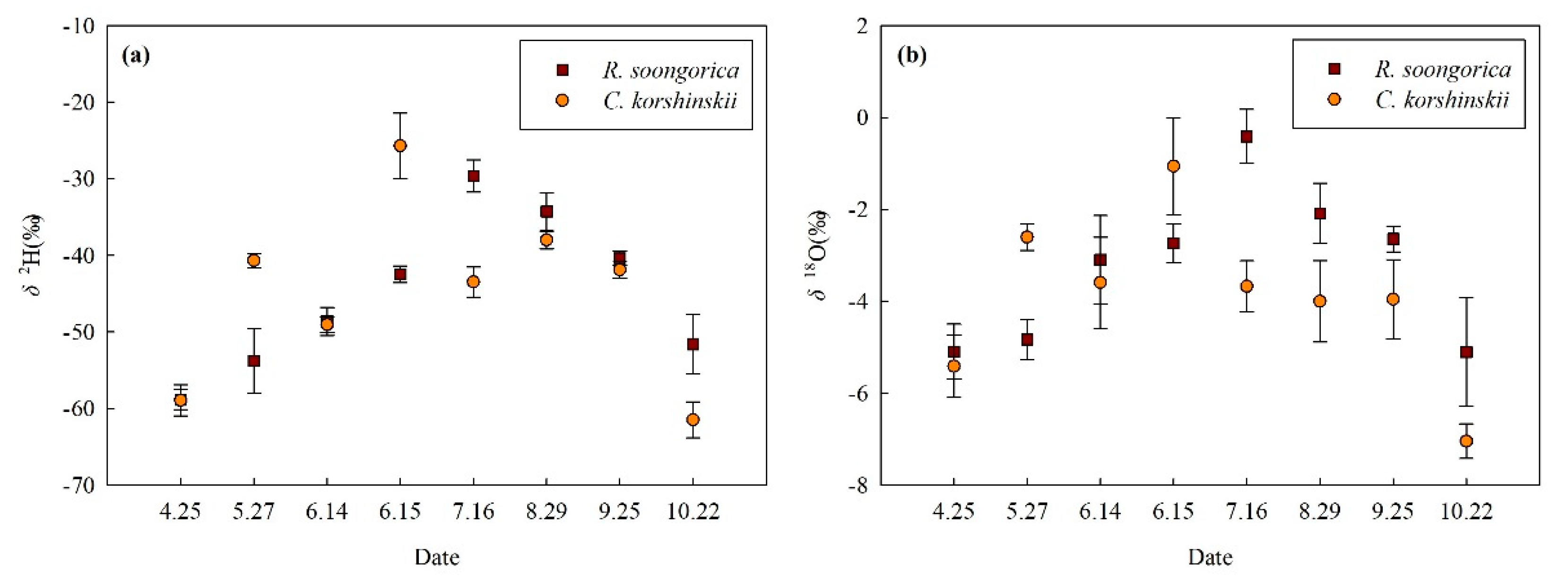
3.2. Soil Moisture and Isotopic Composition
3.3. Formatting of Mathematical Components
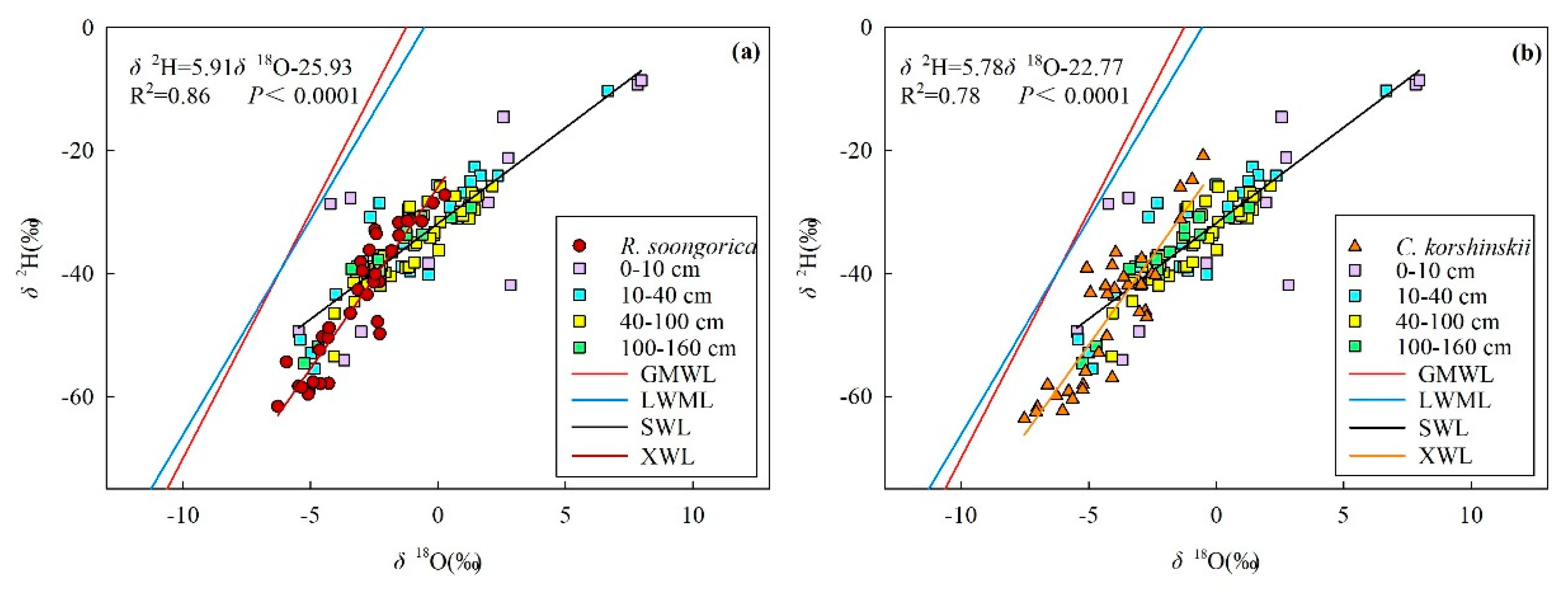
3.4. Main Water-Absorptive Horizon of Plant
3.5. Seasonal Variations in the Proportion of Plant Water Uptake
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sprenger, M.; Leistert, H.; Gimbel, K.; Weiler, M. Illuminating hydrological processes at the soil-vegetation-atmosphere interface with water stable isotopes. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 674–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, B.J.; Lu, N.; Zhang, L. Seasonal variation in water uptake patterns of three plant species based on stable isotopes in the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.D.; Zhao, X.N.; Li, H.C.; Guo, L.; Lv, T.; Wu, P.T. Exotic shrub species (Caragana korshinskii) is more resistant to extreme natural drought than native species (Artemisia gmelinii) in a semiarid revegetated ecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 263, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossiord, C.; Sevanto, S.; Bonal, D.; Isaac, B.; Dawson, T.E.; Max, R.; Wang, W.Z.; McDowell, N. Prolonged warming and drought modify belowground interactions for water among coexisting plants. Tree Physiol. 2018, 39, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, T.E.; Mambelli, S.; Plamboeck, A.H.; Templer, P.H.; Tu, K.P. Stable isotopes in plant ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 507–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaristo, J.; McDonnell, J.J.; Scholl, M.A.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Chun, K.P. Insights into plant water uptake from xylem-water isotope measurements in two tropical catchments with contrasting moisture conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3210–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossiord, C.; Sevanto, S.; Dawson, T.E.; Adams, H.D.; Collins, A.D.; Dickman, L.T.; Newman, B.D.; Stockton, E.A.; McDowell, N.G. Warming combined with more extreme precipitation regimes modifies the water sources used by trees. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Ma, C.C.; Gao, Y.B. Primary Study on Reproduction Strategies of Caragana roborovskyi in the Arid Desert Region. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2012, 20, 434–438. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.H.; LI, Y.; Jiao, J. Quantity Dynamics of Reaumuria soongorica Populations from Different Habitats in the South-north Hills in Lanzhou. J. Nat. Resour. 2011, 26, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Q.; Qiu, M.X.; Pu, J.C.; Lu, Z.M. The typical extrexe xerophyit—Reaumuria soongorica in the desert of China. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 1982, 24, 485–488. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Wang, L. Reexamination of the Aridity Conditions in Arid Northwestern China for the Last Decade. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 9594–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y. Water-use strategy of three central Asian desert shrubs and their responses to rain pulse events. Plant Soil 2006, 285, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delzon, S.; Loustau, D. Age-related decline in stand water use: Sap flow and transpiration in a pine forest chronosequence. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 129, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares, R.; Barnard, H.R.; Mao, D.; Revil, A.; Singha, K. Examining diel patterns of soil and xylem moisture using electrical resistivity imaging. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.; Merrifield, M. Mapping groundwater dependent ecosystems in California. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Evaristo, J.; Li, Z.; Si, B.C.; McDonnell, J.J. Tritium analysis shows apple trees may be transpiring water several decades old. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, J.P.; Walker, G.R.; Kennett-Smith, A.K. Field validation of isotopic procedures for determining sources of water used by plants in a semi-arid environment. J. Hydrol. 1995, 167, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.; Dawson, T. Water uptake by plants: Perspectives from stable isotope composition. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, P.Z.; Williams, D.G. Hydrogen isotope fractionation during water uptake by woody xerophytes. Plant Soil 2007, 291, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.H.; Sternber, L.S.L. Hydrogen isotopic fractionation by plant roots during water uptake in coastal wetland plants. In Stable Isotopes & Plant Carbon-Water Relations; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassana, F.F.; Eller, C.B.; Oliveira, R.S.; Dillenburg, L.R. Effects of soil water availability on foliar water uptake of Araucaria angustifolia. Plant Soil 2016, 399, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, D.E.; Ingraham, N.L.; Smith, S.D. Water uptake in woody riparian phreatophytes of the South western United States: A stable isotope study. Ecol. Appl. 1992, 2, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.L.; Gregg, J.W. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too many sources. Oecologia 2003, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.W.; Semmens, B.X. Incorporating uncertainty and prior information into stable isotope mixing models. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnell, AC.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, B.C.; Semmens, B.X. MixSI AR GUI User Manual, Version 3.1. 2013. Available online: http://conserver.iugocafe.org/user/brice.semmens/MixSIAR (accessed on 10 March 2016).
- Leng, X.; Cui, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; An, S. Differential water uptake among plant species in humid alpine meadows. J. Veg. Sci. 2013, 24, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Irrigation depth far exceeds water uptake depth in an oasis cropland in the middle reaches of Heihe River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Seasonal variations in depth of water uptake for a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to drought in an East Asian monsoon region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, N.; Fu, B.J. Inter-comparison of stable isotope mixing models for determining plant water source partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Li, Z.P.; Zhao, L.Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G. Spatial Landscape Pattern according to Slope of Afforestation in Southern and Northern Mountains of Lanzhou City. J. Desert Res. 2006, 26, 604–607. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.H.; Xiao, H.L.; Song, Y.X.; Chen, G.D. Soil Water Variation in Different Terrains and Influence on Plant in Lanzhou Suburb on Western Loess Plateau. J. Desert Res. 2006, 26, 522–526. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Y.; Su, S.P.; Wang, H. Preliminary Investigation into Plant and Vegetation Types in Afforestation Region in Southern and Northern Mountains of Lanzhou City. J. Desert Res. 2006, 26, 564–568. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.C.; Qu, L. Strategy of Vegetation Restoration in Lanzhou North-South Mountains. J. Desert Res. 2006, 26, 493–497. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.G.; Huang, R.; Zhang, J.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Wu, Y.H. Preliminary Study on the Diversity and Arrangement Patterns of Plant Communities at Afforestation Region in Southern and Northern Mountains of Lanzhou City. J. Gansu For. Sci. Technol. 2017, 42, 27–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhang, J.Q.; Xu, H.G.; Zhao, F.; Wu, Y.H. The investigation of plant community structure and dominant species in barren hill area of Lanzhou. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2016, 30, 129–135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Cheng, G.D. Comments on a number of issues of eco-hydrological processes in arid areas. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2001, 46, 1851–1857. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.N.; Wu, P.T.; Wang, W.Z.; Feng, H. Research advance on eco-environmental water requirement. Adv. Water Sci. 2005, 16, 617–622. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, T.E.; Pate, J.S. Seasonal water uptake and movement in root systems of Australian phraeatophytic plants of dimorphic root morphology: A stable isotope investigation. Oecologia 1996, 107, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.G.; Patrickson, S.J.; Ehleringer, J.R. Water extraction times for plant and soil materials used in stable isotope analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.R.; Peng, X.H.; Shen, Y.J.; Chen, X.M. Measurements of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in liquid water by isotope ratio infrared spectroscopy (IRIS) and their spectral contamination corrections. Chin. J. Ecol. 2013, 32, 1181–1186. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.J.; Wen, X.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Han, J.Y.; Sun, X.M.; Li, X.B. Potential impacts organic contaminant on δ18O and δD in leaf and xylem water detected by isotope ratio infrared spectroscopy. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2012, 20, 1359–1365. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, N.M.; Griffis, T.J.; Lee, X.; Baker, J.M. Identification and correction of spectral contamination in 2H/1H and 18O/16O measured in leaf, stem, and soil water. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 3360–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.J.; Xiao, H.L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.X.; Cheng, G.D.; Zhou, M.X.; Yin, L.; McCabe, M.F. Detailed assessment of isotope ratio infrared spectroscopy and isotope ratio mass spectrometry for the stable isotope analysis of plant and soil waters. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 3071–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric water. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Zhao, X.N.; Gao, X.D.; Pan, Y.H. Soil water use strategy of dominant species in typical natural and planted shrubs in loess hilly region. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 175–185. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, J.J.; Chen, T.T. Water sources of five dominant desert plant species in Nuomuhong area of Qaidam Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 6277–6286. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.G.; Fu, B.J. Soil water migration in the unsaturated zone of semiarid region in China from isotope evidence. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.K. Seasonal variations of oxygen-18 in soil moisture and estimation of recharge in esker and moraine formations. Hydrol. Res. 1984, 15, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zheng, X.J.; Tang, L.S.; Li, Y. Differences and similarities between water sources of Tamarix ramosissima, Nitraria sibirica and Reaumuria soongorica in the southeastern Junggar Basin. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2013, 37, 665–673. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Qi, Y.S.; Xu, X. Water sources of Medicago sativa grown in different slope positions in Yanchi County of Ningxia. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 38, 1226–1240. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Zheng, X.J.; Tang, L.S.; Li, Y. Stable oxygen isotopes reveal distinct water use patterns of two Haloxylon species in the Gurbantünggüt Desert. Plant Soil 2015, 389, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, W.Z.; Zheng, X.J.; Li, S.J. Root distribution of Nitraria sibirica with seasonally varying water sources in a desert habitat. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazis, C.; Feng, X.H. A stable isotope study of soil water: Evidence for mixing and preferential flow paths. Geoderma 2004, 119, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.W.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, C.C.; Xiao, X. Contrasting water use pattern of introduced and native plants in an alpine desert ecosystem, Northeast QinghaiTibet Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Liu, W.Y.; Li, P.J.; Duan, W.P.; Li, H.M. Dry season water uptake by two dominant canopy tree species in a tropical seasonal rainforest of Xishuangbanna, SW China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbjornsen, H.; Shepherd, G.; Helmers, M.; Mora, G. Seasonal patterns in depth of water uptake under contrasting annual and perennial systems in the Corn Belt Region of the Midwestern U.S. Plant Soil 2008, 308, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Jia, Z.Q.; Lu, Q.; Hao, Y.G.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, L.; Qi, Y.L. Water Use Strategy of Five Shrubs in Ulanbuh Desert. Sci. Silvae Sin 2010, 46, 15–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qu, D.; Duan, W.; Wang, J.; Su, P.; Guo, R. Water Use Strategies of Dominant Species (Caragana korshinskii and Reaumuria soongorica) in Natural Shrubs Based on Stable Isotopes in the Loess Hill, China. Water 2020, 12, 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071923
Zhang Y, Zhang M, Qu D, Duan W, Wang J, Su P, Guo R. Water Use Strategies of Dominant Species (Caragana korshinskii and Reaumuria soongorica) in Natural Shrubs Based on Stable Isotopes in the Loess Hill, China. Water. 2020; 12(7):1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071923
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Mingjun Zhang, Deye Qu, Wenguang Duan, Jiaxin Wang, Pengyan Su, and Rong Guo. 2020. "Water Use Strategies of Dominant Species (Caragana korshinskii and Reaumuria soongorica) in Natural Shrubs Based on Stable Isotopes in the Loess Hill, China" Water 12, no. 7: 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071923
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, M., Qu, D., Duan, W., Wang, J., Su, P., & Guo, R. (2020). Water Use Strategies of Dominant Species (Caragana korshinskii and Reaumuria soongorica) in Natural Shrubs Based on Stable Isotopes in the Loess Hill, China. Water, 12(7), 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071923





