Effects of Indigenous Cultivation Practices on Soil Conservation in the Hilly Semiarid Areas of Western Sudan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method and Materials
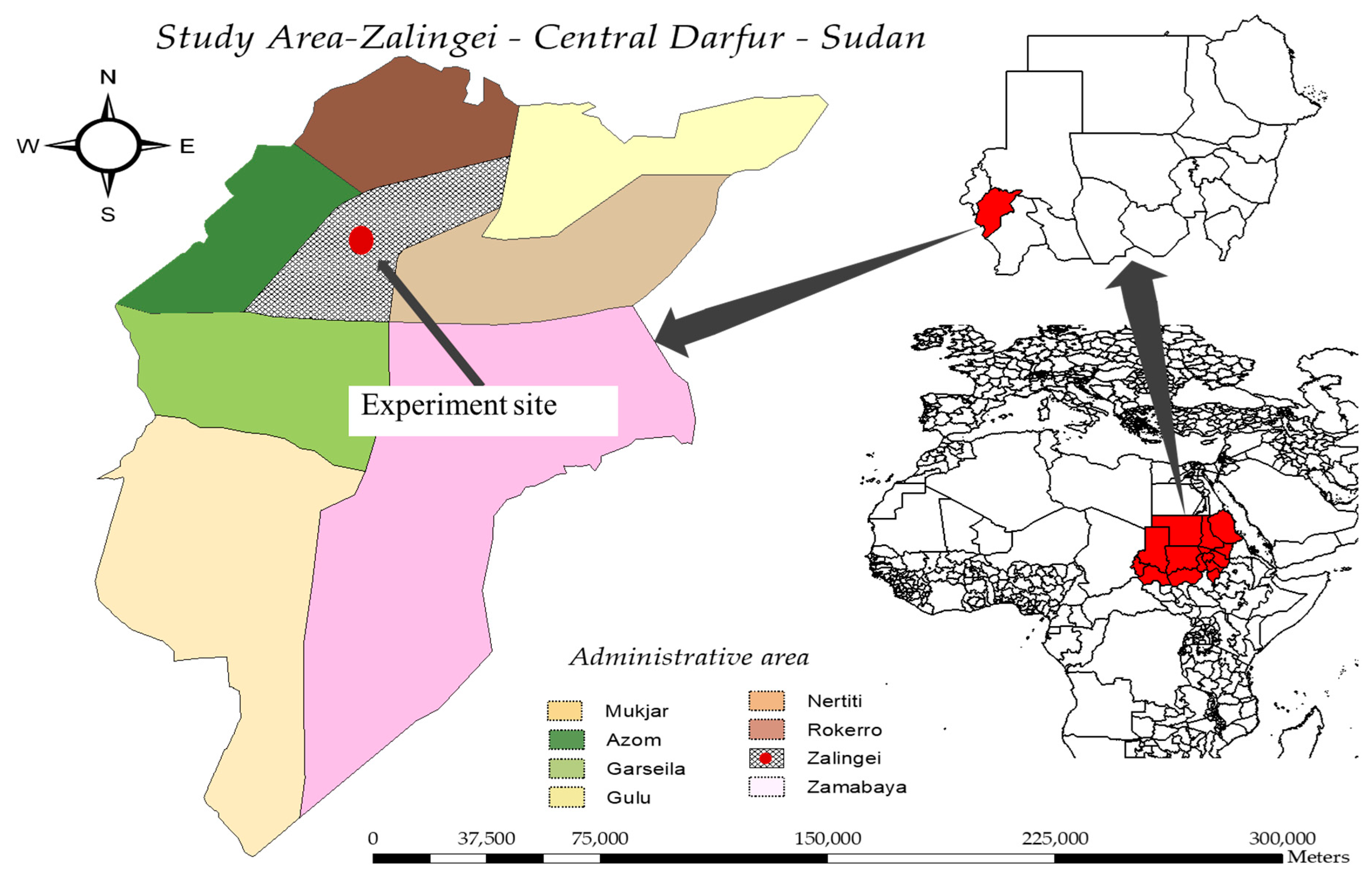
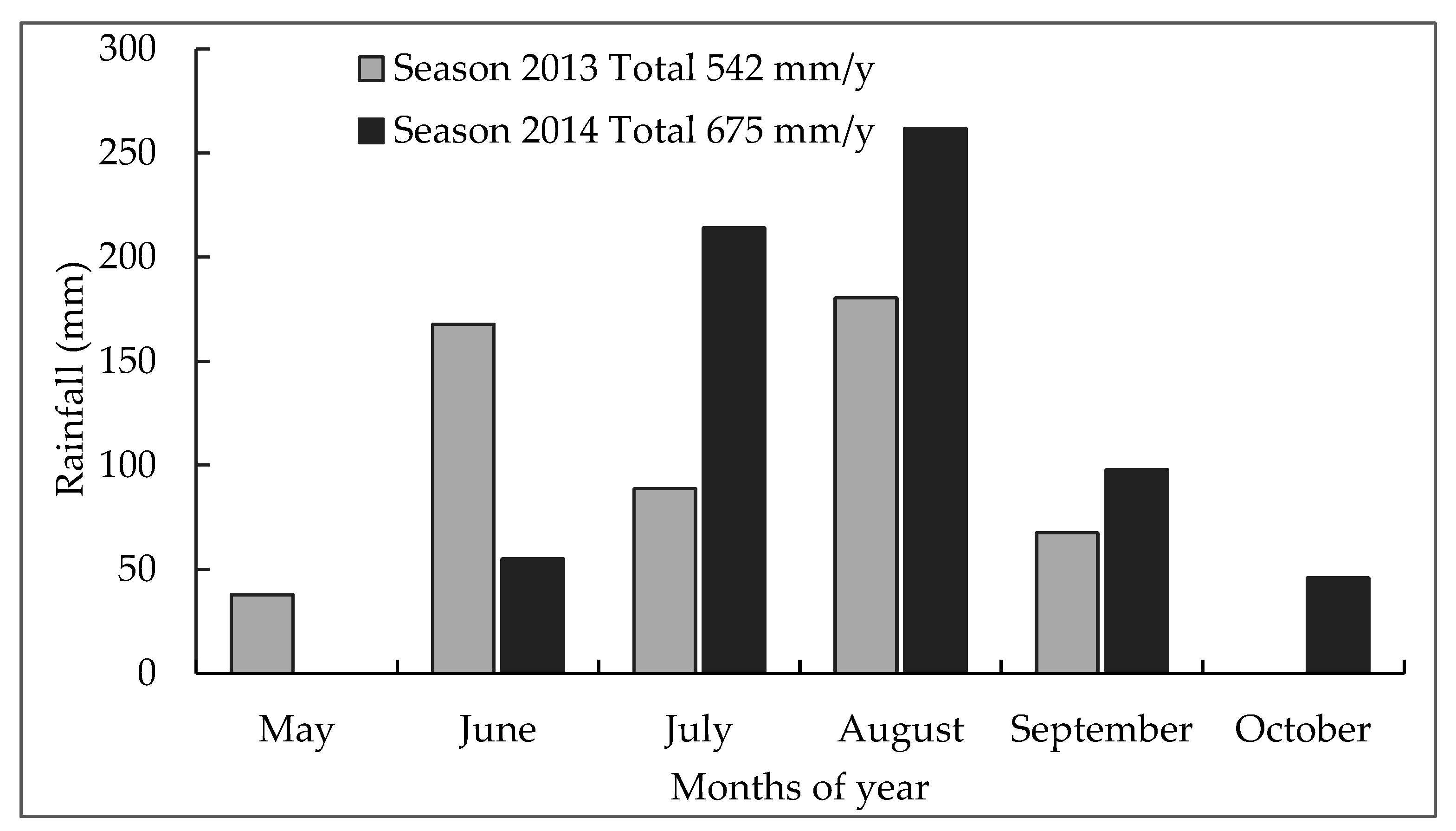
2.1. Study Site
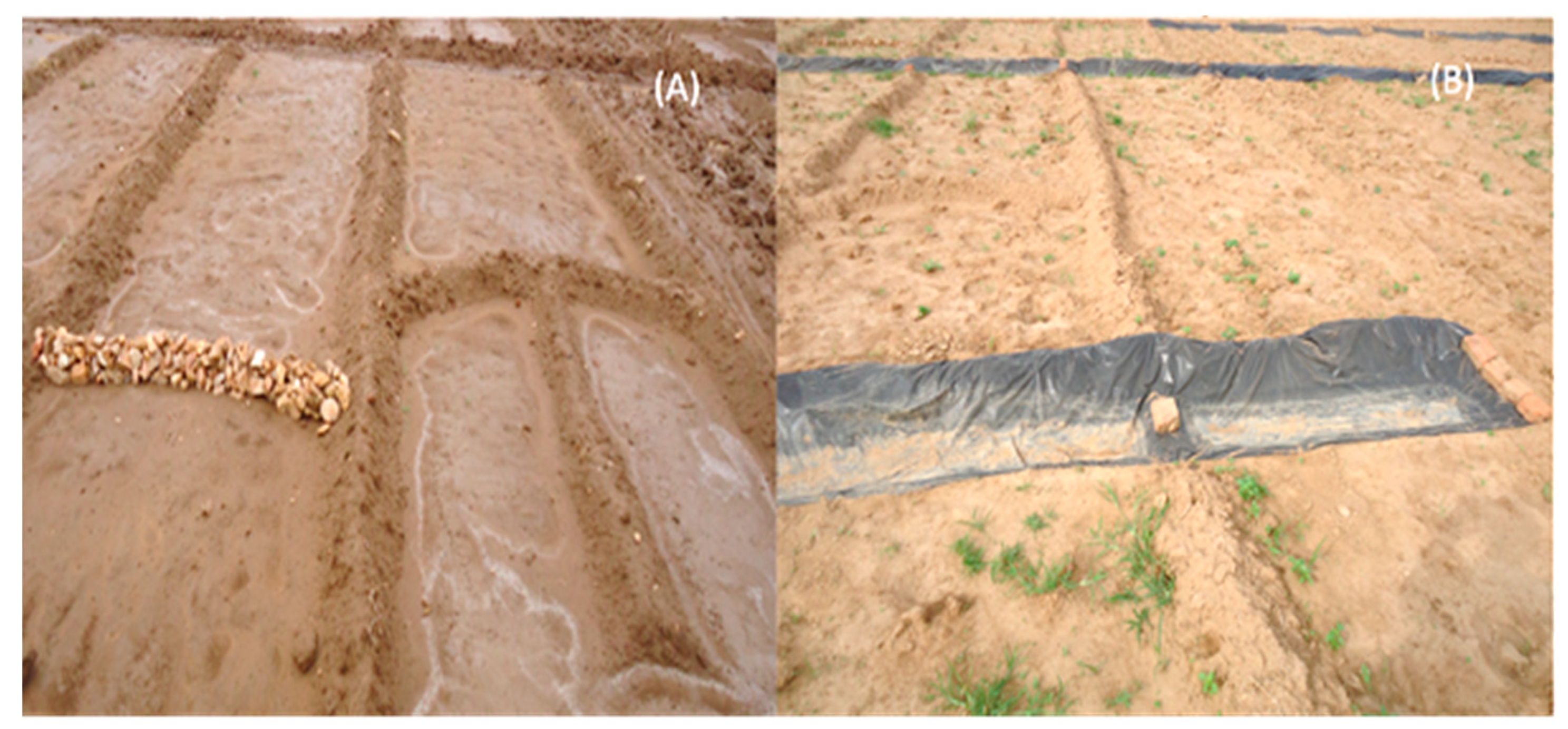
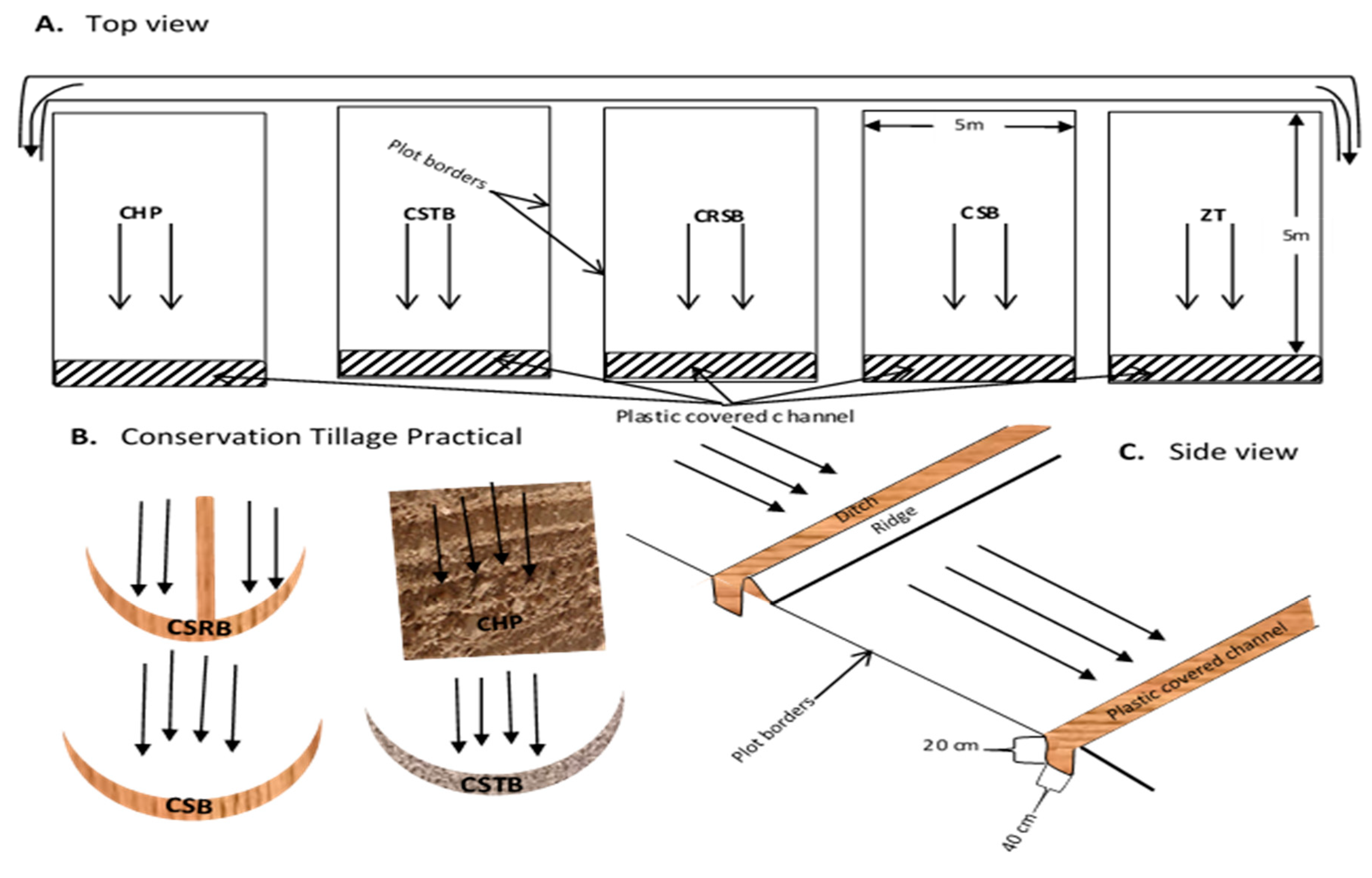
2.2. Experimental Design:
2.3. Measurement of Soil Losses:
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
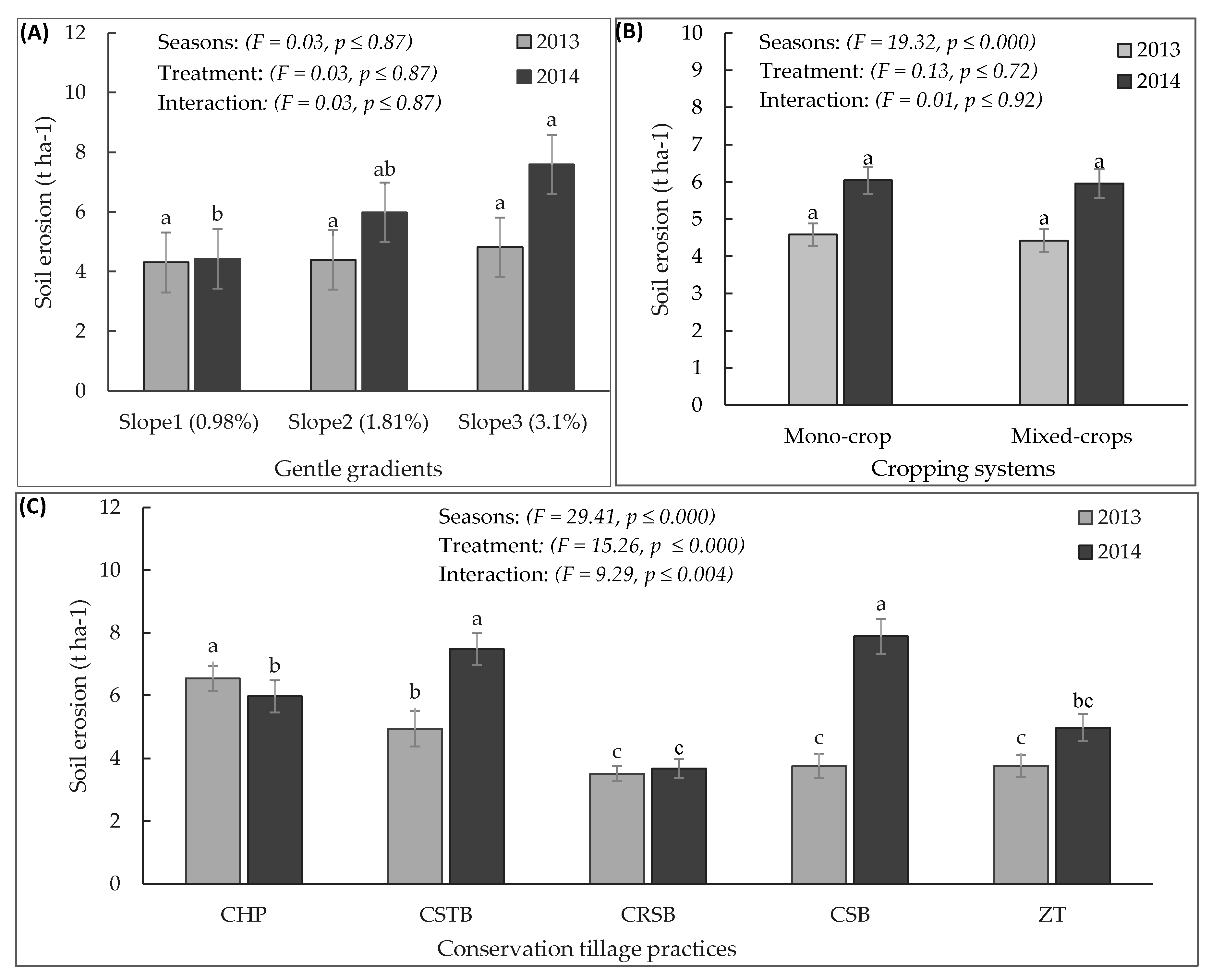
3.1. Soil Erosion
3.2. Effect of the Land Slopes and Cropping System
3.3. Effect of the Conservation Tillage Practices
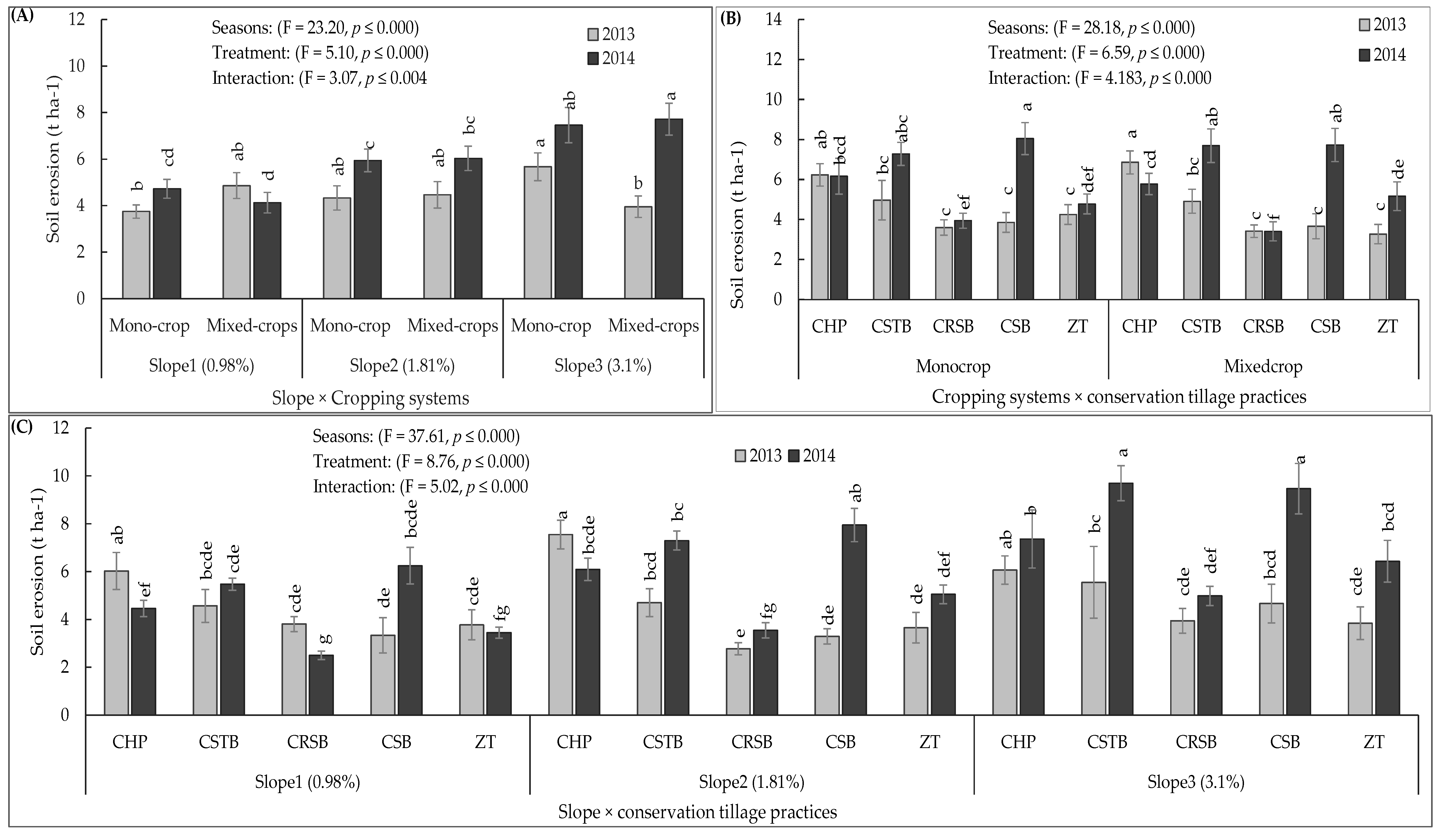
3.4. Interaction of the Slope and Cropping System
3.5. Interactions between Cropping Systems and Conservation Tillage Practices
3.6. Effects of the Slope Combined with Conservation Tillage Techniques
3.7. Interactions of Slope (S), Cropping Systems (CS), Conservation Tillage Practice (CTP)
3.8. Correlation Coefficients of Linear and Quadratic Relationships between Slope, Cropping System, Conservation Tillage Practical to the Soil Erosion.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Araya, A.; Stroosnijder, L. Effects of tied ridges and mulch on barley (Hordeum vulgare) rainwater use efficiency and production in Northern Ethiopia. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeboye, O.B.; Schultz, B.; Adekalu, K.O.; Prasad, K. Soil water storage, yield, water productivity and transpiration efficiency of soybeans (Glyxine max L. Merr) as affected by soil surface management in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-L.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Fan, J.-W.; Turner, N.C.; He, J.; Wang, T.; Li, F.-M. Exogenous abscisic acid reduces water loss and improves antioxidant defence, desiccation tolerance and transpiration efficiency in two spring wheat cultivars subjected to a soil water deficit. Funct. Plant Biol. 2013, 40, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Meyer, R.; Yadav, S.S.; Redden, R.J.; Hatfield, J.L.; Lotze-Campen, H.; Hall, A.E. Synthesis of regional impacts and global agricultural adjustments. Crop. Adapt. Clim. Chang. 2011, 26, 156–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.X.; Zhu, A.X. Assessment of soil erosion and conservation on agricultural sloping lands using plot data in the semi-arid hilly loess region of China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2014, 2, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ighodaro, I.D.; Lategan, F.S.; Yusuf, S.F.G. The impact of soil erosion on agricultural potential and performance of Sheshegu community farmers in the Eastern Cape of South Africa. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 5, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Littleboy, M.; Freebairn, D.M.; Hammer, G.L.; Silburn, D.M. Impact of soil erosion on production in cropping systems. II. Simulation of production and erosion risks for a wheat cropping system. Soil Res. 1992, 30, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Kumar, U. Integrated approach of universal soil loss equation (USLE) and geographical information system (GIS) for soil loss risk assessment in Upper South Koel Basin, Jharkhand. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 4, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobo, G.P.; Bonilla, C.A. Predicting soil loss and sediment characteristics at the plot and field scales: Model description and first verifications. Catena 2019, 172, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarello, V.; Ferro, V.; Giordano, G. Testing alternative erosivity indices to predict event soil loss from bare plots in Southern Italy. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Falkenmark, M. Agriculture: Increase water harvesting in Africa. Nature 2015, 519, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.P.; Rockström, J.; Oweis, T.Y. Rainfed agriculture: Unlocking the potential. CABI. 2009, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Karadsheh, E.A.; Akroush, S.; Mazahreh, S. Land Degradation in Jordan–Review of Knowledge Resources; OASIS Country Report 1, No. 565–2016-38924; ICARDA and USAID: Aleppo, Syria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Reicosky, D.C. Conservation tillage is not conservation agriculture. J. Soil water Conserv. 2015, 70, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araya, T.; Cornelis, W.M.; Nyssen, J.; Govaerts, B.; Getnet, F.; Bauer, H.; Amare, K.; Raes, D.; Haile, M.; Deckers, J. Medium-term effects of conservation agriculture-based cropping systems for sustainable soil and water management and crop productivity in the Ethiopian highlands. Field Crops Res. 2012, 132, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, C.M.; Liang, X.; Linquist, B.A.; Van Groenigen, K.J.; Lee, J.; Lundy, M.E.; Van Gestel, N.; Six, J.; Venterea, R.T.; Van Kessel, C. Productivity limits and potentials of the principles of conservation agriculture. Nature 2015, 517, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miehe, S. Acacia albida and other multipurpose trees on the Fur farmlands in the Jebel Marra highlands, Western Darfur, Sudan. Agrofor. Syst. 1986, 4, 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddig, A.A.H. Biodiversity of Sudan: Between the harsh conditions, political instability and civil wars Ecological indicators of ecosystem changes View project. Biodivers. J. 2014, 5, 545–555. [Google Scholar]
- Marcu, A.; Viespe, C. Laser-grown ZnO nanowires for room-temperature SAW-sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Effects of rainfall intensity fluctuations on infiltration and runoff: Rainfall simulation on dryland soils, Fowlers Gap, Australia. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2211–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metreo. Jabel Marra Rural Development Project, Meteorological Division; Annual Report; Ministry of Agriculture: Zalingei, Sudan, 2011.
- States, D.; Motalab, A.; Khatir, M.; Bahar, A.H.; Adam, K.I.; Mohamed, A.A.; Ali, S.A.M. Chemical Composition of New Phenotype Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L) (Locally named Barbarei) Grains and Stover in South and West Darfur States, (Sudan) ARPN. J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 683–686. [Google Scholar]
- Radwanski, S.A.; Wickens, G.E. The ecology of Acacia albida on mantle soils in Zalingei, Jebel Marra, Sudan. J. Appl. Ecol. 1967, 4, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, K.A.; Gomez, A.A. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.M.; Stamey, W.L. Determining the range of tolerable erosion. Soil Sci. 1965, 100, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamekye, C.; Thiel, M.; Schönbrodt-Stitt, S.; Zoungrana, B.J.B.; Amekudzi, L.K. Soil and Water Conservation in Burkina Faso. West Afr. Sustain. 2018, 10, 3182. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Conservation Tillage Practice (CTP) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHP | CRSB | CSB | CSTB | ZT | F | p | |||
| Season 2013 | S1 | CS1 | 4.7 + 0.81 | 3.19 + 0.53 | 3.3 + 0.14 | 2.87 + 0.53 | 4.66 + 0.19 | 1.79 | 0.09 |
| CS2 | 7.35 + 0.78 | 5.94 + 0.46 | 4.32 + 0.46 | 3.8 + 1.5 | 2.89 + 1.07 | ||||
| S2 | CS1 | 7.19 + 1.05 | 4.23 + 0.77 | 2.6 + 0.32 | 3.1 + 0.52 | 4.5 + 1.03 | |||
| CS2 | 7.91 + 0.75 | 5.17 + 0.95 | 2.94 + 0.44 | 3.48 + 0.45 | 2.81 + 0.53 | ||||
| S3 | CS1 | 6.8 + 0.47 | 7.47 + 2.39 | 4.91 + 0.5 | 5.6 + 0.34 | 3.57 + 1.21 | |||
| CS2 | 5.32 + 0.99 | 3.63 + 1.33 | 2.99 + 0.39 | 3.73 + 1.51 | 4.11 + 0.91 | ||||
| Season 2014 | S1 | CS1 | 5.16 + 0.09 | 5.78 + 0.39 | 2.87 + 0.07 | 6.25 + 1.16 | 3.55 + 0.37 | 0.52 | 0.83 |
| CS2 | 3.77 + 0.27 | 5.16 + 0.27 | 2.12 + 0.11 | 6.25 + 1.26 | 3.34 + 0.36 | ||||
| S2 | CS1 | 5.55 + 0.75 | 7.42 + 0.64 | 3.91 + 0.52 | 7.92 + 1.08 | 4.9 + 0.46 | |||
| CS2 | 6.63 + 0.5 | 7.17 + 0.61 | 3.17 + 0.33 | 7.97 + 1.13 | 5.2 + 0.73 | ||||
| S3 | CS1 | 7.79 + 2.68 | 8.64 + 1.21 | 5.03 + 0.49 | 9.97 + 1.31 | 5.88 + 1.13 | |||
| CS2 | 6.94 + 0.11 | 10.74 + 0.3 | 4.94 + 0.75 | 8.96 + 1.89 | 6.98 + 1.49 | ||||
| Equation | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|
| Soil erosion = 2.599 + 1.497(season) + 0.985(S) − 0.119(CS) − 0.417(CTP) | 0.37 | *** |
| Soil erosion = 2.437 + 1.497(season) + 0.985(S × CS) − 0.201(S × CTP) − 216(CS × CTP) | 0.37 | *** |
| Soil erosion = 1.94 + 1.497(season) + 0.069(S × CS × CTP) | 0.23 | *** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
I. A. Ahmed, A.; M. Eldoma, I.; A. H. Elaagip, E.E.; Hou, F. Effects of Indigenous Cultivation Practices on Soil Conservation in the Hilly Semiarid Areas of Western Sudan. Water 2020, 12, 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061554
I. A. Ahmed A, M. Eldoma I, A. H. Elaagip EE, Hou F. Effects of Indigenous Cultivation Practices on Soil Conservation in the Hilly Semiarid Areas of Western Sudan. Water. 2020; 12(6):1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061554
Chicago/Turabian StyleI. A. Ahmed, Abdalla, Ibrahim M. Eldoma, Elsadig ElMahdi A. H. Elaagip, and Fujiang Hou. 2020. "Effects of Indigenous Cultivation Practices on Soil Conservation in the Hilly Semiarid Areas of Western Sudan" Water 12, no. 6: 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061554
APA StyleI. A. Ahmed, A., M. Eldoma, I., A. H. Elaagip, E. E., & Hou, F. (2020). Effects of Indigenous Cultivation Practices on Soil Conservation in the Hilly Semiarid Areas of Western Sudan. Water, 12(6), 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061554








