Removal of Phosphate Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Leftover Coal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorbent Preparation and Characterization
2.2. Reagents Used and Adsorbate Prepartaion
2.3. Experimental Set-Up
2.4. Effects of Particle Size
2.5. Effects of Temperature
2.6. Adsorption Kinetics
2.7. Adsorption Isotherm
2.8. Statistical Analysis—Central Composite Design (CCD)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Raw Material Characterization
3.2. Effect of Contact Time and Adsorption Kinetics
3.3. Effect of Initial pH
3.4. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
3.5. Effect of Particle Size
3.6. Effect of Initial Concentration
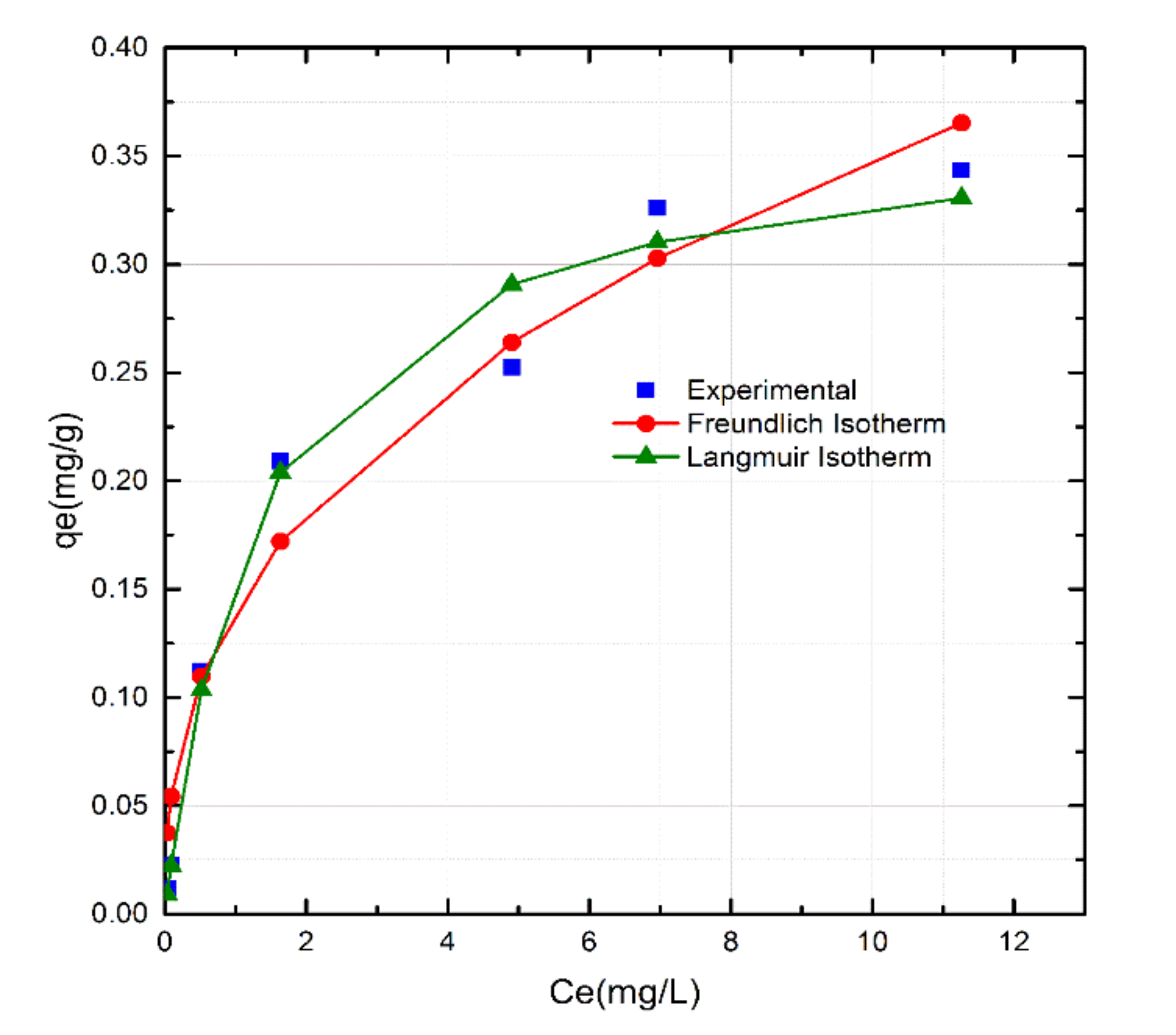
3.7. Adsorption Isotherm and Thermodynamics
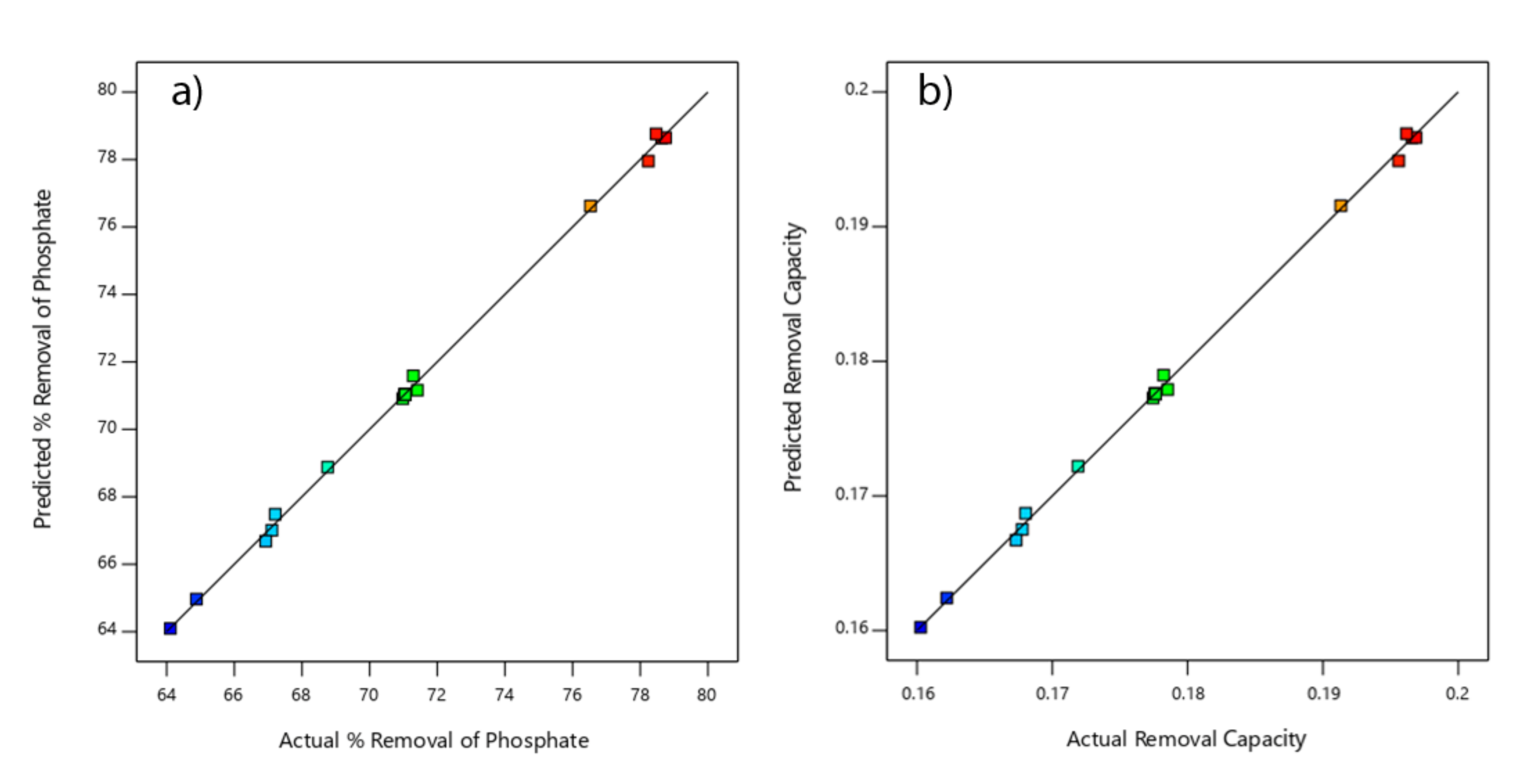
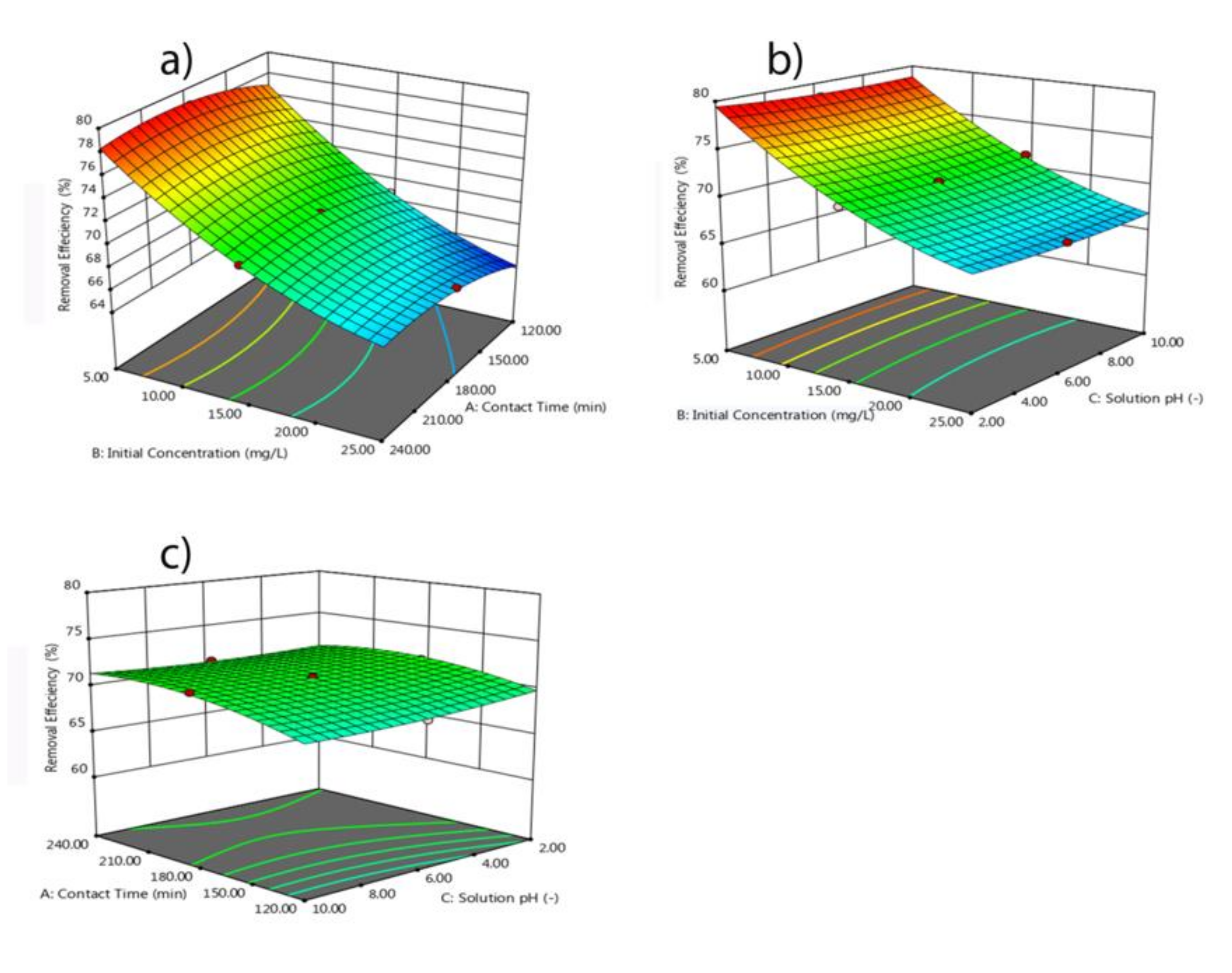
3.8. Central Composite Design (CCD)
4. Conclusions
- When leftover coal is used for phosphate removal from aqueous solutions, design parameters such as initial phosphate concentration, initial solution pH, adsorbent dose, temperature, and contact time must be optimally selected to obtain the highest possible removal. Apparently, the adsorption of phosphate onto leftover coal increased markedly at pH value of 2, which is the actual pH value of most industrial effluents.
- The adsorption kinetics for phosphate removal could be well described by the pseudo-second-order equation with a correlation value of R2 = 0.99 which revealed that, chemisorption was the dominant process.
- Observed temperature effects on phosphate adsorption reveal that the process is exothermic.
- The central composite design (CCD) was found to be an appropriate approach to optimize the variable affecting phosphate adsorption. The obtained quadratic regression model well depicted observed values of percent phosphate removal and phosphate removal capacity.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, J.; Zang, L.; Zha, J.; Mahmood, Q.; He, Z. Phosphate Removal from Secondary Effluents Using Coal Gangue Loaded with Zirconium Oxide. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karageorgiou, K.; Paschalis, M.; Anastassakis, G.N. Removal of Phosphate Species from Solution by Adsorption onto Calcite Used as Natural Adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, A139, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshadi, M.; Eskandarloo, H.; Azizi, M.; Abbaspourrad, A.; Abdolmaleki, M.K.; Eskandarloo, H.; Azizi, M.; Abbaspourrad, A. Synthesis of Highly Monodispersed, Stable, and Spherical NZVI of 20−30 Nm on Filter Paper for the Removal of Phosphate from Wastewater: Batch and Column Study. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11662–11676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Bai, S.; Mu, H.; Naren, G. Investigation of Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solution by Both Coal Gangues. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, I.A.; Viswanathan, N. Development and Reuse of Amine-Grafted Chitosan Hybrid Beads in the Retention of Nitrate and Phosphate. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleka, E.N.; Deliyanni, E.A. Adsorptive Removal of Phosphates from Aqueous Solutions. Desalination 2009, 245, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Kapur, M.; Kumar, P.; Mondal, M.K. Adsorptive Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution Using Rice Husk and Fruit Juice Residue. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 94, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoya, S.; Nakamichi, S.; Kawase, Y. Mechanisms of Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solution by Zero-Valent Iron: A Novel Kinetic Model for Electrostatic Adsorption, Surface Complexation and Precipitation of Phosphate under Oxic Conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 218, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ishaq, M.; Ahmad, I. Evaluation of Coal as Adsorbent for Phosphate Removal. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.K.; Hamdan, A.-H.M.; Chavez, V.M.; Brown, J.D.; Halden, R.U. Mass Balance Model for Sustainable Phosphorus Recovery in a US Wastewater Treatment Plant. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, E.; Lennartz, B. Virgin Volcanic Rocks: Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies for the Adsorption of Cadmium from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabi, N.; Soleimani, M.; Sharififard, H.; Yeganeh, M.M. Optimization of Phosphate Removal from Drinking Water with Activated Carbon Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 15613–15618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tor, A.; Cengeloglu, Y. Removal of Congo Red from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption onto Acid Activated Red Mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaoka, S.; Yamamoto, T. Characteristics of Phosphate Adsorption onto Granulated Coal Ash in Seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benyoucef, S.; Amrani, M. Adsorption of Phosphate Ions onto Low Cost Aleppo Pine Adsorbent. Desalination 2011, 275, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, R.; Jyo, A.; Ihara, T.; Seko, N. Enhanced Trace Phosphate Removal from Water by Zirconium (IV) Loaded Fibrous Adsorbent. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4592–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barca, C.; Gérente, C.; Meyer, D.; Chazarenc, F.; Andrés, Y. Phosphate Removal from Synthetic and Real Wastewater Using Steel Slags Produced in Europe. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2376–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaneian, M.T.; Ghanizadeh, G.; Alizadeh, M.T.H.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Said, F.M. Equilibrium and Kinetics of Phosphorous Adsorption onto Bone Charcoal from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Z.; Lu, S.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, H. Removal and Recovery of Phosphate from Water by Lanthanum Hydroxide Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, N.; Ahmad, M.E.; El Said, W.M.; Moalla, S.M.N. Adsorptive Removal of Phosphorous from Wastewater Using Drinking Water Treatment-Alum Sludge ( DWT-AS ) as Low Cost Adsorbent. Am. J. Chem. Appl. 2015, 2, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Lee, X.; Grattieri, M.; Macazo, F.C.; Cai, R.; Minteer, S.D. A Sustainable Adsorbent for Phosphate Removal: Modifying Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Chitosan. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 12641–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Chu, B.; Amano, Y.; Machida, M. Removal and Recovery of Phosphate from Water by Mg-Laden Biochar: Batch and Column Studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 558, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouamra, F.; Drouiche, N.; Abdi, N.; Grib, H.; Mameri, N.; Lounici, H. Removal of Phosphate from Wastewater by Adsorption on Marble Waste: Effect of Process Parameters and Kinetic Modeling. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 12, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Li, H.; Yao, Z.; Shen, Y.; He, Z.; Yang, X.; Ng, H.Y.; Wang, C.H. Removal of Nitrate and Phosphate by Chitosan Composited Beads Derived from Crude Oil Refinery Waste: Sorption and Cost-Benefit Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngsie, G.; Katika, K.; Fabricius, I.L.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Borggaard, O.K. Phosphate Removal by Iron Oxide-Coated Diatomite: Laboratory Test of a New Method for Cleaning Drainage Water. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saki, H.; Alemayehu, E.; Schomburg, J.; Lennartz, B. Halloysite Nanotubes as Adsorptive Material for Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solution. Water 2019, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, B.; Duan, F. Synthesis of Industrial Solid Wastes/Biochar Composites and Their Use for Adsorption of Phosphate: From Surface Properties to Sorption Mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 571, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantaw, D. The Resource Potential of Coal in Ethiopia–Report; Addis Ababa Institute of Technology: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, L.Y. The Removal of Phosphate by Coal Gangue from Wastewater. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 209, 2005–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regassa, M.; Melak, F.; Birke, W.; Alemayehu, E. Defluoridation of Water Using Natural and Activated Coal. Int. Adv. Res. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2016, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Bhattarai, R.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Fan, Y. Utilization of Coal Fly and Bottom Ash Pellet for Phosphorus Adsorption: Sustainable Management and Evaluation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, G.; Eren, Y.; Ayd, S.; Emik, S.; Tuba, A.; Osra, F.; Wasswa, J. A Facile Polymerisation of Magnetic Coal to Enhanced Phosphate Removal from Solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, N.H.; Ma, H.T.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Eppe, G.; Nguyen, T.T. Removal of Phosphate from Wastewater Using Coal Slag. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, M.E. Evaluation of the Use of Fly Ash as a Low Cost Technology for Phosphorus Removal in Wastewater Treatment. An Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Bowen, J.M. Design and Construction of Phosphorus Removal Structures for Improving Water Quality; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-58658-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I. Determination of Sorbent Point Zero Charge: Usefulness in Sorption Studies. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2009, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, D.; Kannan, P.; Nesakumar, T.; Immanuel, J.; Senthilkumar, A. Biochar from Green Waste for Phosphate Removal with Subsequent Disposal. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, M.; Ali, R.; Rao, K.; Ahmad, R.; Khan, M.A. Adsorption Studies on Parthenium Hysterophorous Weed: Removal and Recovery of Cd (II) from Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, B135, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaithambi, P.; Beyene, D.; Aziz, A.R.A.; Alemayehu, E. Removal of Pollutants with Determination of Power Consumption from Landfill Leachate Wastewater Using an Electrocoagulation Process: Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 69, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadhukhan, B.; Mondal, N.K.; Chattoraj, S. Optimisation Using Central Composite Design (CCD) and the Desirability Function for Sorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution onto Lemna Major. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2016, 2, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saadat, S.; Raei, E.; Talebbeydokhti, N. Enhanced Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solutions Using a Modi Fi Ed Sludge Derived Biochar: Comparative Study of Various Modifying Cations and RSM Based Optimization of Pyrolysis Parameters. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Han, Q.; Li, J.; Li, H. The Behavior of Phosphate Adsorption and Its Reactions on the Surfaces of Fe–Mn Oxide Adsorbent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 76, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek-krowiak, A.; Szafran, R.G.; Modelski, S. Biosorption of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions onto Peanut Shell as a Low-Cost Biosorbent. Desalination 2011, 265, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Gao, B.; Song, W.; Xu, X.; Yue, Q. Modified Biogas Residues as an Eco-Friendly and Easily-Recoverable Biosorbent for Nitrate and Phosphate Removals from Surface Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Fang, L.; Fortner, J.D.; Guan, X.; Lo, I.M.C. Highly Efficient and Selective Phosphate Removal from Wastewater by Magnetically Recoverable La(OH)3/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites. Water Res. 2017, 126, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, T.H.; Hong, S.P.; Yoon, J. Development of Nanoscale Zirconium Molybdate Embedded Anion Exchange Resin for Selective Removal of Phosphate. Water Res. 2018, 134, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.Q.; Tao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.M. Kinetics, Isotherm, Thermodynamic, and Adsorption Mechanism Studies of La(OH)3-Modified Exfoliated Vermiculites as Highly Efficient Phosphate Adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallet, M.; Barthélémy, K.; Ruby, C.; Renard, A.; Naille, S. Investigation of Phosphate Adsorption onto Ferrihydrite by X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 407, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Jung, D.I. Removal of Total Phosphorus (TP) from Municipal Wastewater Using Loess. Desalination 2011, 269, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, S.S.; Das, S.N.; Rath, P. Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption on Treated Sawdust. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 31, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi Nodeh, H.; Sereshti, H.; Zamiri Afsharian, E.; Nouri, N. Enhanced Removal of Phosphate and Nitrate Ions from Aqueous Media Using Nanosized Lanthanum Hydrous Doped on Magnetic Graphene Nanocomposite. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Jung, J.; Pawar, R.R.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.M. Arsenate and Phosphate Removal from Water Using Fe-Sericite Composite Beads in Batch and Fixed-Bed Systems. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Price, N.T.; Angel, M.; Pinilla, G.; Shea, K.E.O. Effective Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution Using Humic Acid Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles. Water Res. 2017, 123, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.D.; Lee, S. Effect of PH and Coexisting Anions on Removai of Phospiiate from Aqueous Soiutions by Inorganic-Based Mesostructures. Water Environ. Res. 2012, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengthamkeerati, P.; Satapanajaru, T.; Chularuengoaksorn, P. Chemical Modification of Coal Fly Ash for the Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solution. Fuel 2008, 87, 2469–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the Modeling of Adsorption Isotherm Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, M.; Mondal, M.K. Mass Transfer and Related Phenomena for Cr ( VI ) Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions onto Mangifera Indica Sawdust. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ge, X.W.; Yu, H.Q. Optimization of Coagulation-Flocculation Process for a Paper-Recycling Wastewater Treatment Using Response Surface Methodology. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 302, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Pseudo First Order | Pseudo Second Order | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe, exp (mg/g) | qe, cal (mg/g) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | qe, exp (mg/g) | qe, cal (mg/g) | K2 (g/mg min) | R2 | |
| 10 | 0.20283 | 0.11676 | 0.195 | 0.96 | 0.20283 | 0.20511 | 7.67 | 0.99 |
| Adsorbent | Freundlich Constants | Langmuir Constants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KF (L/mg) | nF | R2 | KL (L/mg) | qmax (mg/kg) | R2 | RL | |
| Coal leftover | 0.112 | 1.67 | 0.901 | 1.315 | 38.01 | 0.7604 | 0.03–0.60 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mekonnen, D.T.; Alemayehu, E.; Lennartz, B. Removal of Phosphate Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Leftover Coal. Water 2020, 12, 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051381
Mekonnen DT, Alemayehu E, Lennartz B. Removal of Phosphate Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Leftover Coal. Water. 2020; 12(5):1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051381
Chicago/Turabian StyleMekonnen, Dereje Tadesse, Esayas Alemayehu, and Bernd Lennartz. 2020. "Removal of Phosphate Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Leftover Coal" Water 12, no. 5: 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051381
APA StyleMekonnen, D. T., Alemayehu, E., & Lennartz, B. (2020). Removal of Phosphate Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption onto Leftover Coal. Water, 12(5), 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051381






