Heliconia stricta Huber Behavior on Hybrid Constructed Wetlands Fed with Synthetic Domestic Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Characteristics
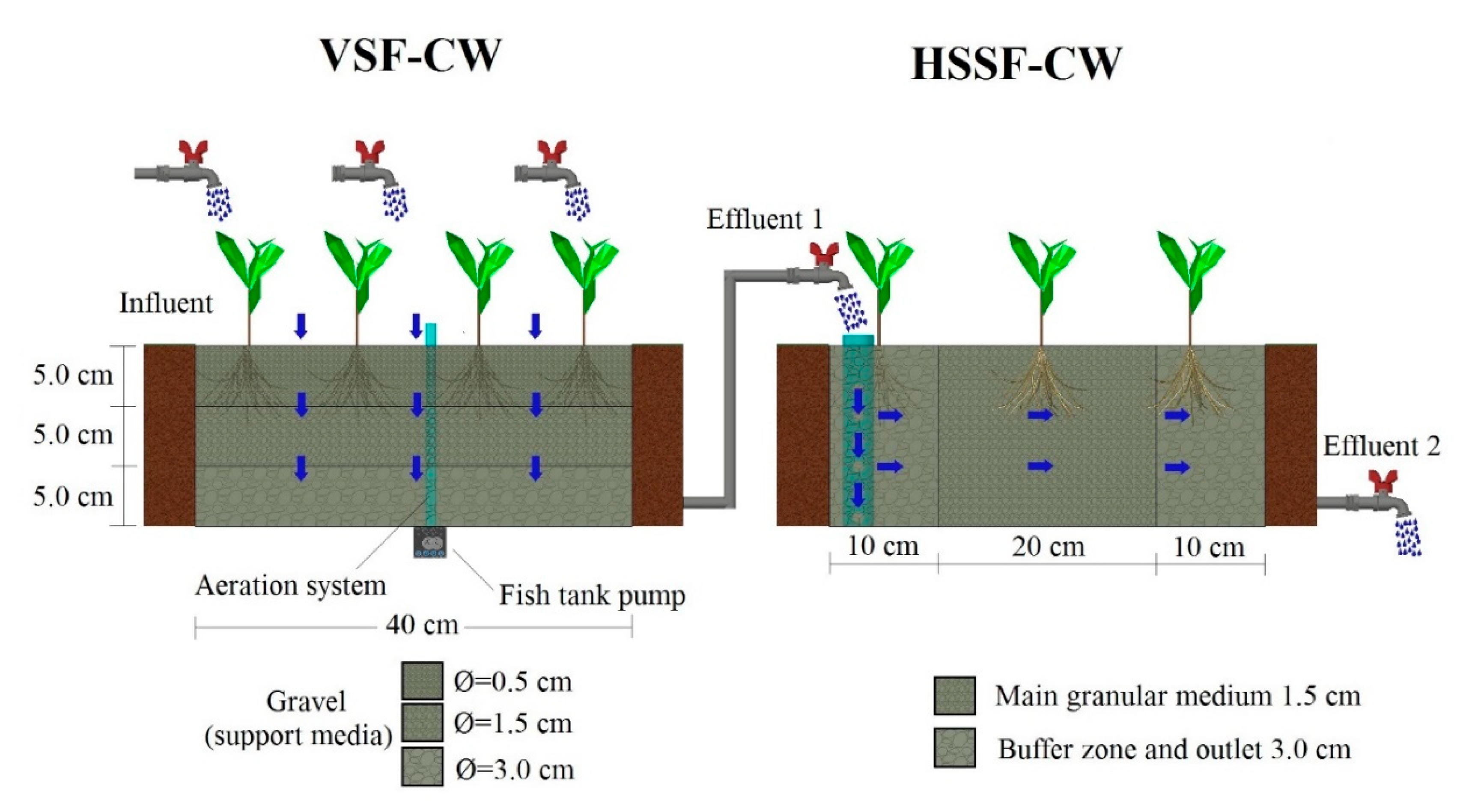
2.2. Experimental Model
2.3. Operational Strategy
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Statistical Analysis
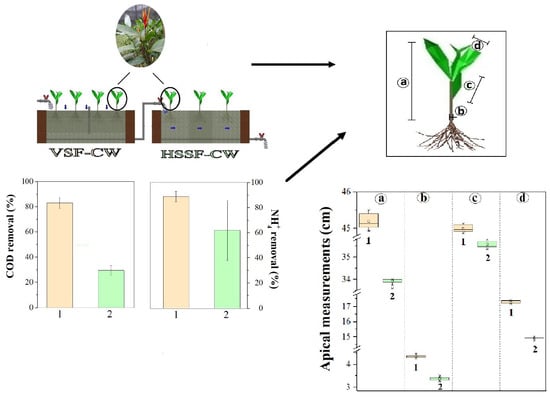
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hybrid System: Operation and Performance
3.2. Heliconia stricta Behavior during the Operation
3.2.1. Heliconia stricta Huber Growth
3.2.2. Heliconia stricta Huber Biomass
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Thebo, A. Global wastewater and sludge production, treatment and use. In Wastewater, 1st ed.; Drechsel, P., Qadir, M., Wichelns, D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Villamar, C.A.; Neubauer, M.E.; Vidal, G. Distribution and availability of copper and zinc in a constructed wetland fed with treated swine slurry from an anaerobic lagoon. Wetlands 2014, 34, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, M.A.; Tarhini, A.; Nasr, J.A. Decentralized approaches to wastewater treatment and management: Applicability in developing countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roefs, I.; Meulman, B.; Vreeburg, J.H.G.; Spiller, M. Centralised, decentralised or hybrid sanitation systems? Economic evaluation under urban development uncertainty and phased expansion. Water Res. 2017, 109, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S. A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfí, M.; Flores, L.; Ferrer, I. Life Cycle Assessment of wastewater treatment systems for small communities: Activated sludge, constructed wetlands and high rate algal ponds. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 161, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Mendoza, A.S.; Bello-Mendoza, R.; Herrera-López, D.; Mejía-González, G.; Calixto-Romo, A. Performance of constructed wetlands with ornamental plants in the treatment of domestic wastewater under the tropical climate of South Mexico. Water Pract. Technol. 2015, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zurita, F.; De Anda, J.; Belmont, M.A. Treatment of domestic wastewater and production of commercial flowers in vertical and horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyola, A.; Padilla-Rivera, A.; Morgan-Sagastume, J.M.; Güereca, L.P.; Hernández-Padilla, F. Typology of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Technologies in Latin America. Clean–Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, O.C.; Türe, C.; Böcük, H.; Çiçek, A.; Yakar, A. Role of plants and vegetation structure on boron (B) removal process in constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrijos, V.; Gonzalo, O.G.; Trueba-Santiso, A.; Ruiz, I.; Soto, M. Effect of by-pass and effluent recirculation on nitrogen removal in hybrid constructed wetlands for domestic and industrial wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2016, 103, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, L.; Zamora-Castro, S.; Vidal-Álvarez, M.; Marín-Muñiz, J. Role of Wetland Plants and Use of Ornamental Flowering Plants in Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yi, N.-K.; Wang, S.; Lu, L.-J.; Huang, X.-F. Impact of plant species on spatial distribution of metabolic potential and functional diversity of microbial communities in a constructed wetland treating aquaculture wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, L.-H.; Zoh, K.-D. Removal characteristics and mechanism of antibiotics using constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzadi, M.; Fátima, K.; Imran, A.; Mirza, M.S.; Khan, Q.M.; Afzal, M. Ecology of bacterial endophytes associated with wetland plants growing in textile effluent for pollutant-degradation and plant growth-promotion potentials. Plant Biosyst. 2015, 150, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, X.; Ho, S.-H.; Wang, L.; Yang, J. Effect of plant species compositions on performance of lab-scale constructed wetland through investigating photosynthesis and microbial communities. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stottmeister, U.; Wießner, A.; Kuschk, P.; Kappelmeyer, U.; Kästner, M.; Bederski, O.; Müller, R.A.; Moormann, H. Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol. Adv. 2003, 22, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Tan, S.K.; Gersberg, R.M.; Zhu, J.; Sadreddini, S.; Li, Y. Nutrient removal in tropical subsurface flow constructed wetlands under batch and continuous flow conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 96, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Hu, Z.; Hou, C.; Liu, H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. New insights for enhancing the performance of constructed wetlands at low temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Nazarudin, M.R.; Tsan, F.Y. Vegetative and reproductive growth behaviour of Xanthostemon chrysanthus (F. Muell.) Benth.–an ornamental tree in Malaysia. Sains. Malays. 2018, 47, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Song, X.; Gong, J. The inhibition and adaptability of four wetland plant species to high concentration of ammonia wastewater and nitrogen removal efficiency in constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 202, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.-C.; Wang, M.; Lai, W.-L.; He, F.-H.; Chen, Z.-H. Plant growth and nutrient removal in constructed monoculture and mixed wetlands related to stubble attributes. Hydrobiologia 2011, 661, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Los Reyes, C.P.; Villamar, C.A.; Neubauer, M.E.; Pozo, G.; Vidal, G. Behavior of Typha angustifolia L. in a free water surface constructed wetlands for the treatment of swine wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part A 2013, 48, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, C.; Zurita, F.; Nani, G.; Reyes, G.; Fernández-Lambert, G.; Cabrera-Hernández, A. Nitrogen Removal from Domestic Wastewater and the Development of Tropical Ornamental Plants in Partially Saturated Mesocosm-Scale Constructed Wetlands. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shelef, O.; Gross, A.; Rachmilevitch, S. Role of Plants in a Constructed Wetland: Current and New Perspectives. Water. 2013, 5, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Gersberg, R.M.; Liu, Y.; Ng, W.J.; Tan, S.K. Application of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in developing countries—A review of recent developments (2000–2013). J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 141, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Naranjo, C.E.; Espinoza-Montero, P.J.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, M.I.; Villamar-Ayala, C.A. Hydraulic Retention Time Influence on Improving Flocculation in the Activated Sludge Processes Through Polyelectrolytes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, E. Ingeniería de Aguas Residuales: Tratamiento, Vertido y Reutilización de Aguas Residuales, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanakis, A.I.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Effects of loading, resting period, temperature, porous media, vegetation and aeration on performance of pilot-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181–182, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, F.S.; Herrera, P.G.; Chiquito, G.M.; Morales, M.F.; Castro, A.P.; Paulo, P.L. Relationship between microbial community and environmental conditions in a constructed wetland system treating greywater. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 139, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.D.H.; Bui, X.T.; Nguyen, D.D.; Nguyen, V.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Dan, P.; Cong-Nguyen, N.; Lin, C. Wastewater treatment and biomass growth of eight plants for shallow bed wetland roofs. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgos, V.; Araya, F.; Reyes-Contreras, C.; Vera, I.; Vidal, G. Performance of ornamental plants in mesocosm subsurface constructed wetlands under different organic sewage loading. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akratos, C.S.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Effect of temperature, HRT, vegetation and porous media on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.J.; Wu, S.Q.; Dai, Y.R.; Liang, W.; Wu, Z.B. Treatment performance of integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland plots for domestic wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 44, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, M.; BISWAS, P.A.S. Rejoinder of diverse organic growing media on morphological attributes of nine Heliconia species and varieties under West Bengal condition. J. Crop Weed. 2019, 15, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Natural Resources Conservation Service. Plants Database. 2018. Available online: www.usda.gov. (accessed on 29 March 2020).
- León-Yánez, S.; Valencia, R.; Pitman, N.; Endara, L.; Ulloa, C.; Navarrete, H. Libro Rojo de las plantas endémicas del Ecuador; Publicaciones del Herbario: Quito, Ecuador, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Enviromental Protection Agency. Folleto Informativo de Tecnología de Aguas Residuales Humedales de Flujo Subsuperficial; United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Wahington, DC, USA, 2000; p. 13.
- APHA AWWA WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater: American Public Health Association, 21st ed.; American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Caselles-Osorio, A.; Puigagut, J.; Segú, E.; Vaello, N.; Granés, F.; García, D.; García, J. Solids accumulation in six full-scale subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Kröpfelová, L. Removal of nitrogen in constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-sureface flow: A review. Wetlands 2009, 29, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, B. Effect of intermittent operation on contaminant removal and plant growth in vertical flow constructed wetlands: A microcosm experiment. Desalination 2010, 262, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, L.; Cunill, C.; Cáceres, R.; Marfà, O. Design and monitoring of horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetlands for treating nursery leachates. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6414–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Ke, F. Full-Scale Experiment on Domestic Wastewater Treatment by Combining Artificial Aeration Vertical- and Horizontal-Flow Constructed Wetlands System. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 5673–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Solís, M.; Villegas, E.; De Anda, J.; López-López, A. The Effect of the Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance of an Ecological Wastewater Treatment System: An anaerobic filter with a constructed wetland. Water 2015, 7, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maine, M.A.; Sanchez, G.C.; Hadad, H.R.; Caffaratti, S.E.; Pedro, M.C.; Mufarrege, M.M.; Di Luca, G.A. Hybrid constructed wetlands for the treatment of wastewater from a fertilizer manufacturing plant: Microcosms and field scale experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prochaska, C.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Removal of phosphates by pilot vertical-flow constructed wetlands using a mixture of sand and dolomite as substrate. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 26, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, N.T.D.; Konnerup, D.; Schierup, H.-H.; Chiem, N.H.; Tuan, L.A.; Brix, H. Kinetics of pollutant removal from domestic wastewater in a tropical horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland system: Effects of hydraulic loading rate. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yan, X.; Gu, X. Evaluation of thermally-modified calcium-rich attapulgite as a low-cost substrate for rapid phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2017, 115, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohla, C.; Kõiv, M.; Bavor, H.J.; Chazarenc, F.; Mander, Ü. Filter materials for phosphorus removal from wastewater in treatment wetlands—A review. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ádám, K.; Søvik, A.K.; Krogstad, T. Sorption of phosphorous to Filtralite-PTM—The effect of different scales. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.; Goharpour, M.; Moharami, S. Contrasting Effects of Four Plant Residues on Phosphorus Sorption-Desorption in Some Phosphorus Fertilized Calcareous Soils. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plan. 2018, 49, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Gajewska, M.; Pytka, A.; Marzec, M.; Gizińska-Górna, M.; Jucherski, A.; Walczowski, A.; Nastawnyc, M.; Kaminska, A.; Baran, S. Influence of the particle size of carbonate-siliceous rock on the efficiency of phosphorous removal from domestic wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenway, M. The Role of Macrophytes in Nutrient Removal using Constructed Wetlands. In Environmental Bioremediation Technologies; Singh, S.N., Tripathi, R.D., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 331–351. [Google Scholar]
- Konnerup, D.; Koottatep, T.; Brix, H. Treatment of domestic wastewater in tropical, subsurface flow constructed wetlands planted with Canna and Heliconia. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lyu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Button, M.; Arias, C.A.; Weber, K.P.; Brix, H.; Carvalho, P.N. Impacts of design configuration and plants on the functionality of the microbial community of mesocosm-scale constructed wetlands treating ibuprofen. Water Res. 2018, 131, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | °C | 19.5 ± 1.6 |
| pH | - | 7.5 ± 0.2 |
| COD | mg L−1 | 596.0 ± 60.0 |
| NH4+ | mg L−1 | 22.5 ± 2.6 |
| NO2− | mg L−1 | 0.02 ± 0.02 |
| NO3− | mg L−1 | 3.4 ± 2.8 |
| PO43− | mg L−1 | 9.3 ± 1.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida-Naranjo, C.E.; Guachamín, G.; Guerrero, V.H.; Villamar, C.-A. Heliconia stricta Huber Behavior on Hybrid Constructed Wetlands Fed with Synthetic Domestic Wastewater. Water 2020, 12, 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051373
Almeida-Naranjo CE, Guachamín G, Guerrero VH, Villamar C-A. Heliconia stricta Huber Behavior on Hybrid Constructed Wetlands Fed with Synthetic Domestic Wastewater. Water. 2020; 12(5):1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051373
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida-Naranjo, Cristina E., Gabriela Guachamín, Víctor H. Guerrero, and Cristina-Alejandra Villamar. 2020. "Heliconia stricta Huber Behavior on Hybrid Constructed Wetlands Fed with Synthetic Domestic Wastewater" Water 12, no. 5: 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051373