Abstract
Constructed wetlands (CWs) represent a highly efficient, eco-friendly and economic alternative for wastewater treatment in decentralized contexts. The adequate selection of the plants used in CWs plays a decisive role in the successful implementation and operation of this technology type. In this work, we studied the behavior of a native tropical plant (Heliconia stricta Huber) for the removal of organic matter and nutrients within a hybrid CW system fed with synthetic domestic wastewater. This hybrid system was composed of two wetlands, a vertical surface flow (VSF-CW) and a horizontal subsurface flow (HSSF-CW), connected in series and being operated with nominal hydraulic loading rates of 12 and 9 mm day−1, respectively. Results evidenced nitrification (nitrite concentration increased up to three times) but not denitrification because nitrate concentration increased in the final effluent. The average removal efficiencies were 86.8%, 96.4%, and 57.0%, for COD, NH4+ and PO43−, respectively. On the other hand, the apical height, basal diameter, leaf length and width increased in relation to initial measurements (between 0.6–7.1%) in plants of both CWs, which demonstrated the ability of the plants to adapt to the operating conditions of the system. This promising performance observed when using Heliconia stricta Huber opens the need for further research and could be particularly interesting in CWs used in tropical areas.
1. Introduction
Worldwide, more than 330 km3 year−1 of municipal wastewater are generated, and less than 60% receive treatment. The quality and quantity of treated wastewater depend on consumption habits, environmental factors and zoning population (rural/urban) [1,2]. In the developing countries, only between 8% and 20% of their wastewater is treated [1,3]. Its low wastewater treatment level is associated to population poverty levels and limited access to existing technologies [4]. Wastewaters without treatment are used mostly for irrigation systems, which has caused almost 88% of waterborne diseases to be located within these countries [4,5].
In developed countries, where the population is mainly urban, the conventional centralized (>2000 inhab.) wastewater treatment technologies (covering over 90% of the population) are used. Conventional centralized technologies achieve high removal efficiencies in organic matter (average 90%) and nutrients (up to 70%) [3]. However, centralized technologies have higher operation and maintenance costs (up to 55% more expensive) than non-conventional or decentralized treatments. In addition, these technologies are more complicated to operate and are not a sustainable solution for wastewater treatment under rural contexts [6]. Therefore, the selection of highly efficient (e.g., up to 98% for organic matter, total suspended solids and nitrogen), eco-friendly (avoiding sludge generation and using lower energy resources), easy to operate and low-cost technologies is important, especially in developing countries and rural contexts. Constructed wetlands (CWs) are an alternative, being the most common passive technologies used worldwide [6,7]. Although it is convenient to use technologies such as CWs, there are fewer of them in developing countries (e.g., around 137 active CWs in Latin America) compared to those in the USA (>8000) and European countries (e.g., >50,000 in Germany) [8,9]. CWs are widely used in the treatment of wastewaters coming from domestic, municipal, agricultural and industrial sources, among others [7].
CWs are complex systems made up mainly by vegetation, substrates, soil, native microorganisms and water, interacting with each other. Each of these components allows the contaminants removal by physical, chemical and biological mechanisms, such as volatilization, sorption, sedimentation, photodegradation, plant uptake and microbial degradation. According to CW hydraulics, they can be classified into three types based on surface flow (HSF-CW, VSF-CW) and subsurface flow (HSSF-CW), which are combined to complement and enhance its performance in hybrid systems [7,10]. The main limitation of using a single CW could be associated with a low nitrogen removal. Whereas if hybrid CWs are used, the nitrogen removal could increase due to the effective combination of nitrification (aerobic conditions, VSF-CW) and denitrification (anaerobic/anoxic conditions, HSSF-CW) processes carried out consecutively [11].
Plants play a very important role within CWs. The plant species commonly used within CWs are macrophytes, which include emergent plants, submerged plants, floating leaf plants and free-floating plants [7]. Plants remove contaminants through two ways: (i) direct function where the contaminants are absorbed by plant uptake processes and (ii) indirect function given by symbiotic association between plants and microorganisms. The roots of plants play an important role as microbial support medium, promoting the formation of different microenvironments (aerobic, anoxic and anaerobic), and producing oxygen and exudates. These conditions stimulate growth, reproduction, diversity and microbial activity. The microorganisms, mainly endophytic bacteria, are responsible for the contaminants transformation, making them bioavailable to plants. Moreover, they promote nitrogen fixation, siderophores production and phosphorus solubilization. In addition, endophytic bacteria protect macrophytes from contaminants’ toxicity due to their high concentrations. Thus, the microorganisms together with the plants facilitate the contaminants’ removal. The main route for nitrogen removal within CWs occurs when nitrification and denitrification processes are carried out by endophyte microorganisms, which are promoted by oxygen and exudates from macrophyte roots [12,13,14,15]. In addition, the plant roots in CWs can improve the substrate characteristics (porosity, permeability), the landscape environment and protect the wetland from environmental conditions (frost, radiation, wind speed) [13,14]. Therefore, the presence of plants improve the contaminant removal, especially of those nutrients that are in excess [16]. Several plants have shown potential to treat domestic wastewater and different industrial effluents, so they are used in CWs. Among the contaminants that CWs have removed from wastewater are organic matter (plants and microorganisms uptake), nutrients (plants and microorganisms uptake and adsorption in the filter bed), dyes (biodegradation and adsorption in the filter bed), heavy metals (bioaccumulation, plant or microorganisms uptake), emerging contaminants (biodegradation and adsorption in the filter bed) and other toxic compounds [5,10,13,14,15]. In the case of nutrients, plants could remove between 15 and 32 mg g−1 of total nitrogen (5–10% of the total wastewater nitrogen) and between 2 and 6 mg g−1 of total phosphorus (<5% of the total wastewater phosphorus) [12,17].
In tropical zones (mainly developing countries), CWs are more efficient than in temperate and cold zones due to their high temperatures (≥25 °C). Nutrient and organic matter removal efficiencies are at least 10 times higher than in standard CWs, because warm weather and sunlight favor plant growth and microbiological activity year-round [18,19]. The environmental conditions of tropical zones (climate and great biodiversity) allow using unconventional species (ornamental plants) within CWs. Ornamental plants (riverside plants) in tropical areas do not have a defined cycle as aquatic plants in temperate zones, because there are no well-marked seasons. For example, perennial tropical ornamental species can flower at any time of the year, depending on the species. Since the life cycle of ornamental plants depends on the water availability, its use within CWs depends on the hydraulic system [20]. Ornamental plants participate in the contaminant removal and improve the treatment system esthetic value. In addition, this plant type can provide socio-economic benefits to users due to flower production [8]. Due to the wide use of CWs, several studies are currently focused on taking advantage in some way of the plants that are used in them. Species of some ornamental plant families, such as Zantedeschia spp., Canna spp., Cyperus spp., Iris spp., Agapanthus spp., Strelitzia spp., Heliconia spp., etc., have been used for the removal of different contaminant types [14,15,16]. Efficiencies of up to 95% in total suspended solids and organic matter (measured as chemical oxygen demand and biological oxygen demand) have been reached. In the case of ammonium and phosphates, the removal has been between 10% and 90% [21,22,23,24]. It was determined that ornamental plants used within CWs have produced flowers without reducing the CW efficiency. Zurita et al. [8] used Zantedeschia aethiopica, Strelitzia reginae, Anturium andreanum and Agapanthus africanus within a HSSF-CW and a VSF-CW for 12 months, obtaining an average flower production of 60 and 10, respectively. These species could be commercialized or used for industrial purposes in the places where they were utilized. For instance, species of Heliconia spp. family from Ecuador, Thailand, Brazil, and Mexico are currently easily marketed both internally and externally [8,25,26]. For the aforementioned comments, the aim of this work is to evaluate the performance of Heliconia stricta Huber on the removal of organic matter and nutrients, using a hybrid system formed by a VSF-CW connected in series to a HSSF-CW.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Characteristics
Synthetic domestic wastewater was prepared according with the procedure proposed by Almeida-Naranjo et al. [27]. The synthetic domestic wastewater components (34.0 mg L−1 of gelatin, 100.0 mg L−1 of starch, 171.0 mg L−1 of sugar, 200.0 mg L−1 of milk powder, 44.5 mg L−1 of K2HPO4, 150.0 mg L−1 of NaHCO3, 74.2 mg L−1 of (NH4)2SO4 and 3.0 mg L−1 of MgSO4) were dissolved by magnetic stirring in 500 mL of hot tap water (40 °C). Subsequently, drinking water was added to obtain 4.0 L of synthetic wastewater. The synthetic domestic wastewater was prepared immediately before feeding the experimental model to preserve its characteristics. Table 1 summarizes the synthetic domestic wastewater physicochemical characteristics. According to Metcalf [28], the synthetic domestic wastewater composition used in this research resembles the middle contaminant concentration in real domestic wastewater (COD = 500 mg L−1, TN = 40 mg L−1 and TP = 8 mg L−1).

Table 1.
Physicochemical characteristics of synthetic domestic wastewater.
2.2. Experimental Model
The experimental model consisted on two constructed wetlands connected in series, one with vertical surface flow (VSF-CW) followed by a second one with horizontal subsurface flow (HSSF-CW). Each constructed wetland had a 0.08-m2 area and a 16-L volume. The support medium (filter bed material) in each one was 15-cm high and was composed of gravel (size: 0.5, 1.5, and 3.0 cm). These CW dimensions were selected because the research was focused on the study of the microcosm that simulates the conditions in which the plant influences the CW. In several previous studies, the layer depth in which the plant has the greatest influence on CW performance generally ranges between 10 to 50 cm [29,30,31,32,33,34]. Furthermore, the length reached by the Heliconia stricta Huber roots is within the above-mentioned depth range. Malakar et al. [35] determined that the Heliconia stricta Huber roots in different cultivation media presented a length between 2.1 and 7.0 cm.
Inside the VSF-CW, four one-month old Heliconia stricta Huber individuals were placed, while three individuals of the same species were placed within the HSSF-CW. Plants were obtained from a nursery near Quito city (northern Ecuador; location 0°12′21″ N, 78°13′09″ W). Heliconia stricta Huber individuals were verified using taxonomic records from both USDA [36] and León-Yánez [37]. The averages of the apical height, basal diameter and relative abundance were determined before planting them in both CWs, being 44.9/33.6, 4.3/3.3 cm and 48.2/33.9 individual m−2 for VSF-CW/HSSF-CW, respectively. Figure 1 details the CW schemes.
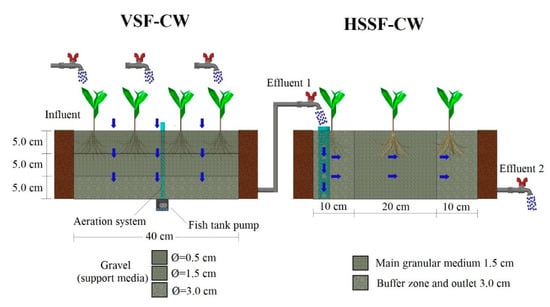
Figure 1.
Experimental model scheme.
2.3. Operational Strategy
In the adapting phase, CWs were fed with tap water for one week (hydraulic start) and later with synthetic domestic wastewater. CWs operated in series using nominal hydraulic loading rates of 0.012 and 0.009 m3 m−2 day−1 for VSF-CW and HSSF-CW, respectively. Synthetic domestic wastewater was fed and drained manually in a cyclic way according to that suggested by EPA (2000) [38]. The hydraulic retention time (HRT) for the VSF-CW was three days with a 4 h daily aeration (36 h HRT with 12 h aeration, loading rate = 12 mm day−1), while the synthetic domestic wastewater treated in VSF-CW was fed to the HSSF-CW. The aerated conditions within the VSF-CW was achieved using a fish tank pump (2.0 L min−1). The HRT for the HSSF-CW was four days (loading rate = 9 mm day−1); this CW worked without aeration. To determine the influence of synthetic domestic wastewater nutrients on Heliconia stricta Huber, its behavior was monitored using two individuals kept outside the wetlands (control) and feeding them with tap water (control). The control plants remained in the original substrate (soil), in a container with the same conditions as the hybrid system. The experimentation was carried out under laboratory conditions, with an average daily temperature and luminosity of 27 °C and 12 h, respectively. CWs were operated for 50 days.
2.4. Analytical Methods
Influent and effluent samples from the hybrid CW system were subjected to a physicochemical evaluation. Organic matter measured as Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) was assessed according with APHA-AWWA-WEF [39], using the Hach Method 8000 (low range: 3–150 mg COD L−1 and high range: 20–1500 mg COD L−1). Moreover, nutrients in the form of ammonia (NH4+), nitrates (NO3−), nitrites (NO2−) and phosphates (PO43−) were measured. Phosphates, nitrates, nitrites and ammonia were quantified using PhosVer 3 with Ascorbic Acid Digestion Hach Method 8048 (Range: from 0.02 to 1.10 mg PO43− L−1), Cadmium Reduction Hach Method 8039 (Range: 0.3 to 30.0 mg NO3− L−1), Diazotination Hach Method 8507 (Range 0.002 to 0.3 mg NO2− L−1) and Nessler Hach Method 8038 (Range 0.02 to 2.50 mg NH3-N L−1), respectively. Additionally, daily measurements of pH and temperature were performed using a Thermo Scientific Orion 5-Star Plus equipment (relative precision: ±0.002) and a multi-parameter PCE A-420, respectively. Hach Methods coming from Chemical Company USA. (Seattle, WA, USA)
Apical height, basal diameter, leaf number, leaf length, leaf width and relative abundance were determined weekly according with the methodology described by Villamar et al. [2].
At the end of the CW operation, the plant biomass and the microbial biofilm were measured. The dry-weight of the plants was determined at 75 °C for 24 h, being measured as Volatile Suspended Solids (VSS), Fixed Solids (FS) and Total Solids (TS), using a method based on 2540-B APHA-AWWA-WEF [39]. The microbial biofilm was quantified from volatile solids suspended concentration. One hundred and eighty grams of gravel taken from the entire CW height was placed with 150 mL of a buffer solution prepared with K2HPO4 and KH2PO4. It was sonicated for three minutes to separate the biofilm. Finally, the solid concentrations were determined using analysis codes 2540B and 2540B, for total suspended solids and volatile suspended solids, respectively [40].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The data collected was analyzed by applying a variance analysis (ANOVA) with a significance (p) of 0.05. Significant differences between type of wetland (VSF-CW and HSSF-CW), performance (COD, NH4+, NO3−, NO2−, PO43−) and allometric measurements (apical length, basal diameter, length of leaves, width of leaves, number of leaves and abundance) were analyzed. Normality (Shapiro–Wilk test) and parametric/non-parametric variance analyses (paired t-test/ Wilcoxon test) were used. The statistical software used were OriginPro 2018 and InfoStat-Statistical (version 2017) (Oringin Lab, Northampton, MA, USA and National University of Córdoba, Córdoba, Argentine; respectively).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hybrid System: Operation and Performance
Temperature and pH conditions are in the ranges that favor the contaminants’ removal (>15 °C and pH 6.5–8.5) [24]. Wastewater temperature remained in a range from 19.5 to 28.8 °C and 18.5 to 27.6 °C inside the VSF-CW and HSSF-CW, respectively. This may occur because the research was conducted in summer. The pH measured in water samples taken from each CW was in a range between 6.9 and 7.7 for the hybrid system. This small variation occurs due to the buffer effect that characterizes the CWs.
Figure 2 shows the efficiency in the removal of organic matter and nutrients in each CW. The range of the COD concentrations in the effluent went from 73.0 to 153.5 mg L−1 for VSF-CW and 55.0 to 143.5 mg L−1 for HSSF-CW. The COD removal efficiencies were higher in the VSF-CW than the HSSF-CW, achieving average performances of 83.0% (±4.2%) and 29.4% (±3.8%), respectively. The average COD removal efficiencies in the VSF-CW were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than in the HSSF-CW. The COD removal in VFS-CW is higher to those presented by Zurita et al. [8] (around 77.2%) who used ornamental plants (Zantedeschia aethiopica). The higher efficiency in the VSF-CW is product of the aeration that this wetland had. The aeration could be improved because this CW type has a batch operation (intermittently), thus improving the oxygen transfer between the wetland and the atmosphere [2,41]. By improving the transfer, oxygen is retained in the pores of the filter bed and the organic matter removal increases [25].
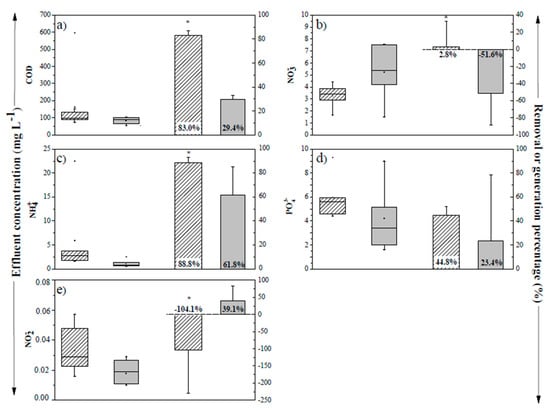
Figure 2.
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and nutrients effluent concentrations and removal in constructed wetlands (CWs). Striped columns: VSF-CW and gray columns: HSSF-CW. (a) COD, (b) NO3−, (c) NH4+, (d) PO43−. (e) NO2−,
The ammonia removal efficiencies were significantly higher (p = 0.002) in the VSF-CW than in the HSSF-CW, achieving average performances of 88.8% (±4.1%) and 61.8% (±23.7%), respectively. The removal efficiency of ammonia obtained in the VSF-CW is similar to the results obtained by Zurita et al. [8] and Nakase et al. [24], who obtained around 80% of ammonium removal in a VSF-CW using ornamental species. In the first three weeks of our system operation, the ammonia removal within the VSF-CW was higher than 90%, then decreased approximately 7% in the following weeks. The VSF-CW studied by Zurita et al. [8] showed a similar behavior; the authors indicate that it is probably because, initially, the substrate (support medium) adsorbs the contaminant, but this phenomenon decreases over time. Subsequently, nitrification and plant uptake become more important. The ammonium removal was higher in the VSF-CW because an intermittent operation and the oxygenation promote the nitrification process [26,41,42]. In this study, the nitrification process began, which is why the nitrite concentration increased (up to three times). Nitrates have a variable behavior (generation and removal), obtaining positive and negative removals. The negative removals are the product of nitrites to nitrates transformation due to nitrification. Meanwhile, positive removals may be related to the generation of anoxic micro zones, because the oxygen decreases inside VSF-CWs. Thus, the denitrification process in VSF-CW is not favored; this behavior is common in this type of CWs according to several authors [29]. Although in some weeks the nitrates removal percentage was positive, as a result of anoxic zones formation in the VSF-CW [8].
The ammonia removal in HSSF-CW is in the range reported for this CW type [42]. According to Zhang et al. [26], the HSSF-CW has adequate conditions for the denitrification process. However, in the case of nitrates, it was observed that the concentration increases in the effluent, which is the opposite of what is shown in other studies. The nitrites (0.02 ± 0.01 mg L−1) presence in the effluent confirms that the effective denitrification process is not produced [43]. Zurita et al. [8] reported nitrification due to fact that ammonium removal achieved values around 61.8%, but nitrate removed by denitrification was immediately replaced by nitrate produced by nitrification (in this study nitrite removal is around 39%). The effective nitrification in our HSSF-CW indicates that there was oxygen inside it, which could have come from the VSF-CW. Pan et al. [44] explain the possible cause of this phenomenon in a hybrid system similar to the one in our study. The authors reported that ammonium removal within the VSF-CW is produced by the oxygen presence from an aeration system, since nitrification is favored. However, they reported a low nitrate removal in HSSF-CW (around 34.3%) due to the remaining oxygen present in the VSF-CW effluent because of the excessive aeration of this CW. In our work, air flow was 1.4 m3 during HRT of 36 h. According to these authors, this problem could be solved by increasing the HRT within HSSF-CWs. Short HRT in VSF-CW limits the denitrification process in HSSF-CW because denitrifying bacteria cannot adapt to previously oxygenated influents VSF-CW [44]. According to previous authors, the HRT required to efficiently remove nutrients from wastewater goes from 10 to 13 days [45]. In other words, the HRT within HSSF-CW should be increased by at least six days in our study. Additionally, it is important to mention that nitrification processes occur in the presence of biodegradable organic matter. The organic matter concentration in the influent of HSSF-CW was 101.6 (±25.2) mg L−1 and it is probably not enough for denitrification processes because around 83% was removed in VSF-CW [11,43]. Some authors indicate that when the organic matter present in the wastewater is not enough, the organic matter contribution from the macrophytes (roots exudation or dead plant detritus) is an important organic matter source to allow the denitrification process to take place. The capacity of external organic matter contribution depends on the macrophyte species used. However, this capacity is also related to the maturity of the CWs and plants. That is, the more mature the plants are, the greater organic matter content inside the CW sediments (organic matter hydrolysis by accretion). Therefore, there will be greater organic matter availability for the denitrification process [43,44,46]. In our study, the Heliconia stricta Huber plants used were very young (one month old), being monitored for 50 days, so the organic matter production from them will be practically nil. Finally, the data statistical analysis for both CWs indicated that there were significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) in the percentages of nitrates (p = 0.002) and NO2− (p = 0.003) removal.
The phosphates effluent concentration inside the VSF-CW and HSSF-CW was increasing over time from 4.6 to 5.9 and from 1.6 to 9 mg L−1, respectively. The average phosphates removal in the VSF-CW was higher than in the HSSF-CW, achieving average performances of 44.8% and 23.4%, respectively. However, the phosphates removal between both CWs do not show significant differences (p = 0.296). The phosphates removal in the VSF-CW was comparable to the results shown by Prochaska and Zouboulis [47] (around 45%), where they used sand and dolomite as support medium. The main ways for phosphorus removal (in their different forms) in CWs are adsorption processes given by CW support medium, also chemical precipitation and uptake by microorganisms and plants. Nevertheless, the adsorption on the support material predominates inside saturated subsurface flow CWs, achieving values that vary between 0.012 and 0.42 g P g−1 support material. The adsorption and chemical precipitation of phosphorus in CWs is mainly related to the bonds it forms with the calcium, aluminum and iron contained in the support medium. According to Trang et al. [48], the increase of the phosphorous concentration in the effluent shows that the adsorption sites in the filter bed material were reduced by the phosphorus presence. When conventional materials (sand and gravel) are used as support medium, the phosphorus removal occurs only for a certain time (from two months or less up to five years, depending on the scale of the CW), due to their low calcium (<15%; however, the phosphorous removal depends on the form of calcium and pH), aluminum and iron content. This is also affected by operational parameters (e.g., hydraulic loading rate, quantity of support material, among others) and wastewater composition [49,50,51]. Indeed, if the phosphates concentration increases in the effluent over time, this indicates that its removal occurs mainly by adsorption on the support material. According to data obtained in previous researches, the plants’ uptake is less than adsorption, reporting values between 0.002 to 0.006 g P g−1 dry plant [33,49,50]. In this work, uptake by plants and microorganisms did not contribute significantly (p < 0.05) to the phosphates removal because their growth was lower, being between 0.6% and 7.1% for plants and between 0.5 and 0.9 mg cm−2 for biofilms, in each CW.
Phosphates in the HSSF-CW effluent reached higher mean concentrations (9 mg PO43− L−1) than in the influent and therefore negative removal efficiencies (up to −60.7%) were obtained. This factor could be produced by phosphates desorption from gravel due to the presence of other substances that compete with phosphorus for adsorption sites or by mineralization of organic phosphorous. In addition, phosphorus/phosphates desorption from the support material occurs because materials such as sand, gravel, and rock have been found to be a poor alternative for long-term phosphorous storage (principally due to their low calcium content, which is less than 15%) [5,52]. Moreover, the newly support material has a greater phosphorus adsorption capacity than a material that has already been used for a period [44].
The phosphates removal was higher in VSF-CW probably because of the size difference of the gravel used and the greater surface area available. Indeed, the VSF-CW gravel surface area was higher (around 50%) than the HSSF-CW gravel surface area. In some previous researches, the phosphorus removal efficiency increases with decreasing the support material size because it increases the specific surface of the material and consequently the adsorption sites. However, the fine material (<5 mm) used in our study could cause clogging, although the material size used depends on material composition, hydraulic loading rates, HRT and initial phosphorous concentration [33,49,50,53]. The low phosphates removal, as in the nitrates case inside the HSSF-CW occurs due to the short HRT. If the contact time between support material, plants and microorganism increases the biodegradation processes can occur [26,42,48]. By increasing the HRT, phosphorus has enough time to deposit on the support material and the roots of plants that growth in soil contact (Heliconia is a riparian plant) could absorb phosphates, thus decreasing the amount of phosphorus in the effluent [48,54].
Considering the hybrid CW, the removal efficiencies were 86.8%, 96.4%, −56.3%, 5.9% and 57.0%, for COD, NH4+, NO3−, NO2− and PO43−, respectively. According to the review carried out by Zhang et al. [26], hybrid CWs have high organic matter (85.7%) and ammonia (80.1%) removal. While the removal of nitrates and phosphorous achieved moderate efficiencies reaching 63.6% and 54.8%, respectively. In other case studies in which the second CW is an HSSF-CW, nitrate removal does not occur (rather, there is nitrates generation, −62.7%) or the removal is very low, and there is no denitrification [46]. The efficiency achieved in this type of CW depends on the wastewater quality, the CW configuration, the HRT, the plant type and the support medium used. Comparing these results with those found in our study, we could say that Heliconia stricta Huber is a species that could be used within CWs. This is because Heliconia stricta Huber growth is not affected within hybrid systems. We can also mention that if larger experimentation times are used (at least one year) it would be possible to determine additional economic and social value (flower generation) for this wastewater treatment type, even though this last condition was not directly observed in this work because of the youth of the species studied. The relatively short time during which this research (50 days) was conducted is justified because plants in tropical and subtropical zones do not have a defined vegetative cycle, so when the system is stable, an already representative result could be achieved. Stability is reached when the system shows at least one stable contaminant removal efficiency.
3.2. Heliconia stricta Behavior during the Operation
3.2.1. Heliconia stricta Huber Growth
The plants allometric measurements (apical growth, basal growth, leaf width and length) in both CWs are shown in Figure 3. The maximum apical height of the Heliconia stricta Huber was 44.5 and 34 cm for VSF-CW and HSSF-CW, respectively. The plants in both CWs grew 1.2% approximately, during the seven weeks of operation. On the other hand, the basal diameter increased from 4.3 to 4.5 cm and from 3.2 to 3.5 cm for VSF-CW and HSSF-CW, respectively. This represents an increase of 4.5% and 7.1%, respectively.
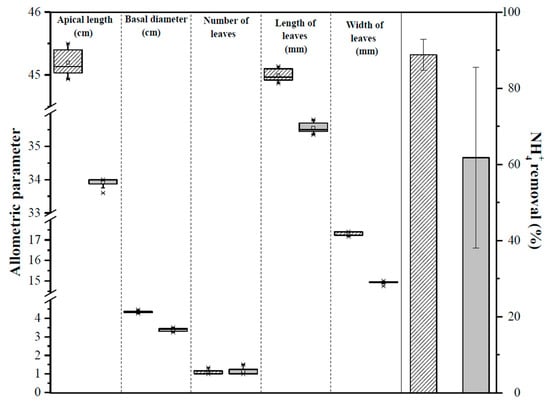
Figure 3.
Allometric measurements of Heliconia stricta and NH4+ removal. Striped columns: VSF-CW and gray columns: HSSF-CW.
The individual leaves in both VSF-CW and HSSF-CW decreased in number (50% approximately) during the experimentation time. Meanwhile, the number of leaves was similar in both CWs (around 1.1 leaves per individual). However, the leaves increased their size, changing length from 44.9 to 45.5 mm (VSF-CW) and from 35.4 to 35.8 mm (HSSF-CW). The leaf width varied from 17.2 to 17.4 mm and from 14.8 to 15.0 mm inside the VSF-CW and HSSF-CW, respectively. The average longitudinal/transverse growth of the leaves was 2.7/2.3 mm and 4.5/2.5 mm for the VSF-CW and HSSF-CW, respectively. The allometric measurements values do not present significant differences between the two CWs (p > 0.05).
The development of Heliconia stricta Huber continues over time; that is, despite the low growth of its apical height, basal diameter and leaf dimensions, the Heliconias grew every certain period. This coincides with the results obtained by Méndez-Mendoza et al. [7] and Konnerup et al. [54] that worked with the same and other Heliconia species. This behavior indicates that these plants tolerate the stress to which they are subject, and they do not show toxicity symptoms or nutrient deficiencies [5,7,55].
Figure 3 shows a relationship between allometric measurements and the ammonia removal. The plant growth has no direct effect on the contaminant removal. This is because Heliconia stricta Huber plants grew only a small amount. Nevertheless, this growth was higher in HSSF-CW than in VSF-CW. The NH4+ removal inside CWs is carried out mainly by volatilization (at pH = 9.3), nitrification, accumulation in media and uptake by plants [32]. In the VSF-CW, the principal pathway was nitrification, however the plants could uptake a part of ammonia. In the HSSF-CW, there is no adequate denitrification process; probably the plants uptake more ammonia than in the VSF-CW. This is shown in a higher increase of the basal diameter, leaf width and length of Heliconia stricta Huber in the HSSF-CW, reaching 2.7%, 0.4% and 0.7%, respectively. The relative abundance was 33.3% higher in the HSSF-CW than in the VSF-CW. The average relative abundance for the VSF-CW was 48.2 individual m−2 and for the HSSF-CW was 33.9 individual m−2. Thus, the relative abundance within the VSF-CW decreased in the sixth week because an individual had to be removed, but it returned to its initial value due to a new individual appearance. For the HSF-CW, the relative abundance decreased by the third week, but it later recovered, and even surpassed the initial abundance.
Despite the small growth of the plants, they favored the initial microorganism growth. The initial biofilm growth was influenced by the microorganisms present in the plants, since synthetic domestic wastewater was used in the experiment even in the adaptation phase. The subsequent development of the biofilm was the product of the plant growth and the presence of organic matter and nutrients from wastewater. At the end of the research, 0.5 (±0.005) and 0.9 (±0.003) mg cm−2 of biofilm, or 33.9 (±0.4) and 31.3 (±0.1) g biofilm, were reached in VSF-CW and HSSF-CW, respectively. There were significant differences (p < 0.05) between the HSSF-CW and VFS-CW biofilm produced. It would be expected greater biofilm formed from VSF-CW than biofilm from HSSF-CW. However, this may occur because the VSF-CW was an aerated system, increasing continuous turbulent flow within the microcosm that causes the continuous detachment of the biofilm. In this process, the biofilm would move to the interstitial water [56].
3.2.2. Heliconia stricta Huber Biomass
Figure 4 shows the biomass produced at the end of the study period. The dry matter obtained shows a ratio of root biomass to aerial biomass of approximately 2.4 (VSF-CW), 8.0 (HSSF-CW) and 3.7 (control plants). The highest increased biomass occurred within the VSF-CW, due to the greatest removal of ammonia and phosphates and the highest biofilm quantity compared to the HSSF-CW. Although the nutrients uptake by plants is low compared to their other removal routes (uptake by microorganisms and adsorption on the support medium), we could say that the uptake was higher inside VSF-CW plants. This is consistent with that mentioned by Vo et al. [31]. Heliconia stricta Huber plants used in the control had similar mass in leaves and roots per unit area that Heliconias used in the VSF-CW, with approximately 6.1 and 110.4 g m−2 less in the control, respectively. Regarding the stems mass, the difference between the plants is greater in VSF-CW (2.1 times). However, the HSSF-CW plants had less biomass than the control plants for leaves (1.9 times), for roots (1.1 times) and for stems (2.5 times). The higher plant growth, lower biomass values and the lower biofilm growth could be attributed to the low concentration of organic matter and the adequate conditions to produce denitrification. As a result, it is believed that the plants had the best conditions to adsorb the nutrients available in this CW compared with microorganisms, but this was not enough to increase their biomass. However, if both CWs are compared, it is observed that the growth of plant biomass and biofilm is greater in the VSF-CW. This is linked to the removal of organic matter, nutrients and operating conditions in this CW, which appears to be more favorable than in the HSSF-CW.
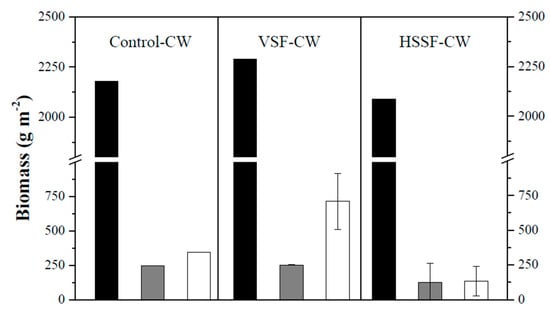
Figure 4.
Plant biomass measurements within hybrid system. Black column: root zone, gray column: leaves, and white column: stems.
Considering these results, we can determine that the biofilm (microorganisms) from VSF-CW has a greater participation in the removal of nutrients and organic matter than the Heliconia. In the HSSF-CW, the plants have the higher incidence in the removal of COD and nutrients in spite of the nutrients availability and the operating conditions in this CW, which are not the most suitable. In other words, Heliconia stricta can be used to remove nutrients and organic matter even in non-favorable conditions.
4. Conclusions
The route of removal of ammonia, nitrites and nitrates in the VSF-CW was through the action of microorganisms and indirectly supported by plants. The Heliconia stricta Huber provided the favorable conditions for the microorganisms to develop and remove the nutrients and organic matter. In HSSF-CW, the Heliconia stricta Huber had a greater participation in the contaminants removal. In the case of phosphates, the support material was the one that predominated in adsorption. Plants and microorganisms also uptake phosphates, but in smaller quantities. This uptake probably occurs in a similar way to that of ammonium and nitrites. Thus, Heliconia stricta Huber is an alternative native plant that can be used in hybrid systems targeted to tropical zones. In specific, Heliconia stricta Huber within VSF-CW and HSSF-CW favors the global removal of organic matter (up to 86.7%) and nutrients (NH4+: 96.4%, PO43−: 57%) from domestic wastewater. However, oxic environments (VSF-CW) are more adequate for Heliconia stricta Huber than anoxic environments (HSSF-CW). This is also related to the ability to interact with nitrification processes, increasing them up to three times compared to the initial nitrite concentration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-A.V.; Data curation, C.E.A.-N.; Formal analysis, C.E.A.-N., V.H.G., Funding acquisition, C.-A.V.; Investigation, G.G., C.-A.V.; Methodology, G.G., C.-A.V.; Project administration, C.-A.V.; Resources, C.-A.V.; Supervision, C.-A.V., Validation, V.H.G., C.-A.V.; Visualization, C.E.A.-N.; Writing—original draft, C.E.A.-N.; Writing—review & editing, C.E.A.-N., V.H.G., C.-A.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by FONDECYT (Grant project 11190352) from Chile. The authors also thank the support from Escuela Politécnica Nacional (Grant project PIS-18-01).
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Jorge Escobar Ortiz for his contribution to the graphics used in this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Thebo, A. Global wastewater and sludge production, treatment and use. In Wastewater, 1st ed.; Drechsel, P., Qadir, M., Wichelns, D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Villamar, C.A.; Neubauer, M.E.; Vidal, G. Distribution and availability of copper and zinc in a constructed wetland fed with treated swine slurry from an anaerobic lagoon. Wetlands 2014, 34, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, M.A.; Tarhini, A.; Nasr, J.A. Decentralized approaches to wastewater treatment and management: Applicability in developing countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roefs, I.; Meulman, B.; Vreeburg, J.H.G.; Spiller, M. Centralised, decentralised or hybrid sanitation systems? Economic evaluation under urban development uncertainty and phased expansion. Water Res. 2017, 109, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S. A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Design and operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfí, M.; Flores, L.; Ferrer, I. Life Cycle Assessment of wastewater treatment systems for small communities: Activated sludge, constructed wetlands and high rate algal ponds. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 161, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Mendoza, A.S.; Bello-Mendoza, R.; Herrera-López, D.; Mejía-González, G.; Calixto-Romo, A. Performance of constructed wetlands with ornamental plants in the treatment of domestic wastewater under the tropical climate of South Mexico. Water Pract. Technol. 2015, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita, F.; De Anda, J.; Belmont, M.A. Treatment of domestic wastewater and production of commercial flowers in vertical and horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyola, A.; Padilla-Rivera, A.; Morgan-Sagastume, J.M.; Güereca, L.P.; Hernández-Padilla, F. Typology of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Technologies in Latin America. Clean–Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, O.C.; Türe, C.; Böcük, H.; Çiçek, A.; Yakar, A. Role of plants and vegetation structure on boron (B) removal process in constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrijos, V.; Gonzalo, O.G.; Trueba-Santiso, A.; Ruiz, I.; Soto, M. Effect of by-pass and effluent recirculation on nitrogen removal in hybrid constructed wetlands for domestic and industrial wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2016, 103, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, L.; Zamora-Castro, S.; Vidal-Álvarez, M.; Marín-Muñiz, J. Role of Wetland Plants and Use of Ornamental Flowering Plants in Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yi, N.-K.; Wang, S.; Lu, L.-J.; Huang, X.-F. Impact of plant species on spatial distribution of metabolic potential and functional diversity of microbial communities in a constructed wetland treating aquaculture wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, L.-H.; Zoh, K.-D. Removal characteristics and mechanism of antibiotics using constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzadi, M.; Fátima, K.; Imran, A.; Mirza, M.S.; Khan, Q.M.; Afzal, M. Ecology of bacterial endophytes associated with wetland plants growing in textile effluent for pollutant-degradation and plant growth-promotion potentials. Plant Biosyst. 2015, 150, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, X.; Ho, S.-H.; Wang, L.; Yang, J. Effect of plant species compositions on performance of lab-scale constructed wetland through investigating photosynthesis and microbial communities. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stottmeister, U.; Wießner, A.; Kuschk, P.; Kappelmeyer, U.; Kästner, M.; Bederski, O.; Müller, R.A.; Moormann, H. Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol. Adv. 2003, 22, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Tan, S.K.; Gersberg, R.M.; Zhu, J.; Sadreddini, S.; Li, Y. Nutrient removal in tropical subsurface flow constructed wetlands under batch and continuous flow conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 96, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Hu, Z.; Hou, C.; Liu, H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. New insights for enhancing the performance of constructed wetlands at low temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Nazarudin, M.R.; Tsan, F.Y. Vegetative and reproductive growth behaviour of Xanthostemon chrysanthus (F. Muell.) Benth.–an ornamental tree in Malaysia. Sains. Malays. 2018, 47, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Song, X.; Gong, J. The inhibition and adaptability of four wetland plant species to high concentration of ammonia wastewater and nitrogen removal efficiency in constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 202, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.-C.; Wang, M.; Lai, W.-L.; He, F.-H.; Chen, Z.-H. Plant growth and nutrient removal in constructed monoculture and mixed wetlands related to stubble attributes. Hydrobiologia 2011, 661, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Los Reyes, C.P.; Villamar, C.A.; Neubauer, M.E.; Pozo, G.; Vidal, G. Behavior of Typha angustifolia L. in a free water surface constructed wetlands for the treatment of swine wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part A 2013, 48, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, C.; Zurita, F.; Nani, G.; Reyes, G.; Fernández-Lambert, G.; Cabrera-Hernández, A. Nitrogen Removal from Domestic Wastewater and the Development of Tropical Ornamental Plants in Partially Saturated Mesocosm-Scale Constructed Wetlands. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelef, O.; Gross, A.; Rachmilevitch, S. Role of Plants in a Constructed Wetland: Current and New Perspectives. Water. 2013, 5, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Gersberg, R.M.; Liu, Y.; Ng, W.J.; Tan, S.K. Application of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in developing countries—A review of recent developments (2000–2013). J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 141, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Naranjo, C.E.; Espinoza-Montero, P.J.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, M.I.; Villamar-Ayala, C.A. Hydraulic Retention Time Influence on Improving Flocculation in the Activated Sludge Processes Through Polyelectrolytes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, E. Ingeniería de Aguas Residuales: Tratamiento, Vertido y Reutilización de Aguas Residuales, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanakis, A.I.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Effects of loading, resting period, temperature, porous media, vegetation and aeration on performance of pilot-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181–182, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, F.S.; Herrera, P.G.; Chiquito, G.M.; Morales, M.F.; Castro, A.P.; Paulo, P.L. Relationship between microbial community and environmental conditions in a constructed wetland system treating greywater. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 139, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.D.H.; Bui, X.T.; Nguyen, D.D.; Nguyen, V.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Dan, P.; Cong-Nguyen, N.; Lin, C. Wastewater treatment and biomass growth of eight plants for shallow bed wetland roofs. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, V.; Araya, F.; Reyes-Contreras, C.; Vera, I.; Vidal, G. Performance of ornamental plants in mesocosm subsurface constructed wetlands under different organic sewage loading. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akratos, C.S.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Effect of temperature, HRT, vegetation and porous media on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.J.; Wu, S.Q.; Dai, Y.R.; Liang, W.; Wu, Z.B. Treatment performance of integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland plots for domestic wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 44, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, M.; BISWAS, P.A.S. Rejoinder of diverse organic growing media on morphological attributes of nine Heliconia species and varieties under West Bengal condition. J. Crop Weed. 2019, 15, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Natural Resources Conservation Service. Plants Database. 2018. Available online: www.usda.gov. (accessed on 29 March 2020).
- León-Yánez, S.; Valencia, R.; Pitman, N.; Endara, L.; Ulloa, C.; Navarrete, H. Libro Rojo de las plantas endémicas del Ecuador; Publicaciones del Herbario: Quito, Ecuador, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Enviromental Protection Agency. Folleto Informativo de Tecnología de Aguas Residuales Humedales de Flujo Subsuperficial; United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Wahington, DC, USA, 2000; p. 13.
- APHA AWWA WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater: American Public Health Association, 21st ed.; American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Caselles-Osorio, A.; Puigagut, J.; Segú, E.; Vaello, N.; Granés, F.; García, D.; García, J. Solids accumulation in six full-scale subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Kröpfelová, L. Removal of nitrogen in constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-sureface flow: A review. Wetlands 2009, 29, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, B. Effect of intermittent operation on contaminant removal and plant growth in vertical flow constructed wetlands: A microcosm experiment. Desalination 2010, 262, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, L.; Cunill, C.; Cáceres, R.; Marfà, O. Design and monitoring of horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetlands for treating nursery leachates. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6414–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Ke, F. Full-Scale Experiment on Domestic Wastewater Treatment by Combining Artificial Aeration Vertical- and Horizontal-Flow Constructed Wetlands System. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 5673–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Solís, M.; Villegas, E.; De Anda, J.; López-López, A. The Effect of the Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance of an Ecological Wastewater Treatment System: An anaerobic filter with a constructed wetland. Water 2015, 7, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maine, M.A.; Sanchez, G.C.; Hadad, H.R.; Caffaratti, S.E.; Pedro, M.C.; Mufarrege, M.M.; Di Luca, G.A. Hybrid constructed wetlands for the treatment of wastewater from a fertilizer manufacturing plant: Microcosms and field scale experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, C.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Removal of phosphates by pilot vertical-flow constructed wetlands using a mixture of sand and dolomite as substrate. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 26, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, N.T.D.; Konnerup, D.; Schierup, H.-H.; Chiem, N.H.; Tuan, L.A.; Brix, H. Kinetics of pollutant removal from domestic wastewater in a tropical horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland system: Effects of hydraulic loading rate. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yan, X.; Gu, X. Evaluation of thermally-modified calcium-rich attapulgite as a low-cost substrate for rapid phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2017, 115, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohla, C.; Kõiv, M.; Bavor, H.J.; Chazarenc, F.; Mander, Ü. Filter materials for phosphorus removal from wastewater in treatment wetlands—A review. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ádám, K.; Søvik, A.K.; Krogstad, T. Sorption of phosphorous to Filtralite-PTM—The effect of different scales. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.; Goharpour, M.; Moharami, S. Contrasting Effects of Four Plant Residues on Phosphorus Sorption-Desorption in Some Phosphorus Fertilized Calcareous Soils. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plan. 2018, 49, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Gajewska, M.; Pytka, A.; Marzec, M.; Gizińska-Górna, M.; Jucherski, A.; Walczowski, A.; Nastawnyc, M.; Kaminska, A.; Baran, S. Influence of the particle size of carbonate-siliceous rock on the efficiency of phosphorous removal from domestic wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenway, M. The Role of Macrophytes in Nutrient Removal using Constructed Wetlands. In Environmental Bioremediation Technologies; Singh, S.N., Tripathi, R.D., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 331–351. [Google Scholar]
- Konnerup, D.; Koottatep, T.; Brix, H. Treatment of domestic wastewater in tropical, subsurface flow constructed wetlands planted with Canna and Heliconia. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lyu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Button, M.; Arias, C.A.; Weber, K.P.; Brix, H.; Carvalho, P.N. Impacts of design configuration and plants on the functionality of the microbial community of mesocosm-scale constructed wetlands treating ibuprofen. Water Res. 2018, 131, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).