Suspended Sediment Transport Responses to Increasing Human Activities in a High-Altitude River: A Case Study in a Typical Sub-Catchment of the Yarlung Tsangpo River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
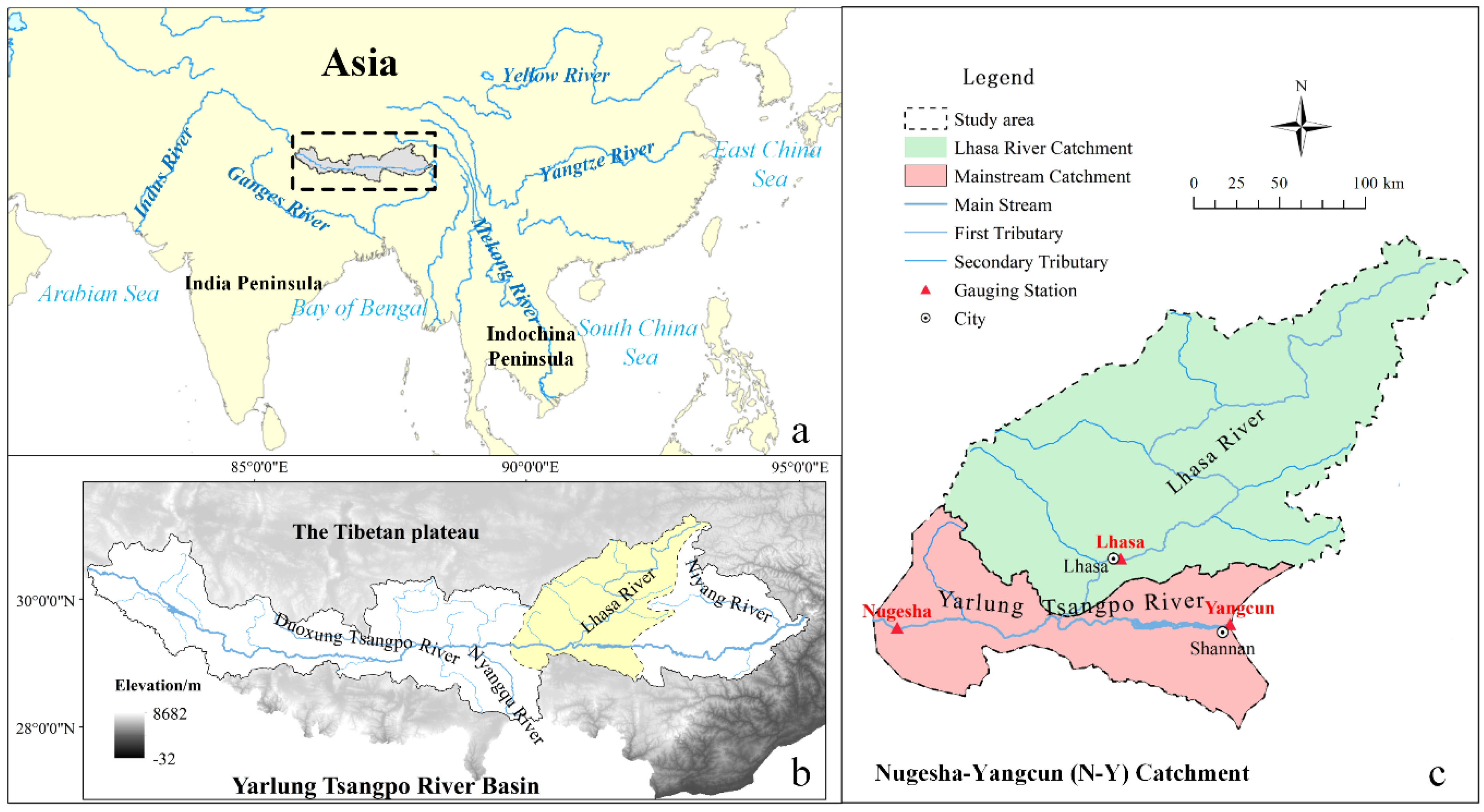
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Estimation of the Undisturbed and Missing SSCs
3.2. Sediment Load in the N–Y Reach
3.3. Contributions of the Lhasa River to the N–Y Reach
3.4. Anomalous SSC in the Lhasa River and Mainstream Response
4. Discussion
4.1. Human Activities in the N–Y Reach
4.2. Potential Changes in Other Reaches
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate Change Will Affect the Asian Water Towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milliman, J.D.; Meade, R.H. World-Wide Delivery of River Sediment to the Oceans. J. Geol. 1983, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Yang, Z.S.; Saito, Y.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, X.X.; Wang, Y. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950–2005): Impacts of climate change and human activities. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 57, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.; Church, M.; Yan, Y.X.; Slaymaker, O. Spatial and temporal variation of in-reach suspended sediment dynamics along the mainstem of Changjiang (Yangtze River), China. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W11551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.J.; Lu, X.X.; Kummu, M. Sediment load estimates and variations in the Lower Mekong River. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suif, Z.; Fleifle, A.; Yoshimura, C.; Saavedra, O. Spatio-temporal patterns of soil erosion and suspended sediment dynamics in the Mekong River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.J.; Fagherazzi, S.; Mei, X.F.; Gao, J.J. Decline in suspended sediment concentration delivered by the Changjiang (Yangtze) River into the East China Sea between 1956 and 2013. Geomorphology 2016, 268, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Li, R.; Chen, L.L.; Lin, P.F. Did streamflow or suspended sediment concentration changes reduce sediment load in the middle reaches of the Yellow River? J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.F.; Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.Y. Human impacts on sediment in the Yangtze River: A review and new perspectives. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 162, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Rhoads, B.L.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.C.; Zhang, X. Impacts of large dams on the complexity of suspended sediment dynamics in the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Zhang, W.C.; Liu, T.; Li, Q.L. Runoff dynamics and associated multi-scale responses to climate changes in the middle reach of the Yarlung Tsangpo River basin, China. Water 2018, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudra, K. Changing river courses in the western part of the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta. Geomorphology 2014, 227, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manh, N.V.; Dung, N.V.; Hung, N.N.; Kummu, M.; Merz, B.; Apel, H. Future sediment dynamics in the Mekong Delta floodplains: Impacts of hydropower development, climate change and sea level rise. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 127, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.M.; Xu, M.Z.; Jiang, E.H.; Wang, G.H.; Hu, H.C.; Liu, X. Temporal variations of runoff and sediment load in the upper Yellow River, China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.G. Variations in Basin Sediment Yield and Channel Sediment Transport in the Upper Yangtze River and Influencing Factors. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2019, 24, 05019016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.F.; Tian, L.D.; Yao, T.D.; Gong, T.L.; Yin, C.L.; Yu, W.S. Temporal and spatial variations of δ18O in precipitation of the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Gao, X.J.; Zhang, D.F.; Giorgi, F. Climate change over the Yarlung Tsangpo–Brahmaputra River Basin in the 21st century as simulated by a highresolution regional climate model. Quat. Int. 2011, 244, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.M.; Zuo, D.P.; Xu, Z.X.; Cai, S.Y.; Gao, X.X. Analysis of vegetation condition and its relationship with meteorological variables in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin of China. Proc. IAHS 2018, 379, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.L.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.W. Variations in the Key Hydrological Elements of the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Water Sci. and Tech.: W. Sup 2018, 19, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Fu, S.H.; Shi, X.N.; Chen, Y.; Jagirani, M.D.; Zeng, C. Assessment of soil erosion risk and its response to climate change in the mid-Yarlung Tsangpo River region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuo, L.; Li, N.; Liu, Z.; Ding, J.; Liang, L.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Gong, T.L. Warming and human activities induced changes in the Yarlung Tsangpo basin of the Tibetan plateau and their influences on streamflow. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 25, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, L. Responses of hydrological processes to climate change in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 2057–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Hu, H.C.; Tian, F.Q.; Li, C.; Khan, M.Y.A. Projected climate change impacts on future streamflow of the Yarlung Tsangpo-Brahmaputra River. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 175, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Thieme, M.; Geenen, B.; Tickner, D.; Antonelli, F.; Babu, S.; Borrelli, P.; Cheng, L.; Crochetiere, H.; et al. Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers. Nature 2019, 569, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.F.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Miao, L.Z.; Hou, J.; Yuan, Q.S. Shift in bacterioplankton diversity and structure: Influence of anthropogenic disturbances along the Yarlung Tsangpo River on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Sci. Rep. UK 2017, 7, 12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.P.; Xu, Z.X.; Feng, Y.C.; Liu, M.; Liu, W.F. Changes of land cover in the Yarlung Tsangpo River basin from 1985 to 2005. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.B. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.F.; Graf, H.F. Recent land cover changes on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. Clim. Chang. 2009, 94, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, F.; Xue, X.; You, U.G.; Huang, C.H.; Dong, S.Y.; Liao, J.; Duan, H.C.; Tsunekawa, A.; Wang, T. Changes of soil properties regulate the soil organic carbon loss with grassland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.S.; Li, H.D.; Sun, M.; Jiang, J. Dynamics of aeolian sandy land in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin of Tibet, China from 1975 to 2008. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 86–87, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, A.B.; Liu, S.Z.; Fan, J.R.; Zhu, Y.P. Current changes on sedimentation and control its method in middle Yalungtsangpo River. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 16, 148–150. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yao, Z.J.; Gong, T.L.; Wang, H.; Chu, D.; Liu, L.S.; Zhang, F. The trend on runoff variations in the Lhasa River Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wu, J.P.; Bianba, D.J.; Gama, Q.Z.; Zhu, X.L. Characterization of Soil Nutrient Status of Areas to be Afforested in Tibet, China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 421–433. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H. The Impacts of Afforestation on Changes of Soil Organic Carbon and Major Nutrients in the Mid-Watershed of “One River and Two Tributaries” in Tibet. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences, Beijing, China, 2018. Available online: http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82201-1018253315.htm (accessed on 1 April 2018). (In Chinese).
- Shi, X.N.; Zhang, F.; Lu, X.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Gong, T.L.; Wang, G.X.; Zhang, H.B. Spatiotemporal variations of suspended sediment transport in the upstream and midstream of the Yarlung Tsangpo River (the upper Brahmaputra), China. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2018, 43, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.J. Monitoring suspended sediments and associated chemical constituents in urban environments: Lessons from the city of Atlanta, Georgia, USA Water Quality Monitoring Program. J. Soils Sediments 2009, 9, 342–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.G.; Owens, P.N. Sediments in urban river basins: A review of sediment-contaminant dynamics in an environmental system conditioned by human activities. J. Soils Sediments 2009, 9, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.; Grabowski, R.C.; Rickson, R.J. Suspended sediment transport dynamics in rivers: Multi-scale drivers of temporal variation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 166, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wohl, E. Legacy effects on sediments in river corridors. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 147, 30–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Yu, G.A.; Wang, X.Z.; Melching, C.S.; Liu, L. Sediment storage and morphology of the Yalu Tsangpo valley due to uneven uplift of the Himalaya. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.K.; Li, W.P.; Fan, J.H.; Cheng, G.W. Determining critical support discharge of a riverhead and river network analysis: Case studies of Lhasa River and Nyangqu River. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, W.Q.; Shang, E.P.; Zhang, Y.L. Assessment and origin Analysis on wetland vulnerability in Lhasa River basin of Tibet Autonomous Region. Wetland Sci. 2014, 12, 7–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y.; Li, Z.W.; Gao, P.; Huang, C.; Hu, T.S. Response of the Downstream Braided Channel to Zhikong Reservoir on Lhasa River. Water 2018, 10, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luozhu, N.; Wang, J.Q.; Xu, X.Y. Analysis of Runoff Variation Characteristics and Trends in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. J. China Hydrol. 2011, 31, 76–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Su, F.G.; Yang, D.P.; Hao, Z.H.; Tong, K. Discharge regime and simulation for the upstream of major rivers over Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 8500–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, A.; Cerdan, O.; Delmas, M.; Desmet, M. Variability of suspended sediment yields within the Loire river basin (France). J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselman, N.E.M. Fitting and interpretation of sediment rating curves. J. Hydrol. 2000, 234, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.; Fӧrstner, U. General Relationship between Suspended Sediment Concentration and Water Discharge in the Alpenrhein and some other Rivers. Nature 1968, 217, 244–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.L.; Shi, C.X.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Shao, W.W. Sediment rating curves in the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia reaches of the upper Yellow River and their implications. Quat. Int. 2012, 282, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Pappagallo, G.; Lo Porto, A. Temporal variability of suspended sediment transport and rating curves in a Mediterranean river basin: The Celone (SE Italy). Catena 2015, 128, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, C.J.; Church, M. Suspended sediment transport regime in a debris-flow gully on Vancouver Island, British Columbia. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 861–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Y.; Yan, M.; Cai, Q.G.; Fang, H.Y. Suspended sediment dynamics at different time scales in the Loushui River, south-central China. Catena 2016, 136, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöthe, J.; Hillebrand, G.; Hoffmann, T. Sediment rating and annual cycles of suspended sediment in German upland rivers. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 40, 04020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, L.C. Sediment transport, Part II: Suspended load transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1989, 110, 1613–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, G.F.; Zhang, T.; Tan, S.Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Lu, H. Study on sedimentary calamity of Najin hydroelectric station in Tibet. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. A 2000, 15, 505–560. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, Z.W.; Chen, X.J.; Li, X.Q. Dynamic changes of soil erosion in the middle reaches of Yarlung Tsangpo River. Geospat. Inf. 2011, 9, 51–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Gang, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.L.; An, R.; Wang, K.; Inakwu, O.; et al. Quantitative assess the driving forces on the grassland degradation in the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, in China. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 33, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Tang, X.Y. Study on Sand Liquefaction in the Site of Zhanang Bridge. Subgrade Eng. 2013, 5, 39–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H. Research on Highway Planning in Lhasa. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2009. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Station | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude (m) | Catchment Area (104 km2) | Measurement Period | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Month | |||||
| Lhasa | 91°09′ | 29°38′ | 3650 | 2.6 | 2014–2017 | Jan.–Dec |
| Apr.–Oct | ||||||
| Nugesha | 89°45′ | 29°18′ | 3720 | 10.6 | 2014–2017 | Jan.–Dec |
| May–Oct. | ||||||
| Yangcun | 91°49′ | 29°16′ | 3500 | 15.2 | 2014–2017 | Jan.–Dec |
| Years | Lhasa | Nugesha | Yangcun | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation 1 (mm) | Qyr (108m3/year) | Precipitation (mm) | Qyr (108m3/year) | Precipitation (mm) | Qyr (108m3/year) | |
| 2014 | 595.3 | 98.8 | 376.9 | 156.5 | 363.3 | 348.7 |
| 2015 | 422.7 | 46.7 | 214.8 | 74.0 | 246.9 | 186.1 |
| 2016 | 520.7 | 82.8 | 429.2 | 204.9 | 441.9 | 334.2 |
| 2017 | 532.8 | 96.2 | 427.4 | 208.2 | 412.6 | 337.2 |
| Mean (2014–2017) | 517.9 | 80.6 | 362.1 | 159.8 | 366.2 | 299.6 |
| Mean 2 (2007–2009) | 506.3 | 378.2 | 158.1 | 361.4 | 305.8 | |
| Mean 3 (Pre) | 515.9 | 90.8 | 360.1 | 162.3 | 368.7 | 298.9 |
| Fitting Parameters or Correlation Coefficient 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | 2.24 × 10−4 | |||
| β | 0.87 | |||
| a | 2.55 × 10−6 | 7.47 × 10−11 | 0.50 | |
| b | 1.55 | −1.60 × 10−7 | −1.56 | |
| c | 1.50× 10−2 | 2.12 × 10−4 | −0.83 | |
| d | 6.87× 10−3 | |||
| R2 | 0.57 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.61 |
| Station | Power Curve | Log-Transformed Data Fitted with Quadratic Polynomials | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α1 | β | R2 | a | b | c | R2 | |
| Nugesha (2014–2017) | 2.34 × 10−4 | 1.06 | 0.64 | 0.17 | 0.13 | −2.39 | 0.64 |
| Yangcun(2014–2017) | 1.01 × 10−4 | 1.05 | 0.66 | 0.96 | −4.62 | 4.24 | 0.72 |
| Nugesha (2007–2009) | 4 × 10−4 | 1.01 | 0.54 | ||||
| Yangcun (2007–2009) | 2 × 10−4 | 1.03 | 0.66 | ||||
| Year | Nugesha | Yangcun | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | β | R2 | α | β | R2 | |
| 2014 | 3.9 × 10−4 | 1.00 | 0.60 | 1.0 × 10−5 | 1.17 | 0.77 |
| 2015 | 8.1 × 10−5 | 1.23 | 0.37 | 4.5 × 10−4 | 0.81 | 0.34 |
| 2016 | 1.3 × 10−4 | 1.13 | 0.67 | 5.1 × 10−4 | 0.86 | 0.68 |
| 2017 | 4.2 × 10−4 | 0.98 | 0.59 | 6.7 × 10−5 | 1.09 | 0.77 |
| Pre 1 | 4 × 10−4 | 1.01 | 0.54 | 2 × 10−4 | 1.03 | 0.66 |
| Yeas | Cropland | Forestland | Grassland | Water Bodies | Urban Area | Barren or Sparsely Vegetated Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2.4% | 3.8% | 71.4% | 2.9% | 0.2% | 19.3% |
| 2018 | 3.4% | 10.4% | 59.6% | 3.6% | 0.2% | 22.7% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Lin, B.; Sun, J.; Luozhu, N.; Da, P.; Dawa, J. Suspended Sediment Transport Responses to Increasing Human Activities in a High-Altitude River: A Case Study in a Typical Sub-Catchment of the Yarlung Tsangpo River. Water 2020, 12, 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040952
Huang Z, Lin B, Sun J, Luozhu N, Da P, Dawa J. Suspended Sediment Transport Responses to Increasing Human Activities in a High-Altitude River: A Case Study in a Typical Sub-Catchment of the Yarlung Tsangpo River. Water. 2020; 12(4):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040952
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhe, Binliang Lin, Jian Sun, Nima Luozhu, Ping Da, and Jinmei Dawa. 2020. "Suspended Sediment Transport Responses to Increasing Human Activities in a High-Altitude River: A Case Study in a Typical Sub-Catchment of the Yarlung Tsangpo River" Water 12, no. 4: 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040952
APA StyleHuang, Z., Lin, B., Sun, J., Luozhu, N., Da, P., & Dawa, J. (2020). Suspended Sediment Transport Responses to Increasing Human Activities in a High-Altitude River: A Case Study in a Typical Sub-Catchment of the Yarlung Tsangpo River. Water, 12(4), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040952





