Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
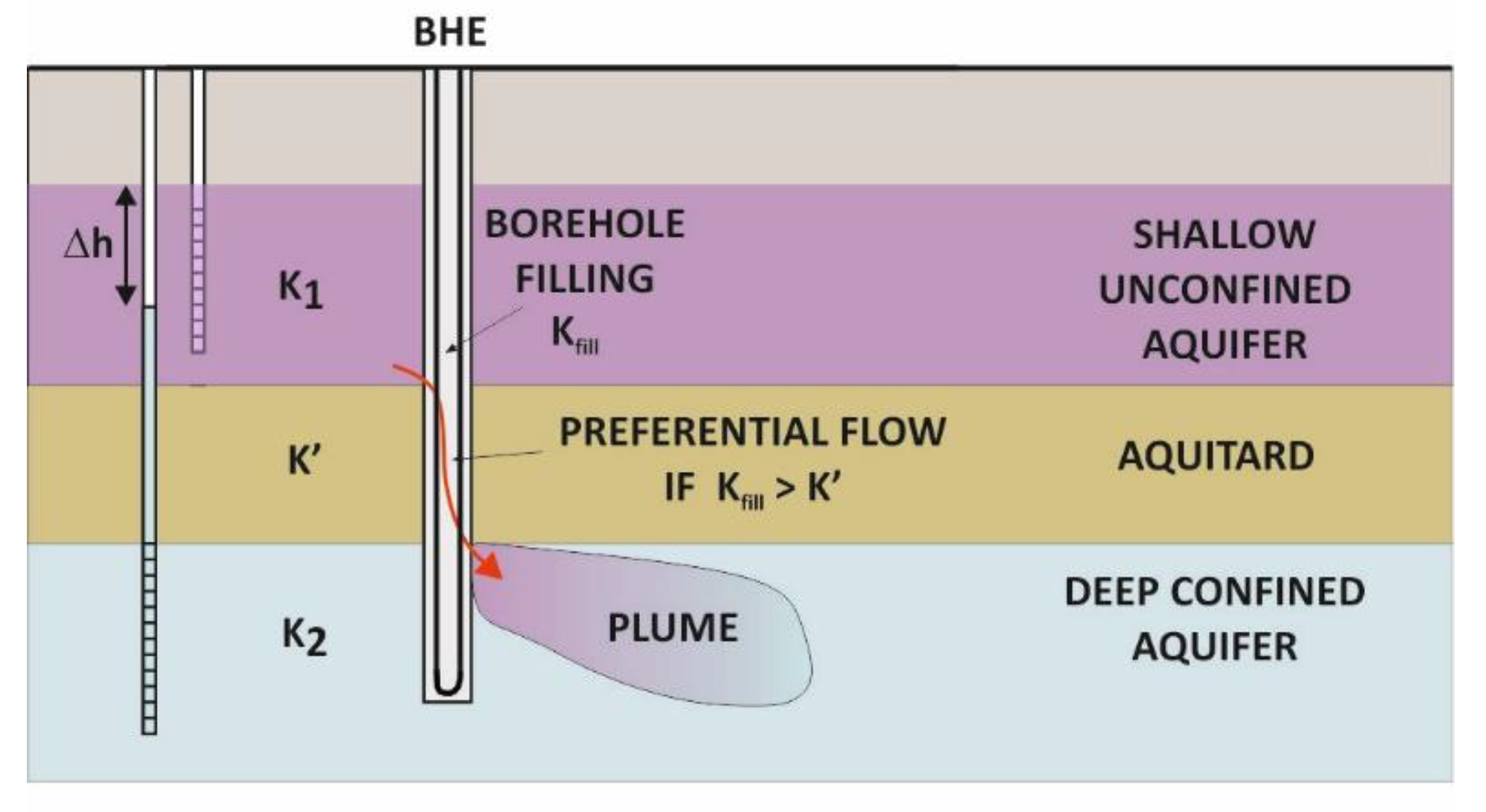
2.1. Conceptual Model
2.2. Numerical Model
3. Results
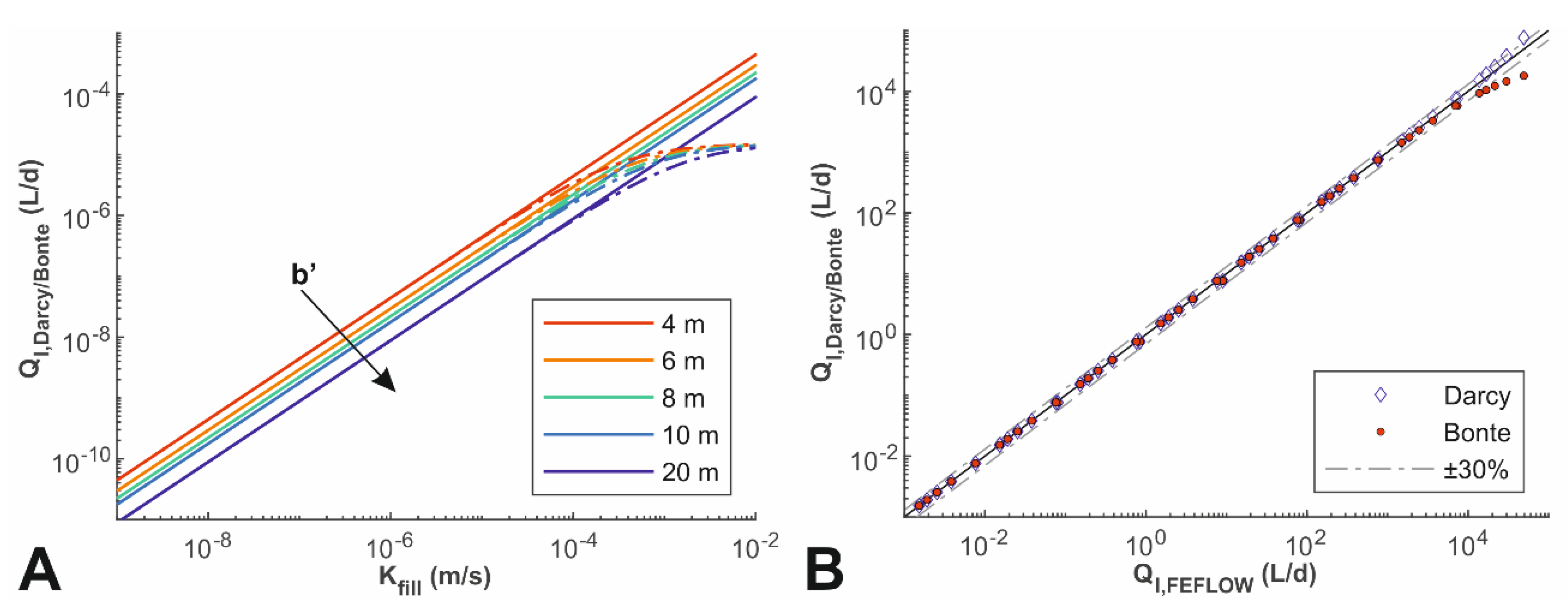
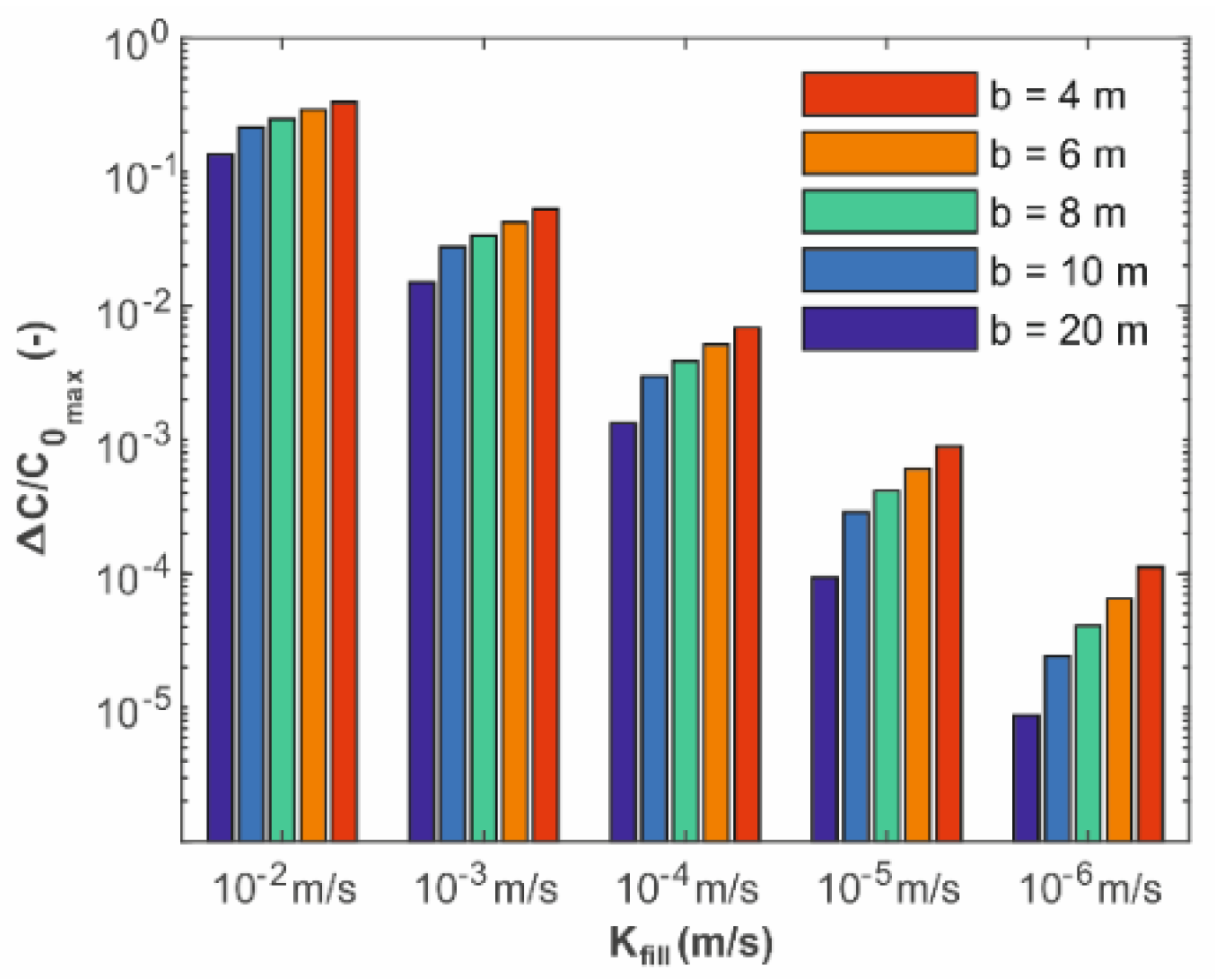
3.1. Evaluation of Borehole Leakage Rates
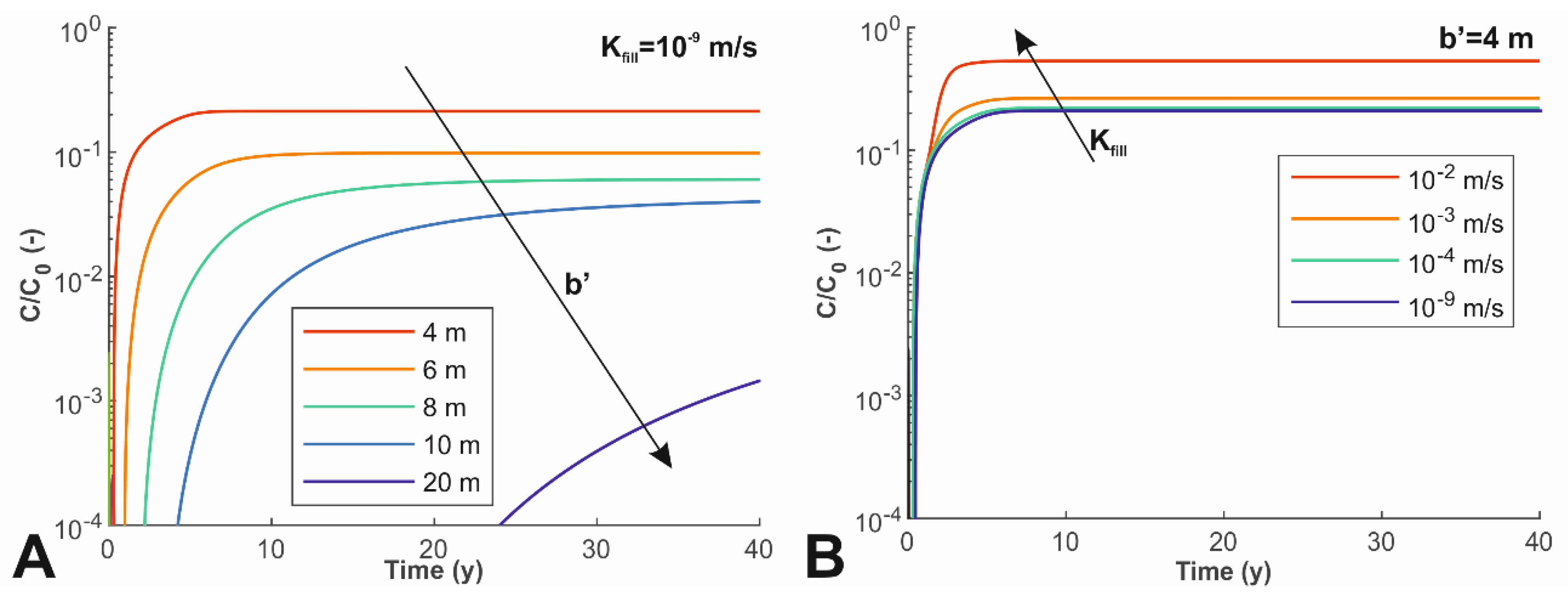
3.2. Propagation of Contaminants in the Deep Aquifer
3.3. Cross-Contamination Effect of the Borehole
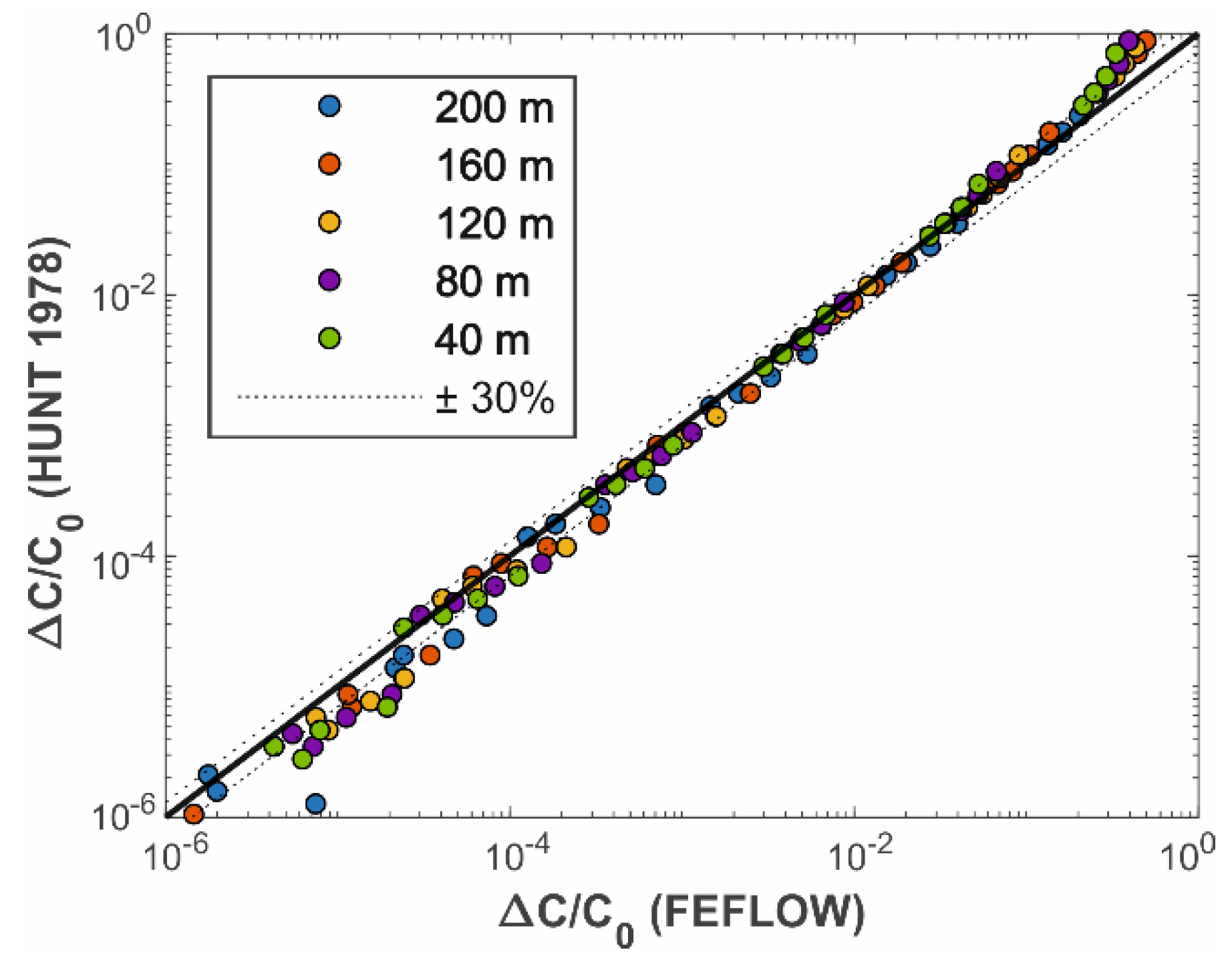
3.4. Analytical Modelling of the Propagation of Contaminants in the Deep Aquifer
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casasso, A.; Capodaglio, P.; Simonetto, F.; Sethi, R. Environmental and Economic Benefits from the Phase-out of Residential Oil Heating: A Study from the Aosta Valley Region (Italy). Sustainability 2019, 11, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivoire, M.; Casasso, A.; Piga, B.; Sethi, R. Assessment of Energetic, Economic and Environmental Performance of Ground-Coupled Heat Pumps. Energies 2018, 11, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saner, D.; Juraske, R.; Kübert, M.; Blum, P.; Hellweg, S.; Bayer, P. Is it only CO2 that matters? A life cycle perspective on shallow geothermal systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1798–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, P.; Saner, D.; Bolay, S.; Rybach, L.; Blum, P. Greenhouse gas emission savings of ground source heat pump systems in Europe: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Mun, H.-S.; Bostami, A.B.M.R.; Ahmed, S.T.; Park, K.-J.; Yang, C.-J. Evaluation of a ground source geothermal heat pump to save energy and reduce CO2 and noxious gas emissions in a pig house. Energy Build. 2016, 111, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, L.; Antelmi, M.; Angelotti, A.; Formentin, G. Geothermal heat pumps for sustainable farm climatization and field irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 195, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmi, G.; Zarrella, A.; De Carli, M.; Moretto, S.; Galgaro, A.; Cultrera, M.; Di Tuccio, M.; Bernardi, A. Ground source heat pump systems in historical buildings: Two Italian case studies. Energy Procedia 2017, 133, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanaugh, S.P.; Rafferty, K.D. Geothermal Heating and Cooling: Design of Ground-Source Heat Pump Systems; ASHRAE: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2014; ISBN 1-936504-85-5. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, D. An Introduction to Thermogeology: Ground Source Heating and Cooling; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 1-118-44750-6. [Google Scholar]
- Casasso, A.; Sethi, R. Assessment and Minimization of Potential Environmental Impacts of Ground Source Heat Pump (GSHP) Systems. Water 2019, 11, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prestor, J.; Pestotnik, S.; Zosseder, K.; Böttcher, F.; Capodaglio, P.; Götzl, G.; Bottig, M.; Weilbold, J.; Maragna, C.; Martin, J.-C.; et al. Overview and Analysis of Regulation Criteria and Guidelines for Nsge Applications in the Alpine Region. Greta Project Deliverable 2.1.1. Available online: http://bit.ly/2S8mMGy (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Santi, P.M.; McCray, J.E.; Martens, J.L. Investigating cross-contamination of aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gass, T.E.; Lehr, J.H.; Heiss, H.W. Impact of Abandoned Wells on Ground Water. Report EPA-600/3-77-095. Available online: https://bit.ly/2ZTa8hh (accessed on 28 June 2019).
- Javandel, I.; Tsang, C.F.; Witherspoon, P.A.; Morganwalp, D. Hydrologic detection of abandoned wells near proposed injection wells for hazardous waste disposal. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avcι, C.B. Flow occurrence between confined aquifers through improperly plugged boreholes. J. Hydrol. 1992, 139, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, C.B. Evaluation of flow leakage through abandoned wells and boreholes. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 2565–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordbotten, J.M.; Celia, M.A.; Bachu, S. Analytical solutions for leakage rates through abandoned wells. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihan, A.; Zhou, Q.; Birkholzer, J.T. Analytical solutions for pressure perturbation and fluid leakage through aquitards and wells in multilayered-aquifer systems. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonte, M.; Zaadnoordijk, W.J.; Maas, K. A Simple Analytical Formula for the Leakage Flux through a Perforated Aquitard. Groundwater 2015, 53, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, A.; Prevot, A.B.; Buoso, S.; De Luca, D.A.; Lasagna, M.; Malandrino, M.; Maurino, V. Impacts of borehole heat exchangers (BHEs) on groundwater quality: The role of heat-carrier fluid and borehole grouting. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, H.; Mousavi Ajarostaghi, S.S.; Rosen, M.A.; Pourfallah, M. A Comprehensive Review of Backfill Materials and Their Effects on Ground Heat Exchanger Performance. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delaleux, F.; Py, X.; Olives, R.; Dominguez, A. Enhancement of geothermal borehole heat exchangers performances by improvement of bentonite grouts conductivity. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 33–34, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, K.; Choi, H.; Choi, H.P. Characteristics of thermally-enhanced bentonite grouts for geothermal heat exchanger in South Korea. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viccaro, M. Doped bentonitic grouts for implementing performances of low-enthalpy geothermal systems. Geotherm Energy 2018, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allan, M.L.; Philippacopoulos, A.J. Thermally Conductive Cementitious Grouts for Geothermal Heat Pumps. Progress Report FY 1998. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/760977 (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Park, M.; Min, S.; Lim, J.; Choi, J.M.; Choi, H. Applicability of cement-based grout for ground heat exchanger considering heating-cooling cycles. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indacoechea-Vega, I.; Pascual-Muñoz, P.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Calzada-Pérez, M.A. Experimental characterization and performance evaluation of geothermal grouting materials subjected to heating–cooling cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacombe, S.; Sudicky, E.A.; Frape, S.K.; Unger, A.J.A. Influence of Leaky Boreholes on Cross-Formational Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diersch, H.J.G. FEFLOW. Finite Element Modeling of Flow, Mass and Heat Transport in Porous and Fractured Media; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-642-38738-8. [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt, M.A.; Bradbury, K.R.; Gotkowitz, M.B.; Cherry, J.A.; Parker, B.L. Human Enteric Viruses in Groundwater from a Confined Bedrock Aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6606–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, E.-H.; Lee, E.; Lee, K.-K. Impact of leaky wells on nitrate cross-contamination in a layered aquifer system: Methodology for and demonstration of quantitative assessment and prediction. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Martínez, J.; Aravena, R.; Candela, L. The Role of Leaky Boreholes in the Contamination of a Regional Confined Aquifer. A Case Study: The Campo de Cartagena Region, Spain. WaterAirSoil Pollut. 2011, 215, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, A.; Casaccio, D.; De Luca, D.A.; Destefanis, E.; Lasagna, M.; Masciocco, L.; Ossella, L.; Tonussi, M.; Governa, M.; Pietricig, M. Idrogeologia della Pianura Piemontese (Hydrogeology of the Piemonte Plain, NW Italy); Università degli Studi di Torino—DST: Regione Piemonte, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, B. Dispersive sources in uniform ground-water flow. J. Hydraul. Div. 1978, 104, 75–85. [Google Scholar]

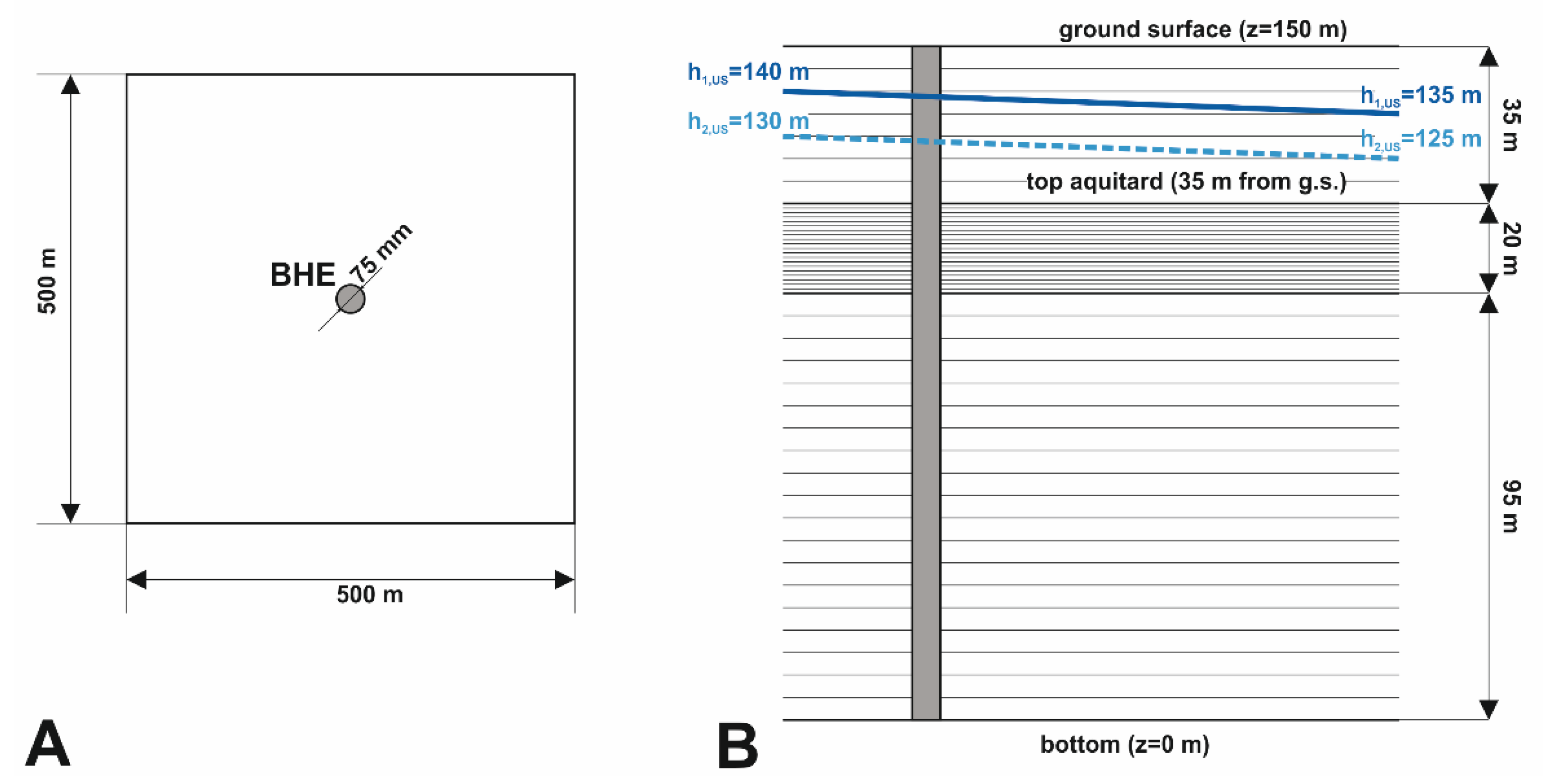
| Parameter | Shallow Aquifer | Aquitard | Deep Aquifer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic conductivity | K1 = 10−3 m/s | KA = 10−9 m/s | K2 = 10−4 m/s |
| Longitudinal hydraulic gradient | 0.01 | - | 0.01 |
| Darcy velocity of aquifer | v1 = 10−5 m/s | - | v2 = 10−6 m/s |
| Thickness | b1 = 35 m | b′ = 4 to 20 m | b2 = 115 m − b′ |
| Flow BC | h1,US = 140 m h1,DS = 135 m | h2,US = 130 m h2,DS = 125 m | |
| Mass-transport BC | C0 = 100 mg/L upstream | none | C = 0 mg/L upstream |
| Total porosity | ε = 0.3 | ||
| Effective porosity | ne = 0.2 | ||
| Longitudinal dispersivity | αL = 5 m | ||
| Transversal dispersivity | αT = 0.5 m | ||
| Hydraulic head difference | Δh = 10 m | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casasso, A.; Ferrantello, N.; Pescarmona, S.; Bianco, C.; Sethi, R. Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers? Water 2020, 12, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041174
Casasso A, Ferrantello N, Pescarmona S, Bianco C, Sethi R. Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers? Water. 2020; 12(4):1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041174
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasasso, Alessandro, Natalia Ferrantello, Simone Pescarmona, Carlo Bianco, and Rajandrea Sethi. 2020. "Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers?" Water 12, no. 4: 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041174
APA StyleCasasso, A., Ferrantello, N., Pescarmona, S., Bianco, C., & Sethi, R. (2020). Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers? Water, 12(4), 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041174







