Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Conceptual Model
2.2. Numerical Model
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Borehole Leakage Rates
3.2. Propagation of Contaminants in the Deep Aquifer
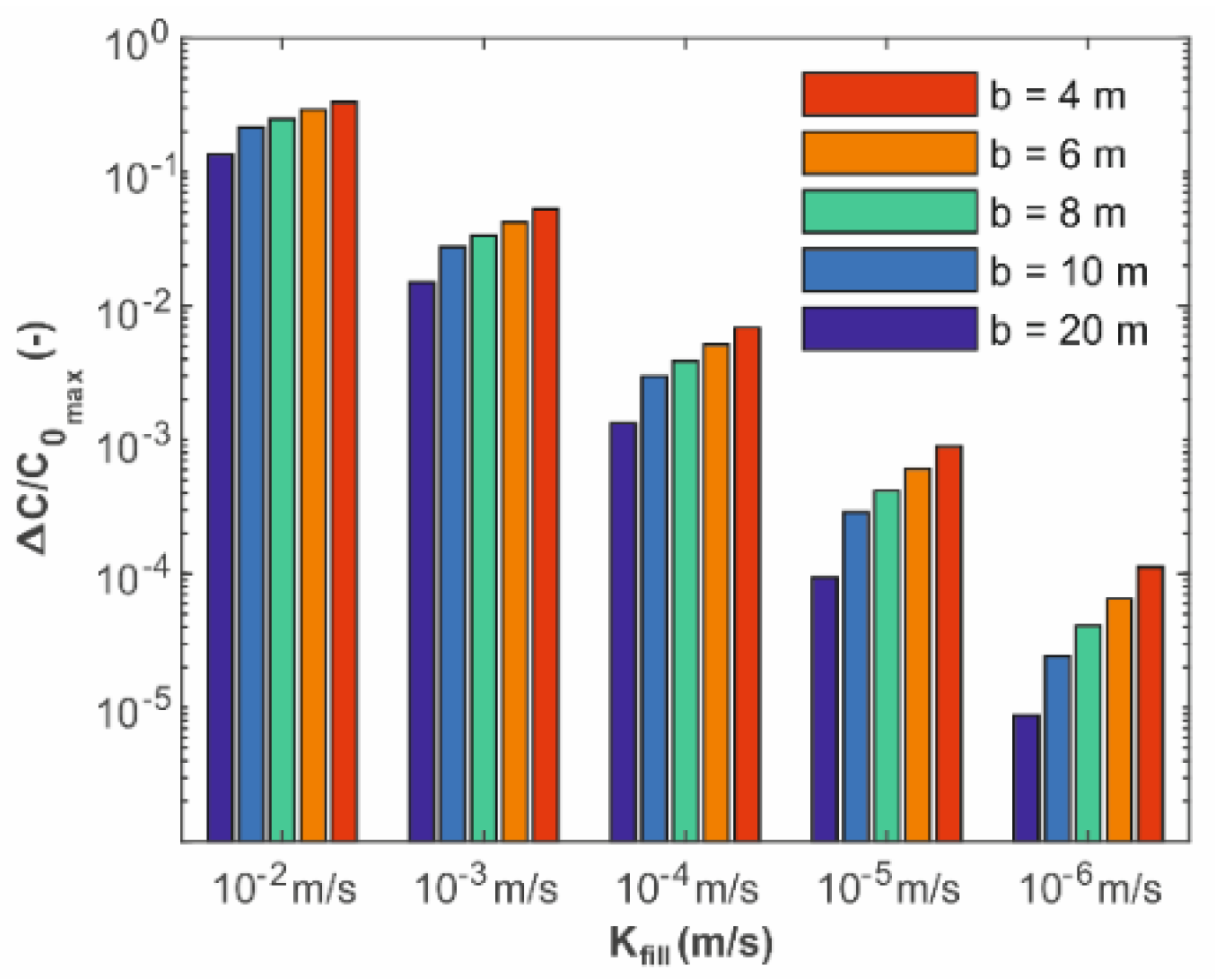
3.3. Cross-Contamination Effect of the Borehole
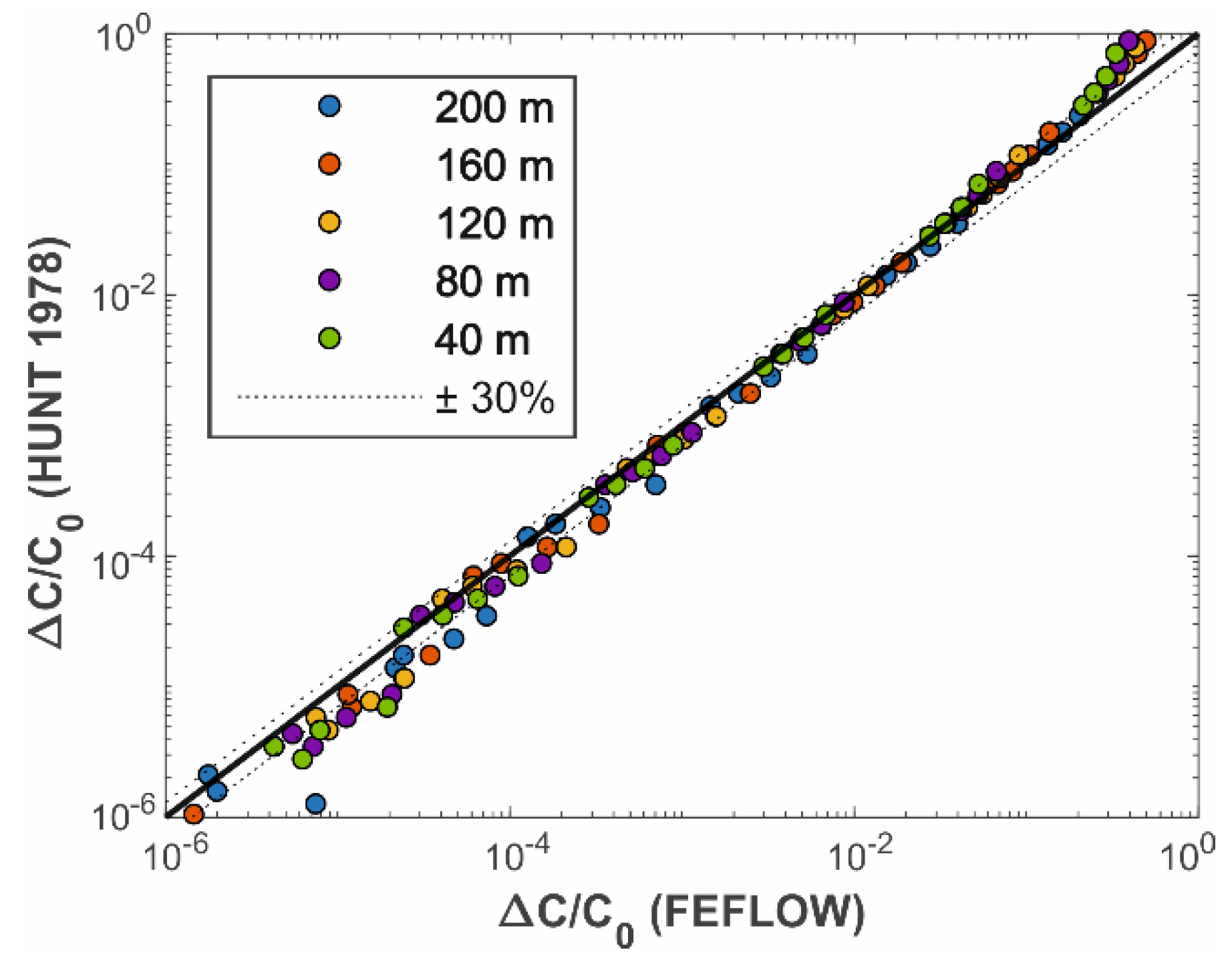
3.4. Analytical Modelling of the Propagation of Contaminants in the Deep Aquifer
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casasso, A.; Capodaglio, P.; Simonetto, F.; Sethi, R. Environmental and Economic Benefits from the Phase-out of Residential Oil Heating: A Study from the Aosta Valley Region (Italy). Sustainability 2019, 11, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoire, M.; Casasso, A.; Piga, B.; Sethi, R. Assessment of Energetic, Economic and Environmental Performance of Ground-Coupled Heat Pumps. Energies 2018, 11, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saner, D.; Juraske, R.; Kübert, M.; Blum, P.; Hellweg, S.; Bayer, P. Is it only CO2 that matters? A life cycle perspective on shallow geothermal systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1798–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, P.; Saner, D.; Bolay, S.; Rybach, L.; Blum, P. Greenhouse gas emission savings of ground source heat pump systems in Europe: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Mun, H.-S.; Bostami, A.B.M.R.; Ahmed, S.T.; Park, K.-J.; Yang, C.-J. Evaluation of a ground source geothermal heat pump to save energy and reduce CO2 and noxious gas emissions in a pig house. Energy Build. 2016, 111, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, L.; Antelmi, M.; Angelotti, A.; Formentin, G. Geothermal heat pumps for sustainable farm climatization and field irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 195, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmi, G.; Zarrella, A.; De Carli, M.; Moretto, S.; Galgaro, A.; Cultrera, M.; Di Tuccio, M.; Bernardi, A. Ground source heat pump systems in historical buildings: Two Italian case studies. Energy Procedia 2017, 133, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanaugh, S.P.; Rafferty, K.D. Geothermal Heating and Cooling: Design of Ground-Source Heat Pump Systems; ASHRAE: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2014; ISBN 1-936504-85-5. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, D. An Introduction to Thermogeology: Ground Source Heating and Cooling; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 1-118-44750-6. [Google Scholar]
- Casasso, A.; Sethi, R. Assessment and Minimization of Potential Environmental Impacts of Ground Source Heat Pump (GSHP) Systems. Water 2019, 11, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestor, J.; Pestotnik, S.; Zosseder, K.; Böttcher, F.; Capodaglio, P.; Götzl, G.; Bottig, M.; Weilbold, J.; Maragna, C.; Martin, J.-C.; et al. Overview and Analysis of Regulation Criteria and Guidelines for Nsge Applications in the Alpine Region. Greta Project Deliverable 2.1.1. Available online: http://bit.ly/2S8mMGy (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Santi, P.M.; McCray, J.E.; Martens, J.L. Investigating cross-contamination of aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gass, T.E.; Lehr, J.H.; Heiss, H.W. Impact of Abandoned Wells on Ground Water. Report EPA-600/3-77-095. Available online: https://bit.ly/2ZTa8hh (accessed on 28 June 2019).
- Javandel, I.; Tsang, C.F.; Witherspoon, P.A.; Morganwalp, D. Hydrologic detection of abandoned wells near proposed injection wells for hazardous waste disposal. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcι, C.B. Flow occurrence between confined aquifers through improperly plugged boreholes. J. Hydrol. 1992, 139, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, C.B. Evaluation of flow leakage through abandoned wells and boreholes. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 2565–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordbotten, J.M.; Celia, M.A.; Bachu, S. Analytical solutions for leakage rates through abandoned wells. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihan, A.; Zhou, Q.; Birkholzer, J.T. Analytical solutions for pressure perturbation and fluid leakage through aquitards and wells in multilayered-aquifer systems. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonte, M.; Zaadnoordijk, W.J.; Maas, K. A Simple Analytical Formula for the Leakage Flux through a Perforated Aquitard. Groundwater 2015, 53, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, A.; Prevot, A.B.; Buoso, S.; De Luca, D.A.; Lasagna, M.; Malandrino, M.; Maurino, V. Impacts of borehole heat exchangers (BHEs) on groundwater quality: The role of heat-carrier fluid and borehole grouting. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, H.; Mousavi Ajarostaghi, S.S.; Rosen, M.A.; Pourfallah, M. A Comprehensive Review of Backfill Materials and Their Effects on Ground Heat Exchanger Performance. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaleux, F.; Py, X.; Olives, R.; Dominguez, A. Enhancement of geothermal borehole heat exchangers performances by improvement of bentonite grouts conductivity. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 33–34, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, K.; Choi, H.; Choi, H.P. Characteristics of thermally-enhanced bentonite grouts for geothermal heat exchanger in South Korea. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viccaro, M. Doped bentonitic grouts for implementing performances of low-enthalpy geothermal systems. Geotherm Energy 2018, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, M.L.; Philippacopoulos, A.J. Thermally Conductive Cementitious Grouts for Geothermal Heat Pumps. Progress Report FY 1998. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/760977 (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- Park, M.; Min, S.; Lim, J.; Choi, J.M.; Choi, H. Applicability of cement-based grout for ground heat exchanger considering heating-cooling cycles. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indacoechea-Vega, I.; Pascual-Muñoz, P.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Calzada-Pérez, M.A. Experimental characterization and performance evaluation of geothermal grouting materials subjected to heating–cooling cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, S.; Sudicky, E.A.; Frape, S.K.; Unger, A.J.A. Influence of Leaky Boreholes on Cross-Formational Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diersch, H.J.G. FEFLOW. Finite Element Modeling of Flow, Mass and Heat Transport in Porous and Fractured Media; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-642-38738-8. [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt, M.A.; Bradbury, K.R.; Gotkowitz, M.B.; Cherry, J.A.; Parker, B.L. Human Enteric Viruses in Groundwater from a Confined Bedrock Aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6606–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, E.-H.; Lee, E.; Lee, K.-K. Impact of leaky wells on nitrate cross-contamination in a layered aquifer system: Methodology for and demonstration of quantitative assessment and prediction. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Martínez, J.; Aravena, R.; Candela, L. The Role of Leaky Boreholes in the Contamination of a Regional Confined Aquifer. A Case Study: The Campo de Cartagena Region, Spain. WaterAirSoil Pollut. 2011, 215, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, A.; Casaccio, D.; De Luca, D.A.; Destefanis, E.; Lasagna, M.; Masciocco, L.; Ossella, L.; Tonussi, M.; Governa, M.; Pietricig, M. Idrogeologia della Pianura Piemontese (Hydrogeology of the Piemonte Plain, NW Italy); Università degli Studi di Torino—DST: Regione Piemonte, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, B. Dispersive sources in uniform ground-water flow. J. Hydraul. Div. 1978, 104, 75–85. [Google Scholar]

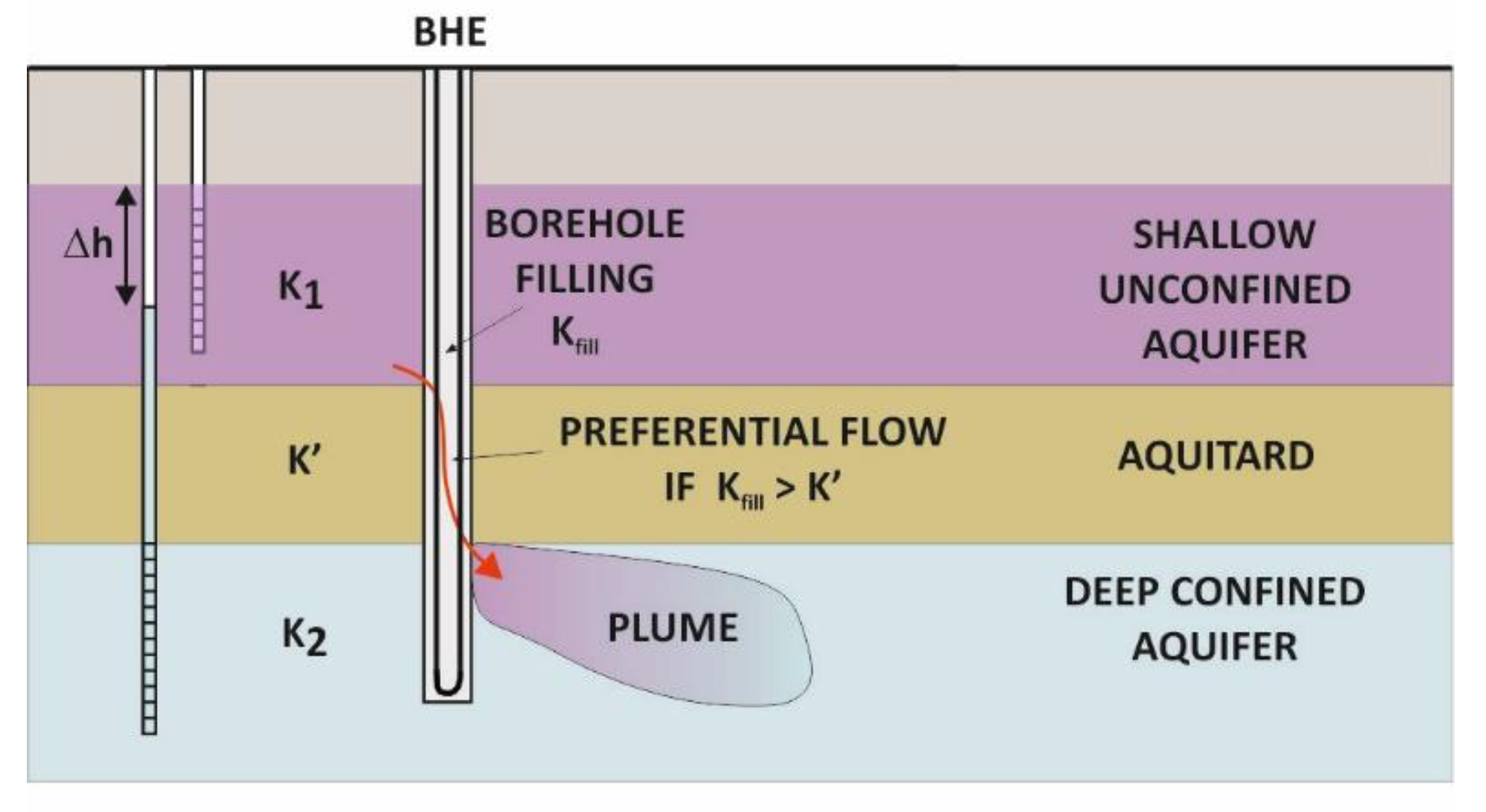
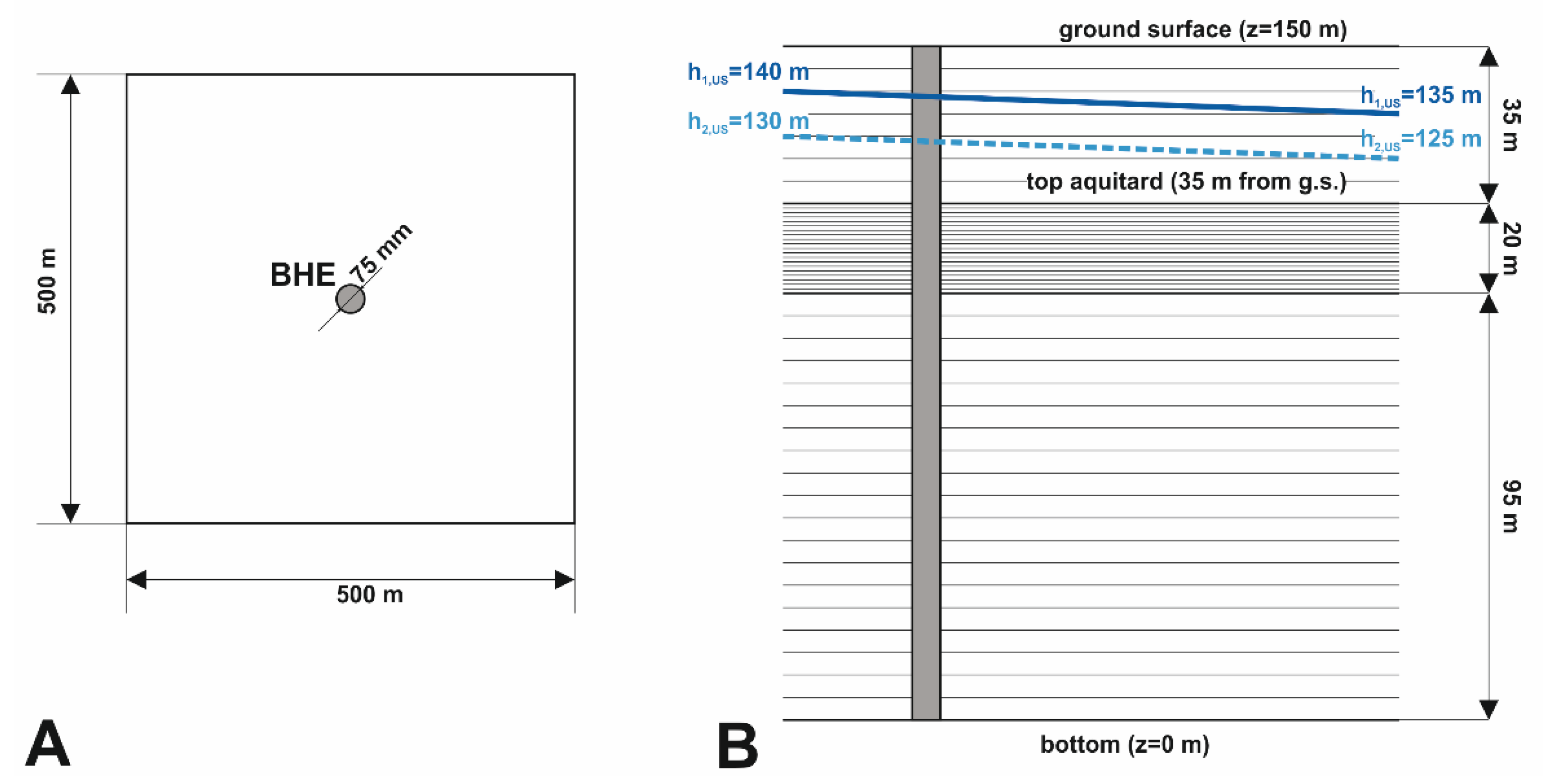
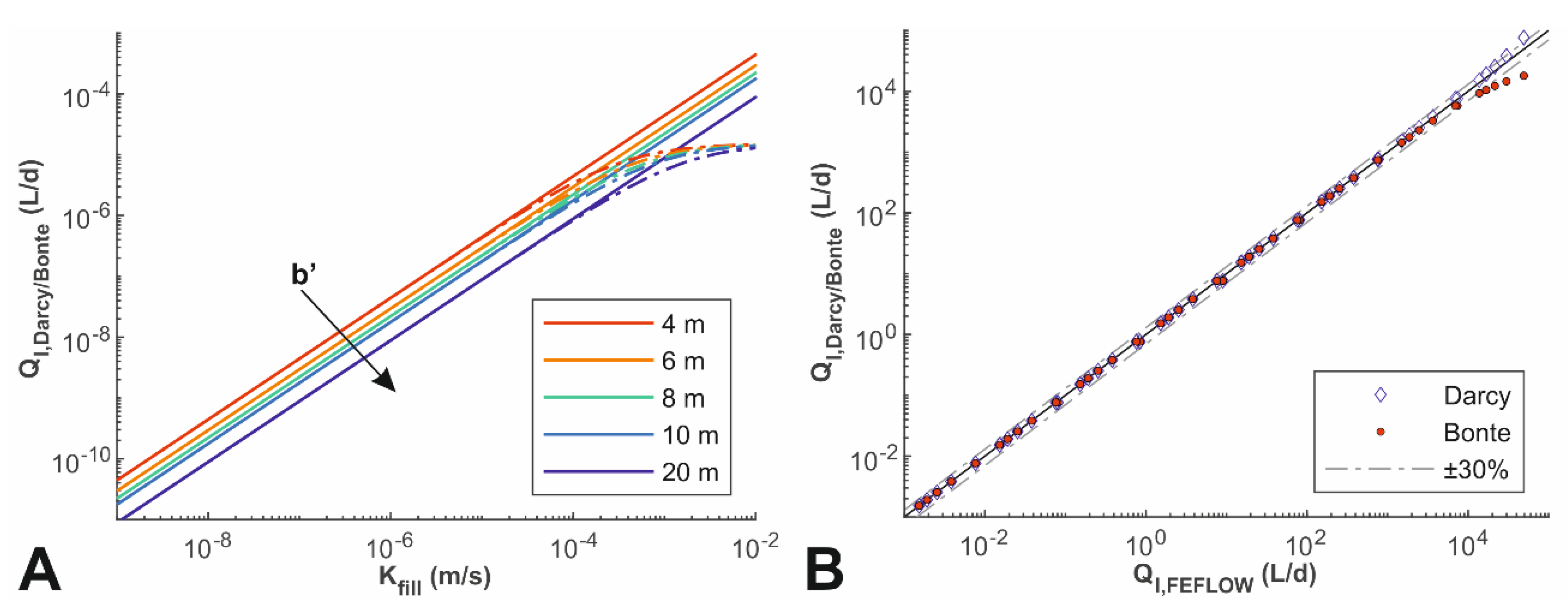
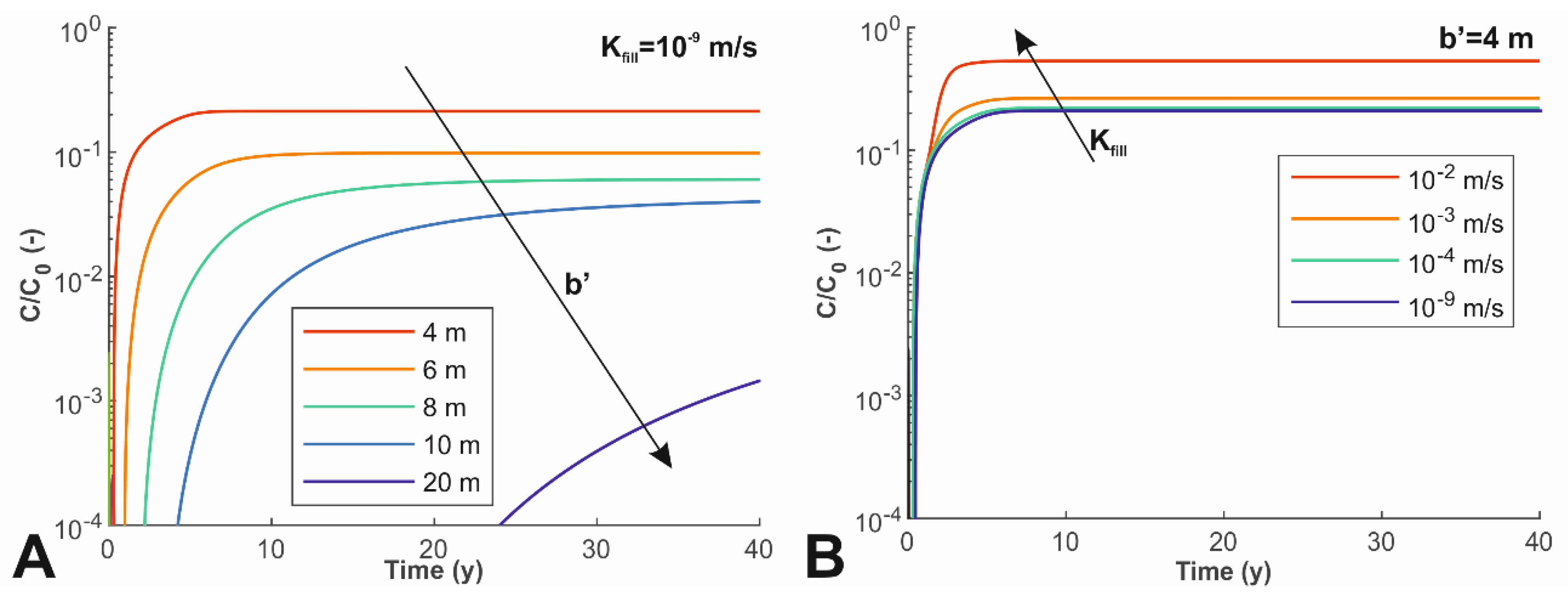
| Parameter | Shallow Aquifer | Aquitard | Deep Aquifer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic conductivity | K1 = 10−3 m/s | KA = 10−9 m/s | K2 = 10−4 m/s |
| Longitudinal hydraulic gradient | 0.01 | - | 0.01 |
| Darcy velocity of aquifer | v1 = 10−5 m/s | - | v2 = 10−6 m/s |
| Thickness | b1 = 35 m | b′ = 4 to 20 m | b2 = 115 m − b′ |
| Flow BC | h1,US = 140 m h1,DS = 135 m | h2,US = 130 m h2,DS = 125 m | |
| Mass-transport BC | C0 = 100 mg/L upstream | none | C = 0 mg/L upstream |
| Total porosity | ε = 0.3 | ||
| Effective porosity | ne = 0.2 | ||
| Longitudinal dispersivity | αL = 5 m | ||
| Transversal dispersivity | αT = 0.5 m | ||
| Hydraulic head difference | Δh = 10 m | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casasso, A.; Ferrantello, N.; Pescarmona, S.; Bianco, C.; Sethi, R. Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers? Water 2020, 12, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041174
Casasso A, Ferrantello N, Pescarmona S, Bianco C, Sethi R. Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers? Water. 2020; 12(4):1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041174
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasasso, Alessandro, Natalia Ferrantello, Simone Pescarmona, Carlo Bianco, and Rajandrea Sethi. 2020. "Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers?" Water 12, no. 4: 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041174
APA StyleCasasso, A., Ferrantello, N., Pescarmona, S., Bianco, C., & Sethi, R. (2020). Can Borehole Heat Exchangers Trigger Cross-Contamination between Aquifers? Water, 12(4), 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041174







