The Influence of Residual Coagulant Al on the Biofilm EPS and Membrane Fouling Potential in Wastewater Reclamation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Al Concentration Selection and Biofilm Cultivation
2.2. Reactor Operation
2.3. EPS Extraction
2.4. EPS Fraction Membrane Fouling Potential
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.5.1. Biofilm Dry Weight
2.5.2. Proteins and Polysaccharides Concentrations
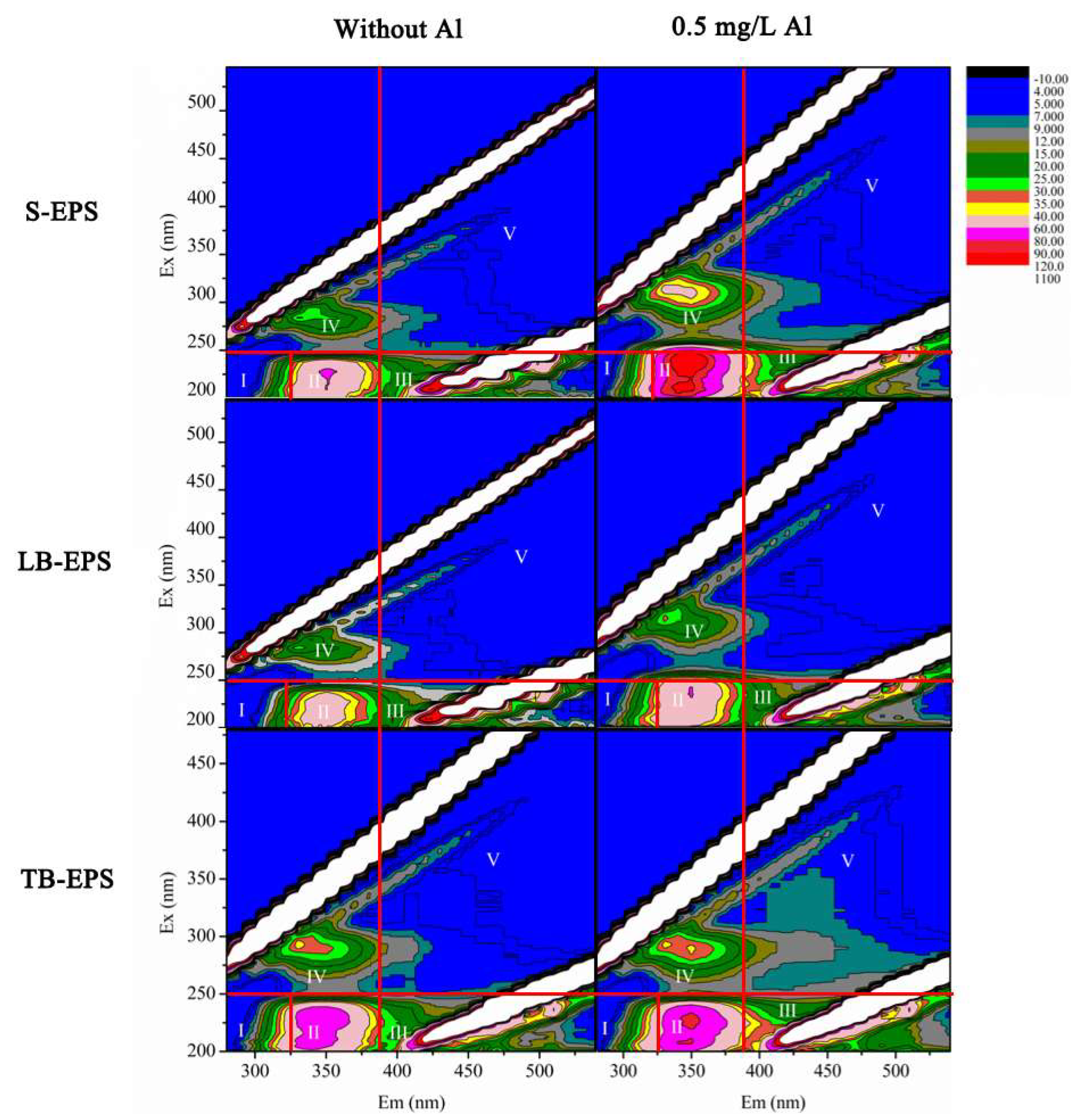
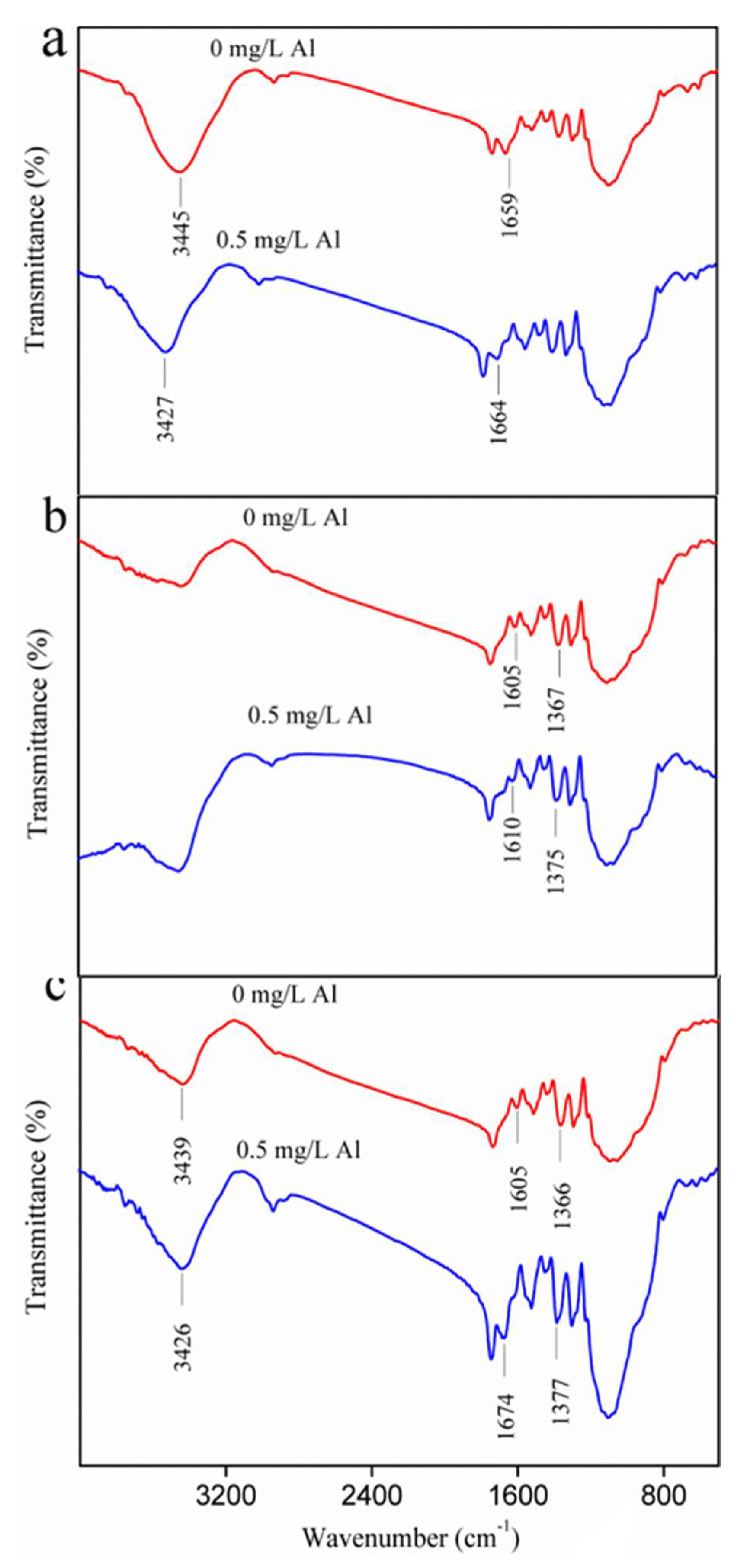
2.5.3. Spectrum Analysis
2.5.4. Hydrophilicity and Hydrophobicity
2.5.5. Zeta Potential
2.6. Aluminum Distribution Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
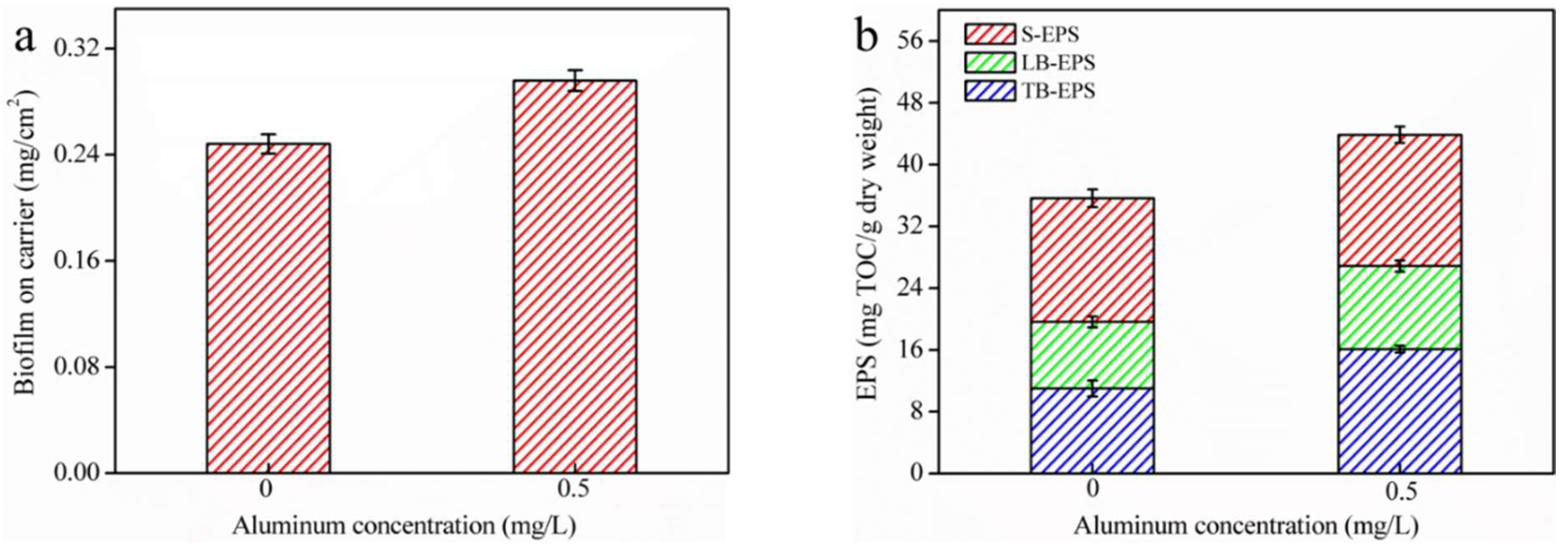
3.1. Acceleration of Biofilm EPS Fractions Formation via Residual Al
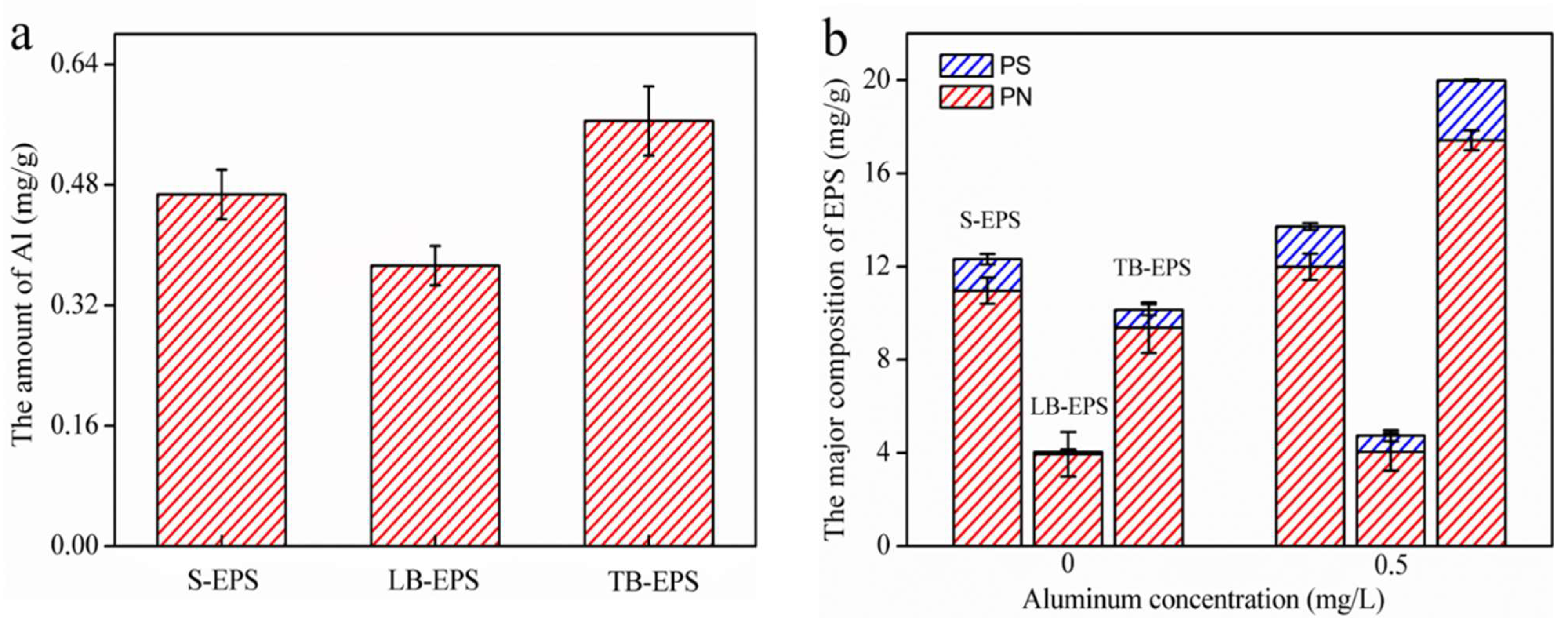
3.2. Al Distribution and Changes in EPS Fractions
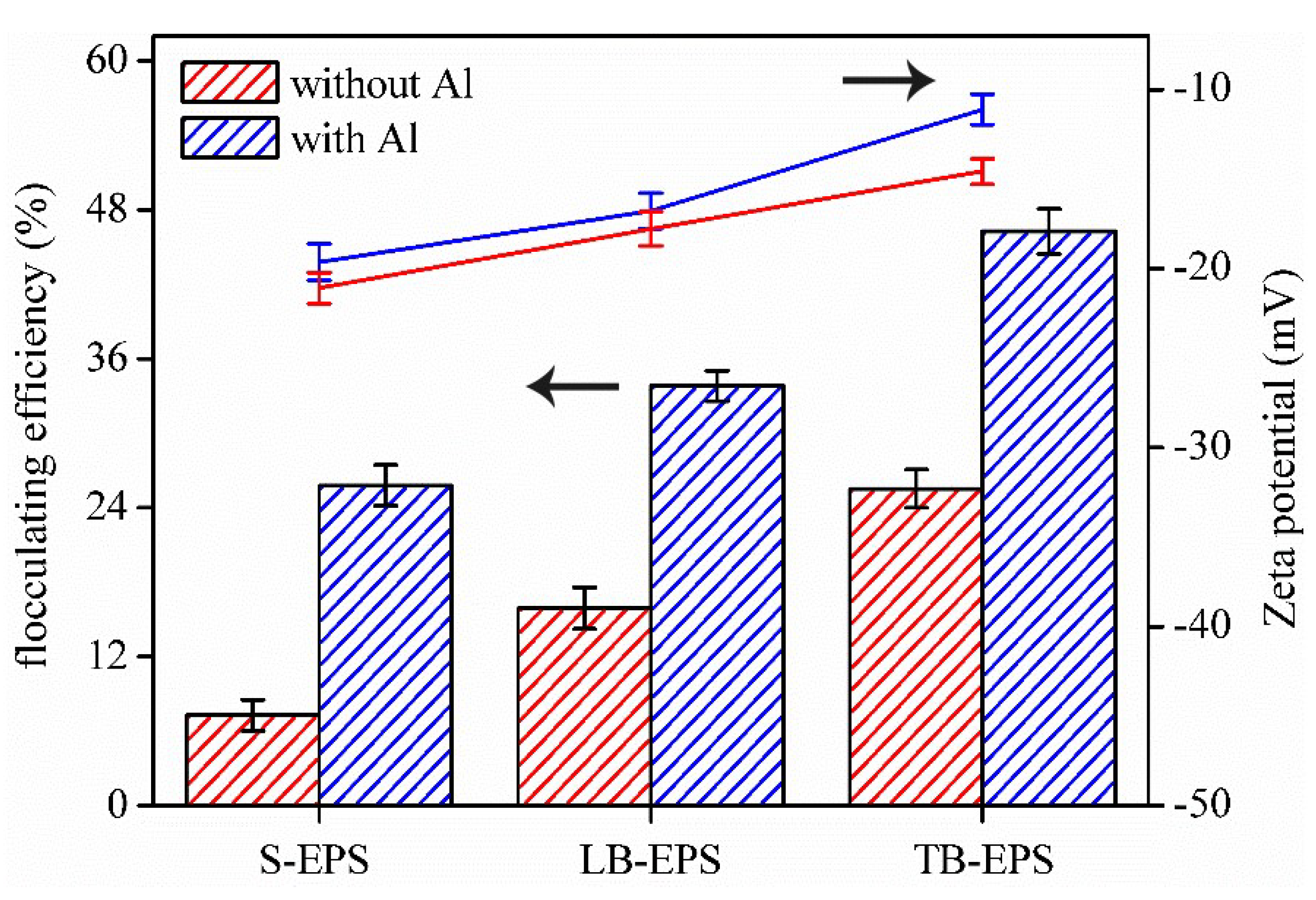
3.3. The Fouling Potential of the EPS Fractions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellona, C.; Drewes, J.E. Viability of a low-pressure nanofilter in treating recycled water for water reuse applications: A pilot-scale study. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3948–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, R.P.; Ferreira, L.M.; Binder, P.; Ramos, J.R. Analysis of foulant layer in all elements of an RO train. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 261, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Voutchkov, N.; Jiang, S. Balancing carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in seawater as a strategy to prevent accelerated membrane biofouling. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matin, A.; Khan, Z.; Zaidi, S.; Boyce, M. Biofouling in reverse osmosis membranes for seawater desalination: Phenomena and prevention. Desalination 2011, 281, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, C.; Laurent, E.; Legube, B.; Thomassin, J.-H.; Mondamert, L.; Labanowski, J. Investigation on the iron-uptake by natural biofilms. Water Res. 2014, 50, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, G.; Hou, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Miao, L.; Ao, Y.; Li, Y.; Lv, B. Effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on production and physicochemical characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances in biofilms in sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 194, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, B.; Wang, D.; Ma, T.; Xia, H.; Yu, D. Influence of wastewater sludge treatment using combined peroxyacetic acid oxidation and inorganic coagulants re-flocculation on characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Water Res. 2016, 88, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmond, P.; Best, J.P.; Morgenroth, E.; Derlon, N. Linking composition of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) to the physical structure and hydraulic resistance of membrane biofilms. Water Res. 2018, 132, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Hu, C.; Qu, J. Effect of aluminum speciation and structure characterization on preferential removal of disinfection byproduct precursors by aluminum hydroxide coagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5067–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhou, D.; Fan, W.; Huo, M.; Crittenden, J.C.; Yu, Z.; Ju, P.; Wang, Y. The effectiveness of coagulation for water reclamation from a wastewater treatment plant that has a long hydraulic and sludge retention times: A case study. Chemosphere 2016, 157, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Huo, M.; Chen, C.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Li, A.; Qiao, B.; Zhou, D.; Crittenden, J.C. Low concentrations of Al (III) accelerate the formation of biofilm: Multiple effects of hormesis and flocculation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Huang, W.; Zhang, C.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Sugiura, N. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on aerobic granulation of algal–bacterial symbiosis system and nutrients removal from synthetic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 187, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, M.; Gallert, C.; Winter, J. Biodegradation of high phenol containing synthetic wastewater by an aerobic fixed bed reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8376–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, G.; Wang, P.; Hou, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Miao, L.; Lv, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F. Insights into the short-term effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on sludge dewatering and related mechanism. Water Res. 2017, 118, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raunkjær, K.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Nielsen, P.H. Measurement of pools of protein, carbohydrate and lipid in domestic wastewater. Water Res. 1994, 28, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Fang, F.; Chen, Y.-P.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.-X.; Li, C.; Guo, J.-S.; Liu, S.-Y.; Huang, Y. Composition of EPS fractions from suspended sludge and biofilm and their roles in microbial cell aggregation. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilén, B.-M.; Lumley, D.; Mattsson, A.; Mino, T. Relationship between floc composition and flocculation and settling properties studied at a full scale activated sludge plant. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4404–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Li, G.; Lin, W.; Hu, H.-Y.; Lu, Y. Coagulation increased the growth potential of various species bacteria of the effluent of a MBR for the treatment of domestic wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 5126–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; You, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Miao, L.; Li, Y.; Ao, Y.; Lv, B.; Yang, Y. Long-term effects of CuO nanoparticles on the surface physicochemical properties of biofilms in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9629–9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-B.; Chang, Q.; Peng, D.-C.; Hou, Y.-P.; Li, H.-J.; Pei, L.-Y. A new classification paradigm of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in activated sludge: Separation and characterization of exopolymers between floc level and microcolony level. Water Res. 2014, 64, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laspidou, C.S.; Rittmann, B.E. A unified theory for extracellular polymeric substances, soluble microbial products, and active and inert biomass. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Liu, M. Exogenous refractory protein enhances biofilm formation by altering the quorum sensing system: A potential hazard of soluble microbial proteins from WWTP effluent. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-J.; Chen, S.-H.; Wang, S.-M.; Luo, H.-Y. Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from biofilm in the process of starting-up a partial nitrification process under salt stress. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation—Emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dai, X.; Zhou, J.-h.; Xu, X.-y. The stability of aerobic granular sludge under 4-chloroaniline shock in a sequential air-lift bioreactor (SABR). Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Du, P. Extraction and structural characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), pellets in autotrophic nitrifying biofilm and activated sludge. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Meng, F.; Chen, G.-H. Spectroscopic characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from a mixed culture dominated by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Water Res. 2015, 68, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q. Relationship between the extracellular polymeric substances and surface characteristics of Rhodopseudomonas acidophila. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Hu, H.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.-x.; Ren, H. Insight into mature biofilm quorum sensing in full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, X.; Huo, M.; Geng, Z. The Influence of Residual Coagulant Al on the Biofilm EPS and Membrane Fouling Potential in Wastewater Reclamation. Water 2020, 12, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041056
Sun S, Zhao Z, Cui X, Huo M, Geng Z. The Influence of Residual Coagulant Al on the Biofilm EPS and Membrane Fouling Potential in Wastewater Reclamation. Water. 2020; 12(4):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041056
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Shu, Zhenhao Zhao, Xiaochun Cui, Mingxin Huo, and Zhi Geng. 2020. "The Influence of Residual Coagulant Al on the Biofilm EPS and Membrane Fouling Potential in Wastewater Reclamation" Water 12, no. 4: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041056
APA StyleSun, S., Zhao, Z., Cui, X., Huo, M., & Geng, Z. (2020). The Influence of Residual Coagulant Al on the Biofilm EPS and Membrane Fouling Potential in Wastewater Reclamation. Water, 12(4), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041056



