Hydrological Characterization of Watering Ponds in Rangeland Farms in the Southwest Iberian Peninsula
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Rainfall Data
2.3. Water Availability and Maximum Surface and Storage Capacity of the Ponds
2.4. Influence of Temporal Rainfall Variability on Water Availability in the Ponds
2.5. Hydrological Response of Ponds to Droughts
2.6. Influence of Pond Size
2.7. Influence of Catchment Area
2.8. Statistical Analyses
2.9. Uncertainties Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Watering Ponds
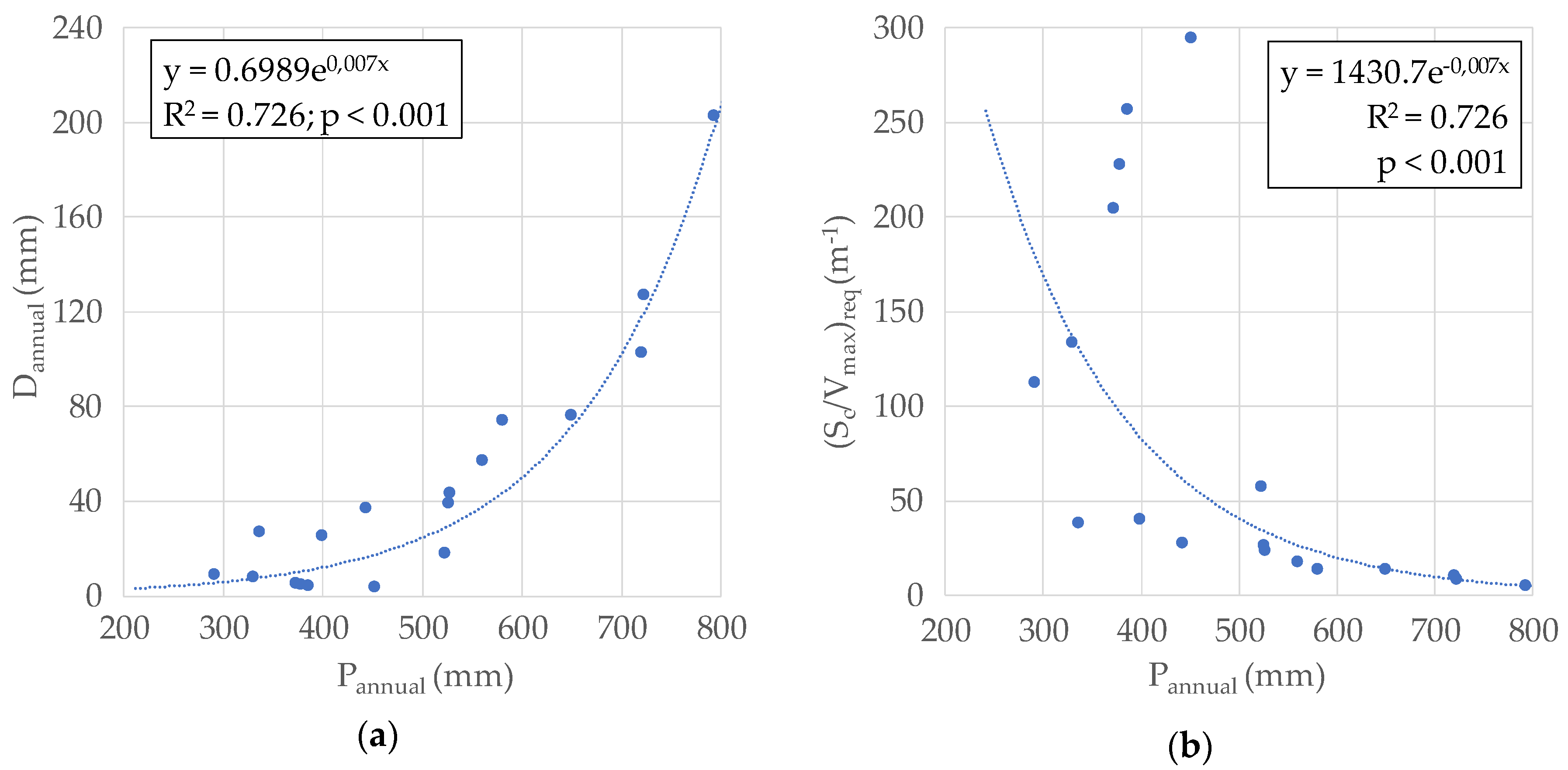
3.2. Influence of Temporal Rainfall Variability on Water Availability in the Ponds
3.3. Hydrological Response of Ponds to Droughts
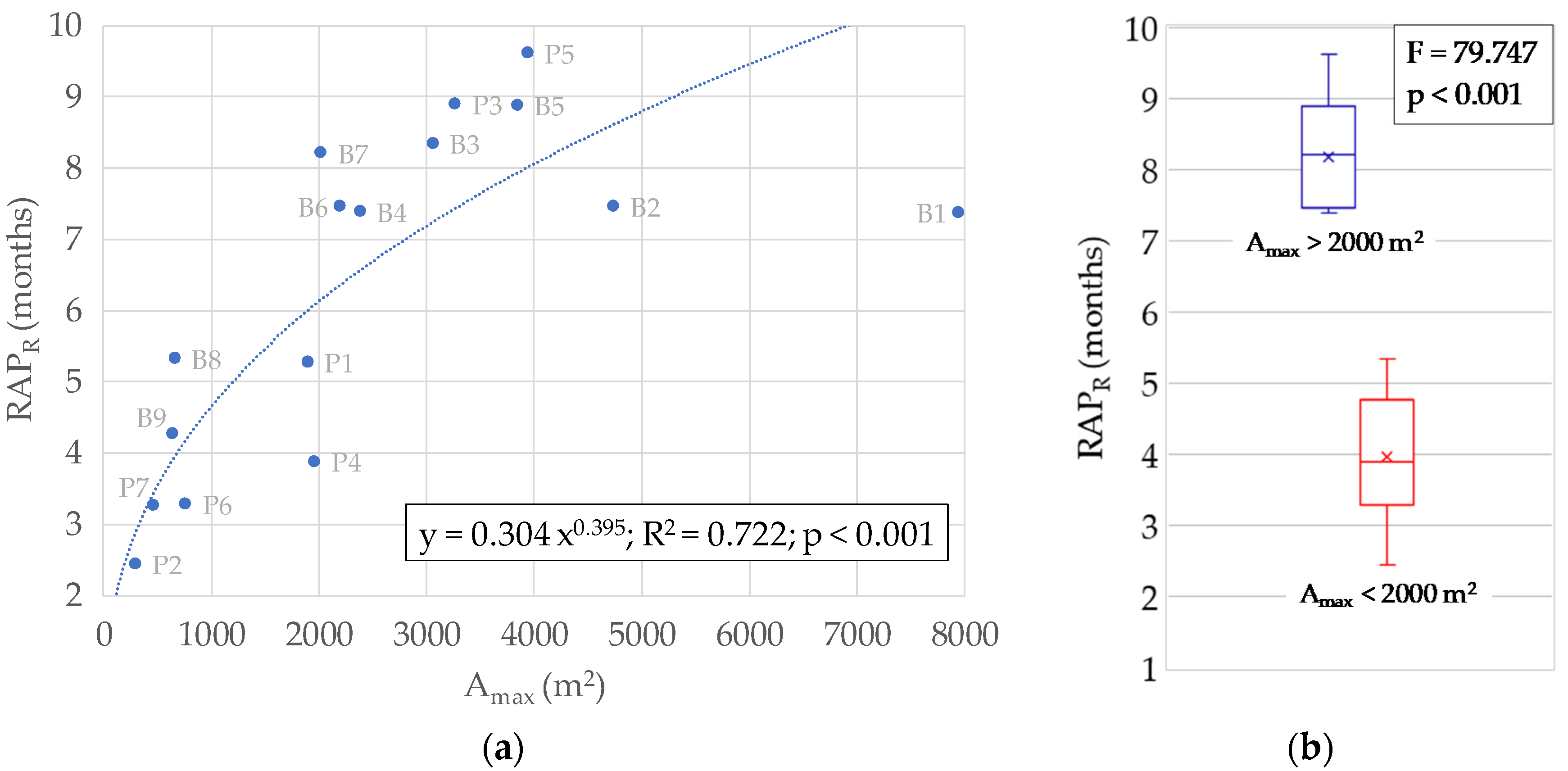
3.4. Influence of Pond Size
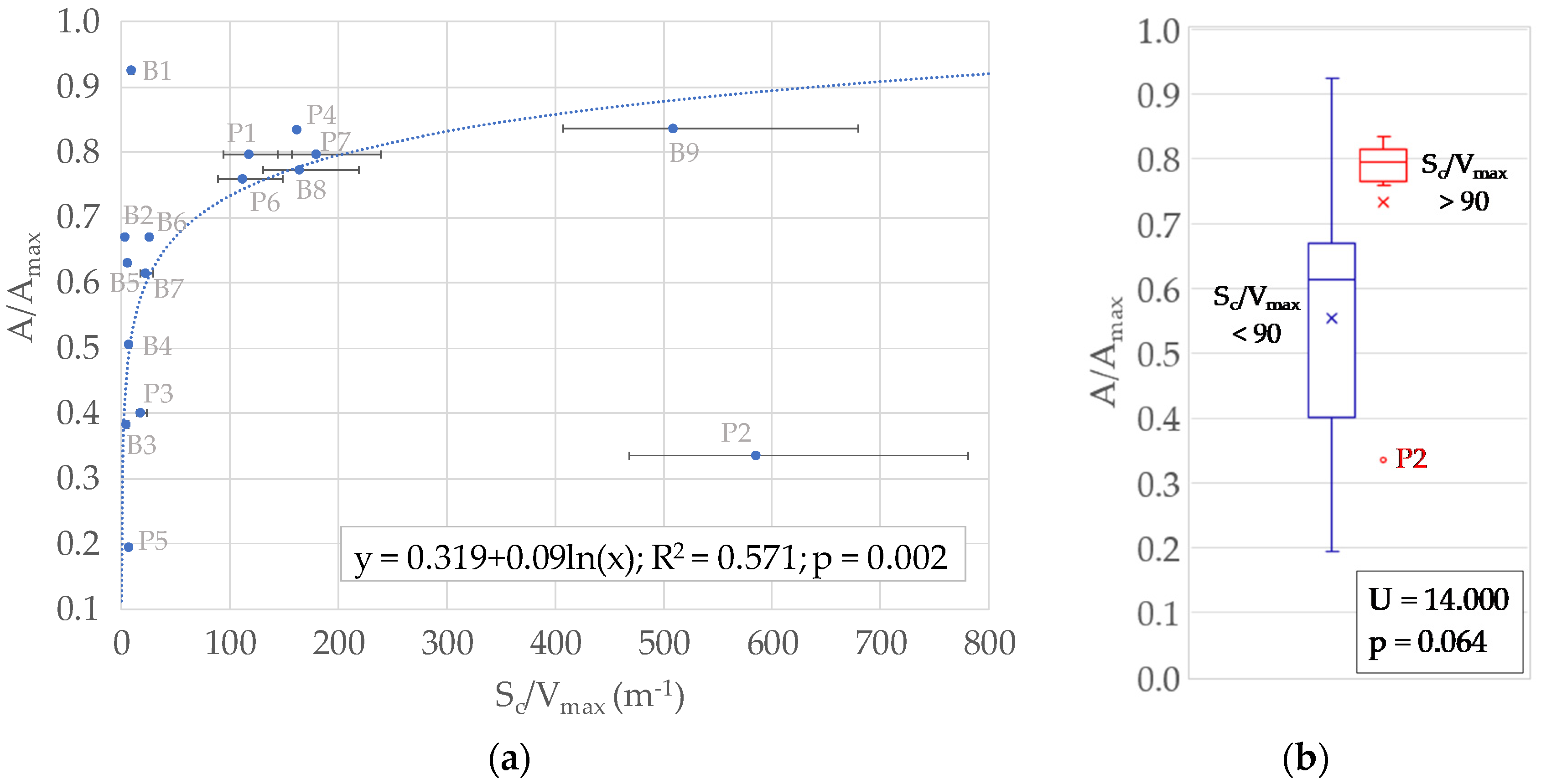
3.5. Influence of Catchment Area
4. Discussion
4.1. Applicability to Other Regions
4.2. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pulido-Fernández, M.; Schnabel, S. La disponibilidad de agua en explotaciones de ganadería extensiva. In Aportaciones a la Geografía Física de Extremadura con especial referencia a las dehesas; Schnabel, S., Lavado-Contador, F., Gómez-Gutiérrez, A., García-Marín, R., Eds.; Fundicotex: Cáceres, Spain, 2010; pp. 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-Parra, J.; Maneta, M.P.; Schnabel, S. Climate and topographic controls on simulated pasture production in a semiarid Mediterranean watershed with scattered tree cover. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1439–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frasier, G.W. Harvesting water for agricultural, wildlife and domestic uses. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1980, 35, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Boers, T.M.; Benasher, J. A review of rainwater harvesting. Agric. Water Manag. 1982, 5, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasage, R.; Verburg, P.H. Evaluation of small scale water harvesting techniques for semi-arid environments. J. Arid Environ. 2015, 118, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayantunde, A.A.; Cofie, O.; Barron, J. Multiple uses of small reservoirs in crop-livestock agro-ecosystems of Volta basin: Implications for livestock management. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 204, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zaag, P.; Gupta, J. Scale issues in the governance of water storage projects. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, J.; Sánchez, E.; Aguilar, F.; Gómez, A.; Lozano, A. Manual práctico de balsas agrícolas. Diseño y gestión para su mejora ambiental; Agencia Andaluza del Agua. Conserjería de Medio Ambiente. Junta de Andalucía: Sevilla, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Casas, J.; Toja, J.; Bonachela, S.; Fuentes, F.; Gallego, I.; Juan, M.; Leon, D.; Penalver, P.; Perez, C.; Sanchez, P. Artificial ponds in a Mediterranean region (Andalusia, southern Spain): Agricultural and environmental issues. Water Environ. J. 2011, 25, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canals, R.M.; Ferrer, V.; Iriarte, A.; Cárcamo, S.; Emeterio, L.S.; Villanueva, E. Emerging conflicts for the environmental use of water in high-valuable rangelands. Can livestock water ponds be managed as artificial wetlands for amphibians? Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duesterhaus, J.L.; Ham, J.M.; Owensby, C.E.; Murphy, J.T. Water balance of a stock-watering pond in the Flint Hills of Kansas. Rangeland Ecol. Manag. 2008, 61, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; van der Kamp, G. Water level changes in ponds and lakes: The hydrological processes. In Plant Disturbance Ecology. The Process and the Response; Johnson, E.A., Miyanishi, K., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 311–339. [Google Scholar]
- Manson, P.W.; Schwartz, G.M.; Allred, E.R. Some aspects of the hydrology of ponds and small lakes; Technical Bulletin 257; Agricultural Experiment Station, University of Minnesota: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, M.; van der Kamp, G.; Rudolph, D.L. Water and solute transfer between a prairie wetland and adjacent uplands, 1. Water balance. J. Hydrol. 1998, 207, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, C.R. Simulating vernal pool hydrologic regimes for two locations in California, USA. Ecol. Model. 2004, 173, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porphyre, T.; Bicout, D.J.; Sabatier, P. Modelling the abundance of mosquito vectors versus flooding dynamics. Ecol. Model. 2005, 183, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.J.; Neary, V.S.; Morgan, K.L. Hydrologic modeling as a development tool for HGM functional assessment models. Wetlands 2006, 26, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, R.B.; Johnson, C.M.; Johnson, L.B. Simulating vernal pool hydrology in central Minnesota, USA. Wetlands 2006, 26, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soti, V.; Puech, C.; Lo Seen, D.; Bertran, A.; Vignolles, C.; Mondet, B.; Dessay, N.; Tran, A. The potential for remote sensing and hydrologic modelling to assess the spatio-temporal dynamics of ponds in the Ferlo Region (Senegal). Hydrol. Earth Sys. Sci. 2010, 14, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garmendia, A.; Pedrola-Monfort, J. Simulation model comparing the hydroperiod of temporary ponds with different shapes. Limnetica 2010, 29, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Young, C.; Abdul-Aziz, O.I.; Dahal, D.; Feng, M.; Liu, S. Simulating the water budget of a Prairie Potholes complex from LiDAR and hydrological models in North Dakota, USA. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asare, E.O.; Tompkins, A.M.; Bomblies, A. A Regional Model for Malaria Vector Developmental Habitats Evaluated Using Explicit, Pond-Resolving Surface Hydrology Simulations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noorduijn, S.L.; Hayashi, M.; Mohammed, G.A.; Mohammed, A.A. A Coupled Soil Water Balance Model for Simulating Depression-Focused Groundwater Recharge. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, P.; Rockstrom, J. Supplemental irrigation for dry-spell mitigation of rainfed agriculture in the Sahel. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 61, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngigi, S.N.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Thome, J.N.; Rockstrom, J.; de Vries, F. Agro-hydrological evaluation of on-farm rainwater storage systems for supplemental irrigation in Laikipia district, Kenya. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 73, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.F.; Gowing, J. A daily water balance modelling approach for simulating performance of tank-based irrigation systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2005, 19, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, B.; Panda, S.N.; Mal, B.C. Rainwater conservation and recycling by optimal size on-farm reservoir. Resour. Conserv. Recyc. 2007, 50, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, G.; Hengsdijk, H.; Jansen, H.C. Review and quantitative assessment of ex situ household rainwater harvesting systems in Ethiopia. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, F.; Agüera, F.; Sánchez-Hermosilla, J. Water balance in artificial on-farm agricultural water reservoirs for the irrigation of intensive greenhouse crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 131, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Paz, J.O.; Feng, G.; Read, J.J.; Adeli, A.; Jenkins, J.N. A Model to Estimate Hydrological Processes and Water Budget in an Irrigation Farm Pond. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 2225–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Ávalos, J. Importance et fonctionnement des petits barrages dans une zone semi-aride du Nord-Mexique. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Magliano, P.N.; Murray, F.; Baldi, G.; Aurand, S.; Paez, R.A.; Harder, W.; Jobbagy, E.G. Rainwater harvesting in Dry Chaco: Regional distribution and local water balance. J. Arid Environ. 2015, 123, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deal, C.; Edwards, J.L.; Pellmann, N.; Tuttle, R.; Woodward, D. Ponds — Planning, Design, Construction; Agriculture Handbook Nº 590; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS): Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Masike, S. The impacts of climate change on cattle water demand and supply in Khurutshe, Botswana. Ph.D. Thesis, International Global Change Institute (IGCI), University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, K.; Morden, R.; Lowe, L.; Nathan, R. Advances in assessing the impact of hillside farm dams on streamflow. Australas. J. Water Resour. 2015, 19, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habets, F.; Molenat, J.; Carluer, N.; Douez, O.; Leenhardt, D. The cumulative impacts of small reservoirs on hydrology: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joffre, R.; Rambal, S.; Ratte, J.P. The dehesa system of southern Spain and Portugal as a natural ecosystem mimic. Agrofor. Sys. 1999, 45, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plieninger, T.; Pulido, F.J.; Schaich, H. Effects of land-use and landscape structure on holm oak recruitment and regeneration at farm level in Quercus ilex L. dehesas. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 57, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.; Carranza, J.; Coleto, J.M.; Díaz, M.; Diéguez, E.; Escudero, A.; Ezquerra, F.J.; López, L.; Fernández, P.; Montero, G.; et al. Libro verde de la dehesa. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229812274_Libro_Verde_de_la_Dehesa/link/551333600cf283ee0833738e/download (accessed on 31 October 2019).
- Plieninger, T.; Hartel, T.; Martin-Lopez, B.; Beaufoy, G.; Bergmeier, E.; Kirby, K.; Montero, M.J.; Moreno, G.; Oteros-Rozas, E.; Van Uytvanck, J. Wood-pastures of Europe: Geographic coverage, social-ecological values, conservation management, and policy implications. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 190, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, S.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, A. The role of interannual rainfall variability on runoff generation in a small dry sub-humid watershed with disperse tree cover. Cuadernos de Investigación Geográfica 2013, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UNEP. World Atlas of Desertification, 1st ed.; Middleton, N., Thomas, D.S.G., Eds.; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop. evapotranspiration: Guidelines for computing crop water requirements; FAO Irrigation and drainage paper nº 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido-Fernández, M.; Schnabel, S.; Lavado-Contador, F.J.; Miralles-Mellado, I.; Ortega-Perez, R. Soil organic matter of Iberian open woodland rangelands as influenced by vegetation cover and land management. Catena 2013, 109, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, S.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Moreno-Marcos, G. Soil and Water Dynamics. In Mediterranean Oak Woodland Working Landscapes: Dehesas of Spain and Ranchlands of California; Campos, P., Huntsinger, L., Oviedo Pro, J.L., Starrs, P.F., Diaz, M., Standiford, R.B., Montero, G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 91–121. [Google Scholar]
- Luke, G.J. Consumption of water by livestock; Resource Management Technical Report No. 60; Department of Agriculture and Food, Government of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 1987.
- CNIG. Centro de descargas del Centro Nacional de Información Geográfica (CNIG), Ministerio de Fomento, Gobernment of Spain. Available online: https://centrodedescargas.cnig.es/CentroDescargas/index.jsp (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Westoby, M.J.; Brasington, J.; Glasser, N.F.; Hambrey, M.J.; Reynolds, J.M. ‘Structure-from-Motion’ photogrammetry: A low-cost, effective tool for geoscience applications. Geomorphol. 2012, 179, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebe, J.R.; van de Giesen, N.; Andreini, M.; Walter, M.T.; Steenhuis, T.S. Determining watershed response in data poor environments with remotely sensed small reservoirs as runoff gauges. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annor, F.O.; van de Giesen, N.; Liebe, J.; van de Zaag, P.; Tilmant, A.; Odai, S.N. Delineation of small reservoirs using radar imagery in a semi-arid environment: A case study in the upper east region of Ghana. Phys. Chem. Earth 2009, 34, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.L.; Young, C.; Feng, M.; Heidemann, K.; Cushing, M.; Mushet, D.M.; Liu, S.G. Demonstration of a conceptual model for using LiDAR to improve the estimation of floodwater mitigation potential of Prairie Pothole Region wetlands. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, L.N.; Sano, E.E.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Passo, D.P. Estimation of Small Reservoir Storage Capacities with Remote Sensing in the Brazilian Savannah Region. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, L.; Grippa, M.; Hiernaux, P.; Peugeot, C.; Mougin, E.; Kergoat, L. Changes in lakes water volume and runoff over ungauged Sahelian watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda, M.; Hayes, M.; Wood, D. Standardized Precipitation Index User Guide; WMO-No. 1090; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Van Loon, A.F. Hydrological drought explained. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.-Water 2015, 2, 359–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NDMC. SPI Program. Available online: https://drought.unl.edu/droughtmonitoring/SPI/SPIProgram.aspx (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Khastagir, A.; Jayasuriya, N. Optimal sizing of rain water tanks for domestic water conservation. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, C.W.; Coles, N.A. Defining reliability for rainwater harvesting systems. In Proceedings of the 19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation (Modsim2011), Perth, Australia, 12–16 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos, A.; Schnabel, S. Hydrological behaviour of a small catchment in the dehesa landuse system (Extremadura, SW Spain). J. Hydrol. 1998, 210, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, S.; Lozano-Parra, J.; Gomez-Gutierrez, A.; Alfonso-Torreno, A. Hydrological dynamics in a small catchment with silvopastoral land use in SW Spain. Cuadernos de Investigacion Geografica 2018, 44, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mati, B.M.; Muchiri, J.M.; Njenga, K.; Penning de Vries, F.; Merrey, D.J. Assessing water availability under pastoral livestock systems in drought-prone Isiolo District, Kenya; Working Paper 106; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, R.; Lowe, L. The hydrologic impacts of farm dams. Austral. J. Water Resour. 2012, 16, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Bichsel, D.; De Marco, P.; Bispo, A.A.; Ilg, C.; Dias-Silva, K.; Vieira, T.B.; Correa, C.C.; Oertli, B. Water quality of rural ponds in the extensive agricultural landscape of the Cerrado (Brazil). Limnology 2016, 17, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallas, P. Water for animals; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Chumchal, M.M.; Drenner, R.W.; Adams, K.J. Abundance and size distribution of permanent and temporary farm ponds in the southeastern Great Plains. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nathan, R.; Morden, R.; Jordan, P. Assessing the impact of farm dams on streamflows, Part I: Development of simulation tools. Austral. J. Water Resour. 2005, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.A.; Prairie, Y.T.; Cole, J.J.; Duarte, C.M.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; McDowell, W.H.; Kortelainen, P.; Caraco, N.F.; Melack, J.M.; et al. The global abundance and size distribution of lakes, ponds, and impoundments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilgrim, D.H.; Chapman, T.G.; Doran, D.G. Problems of Rainfall-Runoff Modeling in Arid and Semiarid Regions. Hydrol. Sci. J.-J. Des. Sci. Hydrol. 1988, 33, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K. Runoff generation in semi-arid areas. In Dryland rivers: Hydrology and geomorphology of semi-arid channels; Bull, L.J., Kirkby, M.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 57–105. [Google Scholar]
- Chamaille-Jammes, S.; Fritz, H.; Murindagomo, F. Climate-driven fluctuations in surface-water availability and the buffering role of artificial pumping in an African savanna: Potential implication for herbivore dynamics. Austral. Ecol. 2007, 32, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, C.; Herrero, J. The water regime of the Monegros playa-lakes as established from ground and satellite data. J. Hydrol. 2005, 310, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castañeda, C.; Garcia-Vera, M.A. Water balance in the playa-lakes of an arid environment, Monegros, NE Spain. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, D.; Coles, N. Assessing storage reliability of farm dams; Resource Management Technical Report no. 245; Department of Agriculture and Food, Government of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 2003.
- Mosley, L.M. Drought impacts on the water quality of freshwater systems; review and integration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 140, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Castro, F.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Tomas-Burguera, M.; Pena-Gallardo, M.; Begueria, S.; El Kenawy, A.; Luna, Y.; Morata, A. High spatial resolution climatology of drought events for Spain: 1961–2014. Internat. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 5046–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.A.; Mantel, S.K. Estimating the uncertainty in simulating the impacts of small farm dams on streamflow regimes in South Africa. Hydrol. Sci. J.-J. Des. Sci. Hydrol. 2010, 55, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
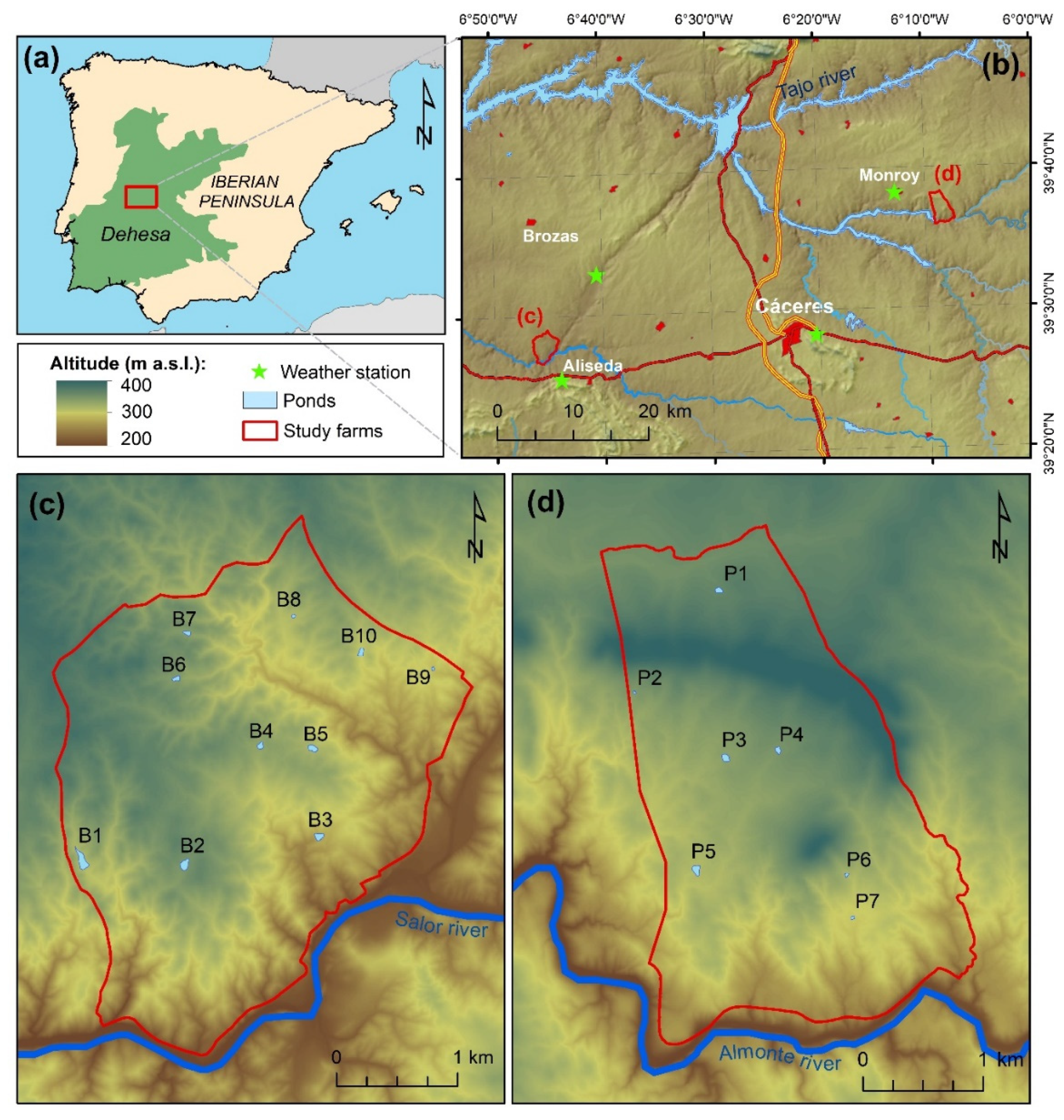
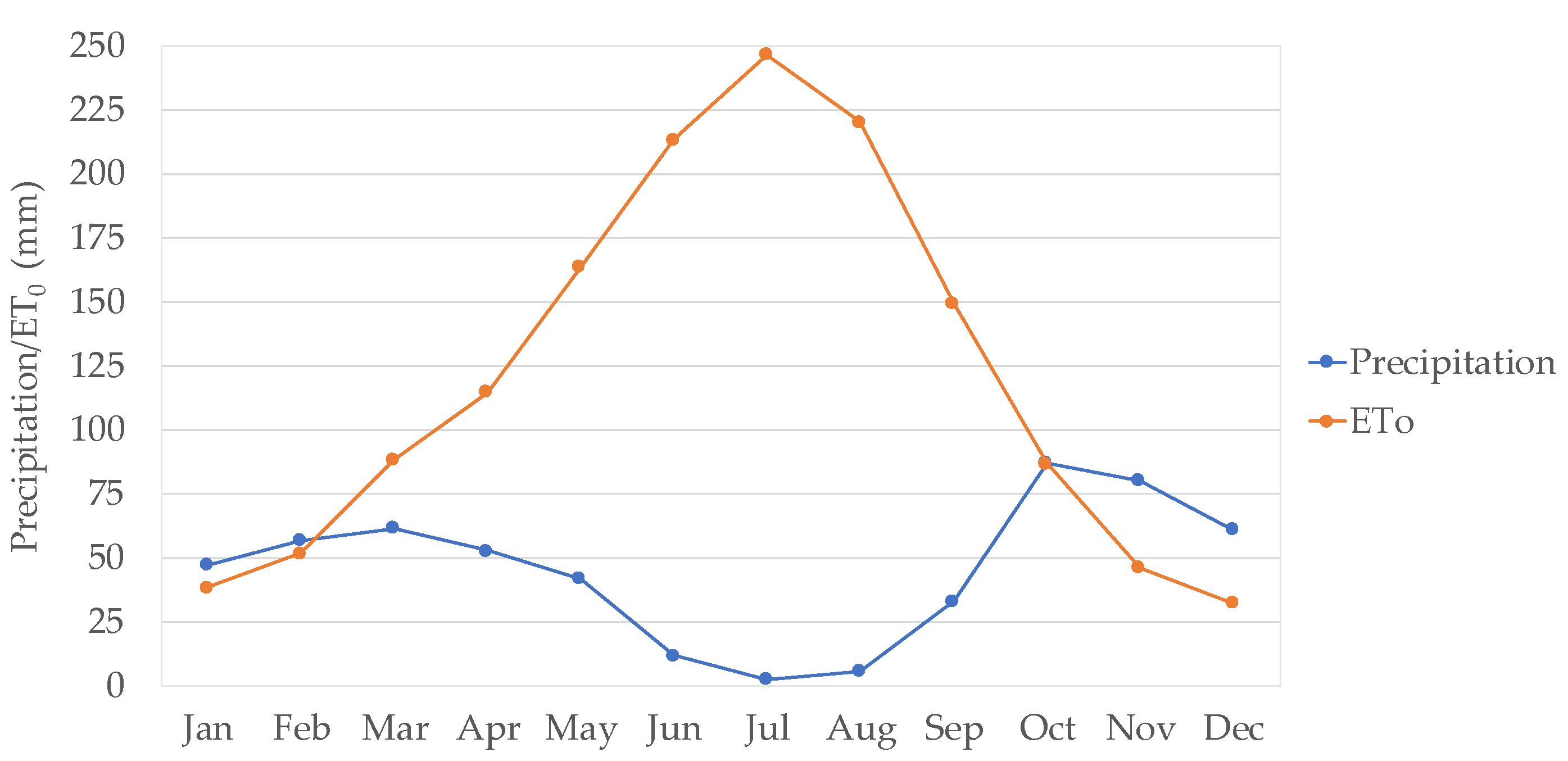


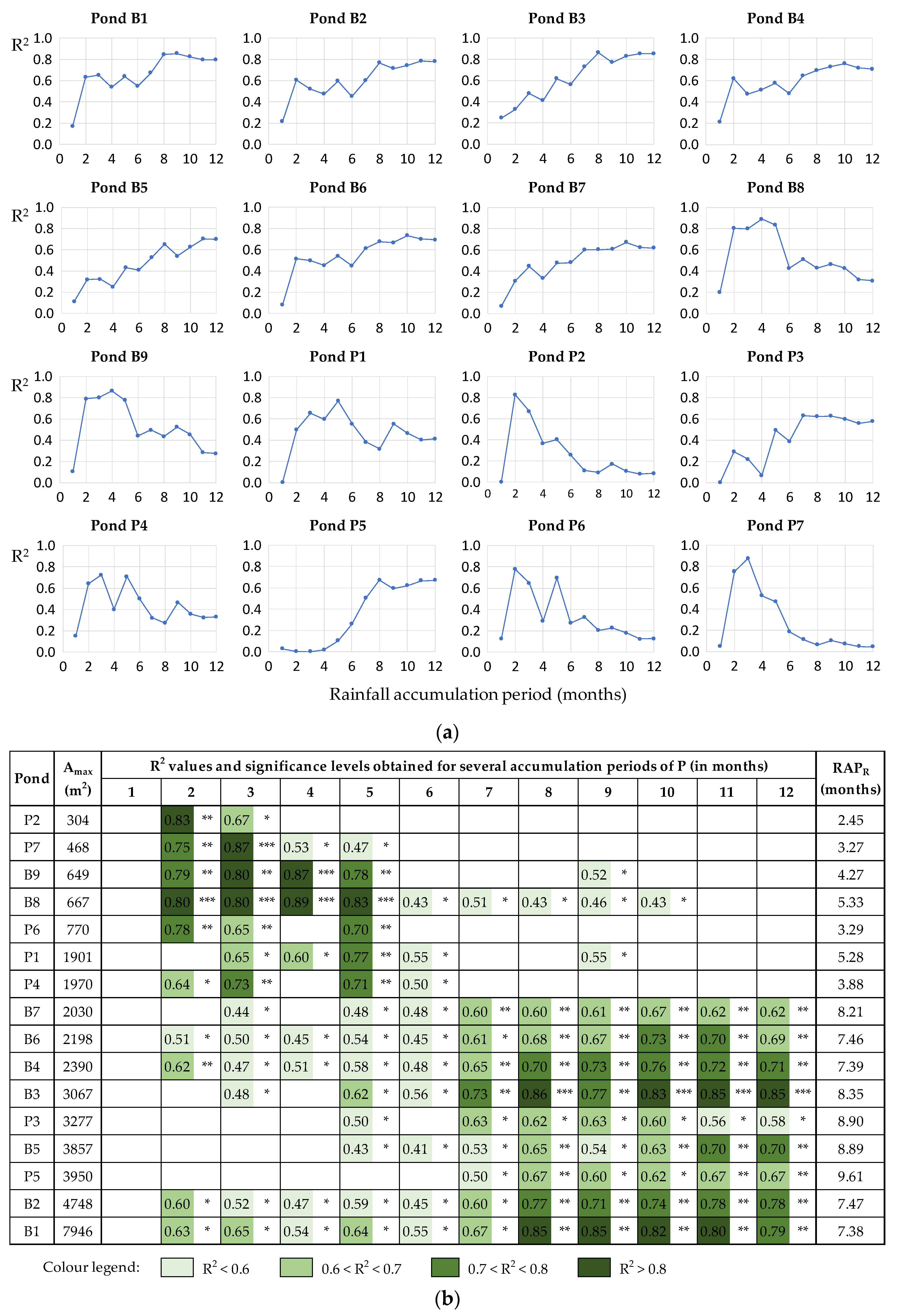

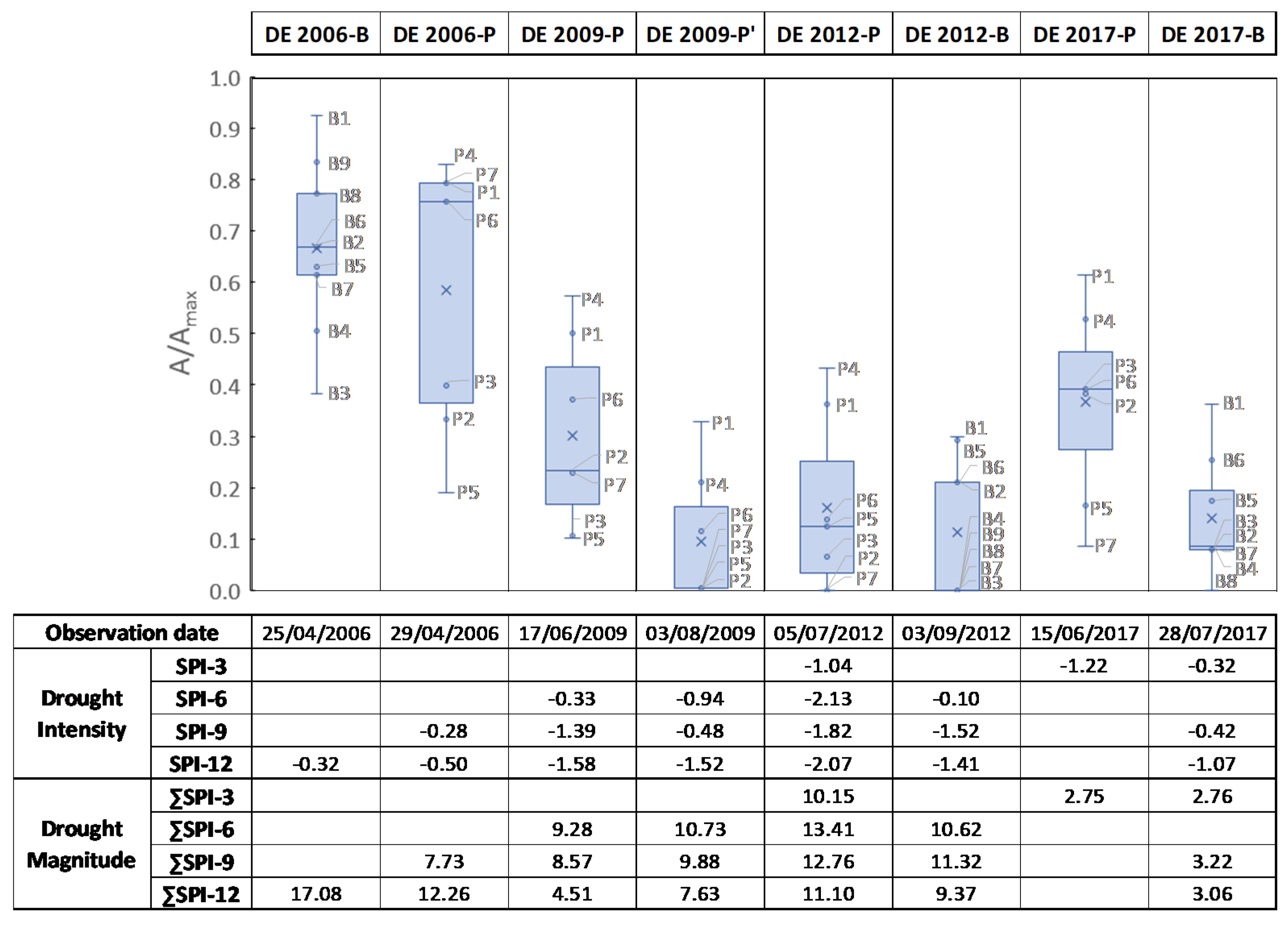

| Study Farm | Area (ha) | Livestock Population (2019 data) | Livestock Water Intake (m3/year) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sheep | Goats | Pigs | Cows | |||
| La Brava | 926 | 60 | 100 | 135 | 897 | |
| Parapuños | 797 | 1200 | 38 | 880 | ||
| Name | Role | Longitude | Latitude | Z (m) | D (km) | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aliseda (La Umbría) | Ref. (La Brava) | 6°43’56’’ W | 39°25’31’’ N | 370 | 4 | 0.81 |
| Brozas (Araya de Arriba) | Aux. (La Brava) | 6°40’30’’ W | 39°32’56’’ N | 335 | 10 | |
| Monroy | Ref. (Parapuños) | 6°12’46’’ W | 39°38’16’’ N | 378 | 5 | 0.76 |
| Cáceres | Aux (Parapuños) | 6°20’20’’ W | 39°28’17’’ N | 394 | 23 |
| Acquisition Date | Ponds that Appear in the Image | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| June 2002 | B2, B3, B4, B5, B7, B8, B9 | 0.50 m | CNIG |
| June 2002 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 | 0.50 m | CNIG |
| March 2003 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5 | Unknown | Google Earth |
| April 2006 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 | 0.50 m | CNIG |
| April 2006 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 | 0.50 m | CNIG |
| Summer 2008 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 | 0.25 m | CNIG |
| Summer 2009 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 | 0.50 m | CNIG |
| August 2009 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 | Unknown | Google Earth |
| June 2010 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 | 0.50 m | CNIG |
| July 2010 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 | 0.25 m | CNIG |
| August 2010 | B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, P3, P5, P6, P7 | Unknown | Google Earth |
| July 2011 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 | Unknown | Google Earth |
| July 2011 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 | Unknown | Google Earth |
| July 2012 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 | 0.50 m | CNIG |
| September 2012 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 | 0.25 m | CNIG |
| August 2013 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 | Unknown | Google Earth |
| June 2016 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 | 0.25 m | CNIG |
| August 2016 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 | 0.25 m | CNIG |
| June 2017 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7 | Unknown | Google Earth |
| July 2017 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 a | Unknown | Google Earth |
| August 2018 | B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9 a, B10 b | Unknown | Google Earth |
| Farm | Pond | Amax (m2) | Vmax (m3) | Sc (m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| La Brava | B1 | 7946 | 30,502 | 275,275 |
| B2 | 4748 | 12,116 | 43,200 | |
| B3 | 3067 | 5534 | 28,300 | |
| B4 | 2390 | 3539 | 25,300 | |
| B5 | 3857 | 8347 | 51,650 | |
| B6 | 2198 | 3351 | 89,100 | |
| B7 | 2030 | 2641 | 58,650 | |
| B8 | 667 | 359 | 58,850 | |
| B9 | 649 | 342 | 174,025 | |
| B10 | 2353 | 3441 | 113,000 | |
| Parapuños | P1 | 1901 | 2347 | 275,826 |
| P2 | 304 | 88 | 51,348 | |
| P3 | 3277 | 6232 | 110,786 | |
| P4 | 1970 | 2158 | 349,162 | |
| P5 | 3950 | 8711 | 57,206 | |
| P6 | 770 | 464 | 51,875 | |
| P7 | 468 | 190 | 34,114 |
| Cluster | Centers of the Final Clusters | Ponds in Each Cluster | Distance from the Cluster Center | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rpond | RAPR (months) | |||
| 1 | 0.93 | 8.18 | B1 | 0.804 |
| B2 | 0.721 | |||
| B3 | 0.225 | |||
| B4 | 0.797 | |||
| B5 | 0.704 | |||
| B6 | 0.725 | |||
| B7 | 0.038 | |||
| P3 | 0.715 | |||
| P5 | 1.430 | |||
| 2 | 0.80 | 3.97 | B8 | 1.365 |
| B9 | 0.313 | |||
| P1 | 1.323 | |||
| P2 | 1.550 | |||
| P4 | 0.212 | |||
| P6 | 0.705 | |||
| P7 | 0.739 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marín-Comitre, U.; Schnabel, S.; Pulido-Fernández, M. Hydrological Characterization of Watering Ponds in Rangeland Farms in the Southwest Iberian Peninsula. Water 2020, 12, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041038
Marín-Comitre U, Schnabel S, Pulido-Fernández M. Hydrological Characterization of Watering Ponds in Rangeland Farms in the Southwest Iberian Peninsula. Water. 2020; 12(4):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041038
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarín-Comitre, Ubaldo, Susanne Schnabel, and Manuel Pulido-Fernández. 2020. "Hydrological Characterization of Watering Ponds in Rangeland Farms in the Southwest Iberian Peninsula" Water 12, no. 4: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041038
APA StyleMarín-Comitre, U., Schnabel, S., & Pulido-Fernández, M. (2020). Hydrological Characterization of Watering Ponds in Rangeland Farms in the Southwest Iberian Peninsula. Water, 12(4), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041038







