How to Sustainably Use Water Resources—A Case Study for Decision Support on the Water Utilization of Xinjiang, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study
2.2. Materials
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Principles of SD
2.3.2. SD Model for Water Decision Support
2.3.3. Model Validity Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development and Utilization of Water Resources in Xinjiang
3.2. Validity Evaluation of SD Models
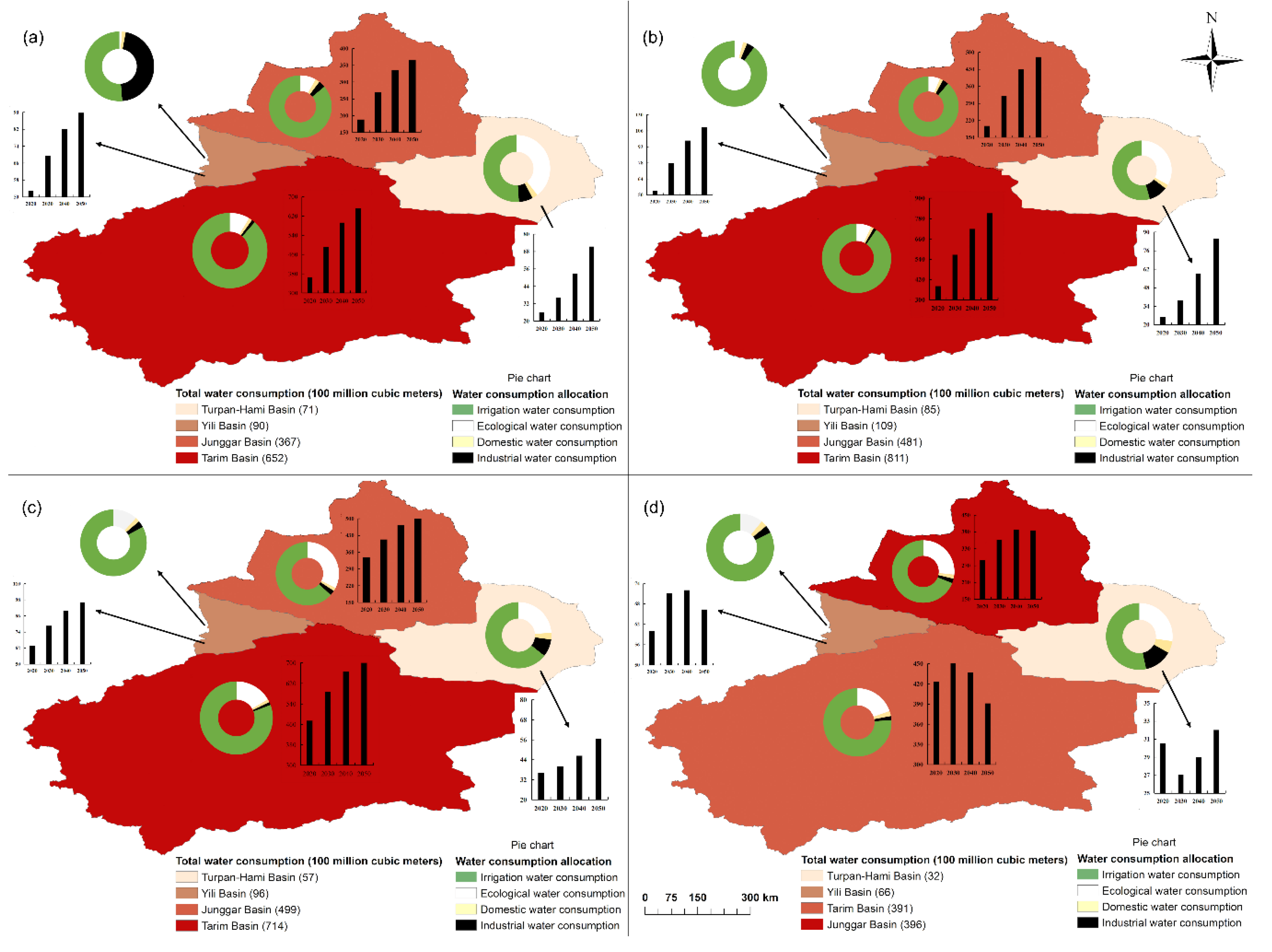
3.3. Simulation and Prediction under Different Scenarios
- Scenario 1
- Scenario 2
- Scenario 3
- Scenario 4
3.4. Decision Support on Sustainable Use of Water Resources
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gain, A.; Giupponi, C.; Wada, Y. Measuring global water security towards sustainable development goals. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 124015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yu, H.; Dai, A.; Wei, Y.; Kang, L. Drylands face potential threat under 2 °C global warming target. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, T.; Gerlak, A.; Giuliani, G. Explaining and Measuring Social-Ecological Pathways: The Case of Global Changes and Water Security. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Tang, J.; Wei, C. Understanding temporal and spatial complexity of precipitation distribution in Xinjiang, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 123, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. Simulating the precipitation in the data-scarce Tianshan Mountains, Northwest China based on the Earth system data products. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M. Water Resources and Sustainable Utilization in Xinjiang; China Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M. Macro-economy layout and water strategy in Xinjiang. Arid Land Geogr. 2006, 29, 617–624. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M. Studies on water resources strategy in Xinjiang. China Water Resour. 2009, 17, 23–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Cycle Mechanism and Water Resources Security in the Arid Region of Northwest China. China Basic Sci. 2015, 2, 17–23. Available online: CNKI:SUN:ZGJB.0.2015-02-003 (accessed on 25 November 2020). (In Chinese).
- Costanza, R.; Rudolf, d.; Braat, L.; Kubiszewski, I.; Fioramonti, L.; Sutton, P.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M. Twenty years of ecosystem services: How far have we come and how far do we still need to go? Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Saghafian, B.; Golian, S. System dynamics approach for simulating water resources of an urban water system with emphasis on sustainability of groundwater. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghashghaie, M.; Marofi, S.; Marofi, H. Using System Dynamics Method to Determine the Effect of Water Demand Priorities on Downstream Flow. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 5055–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Kerachian, R.; Zahraie, B. Monthly water resources and irrigation planning: Case study of conjuctive use of surface and groundwater resources. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2004, 130, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, T.; Kluser, S. Water security as a normative goal or as a structural principle for water governance. In A Critical Approach to International Water Management Trends: Policy and Practice; Palgrave Studies in Water Governance: Policy and Practice; Palgrave MacMillan: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dadson, S.; Hall, J.; Garrick, D.; Sadoff, C.; Grey, D.; Whittington, D. Water security, risk, and economic growth: Insights from a dynamical systems model. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 6425–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotino, S.; Sechi, G.; Zuddas, P. A DSS for water resources management under uncertainty by scenario analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagstad, K.; Semmens, D.; Waage, S.; Winthrop, R. A comparative assessment of decision-support tools for ecosystem services quantification and valuation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, T.; Saracino, A.; Sugg, Z.; Thompson, B.; Martinez, J. Evaluating the Use of Data Platforms for Water Management Decisions; Water in the West; Stanford Digital Repository: Stanford, CA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://purl.stanford.edu/cb612zf3515 (accessed on 31 October 2020).
- Flörke, M.; Schneider, C.; McDonald, R. Water Competition between Cities and Agriculture Driven by Climate Change and Urban Growth. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, J.; Noble, D.; Weatherhead, E. Optimization Model for Alternative Use of Different Quality Irrigation Waters. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1992, 118, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Imura, H. Towards Sustainable Urban Water Resource Management: A Case Study in Tianjin, China. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 9, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazilian, M.; Rogner, H.; Howells, M.; Hermann, S.; Arent, D.; Gielen, D.; Steduto, P.; Mueller, A.; Komor, P.; Tol, R.; et al. Considering the Energy, Water and Food Nexus: Towards an Integrated Modelling Approach. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 7896–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. A General Framework for Analyzing Sustainability of Social-Ecological Systems. Science 2009, 325, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Beck, M.; Hall, J.; Dawson, R.; Heidrich, O. The Energy-Water-Food Nexus: Strategic Analysis of Technologies for Transforming the Urban Metabolism. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 141, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Wang, Y. The Water Resource Sustainable Utilization of Henan Province Based on System Dynamics. J. Irrig. Drain. 2010, 29, 34–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozbahani, R.; Schreider, S.; Abbasi, B. Optimal Water Allocation through a Multi-Objective Compromise between Environmental, Social, and Economic Preferences. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 64, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, Q.; Li, S. An Optimal Water Allocation Model Based on Water Resources Security Assessment and Its Application in Zhangjiakou Region, Northern China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 69, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, A.; Mylopoulos, N.; Vasiliades, L. A Modeling System for the Evaluation of Water Resources Management Strategies in Thessaly, Greece. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1673–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, Y.; Makropoulos, C.; Mimikou, M. Decision support for agriculture water management. Glob. Nest J. 2012, 14, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Ganji, A.; Khalili, D.; Karamouz, M. Development of Stochastic Dynamic Nash Game Model for Reservoir Operation. I. The Symmetric Stochastic Model with Perfect Information. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mianabadi, H.; Mostert, E.; Zarghami, M.; Giesen, N. A New Bankruptcy Method for Conflict Resolution in Water Resources Allocation. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 144, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Tian, J. Complex Adaptive System on Water Resources Allocation System. J. Appl. Sci. 2013, 13, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Guo, S.; Xu, C.; Liu, D.; Chen, L.; Ye, Y. Integrated Optimal Allocation Model for Complex Adaptive System of Water Resources Management (I): Methodologies. J. Hydrol. 2015, 531, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotir, J.; Smith, C.; Brown, G.; Marshall, N.; Johnstone, R. A System Dynamics Simulation Model for Sustainable Water Resources Management and Agricultural Development in the Volta River Basin, Ghana. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, A.; Prasher, S.; Adamowski, J.; Gleeson, T. A System Dynamics Model to Conserve Arid Region Water Resources through Aquifer Storage and Recovery in Conjunction with a Dam. Water 2014, 6, 2300–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, N.; Shang, J.; Zhang, J. Sustainable Utilization of Water Resources in China: A System Dynamics Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 142, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, D.; Dong, H. Simulation study of the sustainable utilization of urban water resources based on system dynamics: A case study of Jiamusi. J. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2016, 16, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Lou, I.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y. A system dynamics urban water management model for Macau, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 50, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, H.; Zhang, B.; Meng, F. System dynamics modeling for sustainable water management of a coastal area in Shandong Province, China. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastelum, J.; Valdes, J.; Stewart, S. A system dynamics model to evaluate temporary water transfers in the Mexican Conchos basin. J. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1285–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehlke, G.; Jacobson, J. System dynamics modeling of transboundary system: The bear river basin model. J. Groundw. 2005, 43, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, D.; Huang, W. Based on system dynamic incentive mechanism research of the water-saving-type city. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2010, 27, 10–13. Available online: CNKI:SUN:CJKB.0.2010-06-004 (accessed on 25 November 2020). (In Chinese).
- Stave, K. A system dynamics model to facilitate public understanding of water management options in Las Vegas Nevada. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 67, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Aghakouchak, A.; Phillips, T. Changes in Concurrent Monthly Precipitation and Temperature Extremes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1402–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prein, A.; Holland, G.; Rasmussen, R.; Clark, M.; Tye, M. Running Dry: The U.S. Southwest’s Drift into a Drier Climate State. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, J.; Anderies, J.; Baggio, J.; Hodbod, J.; Huet, S.; Janssen, M.; Milkoreit, M.; Schoon, M. Exploring Non-Linear Transition Pathways in Social-Ecological Systems. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Xinjiang Water Resources Bulletin in 2014; Xinjiang Water Resources Department: Urumqi, China, 2015. (In Chinese)
- The Xinjiang Water Resources Bulletin in 2015; Xinjiang Water Resources Department: Urumqi, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- The Xinjiang Water Resources Bulletin in 2016; Xinjiang Water Resources Department: Urumqi, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Deng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Development trend of water supply and water demand in the north of the Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang. Arid Land Geogr. 2010, 3, 3. Available online: CNKI:SUN:GHDL.0.2010-03-001 (accessed on 25 November 2020). (In Chinese).
- Kang, S.; Hao, X.; Du, T.; Tong, L.; Su, X.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Huo, Z.; Li, S.; Ding, R. Improving agricultural water productivity to ensure food security in China under changing environment: From research to practice. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Tiwari, K. Okra Crop Response Under Subsurface Drip and Conventional Furrow Irrigation with Varying N Fertilization. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 2429–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porkka, M.; Gerten, D.; Schaphoff, S.; Siebert, S.; Kummu, M. Causes and trends of water scarcity in food production. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Song, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Kang, Y.; Sun, W. Past and future changes in regional crop water requirements in Northwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 137, 2203–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gao, L.; Ren, H.; Ye, Y.; Li, A.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Connor, J.; Wu, J.; Bryan, B. China’s progress towards sustainable land development and ecological civilization. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Shen, Y. Water and ecological security: Dealing with hydroclimatic challenges at the heart of China’s Silk Road. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Tao, S.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Impacts of climate change and irrigation on lakes in arid northwest China. J. Arid Environ. 2018, 154, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H.; Gou, S. Water shortages raised a legitimate concern over the sustainable development of the drylands of northern China: Evidence from the water stress index. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Nie, Q.; Song, C.; Wei, C. Integrating Wavelet Analysis and BPANN to Simulate the Annual Runoff with Regional Climate Change: A Case Study of Yarkand River, Northwest China. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2523–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Deng, M.; Li, Q.; Wufu, A.; Wang, D.; Ma, L. Estimation of regional irrigation water requirements and water balance in Xinjiang, China during 1995–2017. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Statistics Bureau of China. China Statistical Yearbook in 2018; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- Statistics Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region Statistical Yearbook in 2019; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- Statistical Bureau of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps. Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps Statistical Yearbook in 2018; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- Sterman, J. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Forrester, J. World Dynamics; Wright-Allen Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Mathematical Methods in Contemporary Geography; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhao, C.; Fan, B.; Zhu, S. Analysis of impact factor of domestic water in rural area based on gray model. J. Water Resour.Water Eng. 2013, 24. Available online: CNKI:SUN:XBSZ.0.2013-05-011 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- The Thirteenth Five-Year Plan for Modern Agriculture in Xinjiang; Department of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of Xinjiang: Urumqi, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- The Thirteenth Five-Year Plan for New Industrialization in Xinjiang; The Government of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region: Urumqi, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. Response of Ecological Water Requirment to Land Use Change in the Newly Reclaimed Area of Ili River Basin in Xinjiang. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 551–557. Available online: CNKI:SUN:ZGSS.0.2012-02-040 (accessed on 25 November 2020). (In Chinese).
- Wang, C.; Yen, G.; Jiang, M. A grey prediction-based evolutionary algorithm for dynamic multiobjective optimization. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2020, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hao, X.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, R. An analysis of the Ecological Security and Ecological Water Requirements in the Inland River Basin of Arid Region. Adv. Earth Sci. 2008, 23, 732–738. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B. Calculation and Forecast of Ecological Water Demand and Consumption for Floodplain Forest in Arid Area; Tsinghua University: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Katz, D. Let There Be Water: Israel’s Solution for a Water-Starved World. Water Econ. Policy 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N. High-efficient water-saving irrigation development and 13th Five-Year Plan in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. China Water Resour. 2018, 13, 36–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Study on the Influence of the Change of Water Resources and Its Impact on Ecological Security in the Arid: An Example of Ebinur Lake Basin in Xinjiang; Xinjiang University: Urumqi, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Academy of Sciences. Available online: http://www.cas.cn/xw/zjsd/200906/t20090608_641668.shtml (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Zhu, J. Israel’s agricultural miracle: Water-saving irrigation to create a desert oasis. Henan Water Resour. South North Water Divers. 2003, 62–63. (In Chinese). Available online: CNKI:SUN:HNBD.0.2013-06-035 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- McDonald, R.; Weber, K.; Padowski, J.; Flörke, M.; Schneider, C.; Green, P.; Gleeson, T.; Eckman, S.; Lehner, B.; Balk, D.; et al. Water on an Urban Planet: Urbanization and the Reach of Urban Water Infrastructure. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 27, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J. Effects of Different Irrigation Methods on Yield Formation and Water Use Efficiency of Cotton in Xinjiang; Shihezi University: Urumqi, China. [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.; Anderies, J.; Ostrom, E. Robustness of Social-Ecological Systems to Spatial and Temporal Variability. Soc. Nat. Resourc. 2007, 20, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
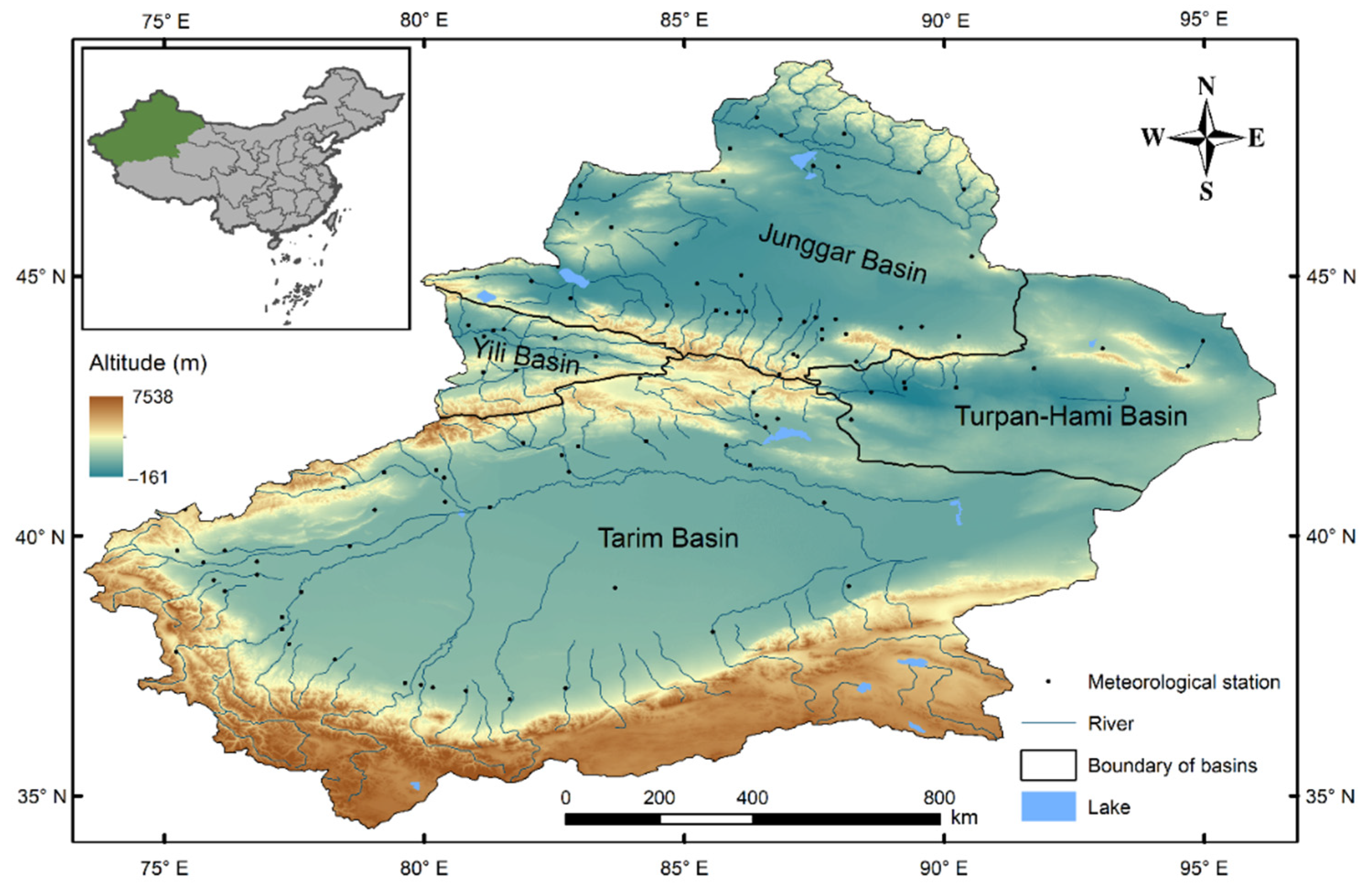

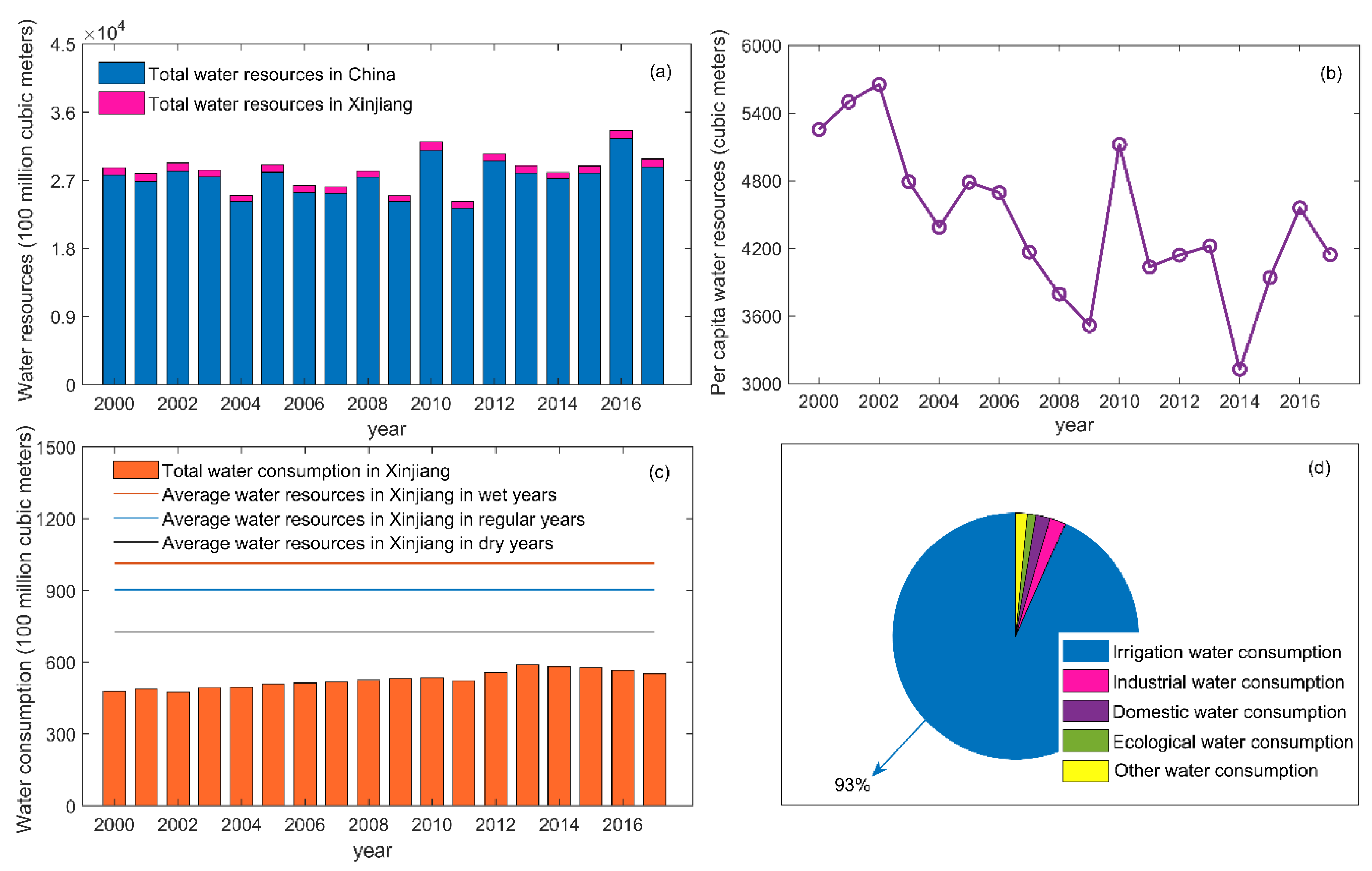
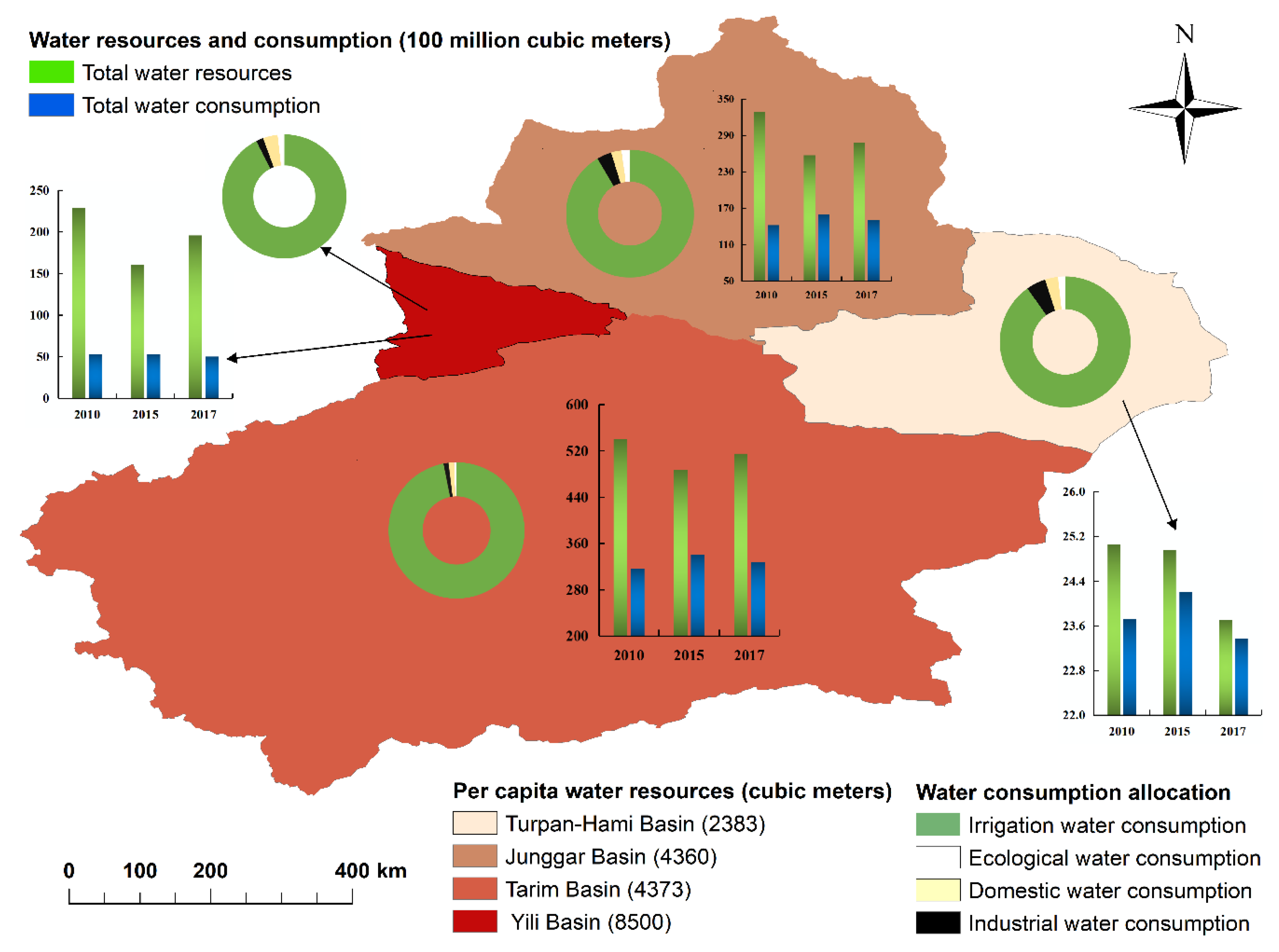
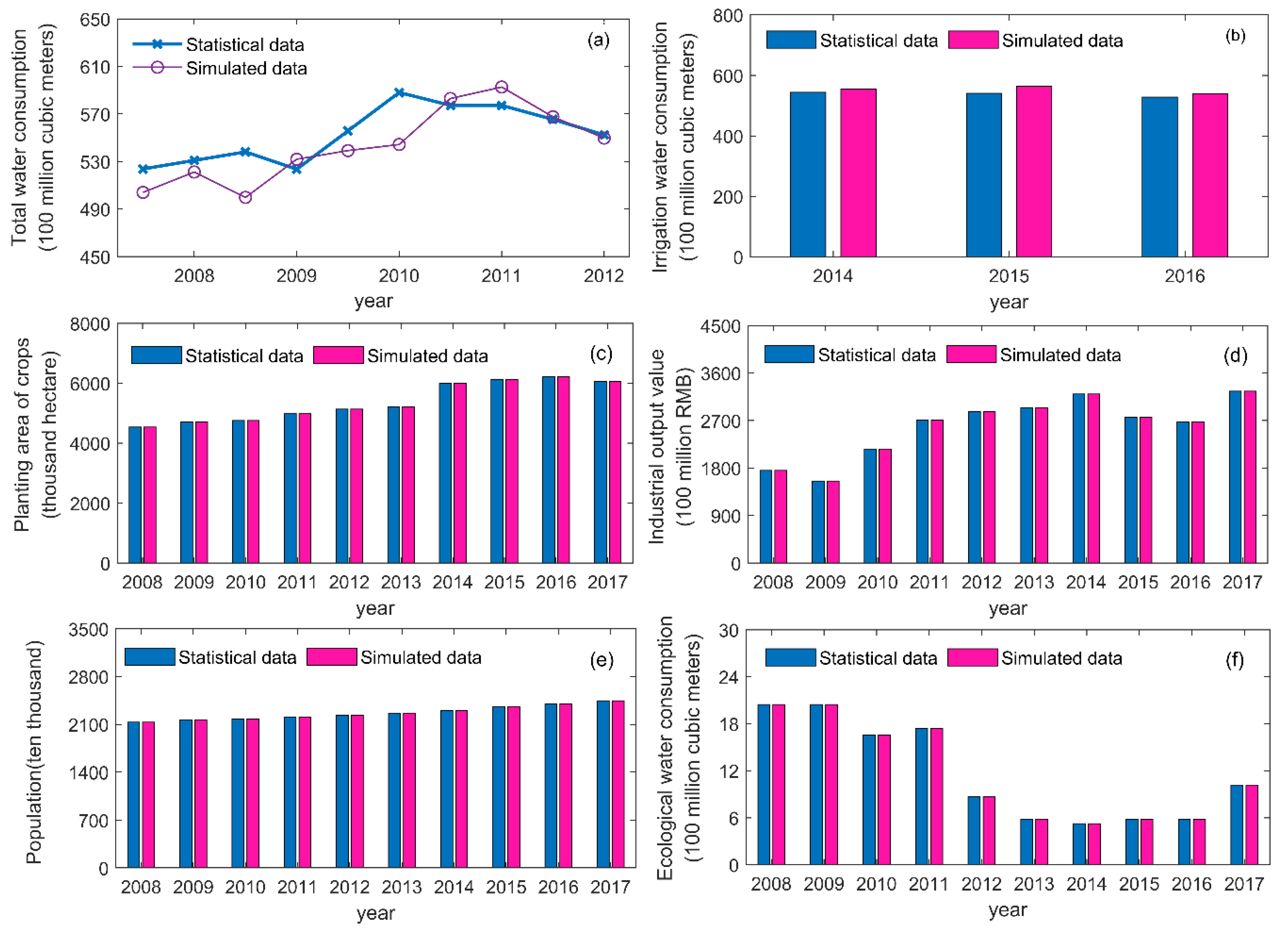

| Sub-Regions | Scope |
|---|---|
| Yili Basin | Counties (Cities) Direct Under Ili Prefecture except Kuytun City, Division 4 of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps |
| Junggar Basin | Urumqi City, Karamay City, Shihezi City, Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Tacheng Administrative Offices, Altay Administrative Offices, Bortala Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, Kuytun City, Division 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11 of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps |
| Turpan-Hami Basin | Turpan City, Hami City, Division 12 and 13 of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps |
| Tarim Basin | Bayangol Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, Kizilsu Kirgiz Autonomous Prefecture, Aksu Administrative Offices, Kashgar Administrative Offices, Hotan Administrative Offices, Division 1, 2, 3, and 14 of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps |
| Parameters | Sensitivity |
|---|---|
| Population growth rate (%) | 0.05 |
| Urbanization rate (%) | 0.10 |
| Water price change rate (%) | 0.01 |
| Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 0.03 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 0.20 |
| Industrial output growth rate (%) | 0.10 |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 0.39 |
| Crop planting area growth rate (%) | 0.27 |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate (%) | 0.24 |
| Scenario | Decision Variable | 2020 | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 89.5 | 89.5 | 89.5 | 89.5 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 40.7 | 40.4 | 40.2 | 40 | |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 8500 | 8000 | 7500 | 7000 | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.520 | 0.610 | 0.680 | 0.730 | |
| Crop planting area growth rate | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.020 | 0.010 | |
| Industrial output value growth rate | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.010 | 0.006 | |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate | 0.120 | 0.050 | 0.020 | 0.010 | |
| Scenario 2 | Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 89.5 | 89.5 | 89.5 | 89.5 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 40.7 | 40.4 | 40.2 | 40 | |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 8500 | 8000 | 7500 | 7000 | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.624 | 0.732 | 0.816 | 0.876 | |
| Crop planting area growth rate | 0.056 | 0.042 | 0.028 | 0.014 | |
| Industrial output value growth rate | 0.042 | 0.021 | 0.014 | 0.008 | |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate | 0.120 | 0.050 | 0.020 | 0.010 | |
| Scenario 3 | Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 89.5 | 89.5 | 89.5 | 89.5 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 40.7 | 40.4 | 40.2 | 40 | |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 8500 | 8000 | 7500 | 7000 | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.520 | 0.610 | 0.680 | 0.730 | |
| Crop planting area growth rate | 0.040 | 0.030 | 0.020 | 0.010 | |
| Industrial output value growth rate | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.010 | 0.006 | |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate | 0.320 | 0.280 | 0.240 | 0.180 | |
| Scenario 4 | Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 85 | 80 | 75 | 70 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 39 | 35 | 32 | 28 | |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 8500 | 7300 | 6000 | 5000 | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.541 | 0.641 | 0.714 | 0.767 | |
| Crop planting area growth rate | 0.042 | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.011 | |
| Industrial output value growth rate | 0.032 | 0.016 | 0.011 | 0.006 | |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate | 0.220 | 0.190 | 0.150 | 0.110 |
| Region | Decision Variable | 2020 | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xinjiang | Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 85 | 80 | 75 | 70 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 39 | 35 | 32 | 28 | |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 8500 | 7300 | 6000 | 5000 | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.541 | 0.641 | 0.714 | 0.767 | |
| Crop planting area growth rate | 0.042 | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.011 | |
| Industrial output value growth rate | 0.032 | 0.016 | 0.011 | 0.006 | |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate | 0.220 | 0.190 | 0.150 | 0.110 | |
| Yili Basin | Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 105 | 95 | 85 | 75 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 70 | 67 | 60 | 54 | |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 7500 | 7000 | 6000 | 5000 | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.420 | 0.473 | 0.536 | 0.599 | |
| Crop planting area growth rate | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.011 | 0.005 | |
| Industrial output value growth rate | 0.042 | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.011 | |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate | 2.120 | 2.790 | 4.950 | 5.050 | |
| Junggar Basin | Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 105 | 95 | 85 | 75 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 29 | 26 | 23 | 21 | |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 6200 | 6000 | 5500 | 5000 | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.788 | 0.861 | 0.903 | 0.935 | |
| Crop planting area growth rate | 0.042 | 0.032 | 0.011 | 0.005 | |
| Industrial output value growth rate | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.011 | 0.001 | |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate | 0.120 | 0.190 | 0.250 | 0.310 | |
| Turpan-Hami Basin | Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 130 | 130 | 120 | 110 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 50 | 50 | 48 | 43 | |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 10000 | 7000 | 6000 | 5000 | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.840 | 0.861 | 0.882 | 0.893 | |
| Crop planting area growth rate | 0.011 | 0.021 | 0.021 | 0.032 | |
| Industrial output value growth rate | 0.021 | 0.024 | 0.043 | 0.062 | |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate | 0.420 | 0.150 | 0.080 | 0.050 | |
| Tarim Basin | Rural domestic water quota (L/(person·day)) | 65 | 60 | 55 | 50 |
| Water consumption per industrial output value of ten thousand Yuan (m3) | 50 | 49 | 45 | 40 | |
| Irrigation water quota (m3/hectare) | 9600 | 8000 | 6300 | 5000 | |
| Urbanization rate | 0.399 | 0.452 | 0.515 | 0.567 | |
| Crop planting area growth rate | 0.035 | 0.021 | 0.011 | 0.005 | |
| Industrial output value growth rate | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.011 | 0.006 | |
| Ecological water consumption growth rate | 0.290 | 0.163 | 0.067 | 0.039 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Tian, S. How to Sustainably Use Water Resources—A Case Study for Decision Support on the Water Utilization of Xinjiang, China. Water 2020, 12, 3564. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123564
Fan M, Xu J, Chen Y, Li D, Tian S. How to Sustainably Use Water Resources—A Case Study for Decision Support on the Water Utilization of Xinjiang, China. Water. 2020; 12(12):3564. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123564
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Mengtian, Jianhua Xu, Yaning Chen, Dahui Li, and Shasha Tian. 2020. "How to Sustainably Use Water Resources—A Case Study for Decision Support on the Water Utilization of Xinjiang, China" Water 12, no. 12: 3564. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123564
APA StyleFan, M., Xu, J., Chen, Y., Li, D., & Tian, S. (2020). How to Sustainably Use Water Resources—A Case Study for Decision Support on the Water Utilization of Xinjiang, China. Water, 12(12), 3564. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123564








