Trend and Variance of Continental Fresh Water Discharge over the Last Six Decades
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method and Dataset
2.1. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition
2.2. Global Discharge Dataset
2.3. Global Precipitation and Surface Air Temperature Datasets
3. Results
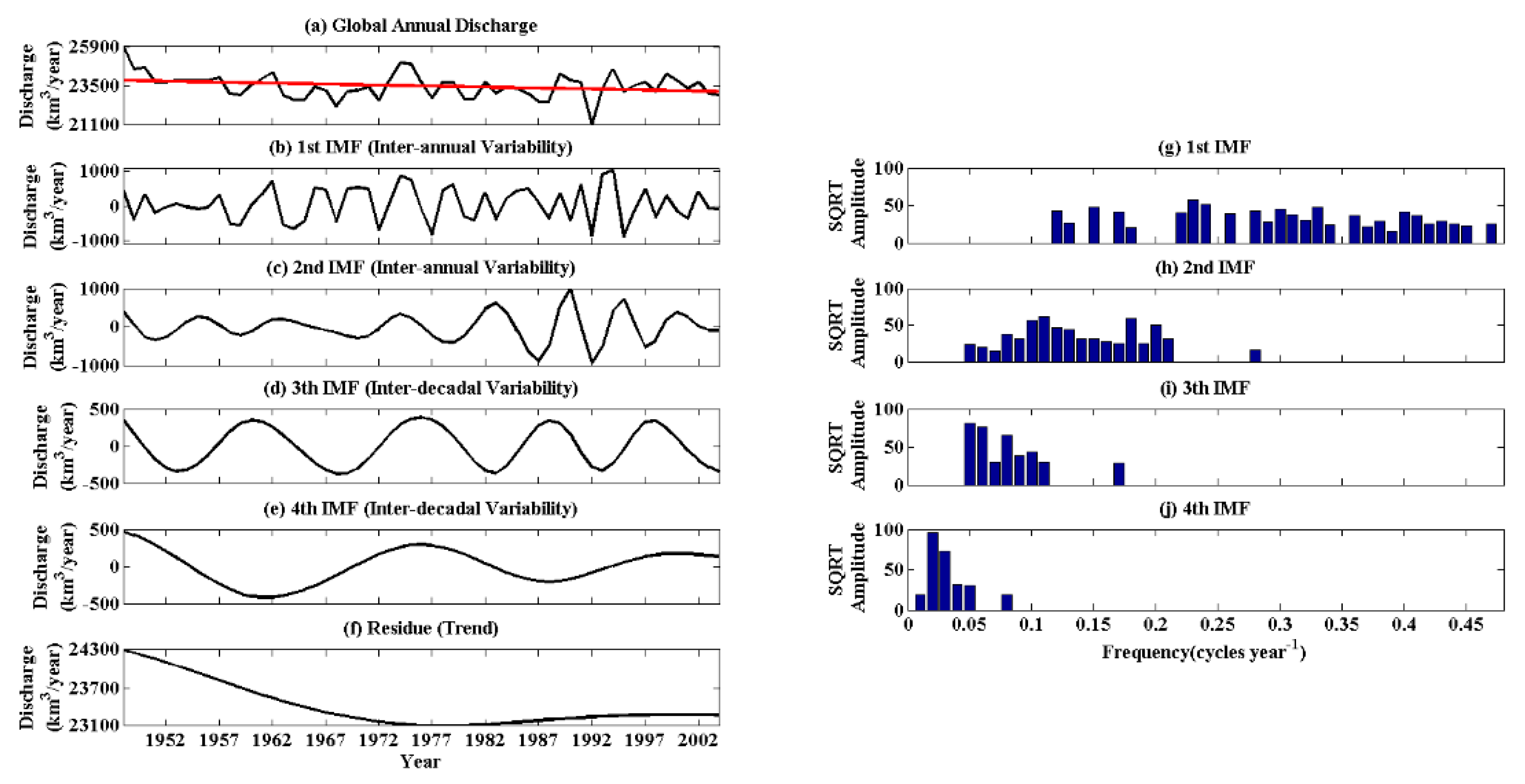
3.1. Global Continental Discharge Trend
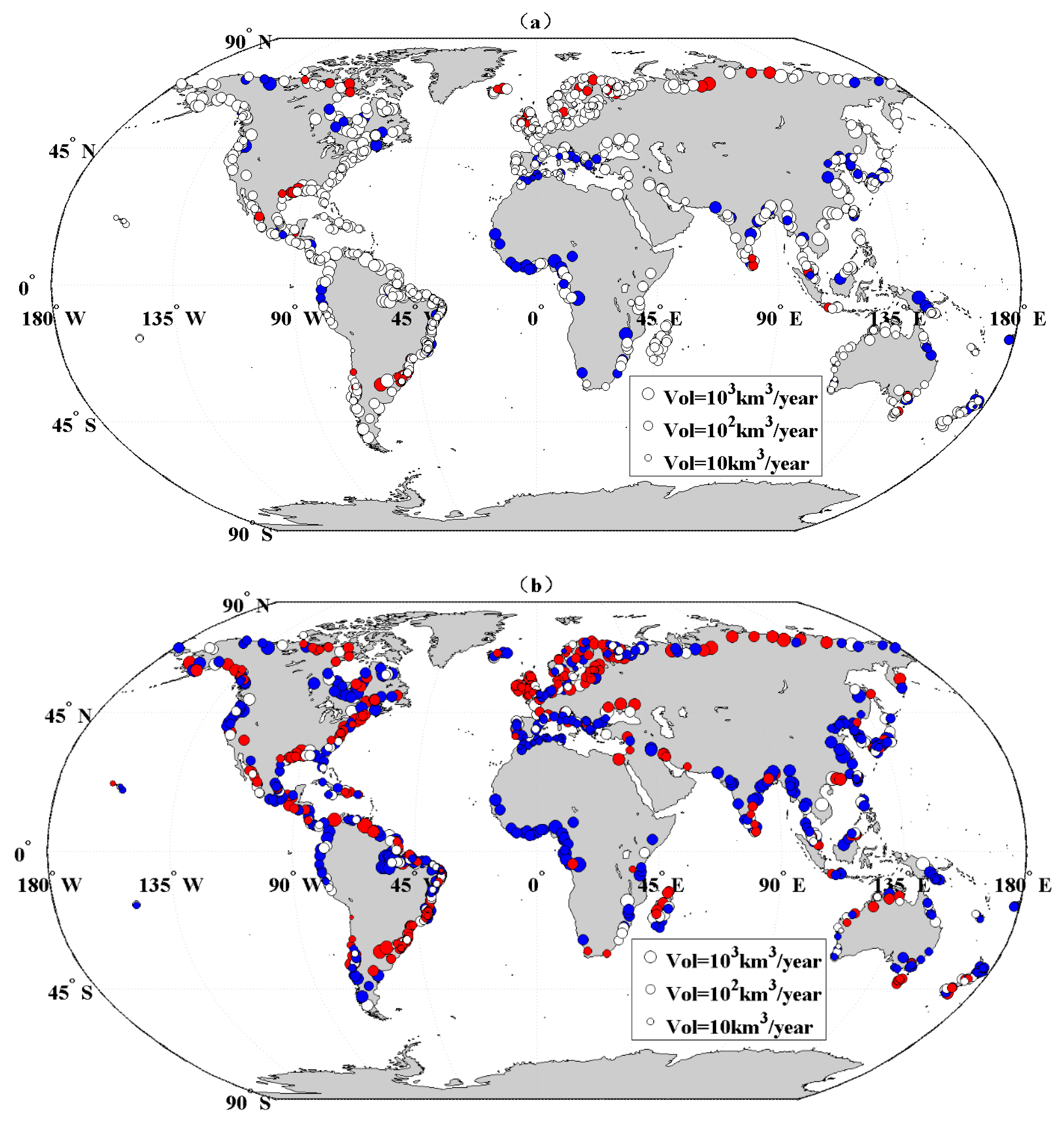
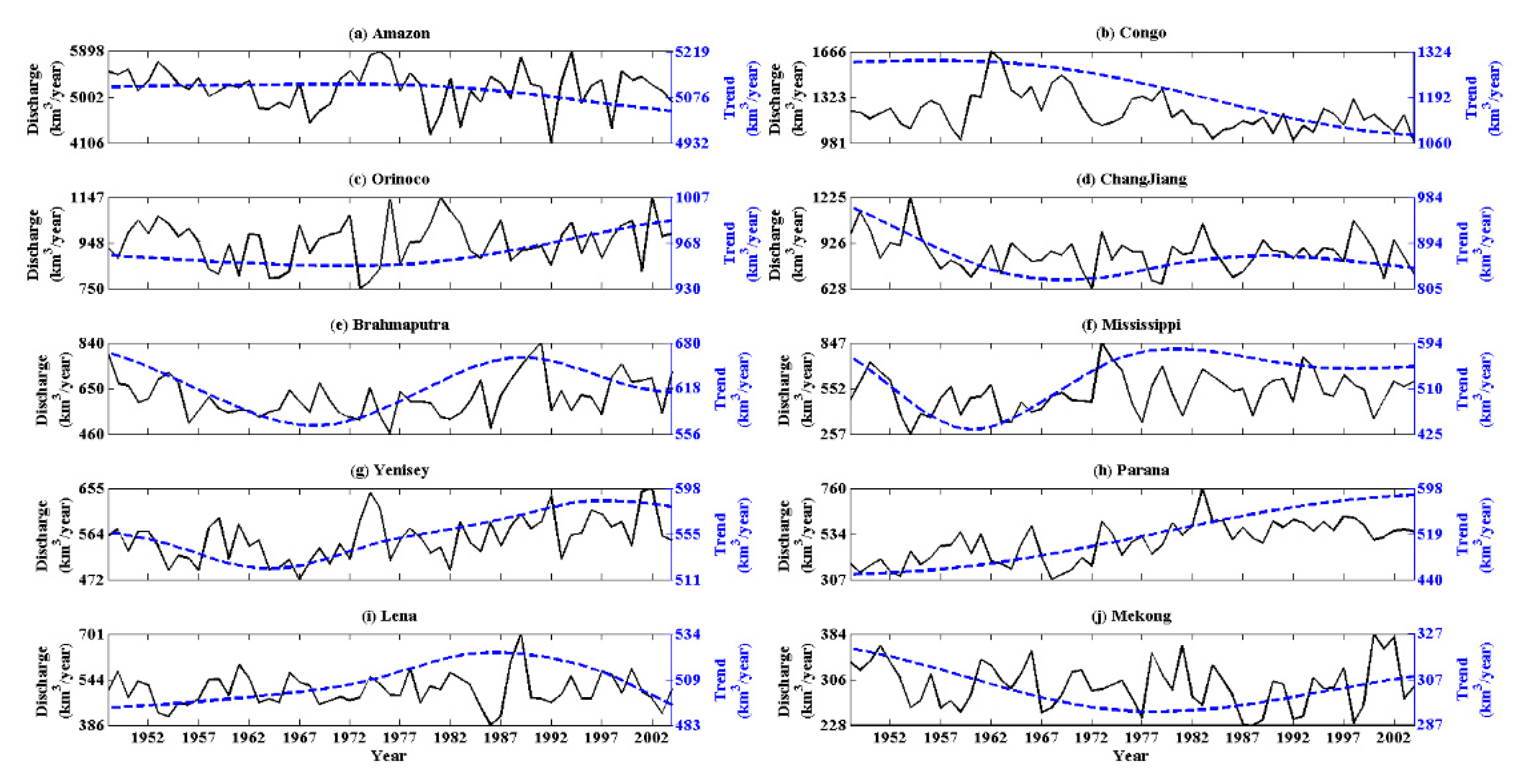
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Variation of River Discharge Trend from 1948 to 2004
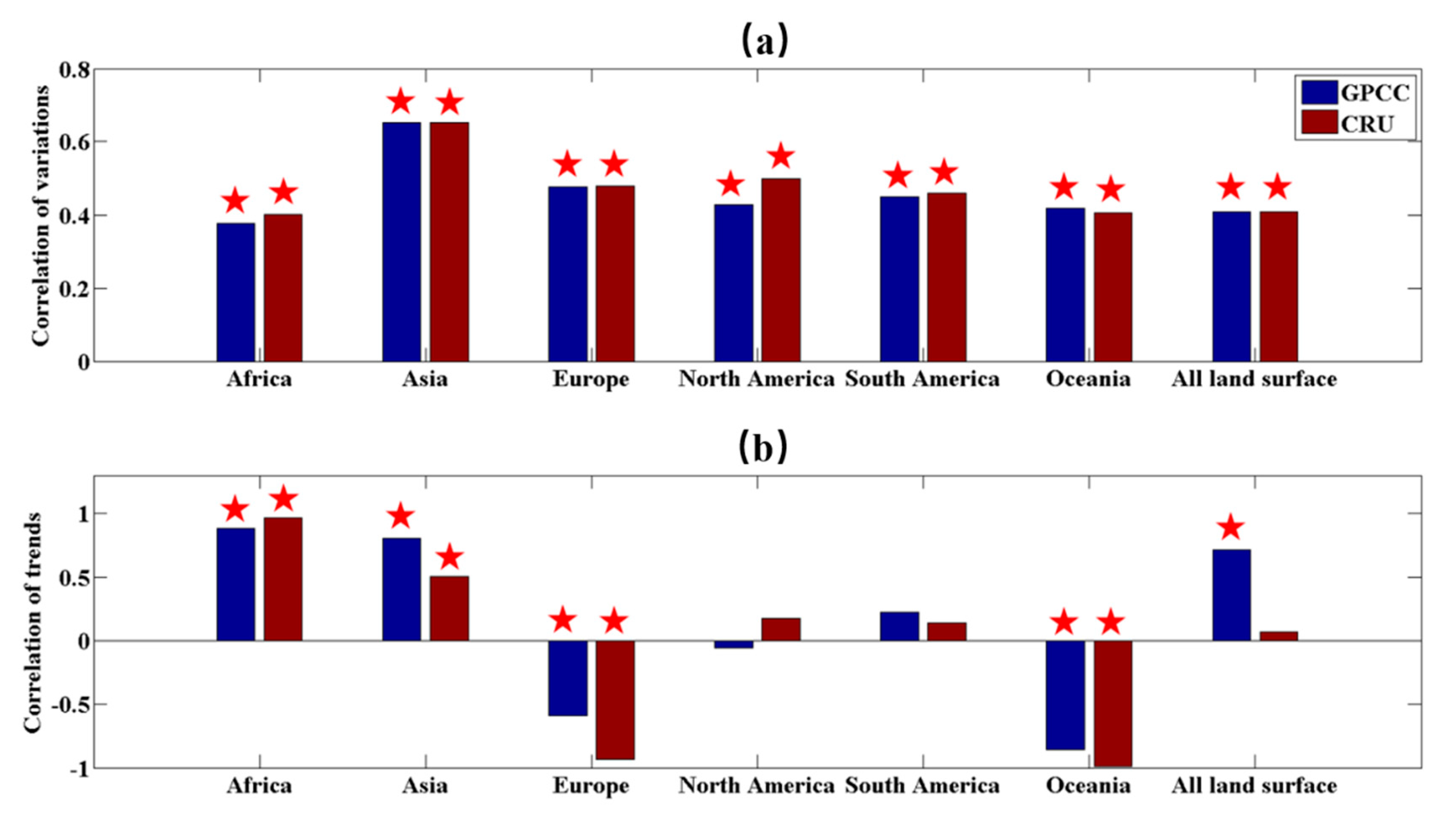
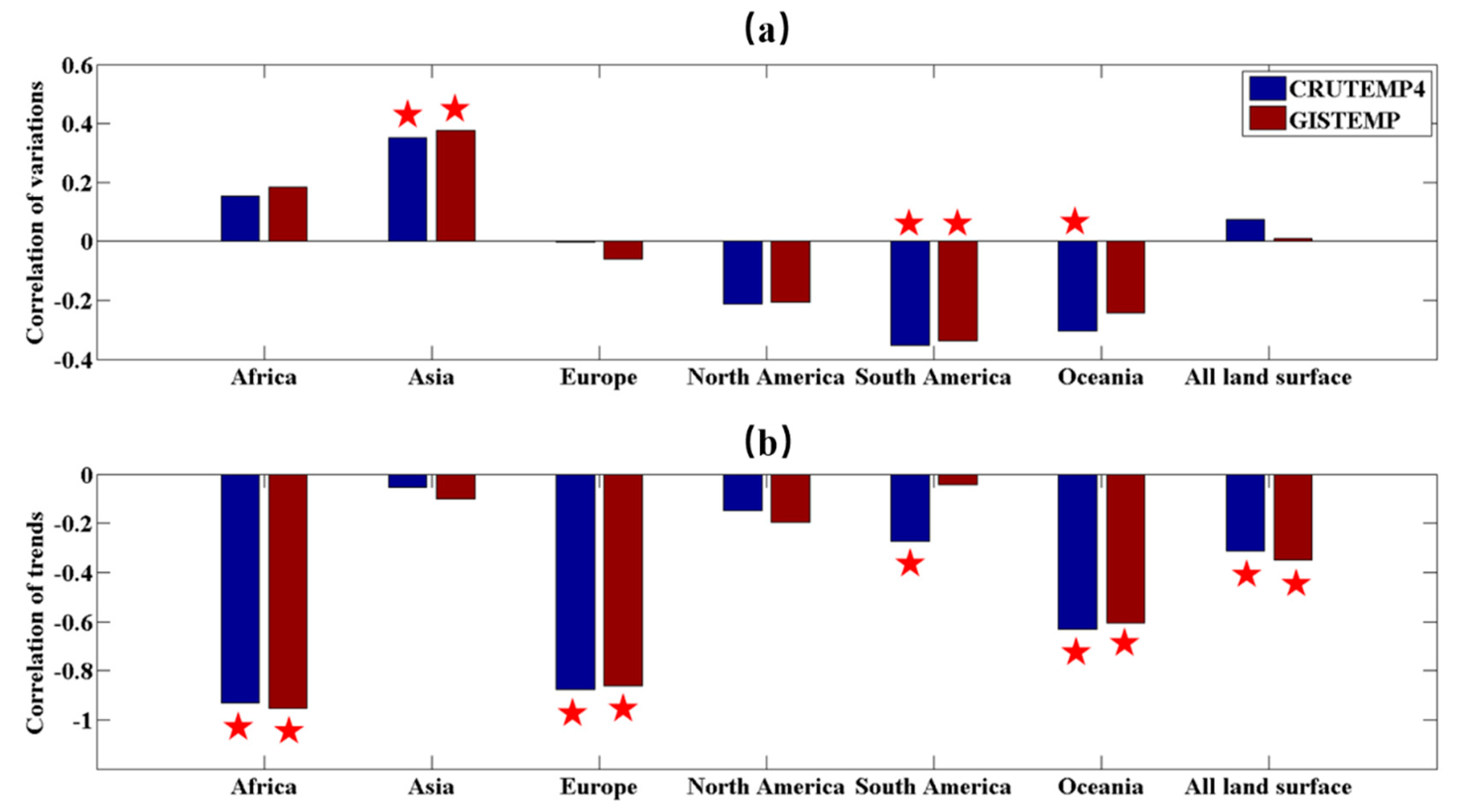
3.3. Influences of Changing Trend and Variance of P and T on the Trend and Variance of River Discharge
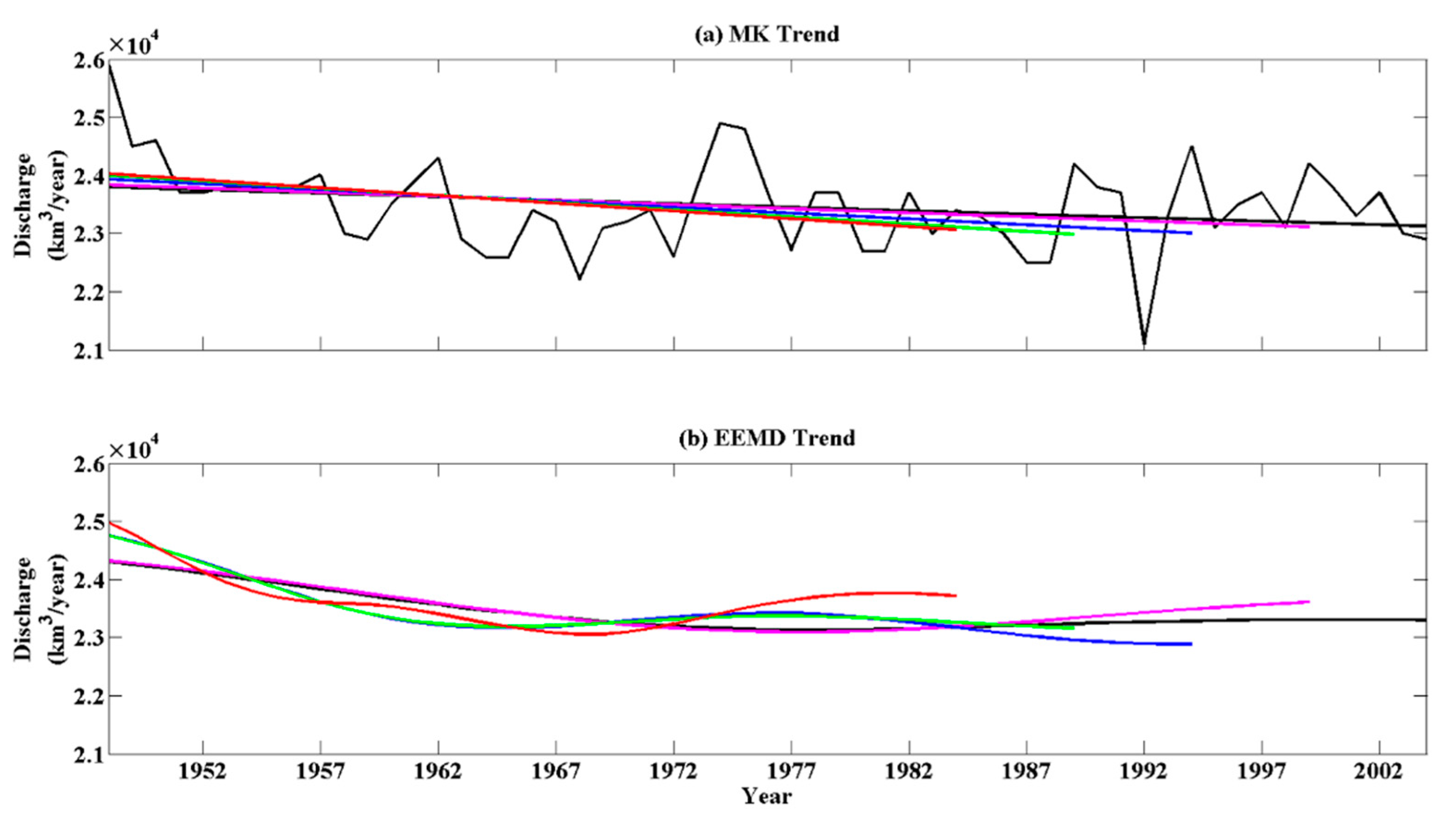
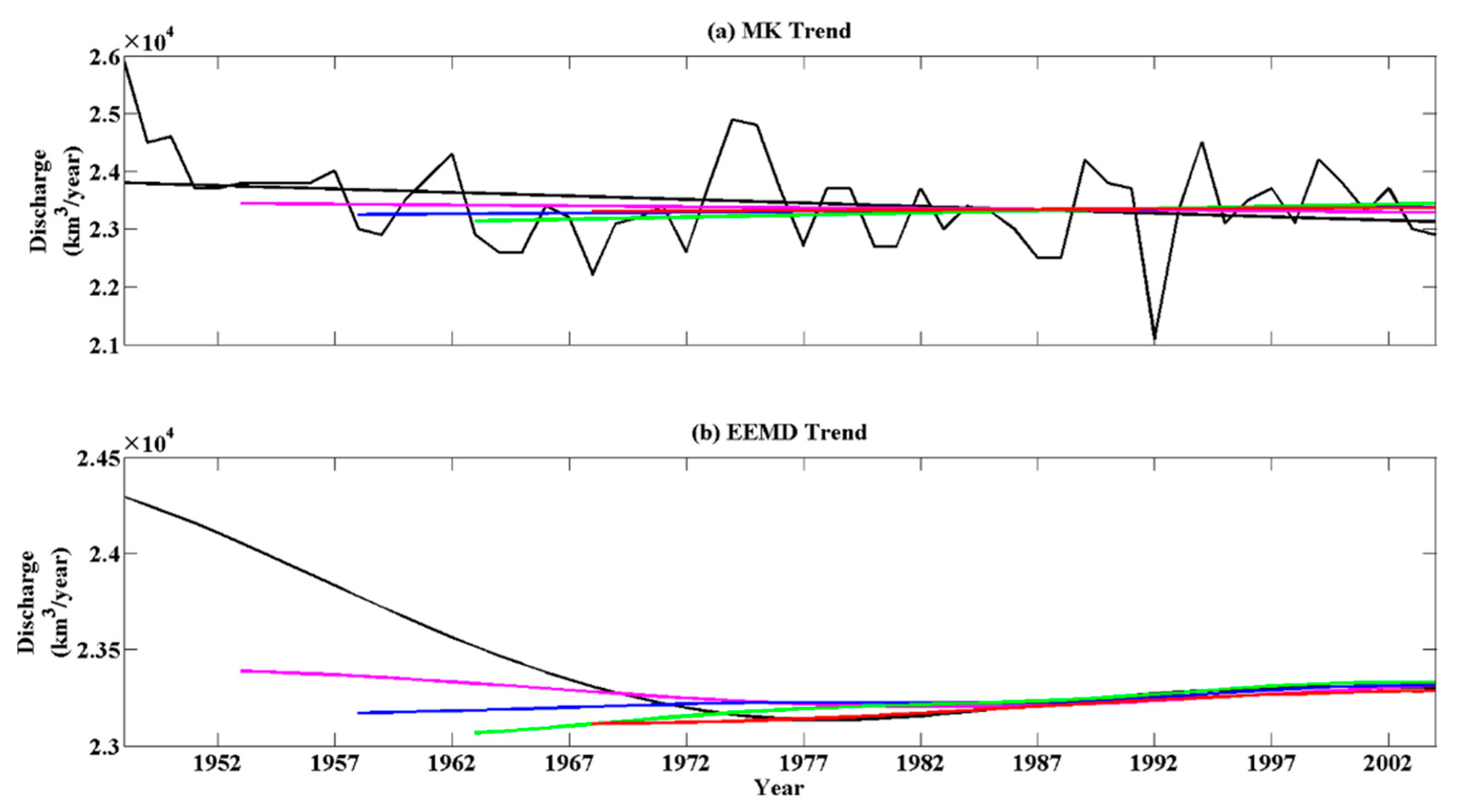
3.4. Sensitivity of the Estimated Global Continental Discharge to the Length of Data Record
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milly, P.C.; Dunne, K.A.; Vecchia, A.V. Global pattern of trends in streamflow and water availability in a changing climate. Nature 2005, 438, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, R.A.; Boucher, O.; Collins, M.; Cox, P.M.; Falloon, P.D.; Gedney, N.; Hemming, D.L.; Huntingford, C.; Jones, C.D.; Sexton, D.M.H.; et al. Projected increase in continental runoff due to plant responses to increasing carbon dioxide. Nature 2007, 448, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.; Betancourt, J.; Falkenmark, M.; Hirsch, R.M.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Stouffer, R.J. Stationarity is dead: Whither water management? Science 2008, 319, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labat, D.; Goddéris, Y.; Probst, J.L.; Guyot, J.L. Evidence for global runoff increase related to climate warming. Adv. Water Resour. 2004, 27, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Qian, T.; Trenberth, K.E.; Milliman, J.D. Changes in continental freshwater discharge from 1948–2004. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkama, R.; Kageyama, M.; Ramstein, G. Relative contributions of climate change, stomatal closure, and leaf area index changes to 20th and 21st century runoff change: A modelling approach using the organizing carbon and hydrology in dynamic ecosystems (ORCHIDEE) land surface model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkama, R.; Marchand, L.; Ribes, A.; Decharme, B. Detection of global runoff changes: Results from observations and CMIP5 experiments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2967–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; Lins, H.F.; McCabe, G.J. Comments on “Evidence for global runoff increase related to climate warming” by Labat et al. Adv. Water Resour. 2005, 28, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; McMahon, T.A. Recent frequency component changes in interannual climate variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Farnsworth, K.L.; Jones, P.D.; Xu, K.H.; Smith, L.C. Climatic and anthropogenic factors affecting river discharge to the global ocean, 1951–2000. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 62, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkama, R.; Decharme, B.; Douville, H.; Ribes, A. Trends in global and basin-scale runoff over the late twentieth century: Methodological issues and sources of uncertainty. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3000–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C. Comparison of the MK test and EMD method for trend identification in hydrological time series. J. Hydrol. 2014, 510, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E.; Long, S.R.; Peng, C.K. On the trend, detrending, and variability of nonlinear and nonstationary time series. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Grifin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Cavadias, G. Power of the Mann–Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J. Hydrol. 2002, 259, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H. Trend detection in hydrologic data: The Mann–Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Roderick, M.L.; Farquhar, G.D. Rainfall statistics, stationarity, and climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2305–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Miao, C.; Kong, D.; Duan, Q.; Lei, X.; Hou, Q.; Li, H. Long-term trends in global river flow and the causal relationships between river flow and ocean signals. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.E. Long-term storage capacity of reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The Empirical Mode Decomposition Method and the Hilbert Spectrum for Non-stationary Time Series Analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R. A new view of nonlinear water waves: The Hilbert spectrum. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1999, 31, 417–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Church, J.A.; Watson, C.S.; King, M.A.; Monselesan, D.; Legresy, B.; Harig, C. The increasing rate of global mean sea-level rise during 1993–2014. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Wu, Z.; Huang, J.; Chassignet, E.P. Evolution of land surface air temperature trend. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N.; Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Ji, F.; Pan, S. Increasing global vegetation browning hidden in overall vegetation greening: Insights from time-varying trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhamdi, F.; Poggi, J.M.; Jaïdane, M. Trend extraction for seasonal time series using ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Adv. Data Anal. 2011, 3, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, A.M.; Poveda, G. Detection of long-term trends in monthly hydro-climatic series of Colombia through Empirical Mode Decomposition. Clim. Chang. 2014, 123, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; New, M.G.; Parker, D.E.; Marun, S.; Rigor, I.G. Surface air temperature and its changes over the past 150 years. Rev. Geophys. 1999, 37, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Ruedy, R.; Glascoe, J.; Sato, M. GISS analysis of surface temperature change. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 30997–31022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Fung, I. Mapping and attribution of change in streamflow in the coterminous united states. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerten, D.; Rost, S.; von Bloh, W.; Lucht, W. Causes of change in 20th century global river discharge. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L20405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohara, D.; Kitoh, A.; Hosaka, M.; Oki, T. Impact of climate change on river discharge projected by multimodel ensemble. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Solomon, S.; Dai, A.; Portmann, R.W. How often will it rain? J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4801–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.; Tignor, M.M.B.; Miller, H.L., Jr.; Chen, Z. (Eds.) Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; p. 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccabe, G.J.; Wolock, D.M. Century-scale variability in global annual runoff examined using a water balance model. Int. J. Clim. 2011, 31, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijssen, B.; O’Donnell, G.M.; Hamlet, A.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Hydrologic sensitivity of global rivers to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2001, 50, 143–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedney, N.; Cox, P.M.; Betts, R.A.; Boucher, O.; Huntingford, C.; Stott, P.A. Detection of a direct carbon dioxide effect in continental river runoff records. Nature 2006, 439, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ciais, P.; Nobletducoudré, N.D.; Labat, D.; Zaehle, S. Changes in climate and land use have a larger direct impact than rising CO2 on global river runoff trends. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzke, C.L.E.; O’Kane, T.J.; Monselesan, D.P.; Risbey, J.S.; Horenko, I. Systematic attribution of observed Southern Hemisphere circulation trends to external forcing and internal variability. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2015, 2, 675–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddeland, I.; Heinke, J.; Biemans, H.; Eisner, S.; Flörke, M.; Hanasaki, N.; Konzmann, M.; Ludwig, F.; Masaki, Y.; Schewe, J.; et al. Global water resources affected by human interventions and climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.M.; Oleson, K.W.; Flanner, M.G.; Thornton, P.E.; Swenson, S.C.; Lawrence, P.J.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Z.-L.; Levis, S.; Sakaguchi, K.; et al. Parameterization improvements and functional and structural advances in version 4 of the Community Land Model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2011, 3, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Zhang, H. Trend and Variance of Continental Fresh Water Discharge over the Last Six Decades. Water 2020, 12, 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123556
Wang C, Zhang H. Trend and Variance of Continental Fresh Water Discharge over the Last Six Decades. Water. 2020; 12(12):3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123556
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chen, and Hui Zhang. 2020. "Trend and Variance of Continental Fresh Water Discharge over the Last Six Decades" Water 12, no. 12: 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123556
APA StyleWang, C., & Zhang, H. (2020). Trend and Variance of Continental Fresh Water Discharge over the Last Six Decades. Water, 12(12), 3556. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123556




