An Integrated Use of GIS, Geostatistical and Map Overlay Techniques for Spatio-Temporal Variability Analysis of Groundwater Quality and Level in the Punjab Province of Pakistan, South Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
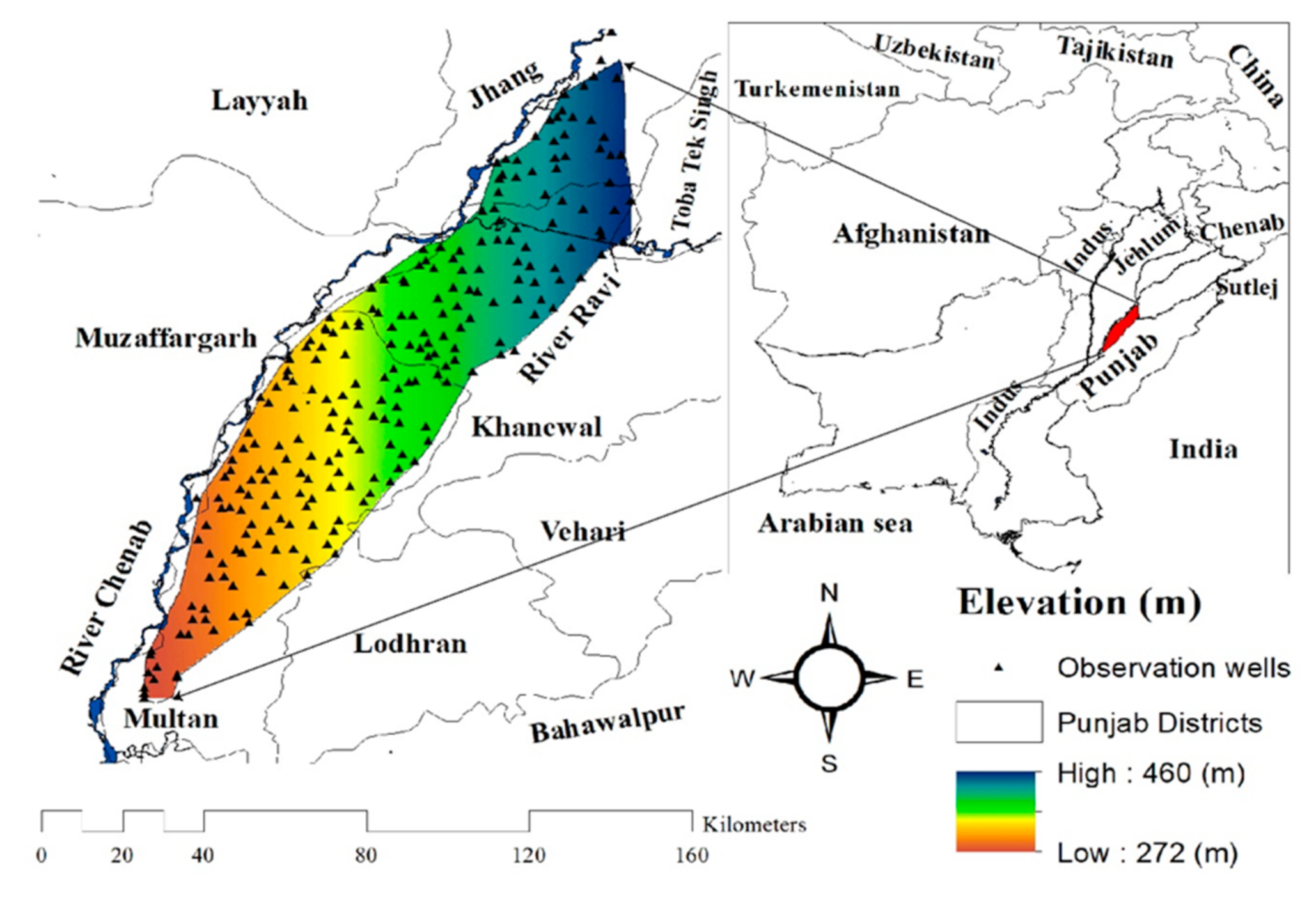
2.1. Appearances of Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
2.3. Spatial Variability Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Spearman’s Rank Corelation Coefficient
3.2. Spatial Modelling of Groundwater Parameters
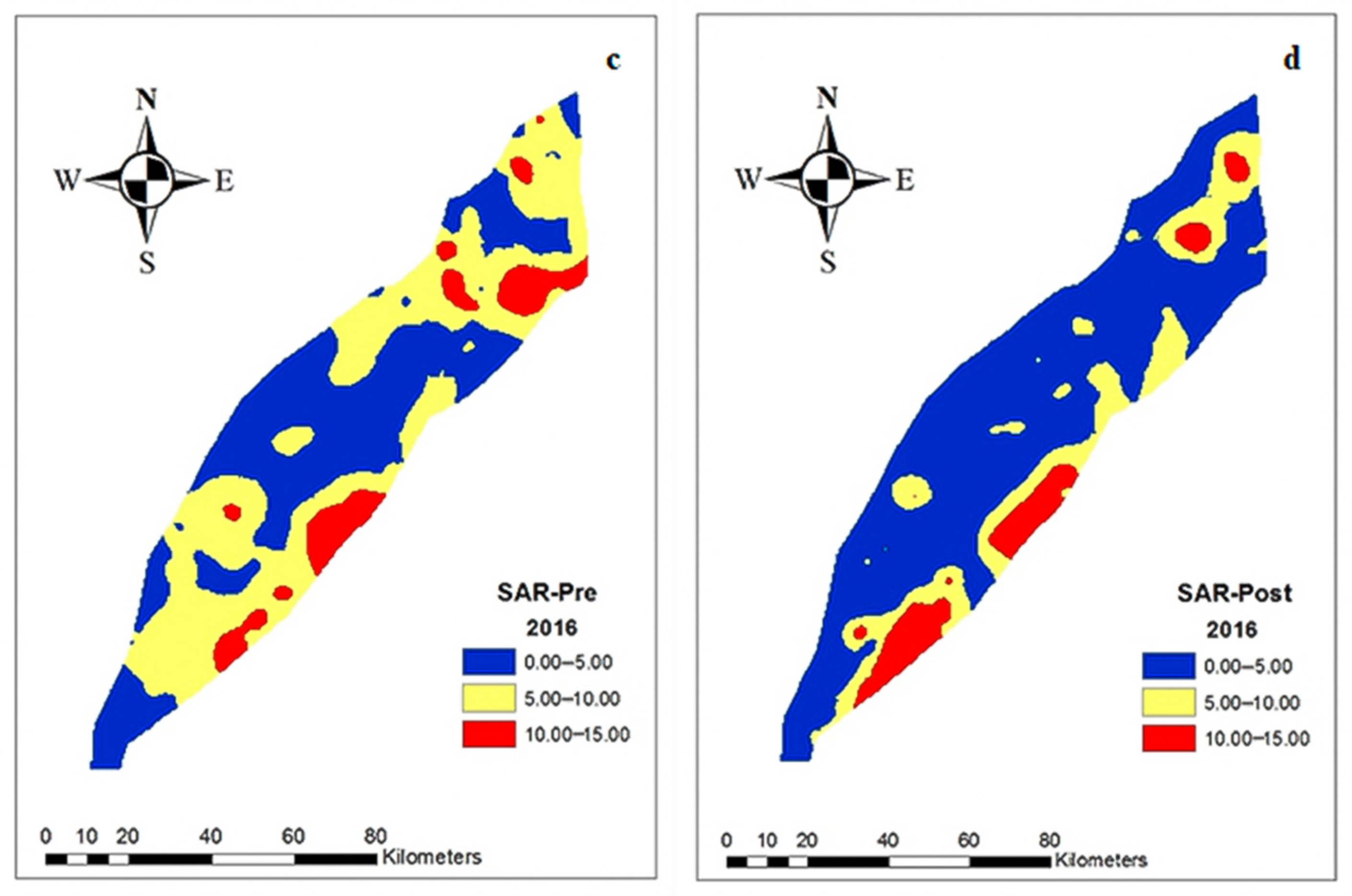
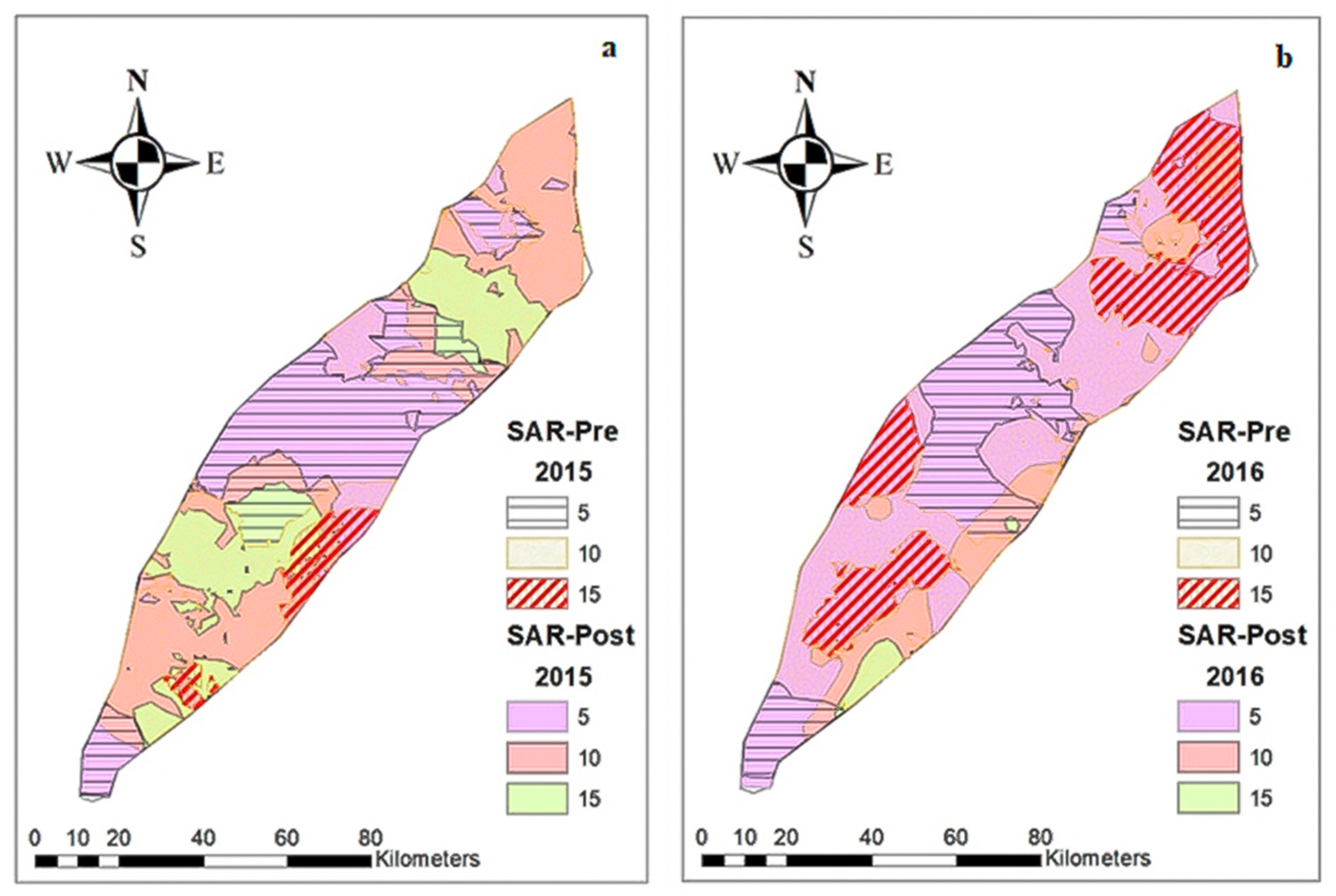
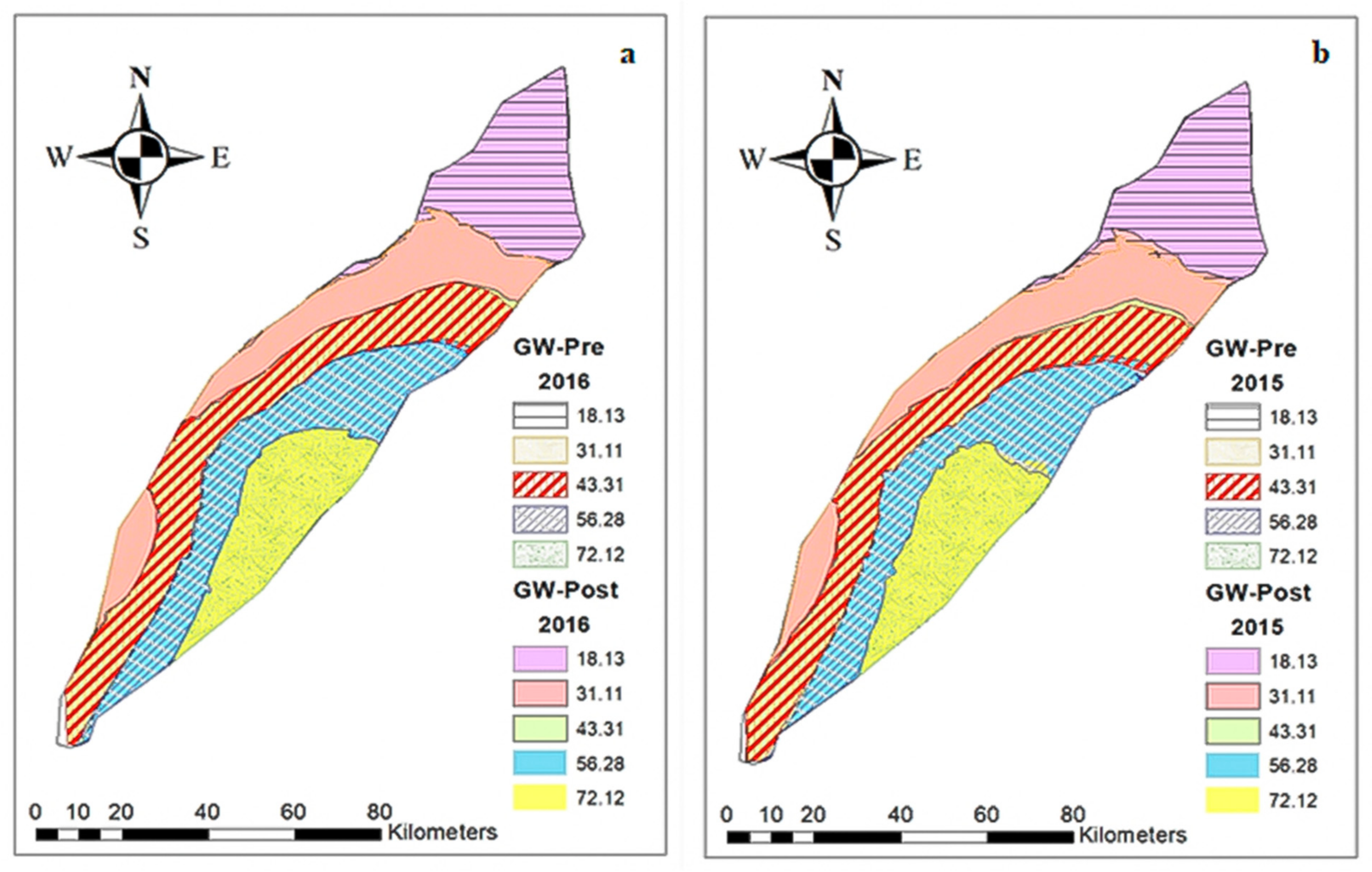
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Groundwater Quality Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasanthavigar, M.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Vijayaragavan, K.; Rajiv Ganthi, R.; Chidambaram, S.; Anandhan, P.; Manivannan, R.; Vasudevan, S. Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 171, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlili-Zrelli, B.; Gueddari, M.; Bouhlila, R. Spatial and temporal variations of water quality of mateur aquifer (Northeastern Tunisia): Suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes. J. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, K.; Feiznia, B.S.; Jannat Rostami, C.M.; Ausati, K. Assessing Temporal and Spatial Variations of Groundwater Quality (A Case Study: Kohpayeh-Segzi); IA University: Borujerd Branch, Iran, 2011; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tatawat, R.K.; Chandel, C.P.S. A hydrochemical profile for assessing the groundwater quality of Jaipur City. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 143, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, H.U.; Mahmood-Khan, Z.; Ali, A.; Mubeen, M.; Anjum, M.N. Site-specific aquifer characterization and identification of potential groundwater areas in Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.; Jabbar, A.; Niazi, M.A.; Mahr, A.B. Managing water availability and requirements in Pakistan: Challenges and way forward. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 54, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Basharat, M. Spatial and temporal appraisal of groundwater depth and quality in LBDC command-issue. Pak. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2012, 11, 14–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zwahlen, F.; Boillat, J. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of central Jianghan Plain, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A.; Magnone, D.; Sovann, C.; Kong, C.; Uhlemann, S.; Kuras, O.; van Dongen, B.E.; Ballentine, C.J.; Polya, D.A. High resolution profile of inorganic aqueous geochemistry and key redox zones in an arsenic bearing aquifer in Cambodia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.F.; Yu, S.E.; Wu, Y.B.; Pan, D.F.; She, D.L.; Ji, J. Seasonal Variations in Groundwater Level and Salinity in Coastal Plain of Eastern China Influenced by Climate. J. Chem. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladejana, J.A.; Kalin, R.M.; Sentenac, P.; Hassan, I. Assessing the impact of climate change on groundwater quality of the shallow coastal aquifer of eastern dahomey basin, southwestern Nigeria. Water 2020, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, T.; Havlík, P.; Schneider, U.A.; Schmid, E.; Kindermann, G.; Obersteiner, M. Agriculture and resource availability in a changing world: The role of irrigation. Water Resour. Res. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nema, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Nema, R.K. Spatial and temporal ground water responses to seasonal rainfall replenishment in an alluvial aquifer. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2017, 10, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili Zrelli, B.; Gueddari, M. Groundwater hydro-geochemistry of Mateur alluvial aquifer (Northern Tunisia). J. Hydrogeol. Hydrol. Eng. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, L.; Boudoukha, A.; Mouni, L. Amultivariate statistical analysis of groundwater chemistry data. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2011, 5, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, R.H.; Lee, J.; Cheong, T.J.; Yum, B.W.; Chang, H.W. Multivariate statistical analysis to identify the major factors governing groundwater quality in the coastal area of Kimje, South Korea. Hydrol. Process. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Z. Assessing hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in limestone terrain via principal component analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Han, D.; Gupta, M.; Mukherjee, S. Integrated framework for monitoring groundwater pollution using a geographical information system and multivariate analysis. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xia, J.; Wu, S.; She, D.; Zou, L. Characterizing and explaining spatio-temporal variation of water quality in a highly disturbed river by multi-statistical techniques. Springerplus 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yan, M.; Wang, J. Spatial variability of the shallow groundwater level and its chemistry characteristics in the low plain around the Bohai sea, north China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 3697–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Peng, J.; Chen, Y.D.; Li, J. Spatial-temporal changes of precipitation structure across the Pearl River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağca, N. Spatial variability of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and irrigation in the Amik Plain (South Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, E.S.E. A proposed model to assess and map irrigation water well suitability using geospatial analysis. Water 2012, 4, 545–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Gupta, M.; Mukherjee, S. Mapping spatial distribution of pollutants in groundwater of a tropical area of India using remote sensing and GIS. Appl. Geomat. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco Castro, R.; Pacheco Ávila, J.; Ye, M.; Cabrera Sansores, A. Groundwater quality: Analysis of Its temporal and spatial variability in a karst aquifer. Groundwater 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, H.U.; Ahmad, I.; Anjum, M.N.; Khan, Z.M.; Iqbal, M.M.; Shakoor, A.; Mubeen, M. Assessing seasonal and long-term changes in groundwater quality due to over-abstraction using geostatistical techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.F.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Chang, P.H. GIS for the assessment of the groundwater recharge potential zone. Environ. Geol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, C.; Marchetti, A.; Farina, R. Francaviglia, R. Application of indicator kriging to evaluate the probability of exceeding nitrate contamination thresholds. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 853–862. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Herath, S.; Avtar, R.; Takeuchi, K. Mapping of groundwater potential zones in Killinochi area, Sri Lanka, using GIS and remote sensing techniques. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Abbas, F.; Ibrahim, M.; Ayyaz, M.M.; Ali, S.; Mahmood, A. Surveillance of heavy metals in maize grown with wastewater and their impacts on animal health in peri-urban areas of multan, Pakistan. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F.; Ahmad, A.; Safeeq, M.; Ali, S.; Saleem, F.; Hammad, H.M.; Farhad, W. Changes in precipitation extremes over arid to semiarid and subhumid Punjab, Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, A.; Arshad, M.; Bakhsh, A.; Ahmed, R. GIS based assessment and delineation of groundwater quality zones and its impact on agricultural productivity. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 52, 837–843. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.K.; Tewari, G.; Kumar, S.; Mancini, P.M. Evaluation of groundwater quality for suitability of irrigation purposes: A case study in the Udham Singh Nagar, Uttarakhand. J. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M. Eaton Significance of Carbonates in Irrigation Waters: Soil Science. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/soilsci/Citation/1950/02000/Significance_of_Carbonates_in_Irrigation_Waters.4.aspx (accessed on 29 November 2020).
- Popugaeva, D.; Kreyman, K.; Ray, A.K. Assessment of Khibiny Alkaline Massif groundwater quality using statistical methods and water quality index. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 98, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.E.; Dungan, J.L.; Beck, L.R. Kriging in the shadows: Geostatistical interpolation for remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabala, L.M.; Mulolwa, A.; Lungu, O. Application of ordinary kriging in mapping soil organic carbon in Zambia. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gia Pham, T.; Kappas, M.; Van Huynh, C.; Hoang Khanh Nguyen, L. Application of ordinary kriging and regression kriging method for soil properties mapping in hilly region of central Vietnam. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrjardi, R.T.; Jahromi, M.Z.; Heidari, A. Spatial distribution of groundwater quality with geostatistics (Case study: Yazd-ardakan plain). Appl. Sci. 2008, 4, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Omran, A.M.; Aly, A.A.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Al-Shayaa, M.S.; Sallam, A.S.; Nadeem, M.E. Geostatistical methods in evaluating spatial variability of groundwater quality in Al-Kharj Region, Saudi Arabia. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4013–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhuang, S.; Qian, H.; Wang, F.; Ji, H. Spatial Variability of the Topsoil Organic Carbon in the Moso Bamboo Forests of Southern China in Association with Soil Properties. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sood, S.; Duggirala, G. Seasonal Variation of Groundwater Quality in Rural Areas of Jaipur District, Rajasthan. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bui, D.D.; Kawamura, A.; Tong, T.N.; Amaguchi, H.; Nakagawa, N. Spatio-temporal analysis of recent groundwater-level trends in the Red River Delta, Vietnam. Hydrogeol. J. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Cheema, T.; Lisa, M.; Azeem, T.; Ali, N.A.; Khan, Z.; Rehman, F.; Rehman, S.U. Statistical analysis tools for the assessment of groundwater chemical variations in wadi bani malik area, Saudi Arabia. Glob. Nest J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Vasanthavigar, M.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Sarathidasan, R.; Gopinath, S. Hydrochemistry of groundwater in a coastal region of Cuddalore district, Tamilnadu, India: Implication for quality assessment. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploum, S.; Laudon, H.; Peralta-Tapia, A.; Kuglerová, L. Are hydrological pathways and variability in groundwater chemistry linked in the riparian boreal forest? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, M.; Jonoski, A.; Essink, G.H.P.O.; Uhlenbrook, S. Assessing the fresh-saline groundwater distribution in the Nile delta aquifer using a 3D variable-density groundwater flow model. Water 2019, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, Q. Geostatistical analysis of temporal and spatial variations in groundwater levels and quality in the Minqin oasis, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, R.; Ma, H. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater in an irrigated region, Northwest China. Water 2019, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Feng, W.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogeochemical characterization and irrigation quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the central-Western Guanzhong basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, H.; De Nijs, T. The map comparison kit. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G.; Huffaker, D.; Denman, K. Useful techniques of validation for spatially explicit land-change models. Ecol. Modell. 2004, 179, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.S.; Yorita, K.L.; Walsh, M.C.; Reynolds, M.G. A method for statistically comparing spatial distribution maps. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2009, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, N.; Jameel, A.; Cheema, S.B.; Ghuffar, A.; Mahmood, A.; Rasul, G. Third successive active monsoon over Pakistan—An analysis and diagnostic study of monsoon 2012. Pak. J. Meteorol. 2013, 9, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, B.; Wu, J. Seasonal and inter-annual variability of groundwater and their responses to climate change and human activities in arid and desert areas: A case study in Yaoba Oasis, Northwest China. Water 2020, 12, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, P.; Mahmudy-Gharaie, M.H.; Ghassemzadeh, F.; Karimi Karouyeh, A. Assessment of groundwater suitability for irrigation in a gold mine surrounding area, NE Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cao, G.; Han, D.; Yuan, H.; Hu, Y.; Shi, P.; Chen, Y. Deformation of the aquifer system under groundwater level fluctuations and its implication for land subsidence control in the Tianjin coastal region. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Seasons | Parameters | Units | Min | Max | Mean | Median | CV (%) | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-monsoon | EC Pre | dS/m | 0.31 | 9.10 | 1.46 | 0.85 | 115.77 | 3.19 |
| SAR Pre | - | 0.02 | 24.11 | 4.91 | 3.88 | 84.97 | 1.89 | |
| RSC Pre | meq/l | 0.00 | 7.80 | 0.76 | 0.00 | 170.43 | 2.00 | |
| GWL Pre | m | 1.58 | 77.08 | 22.06 | 29.91 | 79.74 | 0.30 | |
| Post-monsoon | EC Post | dS/m | 0.37 | 17.50 | 1.59 | 0.95 | 135.34 | 4.46 |
| SAR Post | - | 0.15 | 23.65 | 4.46 | 3.51 | 92.97 | 2.11 | |
| RSC Post | meq/l | 0.00 | 4.60 | 0.68 | 0.00 | 175.22 | 1.69 | |
| GWL Post | m | 1.58 | 78.00 | 21.14 | 30.75 | 98.29 | 0.28 |
| Seasons | Parameters | Units | Min | Max | Mean | Median | CV (%) | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-monsoon | EC | dS/m | 0.36 | 10.8 | 1.50 | 0.94 | 115.75 | 3.19 |
| SAR | - | 0.19 | 28.88 | 5.50 | 4.42 | 86.98 | 1.98 | |
| RSC | meq/l | 0.00 | 7.00 | 0.70 | 0.00 | 174.80 | 1.96 | |
| GWL | m | 1.75 | 75.75 | 19.12 | 28.25 | 103.35 | 0.33 | |
| Post-monsoon | EC | dS/m | 0.29 | 8.80 | 1.41 | 0.85 | 110.71 | 2.73 |
| SAR | - | 0.02 | 40.00 | 4.10 | 2.50 | 118.36 | 3.52 | |
| RSC | meq/l | 0.00 | 7.30 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 224.19 | 3.36 | |
| GWL | m | 1.66 | 76.58 | 17.82 | 26.79 | 112.47 | 0.43 |
| Parameters | Seasonal Comparison (2015) | Seasonal Comparison (2016) | Parameters | Annual Comparison | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | t-Stat | Mean | t-Stat | Mean | t-Stat | ||
| Pre-EC | 1.49 | −0.887 * | 1.57 | 0.901 * | 2015-EC | 1.56 | −0.206 * |
| Post-EC | 1.65 | 1.43 | 2016-EC | 1.59 | |||
| Pre-SAR | 5.01 | 1.032 * | 5.72 | 3.577 | 2015-SAR | 4.80 | 0.291 * |
| Post-SAR | 4.62 | 4.14 | 2016-SAR | 4.69 | |||
| Pre-RSC | 0.78 | 0.623 * | 0.73 | 2.324 | 2015-RSC | 0.75 | 1.324 * |
| Post-RSC | 0.71 | 0.49 | 2016-RSC | 0.62 | |||
| Pre-GWL | 22.60 | 0.165 * | 19.51 | −0.128 * | 2015-GWL | 22.10 | 0.504 * |
| Post-GWL | 21.02 | 20.86 | 2016-GWL | 20.68 | |||
| Boring Depth | Discharge | Screen Length | Pre-EC | Pre-SAR | Pre-RSC | Post-EC | Post-SAR | Post-RSC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boring depth | 1.000 | ||||||||
| Discharge | 0.372 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| Screen length | 0.473 ** | −0.066 | 1.000 | ||||||
| Pre-EC | 0.072 | 0.043 | 0.114 | 1.000 | |||||
| Pre-SAR | 0.090 | 0.036 | 0.105 | 0.783 ** | 1.000 | ||||
| Pre-RSC | −0.043 | −0.029 | −0.031 | 0.117 | 0.416 ** | 1.000 | |||
| Post-EC | 0.177 ** | 0.101 | 0.165 * | 0.930 ** | 0.744 ** | 0.042 | 1.000 | ||
| Post-SAR | 0.136 * | 0.051 | 0.108 | 0.729 ** | 0.810 ** | 0.395 ** | 0.711 ** | 1.000 | |
| Post-RSC | −0.046 | −0.066 | −0.015 | 0.079 | 0.360 ** | 0.842 ** | 0.052 | 0.451 ** | 1.000 |
| Boring depth | 1.000 | ||||||||
| Discharge | 0.372 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| Screen length | 0.473 ** | −0.066 | 1.000 | ||||||
| Pre-EC | 0.140 * | 0.082 | 0.115 | 1.000 | |||||
| Pre-SAR | 0.059 | 0.052 | 0.032 | 0.768 ** | 1.000 | ||||
| Pre-RSC | −0.081 | −0.078 | −0.034 | 0.082 | 0.457 ** | 1.000 | |||
| Post-EC | 0.235 ** | 0.117 | 0.195 ** | 0.403 ** | 0.297 ** | −0.003 | 1.000 | ||
| Post-SAR | 0.142 * | 0.063 | 0.148 * | 0.363 ** | 0.261 ** | −0.062 | 0.783 ** | 1.000 | |
| Post-RSC | −0.039 | 0.058 | 0.014 | 0.029 | 0.036 | 0.109 | −0.069 | 0.242 ** | 1.000 |
| Years | Seasons | Parameter | Model | Range | C0 | C0 + C | C0/(C0 + C) × 100 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | Pre-monsoon | EC | Spherical | 0.354 | 1.527 | 3.055 | 49.98 | 0.793 |
| SAR | Spherical | 0.267 | 8.160 | 17.910 | 45.56 | 0.441 | ||
| RSC | Exponential | 0.147 | 0.265 | 1.701 | 15.57 | 0.537 | ||
| GWL | Gaussian | 1.186 | 65.00 | 842.50 | 7.71 | 0.971 | ||
| Post-monsoon | EC | Exponential | 0.177 | 0.680 | 4.903 | 13.86 | 0.592 | |
| SAR | Exponential | 0.183 | 2.220 | 17.720 | 12.52 | 0.422 | ||
| RSC | Exponential | 0.132 | 0.190 | 1.417 | 13.40 | 0.800 | ||
| GWL | Gaussian | 1.172 | 72.00 | 888.60 | 8.10 | 0.973 | ||
| 2016 | Pre-monsoon | EC | Spherical | 0.289 | 1.372 | 3.184 | 43.09 | 0.771 |
| SAR | Exponential | 0.222 | 5.180 | 23.980 | 21.60 | 0.689 | ||
| RSC | Exponential | 0.579 | 0.844 | 1.689 | 49.97 | 0.938 | ||
| GWL | Gaussian | 1.086 | 51.00 | 771.00 | 6.61 | 0.954 | ||
| Post-monsoon | EC | Exponential | 0.339 | 0.001 | 2.690 | 0.03 | 0.858 | |
| SAR | Exponential | 0.354 | 1.760 | 25.700 | 6.84 | 0.782 | ||
| RSC | Spherical | 0.114 | 0.076 | 1.200 | 6.33 | 0.571 | ||
| GWL | Gaussian | 0.978 | 48.00 | 752.00 | 6.38 | 0.938 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahzad, H.; Farid, H.U.; Khan, Z.M.; Anjum, M.N.; Ahmad, I.; Chen, X.; Sakindar, P.; Mubeen, M.; Ahmad, M.; Gulakhmadov, A. An Integrated Use of GIS, Geostatistical and Map Overlay Techniques for Spatio-Temporal Variability Analysis of Groundwater Quality and Level in the Punjab Province of Pakistan, South Asia. Water 2020, 12, 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123555
Shahzad H, Farid HU, Khan ZM, Anjum MN, Ahmad I, Chen X, Sakindar P, Mubeen M, Ahmad M, Gulakhmadov A. An Integrated Use of GIS, Geostatistical and Map Overlay Techniques for Spatio-Temporal Variability Analysis of Groundwater Quality and Level in the Punjab Province of Pakistan, South Asia. Water. 2020; 12(12):3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123555
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahzad, Huzaifa, Hafiz Umar Farid, Zahid Mahmood Khan, Muhammad Naveed Anjum, Ijaz Ahmad, Xi Chen, Perviaz Sakindar, Muhammad Mubeen, Matlob Ahmad, and Aminjon Gulakhmadov. 2020. "An Integrated Use of GIS, Geostatistical and Map Overlay Techniques for Spatio-Temporal Variability Analysis of Groundwater Quality and Level in the Punjab Province of Pakistan, South Asia" Water 12, no. 12: 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123555
APA StyleShahzad, H., Farid, H. U., Khan, Z. M., Anjum, M. N., Ahmad, I., Chen, X., Sakindar, P., Mubeen, M., Ahmad, M., & Gulakhmadov, A. (2020). An Integrated Use of GIS, Geostatistical and Map Overlay Techniques for Spatio-Temporal Variability Analysis of Groundwater Quality and Level in the Punjab Province of Pakistan, South Asia. Water, 12(12), 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123555







