Evaluation of AnnAGNPS Model for Runoff Simulation on Watersheds from Glaciated Landscape of USA Midwest and Northeast
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
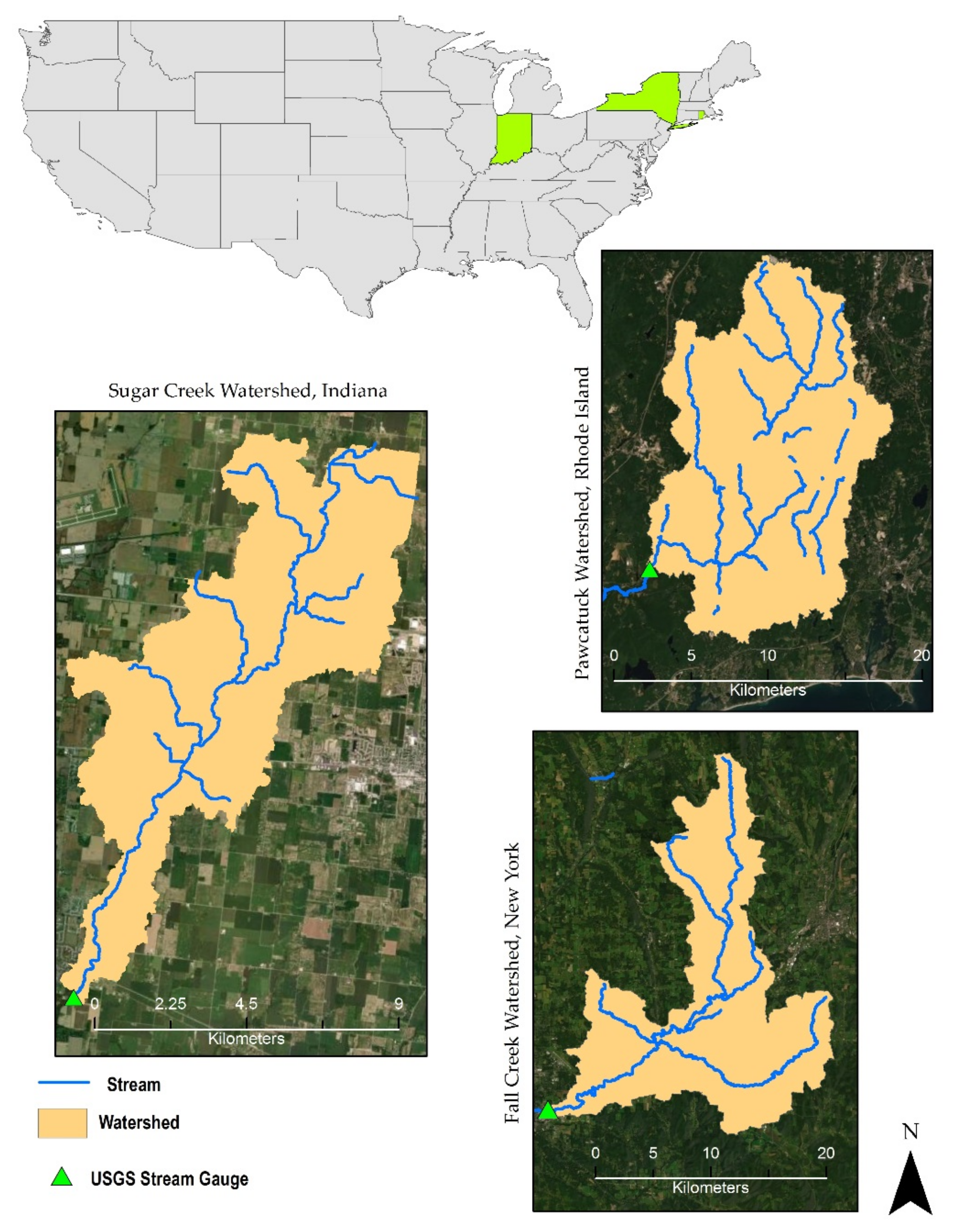
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Description of The AnnAGNPS Model
2.3. Hydrological Modeling Component in AnnAGNPS
2.4. AnnAGNPS Data Input
2.5. Observed Data
2.6. Model Assessment
2.7. Model Calibration, Validation and Sensitivity Analysis for Runoff Simulation
3. Results
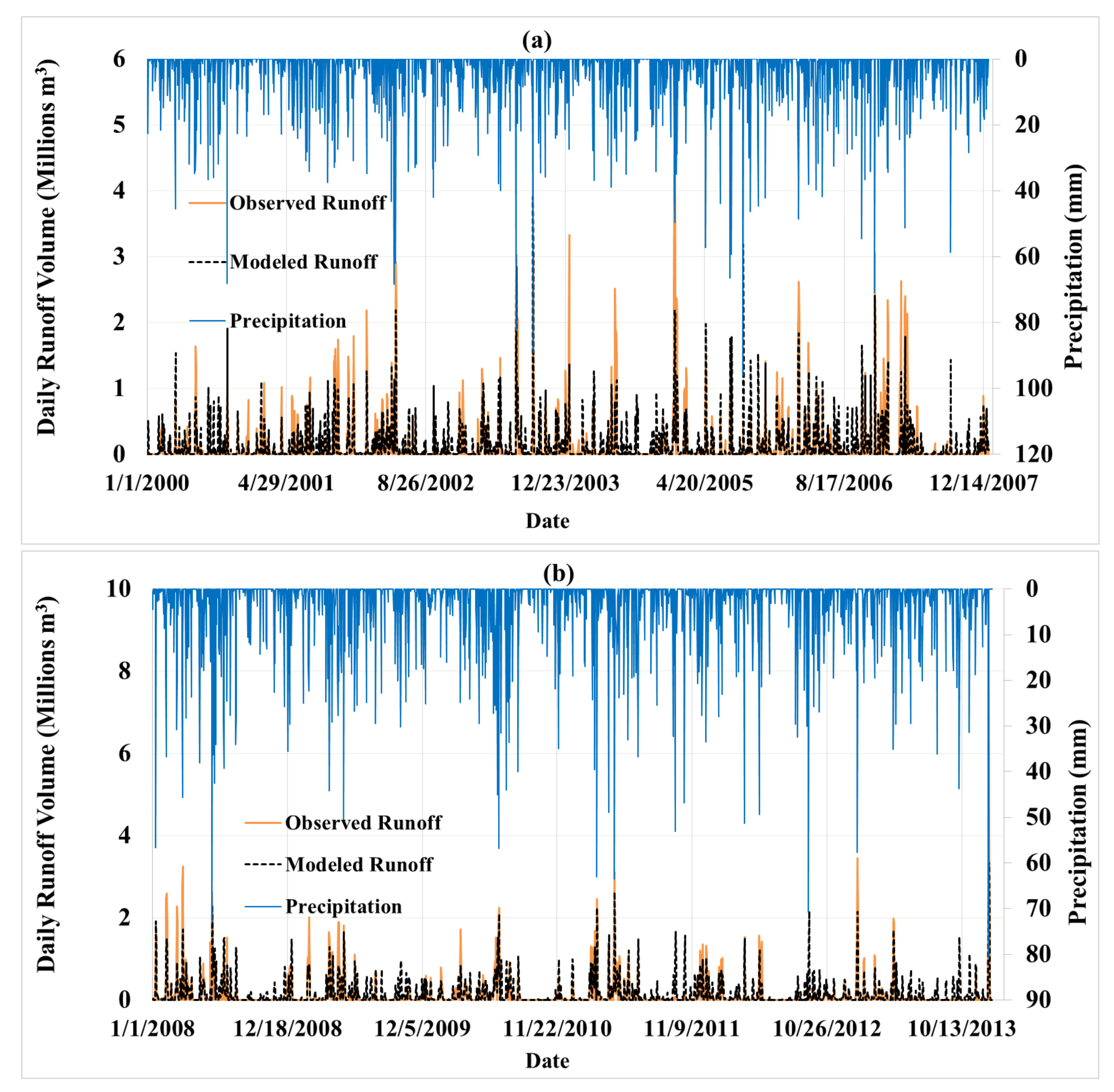
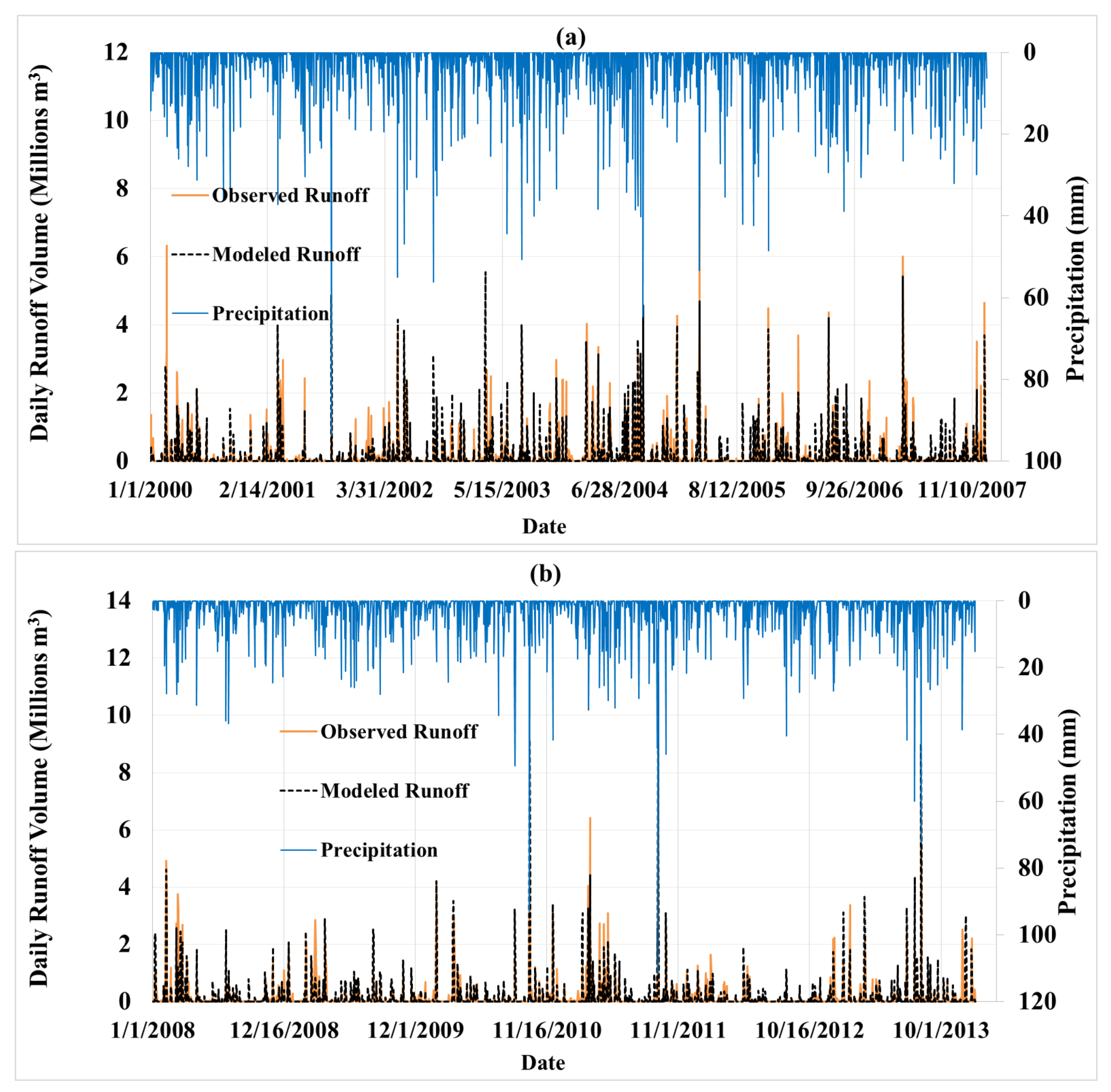
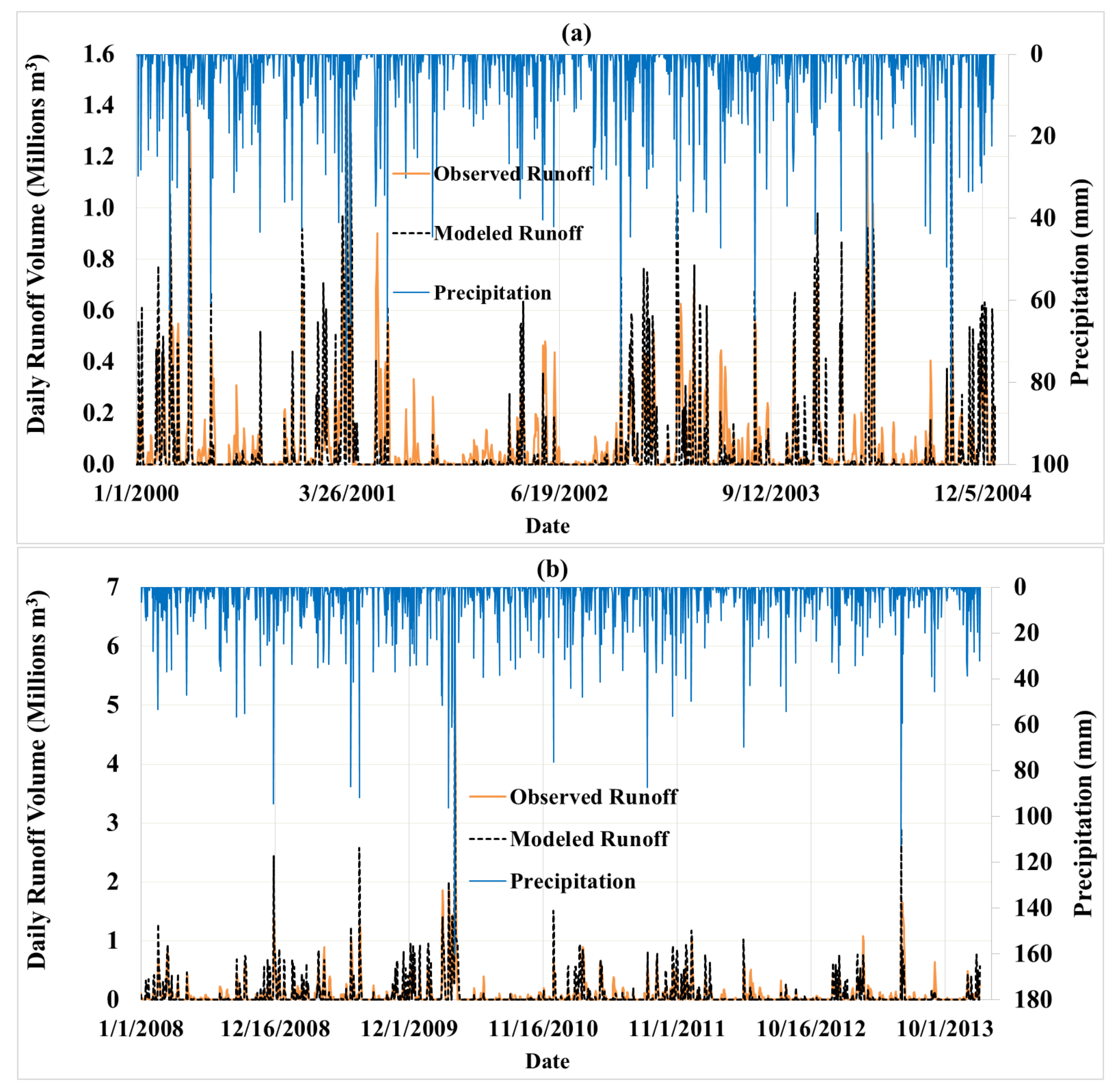
3.1. Runoff Calibration and Validation
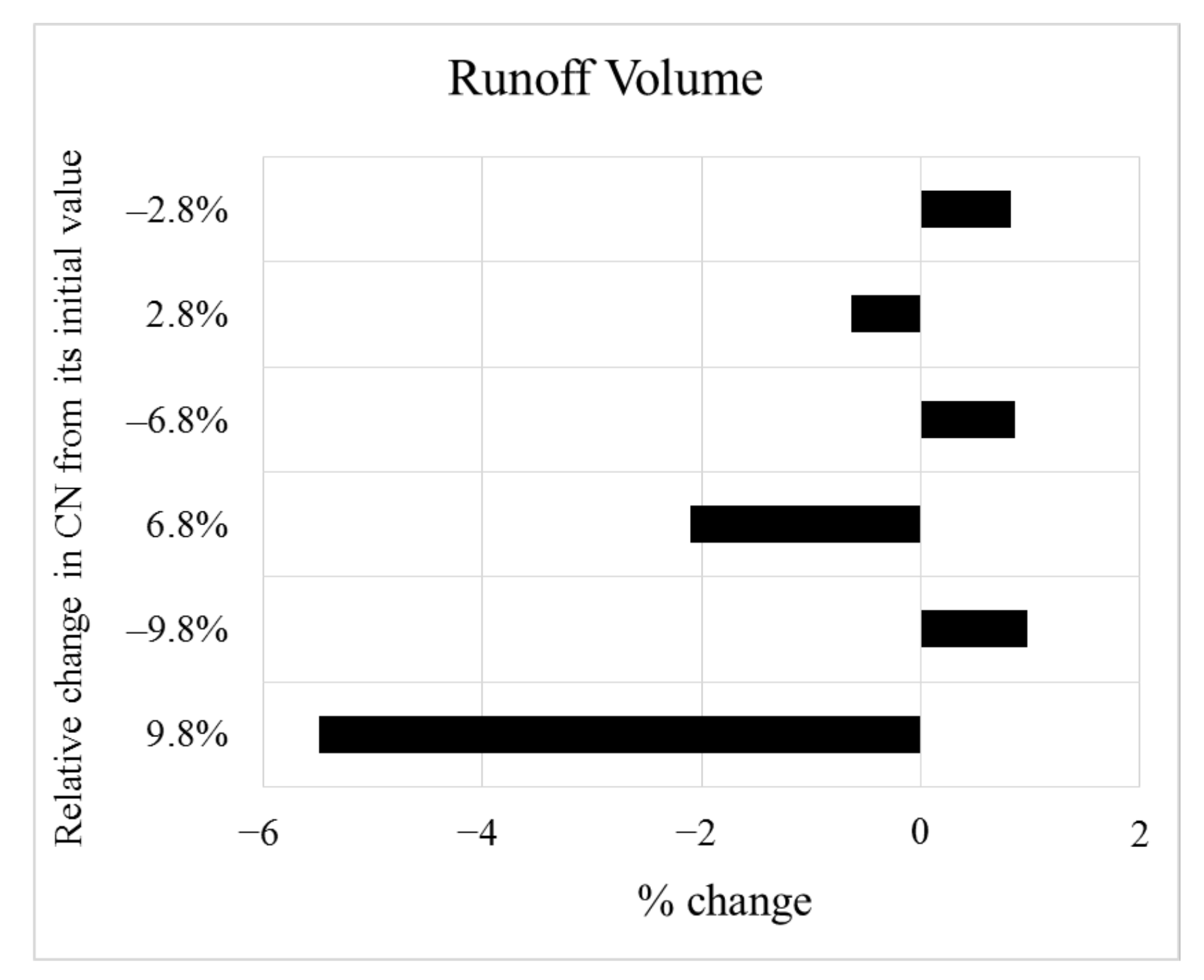
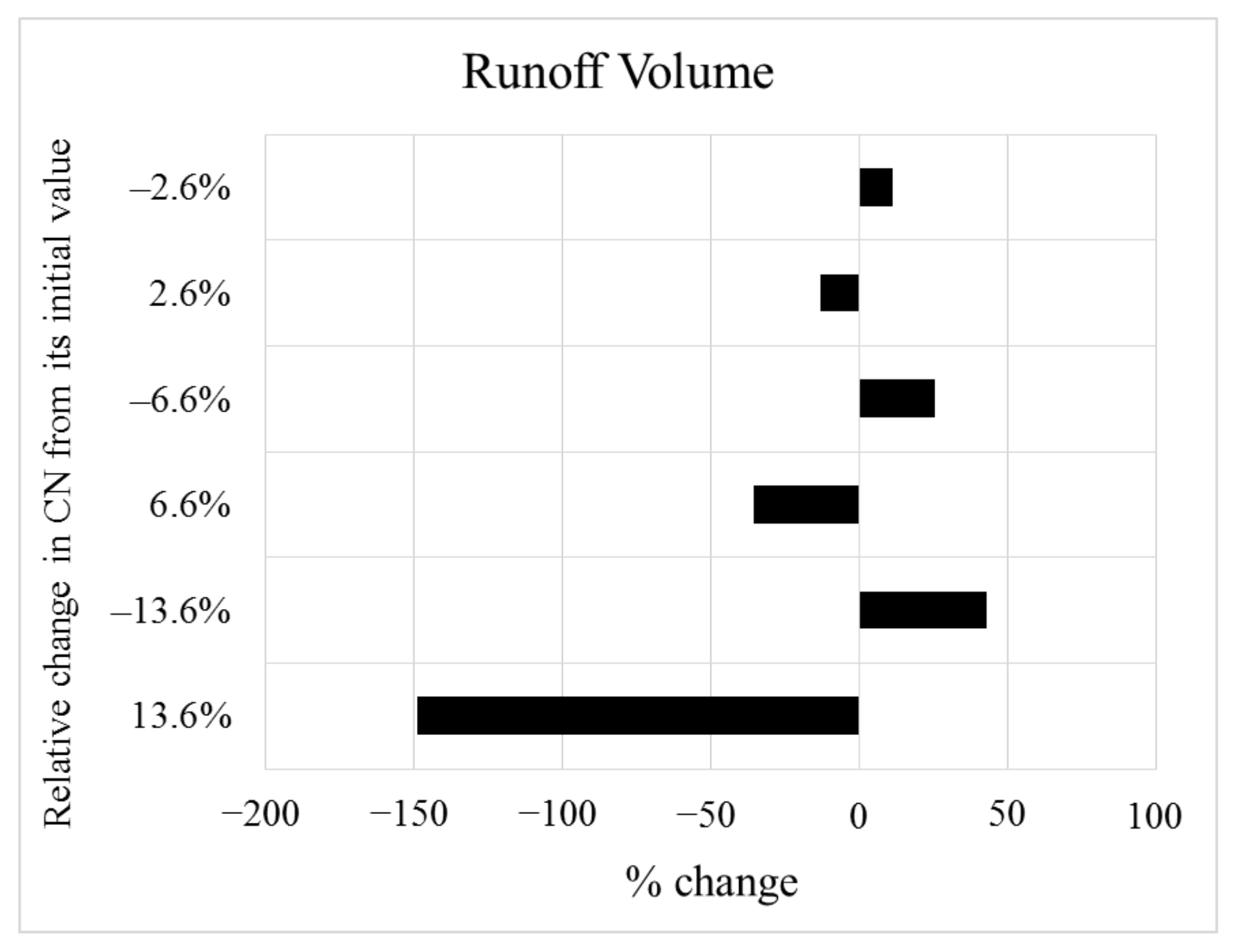
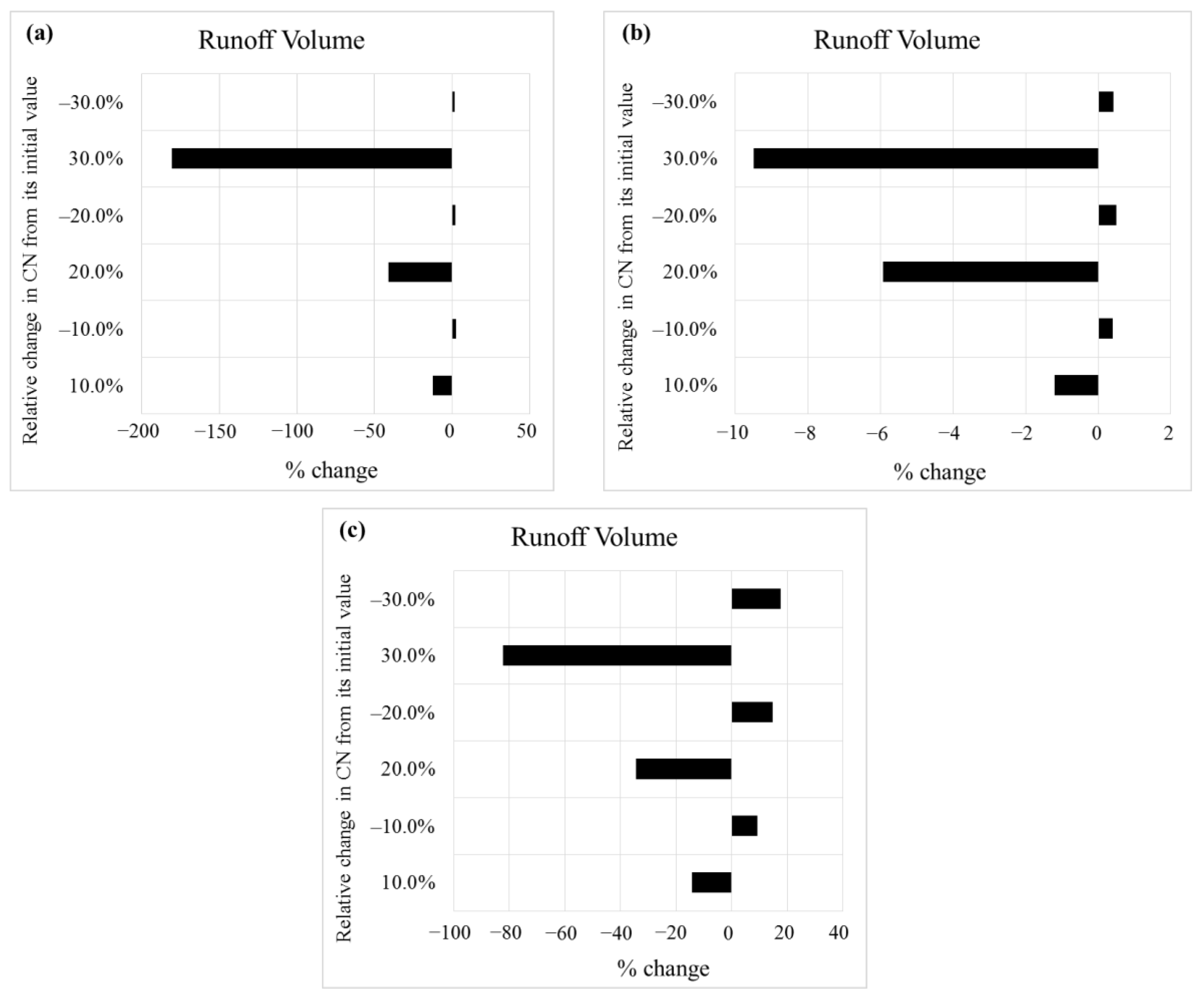
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
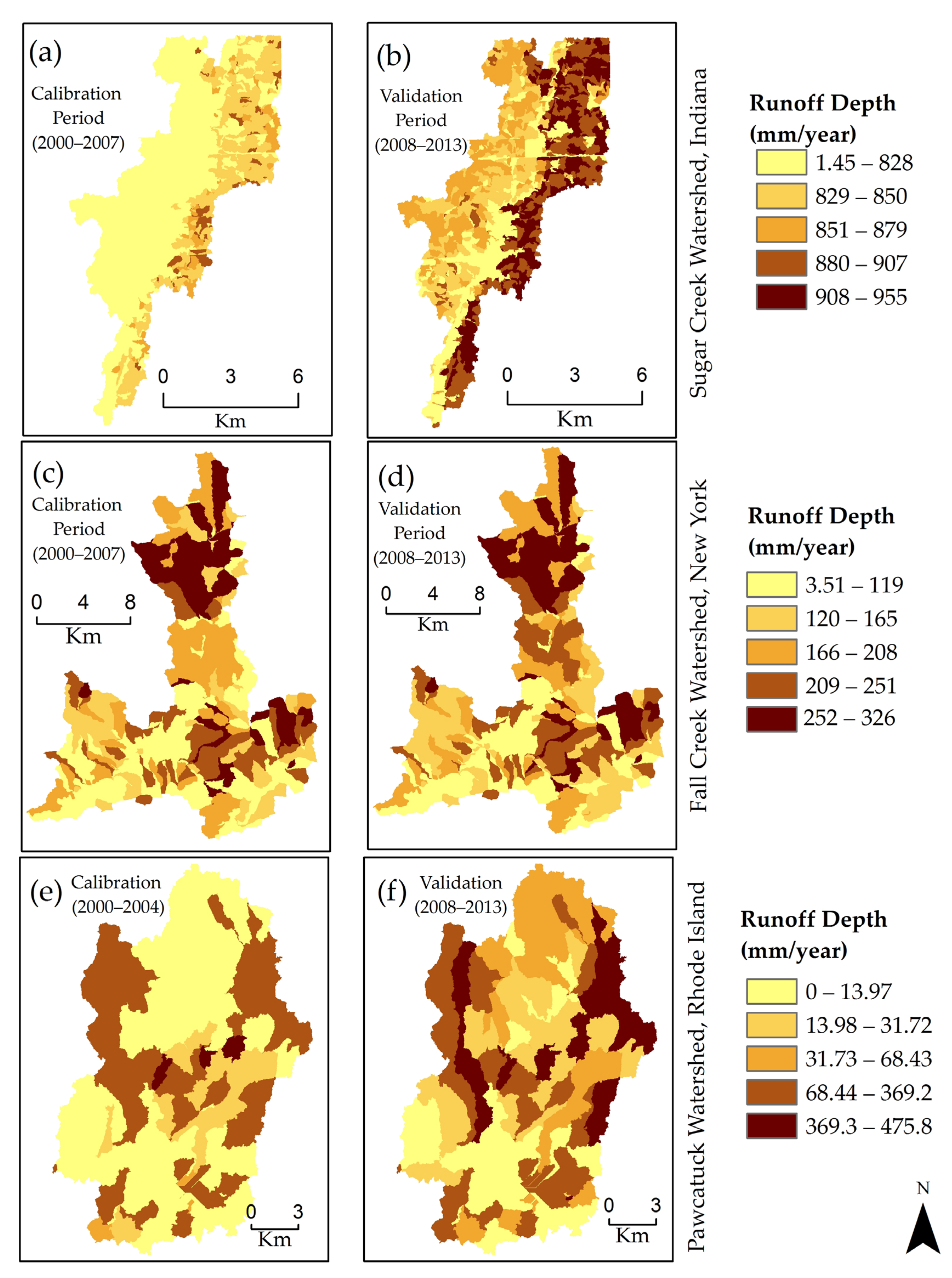
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Runoff Depth
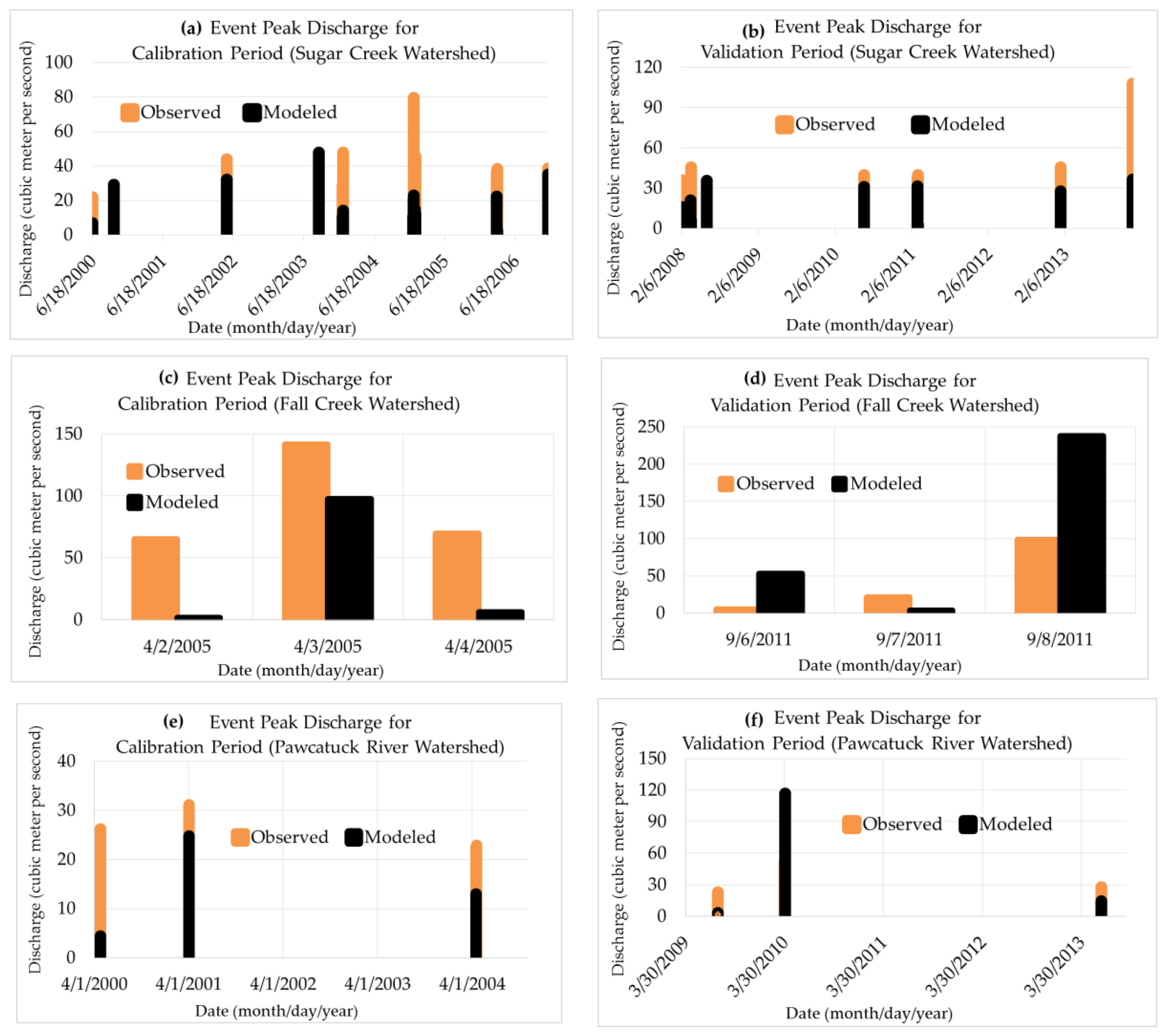
3.4. Model Performance to Estimate Event Peak Discharge
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz, R.J. Overview of hypoxia around the world. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Whitall, D.; Aber, J.; Boyer, E.; Castro, M.; Cronan, C.; Goodale, C.L.; Groffman, P.; Hopkinson, C.; Lambert, K. Nitrogen pollution in the northeastern united states: Sources, effects, and management options. Bioscience 2003, 53, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goolsby, D.A.; Battaglin, W.A.; Aulenbach, B.T.; Hooper, R.P. Nitrogen flux and sources in the Mississippi river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 248, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howarth, R.W.; Anderson, D.B.; Cloern, J.E.; Elfring, C.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Lapointe, B.; Malone, T.; Marcus, N.; McGlathery, K.; Sharpley, A.N. Nutrient Pollution of Coastal Rivers, Bays, and Seas. Issues in Ecology; Ecological Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nixon, S.; Buckley, B.; Granger, S.; Bintz, J. Responses of very shallow marine ecosystems to nutrient enrichment. Human Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2001, 7, 1457–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Wiseman, W.J., Jr. Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E. Anthropogenic Inputs of Nitrogen and Phosphorus and Riverine Export for Illinois, USA. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.L.; Kaushik, N.K.; Trevors, J.T.; Whiteley, H.R. Denitrification in temperate climate riparian zones. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1999, 111, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management (RIDEM). Total Maximum Daily Load Report: The Sakonnet River, Portsmouth Park and The Cove; Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management: Island Park, RI, USA, 2003; Volume 40. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley, A.; Jarvie, H.P.; Buda, A.; May, L.; Spears, B.; Kleinman, P. Phosphorus legacy: Overcoming the effects of past management practices to mitigate future water quality impairment. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1308–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dosskey, M.G. Toward quantifying water pollution abatement in response to installing buffers on crop land. Environ. Manag. 2001, 28, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsch, D.J. Riparian Forest Buffers: Function and Design for Protection and Enhancement of Water Resources; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Northeastern Area, State & Private Forestry, Forest Resources Management: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; Volume 7.
- Gold, A.J.; Groffman, P.M.; Addy, K.; Kellogg, D.Q.; Stolt, M.; Rosenblatt, A.E. Landscape attributes as controls on ground water nitrate removal capacity of riparian zones 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.R. Stream chemistry and riparian zones. In Streams Ground Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 83–110. [Google Scholar]
- Inamdar, S.P.; Sheridan, J.M.; Williams, R.G.; Bosch, D.D.; Lowrance, R.R.; Altier, L.S.; Thomas, D.L. Riparian ecosystem management model (REMM): I. Testing of the hydrologic component for a coastal plain riparian system. Trans. ASAE 1999, 42, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, D.Q.; Gold, A.J.; Groffman, P.M.; Addy, K.; Stolt, M.H.; Blazejewski, G. In situ ground water denitrification in stratified, permeable soils underlying riparian wetlands. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowrance, R.; Vellidis, G.; Wauchope, R.D.; Gay, P.; Bosch, D.D. Herbicide transport in a managed riparian forest buffer system. Trans. ASAE 1997, 40, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterjohn, W.T.; Correll, D.L. Nutrient dynamics in an agricultural watershed: Observations on the role of a riparian forest. Ecology 1984, 65, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidon, P.; Hill, A.R. Denitrification and patterns of electron donors and acceptors in eight riparian zones with contrasting hydrogeology. Biogeochemistry 2004, 71, 259–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidon, P.; Smith, A.P. Upland Controls on the Hydrological Functioning of Riparian Zones in Glacial Till Valleys of the Midwest 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 1524–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altier, L.S.; Lowrance, R.; Williams, R.G.; Inamdar, S.P.; Bosch, D.D.; Sheridan, J.M.; Hubbard, R.K.; Thomas, D.L. Riparian Ecosystem Management Model: Simulator for Ecological Processes in Riparian Zones; Conservation Research Report 46; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Volume 46, p. 216.
- Lowrance, R.; Altier, L.S.; Williams, R.G.; Inamdar, S.P.; Sheridan, J.M.; Bosch, D.D.; Hubbard, R.K.; Thomas, D.L. REMM: The riparian ecosystem management model. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 55, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sopper, W.E.; Lull, H.W. Streamflow characteristics of physiographic units in the northeast. Water Resour. Res. 1965, 1, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingner, R.L.; Theurer, F.D. AnnAGNPS: Estimating Sediment Yield by Particle Size for Sheet and Rill Erosion. In Proceedings of the 7th Interagency Sedimentation Conference, Reno, NV, USA, 25–29 March 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Geter, W.F.; Theurer, F.D. AnnAGNPS-RUSLE sheet and rill erosion. In Proceedings of the First Federal Interagency Hydrologic Modeling Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 19–23 April 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Mehaffey, M.H.; Lopez, R.D.; Bingner, R.L.; Bruins, R.; Erickson, C.; Jackson, M.A. AnnAGNPS model application for nitrogen loading assessment for the future Midwest landscape study. Water 2011, 3, 196–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuercher, B.W.; Flanagan, D.C.; Heathman, G.C. Evaluation of the AnnAGNPS model for atrazine prediction in northeast Indiana. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Tagert, M.L.M.; Paz, J.O.; Bingner, R.L. Application of AnnAGNPS to model an agricultural watershed in east-central mississippi for the evaluation of an on-farm water storage (OFWS) system. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 192, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasarer, L.M.; Bingner, R.L.; Momm, H.G. Characterizing ponds in a watershed simulation and evaluating their influence on streamflow in a Mississippi watershed. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttles, J.B.; Vellidis, G.; Bosch, D.D.; Lowrance, R.; Sheridan, J.M.; Usery, E.L. Watershed–scale simulation of sediment andnutrient loads in Georgia coastal plain streams using the annualized AGNPS model. Trans. ASAE 2003, 46, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parajuli, P.B.; Nelson, N.O.; Frees, L.D.; Mankin, K.R. Comparison of AnnAGNPS and SWAT model simulation results in USDA-CEAP agricultural watersheds in south-central Kansas. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2009, 23, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhanang, S.M. Monitoring and Modeling of Water Quality in Streams of Skaneateles Lake Watershed, NY; State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry: Syracuse, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zema, D.A.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Carrà, B.G.; Denisi, P.; Rodrigues, V.A.; Ranzini, M.; Arcova, F.C.S.; de Cicco, V.; Zimbone, S.M. Simulating the hydrological response of a small tropical forest watershed (Mata Atlantica, Brazil) by the AnnAGNPS model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chahor, Y.; Casalí, J.; Giménez, R.; Bingner, R.L.; Campo, M.A.; Goñi, M. Evaluation of the AnnAGNPS model for predicting runoff and sediment yield in a small Mediterranean agricultural watershed in navarre (Spain). Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 134, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogwo, V. Streamflow and Sediment Yield Prediction using AnnAGNPS Model in Upper Ebonyi River Watershed, South-Eastern Nigeria. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2019, 20, 50–62. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelwahab, O.; Ricci, G.F.; de Girolamo, A.M.; Gentile, F. Modelling soil erosion in a mediterranean watershed: Comparison between SWAT and AnnAGNPS models. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, O.M.M.; Bingner, R.L.; Milillo, F.; Gentile, F. Evaluation of alternative management practices with the AnnAGNPS model in the Carapelle watershed. Soil Sci. 2016, 181, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardello, F.; Zema, D.A.; Zimbone, S.M.; Bingner, R.L. runoff and soil erosion evaluation by the AnnAGNPS model in a small mediterranean watershed. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Rudra, R.P.; Gharabaghi, B.; Gebremeskel, S.; Goel, P.K.; Dickinson, W.T. Applicability of AnnAGNPS for Ontario conditions. Can. Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Baginska, B.; Milne-Home, W.; Cornish, P.S. Modelling nutrient transport in currency creek, NSW with AnnAGNPS and PEST. Environ. Model. Softw. 2003, 18, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Babel, M.S.; Gupta, A.D.; Kazama, F. Evaluation of annualized agricultural nonpoint source model for a watershed in the Siwalik Hills of Nepal. Environ. Model. Softw. 2006, 21, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, C.; Xi, Q.; Li, H.; Pan, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xiong, Z. Assessment of the AnnAGNPS model in simulating runoff and nutrients in a typical small watershed in the Taihu Lake basin, China. Catena 2015, 133, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zema, D.A.; Bingner, R.L.; Denisi, P.; Govers, G.; Licciardello, F.; Zimbone, S.M. Evaluation of runoff, peak flow and sediment yield for events simulated by the AnnAGNPS model in a Belgian agricultural watershed. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshad, A.; Leow, C.S.; Ramlah, A.; Hussin, W.W.; Sanusi, S.M. Applications of AnnAGNPS model for soil loss estimation and nutrient loading for Malaysian conditions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2008, 10, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, A.; Cox, C.A.; Madramootoo, C.A. Evaluation of the AnnAGNPS model for prediction of runoff and sediment yields in St Lucia watersheds. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 97, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidon, P.; Cuadra, P.E. Impact of precipitation characteristics on soil hydrology in tile-drained landscapes. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, T.R. Environmental Setting of the Sugar Creek and Leary Weber Ditch Basins, Indiana, 2002-04; National Water-Quality Assessment Program: Yantai, China, 2006.
- Fenelon, J.M.; Moore, R.C. Transport of agrichemicals to ground and surface water in a small central Indiana watershed. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.S.; Woodbury, P.B.; Pell, A.N.; Lehmann, J. Land-use change and stream water fluxes: Decadal dynamics in watershed nitrate exports. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 1182–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, A.K.; Loucks, D.P. Estimating Non-Point Pollutant Loadings-II: A Case Study in the Fall Creek Watershed, New York. J. Environ. Syst. 1996, 25, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, S.P. Riparian Zone Hydrology and Biogeochemistry as a Function of Stream Evolution Stage in a Glaciated Landscape of the US Northeast; State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry: Syracuse, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt, A.E.; Gold, A.J.; Stolt, M.H.; Groffman, P.M.; Kellogg, D.Q. Identifying riparian sinks for watershed nitrate using soil surveys. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.A.; Onstad, C.A.; Bosch, D.D.; Anderson, W.P. AGNPS: A nonpoint-source pollution model for evaluating agricultural watersheds. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1989, 44, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Government Printing: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Knisel, W.G. CREAMS: A Field Scale Model for Chemicals, Runoff, and Erosion from Agricultural Management Systems; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. EPIC-erosion/productivity impact calculator. I: Model documentation. II: User manual. Tech. Bull. United States Dep. Agric 1990, 1768, 1–377. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, R.A.; Knisel, W.G.; Still, D.A. GLEAMS: Groundwater loading effects of agricultural management systems. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingner, R.L.; Theurer, F.; Yuan, Y. AnnAGNPS Technical Processes, Version 5.4; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. Available online: https://www.wcc.nrcs.usda.gov/ftpref/wntsc/H&H/AGNPS/downloads/AnnAGNPS_Technical_Documentation.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- USDA, S. National Engineering Handbook; Hydrology Section 4; US Department of Agriculture, Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; Chapters 4–10.
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.; Chuang, H.; Iredell, M. The NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhanang, S.M.; Briggs, R.D. Effects of critical source area on sediment yield and streamflow. Water Environ. J. 2014, 28, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models. Part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.D. Factorial sampling plans for preliminary computational experiments. Technometrics 1991, 33, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronshey, R.G.; Roberts, R.T.; Miller, N. Urban hydrology for small watersheds (TR-55 Rev.). In Hydraulics and Hydrology in the Small Computer Age; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 1986; pp. 1268–1273. [Google Scholar]
- van Liew, M.W.; Arnold, J.G.; Garbrecht, J.D. Hydrologic simulation on agricultural watersheds: Choosing between two models. Trans. ASAE 2003, 46, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeurng, C.; Sauvage, S.; Sánchez-Pérez, J. Assessment of hydrology, sediment and particulate organic carbon yield in a large agricultural catchment using the SWAT model. J. Hydrol. 2011, 401, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mapes, K.L.; Pricope, N.G. Evaluating SWAT model performance for runoff, percolation, and sediment loss estimation in low-gradient watersheds of the Atlantic coastal plain. Hydrology 2020, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Khafaji, M.S.; Al-Chalabi, R.D. Assessment and mitigation of streamflow and sediment yield under climate change conditions in Diyala River Basin, Iraq. Hydrology 2019, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeuya, R.M.; Lim, K.J.; Engel, B.A.; Thomas, M.A. Modeling the average annual nutrient losses of two watersheds in Indiana using GLEAMS-NAPRA. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisantino, T.; Bingner, R.; Chouaib, W.; Gentile, F.; Trisorio-Liuzzi, G. Estimation of runoff, peak discharge and sediment load at the event scale in a medium-size Mediterranean watershed using the AnnAGNPS model. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 340–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cover Description | Curve Number for Hydrological Soil Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Values | Values After Calibration | |||||||
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| Row Crop (SR—Poor) | 72 | 81 | 88 | 91 | 74.02 | 83.27 | 90.46 | 93.55 |
| Fallow (CR—Good) | 74 | 83 | 88 | 90 | Not changed | |||
| Woods (Good) | 30 | 55 | 70 | 77 | Not changed | |||
| Urban (85% imp) | 89 | 92 | 94 | 95 | Not changed | |||
| Cover Description | Curve Number for Hydrological Soil Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Values | Values After Calibration | |||||||
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| Row Crop (SR—Poor) | 72 | 81 | 88 | 91 | Not changed | |||
| Urban (Newly graded) | 77 | 86 | 91 | 94 | Not changed | |||
| Woods—Grass (Poor) | 57 | 73 | 82 | 86 | Not changed | |||
| Fallow (CR—Poor) | 76 | 85 | 90 | 93 | Not changed | |||
| Row Crop (C—Poor) | 70 | 79 | 84 | 88 | 74.62 | 84.21 | 89.54 | 93.81 |
| Cover Description | Curve Number for Hydrological Soil Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Values | Values After Calibration | |||||||
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| Row Crop (SR—Good) | 67 | 78 | 85 | 89 | 35.8 | 45.7 | 50.5 | 62.3 |
| Row Crop (C + CR—Good) | 64 | 74 | 81 | 85 | 58.13 | 68 | 74.05 | 78.98 |
| Urban (85% imp) | 89 | 92 | 94 | 95 | Not changed | |||
| Woods (Good) | 30 | 55 | 70 | 77 | 31.5 | 49.5 | 66.5 | 75 |
| Parameter | Calibration Period (1 January 2000 to 31 December 2007) | Validation Period (1 January 2008 to 31 December 2013) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | Monthly | Daily | Monthly | |
| R2 | 0.57 | 0.67 | 0.58 | 0.72 |
| NSE | 0.57 | 0.63 | 0.57 | 0.68 |
| PBIAS | −6.44% | −6.47% | −20.56% | −20.36% |
| RSR | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.65 | 0.57 |
| Parameter | Calibration Period (1 January 2000 to 31 December 2007) | Validation Period (1 January 2008 to 31 December 2013) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | Monthly | Daily | Monthly | |
| R2 | 0.54 | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.66 |
| NSE | 0.51 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.64 |
| PBIAS | 16.48% | 16.59% | −5.50% | −5.51% |
| RSR | 0.70 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.60 |
| Parameter | Calibration Period (1 January 2000 to 31 December 2004) | Validation Period (1 January 2008 to 31 December 2013) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | Monthly | Daily | Monthly | |
| R2 | 0.62 | 0.75 | 0.63 | 0.86 |
| NSE | 0.51 | 0.68 | 0.54 | 0.83 |
| PBIAS | 21.56% | 21.15% | 5.81% | 5.79% |
| RSR | 0.70 | 0.56 | 0.68 | 0.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamanna, M.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Gold, A.J.; Addy, K.; Vidon, P.G.; Bingner, R.L. Evaluation of AnnAGNPS Model for Runoff Simulation on Watersheds from Glaciated Landscape of USA Midwest and Northeast. Water 2020, 12, 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123525
Tamanna M, Pradhanang SM, Gold AJ, Addy K, Vidon PG, Bingner RL. Evaluation of AnnAGNPS Model for Runoff Simulation on Watersheds from Glaciated Landscape of USA Midwest and Northeast. Water. 2020; 12(12):3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123525
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamanna, Marzia, Soni M. Pradhanang, Arthur J. Gold, Kelly Addy, Philippe G. Vidon, and Ronald L. Bingner. 2020. "Evaluation of AnnAGNPS Model for Runoff Simulation on Watersheds from Glaciated Landscape of USA Midwest and Northeast" Water 12, no. 12: 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123525
APA StyleTamanna, M., Pradhanang, S. M., Gold, A. J., Addy, K., Vidon, P. G., & Bingner, R. L. (2020). Evaluation of AnnAGNPS Model for Runoff Simulation on Watersheds from Glaciated Landscape of USA Midwest and Northeast. Water, 12(12), 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123525







