Comparative Use of Quantitative PCR (qPCR), Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR), and Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) in the Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli (STEC) in Environmental Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. STEC Strains Used for This Study
2.2. Specificity of the Assays with Spiked Samples
2.3. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA)
2.4. Multiplex PCR Targeting Virulence Genes for qPCR and ddPCR
2.4.1. Algae Pond Pathogen Quantification and Characterization
2.4.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
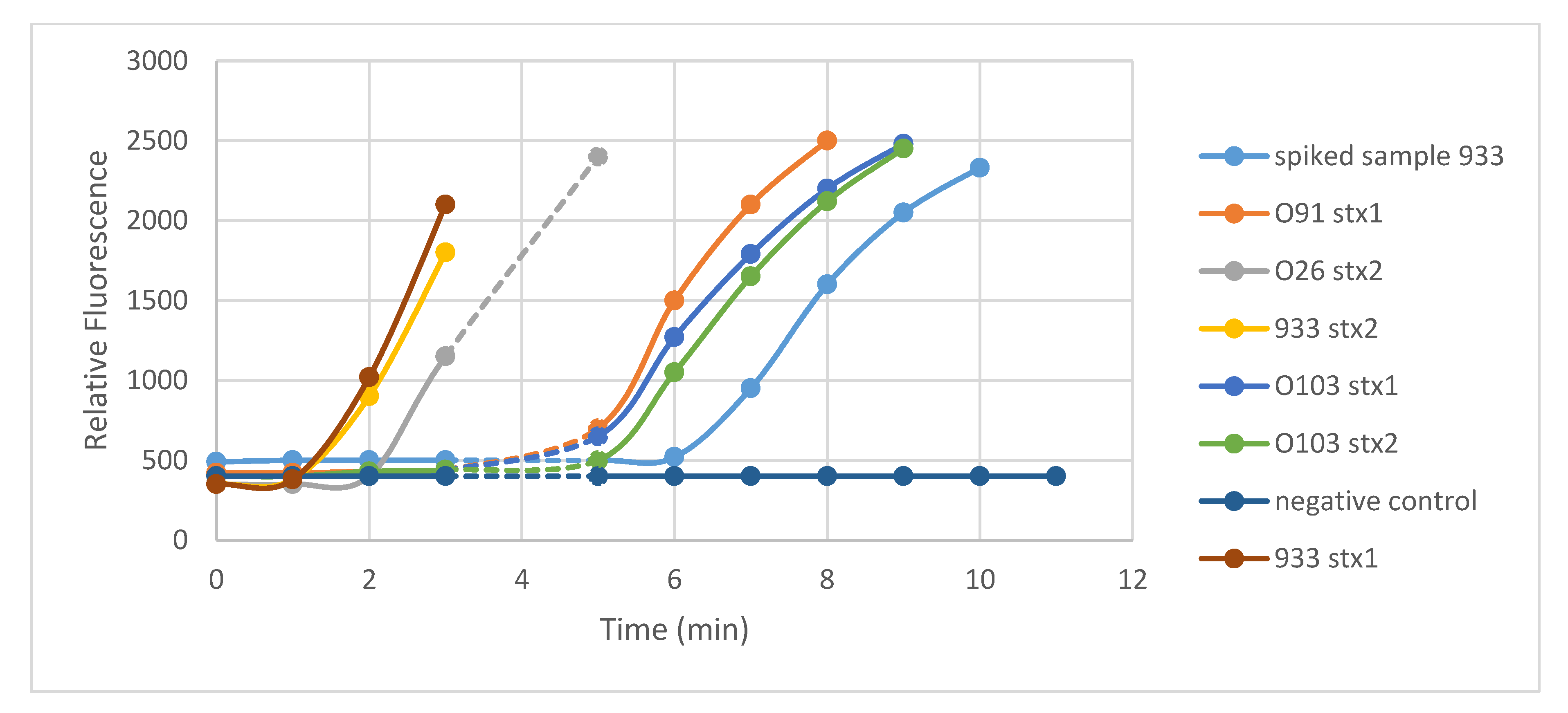
3.1. Specificity of RPA
Assays with Sterile Water Samples Spiked with Pure Cultures of E. coli O157 Strain 933
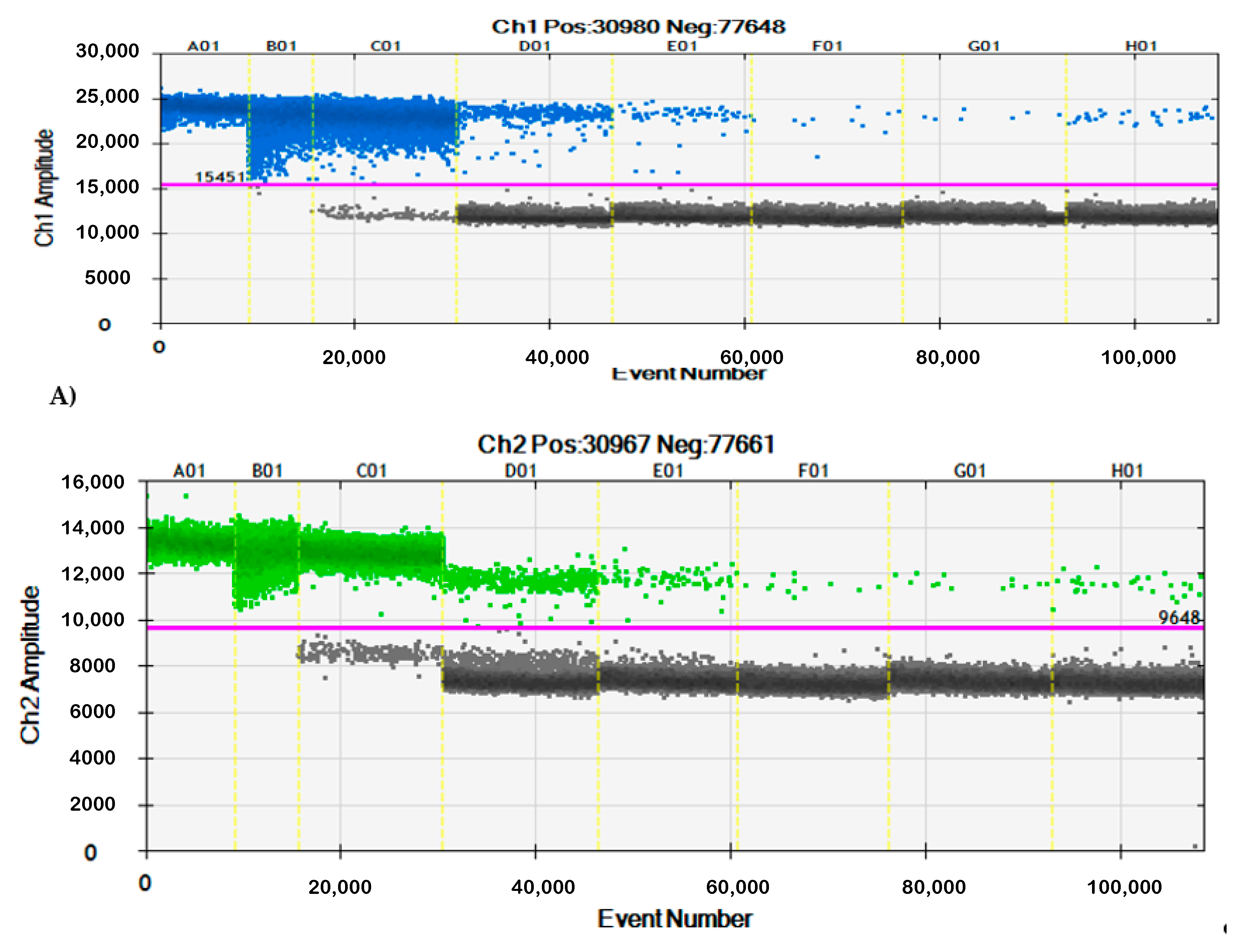
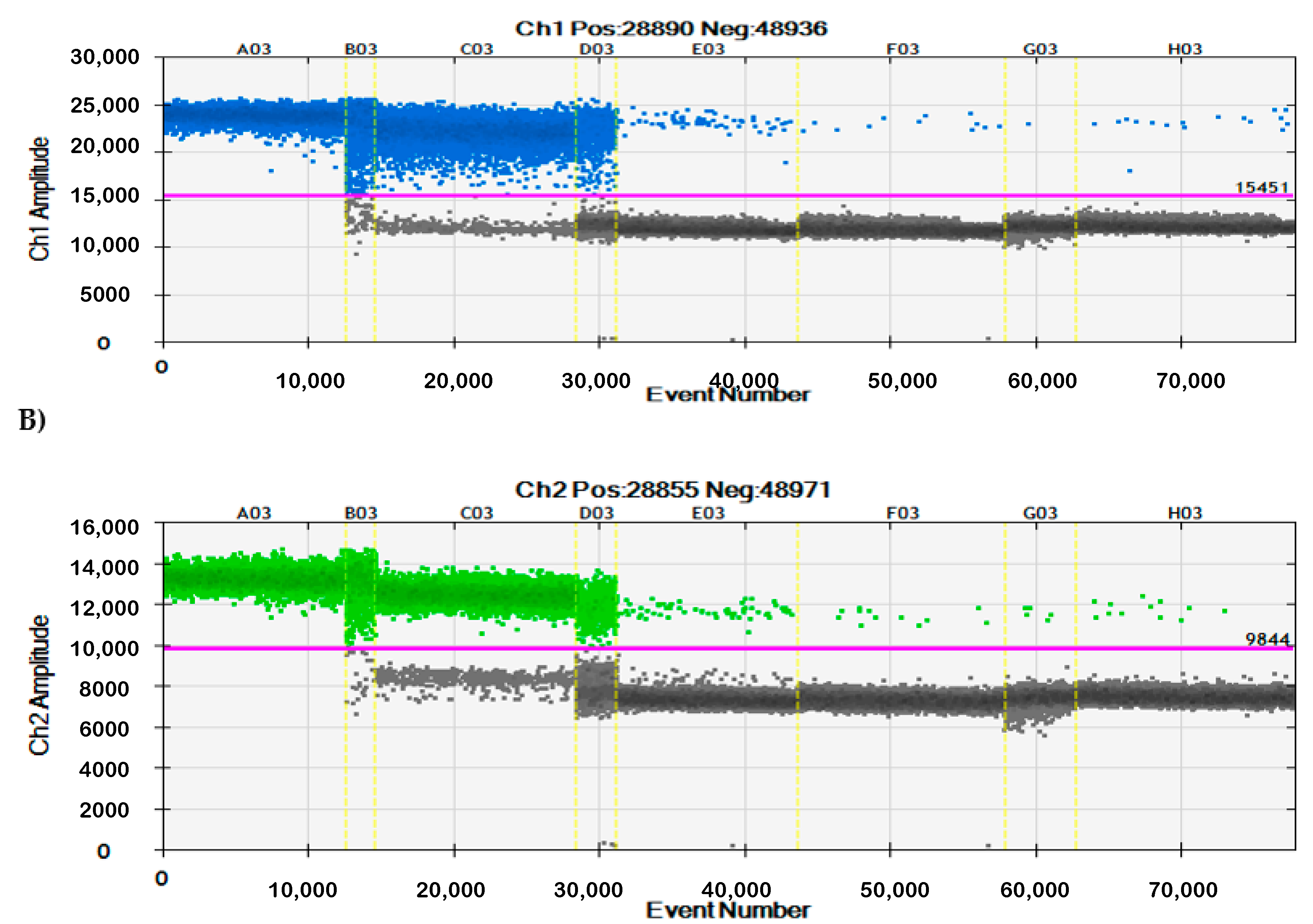
3.2. Specificity of qPCR and ddPCR
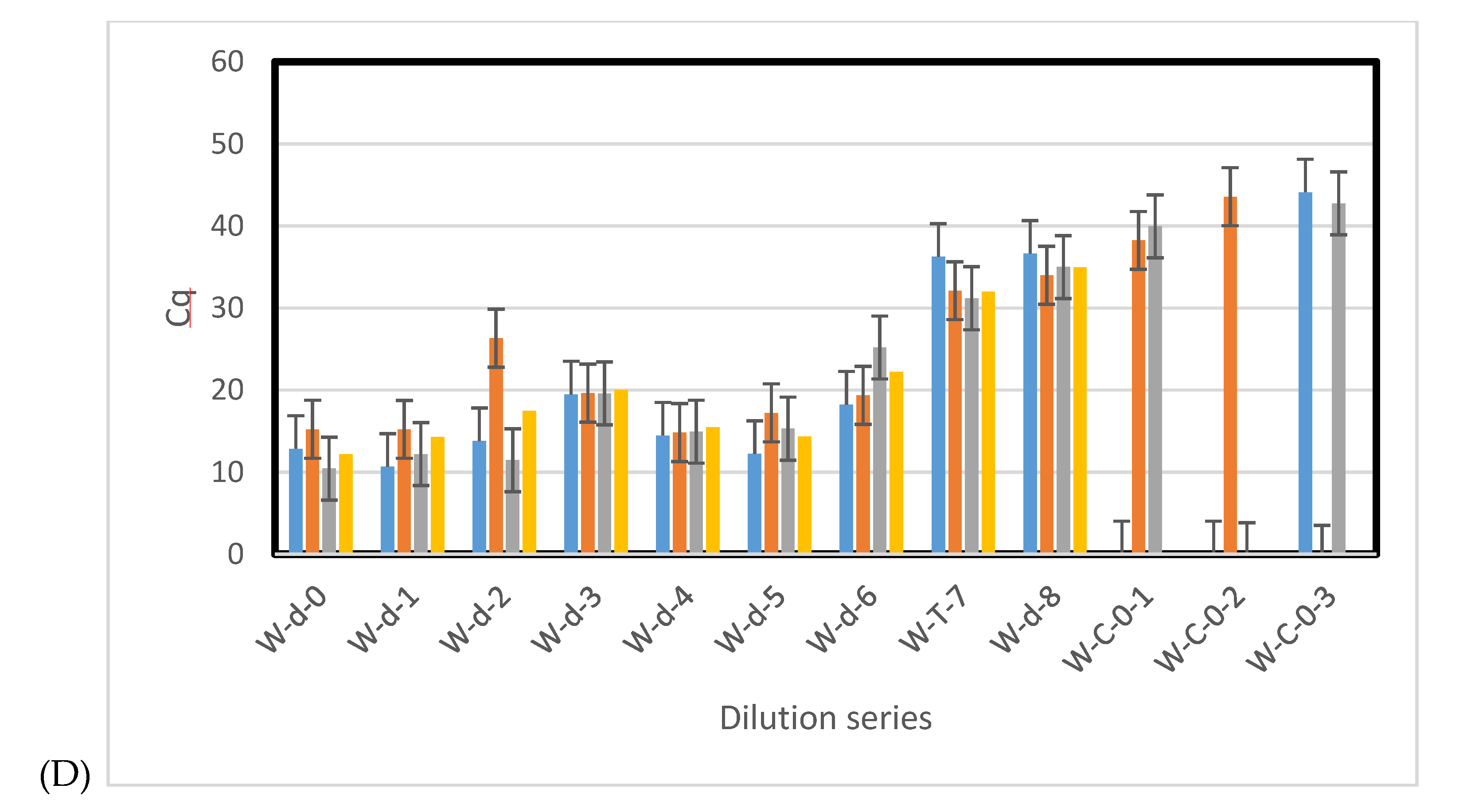
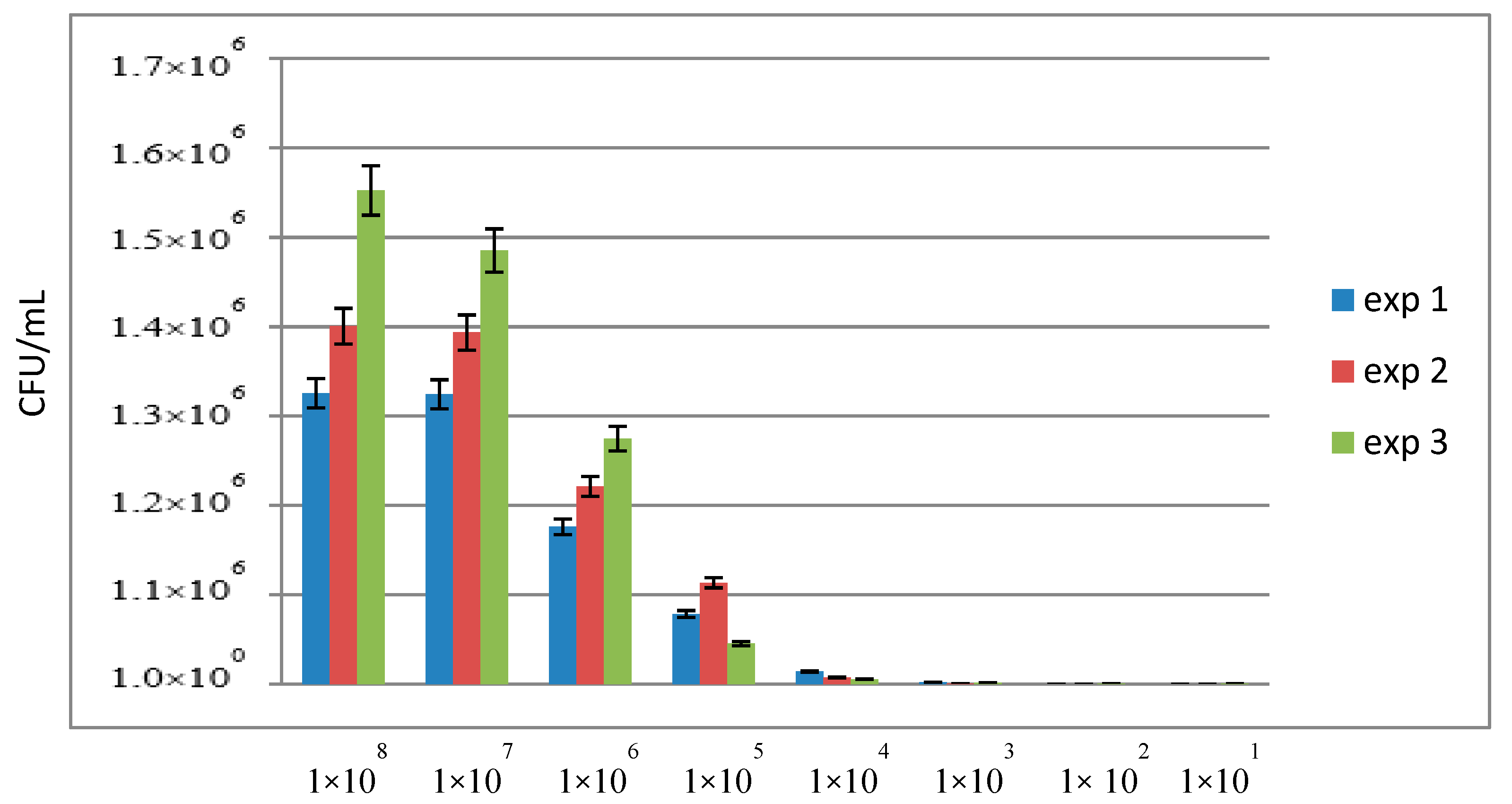
3.3. Sensitivity of qPCR and ddPCR
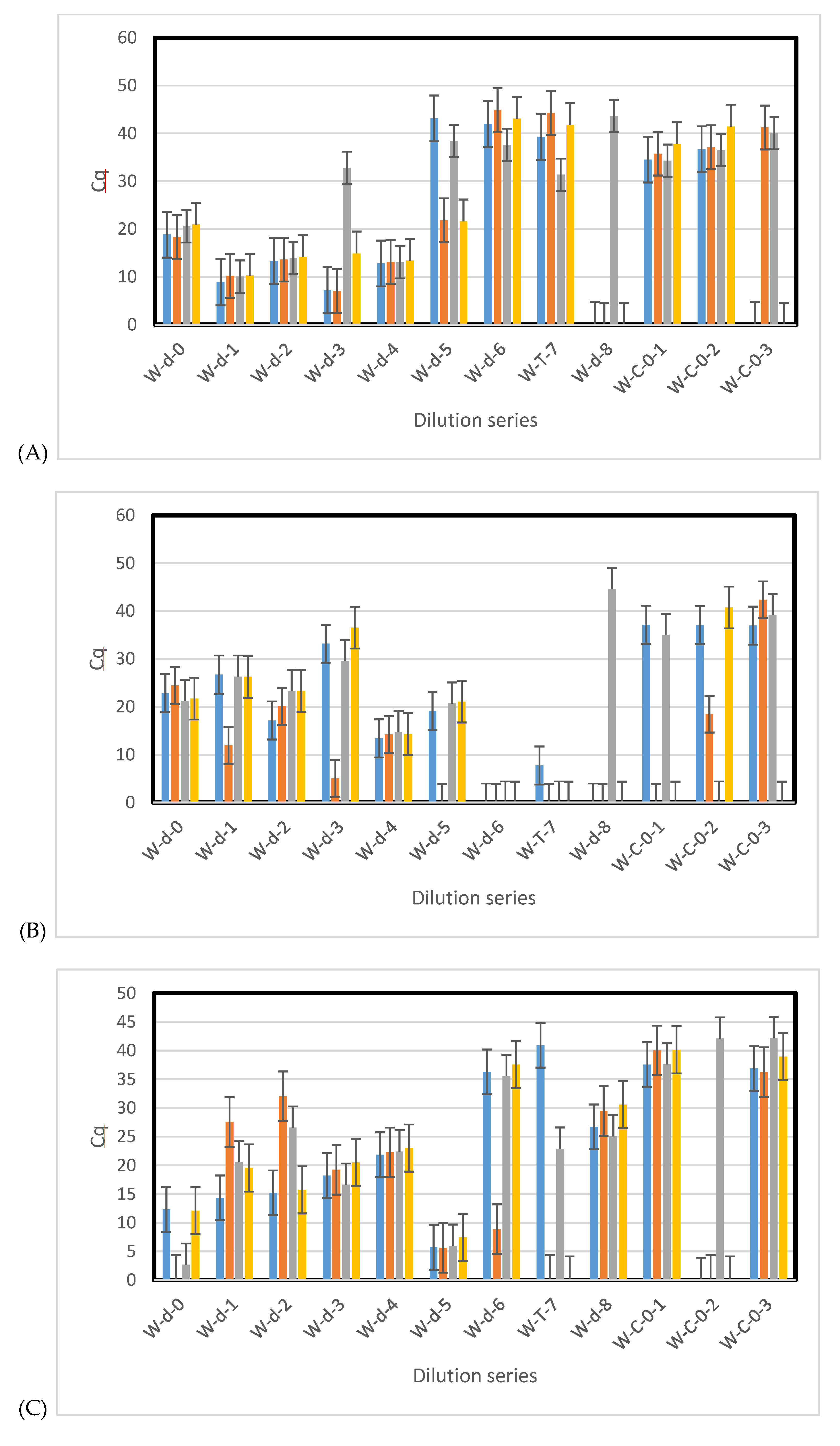
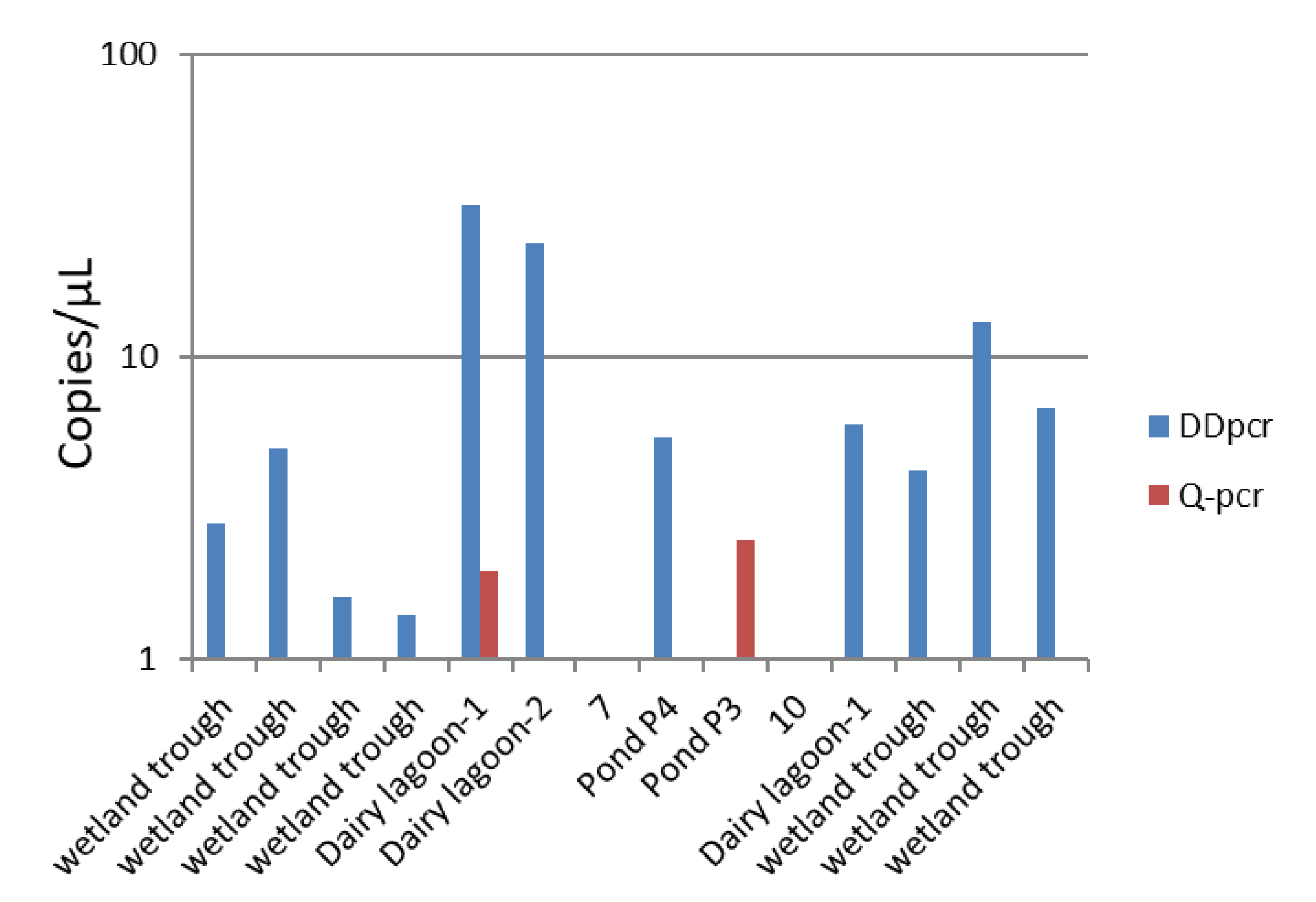
3.4. Environmental Samples
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franz, E.; Semenov, A.V.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; De Vos, O.J.; Bokhorst, J.G.; Van Bruggen, A.H.C. Manure-amended soil characteristics affecting the survival of E. coli O157:H7 in 36 Dutch soils. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, E.; Van Hoek, A.H.A.M.; Bouw, E.; Aarts, H.J.M. Variability of Escherichia coli O157 Strain Survival in Manure-Amended Soil in Relation to Strain Origin, Virulence Profile, and Carbon Nutrition Profile. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8088–8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fremaux, B.; Prigent-Combaret, C.; Delignette-Muller, M.L.; Mallen, B.; Dothal, M.; Gleizal, A.; Vernozy-Rozand, C. Persistence of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O26 in various manure-amended soil types. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 104, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooley, M.B.; Carychao, D.; Crawford-Miksza, L.; Jay, M.T.; Myers, C.; Rose, C.; Keys, C.; Farrar, J.; Mandrell, R.E. Incidence and Tracking of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in a Major Produce Production Region in California. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Watt, P.M.; Grieve, C.M.; Sharma, V.K.; Lyons, S.R. Multiplex fluorogenic real-time PCR for detection and quantification of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in dairy wastewater wetlands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4853–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, M.; Grieve, C. Detection and quantification of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in environmental samples by real-time PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anklam, K.S.; Kanankege, K.S.T.; Gonzales, T.K.; Kaspar, C.W.; Döpfer, D. Rapid and Reliable Detection of Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli by Real-Time Multiplex PCR. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratamico, P.; Wasilenko, J.L.; Garman, B.; Demarco, D.R.; Varkey, S.; Jensen, M.; Rhoden, K.; Tice, G. Evaluation of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Method for Detecting Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli in Beef and Comparison to the U.S. Department of Agriculture Food Safety and Inspection Service Microbiology Laboratory Guidebook Method. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, K.; Selinger, L.B.; Stanford, K.; Guan, L.; Callaway, T.R.; McAllister, T.A. Perspectives on Super-Shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by Cattle. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, D.; Burgess, C.M.; McCabe, E.; Whyte, P.; Duffy, G. Development of a quantitative real time PCR assay to detect and enumerate Escherichia coli O157 and O26 serogroups in bovine recto-anal swabs. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 114, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, L.W.; Shridhar, P.B.; Shi, X.; An, B.; Cernicchiaro, N.; Renter, D.G.; Nagaraja, T.G.; Bai, J. A four-plex real-time PCR assay, based on rfbE, eae, stx1 and stx2 genes, for the detection and quantification of Escherichia coli O157 in cattle feces. Foodborne Path. Dis. 2015, 12, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Gyawali, P.; Toze, S. Quantitative PCR measurements of Escherichia coli including Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli (STEC) in Animal Feces and Environmental Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3084–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Nolan, T. Pitfalls of Quantitative Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Biomol. Tech. JBT 2004, 15, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murinda, S.E.; Ibekwe, A.M.; Zulkaffly, S.; Cruz, A.; Park, S.; Razak, N.; Paudzai, F.M.; Ab Samad, L.; Baquir, K.; Muthaiyah, K.; et al. Real-Time Isothermal Detection of Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli Using Recombinase Polymerase Amplification. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, R.K.; Stewart, G.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification for Diagnostic Applications. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M. Digital PCR hits its stride. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisset, D.; Štebih, D.; Milavec, M.; Gruden, K.; Žel, J. Quantitative Analysis of Food and Feed Samples with Droplet Digital PCR. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.; Burrell, A.M.; Foy, C.A. The applicability of digital PCR for the assessment of detection limits in GMO analysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 231, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, B.J.; Ness, K.D.; Masquelier, D.A.; Belgrader, P.; Heredia, N.J.; Makarewicz, A.J.; Bright, I.J.; Lucero, M.Y.; Hiddessen, A.L.; Legler, T.C.; et al. High-throughput droplet digital PCR system for absolute quantitation of DNA copy number. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8604–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.; Herrmann, J.; Armishaw, P.; Corbisier, P.; Emslie, K.R. Single molecule detection in nanofluidic digital array enables accurate measurement of DNA copy number. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbisier, P.; Bhat, S.; Partis, L.; Xie, V.R.D.; Emslie, K.R. Absolute quantification of genetically modified MON810 maize (Zea mays L.) by digital polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 396, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whale, A.S.; Huggett, J.F.; Cowen, S.; Speirs, V.; Shaw, J.; Ellison, S.; Foy, C.A.; Scott, D.J. Comparison of microfluidic digital PCR and conventional quantitative PCR for measuring copy number variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whale, A.S.; Cowen, S.; Foy, C.A.; Huggett, J.F. Methods for Applying Accurate Digital PCR Analysis on Low Copy DNA Samples. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccollum, G.; Stange, R.; Albrecht, U.; Bowman, K.; Niedz, R.; Stover, E. Development of a qpcr technique to screen for resistance to asiatic citrus canker. Acta Hortic. 2011, 892, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, R.; Fockler, C.; Dollinger, G.; Watson, R. Kinetic PCR Analysis: Real-time Monitoring of DNA Amplification Reactions. Nat. Biotechnol. 1993, 11, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, C.M.; Chevillet, J.R.; Briggs, H.A.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ruf, I.K.; Hindson, B.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Tewari, M. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, T.C.; Sedlak, R.H.; Cook, L.; Jerome, K.R. Tolerance of Droplet-Digital PCR vs Real-Time Quantitative PCR to Inhibitory Substances. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1670–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaegen, B.; De Reu, K.; De Zutter, L.; Verstraete, K.; Heyndrickx, M.; Van Coillie, E. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR and qPCR for the Quantification of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli in Bovine Feces. Toxins 2016, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, N.T.; Plunkett, G., III; Burland, V.; Mau, B.; Glasner, J.D.; Rose, D.J.; Mayhew, G.F.; Evans, P.S.; Gregor, J.; Kirkpatrick, H.A.; et al. Genome sequence of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Nature 2001, 409, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louie, M.; Read, S.; Simor, A.E.; Holland, J.; Louie, L.; Ziebell, K.; Brunton, J.; Hii, J. Application of Multiplex PCR for Detection of Non-O157 Verocytotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli in Bloody Stools: Identification of Serogroups O26 and O111. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 3375–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Terai, A.; Kurazono, H.; Takeda, Y.; Nishibuchi, M. Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of Vero toxin 2 variant genes from Escherichia coli O91:H21 isolated from a patient with the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Microb. Pathog. 1990, 8, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, P.I.; Blom, K.; Hughes, H.J.; Helsel, L.O.; Feng, P.; Swaminathan, B. Molecular characterization of the gene encoding H antigen in Escherichia coli and development of a PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism test for identification of E. coli O157:H7 and O157:NM. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Dey, M.; Abe, A.; Takeda, T. Isogenic Strain of Escherichia coli O157:H7 That Has Lost both Shiga Toxin 1 and 2 Genes. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Ibekwe, M.; Crowley, D.E.; Yang, C.-H. Persistence of Escherichia coli O157 and non-O157 strains in agricultural soils. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 490, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M.E.; Shi, X.; An, B.; Nagaraja, T.G.; Bai., J. Evaluation of a multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction for the quantification of Escherichia coli O157 in cattle feces. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noll, L.W.; Shridhar, P.B.; Shi, X.; An, B.; Cernicchiaro, N.; Renter, D.G.; Nagaraja, T.G.; Bai, J. A four-plex real-time PCR assay, based on rfbE, stx1, stx2, and eae genes, for the detection and quantification of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157 in cattle feces. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ibekwe, M.; Yi, X.; Wang, H.; Yamazaki, A.; Crowley, D.E.; Yang, C.-H. Persistence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Its Mutants in Soils. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, Q.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z. Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR and Quantitative PCR Assays for Quantitative Detection of Xanthomonas citri Subsp. citri. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Murinda, S.E.; Murry, M.A.; Schwartz, G.; Lundquist, T. Microbial community structures in algae cultivation ponds for bioconversion of agricultural wastes from livestock industry for feed production. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, M.B.; Carychao, D.; Gorski, L. Optimized Co-extraction and Quantification of DNA From Enteric Pathogens in Surface Water Samples Near Produce Fields in California. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 FAM (E = 85.2%, R2 = 0.950, slope = −3.735, y – int = 9.744),
FAM (E = 85.2%, R2 = 0.950, slope = −3.735, y – int = 9.744),  HEX (E = 91.7%, R2 = 0.959, slope = −3.520, y – int = 8.178),
HEX (E = 91.7%, R2 = 0.959, slope = −3.520, y – int = 8.178),  Texas Red (E = 92.4%, R2 = 0.963, slope = −3.735, y – int = 8.086),
Texas Red (E = 92.4%, R2 = 0.963, slope = −3.735, y – int = 8.086),  Cy5 (E = 112.0%, R2 = 0.869, slope = −3.064, y – int = 9.002).
Cy5 (E = 112.0%, R2 = 0.869, slope = −3.064, y – int = 9.002).
 FAM (E = 85.2%, R2 = 0.950, slope = −3.735, y – int = 9.744),
FAM (E = 85.2%, R2 = 0.950, slope = −3.735, y – int = 9.744),  HEX (E = 91.7%, R2 = 0.959, slope = −3.520, y – int = 8.178),
HEX (E = 91.7%, R2 = 0.959, slope = −3.520, y – int = 8.178),  Texas Red (E = 92.4%, R2 = 0.963, slope = −3.735, y – int = 8.086),
Texas Red (E = 92.4%, R2 = 0.963, slope = −3.735, y – int = 8.086),  Cy5 (E = 112.0%, R2 = 0.869, slope = −3.064, y – int = 9.002).
Cy5 (E = 112.0%, R2 = 0.869, slope = −3.064, y – int = 9.002).
| Gene | Primer/Probe | Sequence | Fluorescent Dye | Quencher | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| stx1 | Forward Reverse Probe | GCATCCAGAGCAGTTCTGC GCGTCATCGTATACACAGGAG TGTCACTGTCACAGCAGAAGCCTTACG | FAM(dd) TEX (Q) | Iowa Black RQ-Sp | [35] |
| stx2 | Forward Reverse Probe | CAAGAGCGATGTTACGGTTTG GTAAGATCAACATCTTCAGCAGTC ACATAAGAACGCCCACTGAGATCATCCA | FAM(dd) Cy5 (Q) | Iowa Black FQ | [35] |
| rfbEO157 | Forward Reverse Probe | CTGTCCACACGATGCCAATG CGATAGGCTGGGGAAACTAGG TTAATTCCACGCCAACCAAGATCCTCA | HEX(dd) FAM (Q) | Iowa Black FQ | [35] |
| eae | Forward Reverse Probe | AAAGCGGGAGTCAATGTAACG GGCGATTACGCGAAAGATAC CTCTGCAGATTAACCTCTGCCG | HEX(dd &Q) | Iowa Black FQ | [35] |
| Time (h) | stx1 | stx2 | Dilution * Factor | stx1 | stx2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positives | Negatives | Positives | Negatives | Positives | Negatives | Positives | Negatives | ||
| 0 | 27 | 9 | 7 | 29 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 9 | 3 |
| 2 | 29 | 7 | 8 | 28 | 1 | 12 | 0 | 10 | 2 |
| 2 | 12 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |||||
| 3 | 10 | 2 | 8 | 4 | |||||
| 8 | 29 | 7 | 24 | 12 | 4 | 9 | 3 | 6 | 6 |
| 5 | 9 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |||||
| 24 | 27 | 9 | 27 | 9 | 6 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 8 |
| 7 | 11 | 1 | 7 | 5 | |||||
| 8 | 11 | 1 | 6 | 6 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibekwe, M.A.; Murinda, S.E.; Park, S.; Obayiuwana, A.; Murry, M.A.; Schwartz, G.; Lundquist, T. Comparative Use of Quantitative PCR (qPCR), Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR), and Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) in the Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli (STEC) in Environmental Samples. Water 2020, 12, 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123507
Ibekwe MA, Murinda SE, Park S, Obayiuwana A, Murry MA, Schwartz G, Lundquist T. Comparative Use of Quantitative PCR (qPCR), Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR), and Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) in the Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli (STEC) in Environmental Samples. Water. 2020; 12(12):3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123507
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbekwe, Mark A., Shelton E. Murinda, Stanley Park, Amarachukwu Obayiuwana, Marcia A. Murry, Gregory Schwartz, and Trygve Lundquist. 2020. "Comparative Use of Quantitative PCR (qPCR), Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR), and Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) in the Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli (STEC) in Environmental Samples" Water 12, no. 12: 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123507
APA StyleIbekwe, M. A., Murinda, S. E., Park, S., Obayiuwana, A., Murry, M. A., Schwartz, G., & Lundquist, T. (2020). Comparative Use of Quantitative PCR (qPCR), Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR), and Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) in the Detection of Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli (STEC) in Environmental Samples. Water, 12(12), 3507. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123507







