Perforated Baffles for the Optimization of Disinfection Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Model
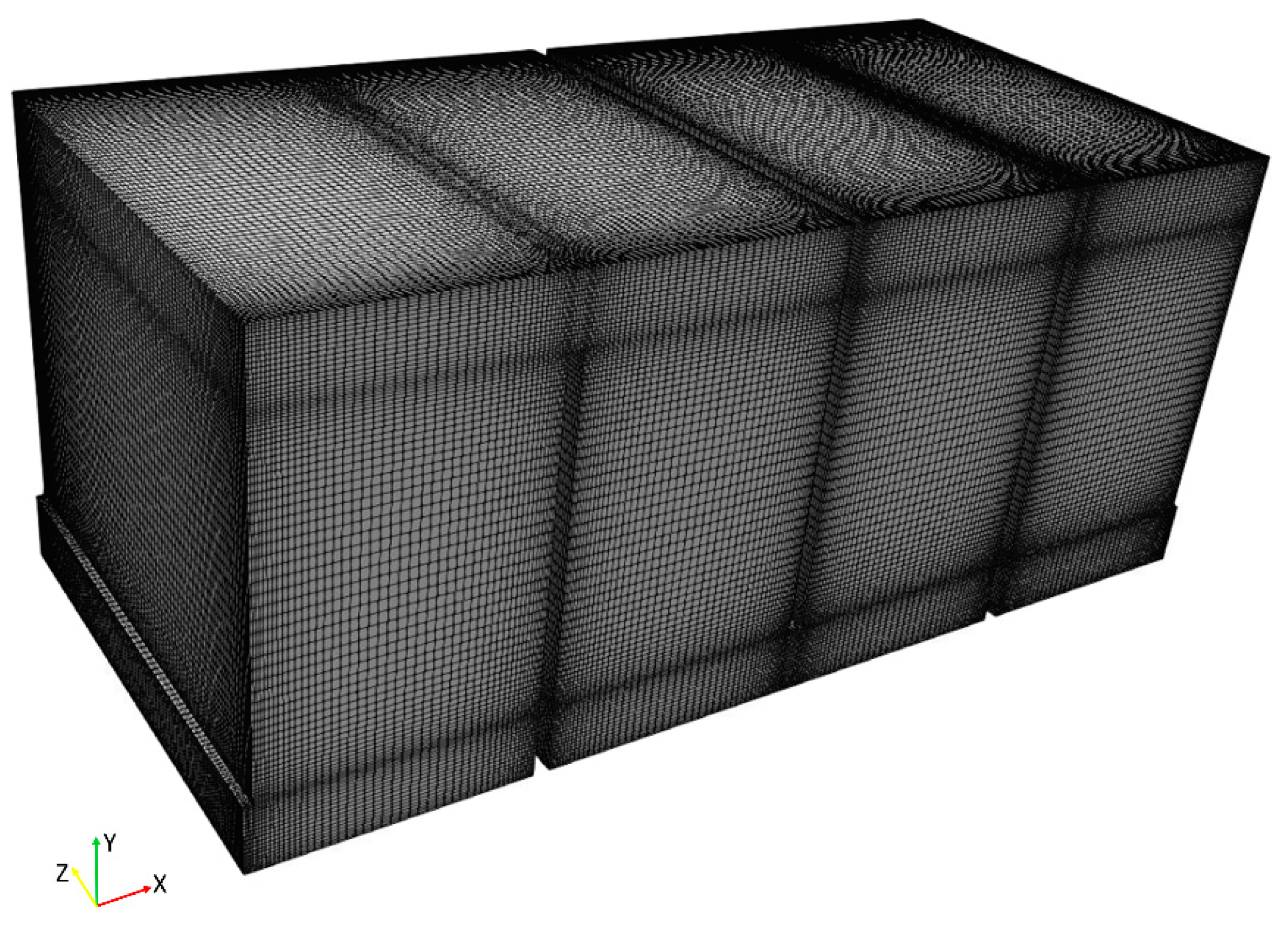
2.1. Computational Domain
2.2. Mathematical Formulation
2.3. Boundary Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
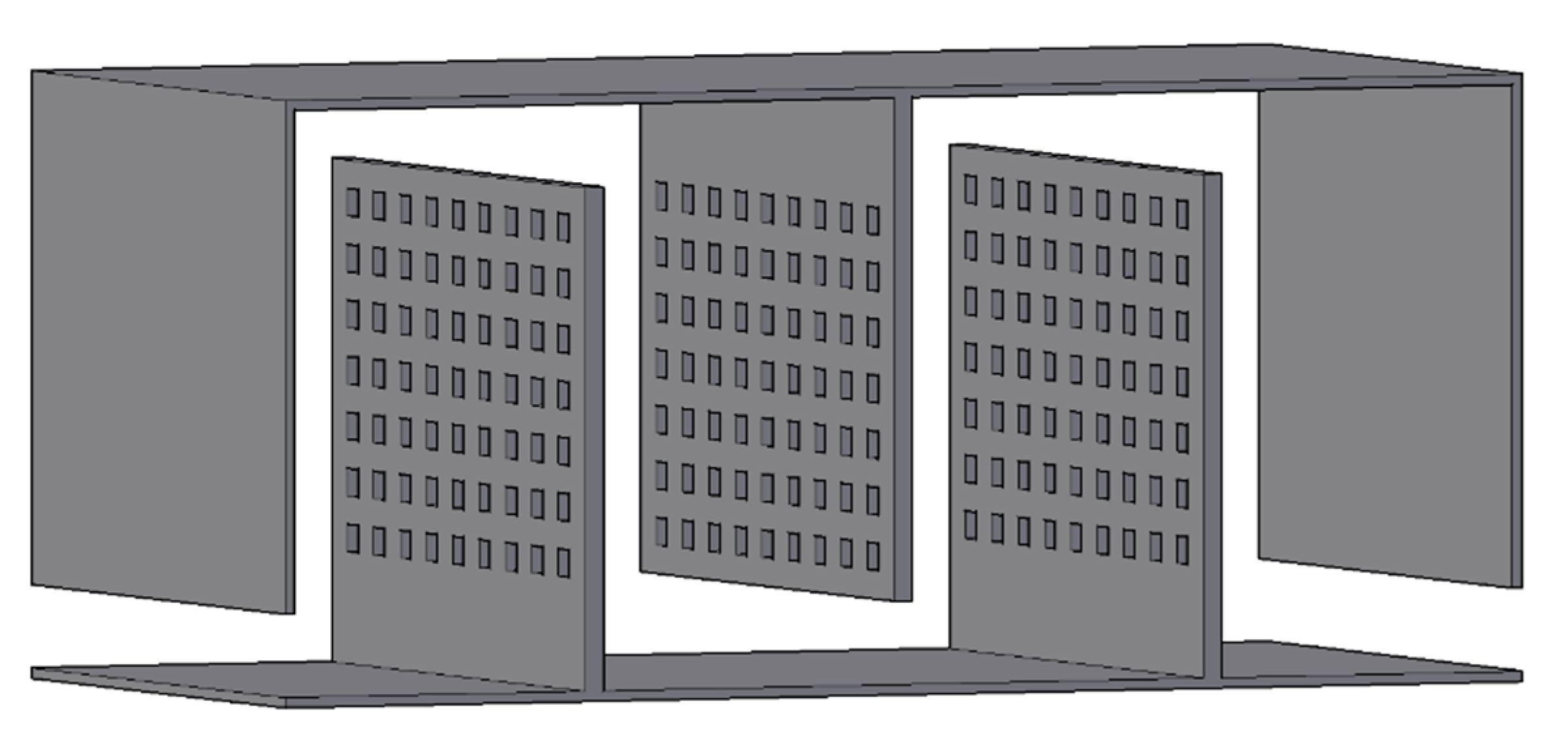
3.1. Perforated Baffles Geometry
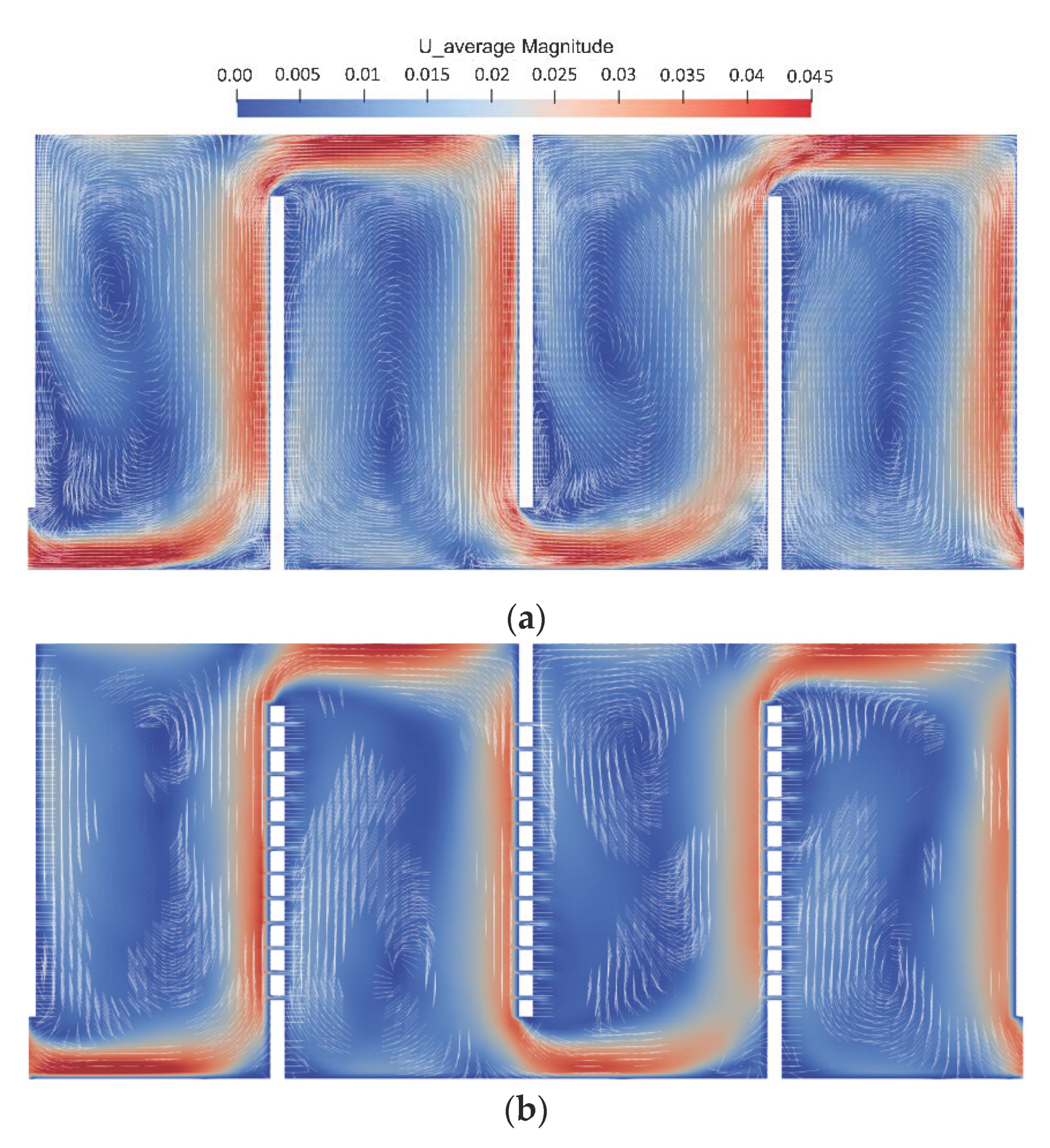
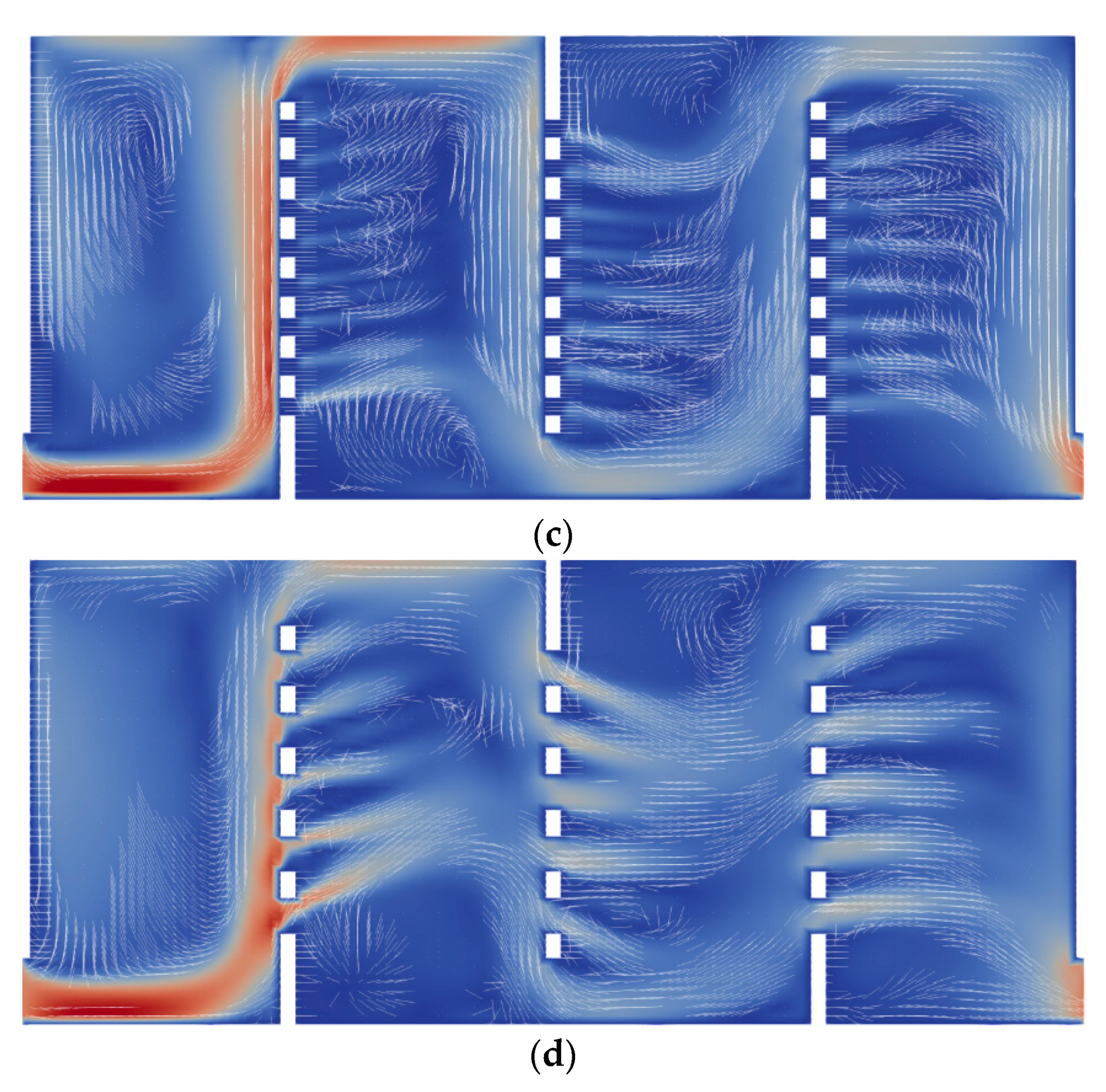
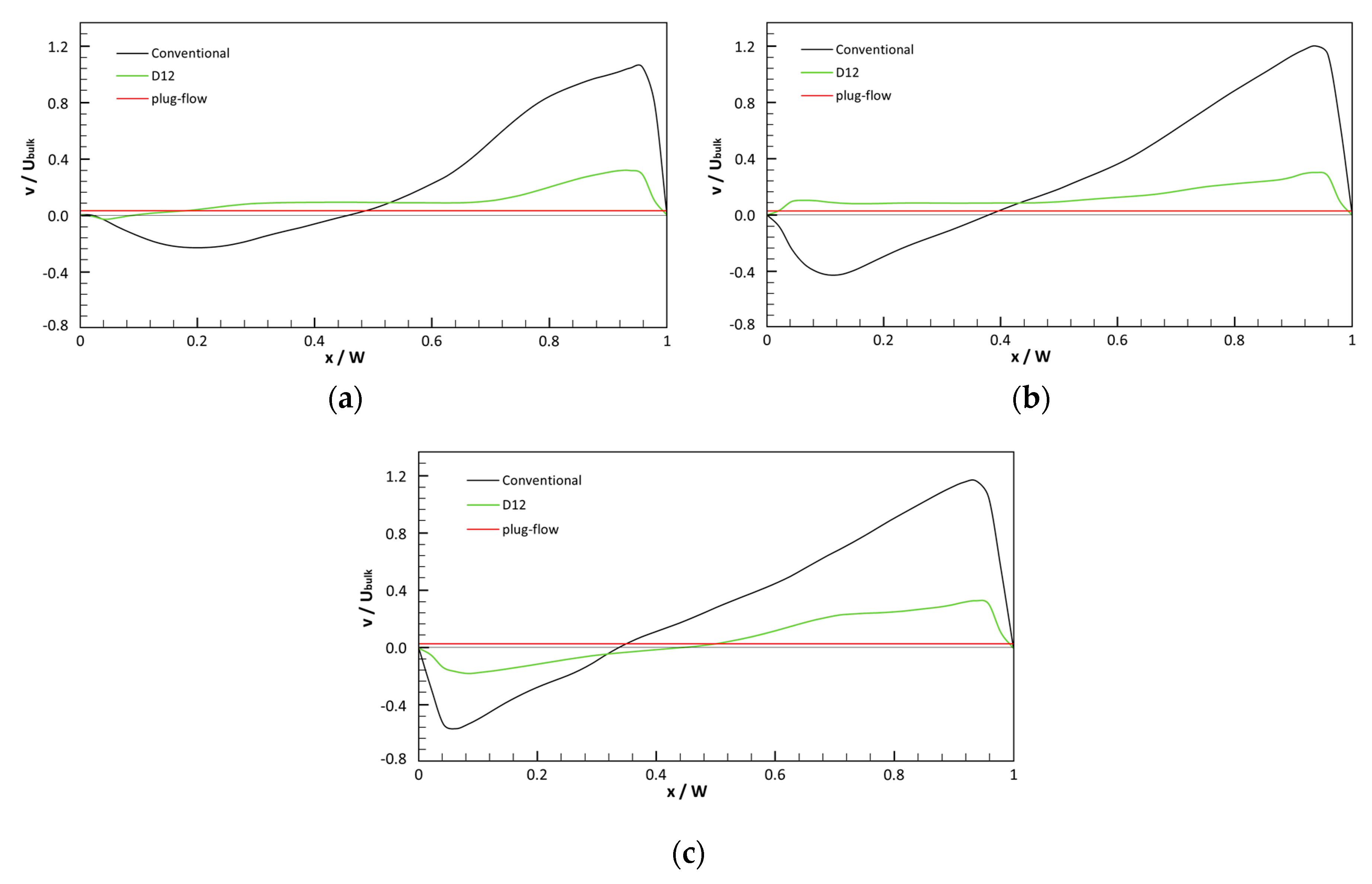
3.2. Flow Analysis
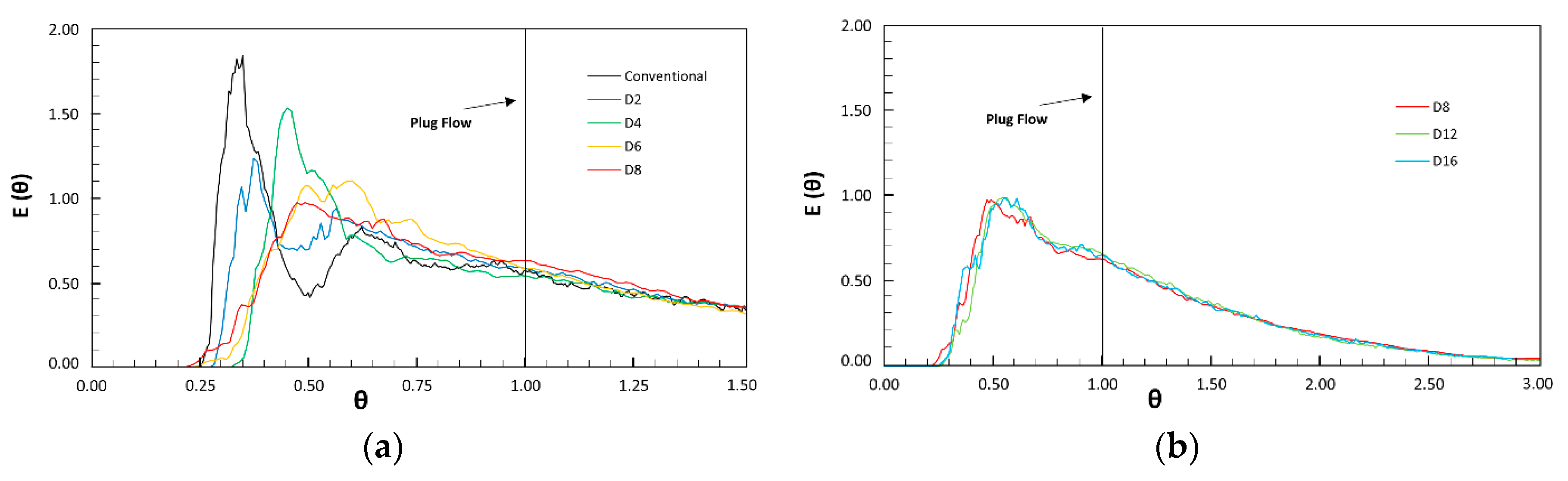
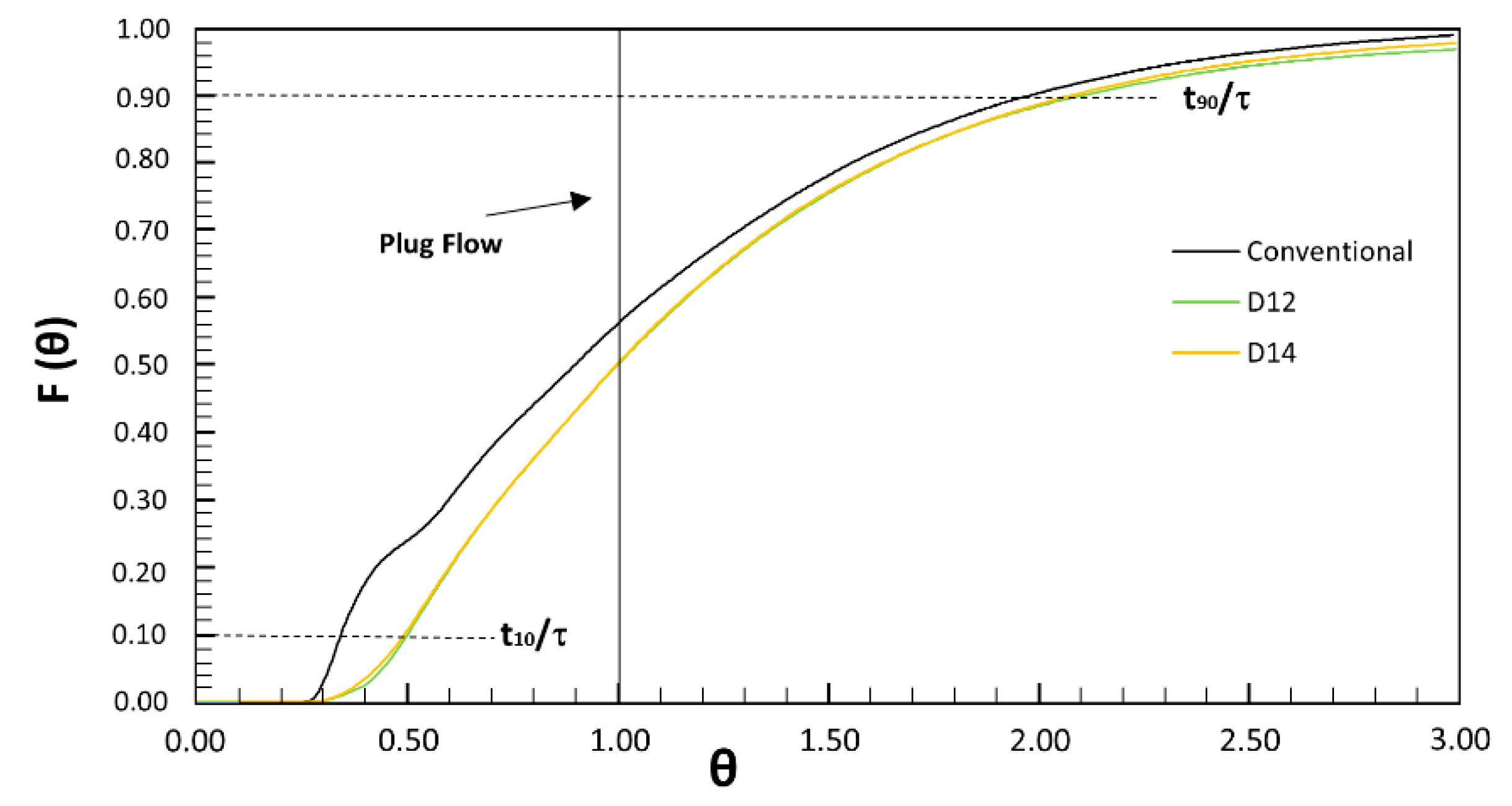
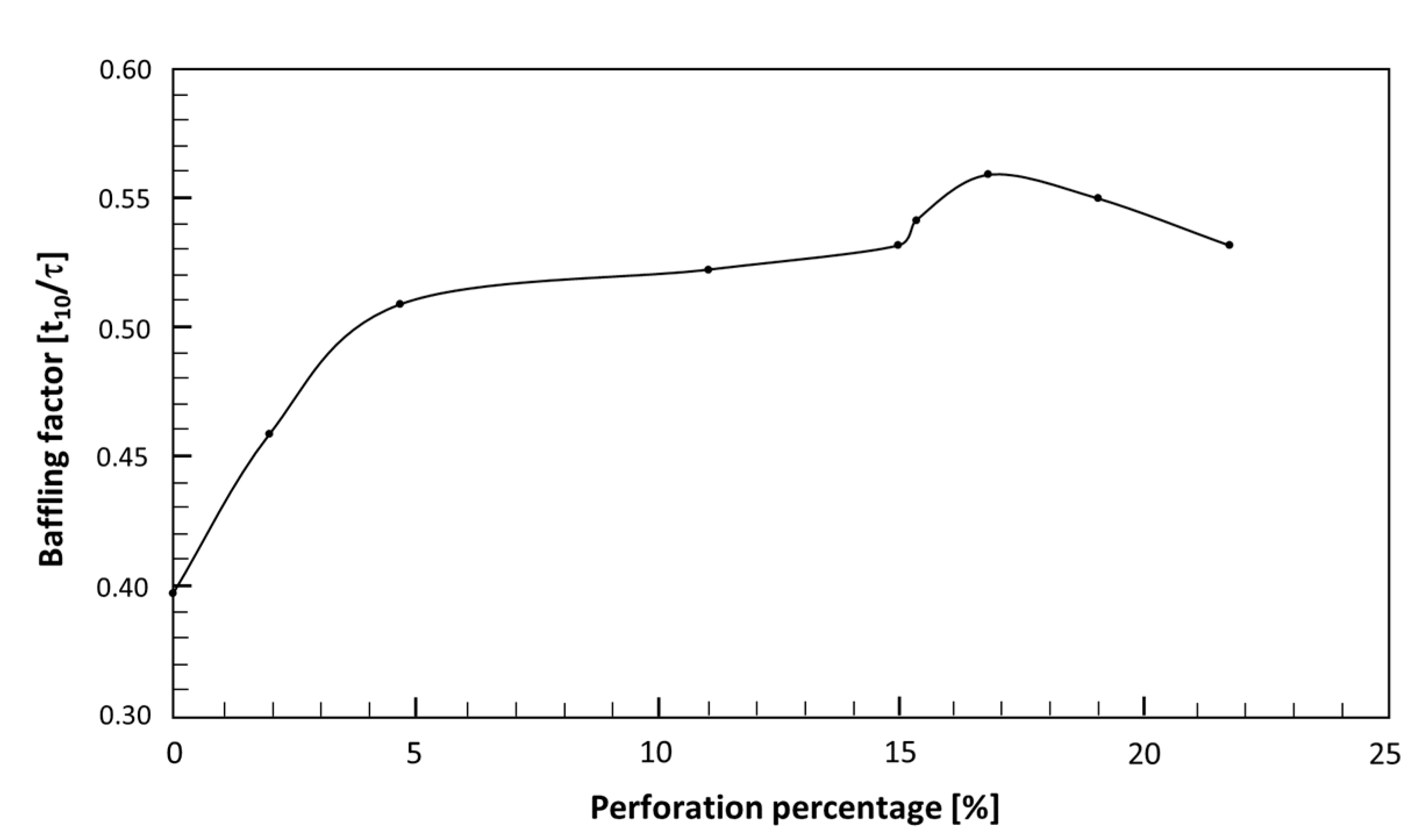
3.3. Tracer Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angeloudis, A.; Stoesser, T.; Gualtieri, C.; Falconer, R.A. Contact tank design impact on process performance. Environ. Model. Assess. 2016, 21, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Kim, D.-I.; Kim, J.; Stoesser, T. Large eddy simulation of flow and tracer transport in multichamber ozone contactors. J. Environ. Eng. 2010, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angeloudis, A.; Stoesser, T.; Falconer, R.A. Predicting the disinfection efficiency range in chlorine contact tanks through a CFD-based approach. Water Res. 2014, 60, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shao, X.; Falconer, R.A. Flow and transport simulation models for prediction of chlorine contact tank flow-through curves. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, R.; Taghipour, R.; Mirgolbabaei, H. Numerical assessment of hydrodynamic characteristics in chlorine contact tank. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2011, 67, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Asce, M.; Tejada-Martínez, A.E.; Zhang, Q. Hydraulic efficiency in RANS of the flow in multichambered contactors. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, E.C.; Do, R. Nascimento Siqueira, performance assessment of hydraulic efficiency indexes. J. Environ. Eng. 2008, 134, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, E.; Aral, M.M. Unified analysis of multi-chamber contact tanks and mixing efficiency based on vorticity field. part I: Hydrodynamic analysis. Water 2016, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aral, M.M.; Demirel, E. Novel slot-baffle design to improve mixing efficiency and reduce cost of disinfection in drinking water treatment. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 143, 06017006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, E.; Aral, M.M. An efficient contact tank design for potable water treatment. Tek. Dergi 2018, 29, 8279–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, E.; Aral, M.M. Liquid sloshing damping in an accelerated tank using a novel slot-baffle design. Water 2018, 10, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kizilaslan, M.A.; Demirel, E.; Aral, M.M. Effect of porous baffles on the energy performance of contact tanks in water treatment. Water 2018, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kizilaslan, M.A.; Nasyrlayev, N.; Demirel, E. A perforated baffle design to improve mixing in contact tanks. Water 2020, 12, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauen, W.B.; Angeloudis, A.; Falconer, R.A. Appraisal of chlorine contact tank modelling practices. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5834–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tejada-Martínez, A.E.; Zhang, Q. Developments in computational fluid dynamics-based modeling for disinfection technologies over the last two decades: A review. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 58, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeloudis, A.; Stoesser, T.; Kim, D.; Falconer, R.A. Modelling of flow, transport and disinfection kinetics in contact tanks. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2014, 167, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, V.; Barbeau, B. Validation of a simple method for predicting the disinfection performance in a flow-through contactor. Water Res. 2014, 49, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Tejada-Martinez, A.; Zhang, Q.; Wicklein, E. Evaluating reactor hydraulics in a cost-effective and environment-friendly way: Numerical tracer study. AWWA Water Sci. 2019, 1, e1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhravi, S.; Eslamian, S.; Fathianpour, N. Assessing the effects of flow distribution on the internal hydraulic behavior of a constructed horizontal subsurface flow wetland using a numerical model and a tracer study. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2017, 17, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrokhi, M.; Rostami, F.; Said, M.A.M.; Yazdi, S.R.S.; Syafalni. The effect of number of baffles on the improvement efficiency of primary sedimentation tanks. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 3725–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tejada-Martinez, A.E.; Lei, H.; Zhang, Q. Indicators for technological, environmental and economic sustainability of ozone contactors. Water Res. 2016, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tejada-Martínez, A.E.; Zhang, Q. Evaluation of large eddy simulation and RANS for determining hydraulic performance of disinfection systems for water treatment. J. Fluids Eng. 2014, 136, 121102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeloudis, A.; Stoesser, T.; Falconer, R.A.; Kim, D. Flow, transport and disinfection performance in small- and full-scale contact tanks. J. Hydro Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilaslan, M.A.; Demirel, E.; Aral, M.M. Efficiency enhancement of chlorine contact tanks in water treatment plants: A full-scale application. Processes 2019, 7, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Tejada-Martínez, A.E.; Zhang, Q. Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes Simulation of the flow and tracer transport in a multichambered ozone contactor. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Elovitz, M.; Roberts, P.J.W.; Kim, J.H. Using 3D LIF to investigate and improve performance of a multichamber ozone contactor. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2010, 102, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, P.; Di Bella, G.; De Marchis, M. Large Eddy Simulation of Contact Tanks for Disinfection in Drinking Water Treatment. In Direct and Large Eddy Simulation XII; García-Villalba, M., Kuerten, H., Salvetti, M., Eds.; DLES 2019 ERCOFTAC Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 27, pp. 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, M. Large eddy simulations of roughened channel flows: Estimation of the energy losses using the slope of the roughness. Comput. Fluids 2016, 140, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Stoesser, T.; Kim, J.H. Modeling aspects of flow and solute transport simulations in water disinfection tanks. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 8039–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pierre, K.C.; Tejada-Martinez, A.E. Impacts of flow and tracer release unsteadiness on tracer analysis of water and wastewater treatment facilities. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Disinfection Profiling and Benchmarking Guidance Manual; Appendix A Rep. No. EPA 816-R-03-004 EPA; USEPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1999.
- Marske, D.M.; Boyle, J.D. Chlorine contact chamber design—A field evaluation. Water Sew. Work. 1973, 120, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
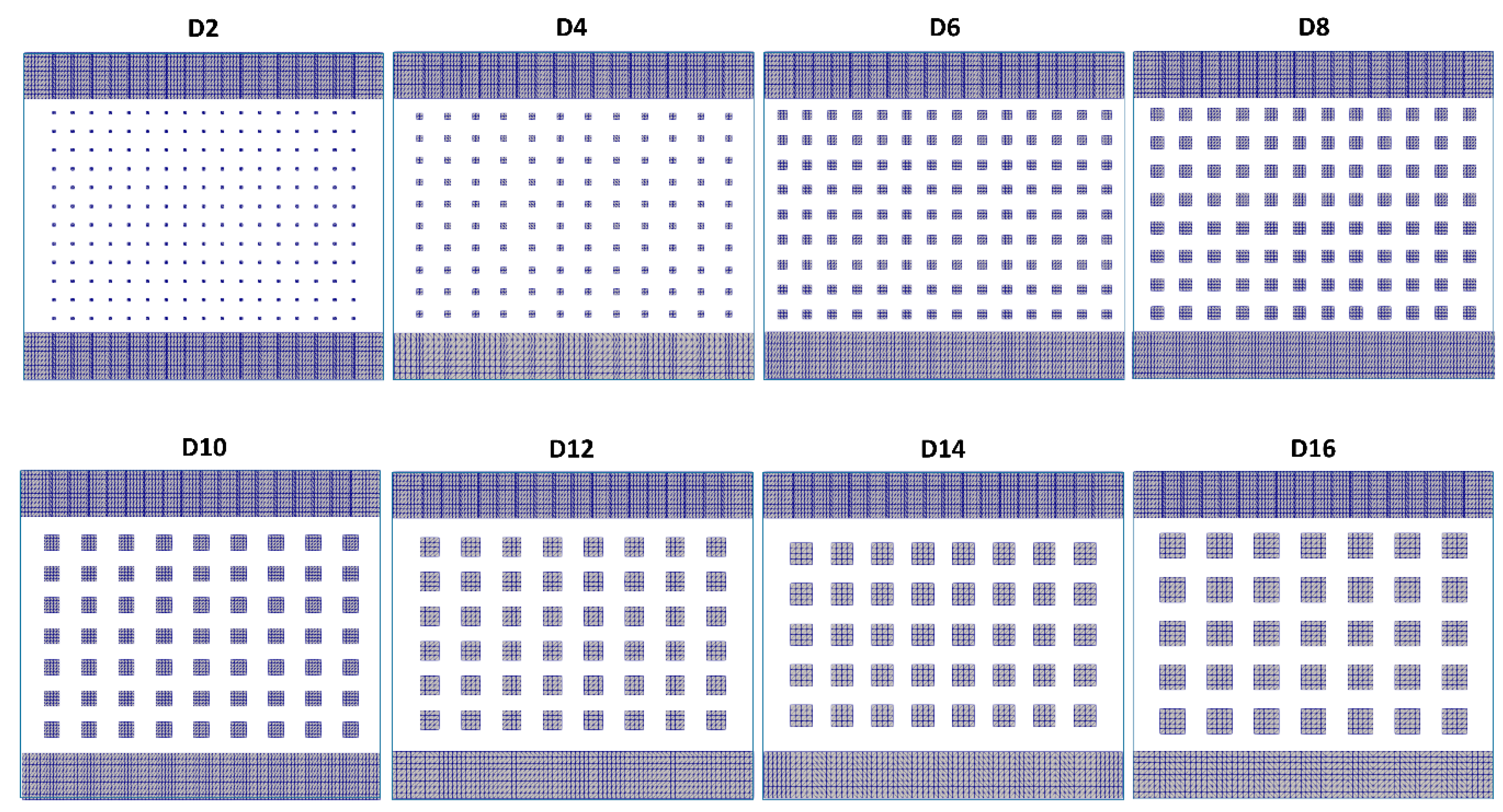
| Design | Hole Side (mm) | Number of Holes | Perforation Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D2 | 2 | 204 | 2.0 |
| D4 | 4 | 120 | 4.6 |
| D6 | 6 | 126 | 11.0 |
| D8 | 8 | 96 | 14.8 |
| D10 | 10 | 63 | 15.2 |
| D12 | 12 | 48 | 16.7 |
| D14 | 14 | 40 | 18.9 |
| D16 | 16 | 35 | 21.6 |
| Baffling Condition | t10/τ |
|---|---|
| Unbaffled (mixed flow) | 0.1 |
| Poor | 0.3 |
| Average | 0.5 |
| Superior | 0.7 |
| Perfect (plug-flow) | 1.0 |
| Design | t10/τ | t90/τ | Mo | σ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | 0.347 | 2.000 | 5.758 | 0.105 |
| D2 | 0.409 | 2.052 | 5.022 | 1.313 |
| D4 | 0.459 | 2.275 | 4.960 | 1.308 |
| D6 | 0.472 | 2.152 | 4.560 | 1.300 |
| D8 | 0.481 | 2.116 | 4.396 | 1.285 |
| D10 | 0.491 | 2.098 | 4.273 | 1.279 |
| D12 | 0.509 | 2.116 | 4.161 | 1.272 |
| D14 | 0.499 | 2.061 | 4.127 | 1.268 |
| D16 | 0.481 | 2.070 | 4.302 | 1.280 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruno, P.; Di Bella, G.; De Marchis, M. Perforated Baffles for the Optimization of Disinfection Treatment. Water 2020, 12, 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123462
Bruno P, Di Bella G, De Marchis M. Perforated Baffles for the Optimization of Disinfection Treatment. Water. 2020; 12(12):3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123462
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruno, Paolo, Gaetano Di Bella, and Mauro De Marchis. 2020. "Perforated Baffles for the Optimization of Disinfection Treatment" Water 12, no. 12: 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123462
APA StyleBruno, P., Di Bella, G., & De Marchis, M. (2020). Perforated Baffles for the Optimization of Disinfection Treatment. Water, 12(12), 3462. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123462







