Technological Reliability and Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment in Two Hybrid Constructed Wetlands in the Roztocze National Park (Poland)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of the Roztocze National Park
2.2. Characteristics of the Experimental Facilities
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
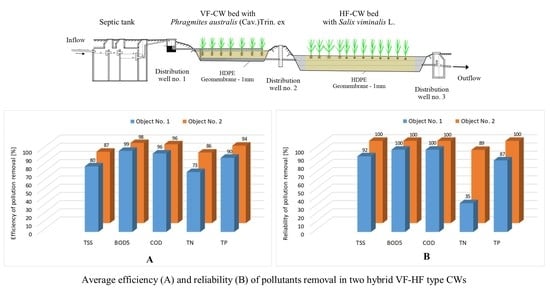
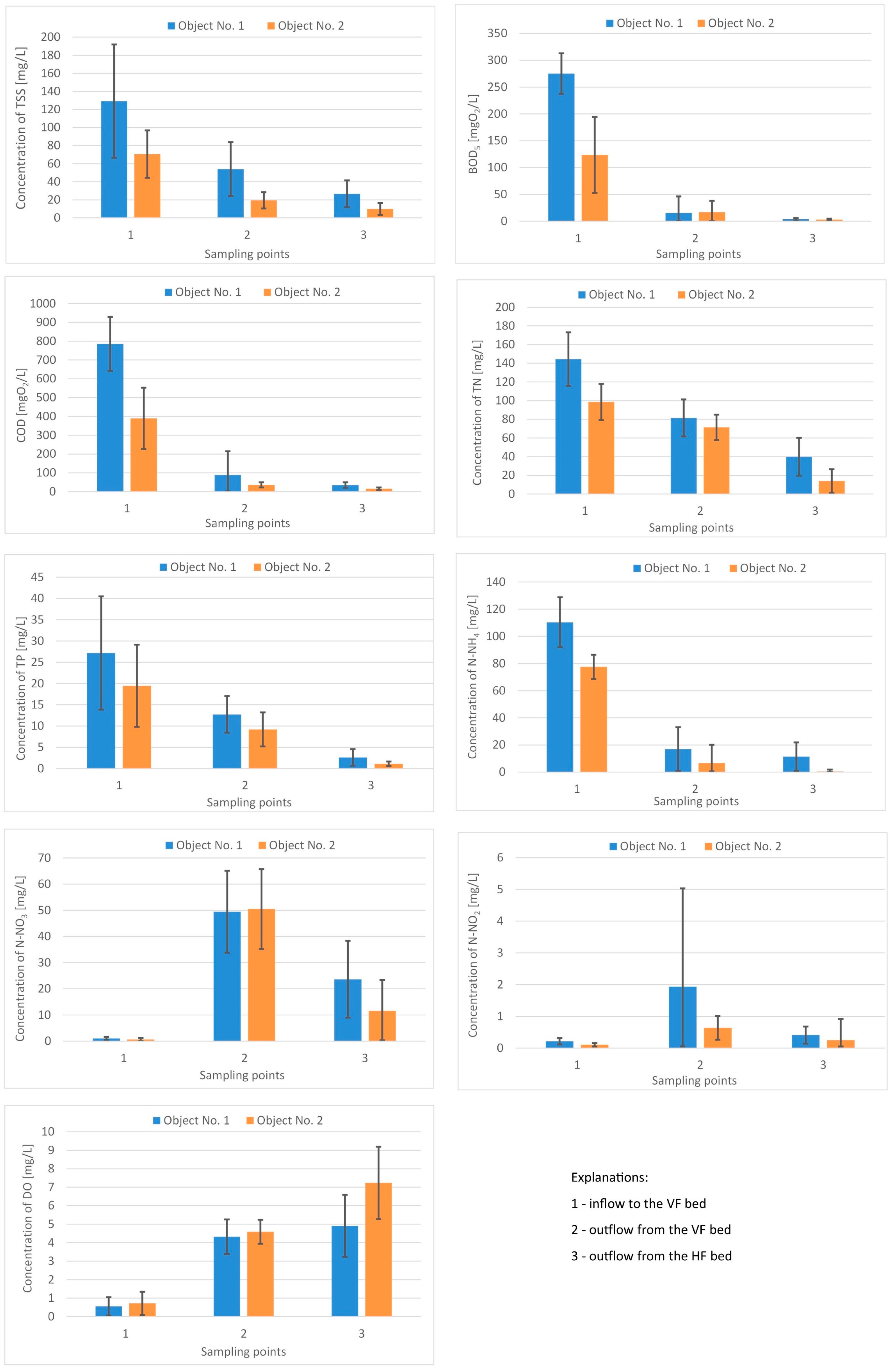
3.1. The Efficiency of Pollutants Removal Processes
3.2. The Technological Reliability of the Studied Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Szczęsna, J.; Wojtanowicz, P. The role of national parks in promoting sustainable and responsible tourism. Barom. Reg. 2014, 12, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Podbrożna, D.; Kopczacka, K.; Marzec, M.; Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Pochwatka, P.; Listosz, A.; Malik, A. The state of water and wastewater management in the municipalities of the Polesie National Park. J. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóżwiakowski, K.; Podbrożna, D.; Kopczacka, K.; Jaguś, M.; Marzec, M.; Listosz, A.; Pochwatka, P.; Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Malik, A. The state of water and wastewater management in the municipalities of the Roztocze National Park. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Nature Conservation Act from 16 April 2004; Dz. U. Nr 92, poz. 880; SEJM: Warsaw, Poland, 2014. (In Polish)
- Lin, S.S.; Shen, S.L.; Zhou, A.; Lyu, H.M. Sustainable development and environmental restoration in Lake Erhai, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.S.; Shen, S.L.; Zhou, A.; Lyu, H.M. Assessment and management of lake eutrophication: A case study in Lake Erhai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.M.; Shen, S.L.; Zhou, A. The development of IFN-SPA: A new risk assessment method of urban water quality and its application in Shanghai. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 124542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.S.; Shen, S.L.; Zhou, A.; Xu, Y.S. Approach based on TOPSIS and Monte Carlo simulation methods to evaluate lake eutrophication levels. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Water 2010, 2, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Five decades of experience. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewska, M.; Obarska-Pempkowiak, H. 20 Years of experience of hybrid constructed wetlands exploitation in Poland. Rocz. Ochr. Sr. 2009, 11, 875–888. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Brix, H. Use of constructed wetlands in water pollution control: Historical development, present status, and future perspectives. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 30, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haberl, R.; Perfler, R.; Mayer, H. Constructed wetlands in Europe. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 32, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalik, P.; Obarska-Pempkowiak, H. Polish experience, with sewage purification in constructed wetlands. In Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment in Europe; Vymazal, J., Brix, H., Cooper, P.F., Green, M.B., Haberl, R., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. Horizontal sub-surface flow and hybrid constructed wetlands systems for wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perttu, K.L.; Kowalik, P.J. Salix vegetation filters for purification of waters and soils. Biomass Bioenergy 1997, 12, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.A.; Brix, H.; Johansen, N.H. Phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater in an experimental two-stage vertical flow constructed wetland system equipped with a calcite filter. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewska, M.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Ghrabi, A.; Masi, F. Impact of influent wastewater quality on nitrogen removal rates in multistage treatment wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12840–21284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gajewska, M.; Skrzypiec, K.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Mucha, Z.; Wójcik, W.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Bugajski, P. Kinetics of pollutants removal in vertical and horizontal flow constructed wetlands in temperate climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiakowski, K. Studies on the efficiency of sewage treatment in chosen constructed wetland systems. Infrastruct. Ecol. Rural Areas 2012, 1, 232. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Marzec, M.; Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Gizińska-Górna, M.; Pytka-Woszczyło, A.; Malik, A.; Listosz, A.; Gajewska, M. 25 years of research and experiences about the application of constructed wetlands in southeastern Poland. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luederitz, V.; Eckert, E.; Lange-Weber, M.; Lange, A.; Gersberg, R.M. Nutrient removal efficiency and resource economics of vertical flow and horizontal flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 18, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, F.; Martinuzzi, N. Constructed wetlands for the Mediterranean countries: Hybrid systems for water reuse and sustainable sanitation. Desalination 2007, 215, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, F.; Caffaz, S.; Ghrabi, A. Multi-stage constructed wetlands systems for municipal wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melián, J.A.H.; Rodríguez, A.J.M.; Araña, J.; Díaz, O.G.; Henríquez, J.J.G. Hybrid constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment and reuse in the Canary Islands. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Types of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Their potential for nutrient removal. In Transformations on Nutrients in Natural and Constructed Wetlands; Vymazal, J., Ed.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 1–93. [Google Scholar]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vymazal, J. The use of hybrid constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment with special attention to nitrogen removal: A review of a recent development. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4795–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Knight, R.L.; Vymazal, J.; Brix, H.; Cooper, P.; Haberl, R. Constructed Wetlands for Pollution Control. Processes, Performance, Design and Operation; Scientific and Technical Report; International Water Association: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S.D. Treatment Wetlands; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, T.H.; Quang, L.N.; Chiem, N.; Brix, H. Treatment of high-strength wastewater in tropical constructed wetlands planted with Sesbania sesban: Horizontal subsurface flow versus vertical downflow. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Mucha, Z.; Generowicz, A.; Baran, S.; Bielińska, J.; Wójcik, W. The use of multi-criteria analysis for selection of technology for a household WWTP compatible with sustainable development. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2015, 3, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brix, H. Treatment of wastewater in the rhizosphere of wetland plants-the root-zone method. Water Sci. Technol. 1987, 19, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Kröpfelová, L. Removal of organics in constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow: A review of the field experience. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3911–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfiya, Y.; Gross, A.; Sklarz, M.; Friedler, E. Reliability of on-site greywater treatment systems in Mediterranean and arid environments—A case study. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfí, M.; Pedescoll, A.; Carretero, J.; Puigagut, J.; García, J. Reliability and economic feasibility of online monitoring of constructed wetlands performance. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 5848–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Bugajski, P.; Mucha, Z.; Wójcik, W.; Jucherski, A.; Nastawny, M.; Siwiec, T.; Mazur, A.; Obroślak, R.; Gajewska, M. Reliability of pollutions removal processes during long-term operation of one-stage constructed wetland with horizontal flow. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Bugajski, P.; Kurek, K.; Nunes de Carvalho, M.F.; Araújo Almeida, M.A.; Siwiec, T.; Borowski, G.; Czekała, W.; Dach, J.; Gajewska, M. The efficiency and technological reliability of biogenic compounds removal during long-term operation of a one-stage subsurface horizontal flow constructed wetland. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 202, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Bugajski, P.; Kurek, K.; Cáceres, R.; Siwiec, T.; Jucherski, A.; Czekała, W.; Kozłowski, K. Technological reliability of pollutant removal in different seasons in one-stage constructed wetland system with horizontal flow operating in the moderate climate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucherski, A.; Nastawny, M.; Walczowski, A.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Gajewska, M. Assessment of the technological reliability of a hybrid constructed wetland for wastewater treatment in a mountain eco-tourist farm in Poland. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzec, M.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Dębska, A.; Gizińska-Górna, M.; Pytka-Woszczyło, A.; Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Listosz, A. The efficiency and reliability of pollutant removal in a hybrid constructed wetland with common reed, manna grass and virginia mallow. Water 2018, 10, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marzec, M.; Gizińska-Górna, M.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Pytka-Woszczyło, A.; Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Gajewska, M. The efficiency and reliability of pollutant removal in a hybrid constructed wetland with giant miscanthus and Jerusalem artichoke in Poland. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Morrison, R.J.; Gangaiya, P.; Miskiewicz, A.G.; Chambers, R.L.; Powell, M. Constructed wetlands as urban water constructed wetlands as urban water quality control ponds - studies on reliability and effectiveness. Wetl. Aust. J. 2016, 28, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q. Enhanced nitrogen removal reliability and efficiency in integrated constructed wetland microcosms using zeolite. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska, E.; Gajewska, M.; Ostojski, A. Reliability of nitrogen removal processes in multistage treatment wetlands receiving high-strength wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszewski, B.M.; Siwek, K.; Gluza, A.; Shuber, P. Climate. In Roztocze. Nature and Human; Grabowski, T., Harasimuk, M., Kaszewski, B.M., Kravchuk, Y., Lorens, B., Michalczyk, Z., Eds.; Roztoczański Park Narodowy: Zwierzyniec, Poland, 2015; pp. 123–133. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Listosz, A.; Gizińska-Górna, M.; Pytka, A.; Marzec, M.; Sosnowska, B.; Chołody, M.; Dyczko, A. Quality of rainwaters outflowing from roofs of garage buildings of park authority of Roztocze National Park. J. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 17, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalczyk, Z.; Kovalchuk, I.; Chmiel, S.; Głowacki, S.; Chabudziński, Ł.; Kharkevych, V.; Voloschyn, P. Waters. In Roztocze. Nature and Human; Grabowski, T., Harasimuk, M., Kaszewski, B.M., Kravchuk, Y., Eds.; Roztoczański Park Narodowy: Zwierzyniec, Poland, 2015; pp. 103–122. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Marzec, M.; Gizińska-Górna, M.; Pytka, A.; Skwarzyńska, A.; Gajewska, M.; Słowik, T.; Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Steszuk, A.; Grabowski, T.; et al. The concept of construction of hybrid constructed wetland for wastewater treatment in Roztoczański National Park. Bar. Reg. 2014, 12, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Gajewska, M.; Marzec, M.; Gizińska-Górna, M.; Pytka, A.; Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Sosnowska, B.; Baran, S.; Malik, A.; Kufel, R. Hybrid constructed wetlands for the National Parks—a case study, requirements, dimensioning, preliminary results. In Natural and Constructed Wetlands. Nutrients, Heavy Metals and Energy Cycling, and Flow; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 247–265. [Google Scholar]
- APHA, (American Public Health Association). Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- APHA, (American Public Health Association). Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Micek, A.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Marzec, M.; Listosz, A.; Malik, A. Efficiency of pollution removal in preliminary settling tanks of household wastewater treatment plants in the Roztocze National Park. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, B. Weibull Analysis; ASQV Quality Press: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 1994; ISBN 087389295X/978-0873892957. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation of the Minister of Maritime Economy and Inland Navigation of 12 July 2019 on Substances Which Are Particularly Harmful to the Aquatic Environment and the Conditions to Be Met When Discharging Wastewater into Water or Soil and When Discharging Rainwater or Snowmelt into Water or Water Installations. 2019; pos. 1311.
- Vymazal, J.; Brix, H.; Cooper, P.F.; Haberl, R.; Perfler, R.; Laber, J. Removal mechanisms and types of constructed wetlands. In Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment in Europe; Vymazal, J., Brix, H., Cooper, P.F., Green, M.B., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 17–66. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.M.; Chen, B.; Zhou, J.B.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xi, X.R.; Lin, C.; Chen, G.Q. A vertical subsur-face—Flow constructed wetland in Beijing. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2008, 13, 1986–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, A.; Arendacz, M.; Gajewska, M.; Obarska-Pempkowiak, H.; Randerson, P.; Kowalik, P. Removal of organic matter and nitrogen in an horizontal subsurface flow (HSSF) constructed wetland under transient loads. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Öövel, M.; Tooming, A.; Mauring, T.; Mander, Ü. Schoolhouse wastewater purification in a LWA-filled hybrid constructed wetland in Estonia. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Li, Y. Enhancement of nitrogen removal in towery hybrid constructed wetland to treat domestic wastewater for small rural communities. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laber, J.; Haberl, R.; Shrestha, R. Two-stage constructed wetland for treating hospital wastewater in Nepal. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Haberl, R.; Moog, O.; Shrestha, R.R. Performance of an anaerobic baffled reactor and hybrid constructed wetland treating high strength wastewater in Nepal—A model for DEWATS. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.C.; De Laune, R.D.; Park, W.Y.; Lim, J.S.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.S.; Heo, J.S. Evaluation of a hybrid constructed wetland for treating domestic sewage from individual housing units surrounding agricultural villages in South Korea. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hogain, S. The design, operation and performance of a municipal hybrid reed bed treatment system. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Inoue, T.; Kato, K.; Ietsugu, H.; Tomita, K.; Nagasawa, T. Potential of hybrid constructed wetland system in treating milking parlor wastewater under cold climatic conditions in northern Hokkaido, Japan. Water Pract. Tech. 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, H.; Arias, C.A. The use of vertical flow constructed wetlands for on-site treatment of domestic wastewater: New Danish guidelines. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, H. Gas exchange through the soil-atmosphere interphase and through dead culms of Phragmites australis in a constructed reed bed receiving domestic sewage. Water Res. 1990, 24, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Kröpfelová, L. Is concentration of dissolved oxygen a good indicator of processes in filtration beds of horizontal-flow constructed wetlands? In Wastewater Treatment, Plant Dynamics and Management; Vymazal, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Gajewska, M.; Obarska-Pempkowiak, H. The influence of configuration and supply of constructed wetland systems on the efficiency of pollution removal. Zeszyty Naukowe Wydz. Budownictwa i Inżynierii Środowiska Politechniki Koszalińskiej. 2005, 22, 503–514. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Gikas, G.D.; Akratos, C.S.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Performance monitoring of a vertical flow constructed wetland treating municipal wastewater. Glob. NEST J. 2007, 9, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Gallert, C.; Winter, J. Bacterial metabolism in wastewater treatment systems. In Environmental Biotechnology. Concepts and Applications; Jördening, H.J., Winter, J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Platze, C.H. Design recommendations for subsurface flow constructed wetlands for nitrification and denitrification. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benham, B.L.; Mote, C.R. Investigating dairy lagoon treatability in a laboratory-scale constructed wetlands system. Trans. ASAE 1999, 42, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiakowski, K.; Wielgosz, E. Numbers of selected physiological groups of bacteria in domestic sewage after various stages of treatment in multi-stage constructed wetland. Teka Kom. Ochr. Kszt. Środ. Przyr. OL PAN 2010, 7, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, B.S.; Park, C.M.; Song, U.; Park, W.J. Nitrate and phosphate removal potentials of three willow species and a bald cypress from eutrophic aquatic environment. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 6, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Kröpfelová, L. A three-stage experimental constructed wetland for treatment of domestic sewage: First 2 years of operations. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.C.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; DeLaune, R.D.; Jugsujinda, A.; Lee, S.T.; Seo, J.Y.; Heo, J.S. Evaluation of 2- and 3-stage combinations of vertical and horizontal flow constructed wetlands treating greenhouse wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 32, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Måhlum, T.; Stǻlnacke, P. Removal efficiency of three cold-climate constructed wetlands treating domestic wastewater: Effects of temperature, seasons, loading rates and input concentrations. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitterer-Reichmann, G.M. Data evaluation of constructed wetlands for treatment of domestic wastewater. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference Wetland Systems for Water Pollution Control; IWA and University of Dar es Salaam: Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, 2002; pp. 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Reeb, G.; Werckmann, M. Looking at the outlet zone of three constructed wetlands treating wastewaters of small communities. In Wetlands—Nutrients, Metals and Msss Cycling; Vymazal, J., Ed.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Tuszyńska, A.; Obarska-Pempkowiak, H.; Worst, W. Efficiency of contaminants removal on hygdrophyte beds with sequential vertical and horizontal wastewater flow. Rocznik Ochrony Środowiska 2004, 6, 115–129. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, P.F.; Job, G.D.; Green, M.B.; Shutes, R.B.E. Reed Beds and Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment; WRc Publications: Medmenham, UK, 1996; p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Lantzke, I.R.; Heritage, A.D.; Pistillo, G.; Mitchell, D.S. Phosphorus removal rates in bucket size planted wetlands with a vertical hydraulic flow. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, H. Do macrophytes play a role in constructed treatment wetlands? Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciupa, R. The experience in the operation of constructed wetlands in North-Eastern Poland. In Proceedings of Fifth International Conference Wetland Systems for Water Pollution Control; IWA and Universität für Bodenkultur:: Vienna, Austria, 1996; Chapter IX/6. [Google Scholar]
- Laber, J.; Haberl, R.; Langergraber, G. Treatment of hospital wastewater with a 2-stage constructed wetland system. In Achievments and Prospects of Phytoremediation in Europe; Haberl, R., Langergraber, G., Eds.; University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2003; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Andraka, D.; Dzienis, L. Required reliability level of wastewater treatment plants according to European and Polish regulations. Zeszyty Naukowe Politechniki Białostockiej Ser. Inżynieria Środowiska 2003, 16, 24–28. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Mucha, Z.; Wójcik, W.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Gajewska, M. Long-term operation of Kickuth-type constructed wetland applied to municipal wastewater treatment in temperate climate. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec, M. Reliability of removal of selected pollutants in different technological solutions of household wastewater treatment plants. J. Water Land Dev. 2017, 35, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
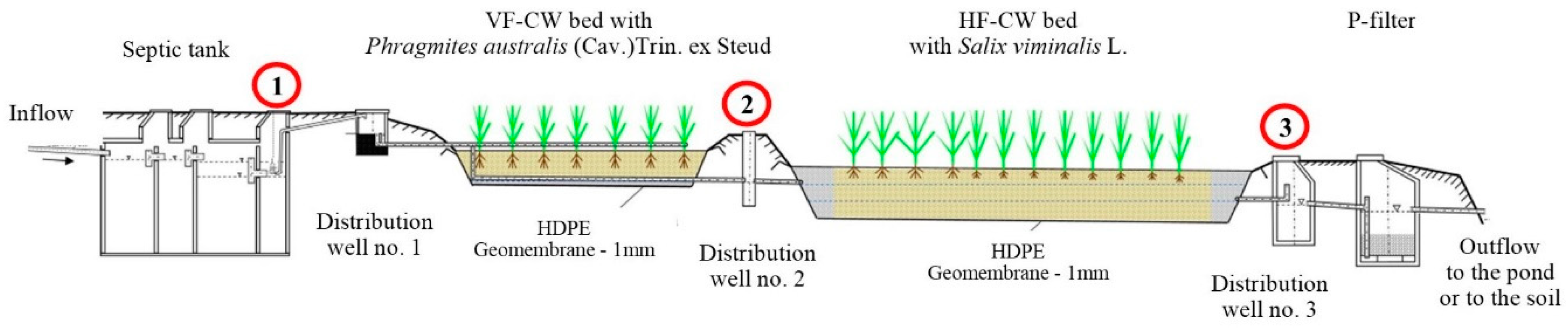

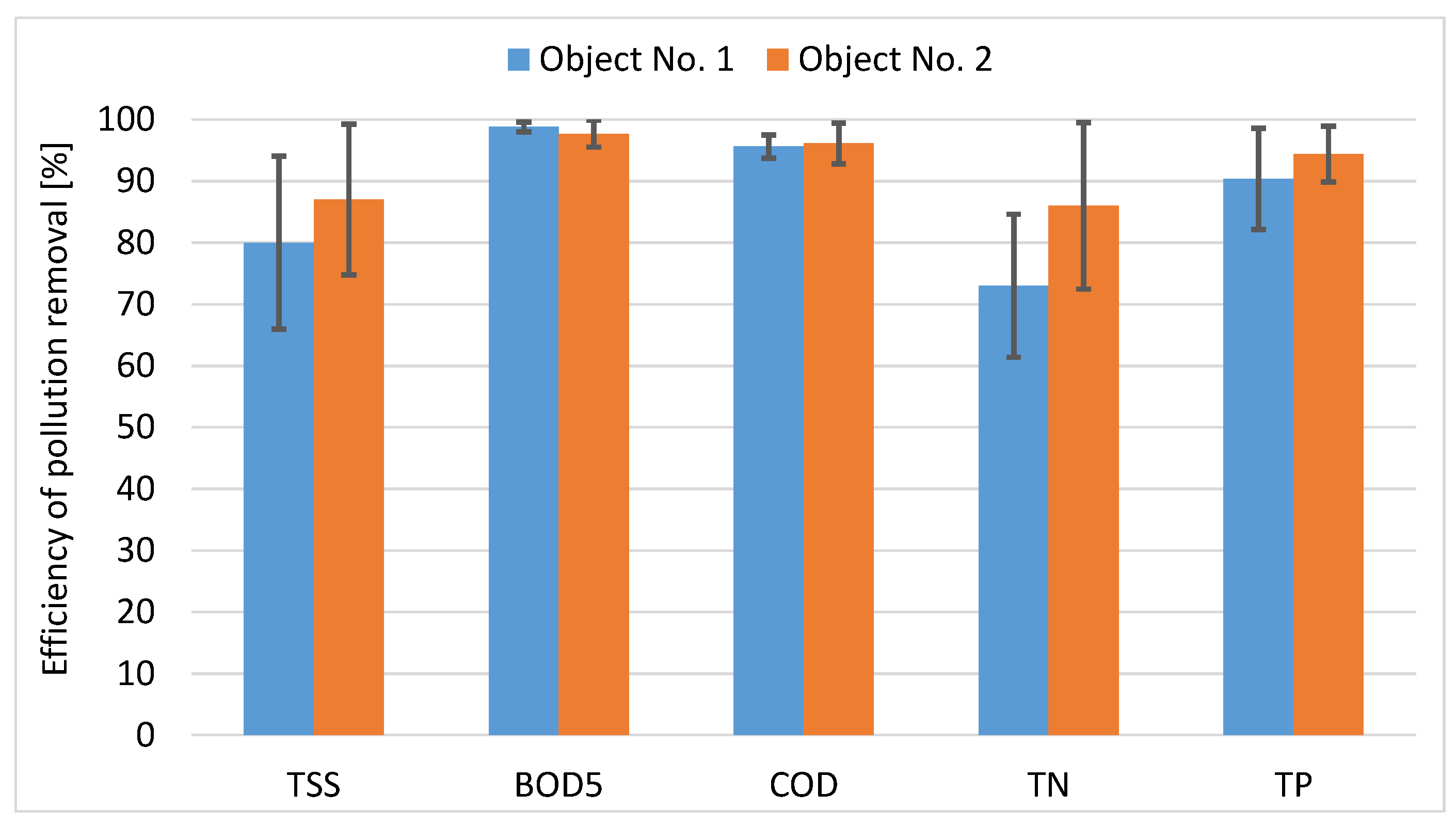
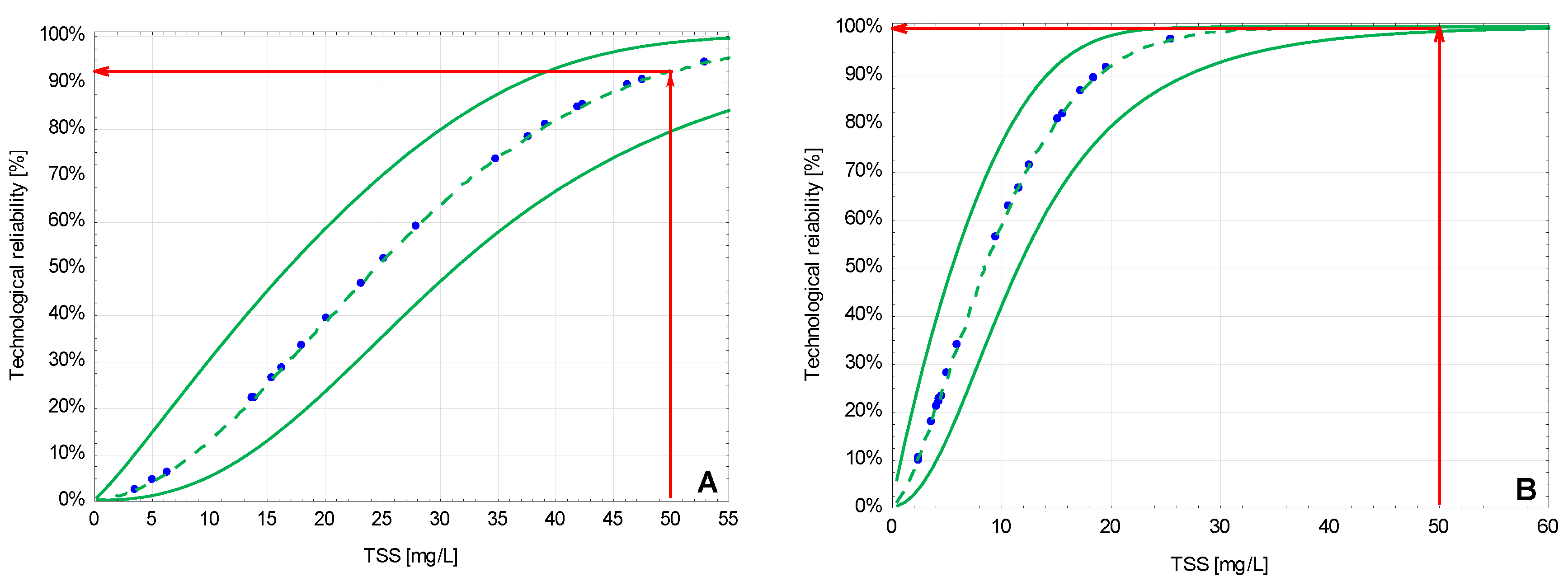

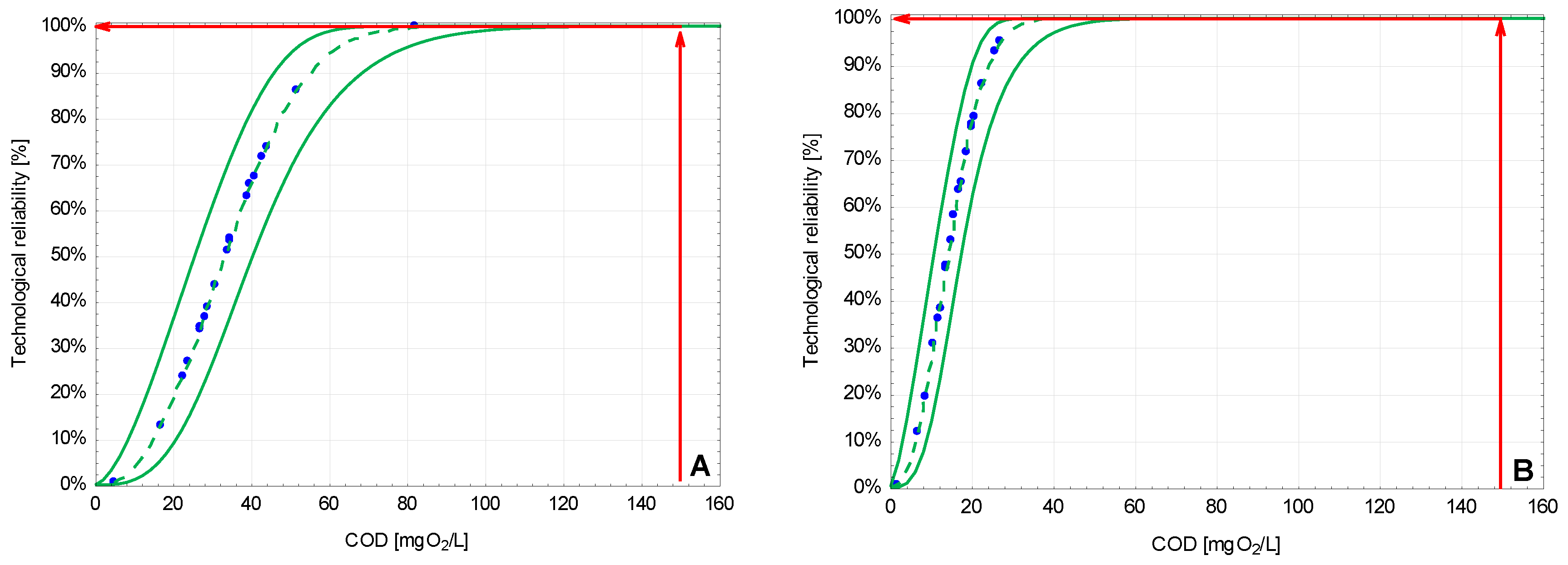
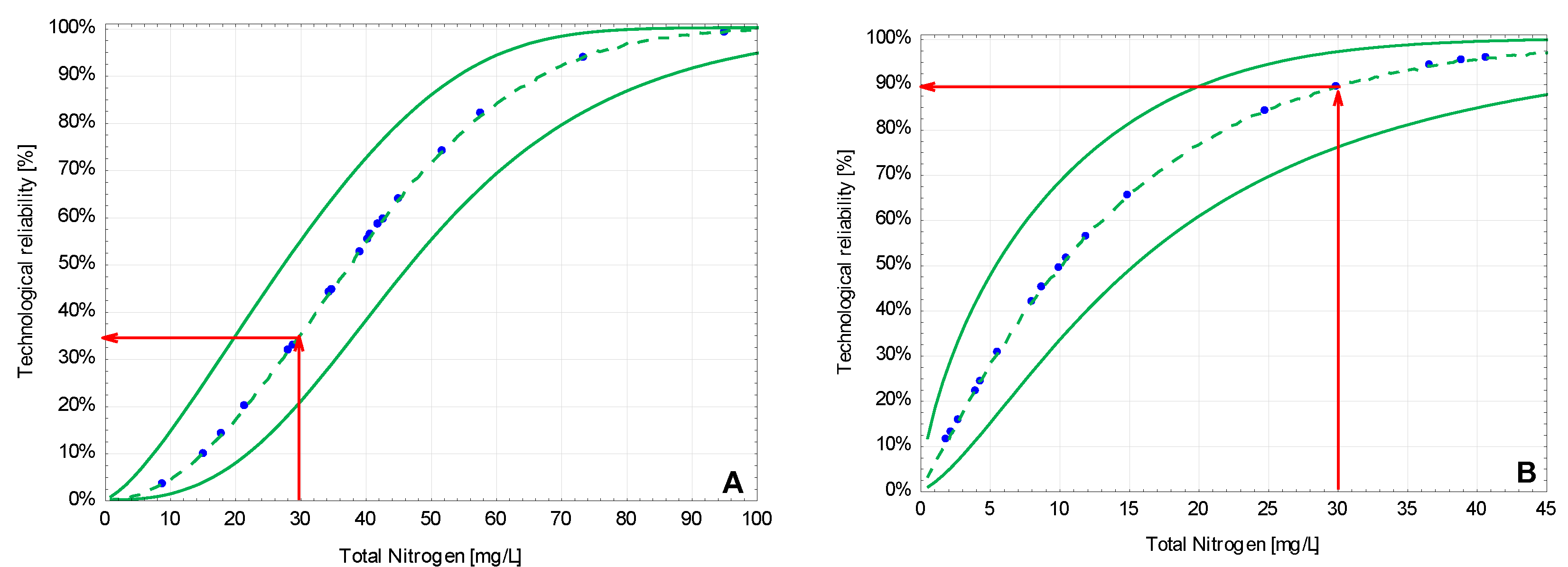
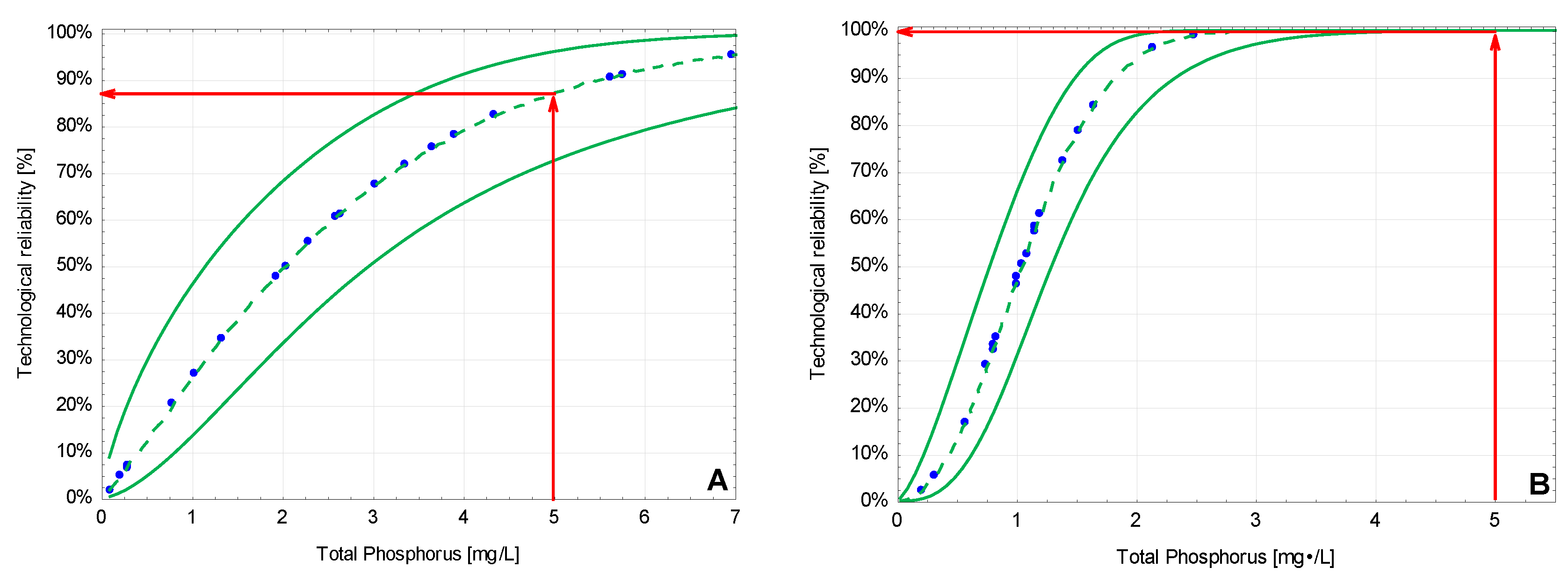
| Facility | No. 1 | No. 2 |
| Start of operation | 2014 | 2014 |
| Number of person equivalent | 4 | 10 |
| Amount of treated wastewater Q (m3/day) | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| Active capacity of the initial settling tank V (m3) | 4.9 | 4.9 |
| Area of bed of the CWs | ||
| Reed bed—VF (m2) | I—18 | I—40 |
| Willow bed—HF (m2) | II—30 | II—56 |
| Total area (m2) | 48 | 96 |
| Bed area per 1 inhabitant (m2/PE) | 12.0 | 9.6 |
| Bed depth (m) | VF—0.9 HF—1.2 | VF—0.9 HF—1.2 |
| Average hydraulic load of the first bed (m3/m2/day) | 0.022 | 0.025 |
| Hydraulic retention time in the bed (day) | VF—3.6 HF—24.0 | VF—3.2 HF—17.9 |
| Wastewater receiver | pond | soil |
| Parameters | 1—Inflow to the 1st Bed (VF) | 2—Outflow from the 1st Bed (VF) | 3—Outflow from the 2nd Bed (HF) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | min | max | min | max | |||||||
| pH | 7.0 | 8.05 | - | 0.25 | 6.06 | 7.68 | - | 0.38 | 6.62 | 7.51 | - | 0.27 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | 0.02 | 1.64 | 0.55 | 0.50 | 2.02 | 5.94 | 4.32 | 0.96 | 1.3 | 8.32 | 4.90 | 1.72 |
| Total suspended solids (mg/L) | 56.0 | 286 | 129 | 64.3 | 8.9 | 107 | 54.0 | 30.5 | 3.7 | 53.1 | 26.7 | 15.3 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 193 | 345 | 275 | 38.6 | 3.4 | 149 | 15.4 | 31.8 | 1.1 | 11.2 | 3.5 | 2.4 |
| CODCr (mg/L) | 575 | 1220 | 785 | 148 | 24.0 | 630 | 88.4 | 130 | 5.2 | 82.0 | 34.8 | 15.3 |
| Ammonium nitrogen (mg/L) | 78.0 | 139 | 110 | 18.9 | 0.28 | 58.0 | 17.0 | 16.5 | 0.12 | 41.4 | 11.4 | 10.8 |
| Nitrate nitrogen (mg/L) | 0.10 | 2.70 | 1.03 | 0.66 | 5.01 | 75.20 | 49.4 | 16.06 | 1.70 | 57.10 | 23.6 | 15.1 |
| Nitrite nitrogen (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.41 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 14.95 | 1.93 | 3.18 | 0.04 | 1.14 | 0.41 | 0.27 |
| Total nitrogen (mg/L) | 82.9 | 209 | 144 | 29.4 | 55.0 | 130 | 81.4 | 20.3 | 9.1 | 95.2 | 39.9 | 20.8 |
| Total phosphorus (mg/L) | 14.2 | 71.8 | 27.2 | 13.7 | 9.1 | 27.0 | 12.7 | 4.4 | 0.1 | 7.0 | 2.6 | 2.0 |
| Parameters | 1—Inflow to the 1st Bed (VF) | 2—Outflow from the 1st Bed (VF) | 3—Outflow from the 2nd Bed (HF) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | min | max | min | max | |||||||
| pH | 6.88 | 7.48 | - | 0.15 | 6.35 | 7.46 | - | 0.26 | 7.52 | 8.35 | - | 0.26 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | 0.02 | 2.33 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 2.84 | 5.90 | 4.59 | 0.67 | 2.35 | 10.7 | 7.24 | 2.01 |
| Total suspended solids (mg/L) | 25.0 | 135 | 70.6 | 26.9 | 4.9 | 46.8 | 19.5 | 9.2 | 2.5 | 25.5 | 9.9 | 6.9 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 22.5 | 295 | 123 | 72.7 | 0.9 | 107 | 16.7 | 21.9 | 0.25 | 7.6 | 3.0 | 1.8 |
| CODCr (mg/L) | 188 | 700 | 390 | 167 | 5.0 | 74.0 | 35.8 | 158 | 2.0 | 27.3 | 15.2 | 6.9 |
| Ammonium nitrogen (mg/L) | 59.0 | 95.0 | 77.5 | 9.2 | 0.03 | 63.1 | 6.6 | 13.9 | 0.01 | 6.2 | 0.49 | 1.4 |
| Nitrate nitrogen (mg/L) | 0.01 | 1.80 | 0.62 | 0.52 | 7.77 | 81.4 | 50.4 | 15.7 | 0.90 | 41.2 | 11.5 | 12.1 |
| Nitrite nitrogen (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 1.61 | 0.64 | 0.39 | 0.01 | 3.04 | 0.25 | 0.68 |
| Total nitrogen (mg/L) | 62.0 | 146 | 98.6 | 19.8 | 46.0 | 103 | 71.3 | 14.0 | 2.0 | 40.8 | 13.8 | 13.1 |
| Total phosphorus (mg/L) | 10.2 | 48.3 | 19.4 | 9.9 | 2.89 | 22.2 | 9.2 | 5.8 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 0.5 |
| Object | No. 1 | No. 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | VF | HF | VF–HF | VF | HF | VF–HF | |
| TSS | APL | 2.87 | 0.72 | 1.08 | 1.77 | 0.35 | 0.74 |
| MRR | 1.67 | 0.36 | 0.85 | 1.28 | 0.17 | 0.63 | |
| BOD5 | APL | 6.11 | 0.21 | 2.29 | 3.08 | 0.30 | 1.28 |
| MRR | 5.77 | 0.16 | 2.26 | 2.66 | 0.24 | 1.25 | |
| COD | APL | 17.44 | 1.18 | 6.54 | 9.75 | 1.23 | 4.06 |
| MRR | 15.48 | 0.71 | 6.25 | 8.03 | 0.96 | 3.90 | |
| TN | APL | 3.20 | 1.09 | 1.20 | 2.47 | 1.27 | 1.03 |
| MRR | 1.39 | 0.55 | 0.87 | 0.68 | 1.03 | 0.88 | |
| N-NH4 | APL | 2.44 | 0.23 | 0.92 | 1.94 | 0.12 | 0.81 |
| MRR | 2.07 | 0.07 | 0.82 | 1.77 | 0.11 | 0.80 | |
| TP | APL | 0.60 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.20 |
| MRR | 0.32 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.19 | |
| Parameter | Parameters of Weibull Distribution | Hollander–Proschan Goodness-of-Fit Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ | c | b | stat | p | |
| Object No. 1—Zwierzyniec | |||||
| TSS | −0.5000 | 1.8225 | 29.973 | −0.1096 | 0.9126 |
| BOD5 | 1.0162 | 1.6296 | 4.0002 | 0.2118 | 0.8322 |
| COD | −1.0000 | 2.3924 | 39.104 | −0.0097 | 0.9922 |
| Total Nitrogen | 2.1111 | 2.0874 | 45.1160 | 0.0944 | 0.9247 |
| Total Phosphorus | 0.0000 | 1.2020 | 2.7683 | −0.2077 | 0.8354 |
| Object No. 2—Florianka | |||||
| TSS | 2.1061 | 1.5301 | 11.0160 | 0.1567 | 0.8754 |
| BOD5 | −0.0500 | 1.7327 | 3.3194 | 0.1058 | 0.9157 |
| COD | −0.5000 | 2.3262 | 16.9940 | −0.3844 | 0.7006 |
| Total Nitrogen | 1.8636 | 1.0891 | 14.2960 | 0.2203 | 0.8255 |
| Total Phosphorus | −0.0500 | 2.1764 | 1.2472 | 0.8150 | 0.9350 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Micek, A.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Marzec, M.; Listosz, A. Technological Reliability and Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment in Two Hybrid Constructed Wetlands in the Roztocze National Park (Poland). Water 2020, 12, 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123435
Micek A, Jóźwiakowski K, Marzec M, Listosz A. Technological Reliability and Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment in Two Hybrid Constructed Wetlands in the Roztocze National Park (Poland). Water. 2020; 12(12):3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123435
Chicago/Turabian StyleMicek, Agnieszka, Krzysztof Jóźwiakowski, Michał Marzec, and Agnieszka Listosz. 2020. "Technological Reliability and Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment in Two Hybrid Constructed Wetlands in the Roztocze National Park (Poland)" Water 12, no. 12: 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123435
APA StyleMicek, A., Jóźwiakowski, K., Marzec, M., & Listosz, A. (2020). Technological Reliability and Efficiency of Wastewater Treatment in Two Hybrid Constructed Wetlands in the Roztocze National Park (Poland). Water, 12(12), 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123435