Sediment Carbon Variations in the Venice Lagoon and Other Transitional Water Systems of the Northern Adriatic Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
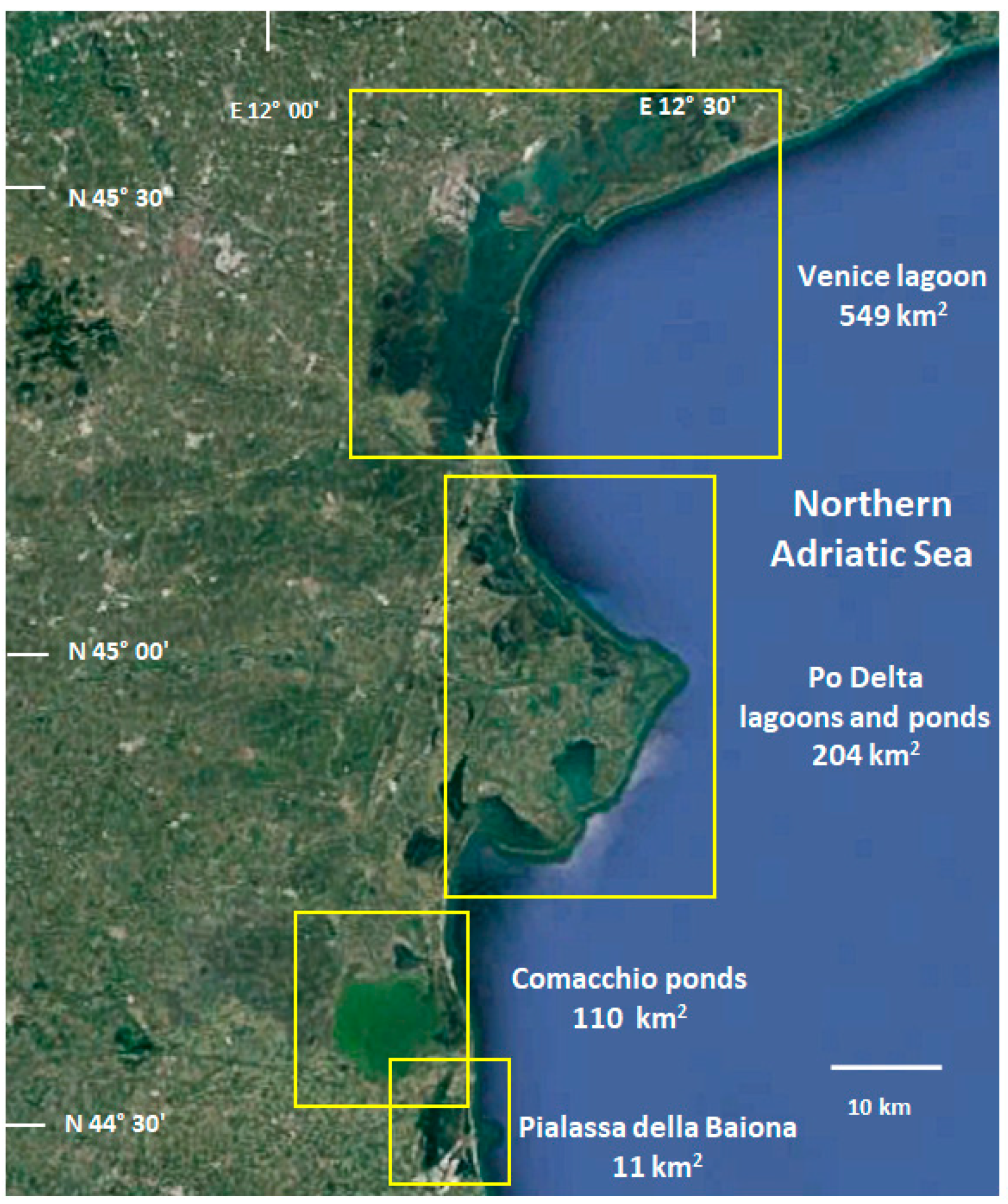
2.1. Description of Study Areas and Sampling Campaigns
2.2. Carbon Determination in Sediment
2.3. Sediment Characteristic Determination
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Carbon Determination and Sediment Characteristics
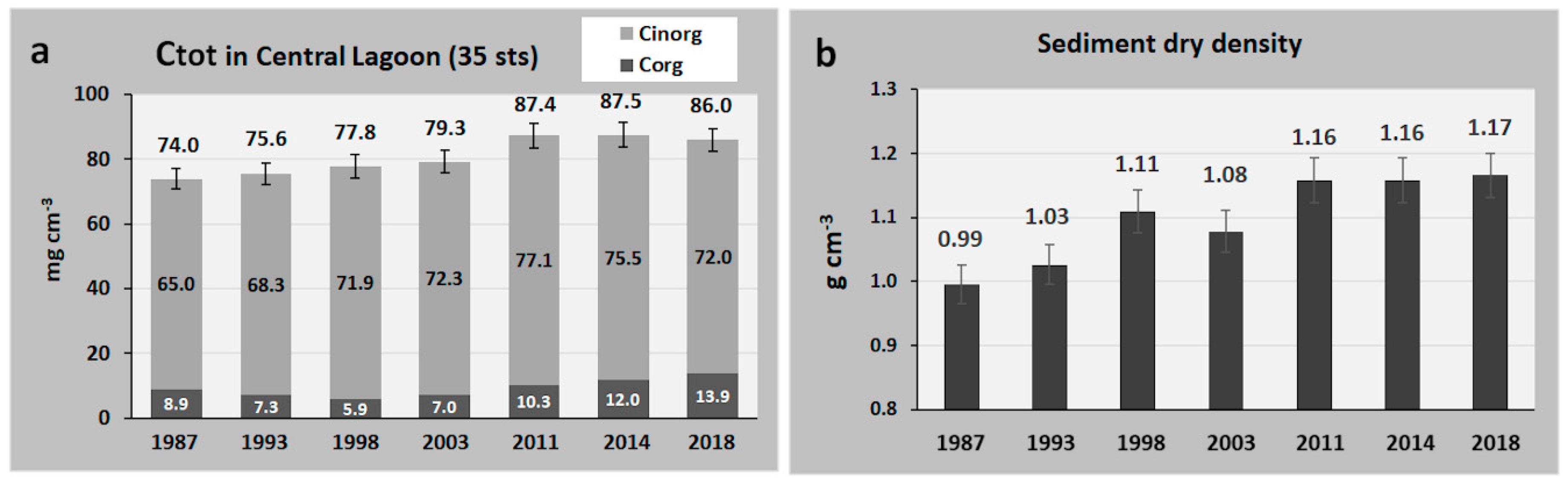
3.2. Carbon Variations in the Venice Lagoon (2003–2018)
3.3. Carbon Variations in all TWSs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castaldelli, G.; Mantovani, S.; Welsh, D.T.; Rossi, R.; Mistri, M.; Fano, E.A. Impact of commercial clam harvesting on water column and sediment physicochemical characteristics and macrobenthic community structure in a lagoon (Sacca di Goro) of the Po River Delta. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 19, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistri, M.; Munari, C.; Pagnoni, A.; Chenet, T.; Pasti, L.; Cavazzini, A. Accumulation of trace metals in crayfish tissues: Is Procambarus clarkii a vector of pollutants in Po Delta inland waters? Eur. Zool. J. 2020, 87, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velasco, J.; Lloret, J.; Millan, A.; Marin, A.; Barahona, J.; Abellan, P.; Sanchez-Fernandez, D. Nutrient and particulate inputs into the Mar Menor lagoon (SE Spain) from an intensive agricultural watershed. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 176, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Pavoni, B.; Marcomini, A.; Orio, A.A. Macroalgae, nutrient cycles and pollutants in the lagoon of Venice. Estuar. Coast. 1992, 15, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefford, B.; Dunlop, J.; Nugegoda1, D.; Choy, S. Understanding salinity thresholds in freshwater biodiversity, freshwater to saline transition. In Salt, Nutrient, Sediment and Interactions: Findings from the National River Contaminants Program; Land & Water Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2007; Chapter 2; pp. 9–28. [Google Scholar]
- Solidoro, C.; Bandelj, V.; Bernardi, F.A.; Camatti, E.; Ciavatta, S.; Cossarini, G.; Facca, C.; Franzoi, P.; Libralato, S.; Melaku Canu, D.; et al. Response of the Venice Lagoon Ecosystem to Natural and Anthropogenic Pressures over the last 50 years. In Coastal Lagoons—Critical Habitats of Environmental Change; Kennish, M.J., Paerl, H.W., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; Chapter 19; pp. 483–511. [Google Scholar]
- Sfriso, A.; Buosi, A.; Mistri, M.; Munari, C.; Franzoi, P.; Sfriso, A.A. Long-term changes of the trophic status in transitional ecosystems of the northern Adriatic Sea, key parameters and future expectations: The lagoon of Venice as a study case. Nat. Conserv. 2019, 34, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trozzi, C.; Vaccaro, R. Environmental impact of port activities. In Maritime Engineering and Ports II; Brebbia, C.A., Olivella, J., Eds.; WIT Press: Rome, Italy, 2000; pp. 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoli, M.; Nizzoli, D.; Viaroli, P.; Turolla, E.; Castaldelli, G.; Fano, E.A.; Rossi, R. Impact of Tapes philippinarum farming on nutrient dynamics and benthic respiration in the Sacca di Goro. Hydrobiologia 2001, 455, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Ceoldo, S.; Silvestri, S.; Ghetti, P.F. Role of macroalgal biomass and clam fishing on spatial and temporal changes in N and P sedimentary pools in the central part of the Venice lagoon. Oceanol. Acta 2003, 26, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sfriso, A.; Buosi, A.; Facca, C.; Sfriso, A.A. Role of environmental factors in affecting macrophyte dominance in transitional environments: The Italian Lagoons as a study case. Mar. Ecol. 2017, 38, e12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranovi, F.; Da Ponte, F.; Torricelli, P. Historical changes in the structure and functioning of the benthic community in the lagoon of Venice. Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 2008, 76, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitacco, V.; Mistri, M.; Aleffi, I.F.; Lardicci, C.; Prato, S.; Tagliapietra, D.; Munari, C. Spatial patterns of macrobenthic alpha and beta diversity at different scales in Italian transitional waters (central Mediterranean). Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci. 2019, 222, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapin, L.; Zucchetta, M.; Sfriso, A.; Franzoi, P. Predicting the response of nekton assemblages to seagrass transplantations in the Venice lagoon: An approach to assess ecological restoration. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2019, 29, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavraro, F.; Bettoso, N.; Zucchetta, M.; D’Aietti, A.; Faresi, L.; Franzoi, P. Body condition in fish as a tool to detect the effects of anthropogenic pressures in transitional waters. Aquat. Ecol. 2019, 53, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani-Soika, A.; Perin, G. L’inquinamento della laguna di Venezia: Studio delle modificazioni chimiche e del popolamento sottobasale dei sedimenti lagunari negli ultimi vent’anni. Boll. Mus. Civ. St. Nat. Venezia 1974, 26, 25–68. [Google Scholar]
- Cossu, A.; De Fraja-Frangipane, E. Stato delle Conoscenze Sullo Inquinamento Della Laguna di Venezia. In Progetto Venezia, Ministero dei Lavori Pubblici, Magistrato alle Acque; Consorzio Venezia Nuova: Venezia, Italy, 1985; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Consorzio Venezia Nuova; Magistrato alle Acque. Nuovi Interventi per la Salvaguardia di Venezia. Rapporto sullo Stato Attuale dell’Ecosistema Lagunare; Studio 1.3.9: Rapporto Finale; Consorzio Venezia Nuova Venezia: Venezia, Italy, 1990; p. 361. [Google Scholar]
- Gačić, M.; Mosquera, I.M.; Kovačević, V.; Mazzoldi, A.; Cardin, V.; Arena, F.; Gelsi, G. Temporal variations of water flow between the Venetian lagoon and the open sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 51, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiol, M.; Facca, C.; Visin, F.; Sfriso, A.; Pavoni, B. Interannual heavy element and nutrient concentration trends in the top sediments of Venice Lagoon (Italy). Mar. Poll. Bull. 2014, 89, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucco, A.; Umgiesser, G. Modeling the Venice Lagoon residence time. Ecol. Model. 2006, 193, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, A.; Zaggia, L.; Collavini, F.; Zonta, R. Freshwater discharge from the drainage basin to the Venice Lagoon (Italy). Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Pavoni, B.; Marcomini, A.; Orio, A.A. Annual variation of nutrients in the lagoon of Venice. Mar. Poll. Bull. 1988, 19, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Marcomini, A. Decline of Ulva growth in the lagoon of Venice. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 58, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Bon, D.; Buosi, A. Macrophytes and ecological status assessment in the Po delta transitional systems, Adriatic Sea (Italy). Application of Macrophyte Quality Index (MaQI). Acta Adriat. 2016, 57, 209–226. [Google Scholar]
- Munari, C.; Mistri, M. Ecological status assessment and response of benthic communities to environmental variability: The Valli di Comacchio (Italy) as a study case. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 81, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfriso, A.; Buosi, A.; Wolf, M.A.; Sfriso, A.A. Invasion of alien macroalgae in the Venice Lagoon, a pest or a resource? Aquat. Invasions 2020, 15, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Emili, A.; Acquavita, A.; Koron, N.; Fraganeli, J. Benthic biogeo-chemical cycling of mercury in two contaminated northern Adriatic coastal lagoons. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, B.A. Method for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) in Soil and Sediment; Ecological Risk Assessment Support Center, Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency: Las Vegas, Nevada, 2002; pp. 1–2.
- Kristensen, E.; Andersen, F.Ø. Determination of organic carbon in marine sediments: A comparison of two CHN analyzer methods. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1987, 109, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froelich, P.N. Analysis of organic carbon in marine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1980, 25, 564–572. [Google Scholar]
- Miozzi, E. Venezia nei Secoli—La Laguna, Grafiche Trevisan, Castelfranco Veneto; Grafiche Trevisan, Castelfranco Veneto: Venice, Italy, 1968; Volume III, p. 543. [Google Scholar]
- Frignani, M.; National, I.; Dinelli, E. Composition of Venice Lagoon sediments: Distribution, sources, settings and recent evolution. GeoActa 2001, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sfriso, A.; Marcomini, A.; Pavoni, B. Relationship between macroalgal biomass and nutrient concentrations in a hypertrophic area of the Venice lagoon. Mar. Environ. Res. 1987, 22, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C. Distribution and production of macrophytes in the lagoon of Venice. Comparison of actual and past abundance. Hydrobiologia 2007, 577, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roner, M.; D’Alpaos, A.; Ghinassi, M.; Marani, M.; Silvestri, S.; Franceschini, E.; Realdon, N. Spatial variation of salt-marsh organic and inorganic deposition and organic carbon accumulation: Inferences from the Venice lagoon, Italy. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 93, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roner, M.; Ghinassi, M.; Fedi, M.; Liccioli, L.; Bellucci, L.G.; Brivio, L.; D’Alpaos, A. Latest Holocene depositional history of the southern Venice Lagoon, Italy. Holocene 2017, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambolati, G.; Putti, M.; Teatini, P.; Camporese, M.; Ferraris, S.; Gasparetto-Stori, G.; Nicoletti, V.; Silvestri, S.; Rizzetto, F.; Tosi, L. Peat Land Oxidation Enhances Subsidence in the Venice Watershed. Eos 2005, 86, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boscolo Brusà, R.; Cacciatore, F.; Ponis, E.; Molin, E.; Delaney, E. Clam culture in the Venice lagoon: Stock assessment of Manila clam (Venerupis philippinarum) populations at a nursery site and management proposals to increase clam farming sustainability. Aquat. Living Resour. 2013, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sfriso, A. Ruppia maritima L. e Ruppia cirrhosa (Petagna) Grande (Helobiae, Spermatophyta) in laguna di Venezia. Lavori Soc. Ven. Sc. Nat. 2008, 33, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Marcomini, A. Sedimentation rates and erosion processes in the lagoon of Venice. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sfriso, A.; Facca, C.; Ceoldo, S.; Pessa, G. Sedimentation rates, erosive processes, grain-size and sediment density changes in the lagoon of Venice. In Scientific Research and Safeguarding of Venice. Corila Research Program 2003 Results; Campostrini, P., Ed.; Multigraf: Spinea, Italy, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Aller, R.C. Mobile deltaic and continental shelf muds as suboxic, fluidized bed reactors. Mar. Chem. 1998, 61, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranovi, F.; Da Ponte, F.; Raicevich, S.; Giovanardi, O. A multidisciplinary study of the immediate effects of mechanical clam harvesting in the Venice Lagoon. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2004, 61, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porzio, L.; Garrard, S.L.; Buia, M.C. The effect of ocean acidification on early algal colonization stages at natural CO2 vents. Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Abdelgawad, H.; Castellano, I.; Lorenti, M.; Delledonne, M.; Beemster, G.T.S.; Asard, H.; Buia, M.C.; Palumbo, A. Physiological and Biochemical Analyses Shed Light on the Response of Sargassum vulgare to Ocean Acidification at Different Time Scales. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, S.A.; Byrne, M.; Ricevuto, E.; Gambi, M.C. The carbon dioxide vents of Ischia, Italy, a natural System to assess impacts of ocean acidification on marine ecosystems: An overview of research and comparisons with other vent systems. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2018, 56, 237–310. [Google Scholar]
- Sfriso, A.; Buosi, A.; Wolf, M.A.; Sciuto, K.; Molinaroli, E.; Mistri, M.; Munari, C.; Moro, I.; Sfriso, A.A. Microcalcareus seaweeds a sentinel of trophic changes and CO2 trapping in transitional waters. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, B.; Calvo, C.; Sfriso, A.; Orio, A.A. Time trend of PCB concentrations in surface sediment from a hypertrophic, macroalgae populated area of the lagoon of Venice. Sci. Total Environ. 1990, 91, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secco, T.; Pellizzato, F.; Sfriso, A.; Pavoni, B. The changing state of contamination in the lagoon of Venice. Part 1. Organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardello, M.; Secco, T.; Pellizzato, F.; Chinellato, M.; Sfriso, A.; Pavoni, B. The changing state of contamination in the lagoon of Venice. Part 2: Heavy metals. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| One-Way ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ctot | Cinorg | Corg | |
| 2003–2011 | p < 0.050 | n.s. | p < 3.26 × 10−15 |
| 2003–2014 | p < 0.025 | n.s. | p < 7.10 × 10−18 |
| 2003–2018 | n.s. | n.s. | p < 2.10 × 10−14 |
| 2011–2014 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 2011–2018 | n.s. | n.s. | p < 0.029 |
| 2014–2018 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| n.s. = not significant | |||
| One-Way ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ctot | Cinorg | Corg | |
| 1987–1993 | n.s. | n.s. | 0.042 |
| 1987–1998 | n.s. | n.s. | 2.49 × 10−4 |
| 1987–2003 | n.s. | n.s. | 0.026 |
| 1987–2011 | n.s. | 0.041 | n.s. |
| 1987–2014 | n.s. | n.s. | 3.13 × 10−4 |
| 1987–2018 | n.s. | n.s. | 3.69 × 10−6 |
| 1993–1998 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 1993–2003 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 1993–2011 | n.s. | n.s. | 8.59 × 10−4 |
| 1993–2014 | n.s. | n.s. | 1.98 × 10−7 |
| 1993–2018 | n.s. | n.s. | 6.14 × 10−9 |
| 1998–2003 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 1998–2011 | n.s. | n.s. | 2.10 × 10−6 |
| 1998–2014 | n.s. | n.s. | 7.84 × 10−11 |
| 1998–2018 | n.s. | n.s. | 1.14 × 10−11 |
| 2003–2011 | n.s. | n.s. | 5.42 × 10−4 |
| 2003–2014 | n.s. | n.s. | 4.08 × 10−7 |
| 2003–2018 | n.s. | n.s. | 4.70 × 10−9 |
| 2011–2014 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| 2011–2018 | n.s. | n.s. | 8.03 × 10−4 |
| 2014–2018 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s |
| Spearman’s Non-Parametric Coefficients | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p < 0.05 per r ≥ 0.19 | |||||||
| pH | Fines | Shells | Dry Density | Corg | Cinorg | Ctot | |
| pH | 1.00 | ||||||
| Fines | −0.59 | −0.59 | |||||
| Shells | 0.27 | −0.34 | 1.00 | ||||
| Dry density | 0.53 | −0.65 | 0.07 | 1.00 | |||
| Corg | −0.25 | 0.32 | 0.26 | −0.42 | 1.00 | ||
| Cinorg | 0.19 | −0.04 | 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.05 | 1.00 | |
| Ctot | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.31 | 0.20 | 0.35 | 0.85 | 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sfriso, A.; Buosi, A.; Tomio, Y.; Juhmani, A.-S.; Chiesa, S.; Greco, M.; Gazzola, C.; Mistri, M.; Munari, C.; Sfriso, A.A. Sediment Carbon Variations in the Venice Lagoon and Other Transitional Water Systems of the Northern Adriatic Sea. Water 2020, 12, 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123430
Sfriso A, Buosi A, Tomio Y, Juhmani A-S, Chiesa S, Greco M, Gazzola C, Mistri M, Munari C, Sfriso AA. Sediment Carbon Variations in the Venice Lagoon and Other Transitional Water Systems of the Northern Adriatic Sea. Water. 2020; 12(12):3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123430
Chicago/Turabian StyleSfriso, Adriano, Alessandro Buosi, Yari Tomio, Abdul-Salam Juhmani, Stefania Chiesa, Marta Greco, Chiara Gazzola, Michele Mistri, Cristina Munari, and Andrea Augusto Sfriso. 2020. "Sediment Carbon Variations in the Venice Lagoon and Other Transitional Water Systems of the Northern Adriatic Sea" Water 12, no. 12: 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123430
APA StyleSfriso, A., Buosi, A., Tomio, Y., Juhmani, A.-S., Chiesa, S., Greco, M., Gazzola, C., Mistri, M., Munari, C., & Sfriso, A. A. (2020). Sediment Carbon Variations in the Venice Lagoon and Other Transitional Water Systems of the Northern Adriatic Sea. Water, 12(12), 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12123430











